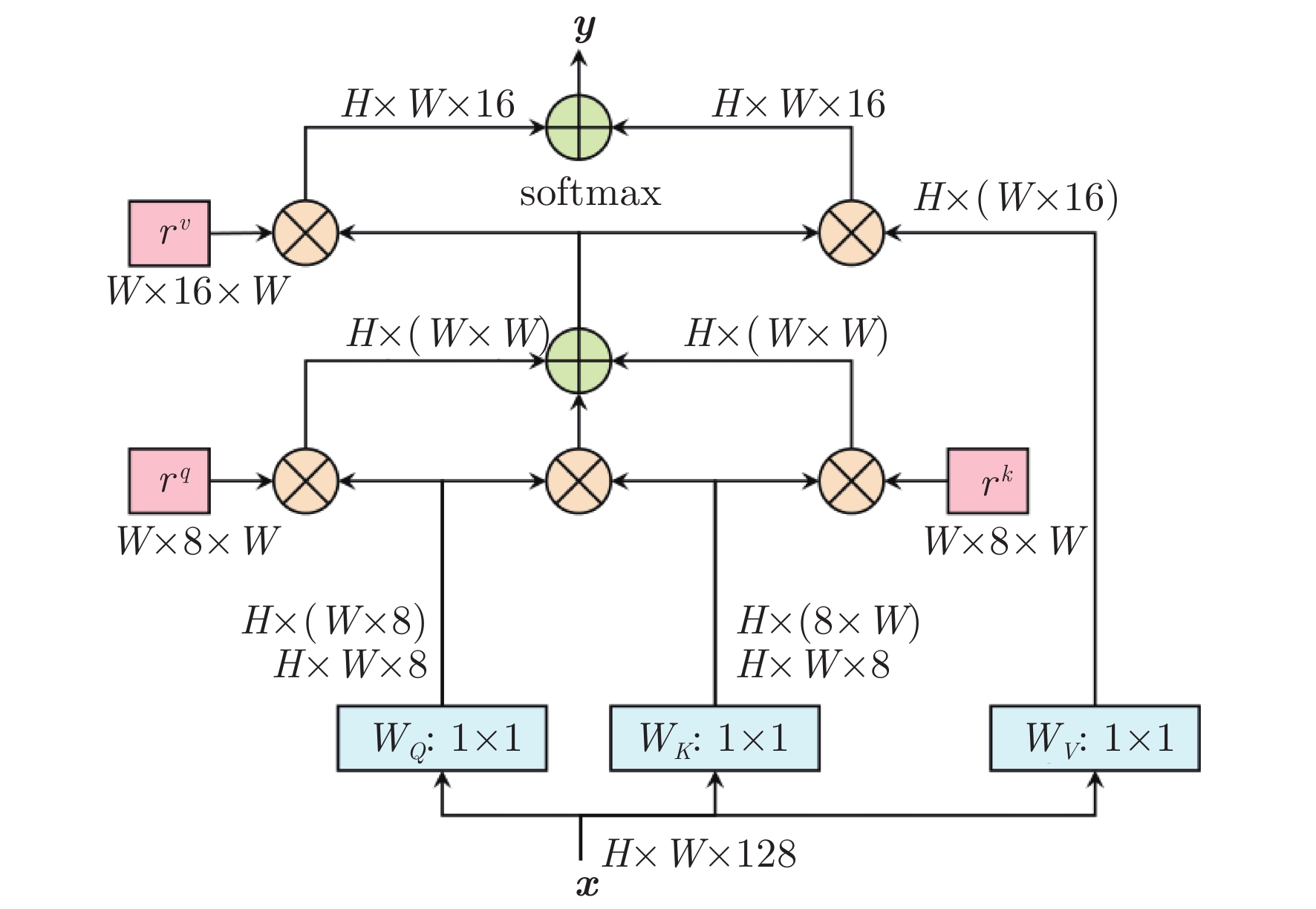
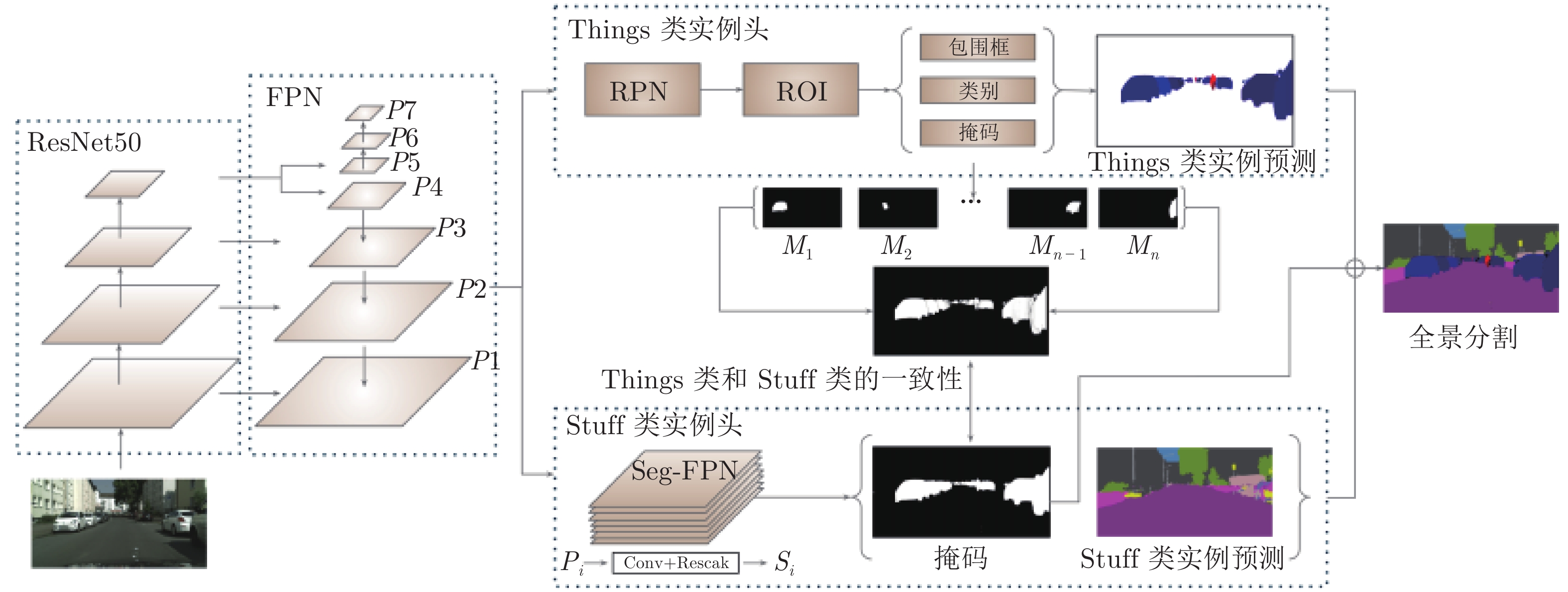
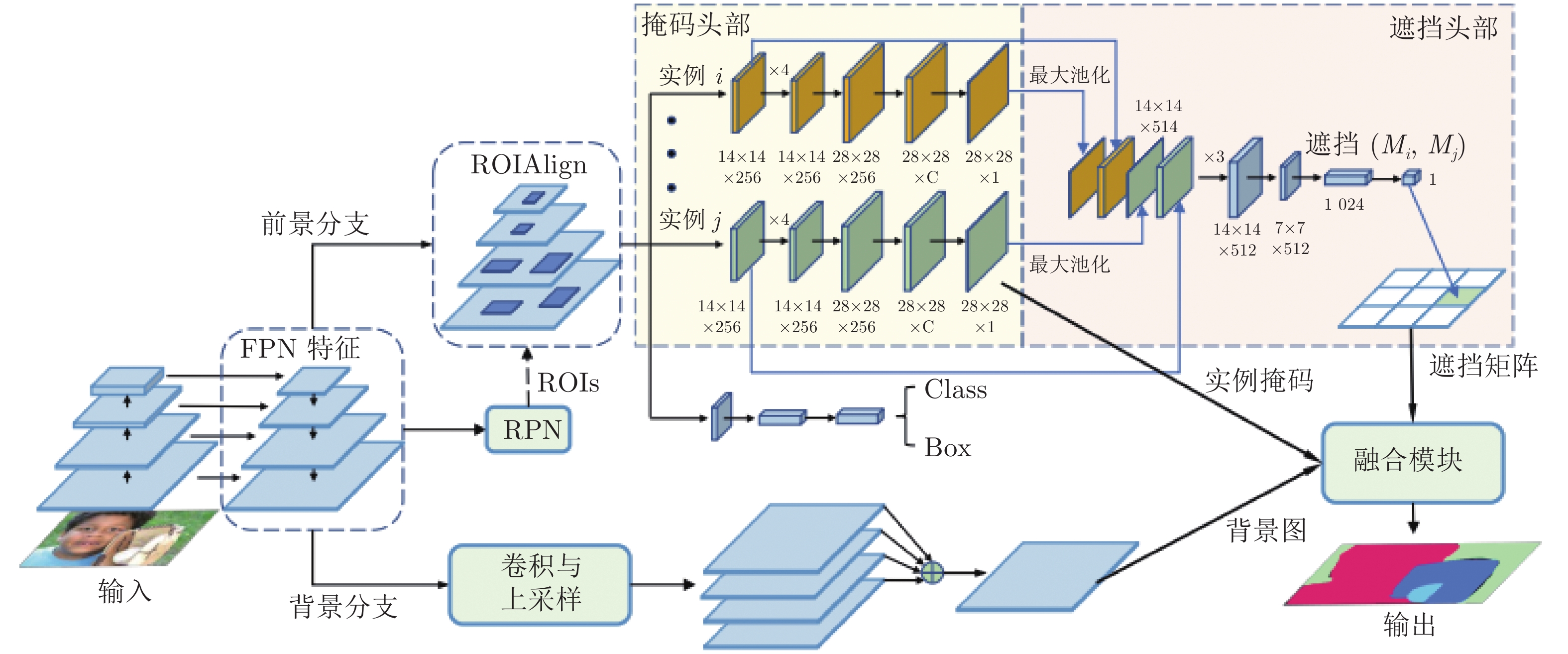
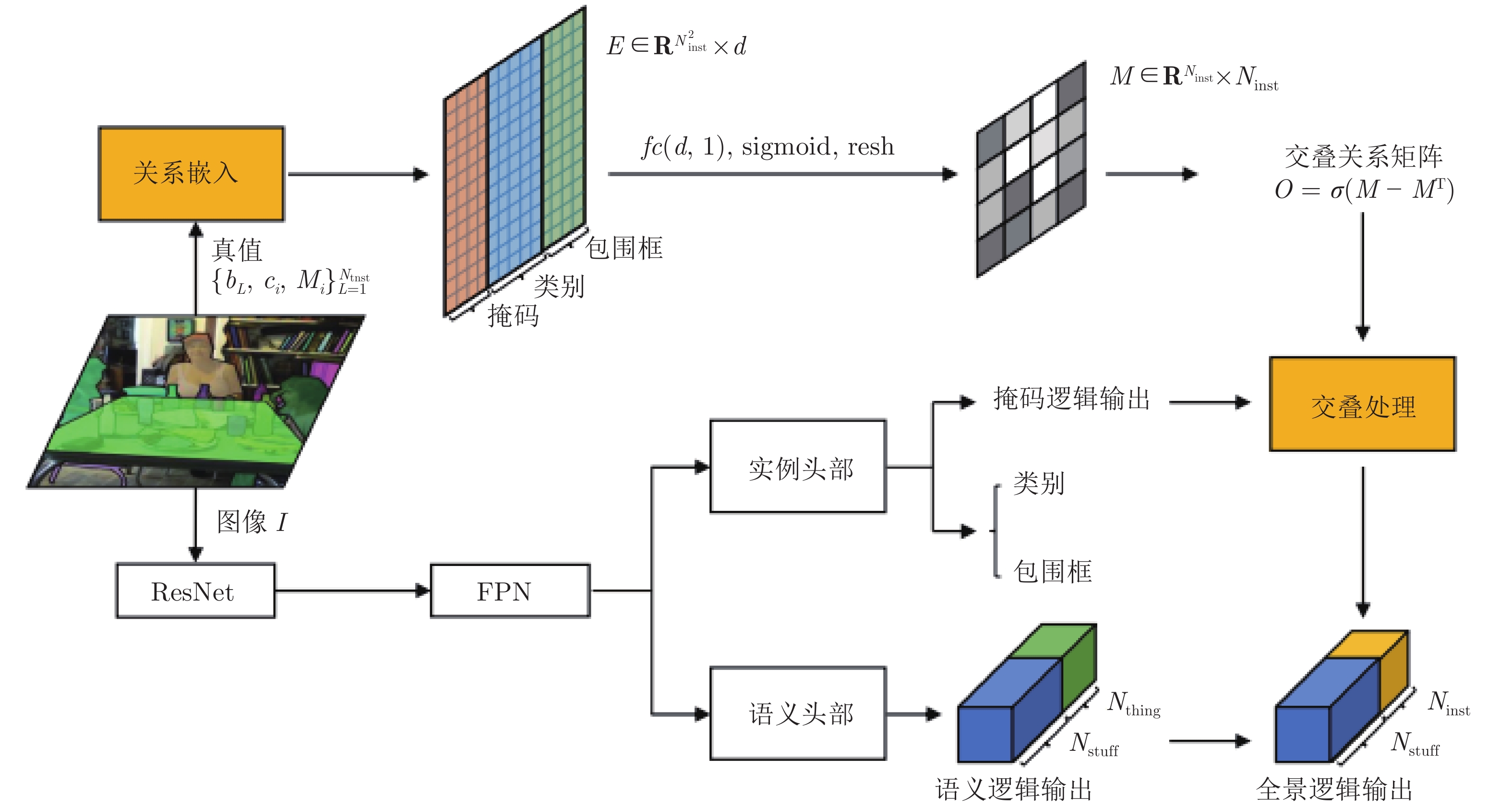
-
摘要:
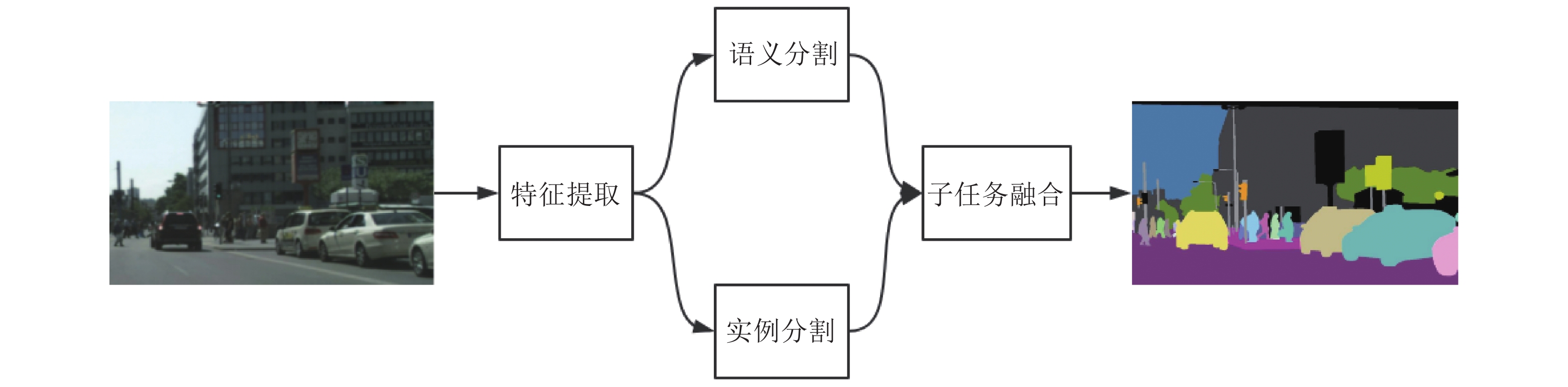
在计算机视觉领域, 全景分割是一个新颖且重要的研究主题, 它是机器感知、自动驾驶等新兴前沿技术的基石, 具有十分重要的研究意义. 本文综述了基于深度学习的全景分割研究的最新进展, 首先总结了全景分割任务的基本处理流程, 然后对已发表的全景分割工作基于其网络结构特点进行分类, 并进行了全面的介绍与分析, 最后对全景分割任务目前面临的问题以及未来的发展趋势做出了分析, 并针对所面临的问题提出了一些切实可行的解决思路.
Abstract:In the field of computer vision, panoptic segmentation is a novel and important research topic. It is the cornerstone of emerging leading-edge technologies such as machine perception and autonomous driving, and has very important significance of research. This paper reviews the research progress of panoptic segmentation based on deep learning methods, summarizes the basic processing flow of panoptic segmentation, and then classifies the already published panoptic segmentation works based on the characteristics of its network structure, and makes a more comprehensive introduction and analysis. Finally, the current problems and future development trends of the panoptic segmentation task are analyzed, and some potential solutions are provided for solving the existing problems.
-
Key words:
- Panoptic segmentation /
- semantic segmentation /
- instance segmentation /
- deep learning
-
表 1 现有单阶段方法性能比较
Table 1 Performance comparison of existing single-stage methods
模型 数据集 PQ mIoU AP mAP Inference time BlitzNet[50] PASCAL VOC — — — 83.8 24 帧/s DeeperLab[52] Mapillary Vistas validation set 31.95 — — — — Generator evaluator-selector net[53] MS COCO 33.7 — — — — FPSNet[22] CityScapes validation set 55.1 — — — 114 ms SpatialFlow[55] MS COCO 2017 test-dev split 47.3 — — 36.7 — Single-shot panoptic segmentation[28] MS COCO val2017 32.4 27.9 33.1 — 21.8 帧/s Panoptic-DeepLab[57] MS COCO val set 39.7 — — — 132 ms Real-time panoptic segmentation
from dense detections[56]MS COCO val set 37.1 — — — 63 ms BBFNet[58] MS COCO-2017 dataset 37.1 — — — — Axial-DeepLab[64] Cityscapes test set 62.8 79.9 34.0 — — EPSNet[62] MS COCO val set 38.6 — — — 53 ms PCV[63] Cityscapes val set 54.2 74.1 — — 182.8 ms 表 2 现有两阶段方法性能对比
Table 2 Performance comparison of existing two-stage methods
模型 数据集 PQ mIoU AP mAP Inference time (ms) Weakly- and semi-supervised
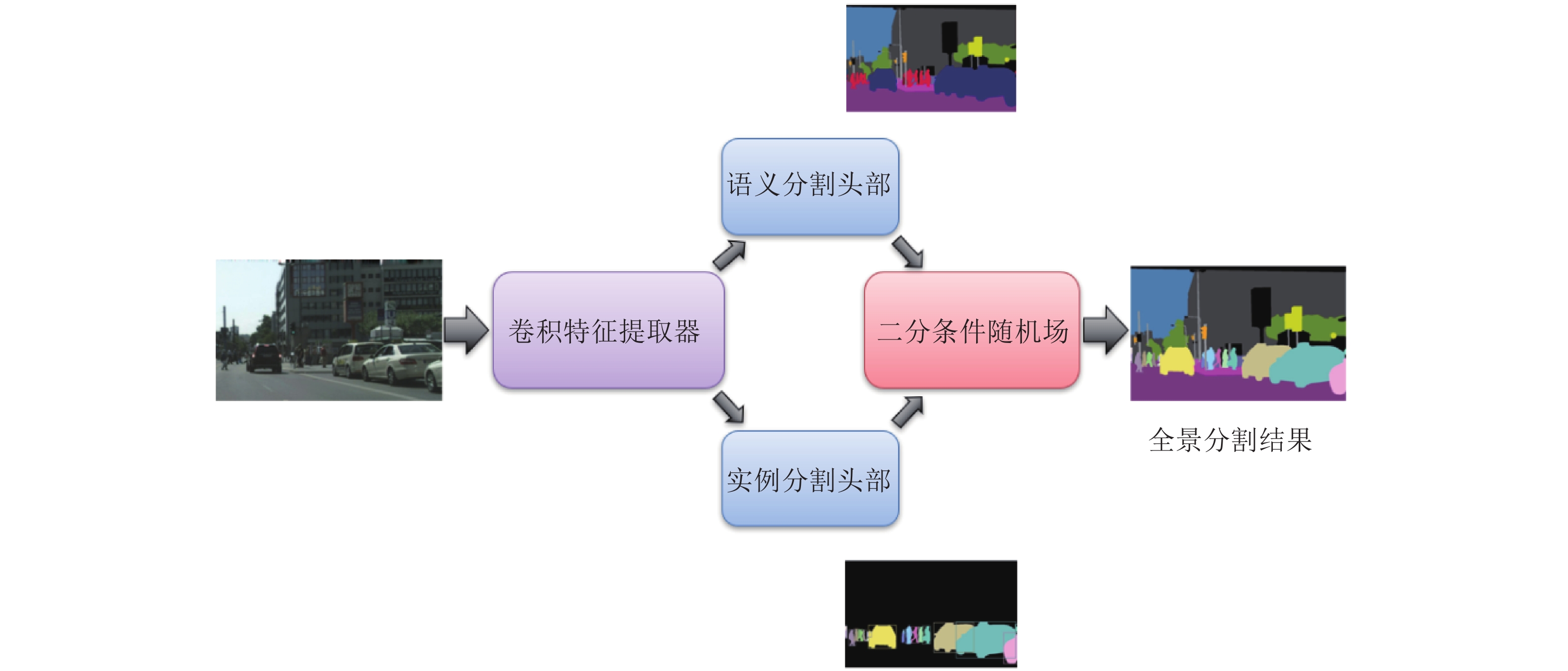
panoptic segmentation[16]VOC 2012 validation set 63.1 — 59.5 — — JSIS-Net[9] MS COCO test-dev 27.2 — — — — TASCNet[10] Cityscapes 60.4 78.7 39.09 — — AUNet[11] Cityscapes val set 59.0 75.6 34.4 — — Panoptic feature pyramid networks[26] MS COCO test-dev 40.9 — — — — UPSNet[27] MS COCO 42.5 54.3 34.3 — 17 Single network panoptic segmentation for
street scene understanding[12]Mapillary Vistas 23.9 — — — 484 OANet[13] MS COCO 2018 panoptic segmentation
challenge test-dev41.3 — — — — OCFusion[68] MS COCO test-dev dataset 46.7 — — — — SOGNet[29] MS COCO 43.7 — — — — PanDA[69] MS COCO subsets 37.4 45.9 28.0 — — BCRF[17] Pascal VOC dataset 71.76 — — — — Unifying training and inference for
panoptic segmentation[70]MS COCO test-dev set 47.2 — — — — BANet[77] MS COCO val set 41.1 — — — — EfficientPS[76] Cityscapes validation set 63.6 79.3 37.4 — 166 -
[1] Kirillov A, He K M, Girshick R, Rother C, Dollar P. Panoptic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019. 9396−9405 [2] 胡涛, 李卫华, 秦先祥. 图像语义分割方法综述. 测控技术, 2019, 38(7): 8−12Hu Tao, Li Wei-Hua, Qin Xian-Xiang. A review on image semantic segmentation. Measurement and Control Technology, 2019, 38(7): 8−12 [3] Yang Y, Hallman S, Ramanan D, Fowlkes C C. Layered object models for image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(9): 1731−1743 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.208 [4] Ladicky L, Russell C, Kohli P, Torr P H S. Associative hierarchical CRFs for object class image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Kyoto, Japan: IEEE, 2009. 739−746 [5] Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640−651 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 [6] Hariharan B, Arbelaez P, Girshick R, Malik J. Simultaneous detection and segmentation. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 297−312 [7] Pinheiro P O, Collobert R, Dollar P. Learning to segment object candidates. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA, USA: MIT Press, 2015. 1990−1998 [8] Zagoruyko S, Lerer A, Lin T Y, Pinheiro P O, Gross S, Chintala S, et al. A MultiPath network for object detection. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1604.02135, April 4, 2016 [9] De Geus D, Meletis P, Dubbelman G. Panoptic segmentation with a joint semantic and instance segmentation network. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.02110, September 6, 2018 [10] Li J, Raventos A, Bhargava A, Tagawa T, Gaidon A. Learning to fuse things and stuff. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.01192, December 4, 2018 [11] Li Y W, Chen X Z, Zhu Z, Xie L X, Huang G, Du D L, et al. Attention-guided unified network for panoptic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019. 7019−7028 [12] De Geus D, Meletis P, Dubbelman G. Single network panoptic segmentation for street scene understanding. In: Proceedings of IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV). Paris, France: IEEE, 2019. 709−715 [13] Liu H Y, Peng C, Yu C Q, Wang J B, Liu X, Yu G, et al. An end-to-end network for panoptic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019. 6165−6174 [14] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556, September 4, 2014 [15] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [16] Li Q Z, Arnab A, Torr P H S. Weakly- and semi-supervised panoptic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 106−124 [17] Jayasumana S, Ranasinghe K, Jayawardhana M, Liyanaarachchi S, Ranasinghe H. Bipartite conditional random fields for panoptic segmentation. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.05307, December 11, 2019 [18] Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger K Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2261−2269 [19] Howard A G, Zhu M L, Chen B, Kalenichenko D, Wang W J, Weyand T, et al. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861, April 17, 2017 [20] Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M L, Zhmoginov A, Chen L C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4510−4520 [21] Howard A, Sandler M, Chen B, Wang W J, Chen L C, Tang M X, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea (South): IEEE, 2019. 1314−1324 [22] De Geus D, Meletis P, Dubbelman G. Fast panoptic segmentation network. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 1742−1749 [23] 肖晓伟, 肖迪, 林锦国, 肖玉峰. 多目标优化问题的研究概述. 计算机应用研究, 2011, 28(3): 805−808Xiao Xiao-Wei, Xiao Di, Lin Jin-Guo, Xiao Yu-Feng. Overview on multi-objective optimization problem research. Application Research of Computers, 2011, 28(3): 805−808 [24] 葛继科, 邱玉辉, 吴春明, 蒲国林. 遗传算法研究综述. 计算机应用研究, 2008, 25(10): 2911−2916Ge Ji-Ke, Qiu Yu-Hui, Wu Chun-Ming, Pu Guo-Lin. Summary of genetic algorithms research. Application Research of Computers, 2008, 25(10): 2911−2916 [25] 巫影, 陈定方, 唐小兵, 朱石坚, 黄映云, 李庆. 神经网络综述. 科技进步与对策, 2002, 19(6): 133−134Wu Ying, Chen Ding-Fang, Tang Xiao-Bing, Zhu Shi-Jian, Huang Ying-Yun, Li Qing. Summarizing of neural network. Science & Technology Progress and Policy, 2002, 19(6): 133−134 [26] Kirillov A, Girshick R, He K M, Dollar P. Panoptic feature pyramid networks. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019. 6392−6401 [27] Xiong Y W, Liao R J, Zhao H S, Hu R, Bai M, Yumer E, et al. UPSNet: A unified panoptic segmentation network. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision andPattern Recognition. Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019. 8810−8818 [28] Weber M, Luiten J, Leibe B. Single-shot panoptic segmentation. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.00764, November 2, 2019 [29] Yang Y B, Li H Y, Li X, Zhao Q J, Wu J L, Lin Z C. SOGNet: Scene overlap graph network for panoptic segmentation, Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(7): 12637−12644 [30] Fukushima K. Neocognitron: A self organizing neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position. Biological Cybernetics, 1980, 36(4): 193−202 doi: 10.1007/BF00344251 [31] LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278−2324 doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [32] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84−90 doi: 10.1145/3065386 [33] Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, et al. Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, MA, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1−9 [34] Chen L C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille A L. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected CRFs. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.7062, December 22, 2014 [35] Chen L C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille A L. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834−848 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [36] Chen L C, Hermans A, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Wang P, Adam H. MaskLab: Instance segmentation by refining object detection with semantic and direction features. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4013−4022 [37] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T, et al. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2015. 234−241 [38] Zhao H S, Shi J P, Qi X J, Wang X G, Jia J Y. Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 6230−6239 [39] He K M, Gkioxari G, Dollar P, Girshick R. Mask R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2980−2988 [40] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 39(6): 1137−1149 [41] Liu S, Qi L, Qin H F, Shi J P, Jia J Y. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018. 8759−8768 [42] Zhang H, Tian Y L, Wang K F, Zhang W S, Wang F Y. Mask SSD: An effective single-stage approach to object instance segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 2078−2093 [43] Everingham M, Eslami S M, Van Gool L, Williams C K I, Winn J, Zisserman A. The PASCAL visual object classes challenge: A retrospective. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 111(1): 98−136 doi: 10.1007/s11263-014-0733-5 [44] Lin T T, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 740−755 [45] Cordts M, Omran M, Ramos S, Rehfeld T, Enzweiler M, Benenson R, et al. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3213−3223 [46] Zhou B L, Zhao H, Puig X, Fidler S, Barriuso A, Torralba A. Scene parsing through ADE20K dataset. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 5122−5130 [47] Neuhold G, Ollmann T, Bulo S R, Kontschieder P. The Mapillary vistas dataset for semantic understanding of street scenes. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 5000−5009 [48] Garcia-Garcia A, Orts-Escolano S, Oprea S, Villena-Martinez V, Garcia-Rodriguez J. A review on deep learning techniques applied to semantic segmentation. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.06857, April 22, 2017 [49] Lateef F, Ruichek Y. Survey on semantic segmentation using deep learning techniques. Neurocomputing, 2019, 338: 321−348 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.02.003 [50] Dvornik N, Shmelkov K, Mairal J, Schmid C. BlitzNet: A real-time deep network for scene understanding. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4174−4182 [51] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C Y, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 21−37 [52] Yang T J, Collins M D, Zhu Y K, Hwang J J, Liu T, Zhang X, et al. DeeperLab: Single-shot image parser. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.05093, February 13, 2019 [53] Eppel S, Aspuru-Guzik A. Generator evaluator-selector net: A modular approach for panoptic segmentation. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.09108, August 24, 2019 [54] Eppel S. Class-independent sequential full image segmentation, using a convolutional net that finds a segment within an attention region, given a pointer pixel within this segment. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.07810, February 20, 2019 [55] Chen Q, Cheng A D, He X Y, Wang P S, Cheng J. SpatialFlow: Bridging all tasks for panoptic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020. [56] Hou R, Li J, Bhargava A, Raventos A, Guizilini V, Fang C, et al. Real-time panoptic segmentation from dense detections. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2020. 8520−8529 [57] Cheng B W, Collins M D, Zhu Y K, Liu T, Huang T S, Adam H, et al. Panoptic-DeepLab. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.04751, October 24, 2019 [58] Bonde U, Alcantarilla P F, Leutenegger S. Towards bounding-box free panoptic segmentation. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.07705, February 18, 2020 [59] Dai J F, Qi H Z, Xiong Y W, Li Y, Zhang G D, Hu H, et al. Deformable convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 764−773 [60] Ballard D H. Generalizing the Hough transform to detect arbitrary shapes. Pattern Recognition, 1981, 13(2): 111−122 doi: 10.1016/0031-3203(81)90009-1 [61] Bai M, Urtasun R. Deep watershed transform for instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2858−2866 [62] Chang C Y, Chang S E, Hsiao P Y, Fu L C. EPSNet: Efficient panoptic segmentation network with cross-layer attention fusion. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10142, March 23, 2020 [63] Wang H C, Luo R T, Maire M, Shakhnarovich G. Pixel consensus voting for panoptic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2020. 9461−9470 [64] Wang H Y, Zhu Y K, Green B, Adam H, Yuille A, Chen L C. Axial-DeepLab: Stand-alone axial-attention for panoptic segmentation. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.07853, March 17, 2020 [65] Arnab A, Torr P H S. Pixelwise instance segmentation with a dynamically instantiated network. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 879−888 [66] Rother C, Kolmogorov V, Blake A. “GrabCut”: Interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2004, 23(3): 309−314 doi: 10.1145/1015706.1015720 [67] Arbelaez P, Pont-Tuset J, Barron J, Marques F, Malik J. Multiscale combinatorial grouping. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, OH, USA: IEEE, 2014. 328−335 [68] Lazarow J, Lee K, Shi K Y, Tu Z W. Learning instance occlusion for panoptic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2020. 10717−10726 [69] Liu Y, Perona P, Meister M. PanDA: Panoptic data augmentation. Liu Y, Perona P, Meister M. PanDA: Panoptic data augmentation. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.12317, November 27, 2019 [70] Li Q Z, Qi X J, Torr P H S. Unifying training and inference for panoptic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2020. 13317−13325 [71] Behley J, Milioto A, Stachniss C. A benchmark for LiDAR-based panoptic segmentation based on KITTI. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.02371, March 4, 2020 [72] Behley J, Garbade M, Milioto A, Quenzel J, Behnke S, Stachniss C, et al. SemanticKITTI: A dataset for semantic scene understanding of LiDAR sequences. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea (South): IEEE, 2019. 9296−9306 [73] Thomas H, Qi C R, Deschaud J E, Marcotegui B, Goulette F, Guibas L. KPConv: Flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea (South): IEEE, 2019. 6410−6419 [74] Milioto A, Vizzo I, Behley J, Stachniss C. RangeNet++: Fast and accurate LiDAR semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Macau, China: IEEE, 2019. 4213−4220 [75] Lang A H, Vora S, Caesar H, Zhou L B, Yang J, Beijbom O. PointPillars: Fast encoders for object detection from point clouds. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019. 12689−12697 [76] Mohan R, Valada A. EfficientPS: Efficient panoptic segmentation. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02307, April 5, 2020 [77] Chen Y F, Lin G C, Li S Y, Bourahla O, Wu Y M, Wang F F, et al. BANet: Bidirectional aggregation network with occlusion handling for panoptic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2020. 3792−3801 [78] Hurtado J V, Mohan R, Burgard W, Valada A. MOPT: Multi-object panoptic tracking. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.08189, April 17, 2020 [79] 张慧, 王坤峰, 王飞跃. 深度学习在目标视觉检测中的应用进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(8): 1289−1305Zhang Hui, Wang Kun-Feng, Wang Fei-Yue. Advances and perspectives on applications of deep learning in visual object detection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1289−1305 [80] Meletis P, Wen X X, Lu C Y, de Geus D, Dubbelman G. Cityscapes-panoptic-parts and PASCAL-panoptic-parts datasets for scene understanding. [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.07944, April 16, 2020 -




 下载:
下载: