Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation With Self-Attention and Relativistic Discriminator Adversarial Networks
-
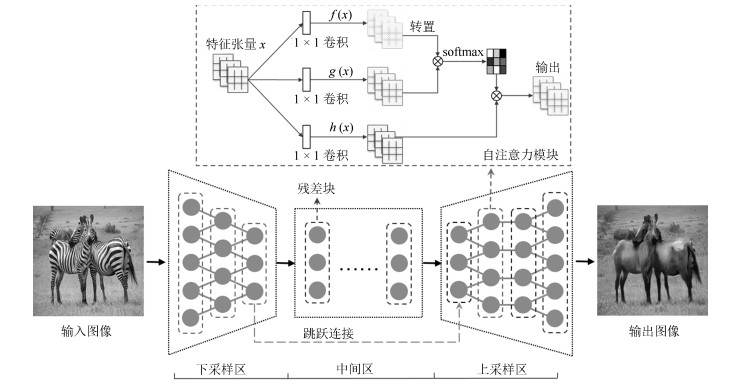
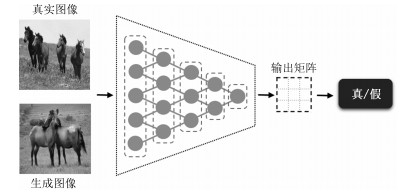
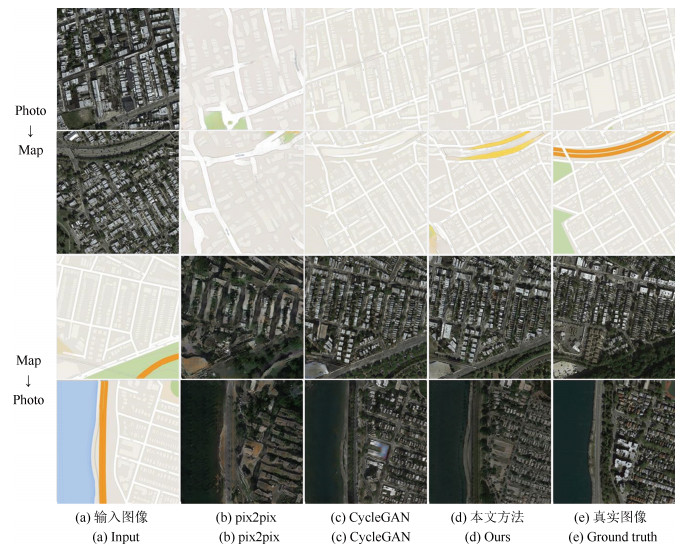
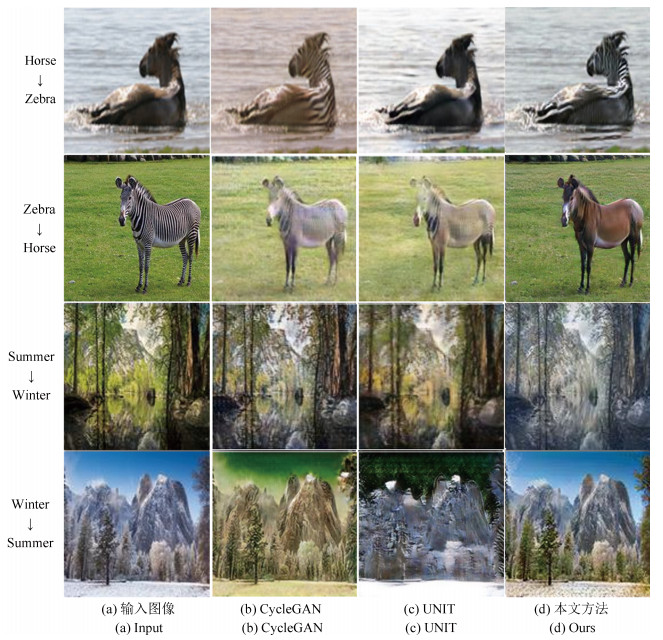
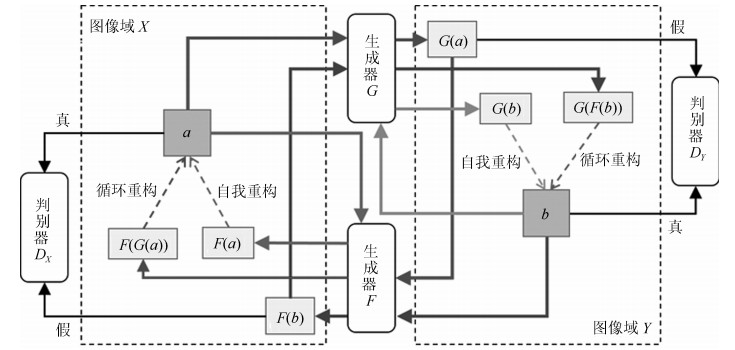
摘要: 无监督图像翻译使用非配对训练数据能够完成图像中对象变换、季节转移、卫星与路网图相互转换等多种图像翻译任务.针对基于生成对抗网络(Generative adversarial network, GAN)的无监督图像翻译中训练过程不稳定、无关域改变较大而导致翻译图像细节模糊、真实性低的问题, 本文基于对偶学习提出一种融合自注意力机制和相对鉴别的无监督图像翻译方法.首先, 生成器引入自注意力机制加强图像生成过程中像素间远近距离的关联关系, 在低、高卷积层间增加跳跃连接, 降低无关图像域特征信息损失.其次, 判别器使用谱规范化防止因鉴别能力突变造成的梯度消失, 增强训练过程中整体模型的稳定性.最后, 在损失函数中基于循环重构增加自我重构一致性约束条件, 专注目标域的转变, 设计相对鉴别对抗损失指导生成器和判别器之间的零和博弈, 完成无监督的图像翻译.在Horse & Zebra、Summer & Winter以及AerialPhoto & Map数据集上的实验结果表明:相较于现有GAN的图像翻译方法, 本文能够建立更真实的图像域映射关系, 提高了生成图像的翻译质量.Abstract: Unsupervised image-to-image translation using unpaired training data can accomplish a variety of image translation tasks such as object transformation, seasonal transfer, and satellite and map transformation. The image-to-image translation method based on generative adversarial network (GAN) has not been satisfying due to the following reasons, the training process is unstable and the irrelevant domain changes greatly, the output images are blurred in detail and low in authenticity. This paper proposes an unsupervised image-to-image translation method with self-attention and relativistic discriminator adversarial networks based on dual learning. Firstly, in the generator, self-attention mechanism is designed to build long-short-range dependency for image generation tasks. Skip-connection between low and high convolution layers help reduce the loss of feature information in irrelevant image domain. Then, in the discriminator, spectral normalization is used to prevent the gradient disappearing caused by the mutation of the discrimination ability to enhance training stability. Finally, in the loss function, the self-reconstruction consistency is added on the basis of loop reconstruction to focus on target image domain change. The relativistic adversarial loss is designed to guide the zero-sum game between generator and discriminator. The experimental results from the Horse & Zebra, Summer & Winter, and AerialPhoto & Map datasets demonstrate that compared with the current image translation methods, our method can establish a more realistic image domain mapping relationship and improve the translation quality of the generated image.
-
Key words:
- Image-to-image translation /
- dual learning /
- generative adversarial networks (GAN) /
- self-attention /
- relativistic discriminator /
- unsupervised learning
1) 本文责任编委 白翔 -
表 1 生成器网络结构参数设置
Table 1 The parameter setting of generator
序号 区域划分 层类型 卷积核 步长 深度 归一化 激活函数 0 下采样 Convolution $ 7 \times 7 $ 1 64 IN ReLU 1 下采样 Convolution $ 3 \times 3 $ 2 128 IN ReLU 2 下采样 Convolution $ 3 \times 3 $ 2 256 IN ReLU 3 中间区 Residual Block $ 3 \times 3 $ 1 256 IN ReLU 4 中间区 Residual Block $ 3 \times 3 $ 1 256 IN ReLU 5 中间区 Residual Block $ 3 \times 3 $ 1 256 IN ReLU 6 中间区 Residual Block $ 3 \times 3 $ 1 256 IN ReLU 7 中间区 Residual Block $ 3 \times 3 $ 1 256 IN ReLU 8 中间区 Residual Block $ 3 \times 3 $ 1 256 IN ReLU 9 上采样 Deconvlution $ 3 \times 3 $ 2 128 IN ReLU 10 上采样 Self-Attention – – – – – 11 上采样 Deconvlution $ 3 \times 3 $ 2 64 IN ReLU 12 上采样 Convolution $ 7 \times 7 $ 1 3 – Tanh 表 2 判别器网络结构参数设置
Table 2 The parameter setting of discriminator
序号 层类型 卷积核 步长 深度 归一化 激活函数 0 Convolution $ 4 \times 4 $ 2 64 – LeakyReLU 1 Convolution $ 4 \times 4 $ 2 128 SN LeakyReLU 2 Convolution $ 4 \times 4 $ 2 256 SN LeakyReLU 3 Convolution $ 4 \times 4 $ 2 512 SN LeakyReLU 4 Convolution $ 4 \times 4 $ 1 1 – – 表 3 本文不同条件分类准确率
Table 3 CA under different conditions
数据集 真实图像 相对对抗 自注意力 自注意力+相对对抗 Horse&Zebra 0.985 0.849 0.862 0.873 Summer&Winter 0.827 0.665 0.714 0.752 表 4 用户调研评价(%)
Table 4 User study (%)
表 5 分类准确率对比
Table 5 Classification accuracy comparison
-
[1] Isola P, Zhu J Y, Zhou T H, Efros A A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1125-1134 [2] Xu F R, Ma B P, Chang H, Shan S G, Chen X L. Style transfer with adversarial learning for cross-dataset person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Perth, Australia: Springer, 2018. [3] Goodfellow I J, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, WardeFarley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2014. 2672-2680 [4] Huang H, Yu P S, Wang C. An introduction to image synthesis with generative adversarial nets. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 1803.04469, 2018. [5] Mirza M, Osindero S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1411.1784, 2014. [6] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2015. 234-241 [7] Zhu J Y, Park T, Isola P, Efros A A. Unpaired image-toimage translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2223 -2232 [8] Liu M Y, Breuel T, Kautz J. Unsupervised image-to-image translation networks. In: Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, California, USA: MIT Press, 2017. 700-708 [9] Miyato T, Kataoka T, Koyama M, Yoshida Y. Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 1802.05957, 2018. [10] He D, Xia Y C, Qin T, Wang L W, Yu N H, Liu T Y, et al. Dual learning for machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: NIPS, 2016. 820-828 [11] Johnson J, Alahi A, Li F F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 694-711 [12] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770-778 [13] Ulyanov D, Vedaldi A, Lempitsky V. Instance normalization: The missing ingredient for fast stylization. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 1607.08022, 2016. [14] Jolicoeur-Martineau A. The relativistic discriminator: A key element missing from standard GAN. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 1807.00734, 2018. [15] Mao X D, Li Q, Xie H R, Lau R Y, Wang Z, Smolley S P. Least squares generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2794-2802 [16] Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252 [17] Heusel M, Ramsauer H, Unterthiner T, Nessler B, Hochreiter S. Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. In: Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, California, USA: MIT Press, 2017. 6626-6637 [18] Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 1412.6980, 2014. [19] Chollet F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1251-1258 [20] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. -




 下载:
下载: