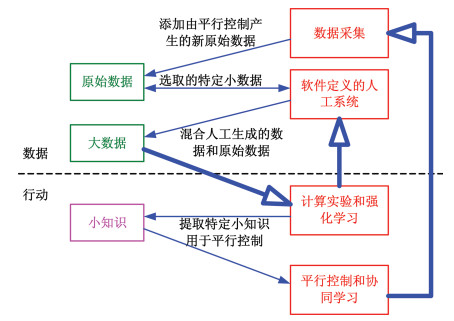
|
[1]
|
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y. Generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27. Montreal, Canada: Curran Associates, Inc., 2014. 2672-2680
|
|
[2]
|
Goodfellow I, Bengio Y, Courville A. Deep Learning. Cambridge, UK: MIT Press, 2016.
|
|
[3]
|
Ratliff L J, Burden S A, Sastry S S. Characterization and computation of local Nash equilibria in continuous games. In: Proceedings of the 51st Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton). Monticello, IL, USA: IEEE, 2013. 917-924
|
|
[4]
|
Goodfellow I. NIPS 2016 tutorial: generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1701.00160, 2016.
|
|
[5]
|
Li J W, Monroe W, Shi T L, Jean S, Ritter A, Jurafsky D. Adversarial learning for neural dialogue generation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1701.06547, 2017.
|
|
[6]
|
Yu L T, Zhang W N, Wang J, Yu Y. SeqGAN: sequence generative adversarial nets with policy gradient. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1609.05473, 2016.
|
|
[7]
|
Hu WW, Tan Y. Generating adversarial malware examples for black-box attacks based on GAN. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1702.05983, 2017.
|
|
[8]
|
Chidambaram M, Qi Y J. Style transfer generative adversarial networks: learning to play chess differently. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1702.06762, 2017.
|
|
[9]
|
Bengio Y. Learning deep architectures for AI. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, 2009, 2(1): 1-127 doi: 10.1561/2200000006
|
|
[10]
|
Kingma D P, Welling M. Auto-encoding variational Bayes. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1312.6114, 2013.
|
|
[11]
|
Rezende D J, Mohamed S, Wierstra D. Stochastic backpropagation and approximate inference in deep generative models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1401.4082, 2014.
|
|
[12]
|
Hinton G E, Sejnowski T J, Ackley D H. Boltzmann Machines: Constraint Satisfaction Networks that Learn. Technical Report No. CMU-CS-84-119, Carnegie-Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1984.
|
|
[13]
|
Ackley D H, Hinton G E, Sejnowski T J. A learning algorithm for Boltzmann machines. Cognitive Science, 1985, 9(1): 147-169 doi: 10.1207/s15516709cog0901_7
|
|
[14]
|
Hinton G E, Osindero S, Teh Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527-1554 doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527
|
|
[15]
|
Bengio Y, Thibodeau-Laufer É, Alain G, Yosinski J. Deep generative stochastic networks trainable by backprop. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1306.1091, 2013.
|
|
[16]
|
Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504-507 http://web.inf.ufpr.br/menotti/ci171-2015-2-1/files/seminario-Victor-slides.pdf
|
|
[17]
|
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444 doi: 10.1038/nature14539
|
|
[18]
|
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA: ACM, 2012. 1097-1105
|
|
[19]
|
He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770-778
|
|
[20]
|
Hinton G, Deng L, Yu D, Dahl G E, Mohamed A R, Jaitly N, Senior A, Vanhoucke V, Nguyen P, Sainath T N, Kingsbury B. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: the shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2012, 29(6): 82-97 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2012.2205597
|
|
[21]
|
Sutskever I, Vinyals O, Le Q V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27. Montreal, Canada: Curran Associates, Inc., 2014. 3104-3112.
|
|
[22]
|
He D, Chen W, Wang L W, Liu T Y. A game-theoretic machine learning approach for revenue maximization in sponsored search. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1406.0728, 2014.
|
|
[23]
|
Silver D, Huang A, Maddison C J, Guez A, Sifre L, van Den Driessche G, Schrittwieser J, Antonoglou I, Panneershelvam V, Lanctot M, Dieleman S, Grewe D, Nham J, Kalchbrenner N, Sutskever I, Lillicrap T, Leach M, Kavukcuoglu K, Graepel T, Hassabis D. Mastering the game of go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature, 2016, 529(7587): 484-489 doi: 10.1038/nature16961
|
|
[24]
|
Schmidhuber J. Learning factorial codes by predictability minimization. Neural Computation, 1992, 4(6): 863-879 doi: 10.1162/neco.1992.4.6.863
|
|
[25]
|
Ganin Y, Ustinova E, Ajakan H, Germain P, Larochelle H, Laviolette F, Marchand M, Lempitsky V. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2016, 17(59): 1-35 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277333816_Domain-Adversarial_Training_of_Neural_Networks
|
|
[26]
|
Chen W Z, Wang H, Li Y Y, Su H, Wang Z H, Tu C H, Lischinski D, Cohen-Or D, Chen B. Synthesizing training images for boosting human 3D pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). Stanford, CA, USA: IEEE, 2016. 479-488
|
|
[27]
|
Szegedy C, Zaremba W, Sutskever I, Bruna J, Erhan D, Goodfellow I, Fergus R. Intriguing properties of neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1312.6199, 2013.
|
|
[28]
|
McDaniel P, Papernot N, Celik Z B. Machine learning in adversarial settings. IEEE Security & Privacy, 2016, 14(3): 68-72 https://www.sec.in.tum.de/assets/lehre/ss12/ml/semniartalk.pdf
|
|
[29]
|
Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein GAN. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1701.07875, 2017.
|
|
[30]
|
Qi G J. Loss-sensitive generative adversarial networks on Lipschitz densities. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1701.06264, 2017.
|
|
[31]
|
Odena A. Semi-supervised learning with generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1606.01583, 2016.
|
|
[32]
|
Mirza M, Osindero S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1411.1784, 2014.
|
|
[33]
|
Donahue J, Krähenbühl P, Darrell T. Adversarial feature learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1605.09782, 2016.
|
|
[34]
|
Chen X, Duan Y, Houthooft R, Schulman J, Sutskever I, Abbeel P. InfoGAN: interpretable representation learning by information maximizing generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: Department of Information Technology IMEC, 2016. 2172-2180
|
|
[35]
|
Odena A, Olah C, Shlens J. Conditional image synthesis with auxiliary classifier GANs. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1610.09585, 2016.
|
|
[36]
|
Ledig C, Theis L, Huszár F, Caballero J, Cunningham A, Acosta A, Aitken A, Tejani A, Totz J, Wang Z H, Shi W Z. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1609.04802, 2016.
|
|
[37]
|
Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014.
|
|
[38]
|
Santana E, Hotz G. Learning a driving simulator. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1608.01230, 2016.
|
|
[39]
|
Gou C, Wu Y, Wang K, Wang F Y, Ji Q. Learning-by-synthesis for accurate eye detection. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). Cancun, Mexico: IEEE, 2016.
|
|
[40]
|
Gou C, Wu Y, Wang K, Wang K F, Wang F Y, Ji Q. A joint cascaded framework for simultaneous eye detection and eye state estimation. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 67: 23-31 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.01.023
|
|
[41]
|
Shrivastava A, Pfister T, Tuzel O, Susskind J, Wang W D, Webb R. Learning from simulated and unsupervised images through adversarial training. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1612.07828, 2016.
|
|
[42]
|
Zhang Y Z, Gan Z, Carin L. Generating text via adversarial training. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 29. Curran Associates, Inc., 2016.
|
|
[43]
|
Reed S, Akata Z, Yan X C, Logeswaran L, Lee H, Schiele B. Generative adversarial text to image synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, NY, USA: ICML, 2016.
|
|
[44]
|
Ho J, Ermon S. Generative adversarial imitation learning. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 29. Curran Associates, Inc., 2016. 4565-4573
|
|
[45]
|
Finn C, Christiano P, Abbeel P, Levine S. A connection between generative adversarial networks, inverse reinforcement learning, and energy-based models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1611.03852, 2016.
|
|
[46]
|
Pfau D, Vinyals O. Connecting generative adversarial networks and actor-critic methods. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1610.01945, 2016.
|
|
[47]
|
王飞跃.平行系统方法与复杂系统的管理和控制.控制与决策, 2004, 19(5): 485-489, 514 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC200405001.htmWang Fei-Yue. Parallel system methods for management and control of complex systems. Control and decision, 2004, 19(5): 485-489, 514 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZYC200405001.htm
|
|
[48]
|
王飞跃.计算实验方法与复杂系统行为分析和决策评估.系统仿真学报, 2004, 16(5): 893-897 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200405008.htmWang Fei-Yue. Computational experiments for behavior analysis and decision evaluation of complex systems. Journal of System Simulation, 2004, 16(5): 893-897 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200405008.htm
|
|
[49]
|
Wang F Y, Zhang J, Wei Q L, Zheng X H, Li L. PDP: parallel dynamic programming. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2017, 4(1): 1-5 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510310
|
|
[50]
|
白天翔, 王帅, 沈震, 曹东璞, 郑南宁, 王飞跃.平行机器人与平行无人系统:框架、结构、过程、平台及其应用.自动化学报, 2017, 43(2): 161-175 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18998.shtmlBai Tian-Xiang, Wang Shuai, Shen Zhen, Cao Dong-Pu, Zheng Nan-Ning, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel robotics and parallel unmanned systems: framework, structure, process, platform and applications. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(2): 161-175 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18998.shtml
|
|
[51]
|
Wang F Y, Wang X, Li L X, Li L. Steps toward parallel intelligence. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2016, 3(4): 345-348 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2016.7510067
|
|
[52]
|
王坤峰, 苟超, 王飞跃.平行视觉:基于ACP的智能视觉计算方法.自动化学报, 2016, 42(10): 1490-1500 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18936.shtmlWang Kun-Feng, Gou Chao, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel vision: an ACP-based approach to intelligent vision computing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1490-1500 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18936.shtml
|
|
[53]
|
王飞跃.关于复杂系统的建模、分析、控制和管理.复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2006, 3(2): 26-34 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZXT200602003.htmWang Fei-Yue. On the modeling, analysis, control and management of complex systems. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 2006, 3(2): 26-34 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZXT200602003.htm
|
|
[54]
|
王飞跃, 刘德荣, 熊刚, 程长建, 赵冬斌.复杂系统的平行控制理论及应用.复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2012, 9(3): 1-12 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZXT201203002.htmWang Fei-Yue, Liu De-Rong, Xiong Gang, Cheng Chang-Jian, Zhao Dong-Bin. Parallel control theory of complex systems and applications. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 2012, 9(3): 1-12 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZXT201203002.htm
|
|
[55]
|
王飞跃.平行控制:数据驱动的计算控制方法.自动化学报, 2013, 39(4): 293-302 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17915.shtmlWang Fei-Yue. Parallel control: a method for data-driven and computational control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(4): 293-302 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17915.shtml
|
|
[56]
|
李力, 林懿伦, 曹东璞, 郑南宁, 王飞跃.平行学习-机器学习的一个新型理论框架.自动化学报, 2017, 43(1): 1-8 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18984.shtmlLi Li, Lin Yi-Lun, Cao Dong-Pu, Zheng Nan-Ning, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel learning——a new framework for machine learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(1): 1-8 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18984.shtml
|




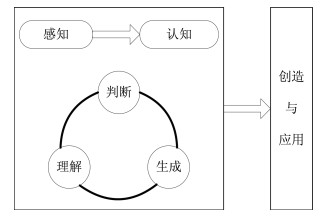
 下载:
下载: