-
摘要: 共识算法是区块链技术的核心要素,也是近年来分布式系统研究的热点.本文系统性地梳理和讨论了区块链发展过程中的32种重要共识算法,介绍了传统分布式一致性算法以及分布式共识领域的里程碑式的重要研究和结论,提出了区块链共识算法的一种基础模型和分类方法,并总结了现有共识算法的发展脉络和若干性能指标,以期为未来共识算法的创新和区块链技术的发展提供参考.Abstract: Consensus algorithm is a key component of the blockchain technology, and also a hot topic in distributed systems research. In this paper, we systematically review and discuss 32 mainstream consensus algorithms emerged in the development process of blockchain. We introduce the classic distributed consistency algorithms, as well as the milestone research efforts and the key conclusions of distributed consensus algorithms. We also propose a novel model and classification approach of blockchain consensus algorithms. In the end, we summarize the consensus algorithms and their performance measures using an evolutionary tree. This is our preliminary research effort towards the blockchain consensus algorithm, aiming at offering useful guidance and reference for future innovation of novel consensus algorithms and the development of blockchain technology.1) 本文责任编委 刘艳军
-
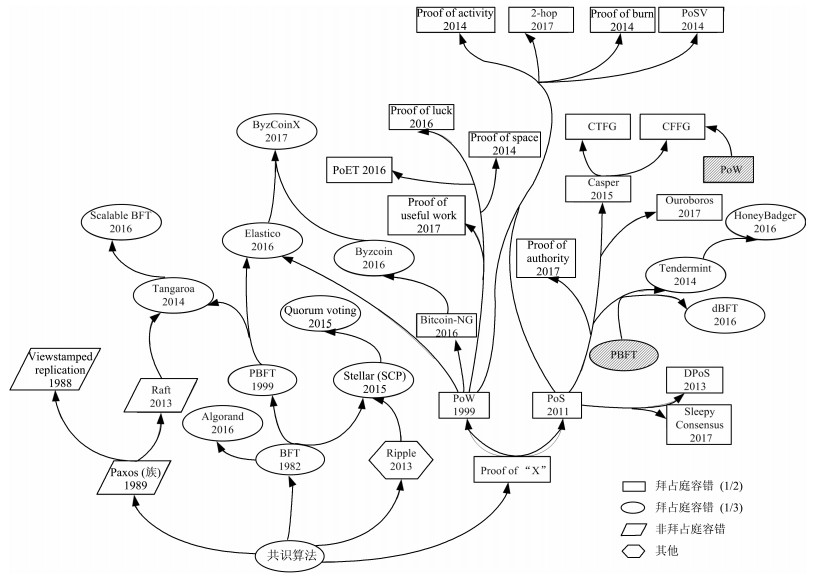
表 1 区块链共识算法汇总表
Table 1 Summary of blockchain consensus algorithms
名称 提出年份 拜占庭容错 基础算法 代表性应用 Viewstamped replication 1988 否 无 BDB-HA Paxos (族) 1989 否 无 Chubby PBFT 1999 是(<1/3) BFT Hyperledger v0.6.0 PoW 1999 是(<1/2) 无 Bitcoin PoS 2011 是(<1/2) 无 Peercoin, Nxt DPoS 2013 是(<1/2) PoS EOS, Bitshares Raft 2013 否 无 etcd, braft Ripple 2013 是(<1/5) 无 Ripple Tendermint 2014 是(<1/3) PoS+PBFT Monax Tangaroa (BFTRaft) 2014 是(<1/3) Raft+PBFT — Proof of activity 2014 是(<1/2) PoW+PoS Decred Proof of burn 2014 是(<1/2) PoW+PoS Slimcoin Proof of space 2014 是(<1/2) PoW Burstcoin Proof of stake velocity (PoSV) 2014 是(<1/2) PoW+PoS ReddCoin Casper 2015 是(<1/2) PoW+PoS Ethereum Quorum voting 2015 是(<1/3) Ripple+Stellar Sawtooth Lake Stellar (SCP) 2015 是(<1/3) Ripple+BFT Stellar Algorand 2016 是(<1/3) PoS+BFT ArcBlock Bitcoin-NG 2016 是(<1/2) PoW — Byzcoin 2016 是(<1/3) BTC-NG — dBFT 2016 是(<1/3) PoS+pBFT NEO Elastico 2016 是(<1/3) PBFT+PoW — HoneyBadger 2016 是(<1/3) Tendermint — PoET 2016 是(<1/2) PoW Sawtooth Lake Proof of luck 2016 是(<1/2) PoW Luckychain Scalable BFT 2016 是(<1/3) Tangaroa Kadena 2-hop 2017 是(<1/2) PoW+PoS — ByzCoinX 2017 是(<1/3) ByzCoin+Elastico OmniLedger Proof of authority 2017 是(<1/2) PoS Parity Proof of useful work 2017 是(<1/2) PoW — Ouroboros 2017 是(<1/2) PoS Cardano Sleepy consensus 2017 是(<1/2) PoS — -
[1] Eisenberg E, Gale D. Consensus of subjective probabilities:the pari-mutuel method. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1959, 30(1):165-168 http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/external-ref?access_num=10.1214/aoms/1177706369&link_type=DOI [2] Nakamoto S. Bitcoin: a peer-to-peer electronic cash system[Online], available: http://bitcoins.info/bitcoin.pdf, April 10, 2018. [3] 袁勇, 王飞跃.区块链技术发展现状与展望.自动化学报, 2016, 42(4):481-494 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18837.shtmlYuan Yong, Wang Fei-Yue. Blockchain:the state of the art and future trends. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4):481-494 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18837.shtml [4] 袁勇, 周涛, 周傲英, 段永朝, 王飞跃.区块链技术:从数据智能到知识自动化.自动化学报, 2017, 43(9):1485-1490 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19125.shtmlYuan Yong, Zhou Tao, Zhou Ao-Ying, Duan Yong-Chao, Wang Fei-Yue. Blockchain technology:from data intelligence to knowledge automation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(9):1485-1490 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19125.shtml [5] 袁勇, 王飞跃.平行区块链:概念、方法与内涵解析.自动化学报, 2017, 43(10):1703-1712 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19148.shtmlYuan Yong, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel blockchain:concept, methods and issues. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(10):1703-1712 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19148.shtml [6] 曾帅, 袁勇, 倪晓春, 王飞跃.面向比特币的区块链扩容: 关键技术, 制约因素与衍生问题.自动化学报, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c180100Zeng Shuai, Yuan Yong, Ni Xiao-Chun, Wang Fei-Yue. Scaling blockchain towards bitcoin: key technologies, constraints and related issues. Acta Automatica Sinica, DOI: 10.16383/j.aas.c180100 [7] Akkoyunlu E A, Ekanadham K, Huber R V. Some constraints and tradeoffs in the design of network communications. In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles. Austin, Texas, USA: ACM, 1975. 67-74 http://www.mendeley.com/research/some-constraints-tradeoffs-design-network-communications/ [8] Gray J N. Notes on data base operating systems. Operating Systems:An Advanced Course. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 1978. 393-481 [9] Pease M, Shostak R, Lamport L. Reaching agreement in the presence of faults. Journal of the ACM, 1980, 27(2):228-234 doi: 10.1145/322186.322188 [10] Lamport L, Shostak R, Pease M. The Byzantine generals problem. ACM Transactions on Programming Languages and Systems, 1982, 4(3):382-401 doi: 10.1145/357172.357176 [11] Fischer M J, Lynch N A, Paterson M S. Impossibility of distributed consensus with one faulty process. Journal of the ACM, 1985, 32(2):374-382 doi: 10.1145/3149.214121 [12] Oki B M, Liskov B H. Viewstamped replication: a new primary copy method to support highly-available distributed systems. In: Proceedings of the 7th Annual ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: ACM, 1988. 8-17 http://www.mendeley.com/catalog/viewstamped-replication-new-primary-copy-method-support-highlyavailable-distributed-systems/ [13] Lamport L. The part-time parliament. ACM Transactions on Computer Systems, 1998, 16(2):133-169 doi: 10.1145/279227.279229 [14] Wattenhofer R. The Science of the Blockchain. USA:CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, 2016. [15] Dwork C, Naor M. Pricing via processing or combatting junk mail. In: Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology. Santa Barbara, California, USA: Springer-Verlag, 1992. 139-147 http://www.springerlink.com/content/l90we8aq0nre2a4n [16] Back A. Hashcash-a denial of service counter-measure[Online], available: http://www.hashcash.org/papers/hashcash.pdf, April 10, 2018. [17] Jakobsson M, Juels A. Proofs of work and bread pudding protocols (extended abstract). Secure Information Networks. Boston, MA, Germany:Springer, 1999. 258-272 http://www.springerlink.com/content/fulltext.pdf?id=doi:10.1007/978-0-387-35568-9_18 [18] Castro M, Liskov B. Practical Byzantine fault tolerance. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation. New Orleans, USA: USENIX Association, 1999. 173-186 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=296824 [19] Gilbert S, Lynch N. Brewer's conjecture and the feasibility of consistent, available, partition-tolerant web services. ACM SIGACT News, 2002, 33(2):51-59 doi: 10.1145/564585 [20] Proof of stake[Online], available: https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Proof_of_Stake, April 11, 2018. [21] Schwartz D, Youngs N, Britto A. The Ripple protocol consensus algorithm[Online], available: https://ripple.com/files/ripple_consensus_whitepaper.pdf, April 10, 2018. [22] BitShares. Delegated proof of stake[Online], available: http://docs.bitshares.org/bitshares/dpos.html, April 10, 2018. [23] Ongaro D, Ousterhout J. In search of an understandable consensus algorithm. In: Proceedings of the USENIX Annual Technical Conference. Philadelphia, PA, USA: USENIX ATC, 2014. 305-319 [24] Lamport L. Paxos made simple. ACM SIGACT News, 2001, 32(4):51-58 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0235401123/ [25] Ren L. Proof of stake velocity: building the social currency of the digital age[Online], available: https://assets.coss.io/documents/white-papers/reddcoin.pdf, April 10, 2018. [26] Proof of burn[Online], available: https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Proof of burn, April 10, 2018. [27] Bentov I, Lee C, Mizrahi A, Rosenfeld M. Proof of activity: extending Bitcoin's proof of work via proof of stake[Online], available: http://eprint.iacr.org/2014/452, April 10, 2018. [28] Duong T, Fan L, Zhou H S. 2-hop blockchain: combining proof-of-work and proof-of-stake securely[Online], available: https://eprint.iacr.org/2016/716, April 10, 2018. [29] Kwon J. Tendermint: consensus without mining[Online], available: https://tendermint.com/static/docs/ten-dermint.pdf, April 10, 2018. [30] Ethereum's Casper protocol explained in simple terms[Online], available: https://www.finder.com/ethereum-casper, April 10, 2018. [31] David B, Gaži P, Kiayias A, Russell A. Ouroboros Praos: an adaptively-secure, semi-synchronous proof-of-stake protocol[Online], available: http://eprint.iacr.org/2017/573, April 10, 2018. [32] Goodman L M. Tezos-a self-amending crypto-ledger position paper[Online], available: https://www.tezos.com/static/papers/position_paper.pdf, April 10, 2018. [33] Miller A, Xia Y, Croman K, Shi E, Song D. The honey badger of BFT protocols. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. Vienna, Austria: ACM, 2016. 31-42 [34] Zamfir V. Introducing Casper "the Friendly Ghost"[Online], available: https://blog.ethereum.org/2015/08/01/introducing-casper-friendly-ghost/, April 10, 2018. [35] Buterin V, Griffith V. Casper the friendly finality gadget[Online], available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1710.09437.pdf, April 10, 2018. [36] Eyal I, Gencer A E, Sirer E G, van Renesse R. Bitcoin-NG: a scalable blockchain protocol. In: Proceedings of the 13th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation. Santa Clara, USA: USENIX Association, 2016. 45-59 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2930615 [37] Kogias E K, Jovanovic P, Gailly N, Khoffi I, Gasser L, Ford B. Enhancing bitcoin security and performance with strong consistency via collective signing. In: Proceedings of the 25th USENIX Security Symposium. Austin, TX, USA: USENIX Association, 2016. 279-296 http://memento.epfl.ch/event/enhancing-bitcoin-security-and-performance-with-st/ [38] Luu L, Narayanan V, Zheng C D, Baweja K, Gilbert S, Saxena P. A secure sharding protocol for open blockchains. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. Vienna, Austria: ACM, 2016. 17-30 http://www.deepdyve.com/lp/association-for-computing-machinery/a-secure-sharding-protocol-for-open-blockchains-GYAJ0F0KdC [39] Kokoris-Kogias E, Jovanovic P, Gasser L, Gailly N, Syta E, Ford B. OmniLedger: A secure, scale-out, decentralized ledger via sharding[Online], available: http://eprint.iacr.org/2017/406, April 10, 2018. [40] Buntinx J P. What is proof of elapsed time?[Online], available: https://themerkle.com/what-is-proof-of-elapsed-time/, April 10, 2018. [41] Milutinovic M, He W, Wu H, Kanwal M. Proof of luck: an efficient blockchain consensus protocol[Online], available: https://eprint.iacr.org/2017/249.pdf, April 10, 2018. [42] Ateniese G, Bonacina I, Faonio A, Galesi A. Proofs of space: when space is of the essence. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Security and Cryptography for Networks. Amalfi, Italy: Springer, 2014. 538-557 doi: 10.1007%2F978-3-319-10879-7_31 [43] Ball M, Rosen A, Sabin M, Vasudevan P V. Proofs of useful work[Online], available: https://allquantor.at/blockchain-bib/pdf/ball2017proofs.pdf, April 10, 2018. [44] Copeland C, Zhong H X. Tangaroa: a byzantine fault tolerant raft[Online], available: http://www.scs.stanford.edu/14au-cs244b/labs/projects/copeland_zhong.pdf, April 10, 2018. [45] Martino W. Kadena: the first scalable, high performance private blockchain[Online], available: http://kadena.io/docs/Kadena-ConsensusWhitePaper-Aug2016.pdf, April 10, 2018. [46] Maziéres D. The stellar consensus protocol: a federated model for internet-level consensus[Online], available: https://www.stellar.org/papers/stellar-consensus-protocol.pdf, April 10, 2018. [47] Gilad Y, Hemo R, Micali S, Vlachos G, Zeldovich N. Algorand: scaling byzantine agreements for cryptocurrencies[Online], available: http://eprint.iacr.org/2017/454, April 10, 2018. [48] Pass R, Shi E. The sleepy model of consensus[Online], available: https://eprint.iacr.org/2016/918.pdf, August 16, 2018. [49] Yuan Y, Wang F Y. Blockchain and cryptocurrencies:model, techniques, and applications. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2018, 48(9):1421-1428 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2854904 [50] Zeng S, Ni X C, Yuan Y, Wang F Y. A bibliometric analysis of blockchain research. In: Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (Ⅳ'18). Changshu, China: IEEE, 2018. 102-107 [51] Ni X C, Zeng S, Han X, Yuan Y, Wang F Y. Organizational management using software-defined robots based on smart contracts. In: Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (Ⅳ'18). Changshu, China: IEEE, 2018. 274-279 [52] Wang S, Yuan Y, Wang X, Li J J, Qin R, Wang F Y. An overview of smart contract: architecture, applications, and future trends. In: Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (Ⅳ'18). Changshu, China: IEEE, 2018. 108-113 [53] Li J J, Yuan Y, Wang S, Wang F Y. Transaction queue game in bitcoin blockchain. In: Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (Ⅳ'18). Changshu, China: IEEE, 2018. 114-119 [54] Qin R, Yuan Y, Wang S, Wang F Y. Economic issues in bitcoin minning and blockchain research. In: Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (Ⅳ'18). Changshu, China: IEEE, 2018. 268-273 -




 下载:
下载: