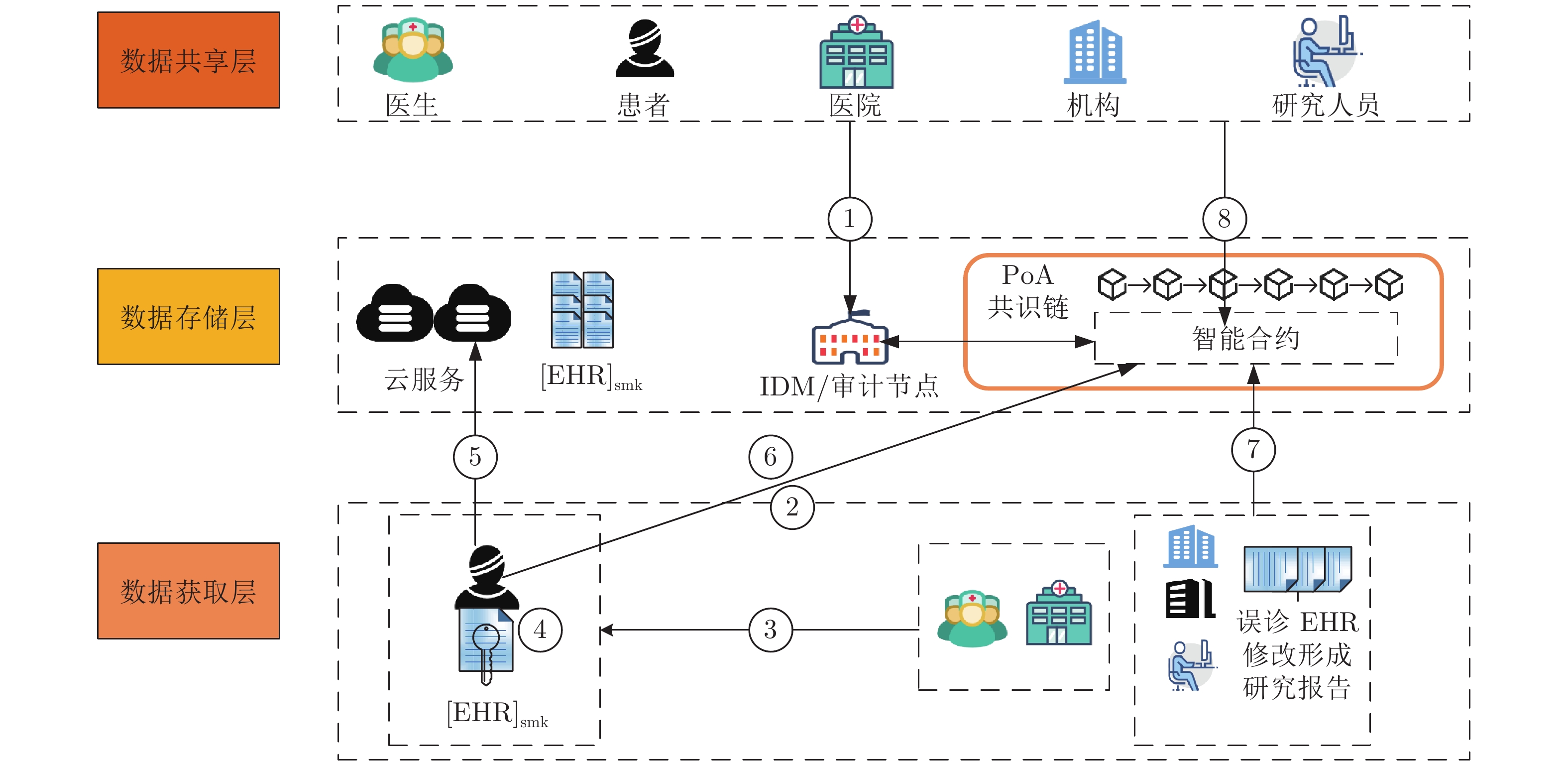
Secure Data Sharing Model Based on Smart Contract With Integrated Credit Evaluation
-
摘要:
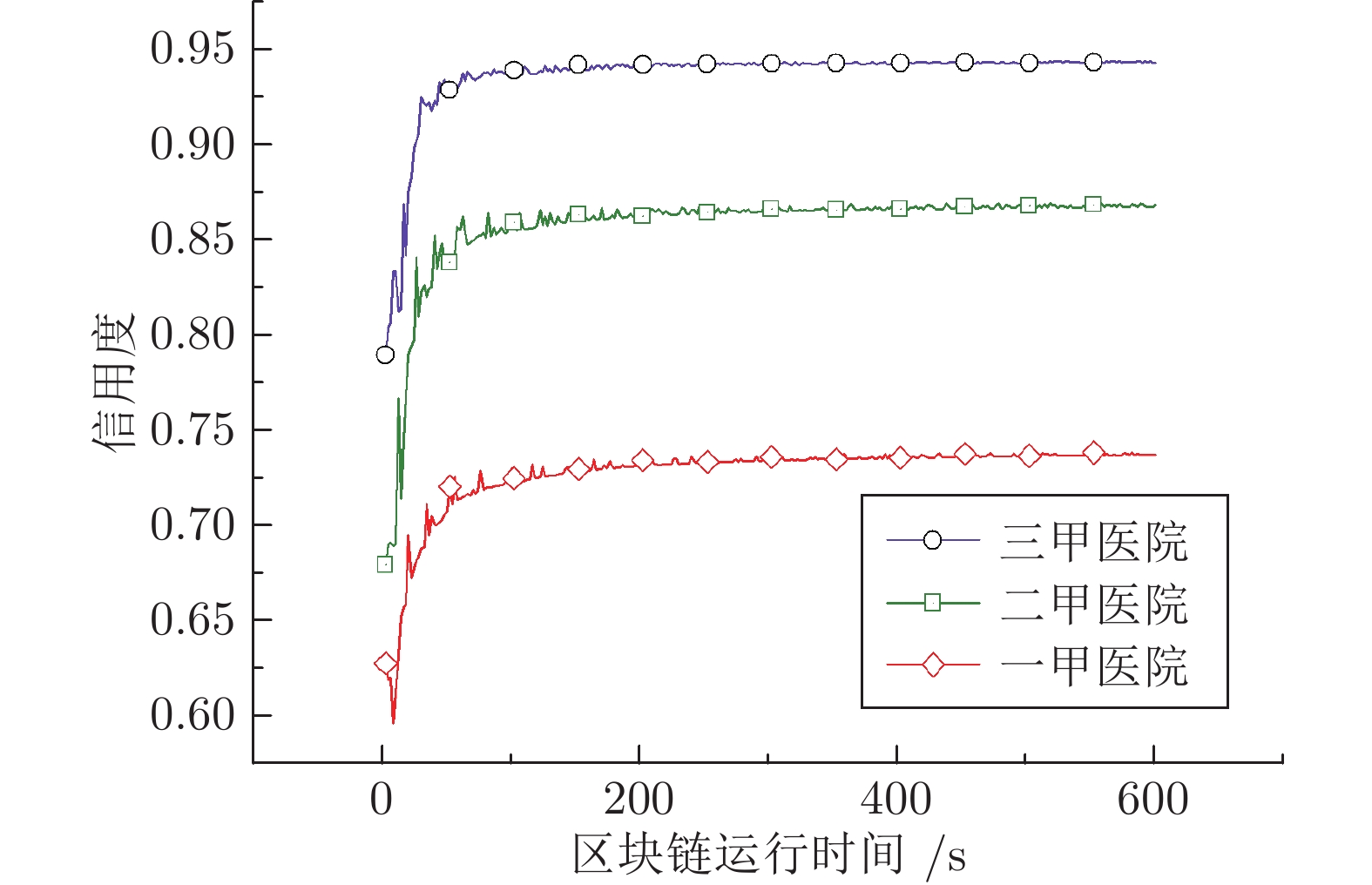
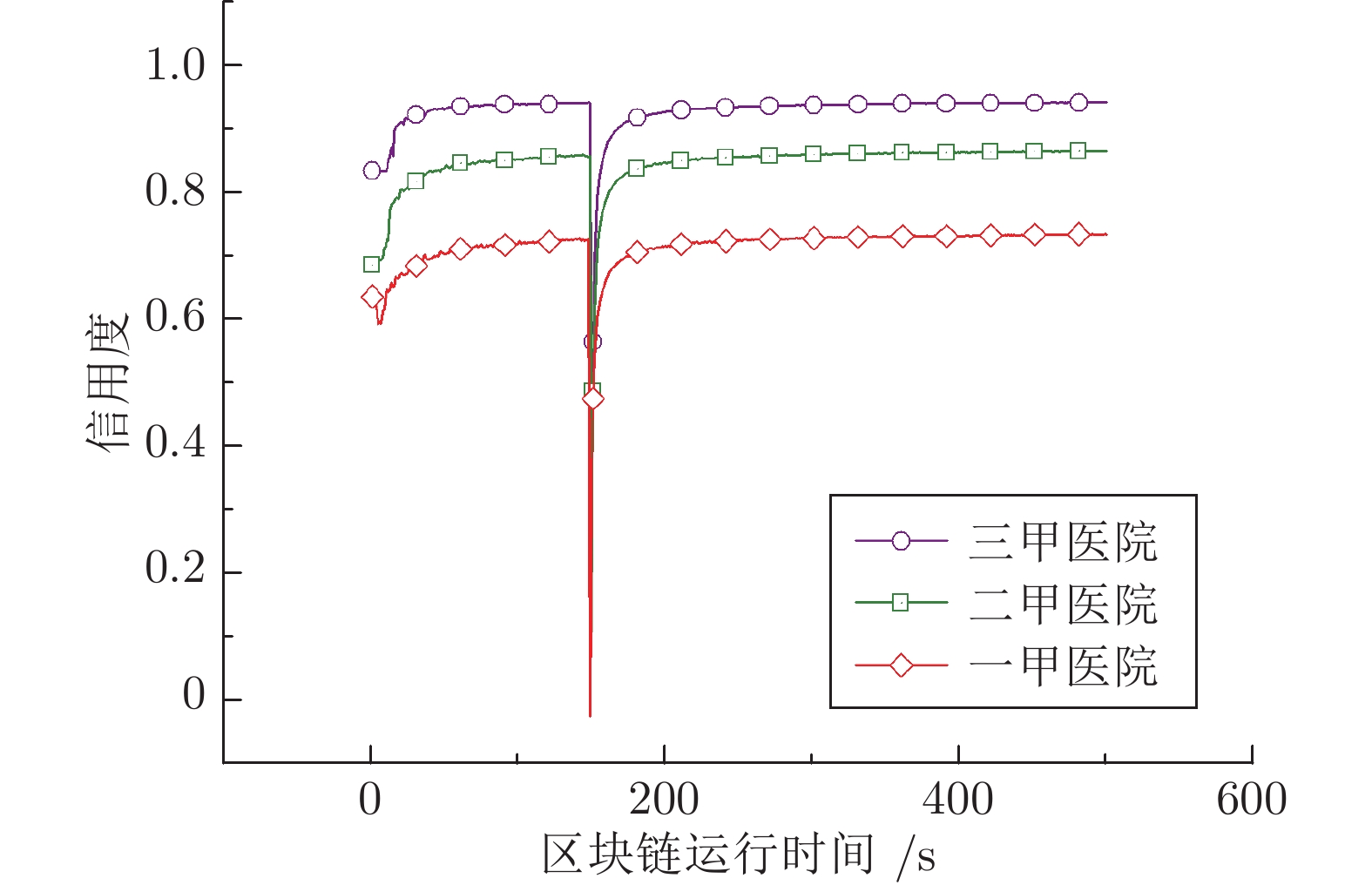
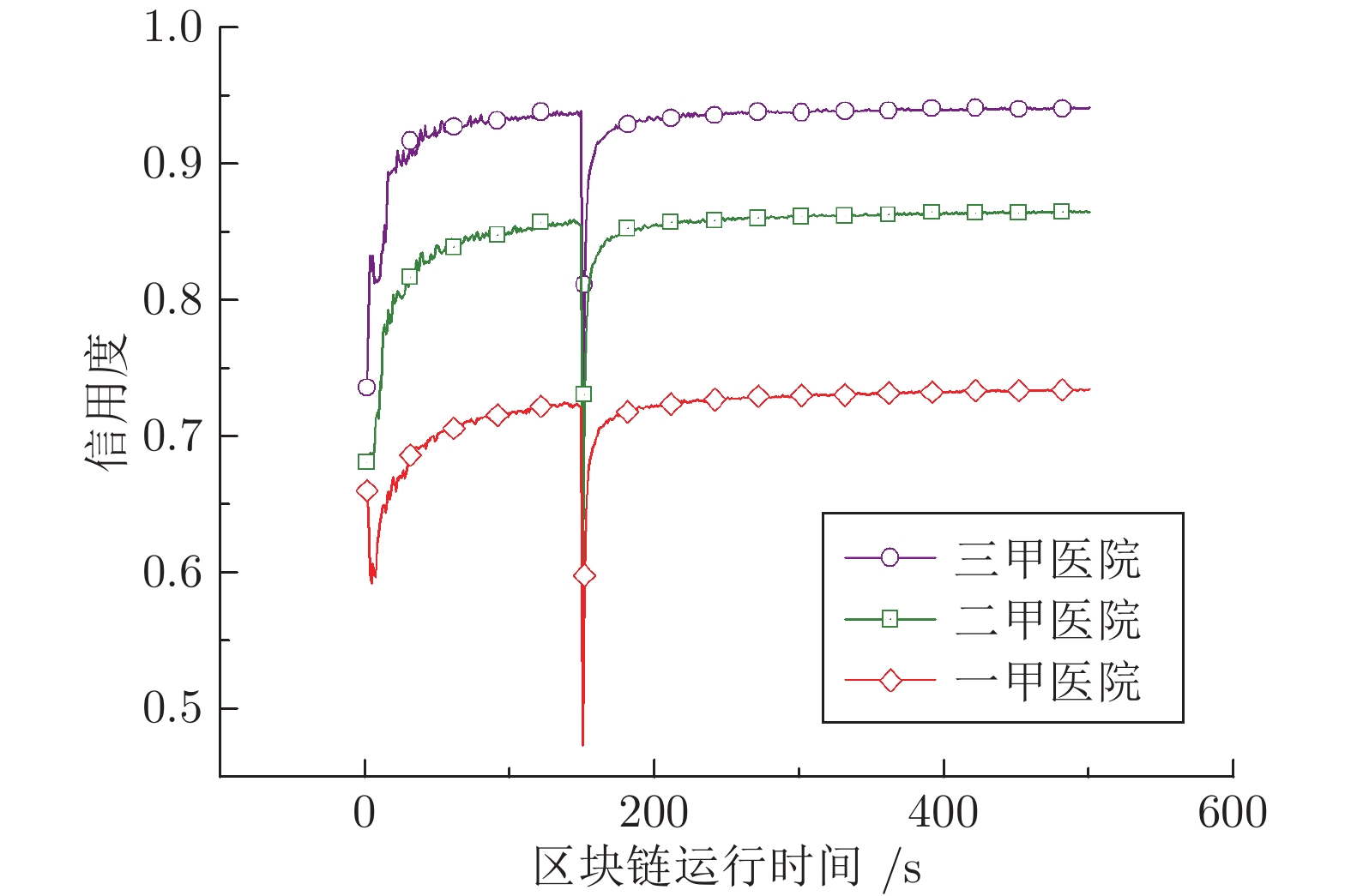
区块链技术是一种新兴技术, 它具备防篡改、去中心化、分布式存储等特点, 可以有效地解决现有数据共享模型中隐私安全、用户控制权不足以及单点故障问题. 本文以电子病历(Electronic health record, EHR)共享为例提出一种基于集成信用度评估智能合约的数据共享访问控制模型, 为患者提供可信EHR共享环境和动态访问控制策略接口. 实验表明所提模型有效解决了患者隐私安全和对EHR控制权不足的问题. 同时就模型的特点、安全性以及性能进行了分析.
Abstract:Blockchain technology is an emerging technology, it has the characteristics of anti-tampering, decentralization, and distributed storage. It can effectively solve the problems of privacy security, insufficient user control rights, and single point failure in the existing data sharing model. This paper takes electronic health record (EHR) sharing as an example and proposes a data sharing access control model based on smart contract with integrated credit evaluation to provide patients with a trusted EHR sharing environment and dynamic access control policy interface. Experiments show that the proposed model effectively solves the problems of patient privacy security and insufficient control of EHR. At the same time, the characteristics, safety and performance of the model are analyzed.
-
Key words:
- Blockchain /
- credit /
- smart contract /
- electronic health record (EHR) /
- access control
-
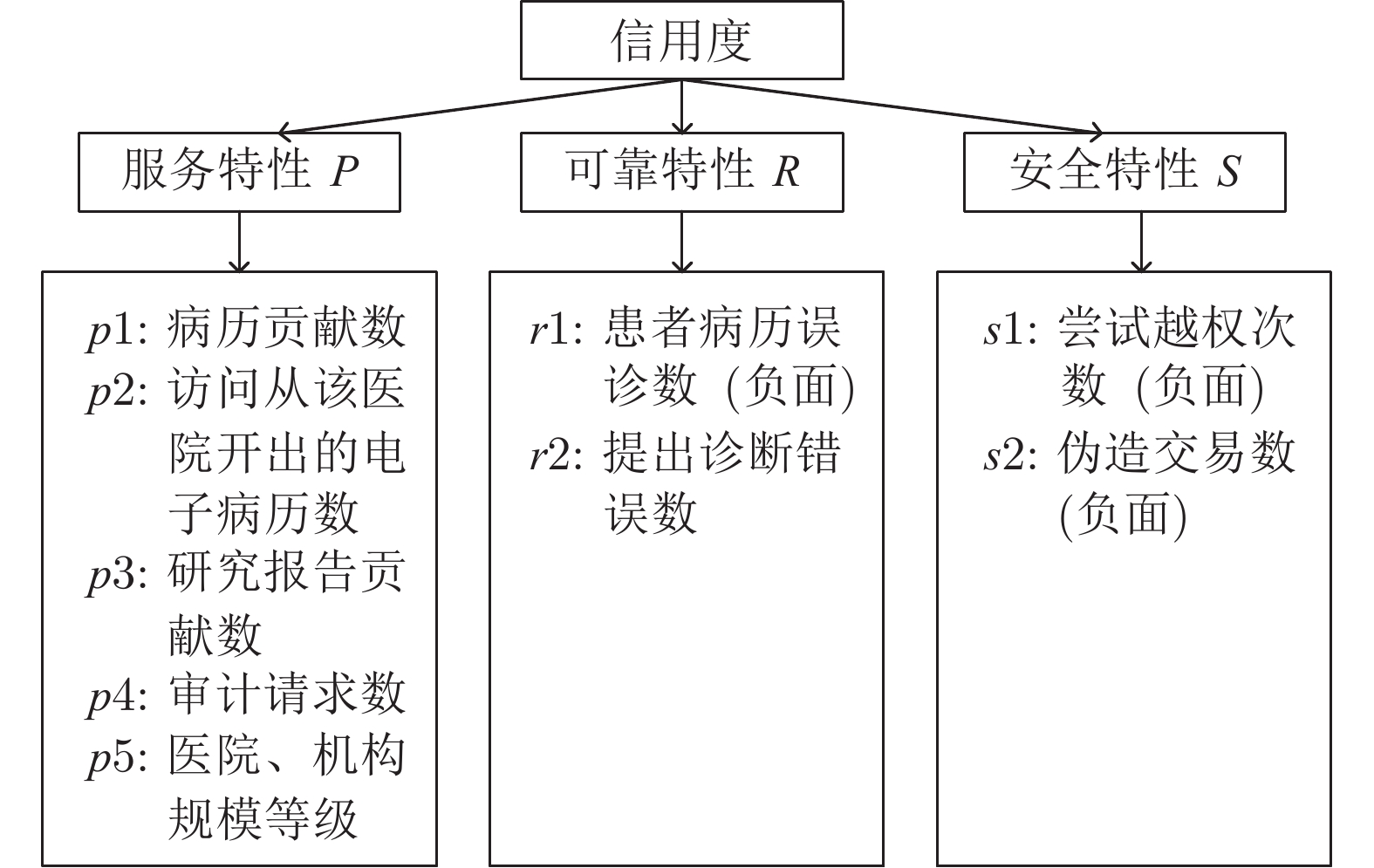
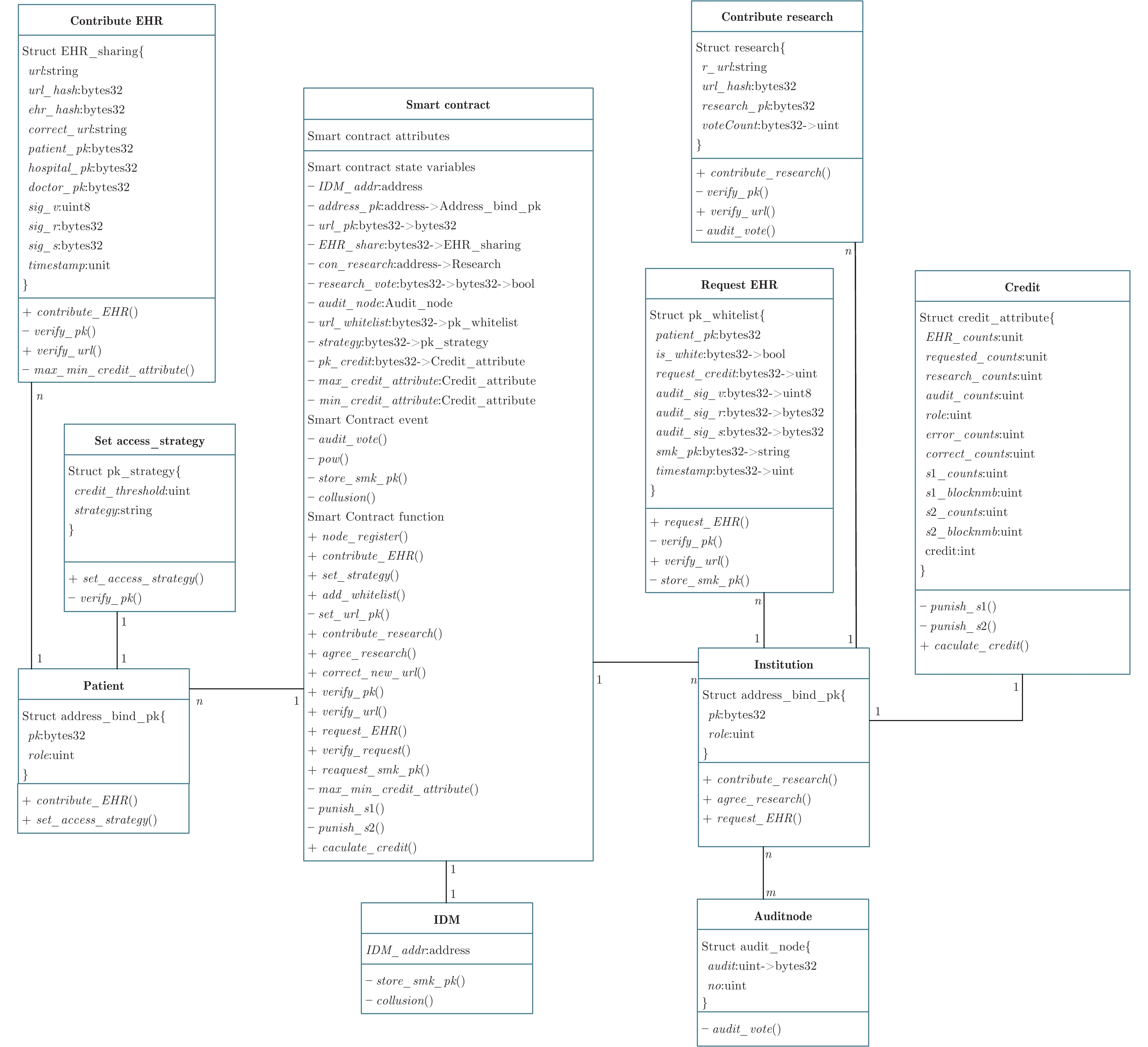
表 1 EHR-SCAC智能合约变量和函数说明
Table 1 Description of EHR-SCAC smart contract variables and functions
智能合约状态变量 功能描述 IDM_addr IDM 的以太坊地址, 用于检测调用合约者是否是 IDM address_pk 由用户的以太坊地址映射到结构体 Address_bind_pk, 记录了用户成员公钥 pk 与以太坊地址的对应关系和用
户的角色信息url_pk 由 EHR 的索引url 的 hash 值映射到 pk, 记录了url 与患者pkp 的对应关系 EHR_share 由 EHR 的索引url 的 hash 值映射到 EHR 结构体 EHR_sharing, 记录了患者共享的 EHR 的具体信息 strategy 由患者成员公钥 pkp 映射到策略结构体 pk_strategy, 记录了患者的访问控制策略 con_research 由 r_url 的 hash 值映射到研究报告结构体 Research, 记录了机构共享的研究报告相关信息 research_vote 由审计节点的成员公钥 pkA 映射到 r_url 的 hash 值, 再映射到 bool 类型值, 记录了审计节点对 r_url 研究报
告是否已经投过票, 防止重复投票audit_node 该变量是审计节点结构体 Audit_node 类型变量, 结构体中的 no 变量用于记录审计节点个数, 也为随机选举审计节点提供参考 pk_credit 由机构的成员公钥 pkI 映射到信用度结构体 Credit_attribute, 记录了机构的信用度属性 url_whitelist 由 EHR 的索引url 的 hash 值映射到白名单结构体 pk_whitelist, 记录患者为共享的 url 设置的白名单成员的
相关信息max_credit_attribute 记录了所有机构中各信用度属性的最大值, 用于信用度计算时信用度属性的归一化处理, 该变量数据类型是信
用度结构体 Credit_attributemin_credit_attribute 记录了所有机构中各信用度属性的最小值, 用于信用度计算时信用度属性的归一化处理, 该变量数据类型是信
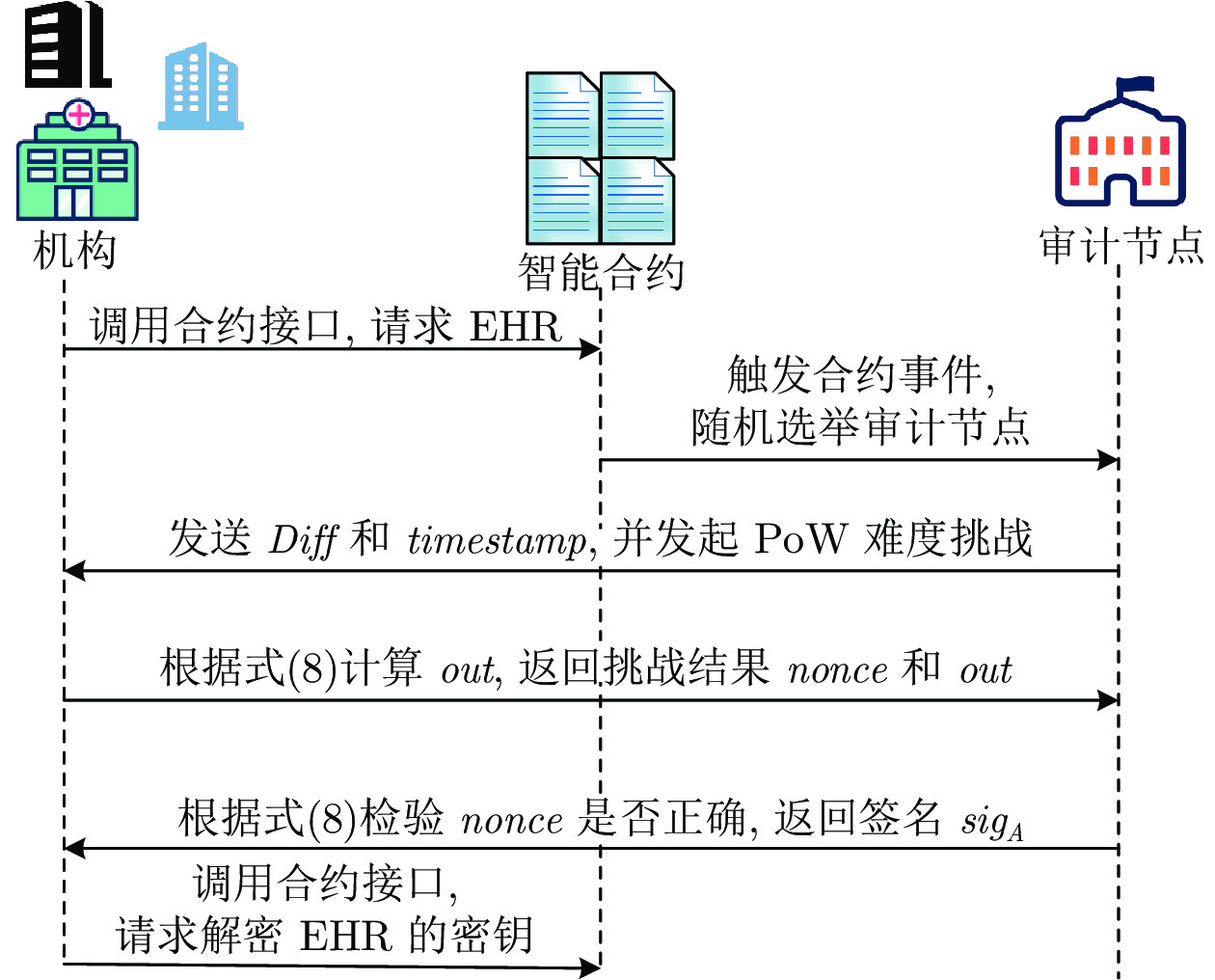
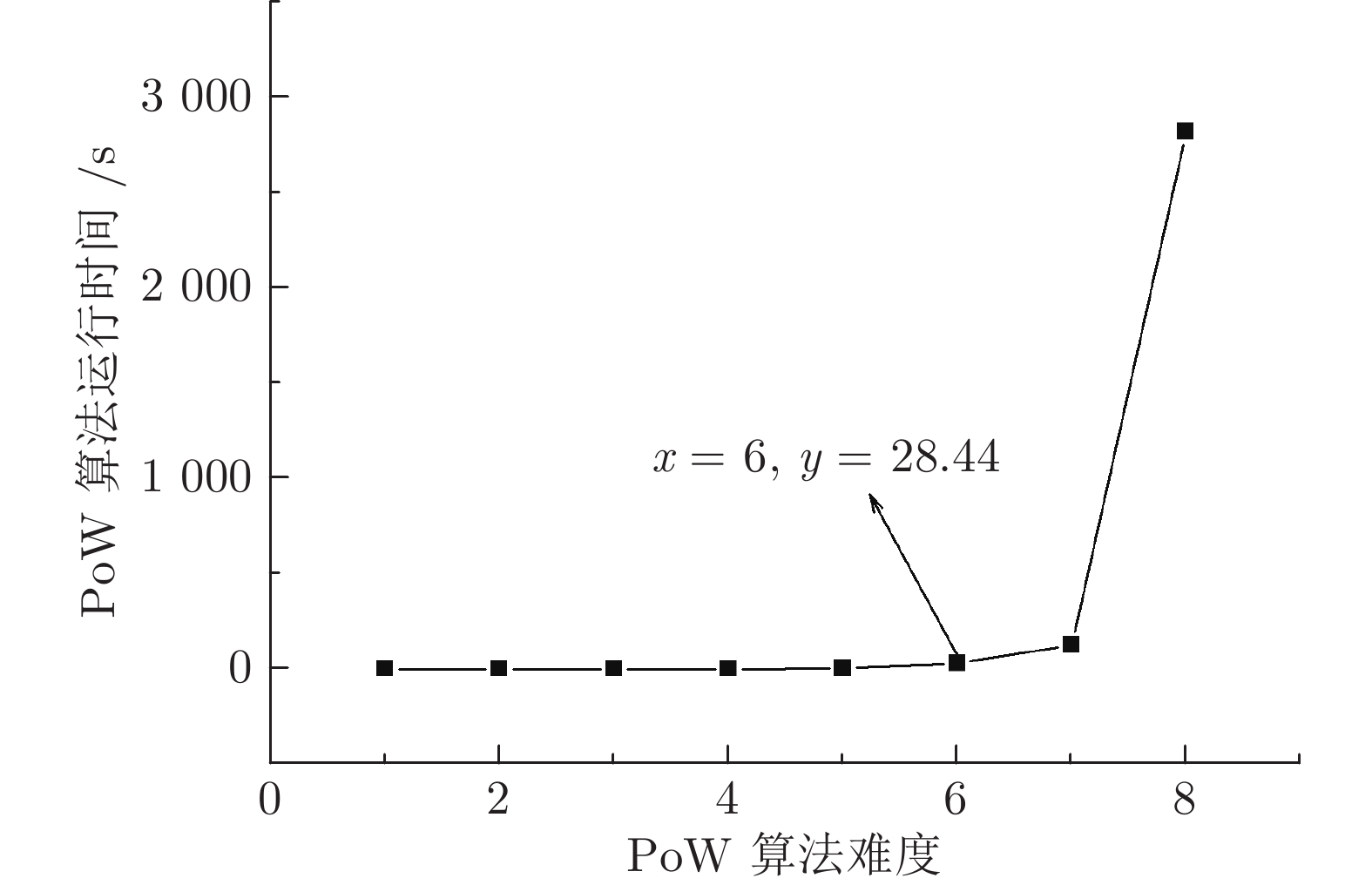
用度结构体 Credit_attribute智能合约事件 功能描述 audit_vote() 机构共享研究报告时, 将会触发 audit_vote() 事件, 监听该事件的审计节点链下审核研究报告, 在时间阈值内达到投票阈值后交易成功上链 pow() 机构请求申请 EHR 的权限时会触发该事件, 审计节点链下会对请求者发起 PoW 挑战 store_smk_pk() 机构在成功请求患者 EHR 后会触发 store_smk_pk() 事件, 监听该事件的IDM会链下通知患者生成重加密密钥[K]p-r. 然后云端执行代理重加密任务, 并将重新加密的解密密钥${[smk]_{p{k_r}}}$发给请求者 collusion() 在请求者调用 request_smk_pk() 函数后, 如果合约检测到请求者存在违规行为, 则合约会计算审计节点共谋的概率$\eta $, 如果$\eta $超过阈值说明审计节点参与共谋, 这时触发 collusion() 事件, 监听该事件的 IDM 会给与共谋节点相应的惩罚 智能合约函数 功能描述 node_register() 用于登记通过身份验证的用户, 仅 IDM 可以调用, 该函数将用户的以太坊地址与成员公钥 pk 的关系记录在变
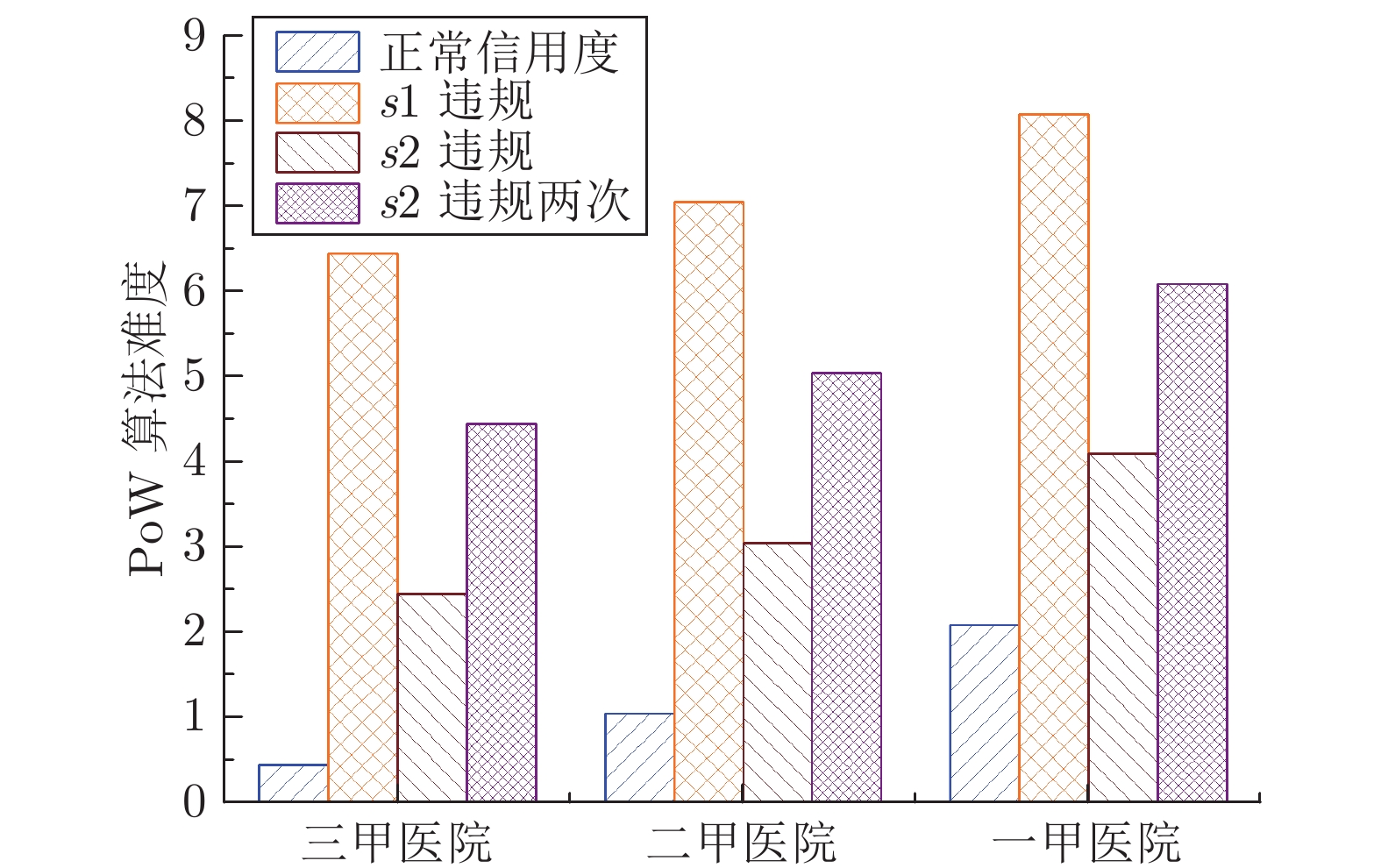
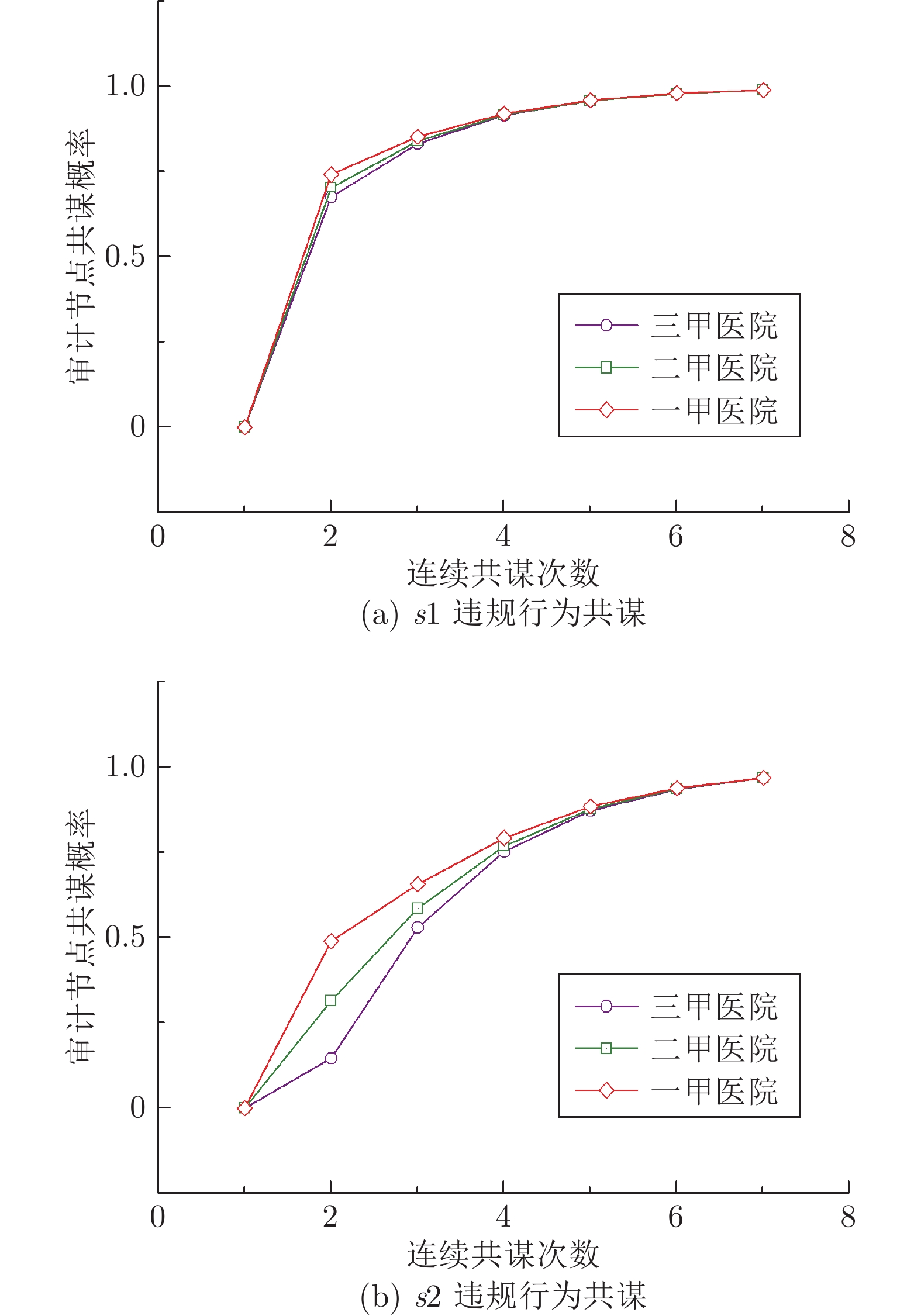
量 address_pk 中contribute_EHR() 用于患者共享 EHR, 该函数会将 EHR 的 url、hash 值等重要信息记录到变量 EHR_share 中 set_strategy() 患者设置访问控制策略的接口, 患者的访问控制策略参数会存储到变量 strategy 中 add_whitelist() 患者设置白名单的接口, 可以为指定的 EHR 设置白名单, 白名单的成员信息被记录在变量 url_whitelist 中 set_url_pk() 将 EHR 的 url 与患者成员公钥 pkp 的关系记录在变量 url_pk 中 contribute_resarch() 机构共享研究报告的接口函数, 研究报告的相关信息被记录在变量 con_research 中 agree_research() 审计节点对机构共享修改的EHR投票的接口, 投票结果记录在变量 con_research 中 correct_new_url() 患者将机构更正后的 EHR 重新上传云端后, 通过调用该函数接口可以将更正后的 url 记录到原先错误 EHR 的记录中, 方便请求者知晓原先的 EHR 存在误诊 verify_pk() 通过变量 address_pk 验证用户是否通过 IDM 的身份认证 verify_url() 通过变量 url_pk 验证 url 的拥有者 request_EHR() 机构请求 EHR 的接口, 申请请求 EHR 的权限(即触发事件 pow(), 随机选举一个审计节点对请求者发起 PoW 挑战) verify_request() 验证请求者是否获取请求该 EHR 的权限(即第2.3.2节中是否解决了 PoW 难题和获得审计节点的签名 sigA) request_smk_pk () 完成 PoW 挑战获得审计节点的签名 sigA 后请求者调用该函数, 验证签名后, 触发事件 store_smk_pk() max_min_credit_attribute() 用于更新所有机构中信用度属性最大值和最小值的函数, 方便计算机构信用度时数据的归一化处理 punish_s1() 惩罚 s1 违规行为函数, 违规行为会被记录到信用度属性 pk_credit 中 punish_s2() 惩罚 s2 违规行为函数, 违规行为会被记录到信用度属性 pk_credit 中 caculate_credit() 计算机构信用度的函数 表 2 EHR-SCAC与其他模型功能特性的对比
Table 2 Comparison of the functional characteristics of EHR-SCAC and other models
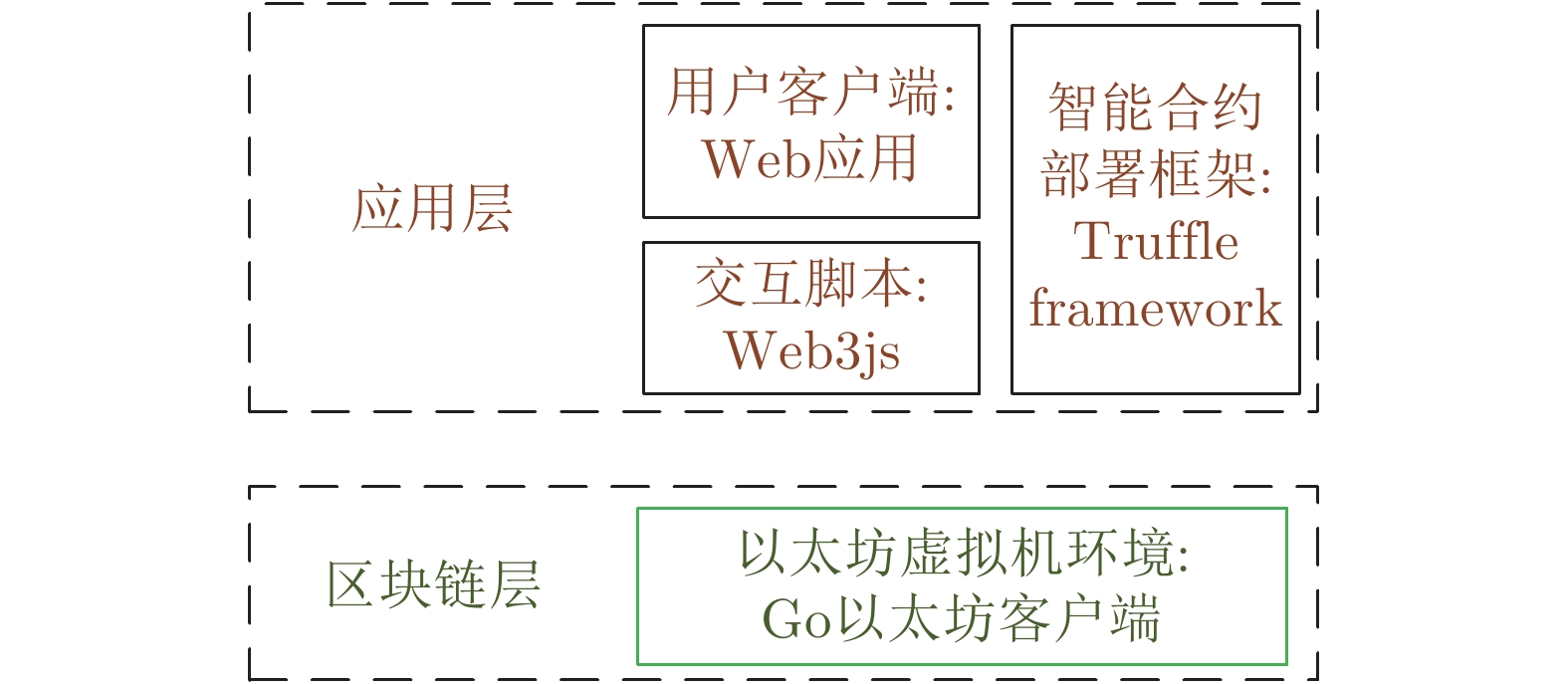
表 3 不同出块时间区块吞吐量和交易处理速度
Table 3 Block throughput and transaction processing speed at different block generation times
出块时
间 (s)平均每个区
块交易数交易吞吐量
(个数/s)交易处理
速度 (ms)1 110.5 110.5 9.04 2 222.5 111.25 8.98 3 332 110.6 9.03 4 439 109.75 9.11 5 551 110.2 9.07 6 658 109.6 9.11 7 764 109.1 9.16 8 875 109.3 9.14 9 986 109.5 9.12 10 1096 109.6 9.12 -
[1] Cao S, Zhang G X, Liu P F, Zhang X S, Neri F. Cloud-assisted secure eHealth systems for tamper-proofing EHR via blockchain. Information Sciences, 2019, 485: 427−440 [2] Eman A K, Nader M, Jameela A J. E-health cloud: Opportunities and challenges. Future Internet, 2012, 4(4): 621−645 [3] Meingast M, Roosta T, Sastry S. Security and privacy issues with health care information technology. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. New York, USA: IEEE, 2006. 5453−5458 [4] Esposito C, Santis A D, Tortora G, Chang H, Choo K K R. Blockchain: A panacea for healthcare cloud-based data security and privacy? IEEE Cloud Computing, 2018, 5(1): 31−37 [5] Liu X H, Liu Q, Peng T, Wu J. Dynamic access policy in cloud-based personal health record (PHR) systems. Information Sciences, 2017, 379: 62−81 [6] Liu X J, Xia Y J, Yang W, Yang F L. Secure and efficient querying over personal health records in cloud computing. Neurocomputing, 2018, 274: 99−105 [7] Au M H, Yuen T H, Liu J K, Susilo W, Huang X Y, Xiang Y, Jiang Z L. A general framework for secure sharing of personal health records in cloud system. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 2017, 90: 46−62 [8] Singh A, Chandra U, Kumar S, Chatterjee K. A secure access control model for e-health cloud. In: Proceedings of TENCON 2019−2019 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON). Kochi, India: IEEE, 2019. 2329−2334 [9] 袁勇, 王飞跃. 区块链技术发展现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(4): 481−494Yuan Yong, Wang Fei-Yue. Blockchain: the state of the art and future trends. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4): 481−494 [10] Azaria A, Ekblaw A, Vieira T, Lippman A. MedRec: Using blockchain for medical data access and permission management. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Open and Big Data (OBD). Vienna, Austria: IEEE, 2016. 25−30 [11] 薛腾飞, 傅群超, 王枞, 王新宴. 基于区块链的医疗数据共享模型研究. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(9): 1555−1562Xue Teng-Fei, Fu Qun-Chao, Wang Cong, Wang Xin-Yan. A medical data sharing model via blockchain. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(9): 1555−1562 [12] Dagher G G, Mohler J, Milojkovic M, Marella P B. Ancile: Privacy-preserving framework for access control and interoperability of electronic health records using blockchain technology. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2018, 39: 283−297 [13] Daraghmi E Y, Daraghmi Y, Yuan S. MedChain: A design of blockchain-based system for medical records access and permissions management. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 164595−164613 [14] 张超, 李强, 陈子豪, 黎祖睿, 张震. Medical Chain: 联盟式医疗区块链系统. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1495−1510Zhang Chao, Li Qiang, Chen Zi-Hao, Li Zu-Rui, Zhang Zhen. Medical chain: Alliance medical blockchain system. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1495−1510 [15] Xia Q, Sifah E B, Smahi A, Amofa S, Zhang X. BBDS: Blockchain-based data sharing for electronic medical records in cloud environments. Information, 2017, 8(2): 44−59 [16] Tang F, Ma S, Xiang Y, Lin C L. An efficient authentication scheme for blockchain-based electronic health records. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 41678−41689 [17] Liu J W, Li X L, Ye L, Zhang H L, Mohsen G. BPDS: A blockchain based privacy-preserving data sharing for electronic medical records. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM). Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates: IEEE, 2018. 1−6 [18] Ethereum Whitepaper [Online], available: https://ethereum.org/en/whitepaper/, April 5, 2020 [19] Ripple interLedger protocol [Online], available: https://interledger.org/overview.html, April 5, 2020 [20] 张凯, 潘晓中. 云计算下基于用户行为信任的访问控制模型. 计算机应用, 2014, 34(4): 1051−1054Zhang Kai, Pan Xiao Zhong. Access control model based on user behavior trust in cloud computing. Journal of Computer Applications, 2014, 34(4): 1051−1054 [21] 王海勇, 潘启青, 郭凯璇. 基于区块链和用户信用度的访问控制模型. 计算机应用, 2020, 40(6): 1674−1679Wang Hai-Yong, Pan Qi-Qing, Guo Kai-Xuan. Access control model based on blockchain and user credit. Journal of Computer Applications, 2020, 40(6): 1674−1679 [22] Huang J Q, Kong L H, Chen G H, Wu M Y, Liu X, Zeng P. Towards secure industrial iot: blockchain system with credit-based consensus mechanism. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(6): 3680−3689 [23] Web3.js−Ethereum JavaScript API [Online], available: https://github.com/ethereum/web3.js/, April 5, 2020 [24] Go Ethereum [Online], available: https://geth.ethereum.org/downloads/, April 5, 2020 [25] Proof-of-authority [Online], available: https://www.poa.network/, April 5, 2020 [26] Solidity document [Online], available: https://soliditycn.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/, April 5, 2020 -




 下载:
下载: