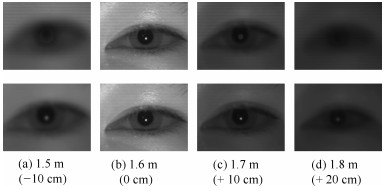
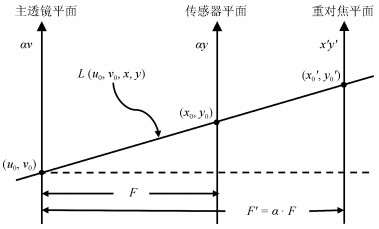
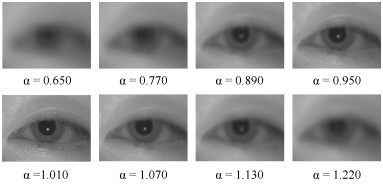
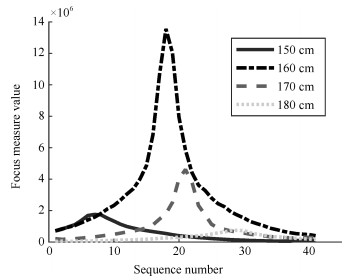
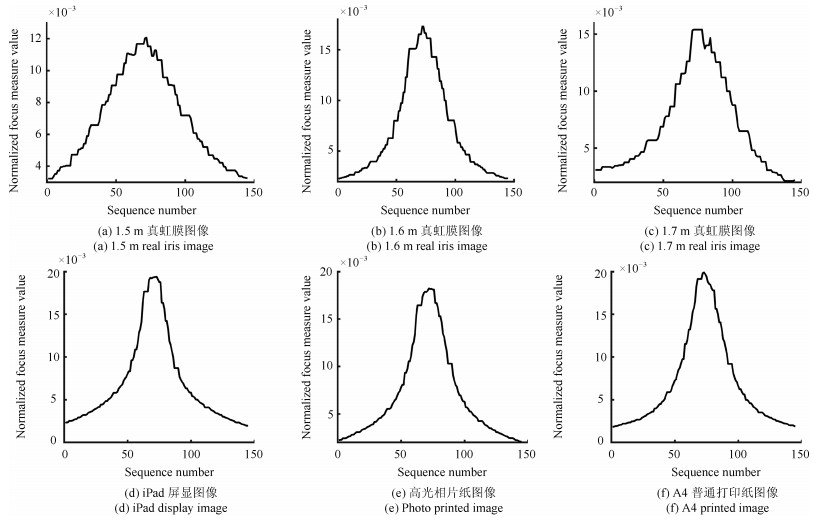
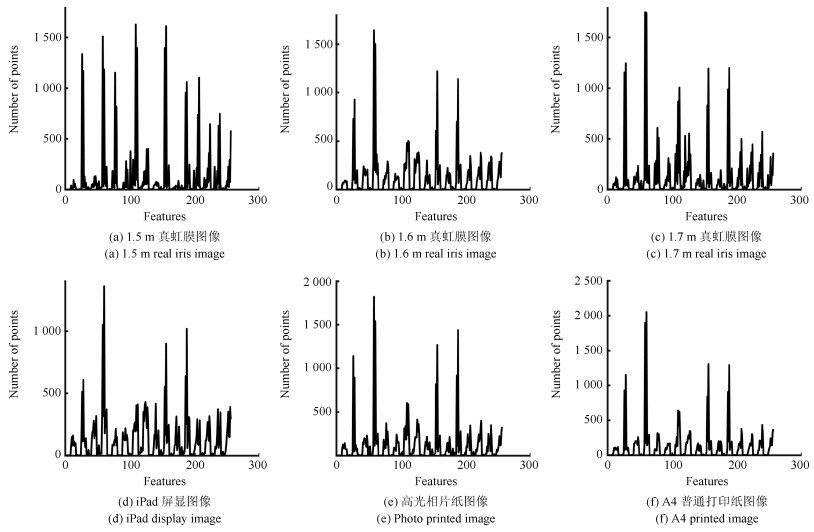
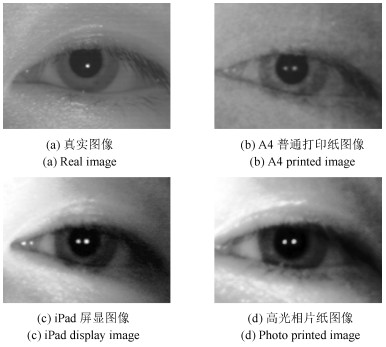
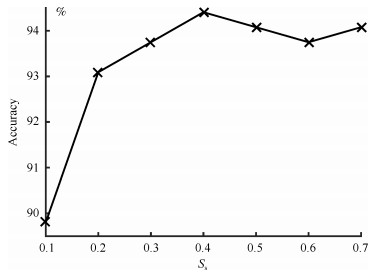
-
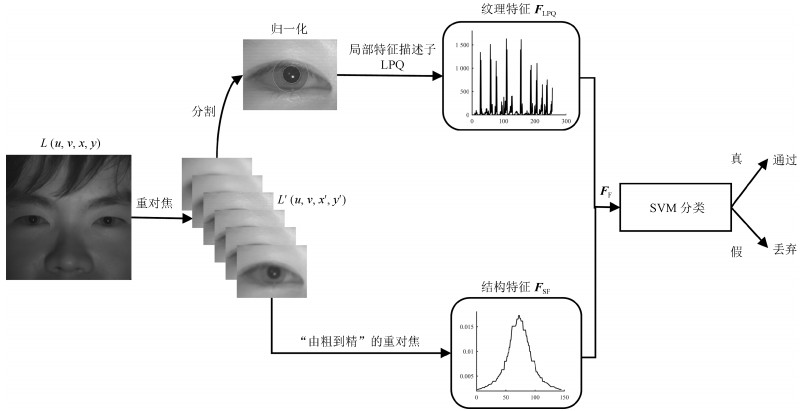
摘要: 光场成像相对传统光学成像是一次重大技术革新,高维光场信息为生物特征识别的发展与创新带来了新机遇.虹膜身份识别技术以其唯一性、稳定性、高精度等优势广泛应用于国防、教育、金融等各个领域,但是现有的虹膜识别系统容易被人造假体虹膜样本欺骗导致误识别.因此,虹膜活体检测是当前虹膜识别研究亟待解决的关键问题.本文提出一种基于计算光场成像的虹膜活体检测方法,通过软硬件结合的方式,充分挖掘四维光场数据的信息.本方法使用实验室自主研发的光场相机采集光场虹膜图像,利用光场数字重对焦技术提取眼周区域的立体结构特征和虹膜图像的纹理特征,进行特征融合与虹膜分类.在自主采集的近红外光场虹膜活体检测数据库上进行实验,本方法的平均分类错误率(Average classification error rate,ACER)为3.69%,在现有最佳方法的基础上降低5.94%.实验结果表明本方法可以准确有效地检测并阻止打印虹膜和屏显虹膜对系统的攻击.Abstract: Light-field (LF) imaging is a new method to capture both intensity and direction information of visual objects, providing promising solutions to biometrics. Iris recognition is a reliable personal identification method, however it is also vulnerable to spoofing attacks, such as iris patterns printed on contact lens or paper. Therefore iris liveness detection is an important module in iris recognition systems. In this paper, an iris liveness detection approach is proposed to take full advantages of intrinsic characteristics in light-field iris imaging. LF iris images are captured by using lab-made LF cameras, based on which the geometric features as well as the texture features are extracted using the LF digital refocusing technology. These features are combined for genuine and fake iris image classification. Experiments were carried out based on the self-collected near-infrared LF iris database, and the average classification error rate (ACER) of the proposed method is 3.69%, which is 5.94% lower than the best state-of-the-art method. Experimental results indicate the proposed method is able to work effectively and accurately to prevent spoofing attacks such as printed and screen-displayed iris input attacks.
-
Key words:
- Iris liveness detection /
- light-field imaging /
- digital refocusing /
- feature fusion
1) 本文责任编委 赖剑煌 -
表 1 虹膜活体检测方法在自主采集的数据库上的表现(%)
Table 1 Performance of iris liveness detection methods on self-collected database (%)
Method Accuracy APCER BPCER ACER Bliinds2[32] 79.61 23.81 16.18 19.99 BRISQUE[33] 86.18 13.69 13.97 13.83 DIIVINE[34] 89.14 5.95 16.91 11.43 BSIF[35] 83.88 16.67 15.44 16.05 DSIFT[36] 76.97 35.12 8.09 21.60 LPQ[26] 90.13 11.90 7.35 9.63 SID[37] 77.30 35.12 7.35 21.24 LBP[38] 82.24 20.83 13.97 17.40 LBPV[39] 79.61 30.95 7.35 19.15 Raghavendra[14] 59.54 32.14 50.74 41.44 Ours_SF 94.41 2.98 8.82 5.90 Ours_Fusion 96.38 2.98 4.41 3.69 -
[1] Ruiz-Albacete V, Tome-Gonzalez P, Alonso-Fernandez F, Galbally J, Fierrez J, Ortega-Garcia J. Direct attacks using fake images in iris verification. In: Proceedings of the 2008 European Workshop on Biometrics and Identity Management. Heidelberg, Berlin: Springer, 2008. 181-190 doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-89991-4_19 [2] Tomeo-Reyes I, Liu-Jimenez J, Rubio-Polo I, Redondo-Justo J, Sanchez-Reillo R. Input images in iris recognition systems: a case study. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Systems Conference. Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2011. 501-505 [3] Gupta P, Behera S, Vatsa M, Singh R. On iris spoofing using print attack. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Stockholm, Sweden: IEEE, 2014. 1681-1686 [4] Yambay D, Doyle J S, Bowyer K W, Czajka A, Schuckers S. LivDet-Iris 2013-iris liveness detection competition 2013. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics. Florida, USA: IEEE, 2014. 1-8 [5] Rigas I, Komogortsev O V. Eye movement-driven defense against iris print-attacks. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2015, 68(12):316-326 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c1715c4dba29f28d79fb758d5225fa7a [6] George A, Routray A. A score level fusion method for eye movement biometrics. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2016, 82(12):207-215 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cf34fa926e1690e97f6b8bc8799668bb [7] Komogortsev O V, Karpov A, Holland C D. Attack of mechanical replicas:liveness detection with eye movements. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 10(4):716-725 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2015.2405345 [8] Connell J, Ratha N, Gentile J, Bolle R. Fake iris detection using structured light. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2013. 8692-8696 [9] Pacut A, Czajka A. Aliveness detection for iris biometrics. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual 2006 International Carnahan Conferences on Security Technology. Kentucky, USA: IEEE, 2006. 122-129 [10] Daugman J G. Recognizing persons by their iris patterns: countermeasures against subterfuge. Biometrics: Personal Identification in a Networked Society. New York: Springer, 1999. 103-121 [11] Lee E C, Park K R, Kim J. Fake iris detection by using Purkinje image. In: Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Biometrics. Heidelberg, Berlin: Springer, 2006. 397-403 [12] Lee S J, Park K R, Kim J. Robust fake iris detection based on variation of the reflectance ratio between the iris and the sclera. In: Proceedings of the 2006 Biometrics Symposium: Special Session on Research at the Biometric Consortium Conference. Baltimore, Maryland: IEEE, 2006. 1-6 [13] Czajka A. Pupil dynamics for iris liveness detection. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 10(4):726-735 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2015.2398815 [14] Raghavendra R, Busch C. Presentation attack detection on visible spectrum iris recognition by exploring inherent characteristics of light field camera. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics. Florida, USA: IEEE, 2014. 1-8 [15] He Z Z, Sun Z N, Tan T T, Wei Z S. Efficient iris spoof detection via boosted local binary patterns. In: Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Biometrics. Heidelberg, Berlin: Springer, 2009. 1080-1090 [16] Komulainen J, Hadid A, Pietikäinen M. Generalized textured contact lens detection by extracting BSIF description from Cartesian iris images. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics. Florida, USA: IEEE, 2014. 1-7 [17] Raghavendra R, Busch C. Robust scheme for iris presentation attack detection using multiscale binarized statistical image features. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 10(4):703-715 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2015.2400393 [18] Alonso-Fernandez F, Bigun J. Exploting periocular and RGB information in fake iris detection. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics. Opatija, Croatia: IEEE, 2014. 1354-1359 [19] Hu Y, Sirlantzis K, Howells G. Iris liveness detection using regional features. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2016, 82:242-250 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2015.10.010 [20] Kohli N, Yadav D, Vatsa M, Singh R, Noore A. Detecting medley of iris spoofing attacks using DESIST. In: Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems. New York, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1-6 [21] Galbally J, Ortiz-Lopez J, Fierrez J, Ortega-Garcia J. Iris liveness detection based on quality related features. In: Proceedings of the 5th IAPR International Conference on Biometrics. New Delhi, India: IEEE, 2012. 271-276 [22] Galbally J, Marcel S, Fierrez J. Image quality assessment for fake biometric detection:application to iris, fingerprint, and face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(2):710-724 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2292332 [23] Czajka A, Bowyer K W, Krumdick M, VidalMata R G. Recognition of image-orientation-based iris spoofing. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2017, 12(9):2184-2196 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2017.2701332 [24] He L X, Li H Q, Liu F, Liu N F, Sun Z N, He Z F. Multi-patch convolution neural network for iris liveness detection. In: Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems. New York, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1-7 [25] Raghavendra R, Raja K B, Busch C. ContlensNet: robust iris contact lens detection using deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Santa Rosa, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1160-1167 [26] Ojansivu V, Rahtu E, Heikkila J. Rotation invariant local phase quantization for blur insensitive texture analysis. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Florida, USA: IEEE, 2008. 1-4 [27] Dansereau D G, Pizarro O, Williams S B. Decoding, calibration and rectification for lenselet-based plenoptic cameras. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, Oregon: IEEE, 2013. 1027-1034 [28] Ng R, Levoy M, Brédif M, Duval G, Horowitz M, Hanrahan P. Light Field Photography with a Hand-Held Plenoptic Camera, Stanford Technical Report CTSR 2005-02, 2005 [29] Ng R. Fourier slice photography. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2005, 24(3):735-744 doi: 10.1145/1073204 [30] Pech-Pacheco J L, Cristóbal G, Chamorro-Martinez J, Fernández-Valdivia J. Diatom autofocusing in brightfield microscopy: a comparative study. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2000. 314-317 [31] Information Technology-Biometrics Presentation Attack Detection-Part 3: Testing, Reporting and Classification of Attacks, ISO/IEC Standard JTC 1/SC 3730107-3, 2014 [32] Saad M A, Bovik A C, Charrier C. Blind image quality assessment:a natural scene statistics approach in the DCT domain. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(8):3339-3352 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2191563 [33] Mittal A, Moorthy A K, Bovik A C. No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(12):4695-4708 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2214050 [34] Moorthy A K, Bovik A C. Blind image quality assessment:from natural scene statistics to perceptual quality. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(12):3350-3364 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2147325 [35] Kannala J, Rahtu E. BSIF: binarized statistical image features. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Tsukuba, Japan: IEEE, 2012. 1363-1366 [36] Lowe D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2):91-110 doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [37] Kokkinos I, Bronstein M, Yuille A. Dense Scale Invariant Descriptors for Images and Surfaces, Research Report, INRIA RR-7914, 2012 [38] Ojala T, Pietikäinen M, Mäenpää T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(7):971-987 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2002.1017623 [39] Guo Z H, Zhang L, Zhang D. Rotation invariant texture classification using LBP variance (LBPV) with global matching. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(3):706-719 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.08.017 -




 下载:
下载: