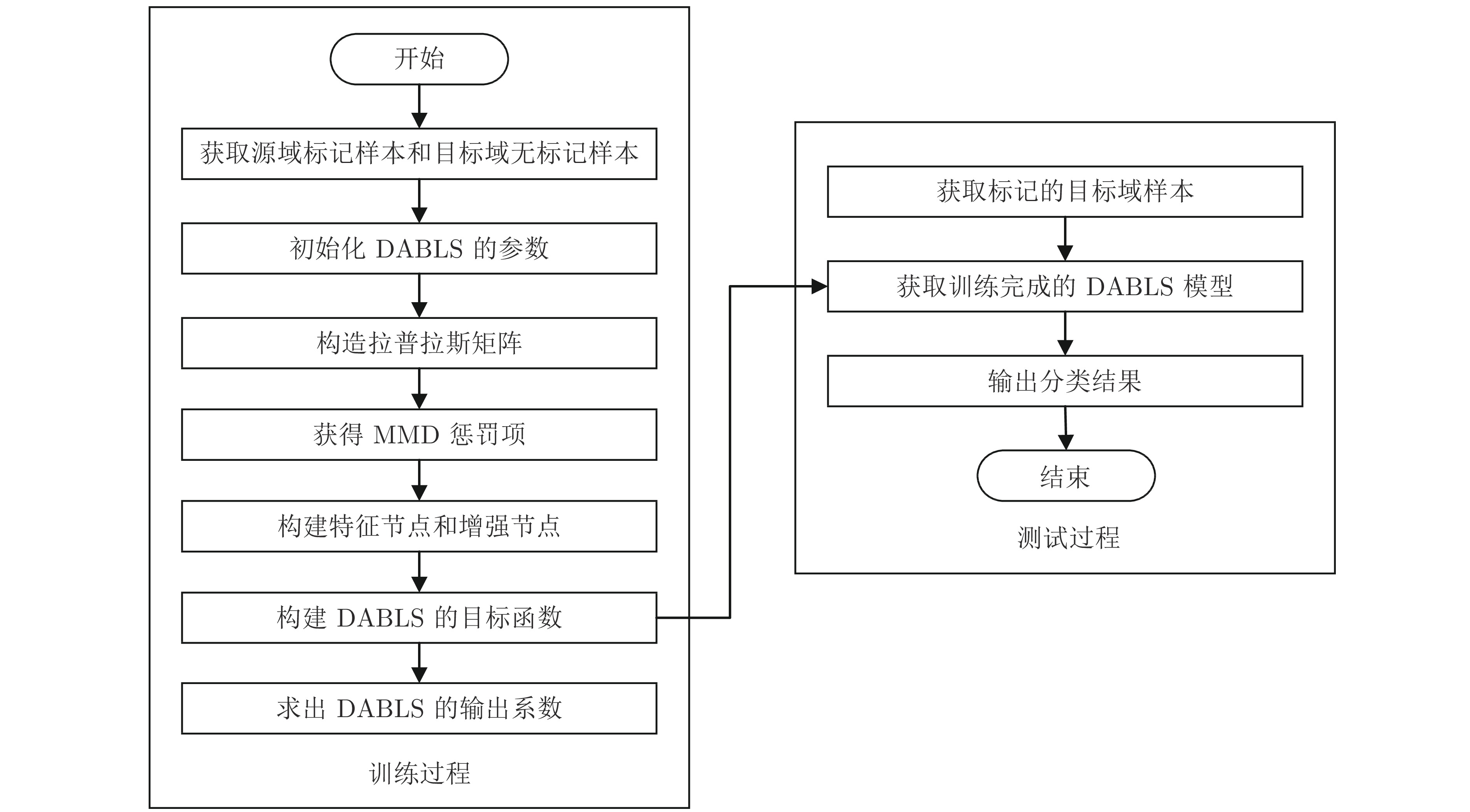
-
摘要: 宽度学习系统(Broad learning system, BLS)作为一种基于随机向量函数型网络(Random vector functionallink network, RVFLN)的高效增量学习系统, 具有快速自适应模型结构选择能力和高精度的特点. 但针对目标分类任务中有标签数据匮乏问题, 传统的BLS难以借助相关领域知识来提升目标域的分类效果, 为此提出一种基于流形正则化框架和最大均值差异(Maximum mean discrepancy, MMD)的域适应BLS (Domain adaptive BLS, DABLS)模型, 实现目标域无标签条件下的跨域图像分类. DABLS模型首先构造BLS的特征节点和增强节点, 从源域和目标域数据中有效提取特征; 再利用流形正则化框架构造拉普拉斯矩阵, 以探索目标域数据中的流形特性, 挖掘目标域数据的潜在信息. 然后基于迁移学习方法构建源域数据与目标域数据之间的MMD惩罚项, 以匹配源域和目标域之间的投影均值; 将特征节点、增强节点、MMD惩罚项和拉普拉斯矩阵相结合, 构造目标函数, 并采用岭回归分析法对其求解, 获得输出系数, 从而提高模型的跨域分类性能. 最后在不同图像数据集上进行大量的验证与对比实验, 结果表明DABLS在不同图像数据集上均能获得较好的跨域分类性能, 具有较强的泛化能力和较好的稳定性.Abstract: As an efficient incremental learning system based on random vector function-link network (RVFLN), broad learning system (BLS) has the characteristics of fast adaptive model structure selection and high precision. However, due to the lack of label data in target classification, the traditional BLS is difficult to improve the classification effect of target domain by using relevant domain knowledge. Therefore, a domain adaptive BLS (DABLS) model based on manifold regularization framework and maximum mean discrepancy (MMD) is developed to achieve cross-domain image classification of target domain under unlabeled condition. Firstly, the feature nodes and enhancement nodes of BLS are constructed to effectively extract features from the data of source domain and target domain. The manifold regularization framework is used to construct Laplacian matrix in order to explore the manifold characteristics of the target domain data and mine the potential information of the target domain data. Then the transfer learning method is used to construct the MMD penalty term between the source domain data and the target domain data to match the projection mean between the source domain and the target domain. The feature nodes, enhancement nodes, MMD penalty term and Laplacian matrix are combined to construct the objective function. Ridge regression analysis is used to solve the objective function to obtain the output coefficients, so as to improve the cross-domain classification performance. Finally, a large number of validation and comparative experiments are carried out on different image data sets, and the experiment results show that the DABLS can better achieve cross-domain classification on different image data sets, and has strong generalization ability and better stability.
-
表 1 数据集的详细描述
Table 1 Detailed description of datasets
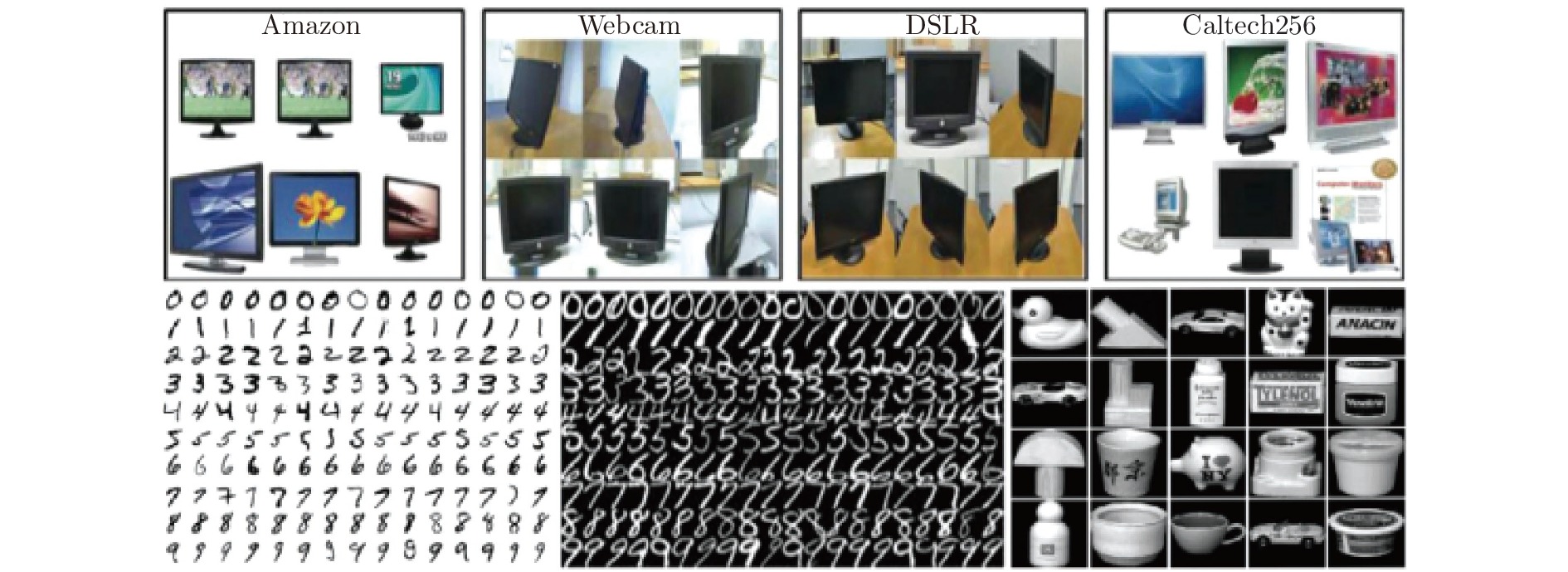
数据集 样本数目 特征维数 类别 子集 USPS 1800 256 10 U MNIST 2000 256 10 M COIL20 1440 1024 20 CO1, CO2 Office 1410 800 10 A, W, D Caltech256 1123 800 10 C ImageNet 7341 4096 5 I VOC2007 3376 4096 5 V 表 2 不同节点数下DABLS的实验结果
Table 2 Experimental results of DABLS with different numbers of nodes
特征
节点增强
节点M→U U→M 精度 (%) 时间 (s) 标准差 精度 (%) 时间 (s) 标准差 100 500 60.41 19.01 1.25 45.25 20.50 1.84 100 1000 63.94 19.59 1.61 47.57 22.46 2.14 100 1500 66.98 21.56 1.49 48.05 26.16 2.27 100 2000 68.54 23.98 1.67 50.13 27.27 1.53 100 2500 68.77 27.15 1.72 50.25 29.27 1.64 100 3000 69.22 33.12 1.81 50.37 32.83 1.78 100 3500 69.31 37.26 1.89 49.91 36.25 1.92 100 4000 68.95 40.96 1.75 49.63 41.17 1.82 150 2000 68.36 25.03 1.87 49.49 27.92 1.72 200 2000 67.53 25.91 2.01 50.08 28.72 1.79 300 2000 66.57 26.41 2.03 49.92 29.62 1.87 400 2000 64.35 26.97 3.37 48.59 30.58 1.95 500 2000 62.96 27.49 4.61 49.38 31.41 1.64 表 3 从源域到目标域的平均分类精度(%)
Table 3 Average classification accuracy from source domain to target domain (%)
任务 BLS SS-BLS TCA CDELM CD-CDBN DABLS M→U 25.34 59.67 54.28 53.27 50.27 68.54 U→M 20.25 29.84 52.00 39.80 41.65 50.13 平均值 22.79 44.75 53.14 46.53 45.96 59.33 表 4 从源域到目标域的平均训练时间(s)
Table 4 Average training time from source domain to target domain (s)
任务/方法 BLS SS-BLS TCA CDELM CD-CDBN DABLS M→U 0.69 12.75 27.14 24.77 548.47 23.98 U→M 0.58 13.18 22.36 23.63 536.95 22.27 平均值 0.64 12.97 24.75 24.20 542.71 23.13 表 5 不同节点数下DABLS的实验结果
Table 5 Experimental results of DABLS with different numbers of nodes
特征
节点增强
节点CO1→CO2 CO2→CO1 精度 (%) 时间 (s) 标准差 精度 (%) 时间 (s) 标准差 100 500 85.43 2.59 1.82 82.70 2.83 1.61 100 1000 86.40 3.17 1.80 83.29 3.35 1.71 100 1500 86.83 3.65 1.32 83.83 3.76 1.52 100 2000 87.33 4.50 1.27 84.04 4.02 1.46 100 2500 87.69 4.93 1.30 84.41 4.85 1.32 100 3000 88.18 5.85 1.12 84.72 5.02 1.28 100 3500 88.26 6.54 1.13 84.16 5.81 1.21 100 4000 87.55 7.61 1.17 83.76 6.10 1.06 150 3000 87.55 6.02 1.15 83.61 6.21 1.21 200 3000 87.09 6.15 1.16 82.95 6.38 1.63 300 3000 85.92 6.64 1.15 81.52 6.62 1.18 400 3000 84.08 7.24 1.20 80.48 6.79 1.20 500 3000 82.29 7.42 1.02 79.51 7.04 1.11 表 6 从源域到目标域的平均分类精度(%)
Table 6 Average classification accuracy from source domain to target domain (%)
任务/方法 BLS SS-BLS TCA CDELM CD-CDBN DABLS CO1→CO2 82.25 83.75 88.61 81.66 84.67 88.12 CO2→CO1 80.63 81.17 86.33 80.19 80.74 84.72 平均值 81.44 82.46 87.47 80.93 82.70 86.42 表 7 从源域到目标域的平均训练时间(s)
Table 7 Average training time from source domain to target domain (s)
任务/方法 BLS SS-BLS TCA CDELM CD-CDBN DABLS CO1→CO2 1.38 3.22 19.98 5.87 125.33 5.35 CO2→CO1 0.85 2.95 14.67 5.48 136.78 5.33 平均值 1.12 3.09 17.32 5.68 131.05 5.34 表 8 不同节点数下DABLS的实验结果
Table 8 Experimental results of DABLS with different numbers of nodes
特征
节点增强
节点A→C W→C 精度(%) 时间(s) 标准差 精度(%) 时间(s) 标准差 500 50 43.63 8.81 0.75 34.69 6.01 0.35 500 100 43.73 8.86 0.53 35.24 6.24 0.91 500 150 43.82 8.92 0.77 35.53 6.50 0.65 500 200 43.92 9.01 0.62 35.61 6.78 0.71 500 300 43.98 9.18 0.85 35.93 6.93 0.92 500 400 44.02 9.53 0.87 36.27 7.21 0.77 500 500 44.29 9.77 0.44 36.50 7.43 0.70 500 600 43.50 9.98 0.61 36.52 7.72 0.93 500 800 43.36 10.52 0.59 36.21 8.01 0.64 500 1000 43.18 10.90 0.82 36.04 8.39 0.33 100 500 42.01 8.72 0.76 32.39 6.48 0.91 200 500 42.36 9.02 0.83 33.95 6.66 0.99 300 500 42.83 9.30 0.65 34.27 6.87 0.92 400 500 43.59 9.53 0.69 36.11 7.12 0.77 600 500 44.25 10.44 0.78 36.17 7.85 0.82 800 500 43.43 10.75 0.65 35.77 8.03 0.69 表 9 从源域到目标域的平均分类精度(%)
Table 9 Average classification accuracy from source domain to target domain (%)
任务/方法 BLS SS-BLS TCA CDELM CD-CDBN DABLS A→C 20.82 42.16 40.78 31.67 35.56 44.29 A→D 17.83 39.40 31.85 32.48 33.79 42.06 A→W 19.61 40.61 37.63 31.47 27.46 42.09 C→A 29.16 49.67 44.89 44.99 38.78 51.68 C→D 24.84 44.20 45.84 35.37 36.94 45.85 C→W 20.46 45.74 36.61 38.92 35.54 47.79 D→A 32.42 35.57 31.52 30.61 28.34 36.73 D→C 30.03 30.19 32.50 28.96 26.79 32.47 D→W 79.98 79.11 87.12 76.95 50.78 80.06 W→A 34.61 37.51 30.69 35.55 30.89 40.01 W→C 31.73 35.29 27.16 32.03 27.26 36.50 W→D 80.81 80.89 90.45 78.99 50.42 82.73 平均值 35.19 46.69 45.38 41.50 35.21 48.52 表 10 从源域到目标域的平均训练时间(s)
Table 10 Average training time from source domain to target domain (s)
任务/方法 BLS SS-BLS TCA CDELM CD-CDBN DABLS A→C 0.78 5.39 36.69 6.83 46.36 9.77 A→D 0.67 0.83 11.73 1.29 33.28 2.76 A→W 0.64 0.99 13.65 1.52 34.23 2.91 C→A 0.68 3.86 35.71 5.74 41.44 8.18 C→D 0.71 0.93 15.05 1.58 35.86 3.71 C→W 0.67 1.09 16.75 1.59 38.37 3.63 D→A 0.59 3.58 11.82 4.14 20.12 5.50 D→C 0.54 5.19 16.21 6.14 26.63 7.45 D→W 0.55 0.79 3.53 0.73 20.48 1.17 W→A 0.58 3.43 14.29 4.33 45.53 5.93 W→C 0.57 5.17 19.05 6.12 56.28 7.43 W→D 0.52 0.69 3.22 0.66 12.40 1.02 平均值 0.62 2.66 16.48 3.39 30.08 4.96 表 11 不同节点数下DABLS的实验结果
Table 11 Experimental results of DABLS with different numbers of nodes
特征
节点增强
节点V→I I→V 精度(%) 时间(s) 标准差 精度(%) 时间(s) 标准差 100 600 74.13 35.25 1.05 66.61 16.62 1.31 150 600 75.94 37.99 0.75 66.83 19.24 0.77 200 600 76.53 42.29 0.59 67.51 22.42 0.62 250 600 77.87 44.51 0.33 67.83 26.03 0.41 300 600 77.65 47.64 0.29 67.81 28.96 0.43 400 600 76.87 53.89 0.36 67.24 31.62 0.45 500 600 75.67 57.13 0.19 67.02 35.37 0.39 600 600 75.20 61.29 0.27 66.86 38.69 0.37 250 200 74.29 26.56 0.73 66.32 14.73 0.87 250 400 77.21 31.59 0.67 67.13 17.33 0.54 250 800 77.23 46.21 0.56 67.69 24.09 0.42 250 1000 76.83 52.68 0.65 67.52 27.55 0.34 250 1500 74.93 65.71 0.46 67.42 36.43 0.31 250 2000 73.86 83.61 0.36 67.33 43.53 0.33 250 2500 71.77 103.38 0.31 66.73 50.92 0.26 表 12 从源域到目标域的平均分类精度(%)
Table 12 Average classification accuracy from source domain to target domain (%)
任务/方法 BLS SS-BLS TCA CDELM CD-CDBN DABLS V→I 76.22 77.03 73.79 76.82 76.02 77.87 I→V 66.32 67.13 64.34 66.85 67.19 67.83 平均值 71.27 72.08 69.06 71.83 71.60 72.85 表 13 从源域到目标域的平均训练时间(s)
Table 13 Average training time from source domain to target domain (s)
任务/方法 BLS SS-BLS TCA CDELM CD-CDBN DABLS V→I 6.37 37.69 52.15 55.04 1039.03 44.51 I→V 3.62 17.32 30.42 33.39 823.35 26.03 平均值 4.96 27.50 41.28 44.25 931.19 35.27 -
[1] Salakhutdinov R, Hinton G. An efficient learning procedure for deep boltzmann machine. Neural Computation, 2014, 24(8): 1967−2006 [2] 林景栋, 吴欣怡, 柴毅, 尹宏鹏. 卷积神经网络结构优化综述. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(1): 24−37Lin Jing-Dong, Wu Xin-Yi, Chai Yi, Yin Hong-Peng. Structure optimization of convolutional neural networks: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 24−37 [3] Hinton G E, Osinderos T Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527−1554 doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 [4] 刘建伟, 谢浩杰, 罗雄麟. 生成对抗网络在各领域应用研究进展. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(12): 2500−2536Liu Jian-Wei, Xie Hao-Jie, Luo Xiong-Lin. Research progress on application of generative adversarial networks in various fields. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(12): 2500−2536 [5] Feng L, Chen Z, Jie W. Video image target monitoring based on RNN-LSTM. Multimedia Tools Applications, 2018, 78(2): 1−18 [6] Chen C L P, Liu Z. Broad learning system: An effective and efficient incremental learning system without the need for deep architecture. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(1): 10−24 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2716952 [7] Chen C L P, Liu Z, Feng S. Universal approximation capability of broad learning system and its structural variations. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networksand Learning Systems, 2019, 30(4): 1191−1204 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2866622 [8] Jin J W, Chen C L P. Regularized robust broad learning system for uncertain data modeling. Neurocomputing, 2018, 322(1): 58−69 [9] 杨刚, 陈鹏, 戴丽珍, 杨辉. 一种基于池计算的宽度学习系统. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(9): 2203−2210Yang Gang, Chen Peng, Dai Li-Zhen, Yang Hui. A broad learning system based on reservoir computing. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(9): 2203−2210 [10] 邹伟东, 夏元清. 基于压缩因子的宽度学习系统的虚拟机性能预测. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(3): 724−734Zou Wei-Dong, Xia Yuan-Qing. Virtual machine performance prediction using broad learning system based on compression factor. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(3): 724−734 [11] Kong Y, Wang X, Cheng Y, Chen C. Hyperspectral imagery classification based on semi-supervised broad learning system. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(5): Article No. 685 doi: 10.3390/rs10050685 [12] 郑云飞, 陈霸东. 基于最小p-范数的宽度学习系统. 模式识别与人工智能, 2019, 32(1): 51−57Zheng Yun-Fei, Chen Ba-Dong. Least p-norm based broad learning system. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 32(1): 51−57 [13] Lin J, Liu Z, Chen C L P, Zhang Y. Quaternion broad learning system: A novel multi-dimensional filter for estimation and elimination tremor in teleoperation. Neurocomputing, 2020, 380: 78−86 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.059 [14] Han M, Feng S B, Chen C L P, Xu M L, Qiu T. Structured manifold broad learning system: A manifold perspective for large-scale chaotic time series analysis and prediction. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2019, 31(9): 1809−1821 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2018.2866149 [15] Fan J H, Wang X, Wang X X, Zhao J H, Liu X X. Incremental wishart broad learning system for fast polsar image classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(12): 1854−1858 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2913999 [16] Feng S, Chen C L P. Fuzzy broad learning system: A novel neuro-fuzzy model for regression and classification. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(2): 414−424 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2857815 [17] Xu M L, Han M, Chen C L P, Qiu T. Recurrent broad learning systems for time series prediction. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(4): 1405−1417 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2863020 [18] Chu F, Liang T, Chen C L P, Wang X S, Ma X P. Weighted broad learning system and its application in nonlinear industrial process modeling. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(8): 3017−3031 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2935033 [19] Liu Y, Wang Y F, Chen L, Zhao J, Wang W, Liu Q L. Incremental Bayesian broad learning system and its industrial application. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2020, 54: 3517−3537 [20] Shi Z H, Chen X M, Zhao C M, He H, Stuphorn V, Wu D R. Multi-view broad learning system for primate oculomotor decision decoding. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2020, 28(9): 1908−1920 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2020.3003342 [21] Zhao H M, Zheng J J, Deng W, Song Y J. Semi-supervised broad learning system based on manifold regularization and broad network. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems—— I: Regular Papers, 2020, 67(3): 983−994 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2019.2959886 [22] Pan S J, Tsang I W, Kwok J T, Yang Q. Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2021, 22(2): 199−210 [23] Li S, Song S J, Huang G, Wu C. Cross-domain extreme learning machines for domain adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(6): 1194−1207 [24] Huang G B. Learning hierarchical representations for face verification with convolutional deep belief networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 2518−2525 -




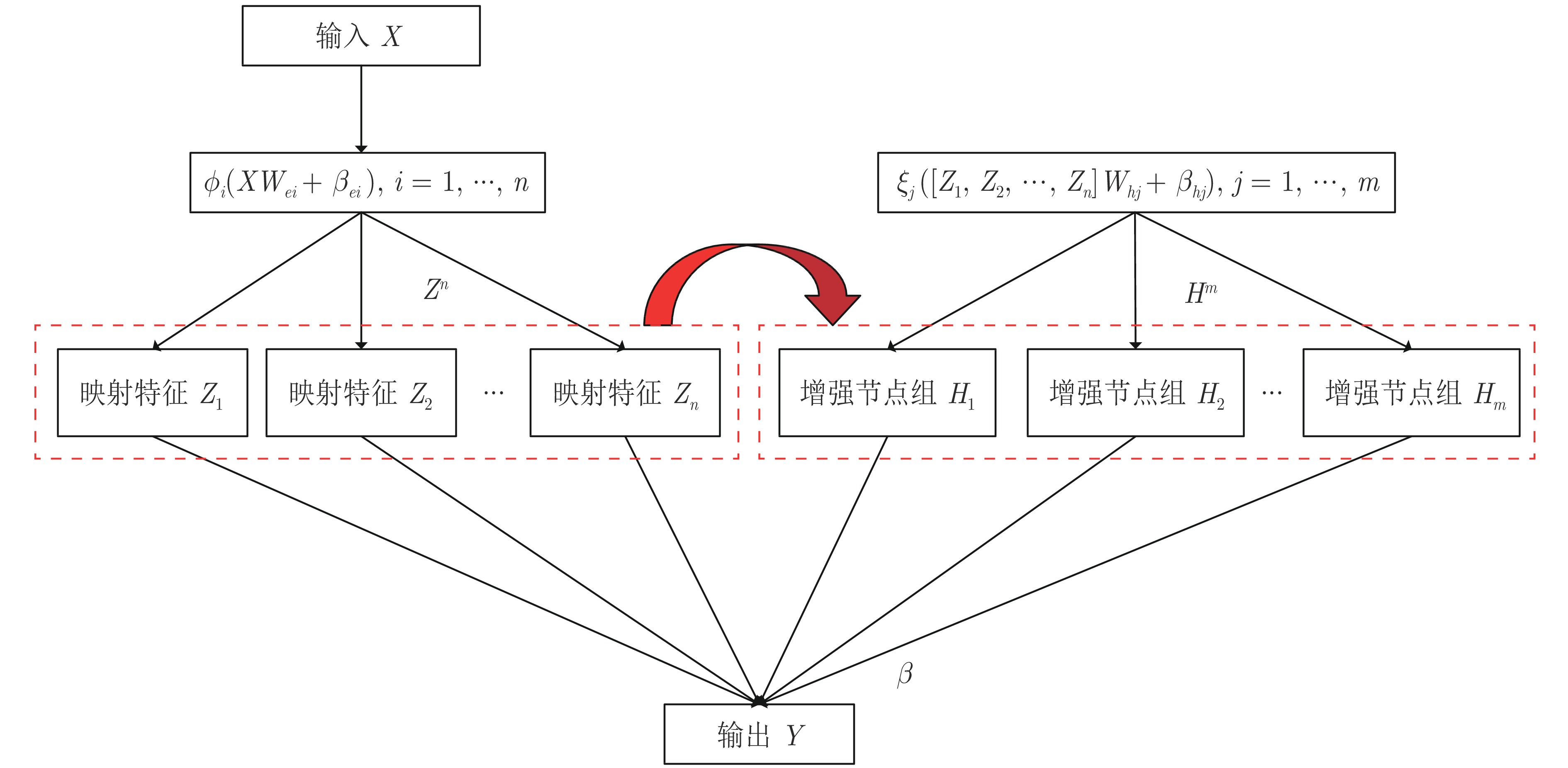
 下载:
下载: