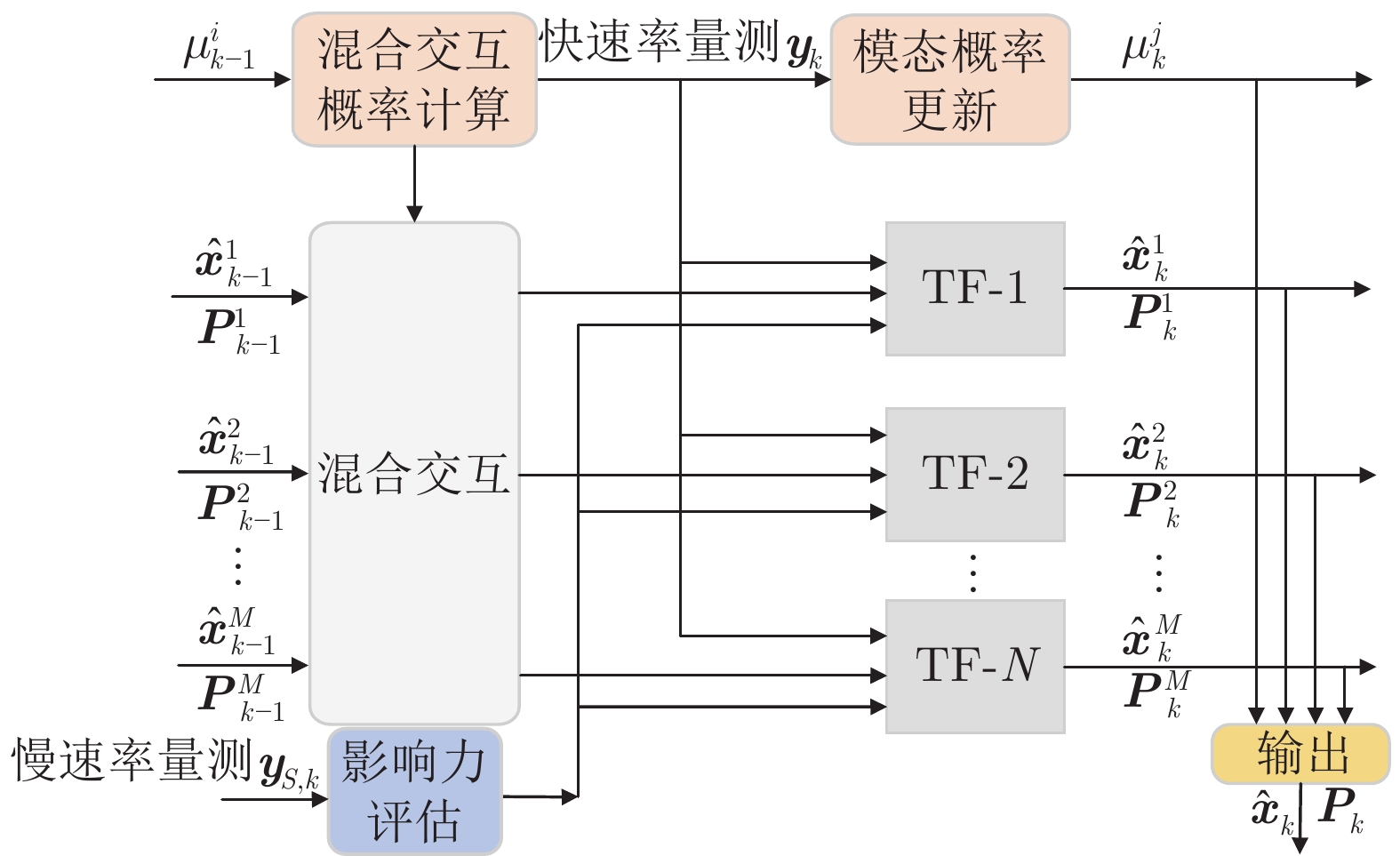
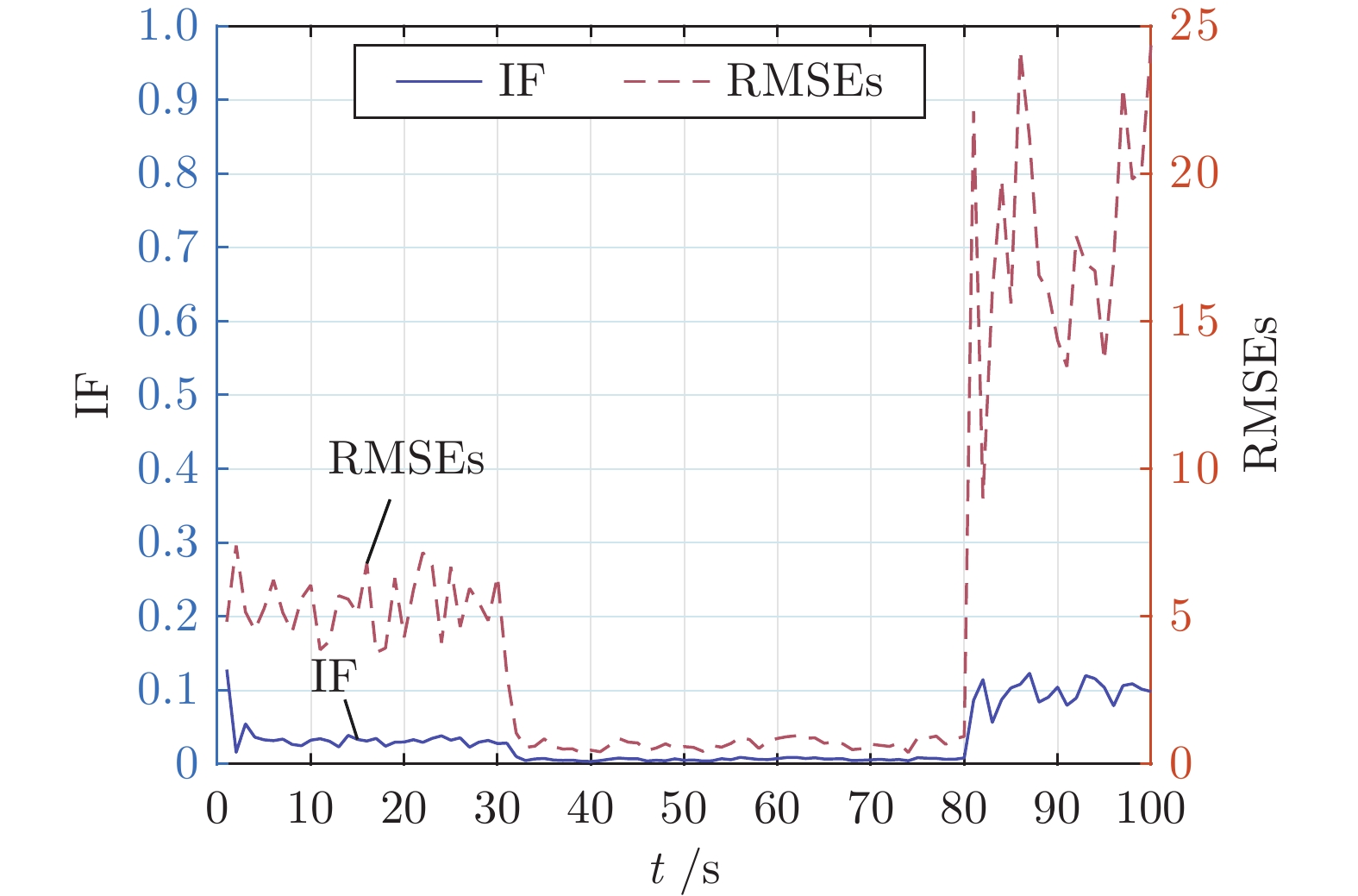
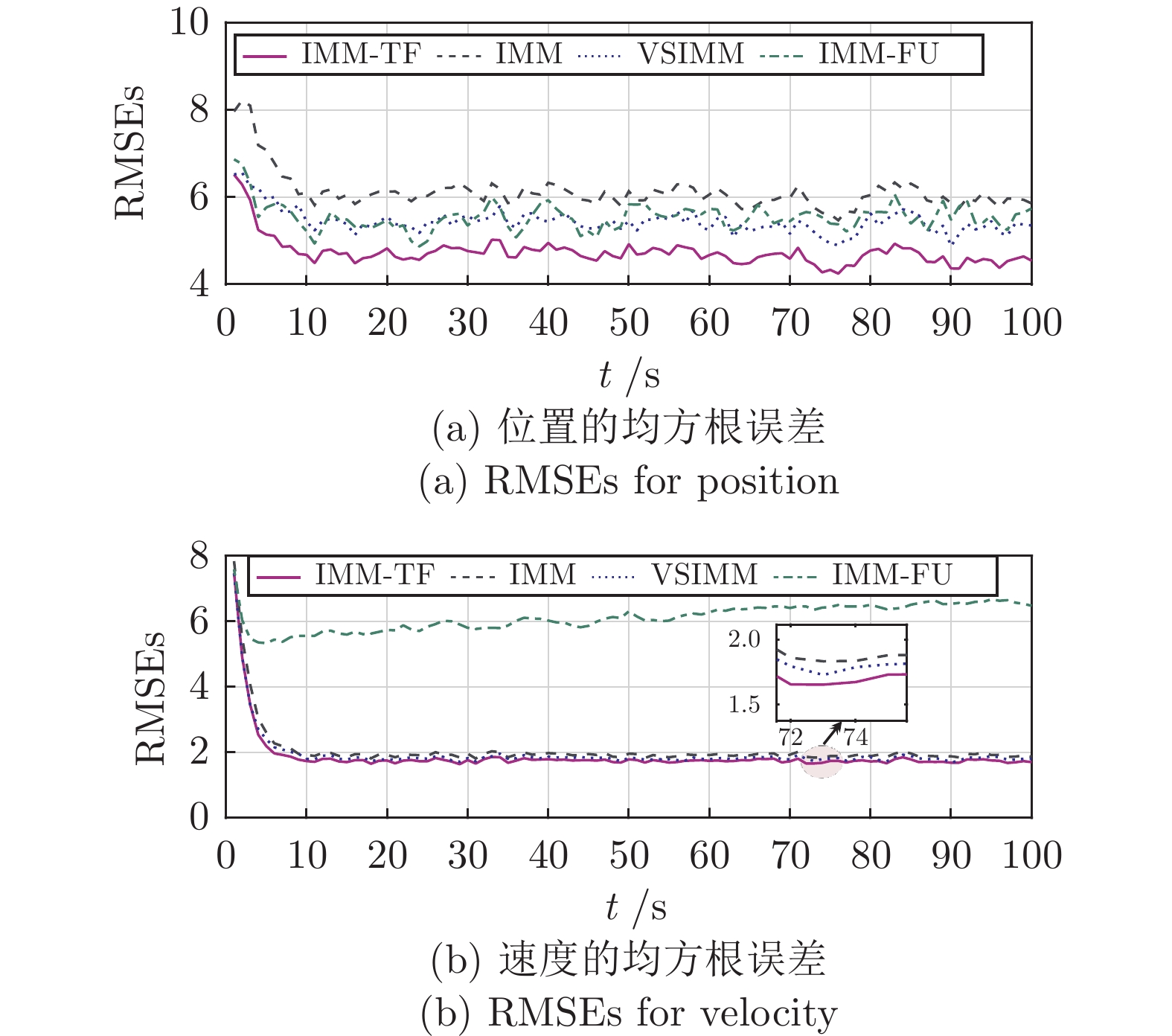
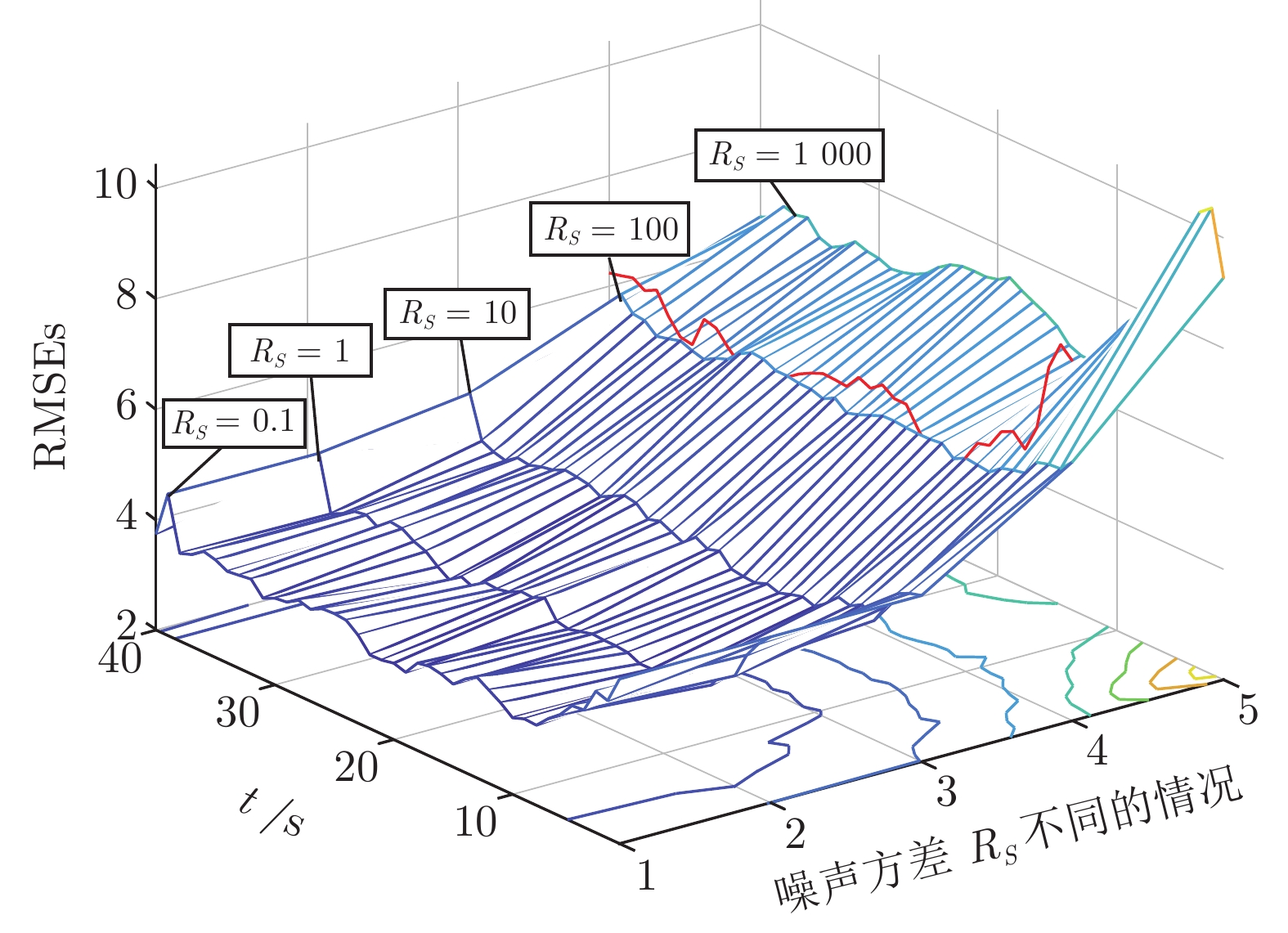
Transfer Interacting Multiple Model State Estimator for Markovian Jump Linear Systems With Multi-rate Measurements
-
摘要: 实际工业过程中, 量测数据除了在线仪表采集的快速率数据, 还有离线化验等慢速率辅助量测数据. 为了更好地利用离线化验数据, 增加在线估计的精度, 针对随机跳变系统, 引入迁移学习思想, 提出迁移交互多模型估计 (Transfer interacting multiple model state estimator, IMM-TF) 新策略. 首先, 将离线化验数据的边缘分布作为可以迁移的知识, 迁移到贝叶斯后验分布, 实现辅助量测数据的充分利用. 其次, 利用KL (Kullback-Leibler) 散度度量知识迁移前后任务间的差异性, 求解最优的贝叶斯迁移估计器. 同时, 结合慢速率量测, 利用平滑策略获取待迁移的估计值, 解决多率量测下的迁移估计难题. 然后, 利用影响力函数构建辅助量测数据与估计性能之间的解析关系, 从而对迁移效果进行定量评价. 最后, 通过在目标跟踪实例中的应用, 表明所提方法的有效性及优越性.Abstract: In industrial processes some measurements are sampled frequently while other measurements are available infrequently and often slow rate. To utilize the slow rate measurements better for improving the accuracy of online estimation, this paper proposes a powerful transfer interacting multiple model state estimator (IMM-TF) for Markovian jump linear systems with multi-rate measurements based on the transfer learning strategy. First, the form of knowledge to be transferred to the Bayesian posterior distribution is designated as the observation predictor derived by using the slow rate measurements. We define universal evaluation of relatedness between the distribution transferred knowledge and ideal posterior distribution from the perspective of Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence to obtain the optimal Bayesian transfer state estimator. Integrated with the slow rate measurements, the smoothing strategy is then proposed to obtain the transferred estimates for solving the difficult problem of transfer state estimator facing multi-rate measurements. Furthermore, the influence function is defined to construct the analytical relationship between the slow rate measurements and the estimation performance, so as to quantitatively evaluate the transfer effect. Finally, the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method are illustrated by an example of target tracking.
-
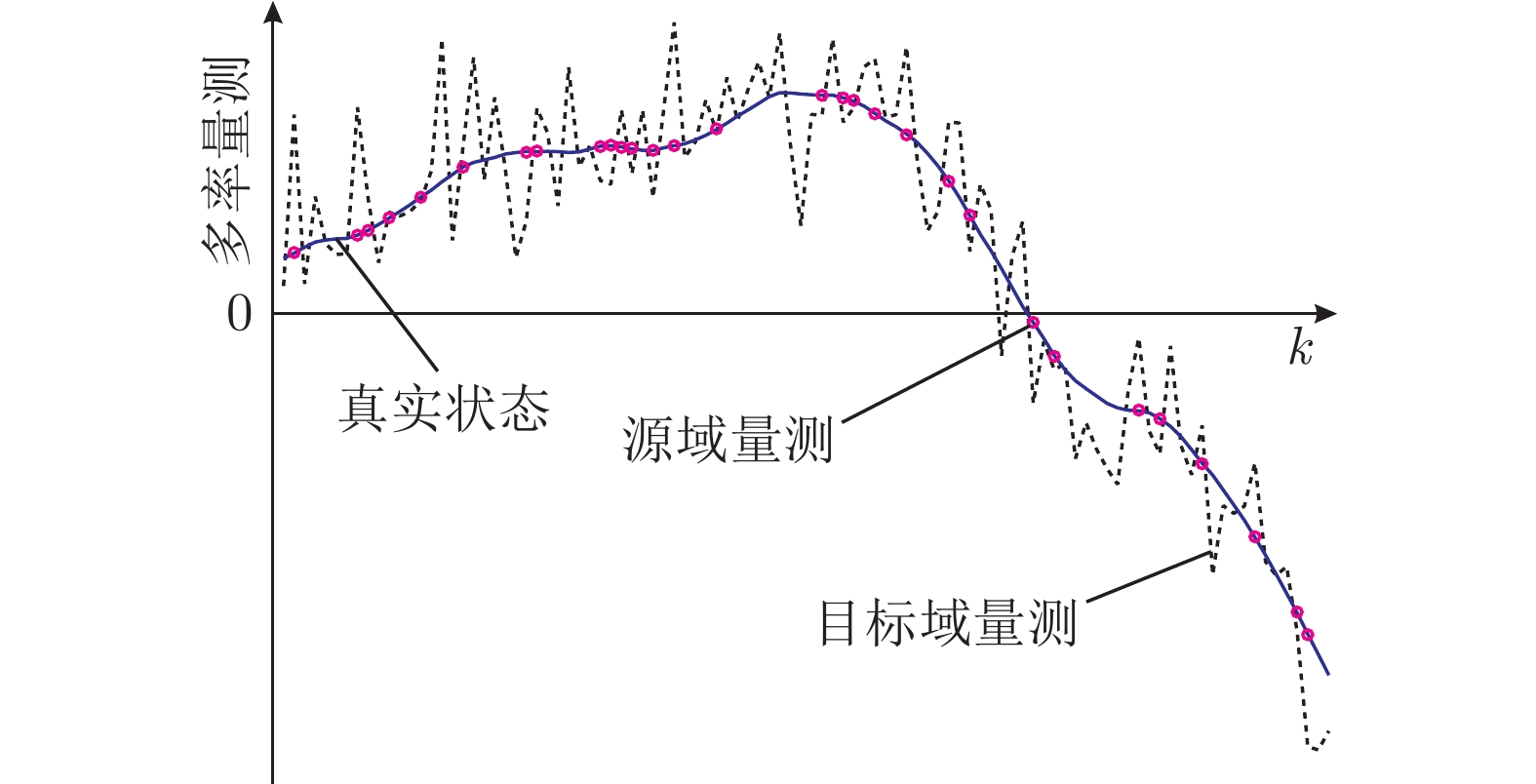
图 1 多率量测过程 (实线表示真实状态, 虚线表示目标域量测 (在线快速率数据), 点表示源域量测 (离线化验数据), 其采样时间可能不规律)
Fig. 1 Multiple source measurements of the process with different sampling rates (Solid lines are true states, and dashed lines represent target measurements. Dots denote source measurements, whose sample time may be irregular)
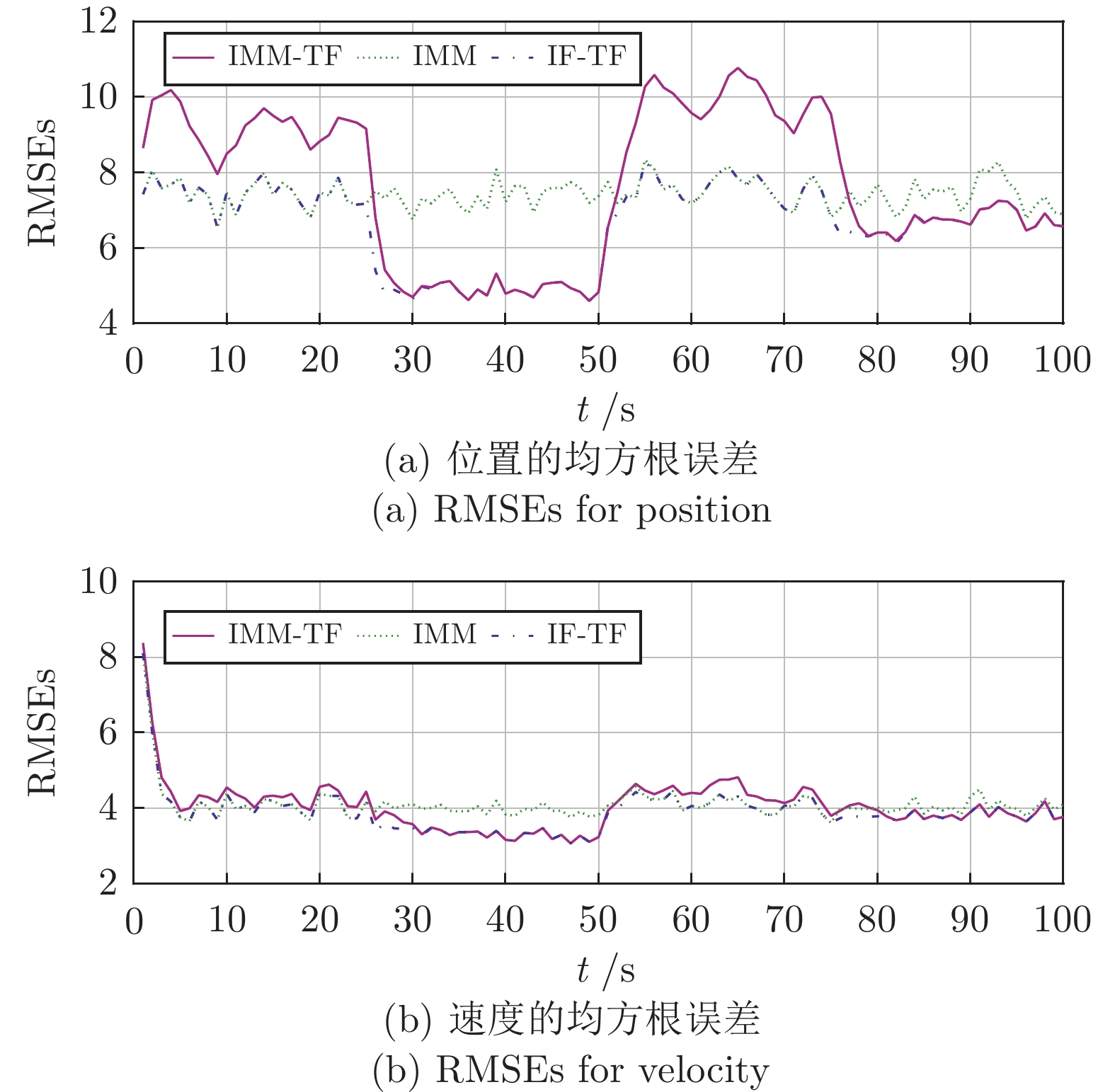
表 1 不同数量的源域数据迁移后的 RMSEs
Table 1 Average RMSEs (per sample) of IMM-TF in the presence of different amount source measurements
源域数据比重 (%) 位置 (m) 速度 (m/s) 10 5.8755 2.0266 30 5.4070 1.9567 50 4.8868 1.8798 70 4.5314 1.8465 99 4.0999 1.7674 -
[1] Wu Y, Luo X L. A novel calibration approach of soft sensor based on multirate data fusion technology. Journal of Process Control, 2010, 20(10): 1252-1260 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2010.09.003 [2] Fatehi A, Huang B. Kalman filtering approach to multi-rate information fusion in the presence of irregular sampling rate and variable measurement delay. Journal of Process Control, 2017, 53: 15-25 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2017.02.010 [3] Fatehi A, Huang B. State estimation and fusion in the presence of integrated measurement. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(9): 2490-2499 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2017.2701143 [4] Gou B, Cheng Y M, de Ruiter A H J. INS/CNS navigation system based on multi-star pseudo measurements. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 95: Article No. 105506 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.105506 [5] Bar-Shalom Y, Campo L. The effect of the common process noise on the two-sensor fused-track covariance. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, 22(6): 803-805 [6] Gao J B, Harris C J. Some remarks on Kalman filters for the multisensor fusion. Information Fusion, 2002, 3(3): 191-201 doi: 10.1016/S1566-2535(02)00070-2 [7] Xie L, Zhu Y J, Huang B, Zheng Y S. Kalman filtering approach to multirate information fusion for soft sensor development. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Information Fusion. Singapore: IEEE, 2012. 641−648 [8] Tian T, Sun S L. Distributed fusion estimation for multisensor multirate systems with packet dropout compensations and correlated noises. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(9): 5762-5772 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2956259 [9] Gopalakrishnan A, Kaisare N S, Narasimhan S. Incorporating delayed and infrequent measurements in Extended Kalman Filter based nonlinear state estimation. Journal of Process Control, 2011, 21(1): 119-129 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2010.10.013 [10] Guo Y F, Zhao Y, Huang B. Development of soft sensor by incorporating the delayed infrequent and irregular measurements. Journal of Process Control, 2014, 24(11): 1733-1739 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2014.09.006 [11] Zhou J, Zhu Y M, You Z S, Song E B. An efficient algorithm for optimal linear estimation fusion in distributed multisensor systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A: Systems and Humans, 2006, 36(5): 1000-1009 doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2006.878986 [12] Wang D, Ha M M, Zhao M M. The intelligent critic framework for advanced optimal control. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2022, 55(1): 1-22 doi: 10.1007/s10462-021-10118-9 [13] 王鼎, 赵明明, 哈明鸣. 基于折扣广义值迭代的智能最优跟踪及应用验证. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 182-193Wang Ding, Zhao Ming-Ming, Ha Ming-Ming. Intelligent optimal tracking with application verifications via discounted generalized value iteration. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 182-193 [14] Salehi Y, Fatehi A, Nayebi M A. State estimation of slow-rate integrated measurement systems in the presence of parametric uncertainties. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2018, 68(10): 3983-3991 [15] Lin H L, Sun S L. Distributed fusion estimator for multisensor multirate systems with correlated noises. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2017, 48(7): 1131-1139 [16] Yan L P, Di C Y, Wu Q M J, Xia Y Q. Sequential fusion for multirate multisensor systems with heavy-tailed noises and unreliable measurements. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 52(1): 523-532 [17] Smith D, Singh S. Approaches to multisensor data fusion in target tracking: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2006, 18(12): 1696-1710 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2006.183 [18] Li W L, Jia Y M. Consensus-based distributed multiple model UKF for jump Markov nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2011, 57(1): 227-233 [19] Li W L, Jia Y M. Distributed consensus filtering for discrete-time nonlinear systems with non-Gaussian noise. Signal Processing, 2012, 92(10): 2464-2470 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.03.009 [20] Song H, Shin V, Jeon M. Mobile node localization using fusion prediction-based interacting multiple model in cricket sensor network. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(11): 4349-4359 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2011.2151821 [21] Fu Z, Angelini F, Chambers J, Naqvi S M. Multi-level cooperative fusion of GM-PHD filters for online multiple human tracking. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 21(9): 2277-2291 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2019.2902480 [22] Shen X J, Zhu Y M, Song E B, Luo Y T. Optimal centralized update with multiple local out-of-sequence measurements. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(4): 1551-1562 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2012885 [23] Chi X B, Jia X C, Cheng F Q, Fan M H. Networked H∞ filtering for Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems under multi-output multi-rate sampling. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(6): 3661-3691 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.10.040 [24] Zhou W D, Liu M M. Robust interacting multiple model algorithms based on multi-sensor fusion criteria. International Journal of Systems Science, 2016, 47(1): 92-106 doi: 10.1080/00207721.2015.1029566 [25] Fu X, Jia Y, Du J, Yu F. New interacting multiple model algorithms for the tracking of the manoeuvring target. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2010, 4(10): 2184-2194 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2009.0583 [26] Li Z, Teng J, Qiu J B, Gao H J. Filtering design for multirate sampled-data systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(11): 4224-4232 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2839674 [27] Li X R, Bar-Shalom Y. Multiple-model estimation with variable structure. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1996, 41(4): 478-493 doi: 10.1109/9.489270 [28] Katsikas S K, Likothanassis S D, Beligiannis G N, Berkeris K G, Fotakis D A. Genetically determined variable structure multiple model estimation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2001, 49(10): 2253-2261 doi: 10.1109/78.950781 [29] Zhao S Y, Ahn C K, Shi P, Shmaliy Y S, Liu F. Bayesian state estimation for Markovian jump systems: Employing recursive steps and pseudocodes. IEEE Systems Man and Cybernetics Magazine, 2019, 5(2): 27-36 doi: 10.1109/MSMC.2018.2882145 [30] Wen L, Gao L, Li X Y. A new deep transfer learning based on sparse auto-encoder for fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(1): 136-144 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2754287 [31] Wang B, Li Z C, Dai Z W, Lawrence N, Yan X F. Data-driven mode identification and unsupervised fault detection for nonlinear multimode processes. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 16(6): 3651-3661 [32] Sun L, Ho W K, Ling K V, Chen T P, Maciejowski J. Recursive maximum likelihood estimation with t-distribution noise model. Automatica, 2021, 132: Article No. 109789 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.109789 [33] Xue W, Luan X L, Zhao S Y, Liu F. A fusion Kalman filter and UFIR estimator using the influence function method. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2021, 9(4): 709-718 [34] Li X R. Multiple-model estimation with variable structure. II. Model-set adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2000, 45(11): 2047-2060 doi: 10.1109/9.887626 -




 下载:
下载: