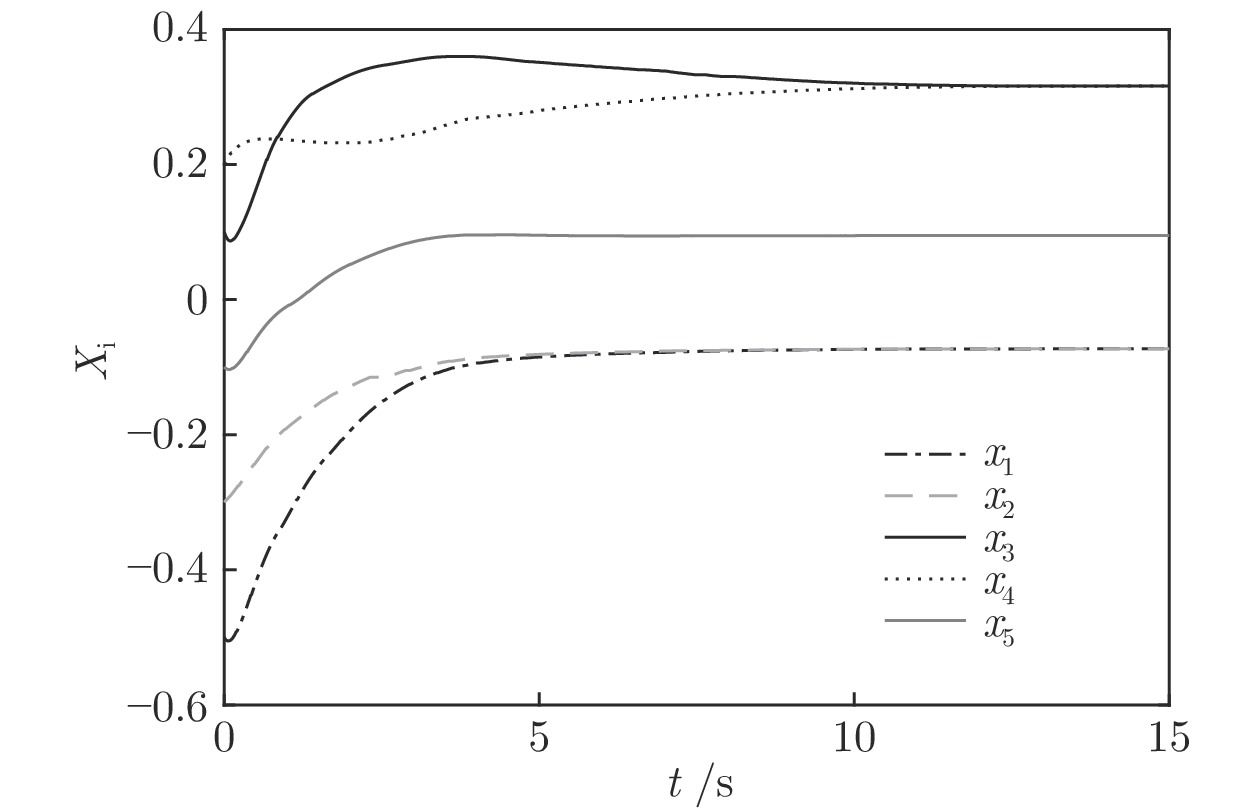
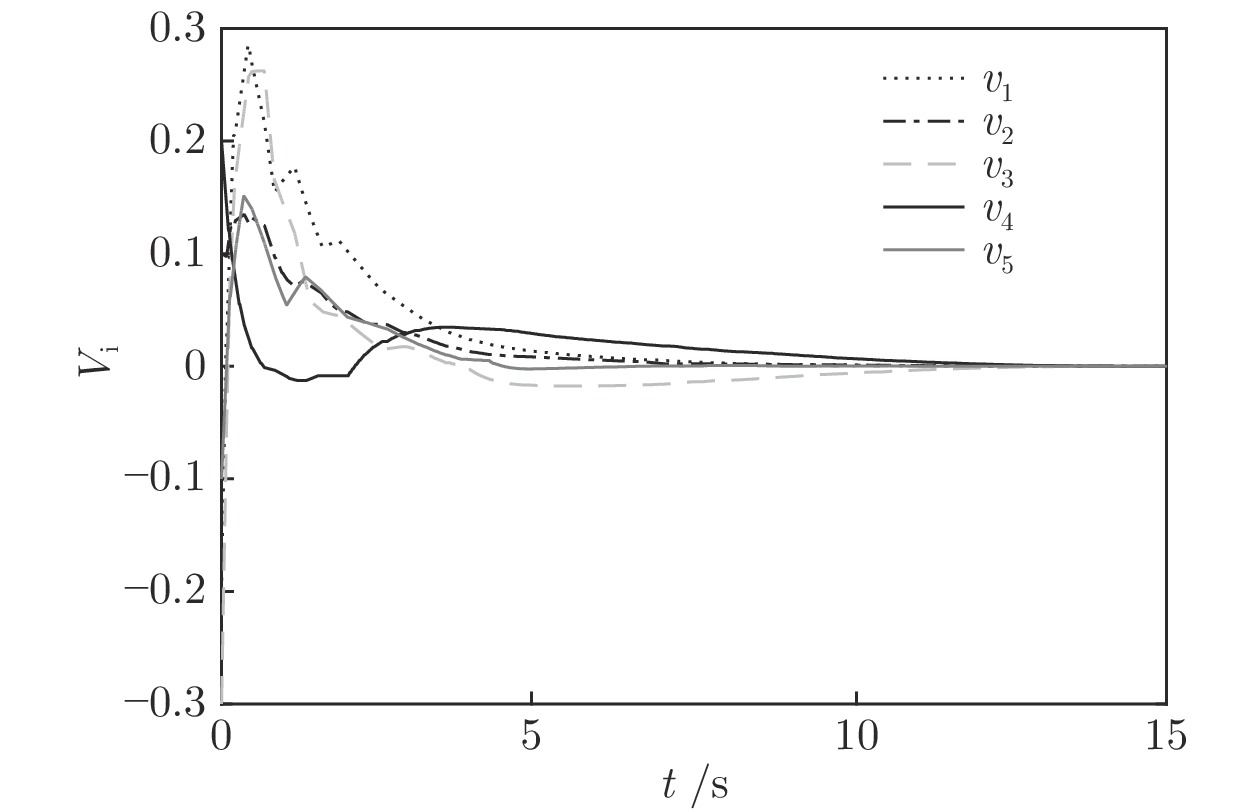
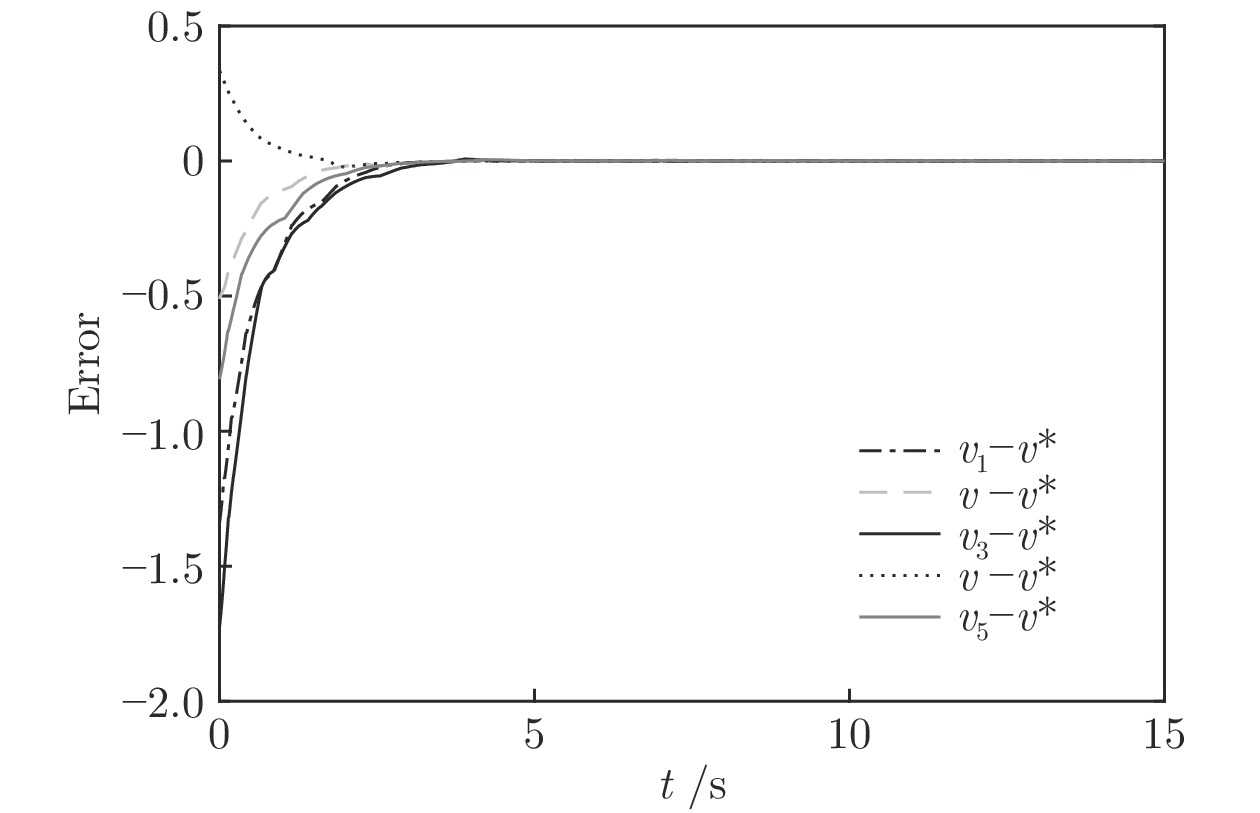
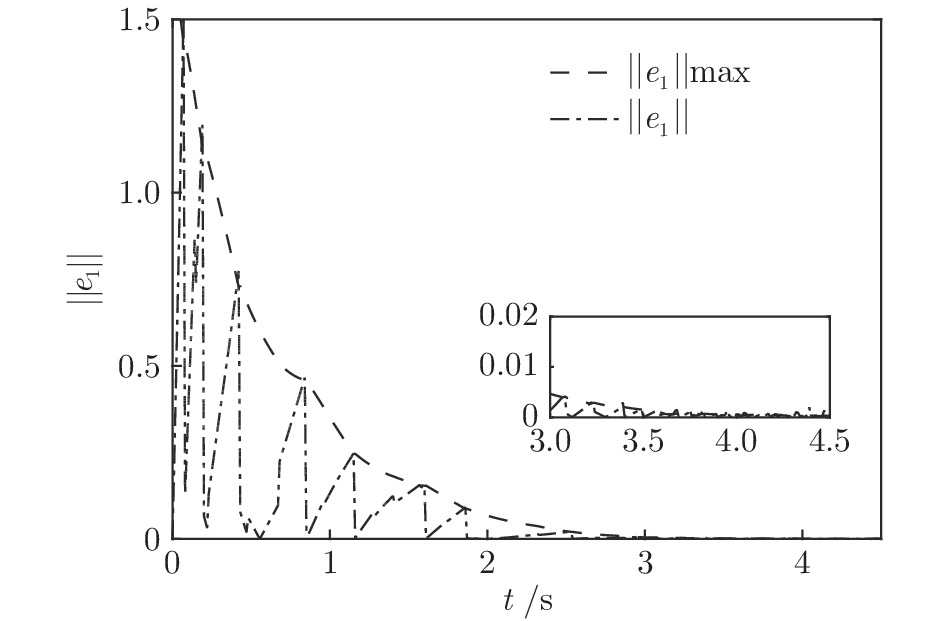
|
[1]
|
Thunberg J, Goncalves J, Hu X. Consensus and formation control on SE(3) for switching topologies[J]. Automatica, 2016, 66(5): 63-82.
|
|
[2]
|
Xiao F, Wang L, Chen J, Gao Y P. Finite-time formation control for multi-agent systems[J]. Automatica, 2009, 45(11): 2605-2611. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.07.012
|
|
[3]
|
Martin S. Multi-agent flocking under topological interactions[J]. Systems & Control Letters, 2014, 69(1): 53-61.
|
|
[4]
|
陈世明, 化俞新, 祝振敏, 赖强. 邻域交互结构优化的多智能体快速蜂拥控制算法[J]. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(12): 2092-2099.CHEN Shi-Ming, HUA Yu-Xin, ZHU Zhen-Min, LAI Qiang. Fast flocking algorithm for multi-agent systems by opti-mizing local interactive topology[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(12): 2092-2099.
|
|
[5]
|
Huang N, Duan Z, Zhao Y. Consensus of multi-agent systems via delayed and intermittent communications[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2015, 9(1): 62-73. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2014.0729
|
|
[6]
|
Zhao M, Peng C, He W L, Song Y. Event-triggered communication for leader-following consensus of second-order multiagent systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(6): 1888-1897. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2716970
|
|
[7]
|
Li J P, Yang Y N, Hua C C, Guan X P. Fixed-time backstepping control design for high-order strict-feedback non-linear systems via terminal sliding mode[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2017, 11(8): 1184-1193. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2016.1143
|
|
[8]
|
Wang H H, Chen B, Lin C, Sun Y M, Wang F. Adaptive flnite-time control for a class of uncertain high-order nonlinear systems based on fuzzy approximation[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2017, 11(5): 677-684. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2016.0947
|
|
[9]
|
Paulo T. Event-triggered real-time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2007, 52(9): 2680-1685.
|
|
[10]
|
Dimos V D, Emilio F, Karl H J. Distributed event-triggered control for multi-agent systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(5): 1291-1297. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2174666
|
|
[11]
|
Hu A H, Cao J, Hu M F, Guo L X. Event-triggered consensus of multi-agent systems with noises[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2015, 352(9): 3489-3503. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2014.08.005
|
|
[12]
|
Fan Y, Feng G, Wang Y, Song C. Distributed eventtriggered control of multi-agent systems with combinational measurements[J]. Automatica, 2013, 49(2): 671-675. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.11.010
|
|
[13]
|
Hu A H, Cao J. Consensus of multi-agent systems via intermittent event-triggered control[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2017, 48(2): 280-287. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2016.1179817
|
|
[14]
|
Zhu Y K, Guan X P, Luo X Y, Li S B. Finite-time consensus of multi-agent system via nonlinear event-triggered control strategy[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2015, 9(17): 2548-2552. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2014.0533
|
|
[15]
|
Yu S H, Wang Y L, Jin L N. Comments on ’Finite-time consensus of multi-agent system via non-linear event-triggered control strategy’[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2017, 11(10): 1658-1661. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2016.0955
|
|
[16]
|
Dong Y, Xian J G. Finite-time event-triggered consensus for non-linear multi-agent networks under directed network topology[J]. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2017, 11(15): 2458-2464. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2017.0085
|
|
[17]
|
Liu J, Yu Y, Sun J, Sun C Y. Distributed event-triggered fixed-time consensus for leader-follower multiagent systems with nonlinear dynamics and uncertain disturbances[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2018, 28(11): 3543-3559 doi: 10.1002/rnc.4098
|
|
[18]
|
Roy S. Scaled consensus[J]. Automatica, 2015, 51 : 259-262. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.10.073
|
|
[19]
|
Meng D, Jia Y. Scaled consensus problems on switching networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(6): 1664-1669. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2479119
|
|
[20]
|
Yu J, Shi Y. Scaled group consensus in multiagent systems with flrst/second-order continuous dynamics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(8): 2259-2271. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2731601
|
|
[21]
|
Meng D, Jia Y. Robust consensus algorithms for multiscale coordination control of multi-vehicle systems with disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(2): 1107-1119. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2478740
|
|
[22]
|
Olfatisaber R, Murray R M. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and timedelays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 2004, 49(9): 1520-1533. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.834113
|
|
[23]
|
Ning B, Jin J, Zheng J C, Man Z H. Finite-time and fixed-time leader-following consensus for multi-agent systems with discontinuous inherent dynamics[J]. International Journal of Control, 2017, 91(6): 1259-1270.
|
|
[24]
|
Zuo Z, Lin T. A new class of flnite-time nonlinear consensus protocols for multi-agent systems[J]. International Journal of Control, 2014, 87(2): 363-370. doi: 10.1080/00207179.2013.834484
|
|
[25]
|
Wei X Y, Yu W W, Wang H, Yao Y Y, Mei F. An observer based fixed-time consensus control for second-order multi-agent systems with disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ Express Briefs, 2019, 66(2): 247-251. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2018.2831922
|




 下载:
下载: