Sparse-to-dense Large Displacement Motion Optical Flow Estimation Based on Deep Matching
-
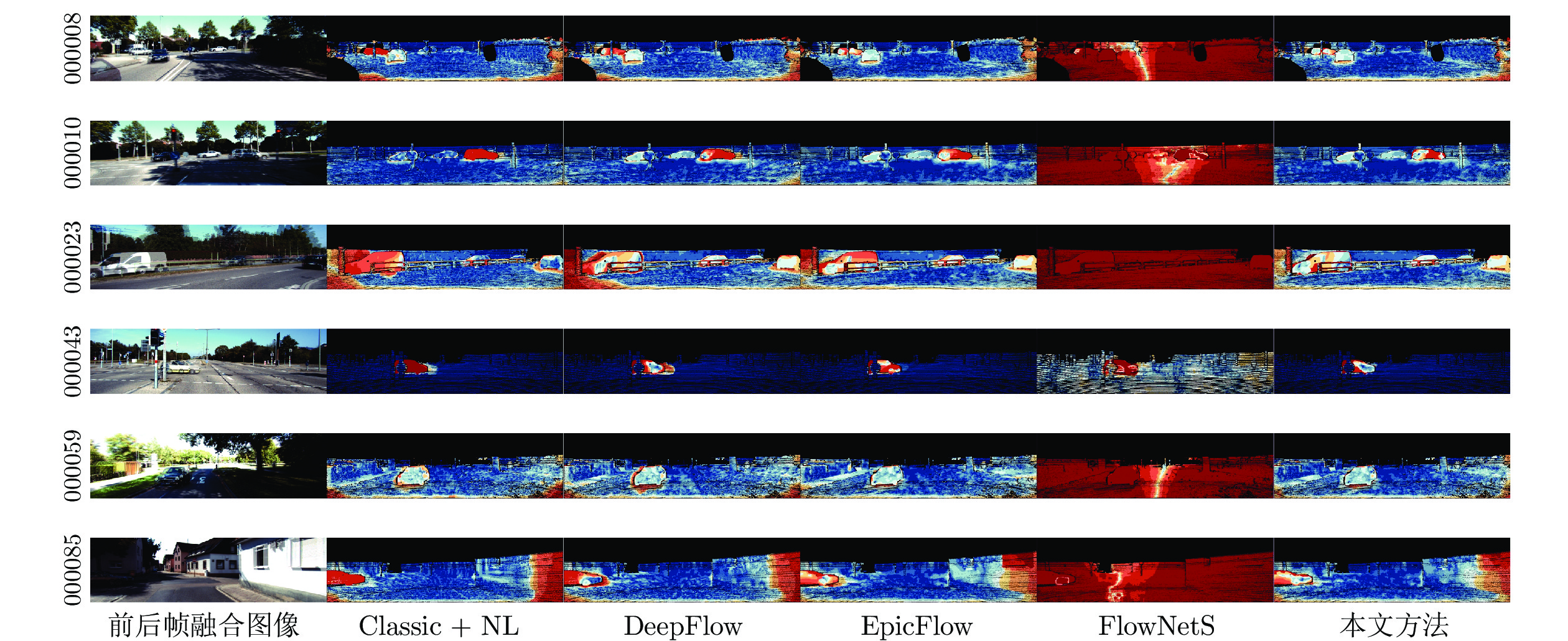
摘要: 针对非刚性大位移运动场景的光流计算准确性与鲁棒性问题, 提出一种基于深度匹配的由稀疏到稠密大位移运动光流估计方法. 首先利用深度匹配模型计算图像序列相邻帧的初始稀疏运动场; 其次采用网格化邻域支持优化模型筛选具有较高置信度的图像网格和匹配像素点, 获得鲁棒的稀疏运动场; 然后对稀疏运动场进行边缘保护稠密插值, 并设计全局能量泛函优化求解稠密光流场. 最后分别利用MPI-Sintel和KITTI数据库提供的测试图像集对本文方法和Classic + NL, DeepFlow, EpicFlow以及FlowNetS等变分模型、匹配策略和深度学习光流计算方法进行综合对比与分析, 实验结果表明本文方法相对于其他方法具有更高的光流计算精度, 尤其在非刚性大位移和运动遮挡区域具有更好的鲁棒性与可靠性.Abstract: In order to improve the accuracy and robustness of optical flow estimation under the non-rigid large displacement motion, we propose a sparse-to-dense large displacement motion optical flow estimation method based on deep matching. First, we utilize the deep matching model to compute an initial sparse motion field from the consecutive two frames of the image sequence. Second, we adopt the gridded neighborhood support optimization scheme to extract the image grids and matching pixels which have the high confidence, and acquire the robust sparse motion field. Third, we interpolate the sparse motion field to obtain the dense motion field and plan a global energy function to estimate the optimized dense optical flow. Finally, we respectively employ the MPI-Sintel and KITTI datasets to compare the performance of the proposed method with several variational, region matching and deep-learning based optical flow approaches including Classic + NL, DeepFlow, EpicFlow and FlowNetS models. The experimental results indicate that the proposed method has the higher computational accuracy compared with those of the other state-of-the-art approaches, especially owns the better robustness and reliability in the areas of non-rigid large displacements and motion occlusions.
-
Key words:
- Dense optical flow /
- deep matching /
- neighborhood support /
- image grid /
- global optimization
-
表 1 MPI-Sintel数据库光流估计误差对比
Table 1 Comparison results of optical flow errors on MPI-Sintel database
表 2 非刚性大位移与运动遮挡图像序列光流估计误差对比
Table 2 Comparison results of optical flow errors on the image sequences including non-rigidly large displacements and motion occlusions
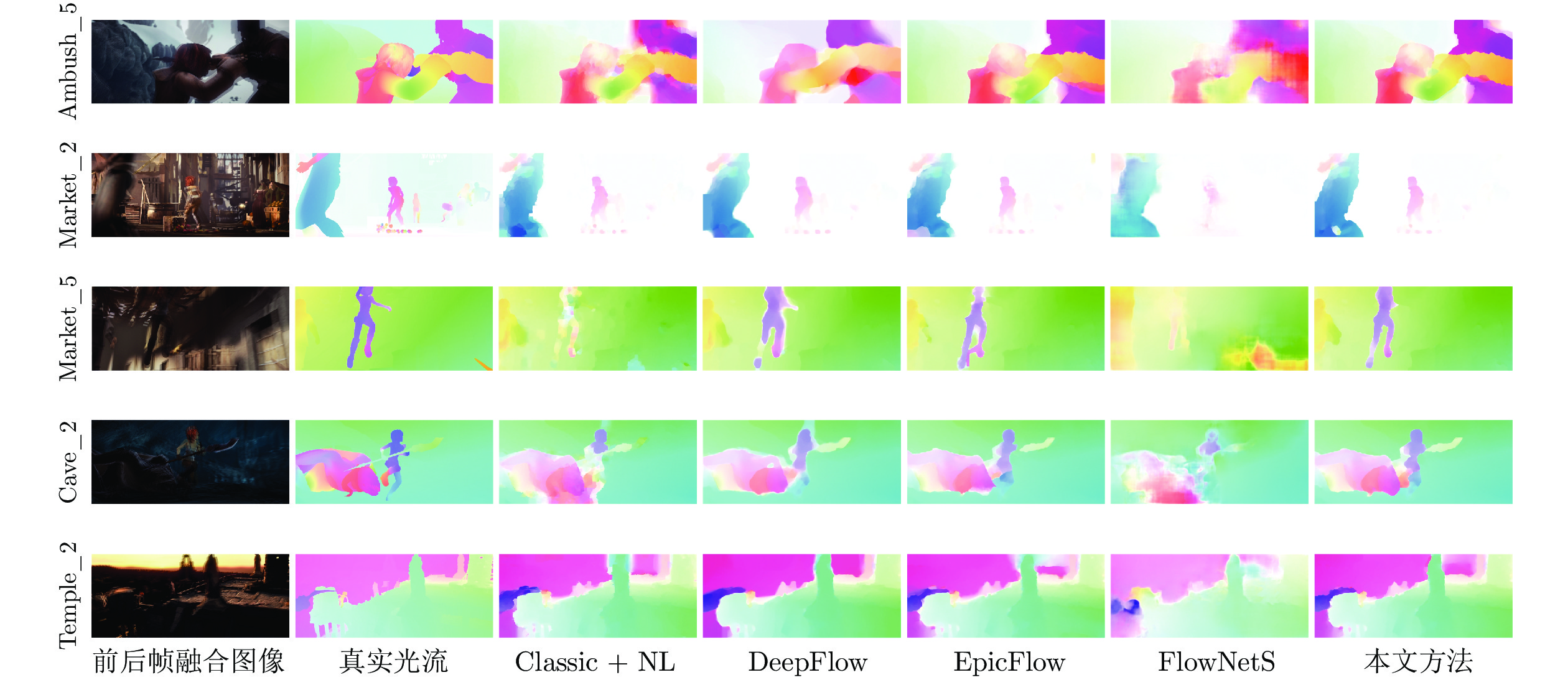
对比方法 平均误差 Ambush_5 Cave_2 Market_2 Market_5 Temple_2 AAE/AEE AAE/AEE AAE/AEE AAE/AEE AAE/AEE AAE/AEE Classic+NL[7] 14.71/9.28 22.53/11.06 15.78/14.03 7.64/0.98 18.93/16.59 8.39/3.72 DeepFlow[18] 10.89/6.66 18.86/8.75 9.23/9.30 8.00/0.85 12.19/11.89 6.15/2.50 EpicFlow[21] 10.64/6.47 19.19/8.48 7.45/7.81 7.91/0.89 12.15/12.47 6.48/2.72 FlowNetS[12] 15.63/9.77 25.37/12.43 17.24./15.66 8.56/1.26 16.56/15.24 10.45/4.24 本文方法 9.77/6.12 18.43/8.43 6.98/7.49 7.05/0.78 10.58/11.35 5.83/2.56 表 3 KITTI数据库光流估计误差对比
Table 3 Comparison results of optical flow errors on KITTI database
表 4 本文方法消融实验结果对比
Table 4 Comparison results of the ablation experiment
消融模型 Alley_2 Cave_4 Market_6 本文方法 0.07 1.16 3.72 无匹配优化 0.09 1.28 5.07 无稠密插值 0.14 1.31 5.85 无全局优化 0.09 1.21 3.84 -
[1] 潘超, 刘建国, 李峻林. 昆虫视觉启发的光流复合导航方法. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(6): 1102-1112.PAN Chao, LIU Jian-Guo, LI Jun-Lin. An optical flow-based composite navigation method inspired by insect vision. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(6): 1102-1112 (in Chinese). [2] Colque R, Caetano C, Andrade M, Schwartz W. Histograms of optical flow orientation and magnitude and entropy to detect anomalous events in Videos. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2017, 27(3): 673-682. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2016.2637778 [3] 王飞, 崔金强, 陈本美, 李崇兴. 一套完整的基于视觉光流和激光扫描测距的室内无人机导航系统. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(11): 1889-1900.WANG Fei, CUI Jin-Qiang, CHEN Ben-Mei, LEE Tong H. A comprehensive uav indoor navigation system based on vision optical flow and laser fastSLAM. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(11): 1889-1900 (in Chinese). [4] 张桂梅, 孙晓旭, 刘建新, 储珺. 基于分数阶微分的TV-L1光流模型的图像配准方法研究. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(12): 2213-2224.ZHANG Gui-Mei, SUN Xiao-Xu, LIU Jian-Xin, CHU Jun. Research on TV-L1 optical flow model for image registration based on fractional-order differentiation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(12): 2213-2224 (in Chinese). [5] Horn B K P, Schunck B G. Determining optical flow. Artificial Intelligence, 1980, 17(1): 185- 203. [6] Brox T, Bruhn A, Papenberg N, Weickert J. High accuracy optical flow estimation based on a theory for warping. In: Proceedings of the 2004 European Conference on Computer Vision. Prague, Czech Republic: Springer, 2004. 25−36 [7] Sun D, Roth S, Black M J. A quantitative analysis of current practices in optical flow estimation and the principles behind them. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2014, 106(2): 115-137. doi: 10.1007/s11263-013-0644-x [8] Drulea M, Nedevschi S. Total variation regularization of local-global optical flow. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Washington DC, USA: IEEE, 2011. 318−323 [9] Perona P, Malik J. Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 1990, 12(7): 629-639. doi: 10.1109/34.56205 [10] Weickert J, Schnörr C. A theoretical framework for convex regularizers in PDE-based computation of image motion. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2001, 45(3): 245- 264. doi: 10.1023/A:1013614317973 [11] Zimmer H, Bruhn A, Weickert J. Optic flow in harmony. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2011, 93(3): 368-388. doi: 10.1007/s11263-011-0422-6 [12] Dosovitskiy A, Fischer P, Ilg E, Häusser P, Hazirbas C, Golkov V, et al. Flownet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 2758−2766 [13] Ilg E, Mayer N, Saikia T, Keuper M, Dosovitskiy A, Brox T. FlowNet 2.0: Evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1647−1655 [14] Ranjan A, Black M J. Optical flow estimation using a spatial pyramid network. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4161−4170 [15] Hui T W, Tang X, Loy C. LiteFlowNet: A lightweight convolutional neural network for optical flow estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 8981−8989 [16] Ilg E, Saikia T, Keuper M, Brox T. Occlusions, motion and depth boundaries with a generic network for disparity, optical flow or scene flow estimation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 614−630 [17] Brox T, Malik J. Large displacement optical flow: descriptor matching in variational motion estimation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(3): 500-513. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.143 [18] Weinzaepfel P, Revaud J, Harchaoui Z, Schmid C. DeepFlow: Large displacement optical flow with deep matching. In: Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 1385−1392 [19] 张聪炫, 陈震, 熊帆, 黎明, 葛利跃, 陈昊. 非刚性稠密匹配大位移运动光流估计. 电子学报, 2019, 47(6): 1316-1323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.06.019ZHANG Cong-xuan, CHEN Zhen, XIONG Fan, LI Ming, GE Li-yue, CHEN Hao. Large displacement motion optical flow estimation with non-rigid dense patch matching. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(6): 1316-1323 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.06.019 [20] Hu Y L, Song R, Li Y S. Efficient coarse-to-fine patch match for large displacement optical flow. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 5704−5712 [21] Revaud J, Weinzaepfel P, Harchaoui Z, Schmid C. Epicflow: Edge-preserving interpolation of correspondences for optical flow. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1164−1172 [22] Hu Y L, Li Y S, Song R. Robust interpolation of correspondences for large displacement optical flow. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 481−489 [23] Revaud J, Weinzaepfel P, Harchaoui Z, Schmid C. DeepMatching: Hierarchical deformable dense matching. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2016, 120(3): 300-323. doi: 10.1007/s11263-016-0908-3 [24] Bian J W, Lin W Y, Matsushita Y, Yeung S K, Nguyen T D, Cheng M M. GMS: Grid-based motion statistics for fast, ultra- robust feature correspondence. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4181−4190 -




 下载:
下载: