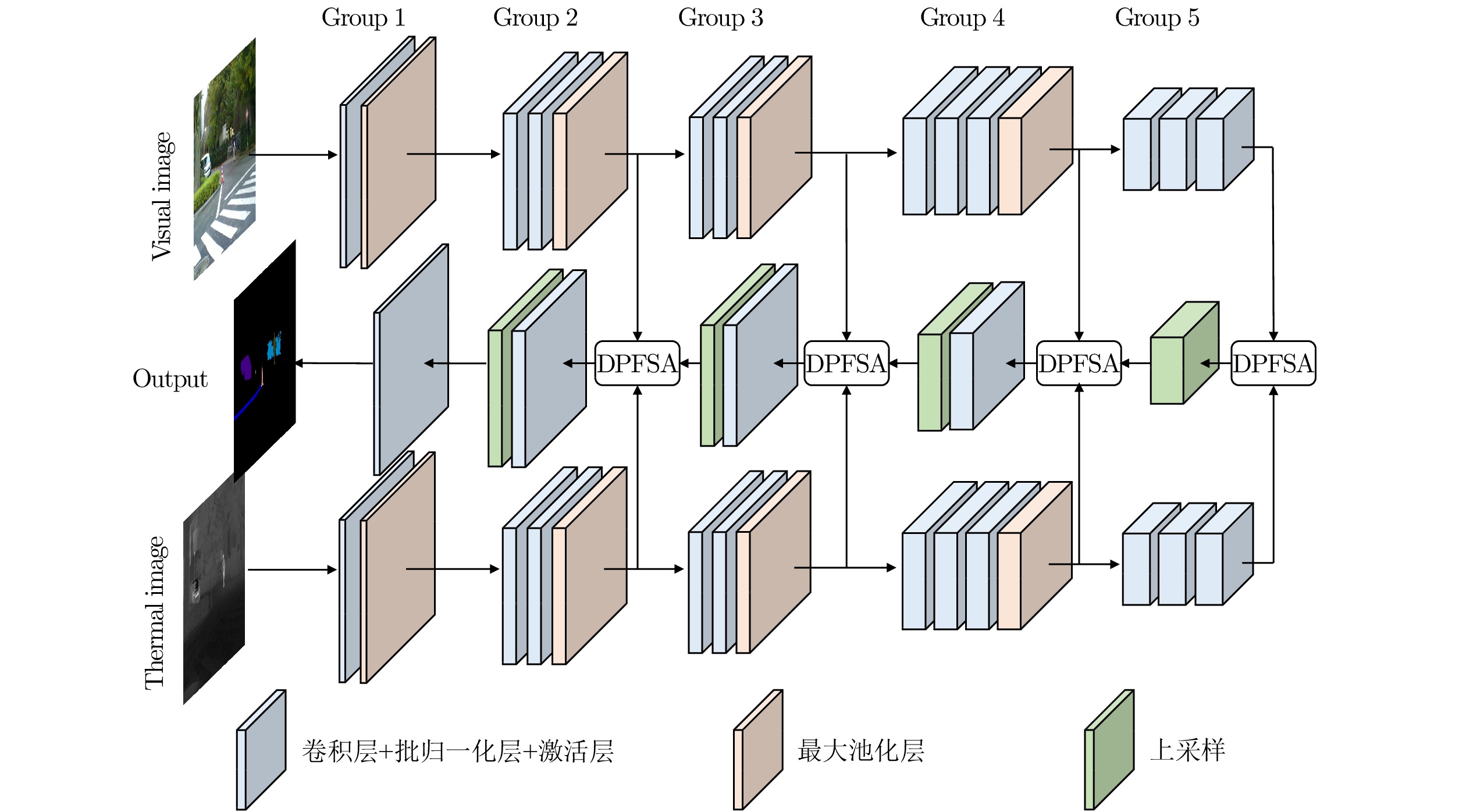
Complex Scene Segmentation Based on Visible and Thermal Images in Driving Environment
-
摘要: 复杂场景分割是自动驾驶领域智能感知的重要任务, 对稳定性和高效性都有较高的要求. 由于一般的场景分割方法主要针对可见光图像, 分割效果非常依赖于图像获取时的光线与气候条件, 且大多数方法只关注分割性能, 忽略了计算资源. 本文提出一种基于可见光与红外热图像的轻量级双模分割网络(DMSNet), 通过提取并融合两种模态图像的特征得到最终分割结果. 考虑到不同模态特征空间存在较大差异, 直接融合将降低对特征的利用率, 本文提出了双路特征空间自适应(DPFSA)模块, 该模块能够自动学习特征间的差异从而转换特征至同一空间. 实验结果表明, 本文方法提高了对不同模态图像的利用率, 对光照变化有更强的鲁棒性, 且以少量参数取得了较好的分割性能.
-
关键词:
- 场景分割 /
- 可见光图像 /
- 红外热图像 /
- 双模分割网络 /
- 双路特征空间自适应模块
Abstract: Complex scene segmentation is an important task of intelligent perception in the field of autonomous driving, which has high requirements for stability and efficiency. Since general scene segmentation methods mainly focus on visible images, the segmentation result is highly dependent on the light and weather conditions at the time of image acquisition, and most methods only focus on segmentation performance and ignore computing resources. This paper proposes a lightweight dual model segmentation network (DMSNet) based on visible and thermal images, which can extract and fuse the features of the two modal images to obtain a final segmentation result. For large differences in the feature spaces of different modalities, direct fusion will reduce the utilization of features. This paper proposes a dual-path feature space adaptation (DPFSA) module, which can automatically learn the differences among features and convert them to the same space. The experimental results show that this method can better utilize the inherent information between different modal images. Moreover, the proposed method is more robust to illumination changes and can achieve good segmentation performance with only a small number of parameters.1) 收稿日期 2021-01-09 录用日期 2021-04-16 Manuscript received January 9, 2021; accepted April 16, 2021 国家自然科学基金 (62076256), 中南大学研究生校企联合创新项目 (2021XQLH048) 资助 Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (62076256), Graduate School-enterprise Joint Innovation Project of Central South University (2021XQLH048) 本文责任编委 张向荣 Recommended by Associate Editor ZHANG Xiang-Rong 1. 中南大学自动化学院 长沙 410083 2. 中南大学计算机学院长沙 410083 3. 湖南省高强度坚固件智能制造工程技术研究中心常德 415701 4. 湖南湘江人工智能学院 长沙 410005 1. School of Automation, Central South University, Changsha410083 2. School of Computer Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083 3. Hunan Engineering2) & Technology Research Center of High Strength Fastener Intelli-gent Manufacturing, Changde 415701 4. Hunan Xiangjiang Ar-tificial Intelligence Academy, Changsha 410005 -
表 1 不同模块在数据集A上的mAcc、mIoU值与参数量比较
Table 1 Comparison of mAcc and mIoU values and parameter values of different modules on dataset A
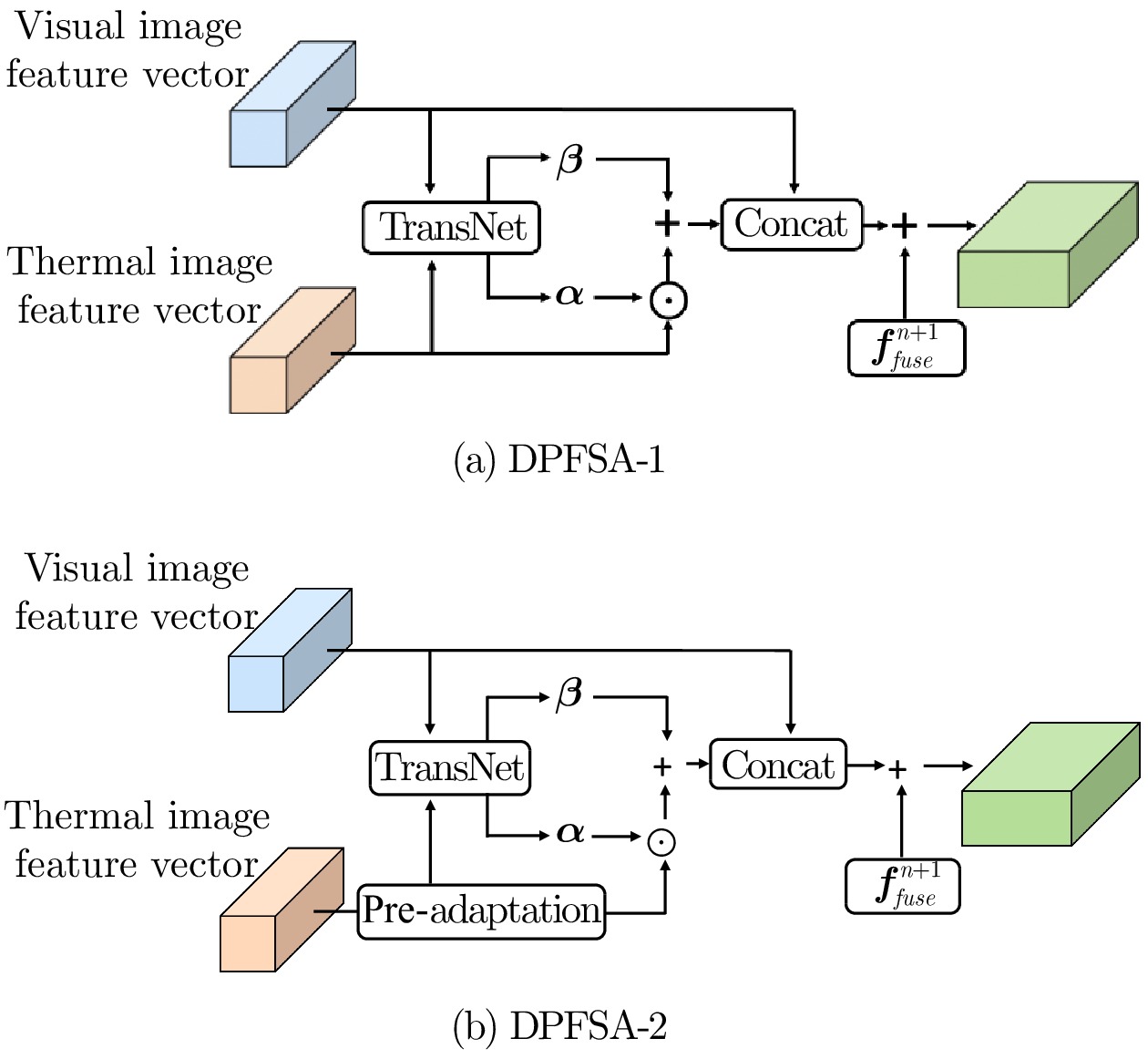
Models mAcc mIoU Parameters MFNet 63.5 64.9 2.81 MB FuseNet 61.9 63.8 46.4 MB DMSNet (DPFSA-1) 65.6 68.1 5.45 MB DMSNet (DPFSA-2) 68.9 65.1 5.54 MB DMSNet (DPFSA) 69.7 69.6 5.63 MB 注: Parameters 代表整个分割模型的参数量, 而非模块的参数量 表 2 不同损失函数在数据集A上的Acc结果与mAcc、mIoU值
Table 2 Acc results and mAcc and mIoU values of different loss functions on dataset A
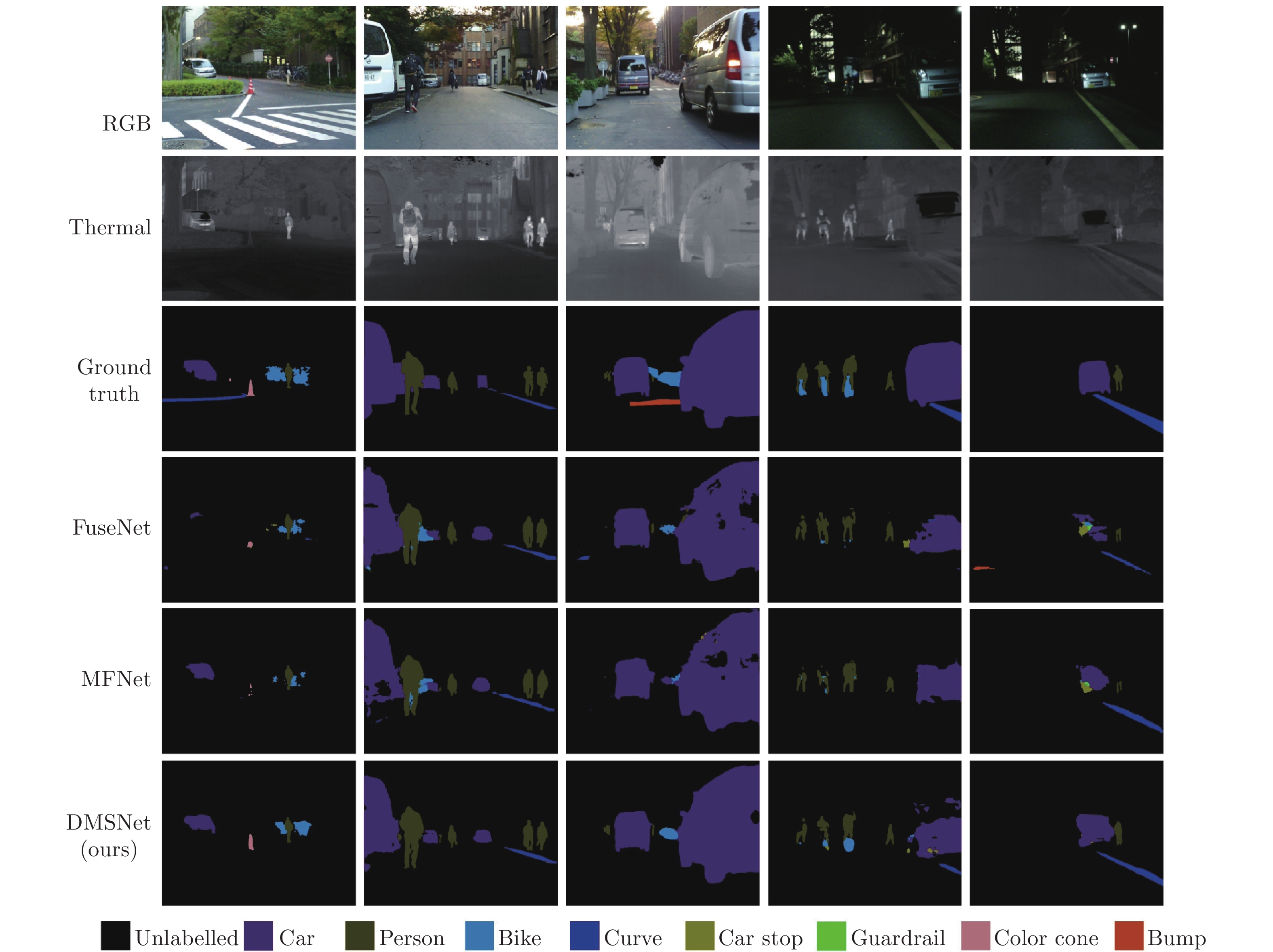
Losses Acc mAcc mIoU 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 CE 97.6 86.5 84.9 77.8 69.5 53.3 0.0 79.8 77.4 69.7 69.6 Focal 97.3 78.7 80.5 67.8 55.1 41.6 0.0 63.5 50.8 59.5 65.6 Dice 96.8 77.7 83.8 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 36.6 0.0 32.8 25.3 CE+Dice 97.6 87.6 83.5 79.5 73.2 47.5 0.0 74.7 92.1 70.7 70.3 注: 表中数字1 ~ 9为分割类别标号, 分别为 1: Unlabeled, 2: Car, 3: Pedestrian, 4: Bike, 5: Curve, 6: Car stop, 7: Guardrail, 8: Color cone, 9: Bump 表 3 不同模型在数据集A上的Acc与IoU结果对比
Table 3 Comparison of Acc and IoU results of different models on dataset A
Models 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 mAcc mIoU Acc IoU Acc IoU Acc IoU Acc IoU Acc IoU Acc IoU Acc IoU Acc IoU SegNet (3ch) 82.6 94.1 67.7 75.6 73.7 80.8 55.9 97.1 39.1 43.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 48.9 86.8 51.7 59.7 SegNet (4ch) 84.4 93.1 85.5 84.7 76.0 74.7 58.2 96.5 44.2 43.6 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 74.4 95.6 57.8 60.9 ENet (3ch) 85.3 92.3 53.8 68.4 67.7 71.7 52.2 95.7 16.9 24.2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 41.5 43.8 ENet (4ch) 75.5 89.6 68.1 71.7 66.8 67.6 63.2 88.5 41.5 34.1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 93.2 78.1 56.2 53.6 FuseNet 76.8 91.2 69.3 80.5 71.2 78.6 60.1 95.8 30.8 28.1 0.0 0.0 68.4 37.9 83.1 98.5 61.9 63.8 MFNet 78.9 92.9 82.7 84.8 68.1 75.7 64.4 97.2 31.6 29.7 0.0 0.0 71.8 40.6 77.1 98.4 63.5 64.9 DMSNet 87.6 95.8 83.5 88.7 79.5 82.5 73.2 97.9 47.5 35.7 0.0 0.0 74.7 62.0 92.1 99.8 70.7 70.3 注: 表中数字2 ~ 9为分割类别标号, 表示法同表 2 表 4 不同模型在数据集B上的Acc与IoU结果对比
Table 4 Comparison of Acc and IoU results of different models on dataset B
Models 2 3 4 5 mAcc mIoU Acc IoU Acc IoU Acc IoU Acc IoU SegNet (3ch) 0.0 0.0 71.2 79.3 0.0 0.0 21.6 47.1 38.4 31.6 SegNet (4ch) 0.0 0.0 62.9 70.1 0.0 0.0 30.5 46.8 38.5 29.2 ENet (3ch) 0.0 0.0 77.6 85.5 0.0 0.0 73.4 90.9 49.9 44.1 ENet (4ch) 0.0 0.0 72.9 74.9 0.0 0.0 74.8 89.6 49.1 41.1 FuseNet 72.7 43.1 91.4 92.3 74.4 78.9 99.9 99.8 87.4 78.5 MFNet 66.7 47.0 88.7 91.0 95.2 90.1 96.3 99.8 89.1 81.9 DMSNet 67.8 43.5 89.1 90.4 96.3 97.5 99.3 99.9 90.2 82.8 注: 表中数字2 ~ 5为分割类别标号, 分别为 2: Fire-Extinguisher, 3: Backpack, 4: Hand-Drill, 5: Survivor 表 5 不同模型在数据集A白天与黑夜环境下的mAcc与mIoU结果对比
Table 5 Comparison of mAcc and mIoU results of different models on dataset A in daytime and nighttime
Models Daytime Nighttime mAcc mIoU mAcc mIoU SegNet (3ch) 47.8 55.5 52.6 61.3 SegNet (4ch) 45.4 49.3 58.2 62.9 ENet (3ch) 42.1 40.8 38.6 39.1 ENet (4ch) 44.1 45.9 57.1 54.3 FuseNet 50.6 61.2 63.4 64.7 MFNet 49.0 63.3 65.8 65.1 DMSNet 57.7 69.1 71.8 71.3 -
[1] Feng D, Haase-Schütz C, Rosenbaum L, et al. Deep multi-modal object detection and semantic segmentation for autonomous driving: Datasets, methods, and challenges. IEEE/ACM transactions on computational biology and bioinformatics, 2021, 22(3): 1341-1360 [2] Li C, Xu J X, Liu Q G, et al. Multi-View Mammographic Density Classification by Dilated and Attention-Guided Residual Learning. IEEE transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020: 1-11 [3] Chen L C, Yang Y, Wang J, Xu W, Yuille A L. Attention to scale: Scale-aware semantic image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3640−3649 [4] Lin D, Ji Y F, Lischinski D, Cohen-Or D, Huang H. Multi-scale context intertwining for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 603−619 [5] Kieu M, Bagdanov A D, Bertini M, Bimbo A D. Task-conditioned domain adaptation for pedestrian detection in thermal imagery. In: Proceedings of the 2020 European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 1−17 [6] Liu T, Lam K M, Zhao R, Qiu G P. Deep cross-modal representation learning and distillation for illumination-invariant pedestrian detection. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, DOI: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3060162 [7] 陈虹, 郭露露, 宫洵, 高炳钊, 张琳. 智能时代的汽车控制. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(7): 1313−1332Chen Hong, Guo Lu-Lu, Gong Xun, Gao Bing-Zhao, Zhang Lin. Automotive control in intelligent era. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(7): 1313−1332 [8] 张新钰, 邹镇洪, 李志伟, 刘华平, 李骏. 面向自动驾驶目标检测的深度多模态融合技术[J]. 智能系统学报, 2020, 15(4): 758-771Zhang Xin-Yu, Zou Zhen-Hong, Li Zhi-Wei, Liu Hua-Ping, Li Jun. Deep multi-modal fusion in object detection for autonomous driving. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2020, 15(4): 1–14 [9] Ha Q, Watanabe K, Karasawa T, Ushiku, Y, Harada, T. MFNet: Towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 5108−5115 [10] Sun Y X, Zuo W X, Liu M. Rtfnet: Rgb-thermal fusion network for semantic segmentation of urban scenes. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, 4(3): 2576-2583 [11] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [12] Zhao X M, Sun P P, Xu Z G, Min H G, Yu H K. Fusion of 3D LIDAR and camera data for object detection in autonomous vehicle applications. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(9): 4901-4913 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2966034 [13] Chen Z, Zhang J, Tao D C. Progressive lidar adaptation for road detection. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2019, 6(3): 693-70 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2019.1911459 [14] Hazirbas C, Ma L, Domokos C, Cremers D. Fusenet: Incorporating depth into semantic segmentation via fusion-based cnn architecture. In: Proceedings of the Asian conference on Computer Vision. Taipei, China: Springer, 2016. 213−228 [15] Zhang Y T, Yin Z S, Nie L Z, Huang S. Attention Based Multi-Layer Fusion of Multispectral Images for Pedestrian Detection. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 165071-165084 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3022623 [16] Guan D Y, Cao Y P, Yang J X, Cao Y L, Yang M Y. Fusion of multispectral data through illumination-aware deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. Information Fusion, 2019, 50: 148-157 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.11.017 [17] Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: ACM, 2015. 448−456 [18] Maas A L, Hannun A Y, Ng A Y. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Atlanta, USA: ACM, 2013. 1−6 [19] Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Fort Lauderdale, Florida, USA: JMLR, 2011. 315−323 [20] Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi S A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision. Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA: IEEE, 2016. 565−571 [21] Shivakumar S S, Rodrigues N, Zhou A, Miller L D, Kumar V, Taylor C J. Pst900: Rgb-thermal calibration, dataset and segmentation network. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Paris, France: IEEE, 2020: 9441−9447 [22] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K M, Dollar P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2980−2988 -




 下载:
下载: