Privacy Preservation Method for Vertical Federated Learning Based on Max-min Strategy
-
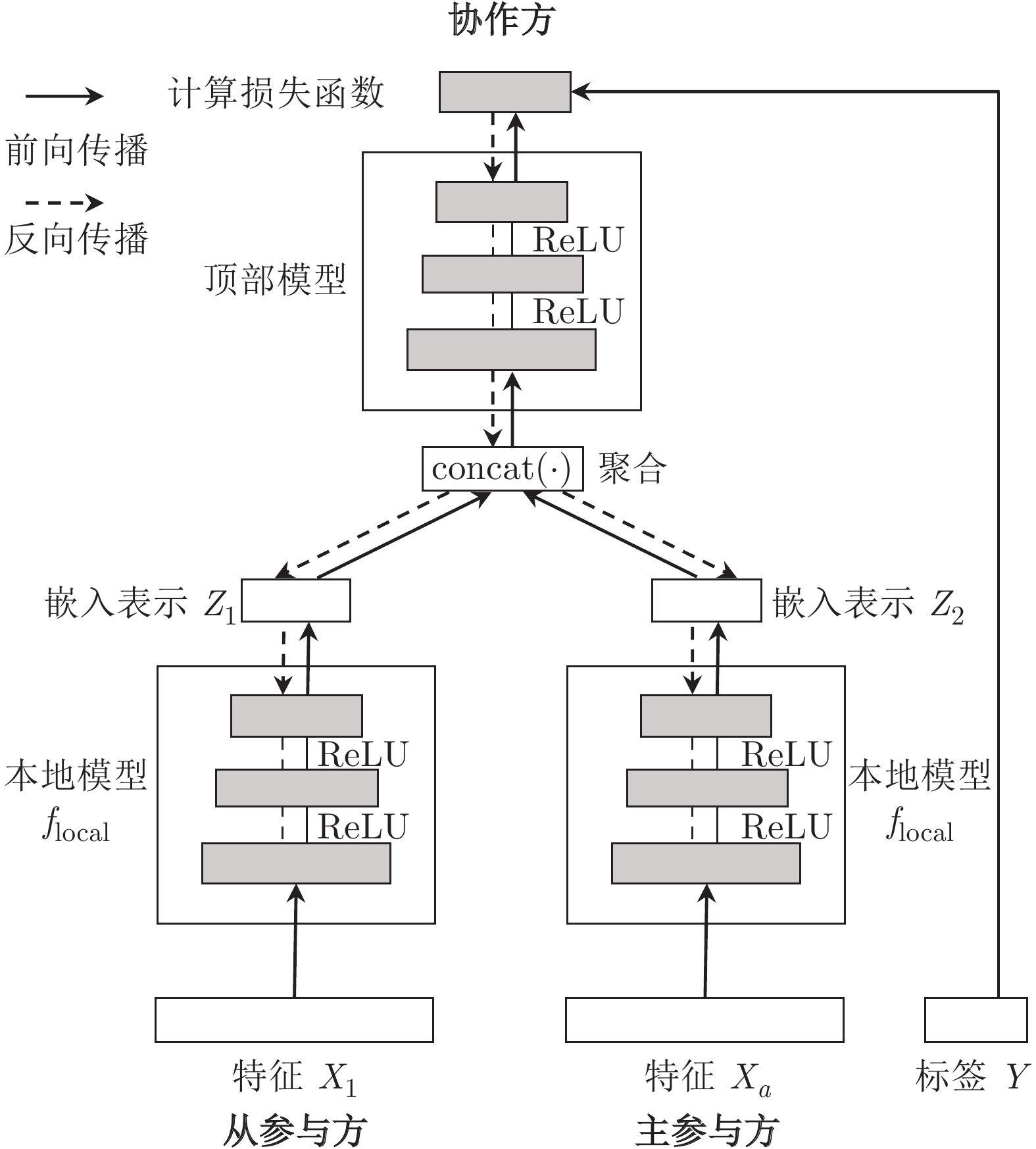
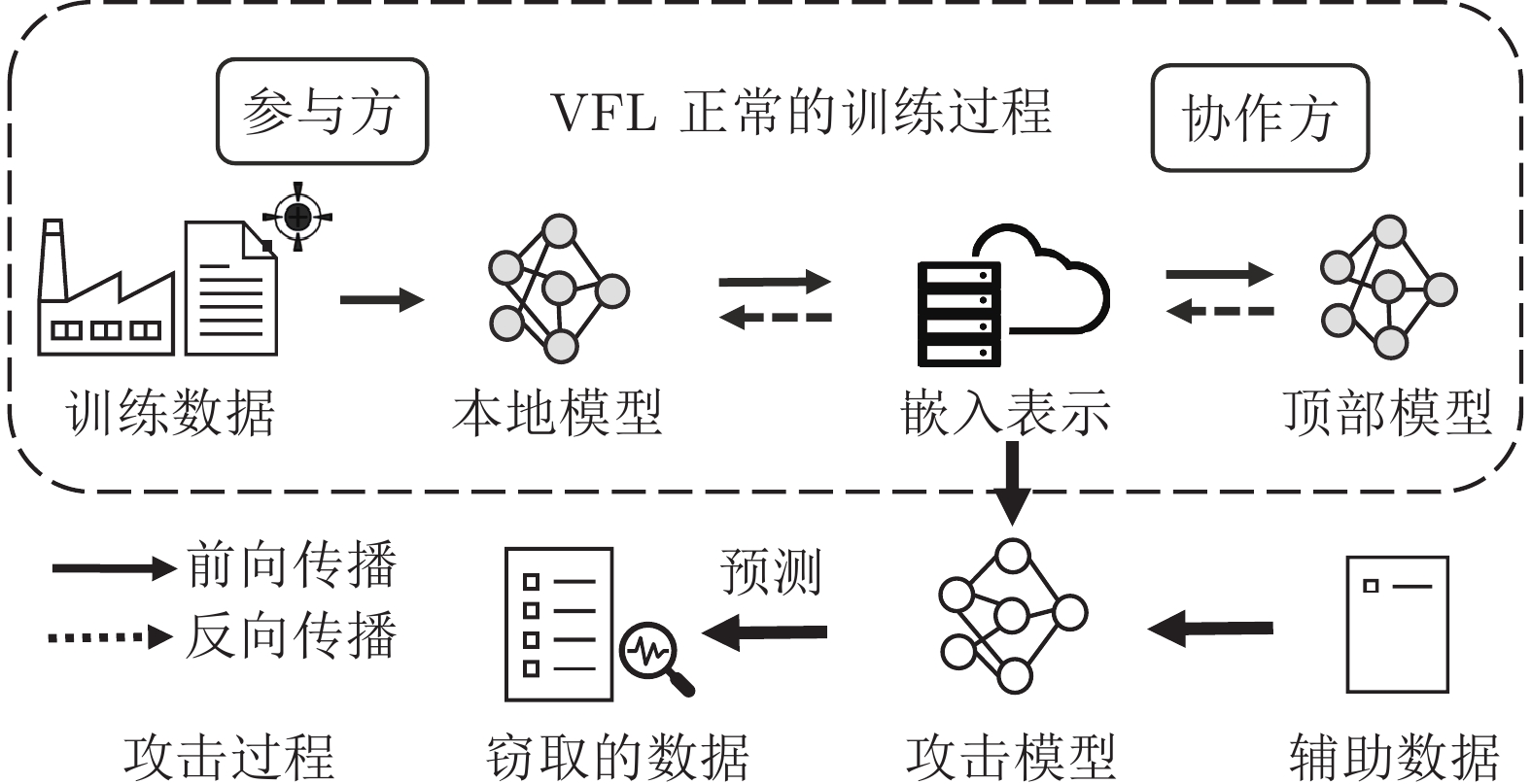
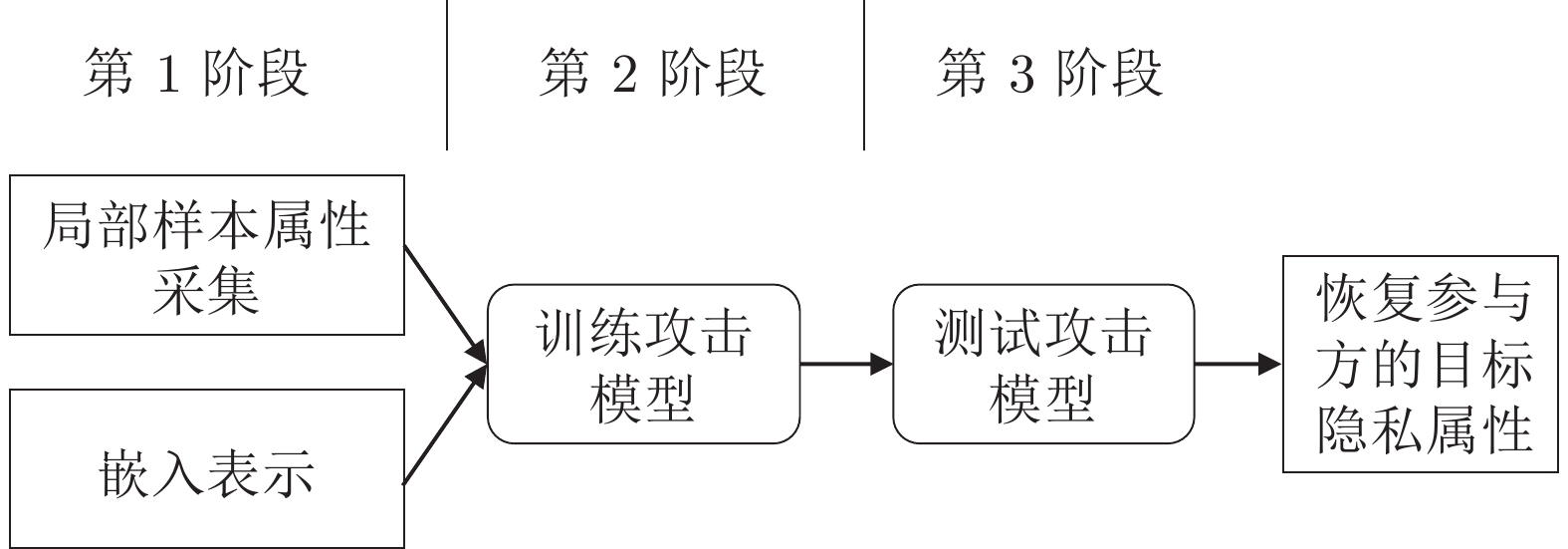
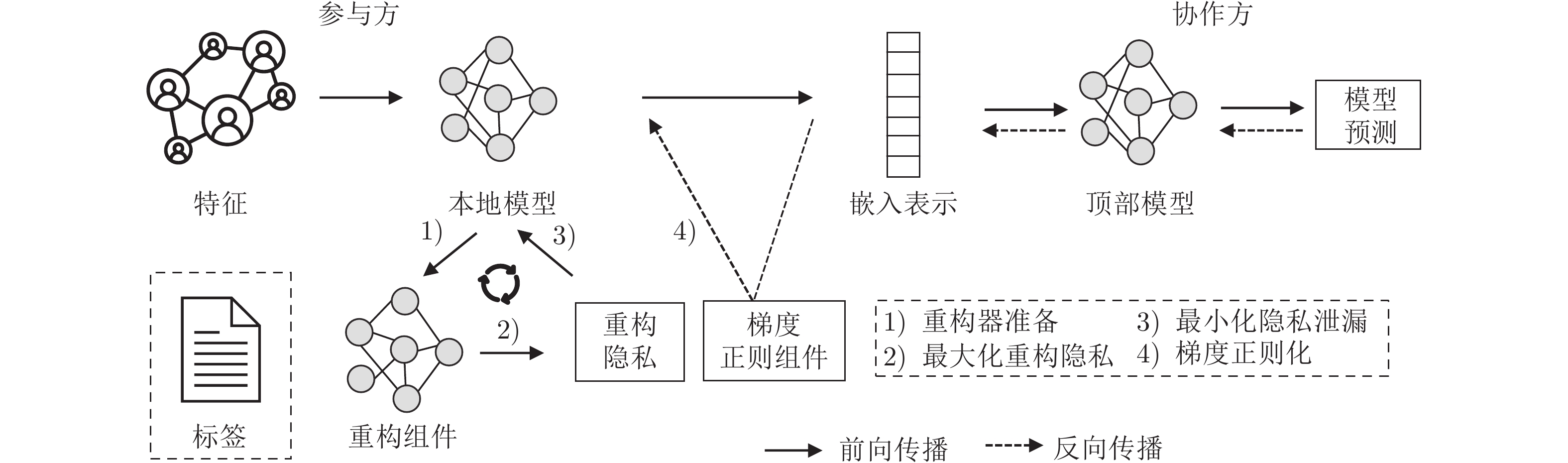
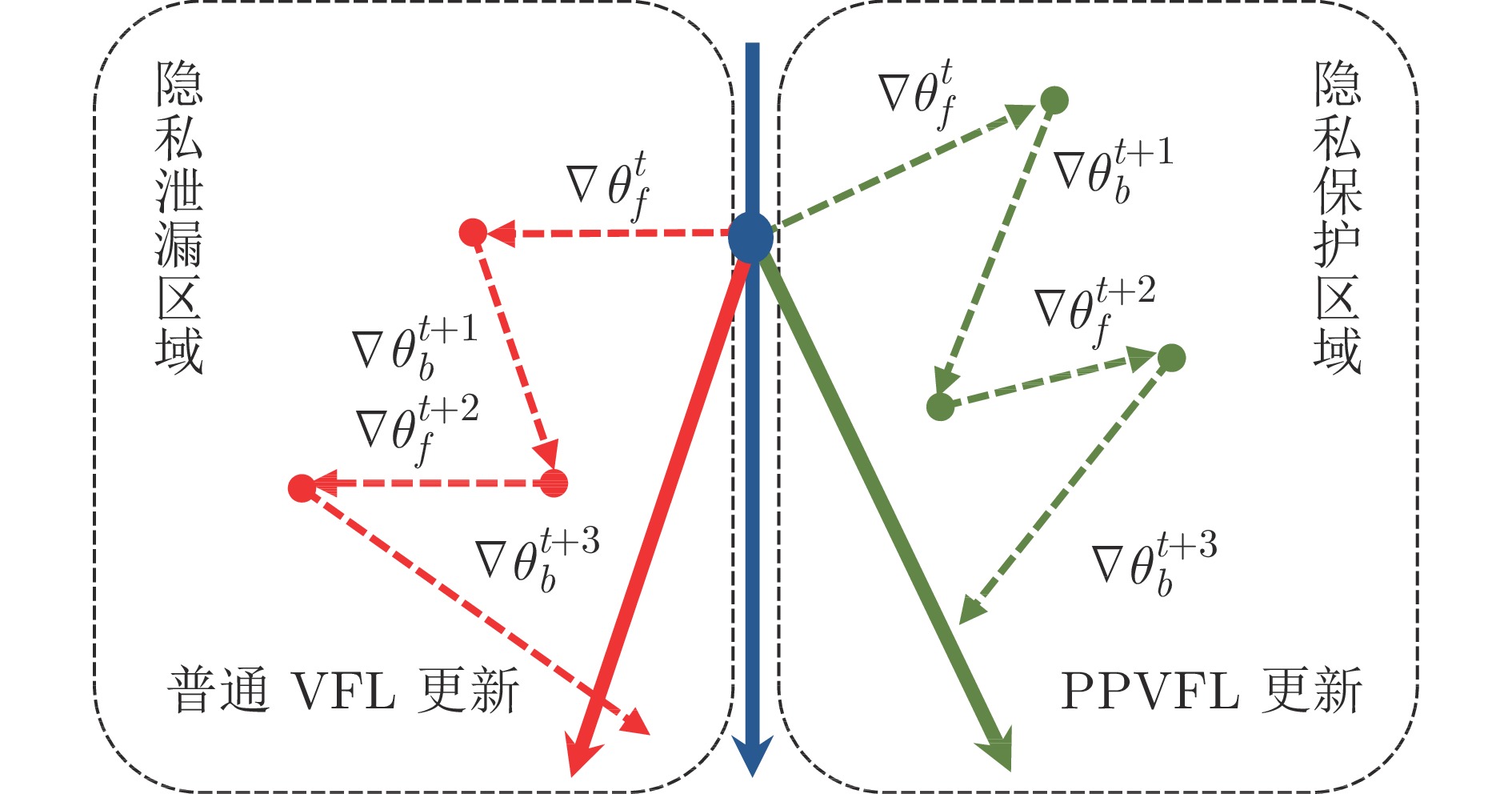
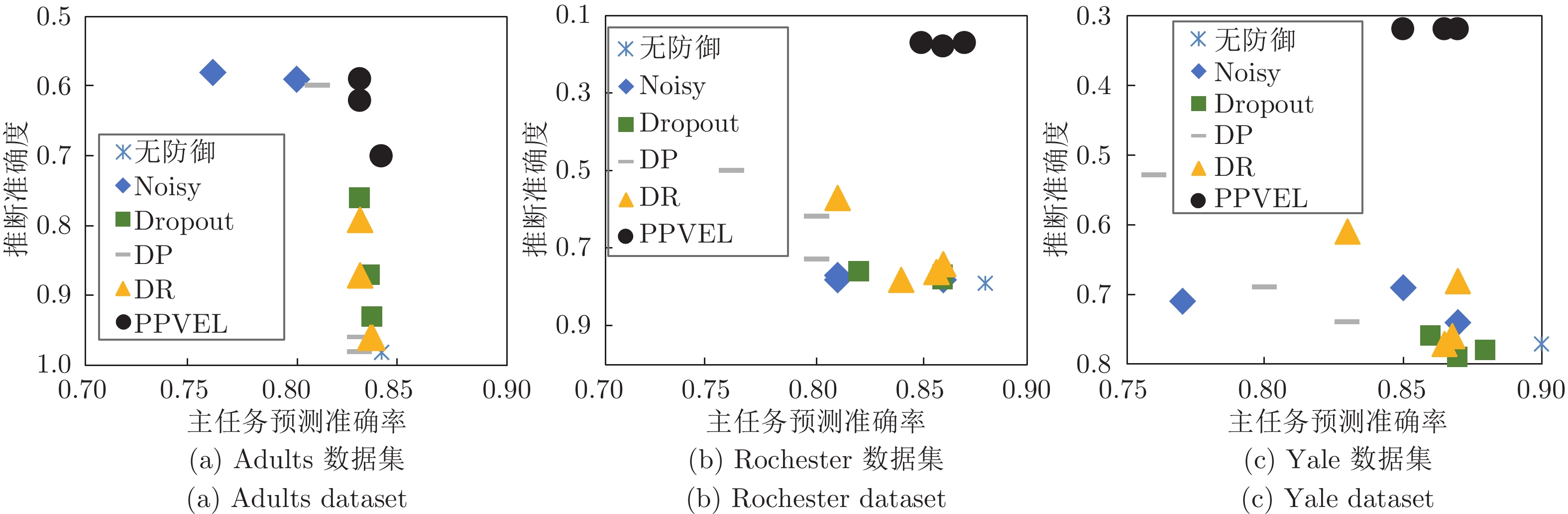
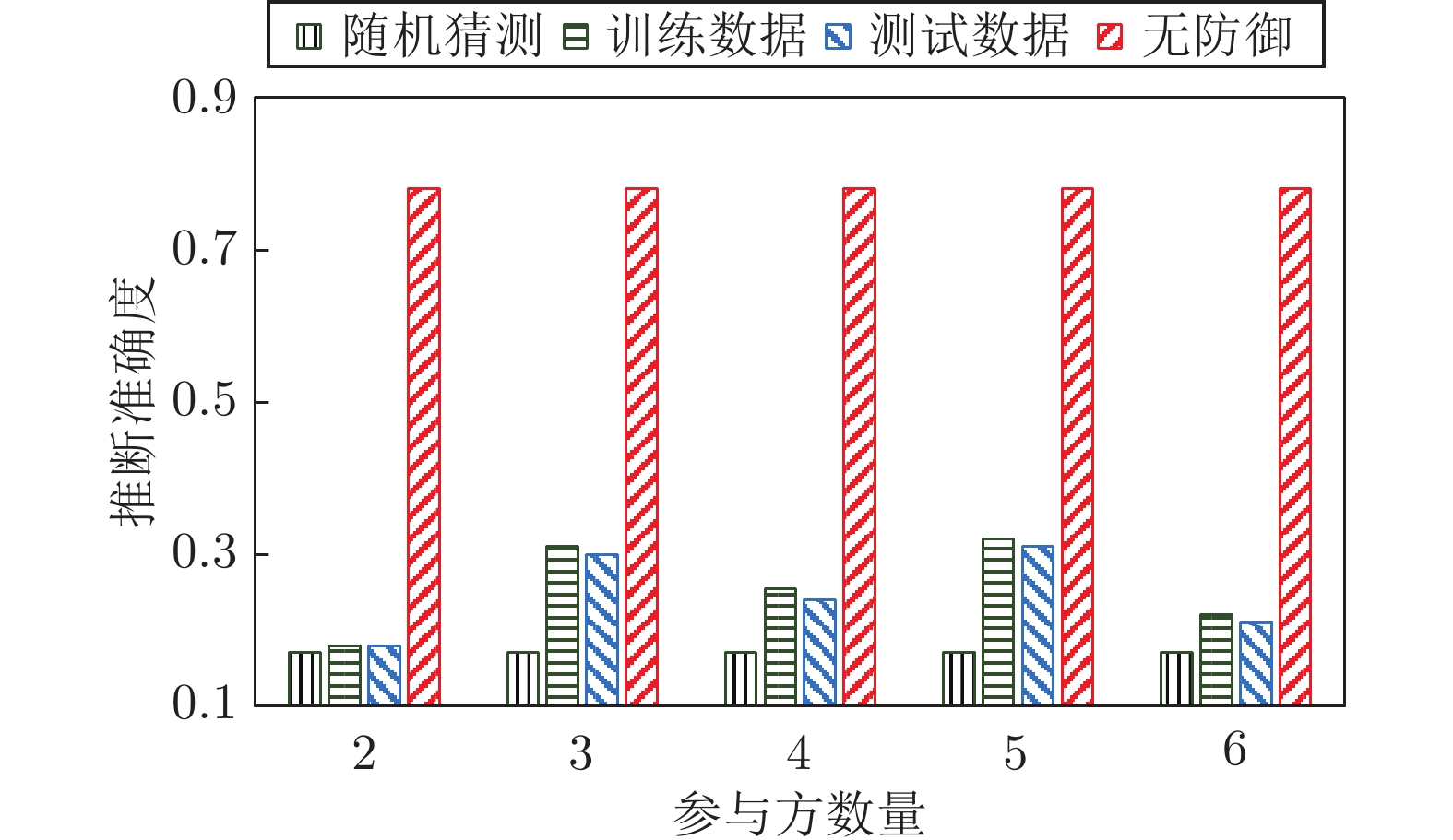
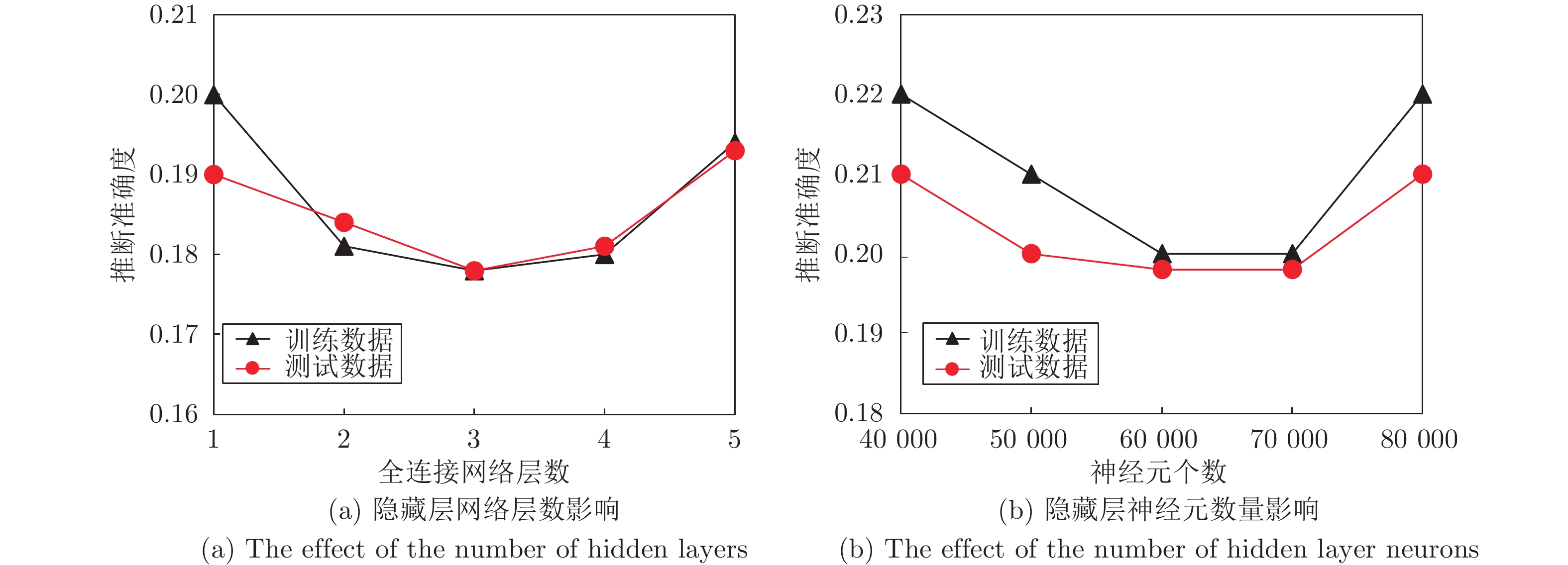
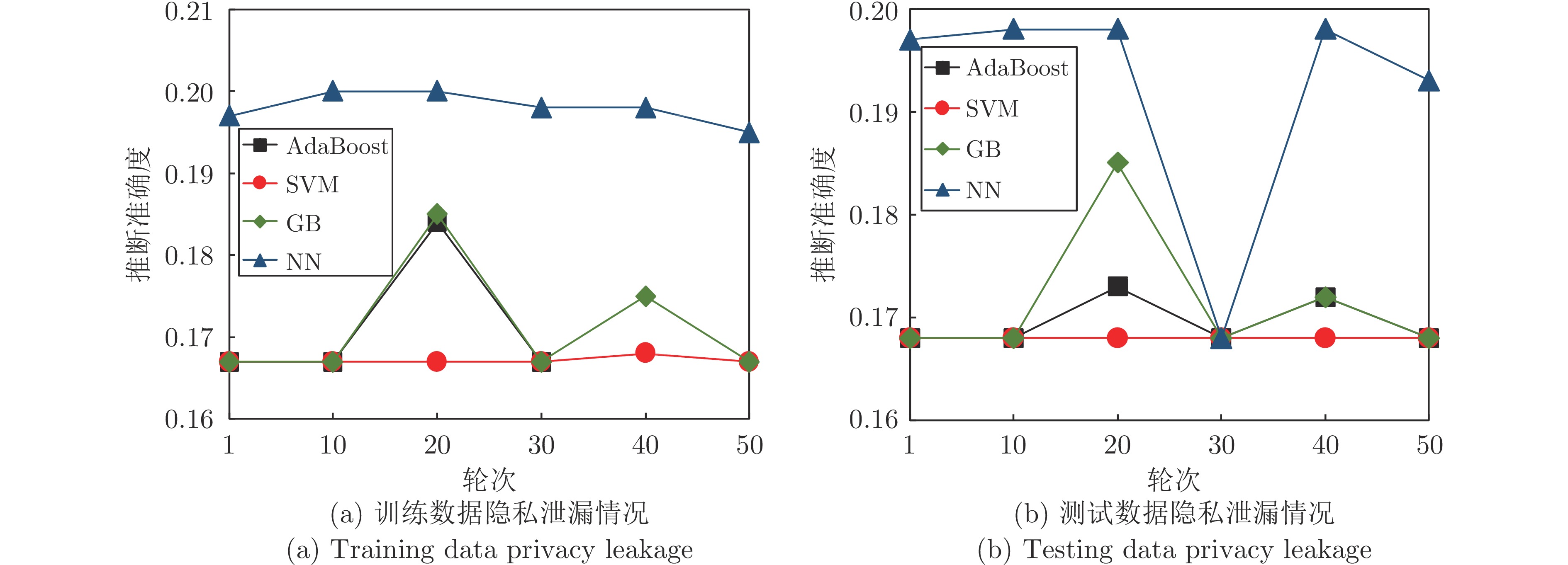
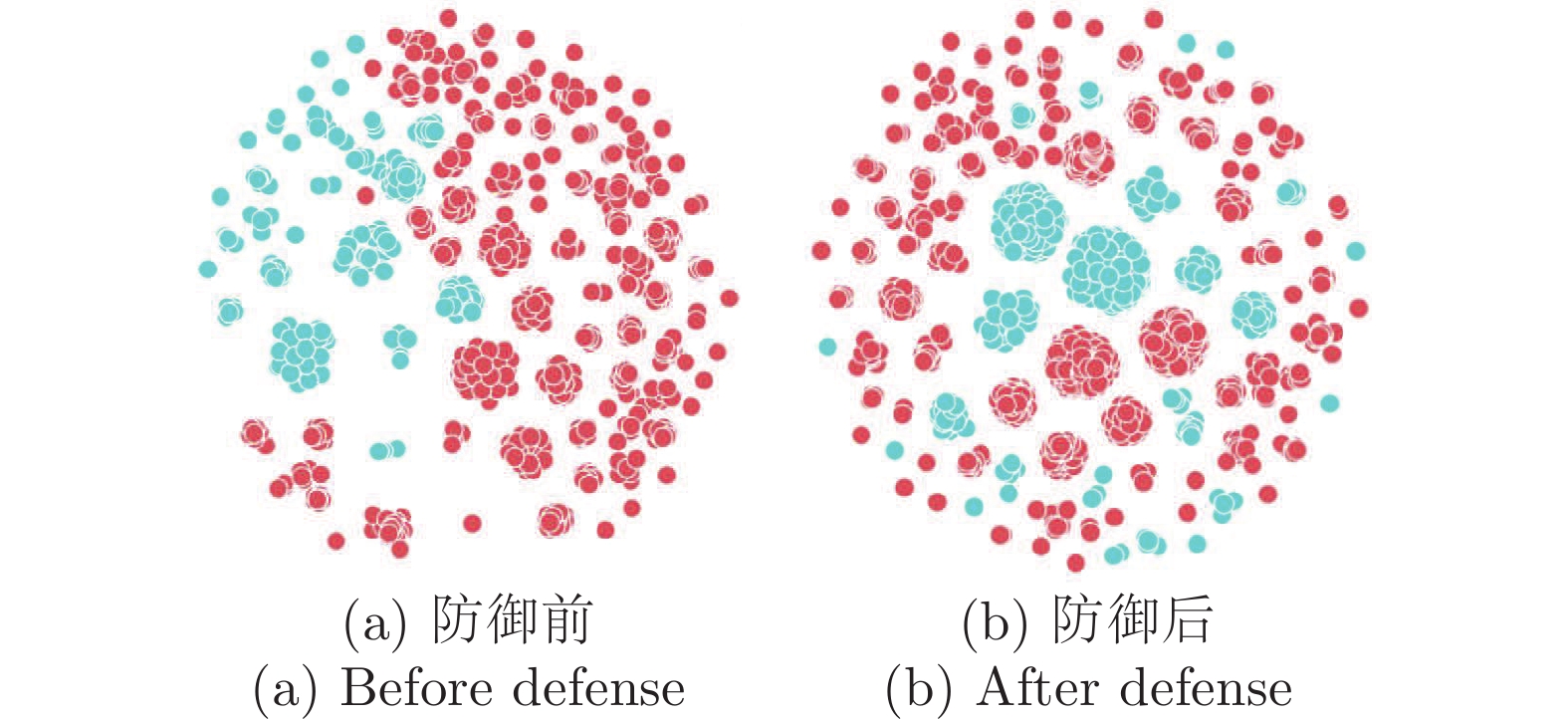
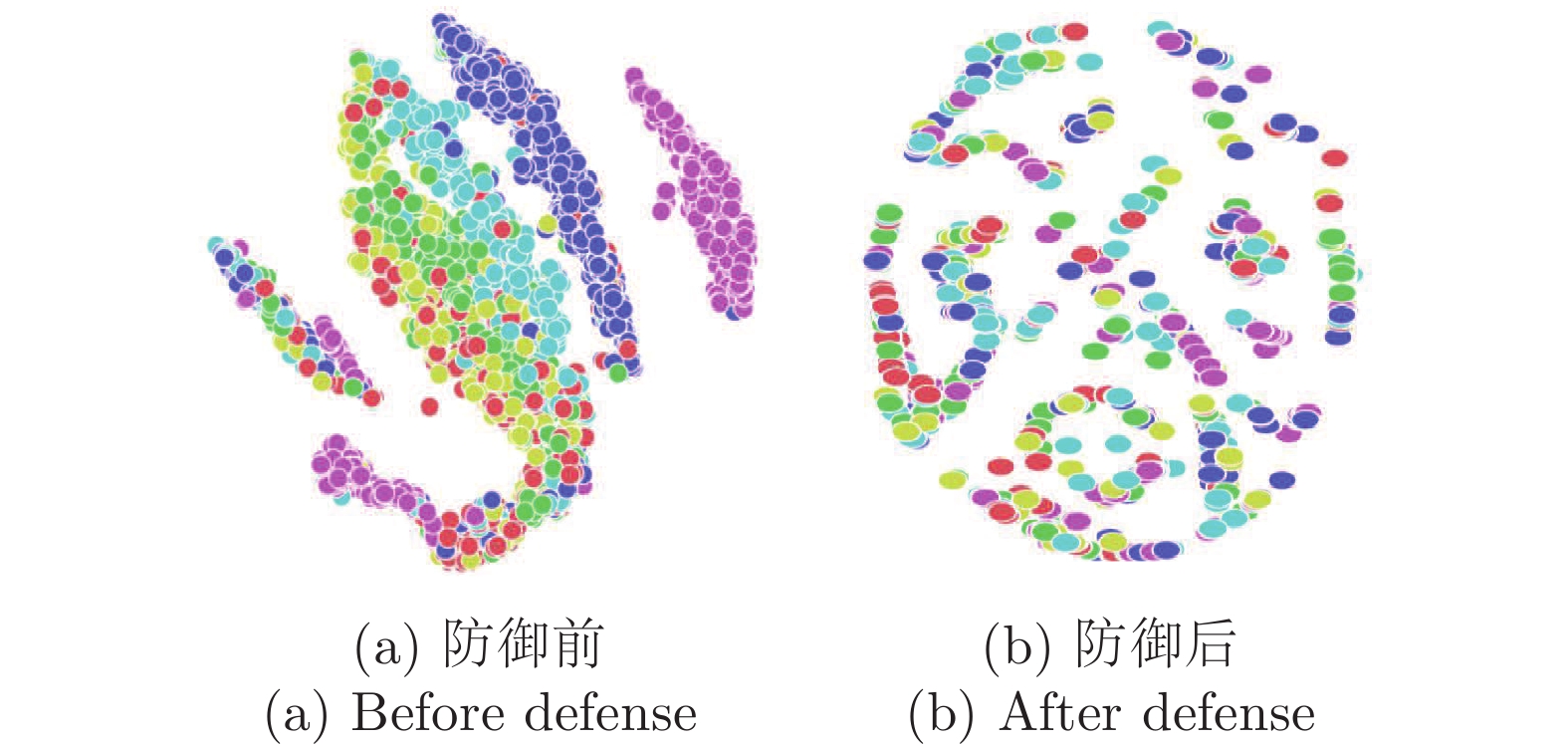
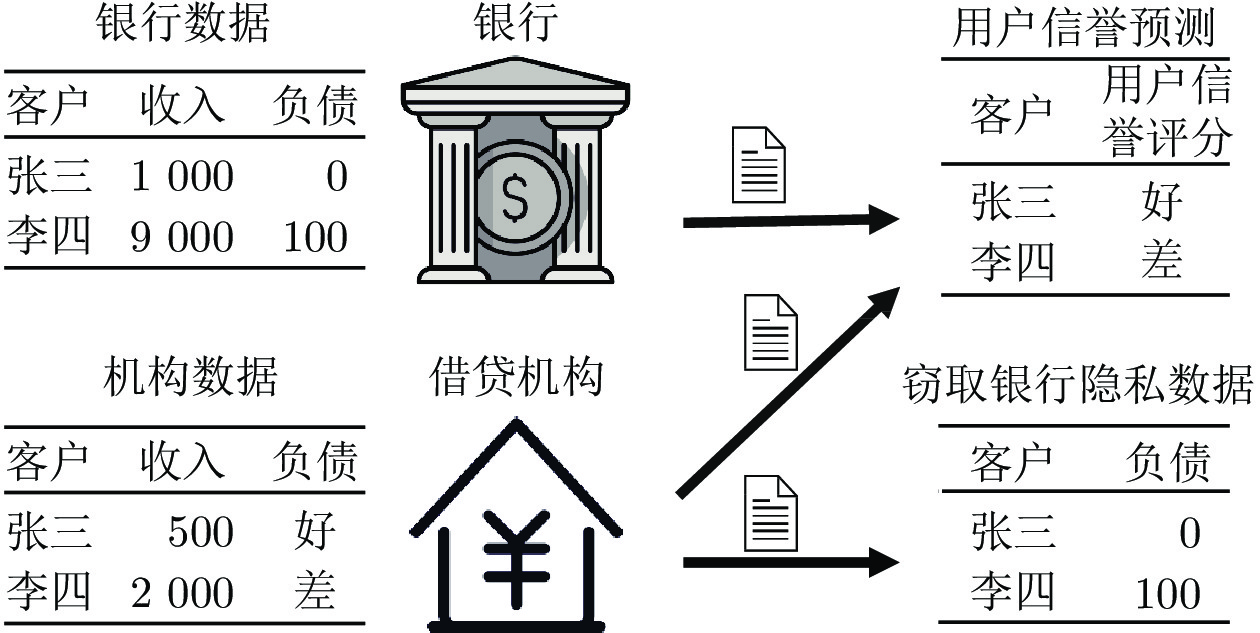
摘要: 纵向联邦学习(Vertical federated learning, VFL)是一种新兴的分布式机器学习技术, 在保障隐私性的前提下, 利用分散在各个机构的数据实现机器学习模型的联合训练. 纵向联邦学习被广泛应用于工业互联网、金融借贷和医疗诊断等诸多领域中, 因此保证其隐私安全性具有重要意义. 首先, 针对纵向联邦学习协议中由于参与方交换的嵌入表示造成的隐私泄漏风险, 研究由协作者发起的通用的属性推断攻击. 攻击者利用辅助数据和嵌入表示训练一个攻击模型, 然后利用训练完成的攻击模型窃取参与方的隐私属性. 实验结果表明, 纵向联邦学习在训练推理阶段产生的嵌入表示容易泄漏数据隐私. 为了应对上述隐私泄漏风险, 提出一种基于最大−最小策略的纵向联邦学习隐私保护方法(Privacy preservation method for vertical federated learning based on max-min strategy, PPVFL), 其引入梯度正则组件保证训练过程主任务的预测性能, 同时引入重构组件掩藏参与方嵌入表示中包含的隐私属性信息. 最后, 在钢板缺陷诊断工业场景的实验结果表明, 相比于没有任何防御方法的VFL, 隐私保护方法将攻击推断准确度从95%下降到55%以下, 接近于随机猜测的水平, 同时主任务预测准确率仅下降2%.Abstract: Vertical federated learning (VFL) is an emerging distributed machine learning that applies to the data distributed in various institutions to realize the joint construction of privacy preservation machine learning models. It has been widely applied to various fields such as industrial internet, financial lending, and medical diagnosis. Therefore, the privacy security research of vertical federated learning highlights its significance. Aiming at the risk of privacy leakage caused by the embedding exchanged by participants in the vertical federated learning protocol, we propose a general property inference attack initiated by the server. The adversary uses the auxiliary data and the embedding exchanged by the vertical federated learning protocol to train the attack model and steal the target privacy property of the participant. The experimental results show that the embedding representation generated by the vertical federated learning during the training and inference process can reveal the information of the personal private property. To deal with the above proposed privacy leakage risk, proposed a privacy preservation method for vertical federated learning based on max-min strategy (PPVFL), which introduces a gradient regular component to ensure the performance of the main task of the training process and adopts a construction component to hide participant's privacy property. Finally, in steel defect diagnosis industrial scenarios, compared to VFL without any defense method, privacy-preserving method reduces attack inference accuracy from 95% to below 55%, which is close to the level of random guessing, while the main task only dropped by 2% of the prediction accuracy.
-
表 1 VFL隐私保护技术优缺点对比
Table 1 Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of VFL privacy protection technology
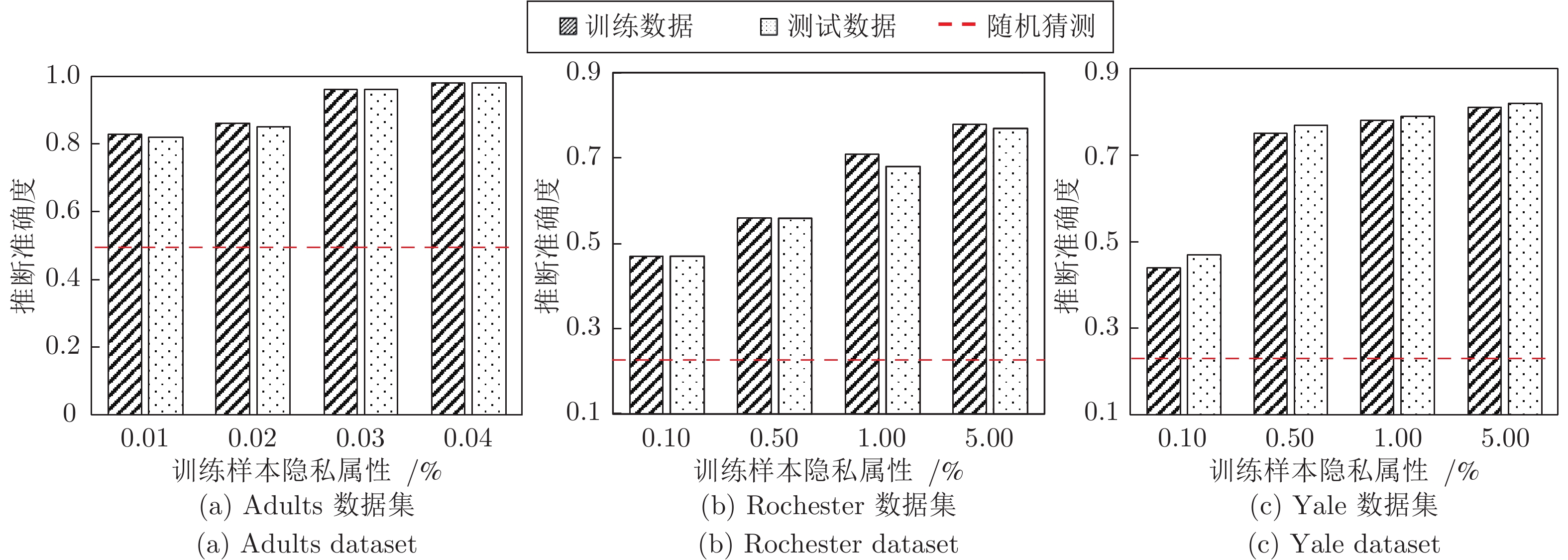
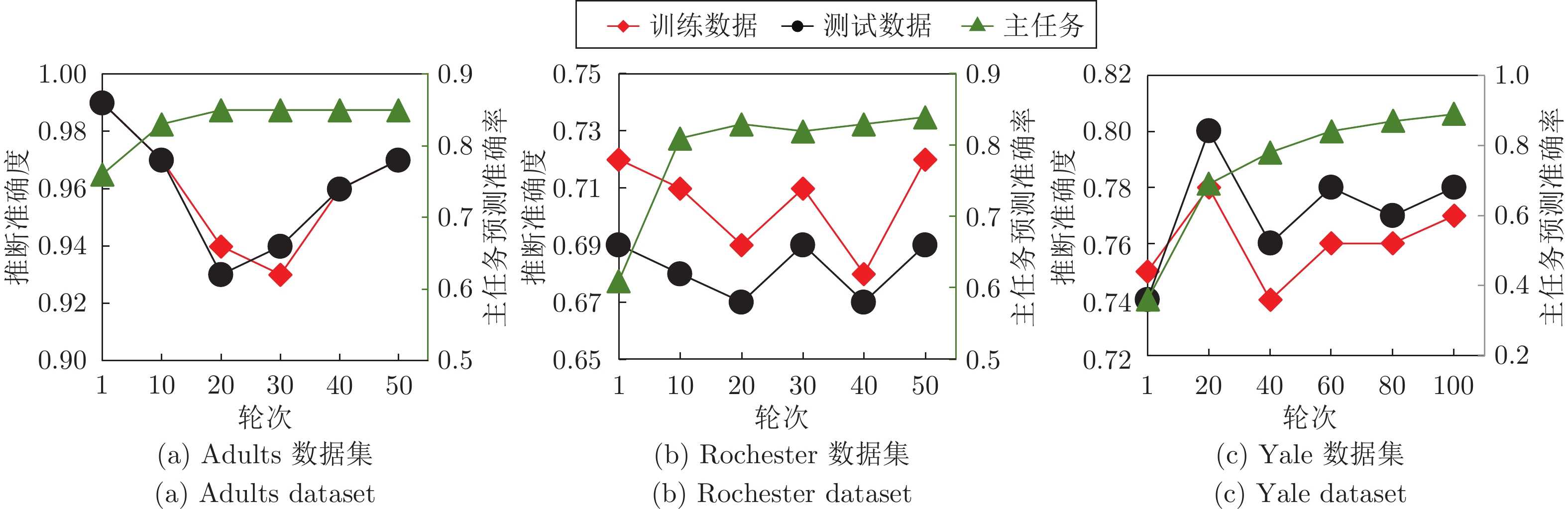
表 2 VFL数据集的基本统计信息
Table 2 The basic statistics of VFL datasets
数据集 样本数 连边关系 标签类别 属性特征 隐私属性 Adults 48842 — 2 14 婚姻 Rochester 4563 167653 6 236 教育 Yale 8578 405450 6 188 种族 表 3 模型结构
Table 3 Model architectures
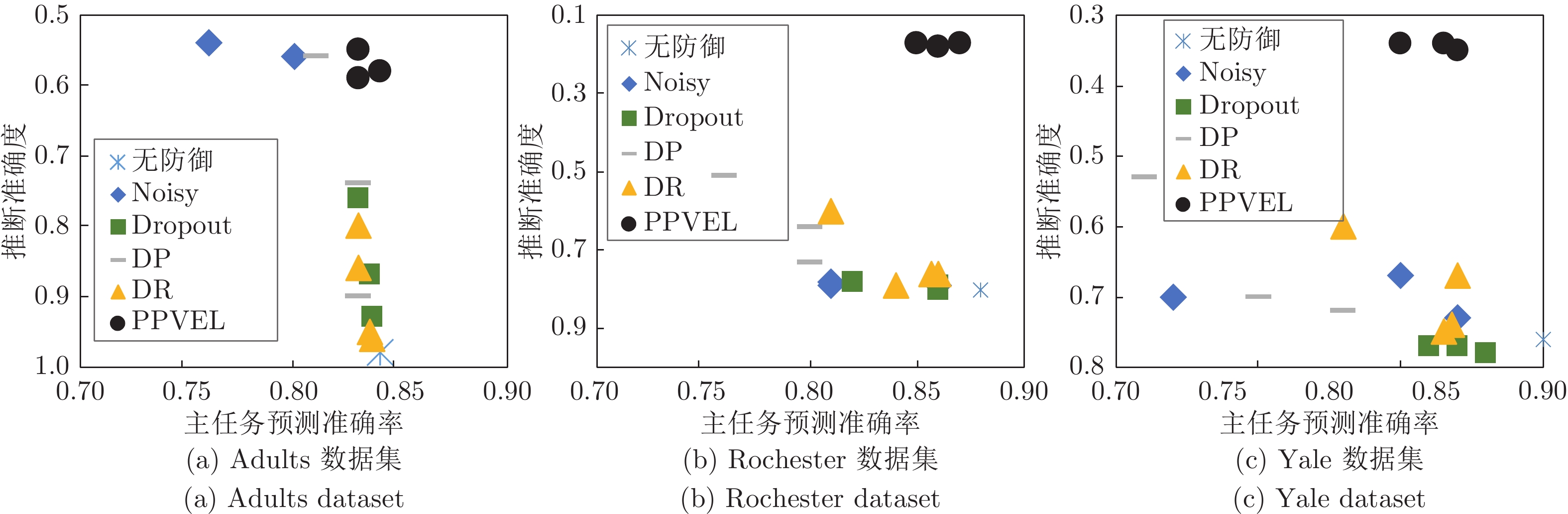
数据集 本地模型 顶部模型 Adults FCNN-1 FCNN-2 Rochester GCN-2 FCNN-2 Yale SGC-2 FCNN-2 表 4 实际工业互联网数据集上的隐私保护效果
Table 4 Privacy protection effect on actual industrial internet dataset
隐私属性 钢板序列 A300 训练数据 测试数据 训练数据 测试数据 推断准确度 权衡值 推断准确度 权衡值 主任务准确率 推断准确度 权衡值 推断准确度 权衡值 主任务准确率 无防御 0.95 0.82 0.96 0.81 0.78 0.74 1.00 0.72 1.03 0.74 Noisy$(\sigma=1.0)$ 0.66 1.00 0.84 0.79 0.66 0.63 0.95 0.62 0.97 0.60 Noisy$(\sigma=5.0)$ 0.60 0.93 0.55 1.02 0.56 0.60 0.83 0.59 0.85 0.50 Dropout$(\eta=0.5)$ 0.91 0.88 0.91 0.88 0.80 0.70 1.03 0.64 1.13 0.72 Dropout$(\eta=0.8)$ 0.86 0.86 0.86 0.86 0.74 0.70 0.96 0.64 1.05 0.67 DP$(\sigma=0.1)$ 0.56 1.21 0.56 1.21 0.68 0.67 1.06 0.65 1.09 0.71 DP$(\sigma=0.2)$ 0.90 0.79 0.89 0.80 0.71 0.68 1.06 0.67 1.07 0.72 DR$(d=8.0)$ 0.87 0.85 0.86 0.86 0.74 0.69 0.80 0.67 0.82 0.55 DR$(d=4.0)$ 0.66 0.97 0.65 0.98 0.64 0.68 0.79 0.64 0.84 0.54 PPVFL$(\lambda=0.1)$ 0.55 1.38 0.57 1.33 0.76 0.60 1.20 0.62 1.16 0.72 PPVFL$(\lambda=0.5)$ 0.55 1.36 0.54 1.39 0.75 0.59 1.20 0.61 1.16 0.71 -
[1] Luckow A, Cook M, Ashcraft N, Weill E, Djerekarov E, Vorster B. Deep learning in the automotive industry: Applications and tools. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data. Washington, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3759−3768 [2] Schneider S, Taylor G W, Kremer S C. Deep learning object detection methods for ecological camera trap data. In: Proceedings of the 15th Conference on Computer and Robot Vision. Toronto, Canada: IEEE, 2018. 321−328 [3] Sangineto E, Nabi M, Culibrk D, Sebe N. Self-paced deep learning for weakly supervised object detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 41(3): 712−725 [4] Scoon C, Ko R K. The data privacy matrix project: Towards a global alignment of data privacy laws. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications. Tianjin, China: IEEE, 2016. 1998−2005 [5] Goddard M. The EU general data protection regulation: Eur-opean regulation that has a global impact. International Journal of Market Research, 2017, 59(6): 703−705 doi: 10.2501/IJMR-2017-050 [6] Yang Q, Liu Y, Chen T J, Tong Y X. Federated machine learning: Concept and applications. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2019, 10(2): 1−19 [7] 张泽辉, 富瑶, 高铁杠. 支持数据隐私保护的联邦深度神经网络模型研究. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(5): 1273−1284Zhang Ze-Hui, Fu Yao, Gao Tie-Gang. Research on federated deep neural network model for data privacy protection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(5): 1273−1284 [8] 张泽辉, 李庆丹, 富瑶, 何宁昕, 高铁杠. 面向非独立同分布数据的自适应联邦深度学习算法. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(12): 2493−2506Zhang Ze-Hui, Li Qing-Dan, Fu Yao, He Ning-Xin, Gao Tie-Gang. Adaptive federated deep learning with non-IID data. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(12): 2493−2506 [9] Nasr M, Shokri R, Houmansadr A. Comprehensive privacy analysis of deep learning: Passive and active white-box inference attacks against centralized and federated learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2019. 739−753 [10] Luca M, Song C, Cristofaro E D, Shmatikov V. Exploiting unintended feature leakage in collaborative learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2019. 691−706 [11] Zhu L, Liu Z, Han S. Deep leakage from gradients. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: 2019. 1−11 [12] 周纯毅, 陈大卫, 王尚, 付安民, 高艳松. 分布式深度学习隐私与安全攻击研究进展与挑战. 计算机研究与发展, 2021, 58(5): 927−943 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2021.20200966Zhou Chun-Yi, Chen Da-Wei, Wang Shang, Fu An-Min, Gao Yan-Song. Research and challenge of distributed deep learning privacy and security attack. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2021, 58(5): 927−943 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2021.20200966 [13] Fu C, Zhang X, Ji S, Chen J Y, Wu J Z, Guo S Q, et al. Label inference attacks against vertical federated learning. In: Proceedings of the USENIX Security. Boston, USA: 2022. 1−18 [14] Ou W, Zeng J H, Guo Z J, Yan W Q, Liu D W, Fuentes S. A homomorphic-encryption-based vertical federated learning sche-me for rick management. Computer Science and Information Systems, 2020, 17(3): 819−834 doi: 10.2298/CSIS190923022O [15] Liu W, Cheng J H, Wang X L, Lu X J, Yin J W. Hybrid differential privacy based federated learning for internet of things. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2022, 124: 1−15 [16] Mehdi M, Al-Fuqaha A. Enabling cognitive smart cities using big data and machine learning: Approaches and challenges. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(2): 94−101 doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700298 [17] Lu Y, Huang X H, Zhang K, Maharjan S, Zhang Y. Blockchain empowered asynchronous federated learning for secure data sharing in internet of vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(4): 4298−4311 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2973651 [18] Dinh C, Pubudu N, Ming D, Aruna S. Blockchain for 5G and beyond networks: A state of the art survey. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2020, 166: 1−45 [19] 韩璇, 袁勇, 王飞跃. 区块链安全问题: 研究现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(1): 206−225Han Xuan, Yuan Yong, Wang Fei-Yue. Security problems on blockchain: The state of the art and future trends. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 206−225 [20] Sun H, Wang Z Y, Huang Y J, Ye J D. Privacy-preserving vertical federated logistic regression without trusted third-party coordinator. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Machine Learning and Soft Computing. Haikou, China: 2022. 132−138 [21] Cheng K, Fan T, Jin Y, Liu Y, Chen T J, Papadopoulos D, et al. Secureboost: A lossless federated learning framework. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2021, 36(6): 1−9 doi: 10.1109/MIS.2021.3132250 [22] Luo X, Wu Y, Xiao X, Ooi B C. Feature inference attack on model predictions in vertical federated learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 37th International Conference on Data Engineering. Chania, Greece: 2021. 181−192 [23] Yang K, Song Z, Zhang Y, Zhou Y F, Sun X H, Wang J X. Model optimization method based on vertical federated learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems. Daegu, South Korea: IEEE, 2021. 1−5 [24] Paramod S, Rohit S, Iiia L, Srinivas D, Sanjit A S. A formal foundation for secure remote execution of enclaves. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. Dallas, USA: 2017. 2435−2450 [25] Florian T, Dan H. Slalom: Fast, verifiable and private execution of neural networks in trusted hardware. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations. New Orleans, USA: 2019. 1−19 [26] Yaroslav G, Lempitsky V. Unsupervised domain adaptation by backpropagation. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: 2015. 1180−1189 [27] Li K, Luo G C, Ye Y, Li W, Ji S H, Cai Z P. Adversarial privacy-preserving graph embedding against inference attack. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 8(8): 6904−6915 [28] Vasisht D, Boutet A, Shejwalkar V. Quantifying privacy leakage in graph embedding. In: Proceedings of the 17th EAI International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services. Darmstadt, Germany: 2020. 76−85 [29] Zhang Z, Chen M, Backes M, Shen Y, Zhang Y. Inference attacks against graph neural networks. In: Proceedings of the USENIX Security. Boston, USA: 2022. 1−18 [30] Liao P, Zhao H, Xu K, Jaakkola T, Gordon G J, Jegelka S, et al. Information obfuscation of graph neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning. Virtual Event: 2021. 6600−6610 [31] Thomas N, Welling M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon, USA: 2017. 1−14 [32] Wu F, Zhang T Y, Souza A H, Fifty C, Yu T, Weinberger K Q. Simplifying graph convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. San Francisco, USA: 2019. 6861−6871 [33] 王婕婷, 钱宇华, 李飞江, 刘郭庆. 消除随机一致性的支持向量机分类方法. 计算机研究与发展, 2020, 57(8): 1581−1593 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20200127Wang Jie-Ting, Qian Yu-Hua, Li Fei-Jiang, Liu Guo-Qing. Support vector machine with eliminating the random consistency. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2020, 57(8): 1581−1593 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20200127 [34] 窦诺, 赵瑞珍, 岑翼刚, 胡绍海, 张勇东. 基于稀疏表示的含噪图像超分辨重建方法. 计算机研究与发展, 2015, 52(4): 943−951 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2015.20140047Dou Nuo, Zhao Rui-Zhen, Cen Yi-Gang, Hu Shao-Hai, Zhang Yong-Dong. Noisy image super-resolution reconstruction based on sparse representation. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2015, 52(4): 943−951 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2015.20140047 -




 下载:
下载: