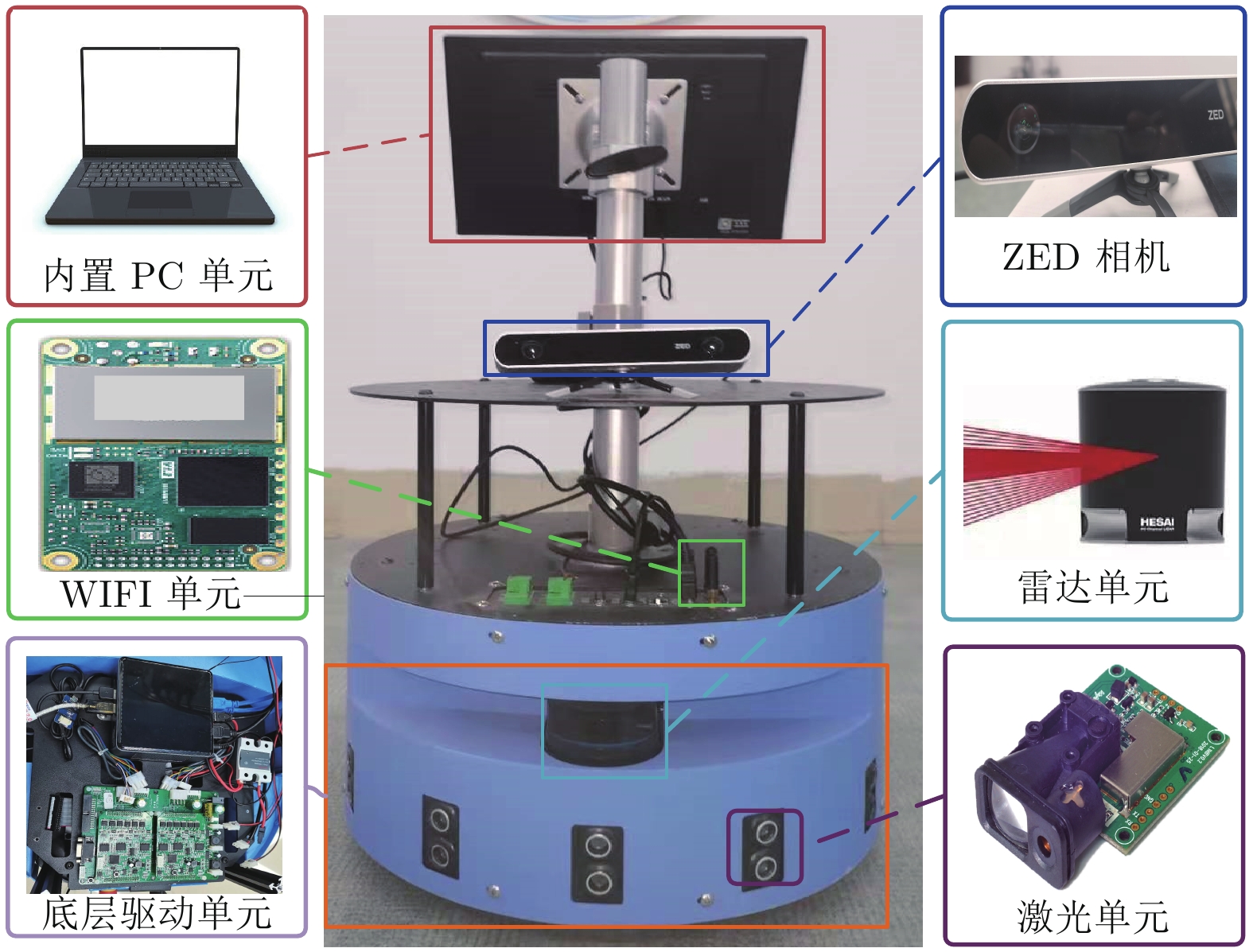
-
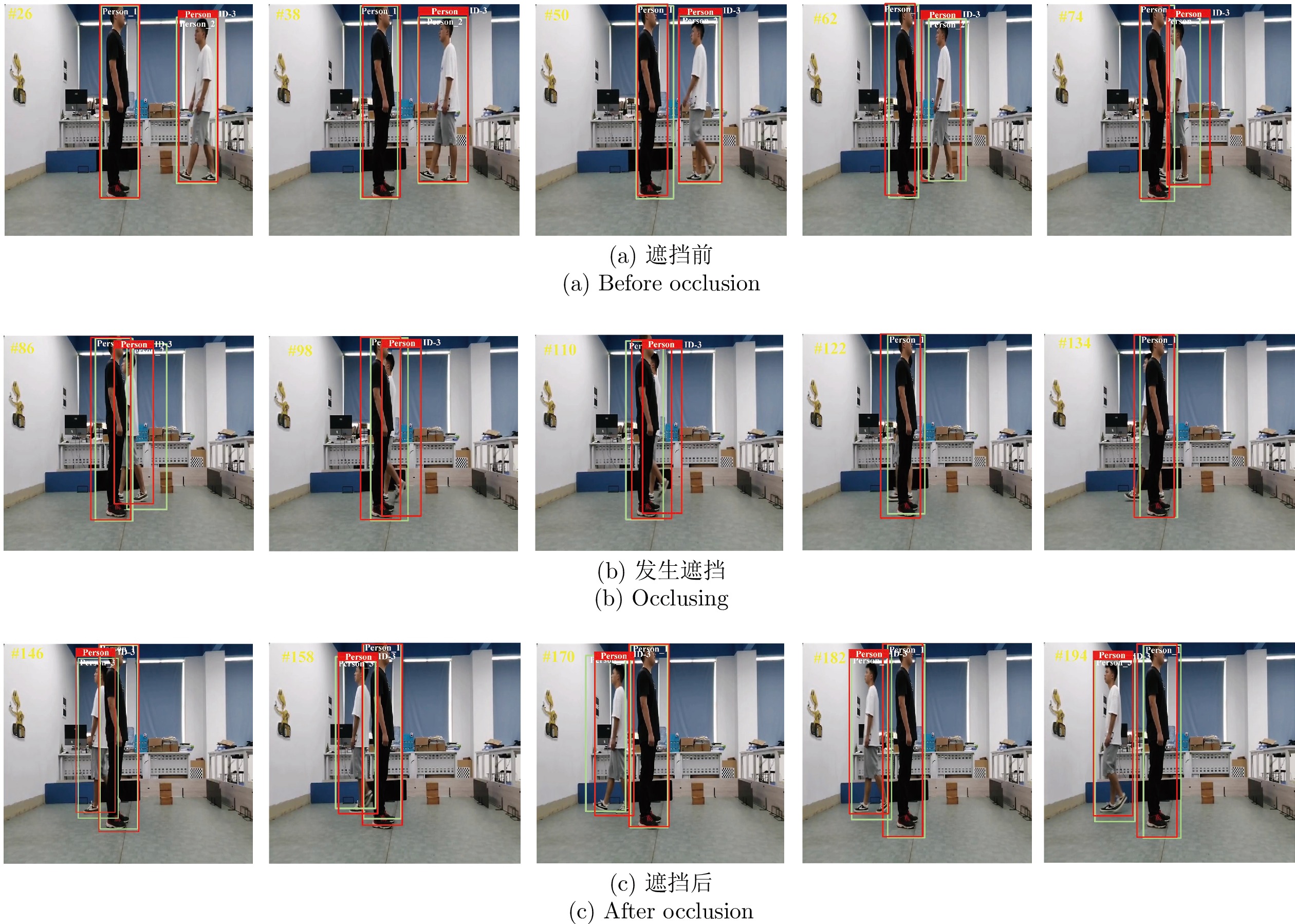
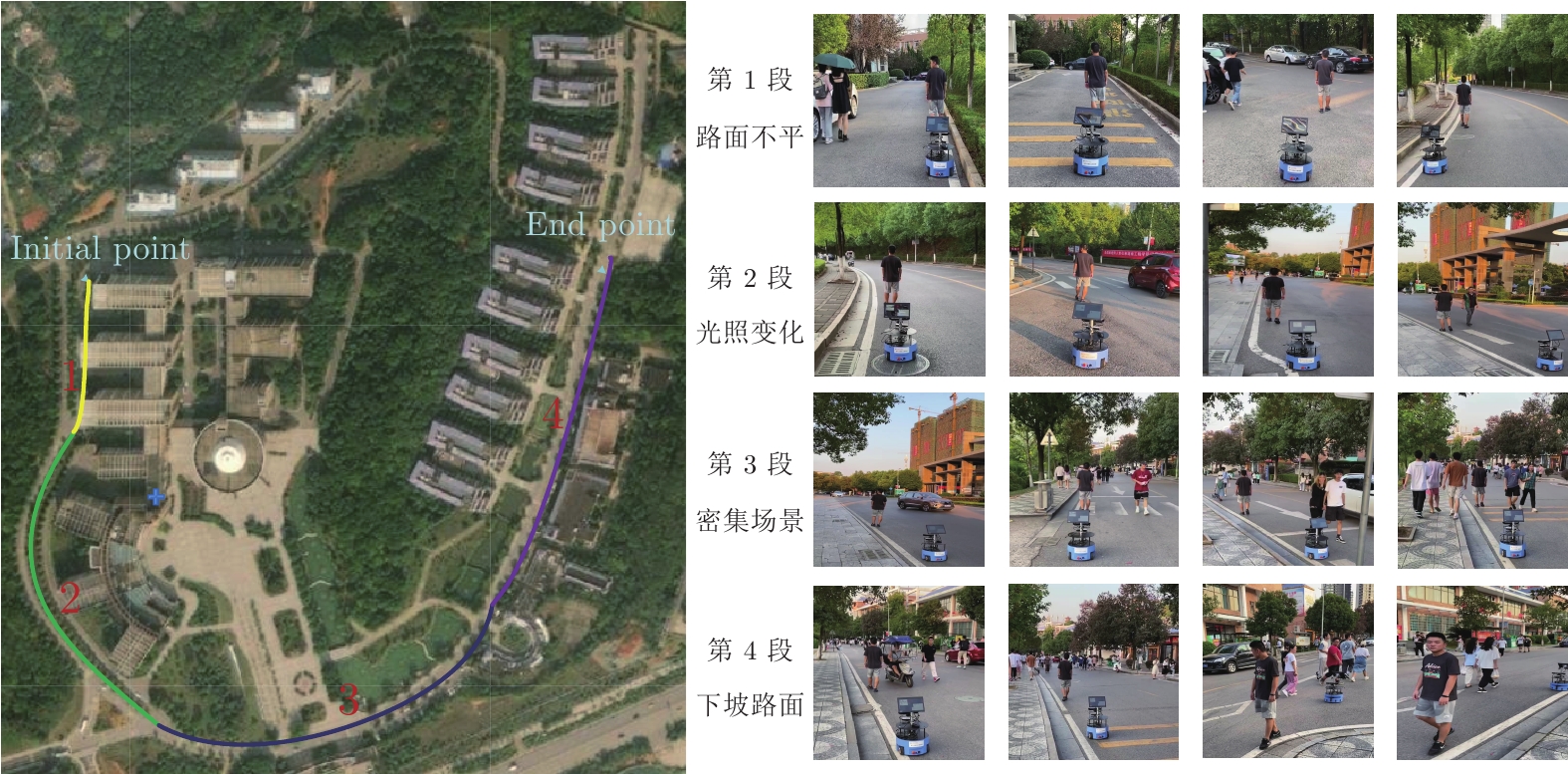
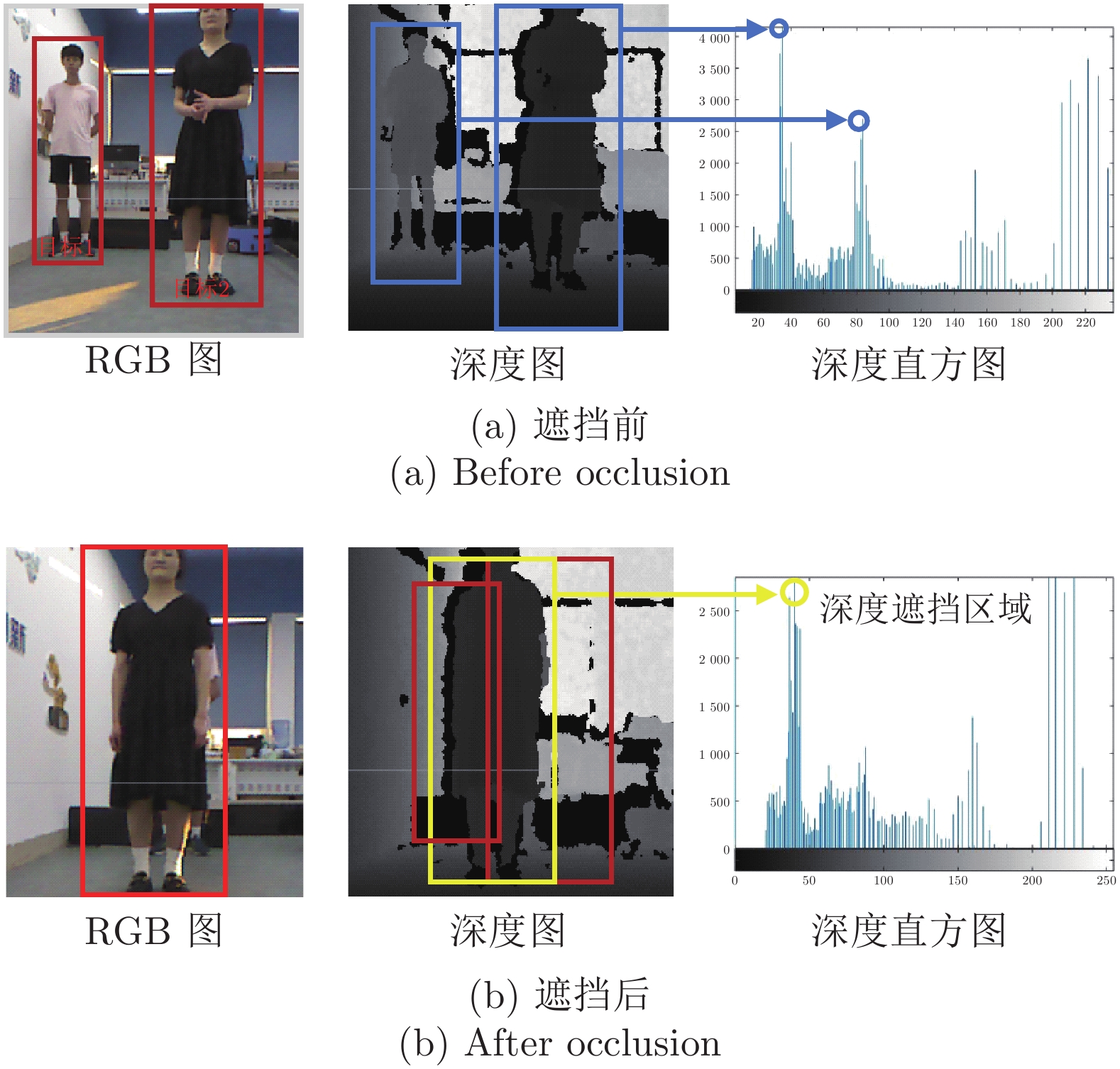
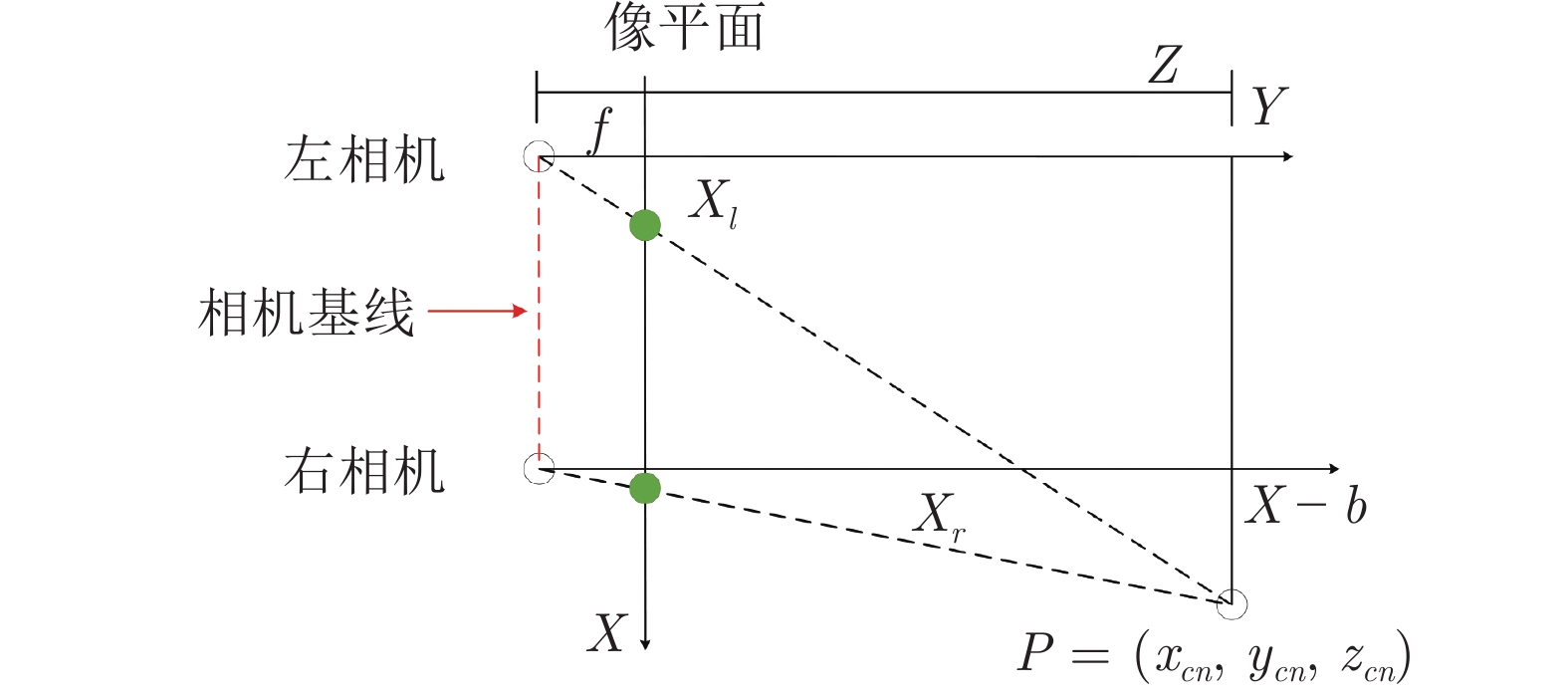
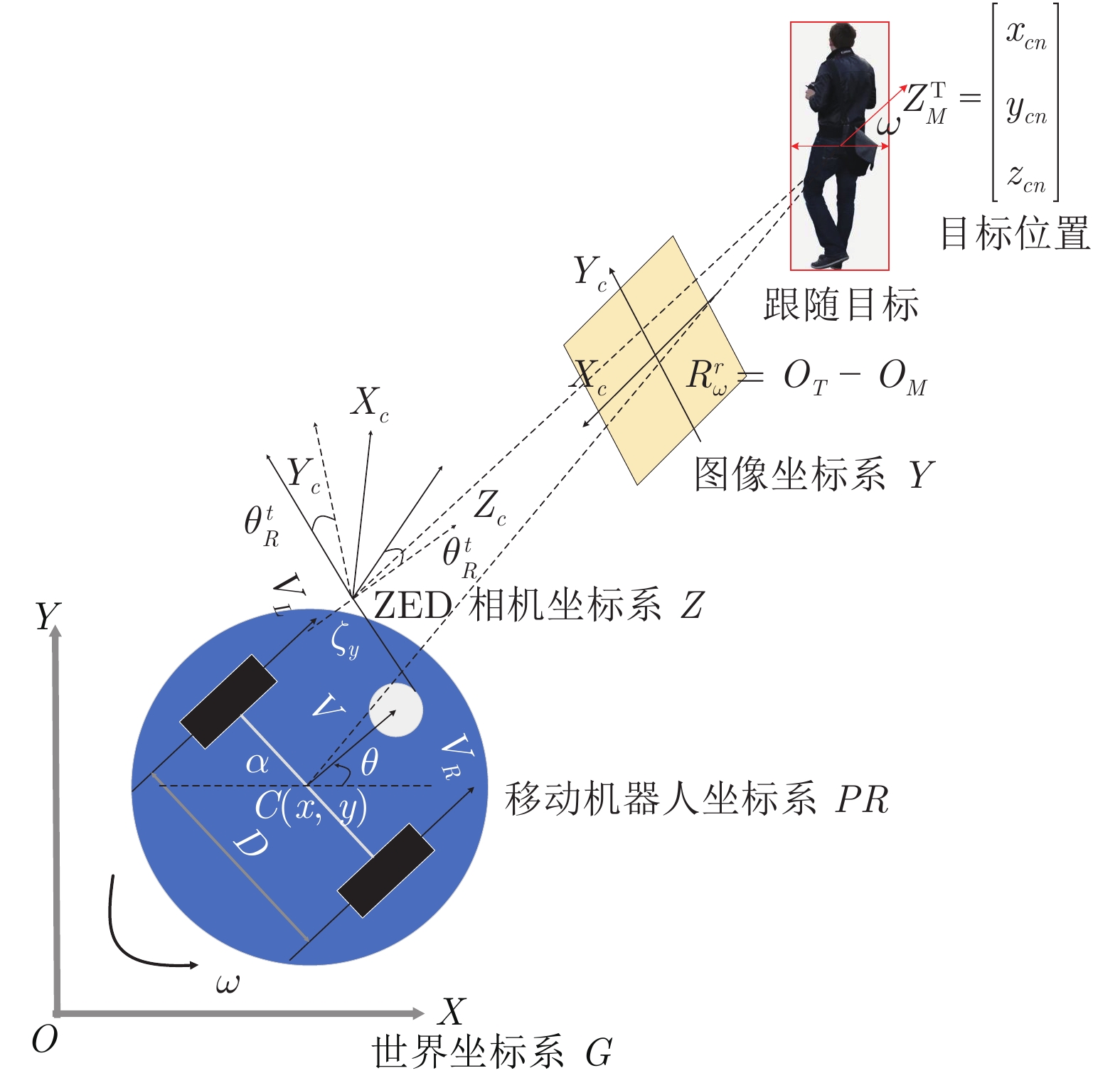
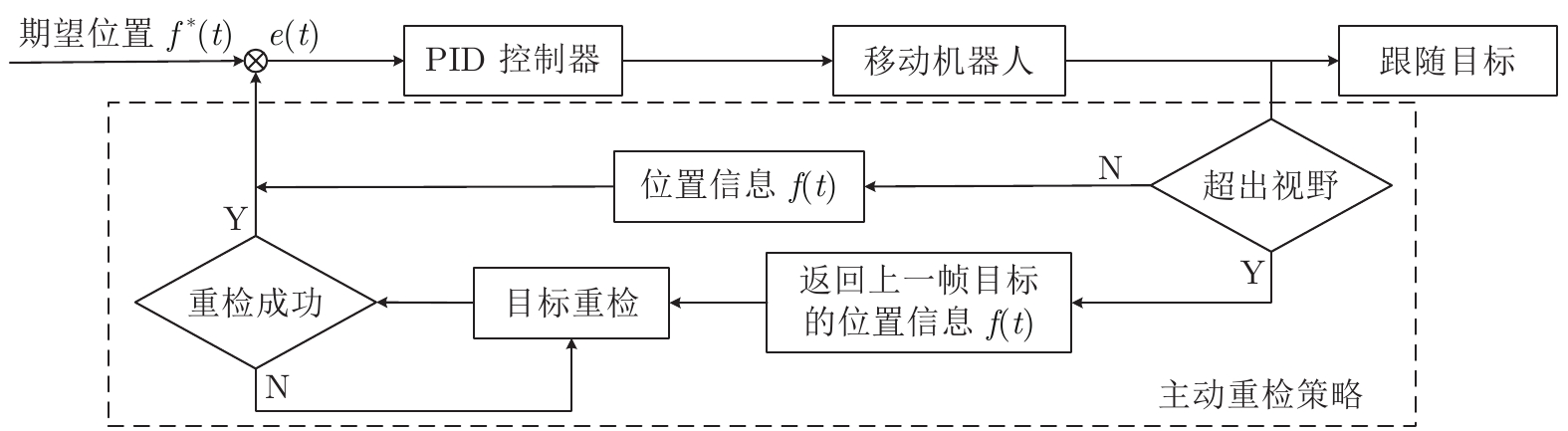
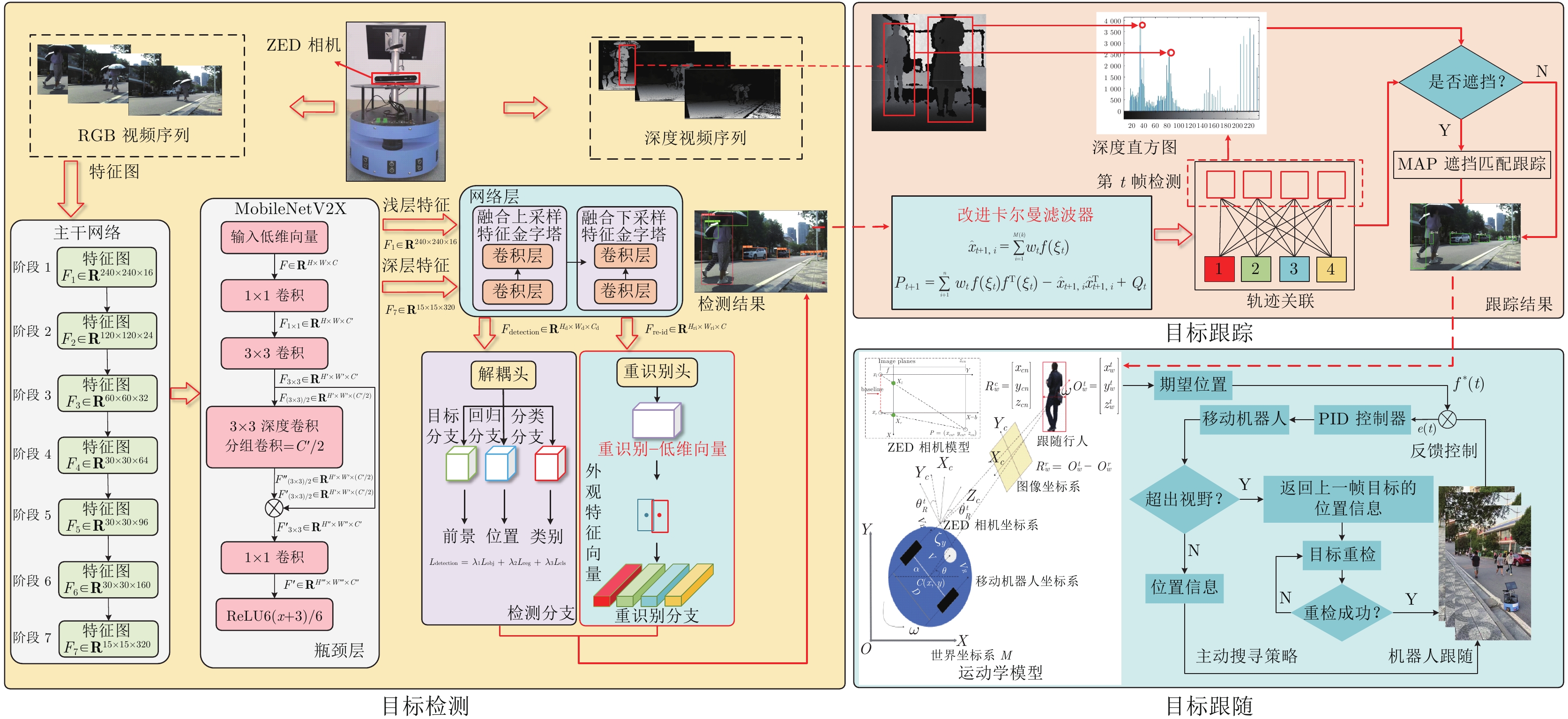
摘要: 针对移动机器人在复杂场景中难以稳定跟随目标的问题, 提出基于改进YOLOX的移动机器人目标跟随方法, 主要包括目标检测、目标跟踪以及目标跟随三个部分. 首先, 以 YOLOX 网络为基础, 在其框架下将主干网络采用轻量化网络 MobileNetV2X, 提高复杂场景中目标检测的实时性. 然后, 通过改进的卡尔曼滤波器获取目标跟踪状态并采用数据关联进行目标匹配, 同时通过深度直方图判定目标发生遮挡后, 采用深度概率信息约束及最大后验概率(Maximum a posteriori, MAP)进行匹配跟踪, 确保机器人在遮挡情况下稳定跟踪目标. 再采用基于视觉伺服控制的目标跟随算法, 当跟踪目标丢失时, 引入重识别特征主动搜寻目标实现目标跟随. 最后, 在公开数据集上与具有代表性的目标跟随方法进行了定性和定量实验, 同时在真实场景中完成了移动机器人目标跟随实验, 实验结果均验证了所提方法具有较好的鲁棒性和实时性.Abstract: A target following method of mobile robot based on improved YOLOX is proposed to solve the problem that mobile robots are difficult to follow the target stably in complex scene. This method mainly includes three parts: Target detection, target tracking and target following. Firstly, the lightweight MobileNetV2X network is adopted under the YOLOX framework to improve the real-time performance of target detection in complex scene. Then, the improved Kalman filter is proposed to obtain the tracking state and data association is used for target matching. When the target is judged by depth-histogram, the depth probability constraint and maximum a posteriori (MAP) probability are utilized for matching, which ensure that the robot tracks the target stably under occlusion. Moreover, target-following algorithm based on servo control is proposed, and re-id feature is introduced to actively search for disappeared targets. Finally, qualitative and quantitative experiments on public data set and in real-world environments demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- Mobile robot /
- YOLOX /
- re-id /
- target following
-
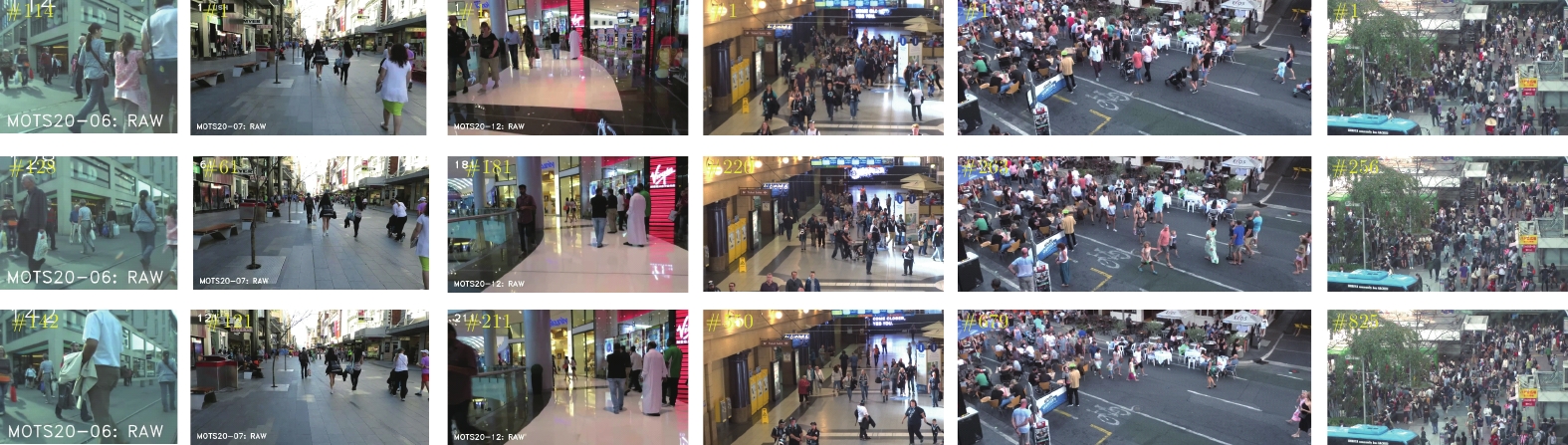
表 1 测试集视频序列
Table 1 Test set video sequences
名称 视频帧率 (帧/s) 分辨率 (像素) 视频时间 (s) 目标数量 目标框数 密集度 场景 MOT2008 25 1920×734 806 (00:32) 279 145301 180.3 步行街 MOT2002 25 1920×1080 2782 (01:51) 296 202215 72.7 室内火车站 HT2114 25 1920×1080 1050 (00:42) 1040 258227 245.9 室内火车站 MOTS2007 30 1920×1080 500 (00:17) 58 12878 25.8 步行街 MOTS2012 30 1920×1080 900 (00:30) 68 6471 7.2 购物中心 MOTS2006 14 640×480 1194 (01:25) 190 9814 8.2 街道 表 2 网络消融实验
Table 2 The ablation studies of the proposed network
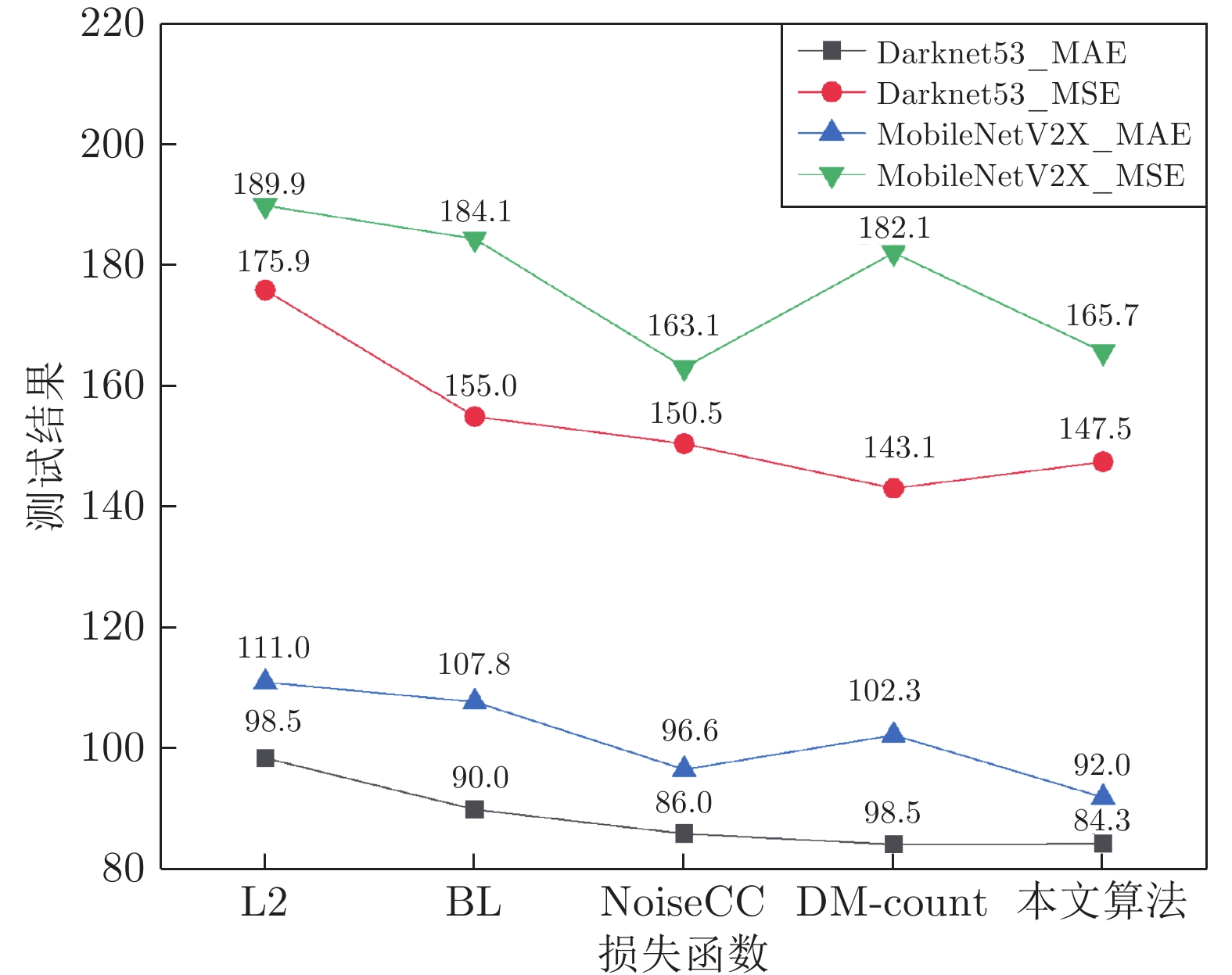
ID 主干网络 Presion Recall F1 mAP Flops (GHz) Darknet53 MobileNetV2X 1 $ \surd $ 0.929 0.980 0.954 0.969 21.79 2 $ \surd $ 0.910 0.972 0.941 0.970 8.65 3 $ \surd $ 0.935 0.974 0.952 0.971 9.46 4 $ \surd $ 0.940 0.980 0.960 0.980 9.85 表 3 各项性能指标
Table 3 Each performance index
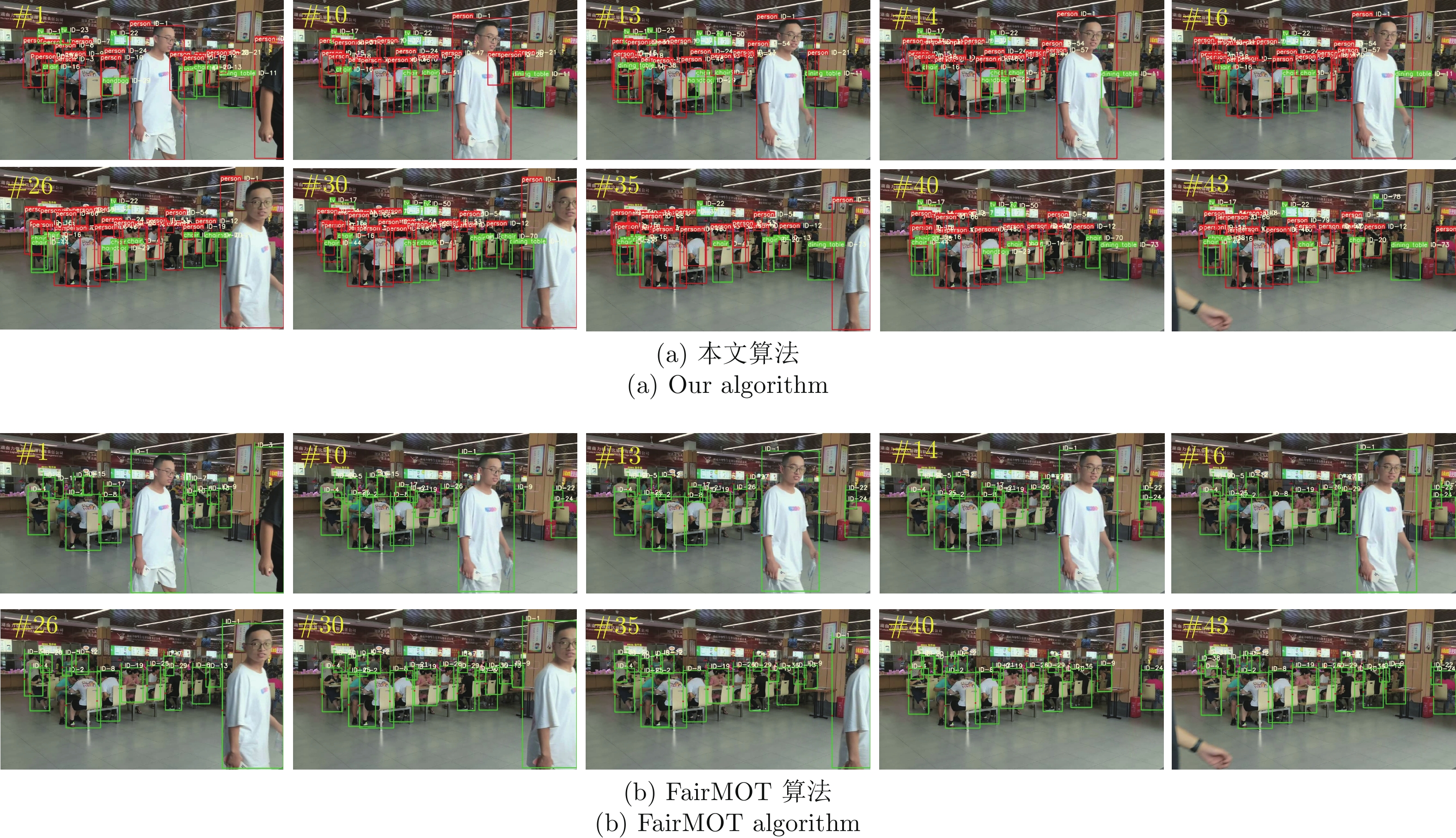
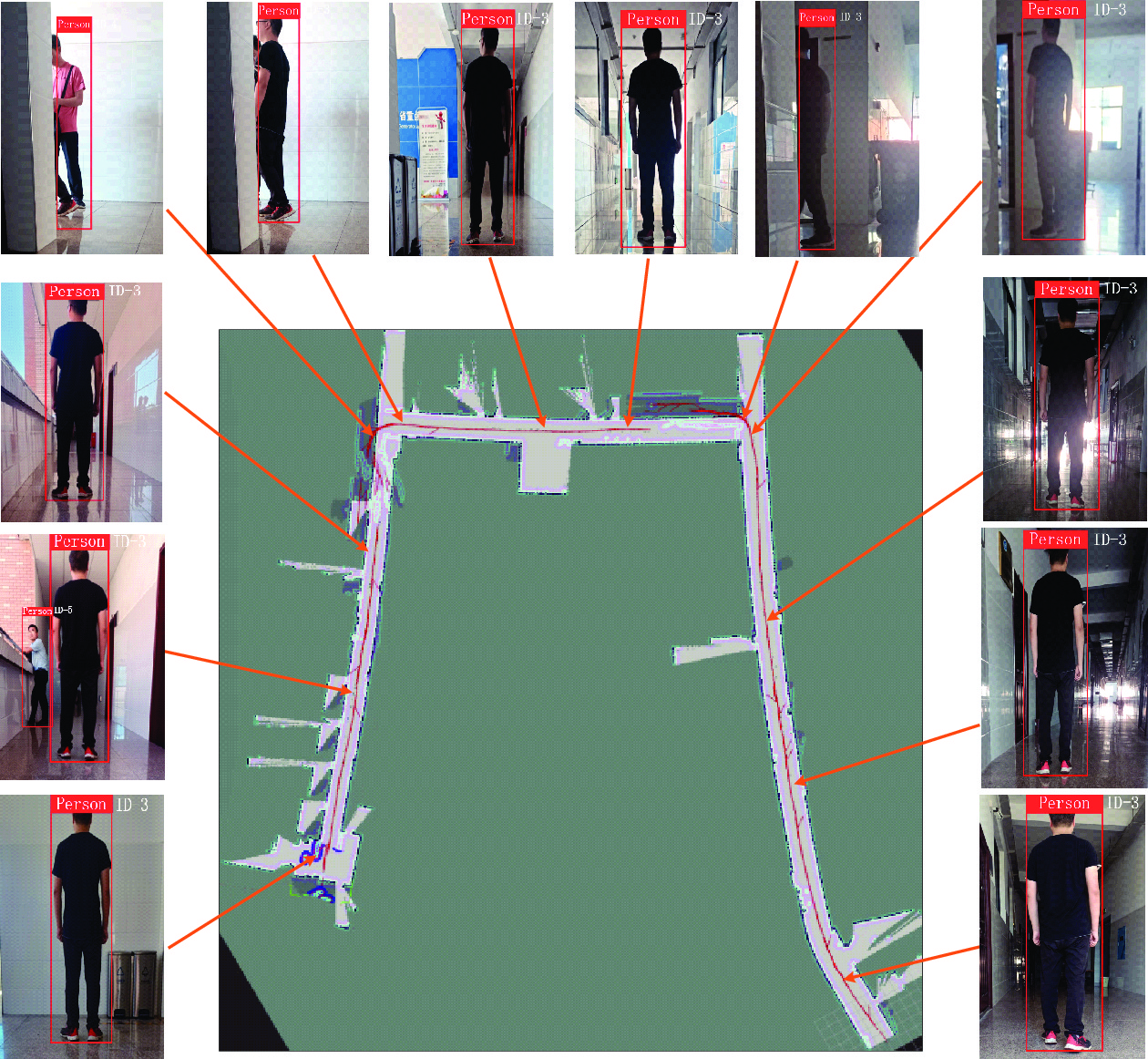
测试集 目标跟踪算法 $ \text{MOTA}\uparrow $ $ \text{IDF1}\uparrow $ $\text{MT}\;(\%) \uparrow$ $\text{ML}\;(\%)\downarrow$ $ \text{IDs}\downarrow $ $\text{FPS}\;(帧/{\rm{s} })\uparrow$ MOT2008 DeepSORT 47.3 55.6 30.10 18.70 625 22 FairMOT 52.3 54.2 36.20 22.30 543 27 CTrack 53.1 54.1 36.00 19.70 736 31 Real-time MOT 52.9 52.3 29.20 20.30 709 34 本文算法 58.6 58.7 40.60 11.00 591 38 MOT2002 DeepSORT 52.6 53.4 19.80 34.70 912 24 FairMOT 59.7 53.6 25.30 22.80 1420 28 CTrack 61.4 62.2 32.80 18.20 781 32 Real-time MOT 63.0 63.8 39.90 22.10 482 29 本文算法 67.9 68.8 44.70 15.90 1074 35 HT2114 DeepSORT 52.4 49.5 21.40 30.70 8431 24 FairMOT 63.0 58.6 31.20 19.90 4137 25 CTrack 66.6 57.4 32.20 24.20 5529 22 Real-time MOT 67.8 64.7 34.60 24.60 2583 21 本文算法 73.7 68.3 38.20 17.30 3303 27 MOTS2007 DeepSORT 53.0 48.0 22.70 28.90 89 23 FairMOT 60.1 49.9 28.40 25.00 135 27 CTrack 61.2 54.0 30.60 21.60 68 30 Real-time MOT 64.0 56.4 33.70 20.30 104 33 本文算法 67.9 59.3 35.90 18.40 98 39 MOTS2006 DeepSORT 55.7 46.3 30.00 27.90 67 19 FairMOT 63.8 49.7 31.80 25.50 79 23 CTrack 65.3 52.6 34.10 24.00 84 25 Real-time MOT 66.9 54.9 36.90 21.20 91 29 本文算法 69.1 57.0 38.00 18.00 71 31 MOTS2012 DeepSORT 49.6 47.9 24.60 26.40 85 17 FairMOT 52.8 49.3 27.50 24.90 68 20 CTrack 55.7 52.1 29.90 21.70 78 23 Real-time MOT 58.1 55.2 34.00 18.50 64 25 本文算法 61.3 56.4 37.50 15.90 58 27 -
[1] 王丽佳, 贾松敏, 李秀智, 王爽. 基于改进在线多示例学习算法的机器人目标跟踪. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(12): 2916-2925Wang Li-Jia, Jia Song-Min, Li Xiu-Zhi, Wang Shuang. Person following for mobile robot using improved multiple instance learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(12): 2916-2925 [2] 曹风魁, 庄严, 闫飞, 杨奇峰, 王伟. 移动机器人长期自主环境适应研究进展和展望. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(2): 205-221 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180493Cao Feng-Kui, Zhuang Yan, Yan Fei, Yang Qi-Feng, Wang Wei. Long-term autonomous environment adaptation of mobile robots: State-of-the-art methods and prospects. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(2): 205-221 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180493 [3] 余铎, 王耀南, 毛建旭, 郑海华, 周显恩. 基于视觉的移动机器人目标跟踪方法. 仪器仪表学报, 2019, 40 (1): 227-235 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1804340Yu Duo, Wang Yao-Nan, Mao Jian-Xu, Zheng Hai-Hua, Zhou Xian-En. Vision-based object tracking method of mobile robot. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2019, 40(1): 227-235 doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1804340 [4] 黄琰, 李岩, 俞建成, 封锡盛. AUV智能化现状与发展趋势. 机器人, 2020, 42(2): 215-231 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.190392Huang Yan, Li Yan, Yu Jian-Cheng, Feng Xi-Sheng. State-of-theart and development trends of AUV intelligence. Robot, 2020, 42(2): 215-231 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.190392 [5] Marvasti-Zadeh S M, Cheng L, Ghanei-Yakhdan H, Kasaei S. Deep learning for visual tracking: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 23(5): 3943-3968 [6] Ciaparrone G, Sánchez F L, Tabik S, Troiano L, Tagliaferri R, Herrera F. Deep learning in video multi-object tracking: A survey. Neurocomputing, 2020, 381(14): 61-88 [7] Yoshimi T, Nishiyama M, Sonoura T, Nakamoto H, Tokura S, Sato H, et al. Development of a person following robot with vision based target detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2006. 5286−5291 [8] 蒋弘毅, 王永娟, 康锦煜. 目标检测模型及其优化方法综述. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(6): 1232-1255 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190756Jiang Hong-Yi, Wang Yong-Juan, Kang Jin-Yu. A survey of object detection models and its optimization methods. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(6): 1232-1255 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190756 [9] Zhang M Y, Liu X L, Xu D, Cao Z Q, Yu J Z. Vision-based target-following guider for mobile robot. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(12): 9360-9371 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2893829 [10] Pang L, Cao Z Q, Yu J Z, Guan P Y, Chen X C, Zhang W M. A robust visual person-following approach for mobile robots in disturbing environments. IEEE Systems Journal, 2019, 14(2): 2965-2968 [11] Zhang Y F, Wang C Y, Wang X G, Zeng W J, Liu W Y. Fairmot: On the fairness of detection and re-identification in multiple object tracking. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(11): 3069-3087 doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01513-4 [12] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 779−788 [13] Hsu W Y, Lin W Y. Ratio-and-scale-aware YOLO for pedestrian detection. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 3029: 934-947 [14] Huang J H, Zhang H Y, Wang L, Zhang Z L, Zhao C M. Improved YOLOv3 model for miniature camera detection. Optics and Laser Technology, 2021, 142: Aricle No. 107133 [15] Bochkovskiy A, Wang C Y, Liao H Y M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934, April 23, 2020 [16] Benjumea A, Teeti I, Cuzzolin F, Bradley A. YOLO-Z: Improving small object detection in YOLOv5 for autonomous vehicles [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.11798, December 22, 2021 [17] Cheng L, Liu W Z. An effective microscopic detection method for automated silicon-substrate ultra-microtome (ASUM). Neural Processing Letters, 2021, 53(3): 1723-1740 doi: 10.1007/s11063-019-10134-5 [18] Conley G, Zinn S C, Hanson T, McDonald K, Beck N, Wen H. Using a deep learning model to quantify trash accumulation for cleaner urban stormwater. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 2022, 93: Aricle No. 101752 [19] Hussain M, Al-Aqrabi H, Munawar M, Hill R, Alsboui T. Domain feature mapping with YOLOv7 for automated edge-based pallet racking inspections. Sensors, 2022, 22(18): Aricle No. 6927 [20] Ge Z, Liu S T, Wang F, Li Z M, Sun J. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO series in 2021 [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.08430, July 18, 2021 [21] Yan F X, Xu Y X. Improved target detection algorithm based on YOLO. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Robotics, Control and Automation Engineering (RCAE). Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2021. 21−25 [22] Wojke N, Bewley A, Paulus D. Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2017. 3645−3649 [23] Han D Y, Peng Y G. Human-following of mobile robots based on object tracking and depth vision. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics, Robotics and Automation (ICMRA). Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2020. 105−109 [24] Addabbo T, Fort A, Mugnaini M, Vignoli V, Intravaia M, Tani M, et al. Smart gravimetric system for enhanced security of accesses to public places embedding a mobilenet neural network classifier. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 1-10 [25] Peng J L, Wang C G, Wan F B, Wu Y, Wang Y B, Tai Y, et al. Chained-tracker: Chaining paired attentive regression results for end-to-end joint multiple-object detection and tracking. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision Springer. Glasgow, UK: Cham, 2020. 145−161 [26] Wang Z D, Zheng L, Liu Y X, Li Y L, Wang S J. Towards real-time multi-object tracking. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision Springer. Glasgow, UK: Cham, 2020. 107−122 [27] Milan A, Leal-Taixé L, Reid L, Roth S, Schindler K. MOT16: A benchmark for multi-object tracking [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.00831, March 2, 2016 [28] Song Y, Zhang Y Y, Liu L. Path following control of tracked mobile robot based on dual heuristic programming. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Control, Automation and Robotics (ICCAR). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2019. 79−84 [29] Aetesam H, Maji S K, Yahia H. Bayesian approach in a learning-based hyperspectral image denoising framework. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 169335-169347 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3137656 [30] Koay H V, Chuah J H, Chow C O. Shifted-window hierarchical vision transformer for distracted driver detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP). Jeju, South Korea: IEEE, 2021. 1−7 -




 下载:
下载: