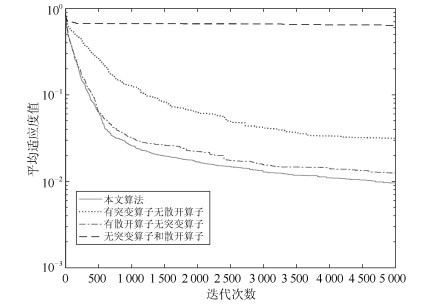
-
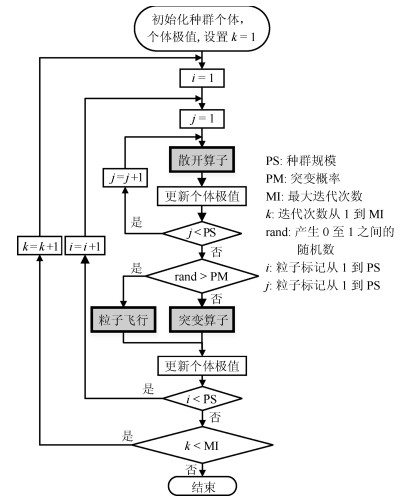
摘要: 符号回归以构建一个能拟合给定数据集的函数模型为目的, 是对基本函数、运算符、变量等进行组合优化的过程.本文提出了一种求解符号回归问题的粒子群优化算法.算法以语法树对函数模型进行表达, 采用基因表达式将语法树编码为一个粒子, 设计了粒子的飞行方法及$r$-邻域环状拓扑的粒子学习关系.为使粒子具有跳出局部极值的能力和减轻粒子快速趋同对全局寻优造成的不利影响, 分别设计了突变算子和散开算子.此外, 为了得到比较简洁的函数模型, 在粒子的评价函数中以罚函数的方式对编码的有效长度进行控制.仿真实验表明, 提出的算法可以获得拟合精度更高、简洁性更好的函数模型.Abstract: Symbolic regression is to construct a function model that fits a given dataset. It is the process of optimally combining various basic functions, operators, and variables. This paper proposes a particle swarm optimization-based algorithm for symbolic regression. In the proposed algorithm, the functional model to be established is represented as a syntax tree, which is encoded as a particle through gene-expression. A specific implementation of particles flying and the $r$-neighborhood learning mechanism of particle swarm were designed. To make particles be capable of jumping out local extremum and to mitigate the negative influence on global optimization resulted from the fast convergence of the particle swarm, mutation and scatter are respectively introduced into the proposed algorithm as operators. Besides, in order to obtain concise functional model, the valid length of the gene-expression-based coding scheme is controlled in manner of introducing a penalty term to the particle evaluation function. Exhaustive simulation experiments are carried out and the results show that, the proposed algorithm can obtain the functional model with higher fitting precision and better conciseness.
-
Key words:
- Gene-expression programming /
- particle swarm optimization /
- symbolic regression /
- evolutionary modeling
1) 本文责任编委 伍洲 -
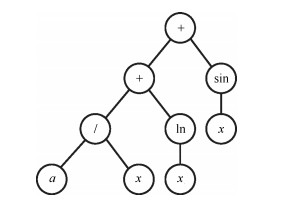
表 1 粒子编码
Table 1 Particle coding
Node code 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 $X$ + exp ln $x$ 2 1 2 $x $ 1 $x $ $x$ 表 2 粒子$X$、$gbest$、$pbest$以及$X'$的编码
Table 2 The code of particle $X$, $gbest$, $pbest$ and $X'$
Node code 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 $X$ + $ x $ $\sin$ $-$ ln $ x $ $a$ $ x $ $ x $ $a$ $ a$ $pbest$ + $ x $ $\cos$ / $-$ $ x $ $a$ $ x $ $a$ $ x $ $a$ $gbest$ $\exp$ + $a$ $-$ ln $a$ $a$ $ x $ $a$ $ x $ $a$ $X'$ + + $\sin$ / ln $ x $ $a$ $ x $ $ x $ $a$ $a$ 表 3 粒子$X$和$X'$的编码
Table 3 The code of particle $X$ and $X'$
Node code 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 $X$ + + sin / ln $ x $ $a$ $ x $ $ x $ $a$ $a$ $X'$ + $\times$ sin cos ln a $a$ $ x $ $ x $ $a$ $a$ 表 4 算法参数
Table 4 Algorithm parameters
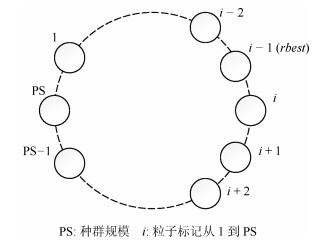
参数 参数取值 节点评价个数 $15\, 000\, 000$ 种群数量 50 首段长度 10 约束长度 18 罚因子 0.0001 环状结构邻域大小 $2r+1, r=2$ 终止符 $x, 1$ (单变量); $x, y$ (双变量) 函数及运算符 $+, -, \times, /$, sin, cos, e$^x$, ln 测试次数 100 表 5 测试函数
Table 5 Benchmark functions
Functions Fitcases $F1=x^3+x^2+x$ 20 random points $\subseteq [-1, 1]$ $F2=x^4+x^3+x^2+x$ 20 random points $\subseteq [-1, 1]$ $F3=x^5+x^4+x^3+x^2+x$ 20 random points $\subseteq [-1, 1]$ $F4=x^6+x^5+x^4+x^3+x^2+x$ 20 random points $\subseteq [-1, 1]$ $F5=\sin(x^2)\cos(x)-1$ 20 random points $\subseteq [-1, 1]$ $F6=\sin(x)+\sin(x+x^2)$ 20 random points $\subseteq [-1, 1]$ $F7={\rm ln}(x+1)+{\rm ln}(x^2+1)$ 20 random points $\subseteq [0, 2]$ $F8=\sqrt x$ 20 random points $\subseteq [0, 4]$ $F9=\sin(x)+\sin(y^2)$ 100 random points $\subseteq [-1, 1]$ $F10=2\sin(x)\cos(y)$ 100 random points $\subseteq [-1, 1]$ 表 6 成功运行百分比(%)
Table 6 Percentage of successful runs (%)
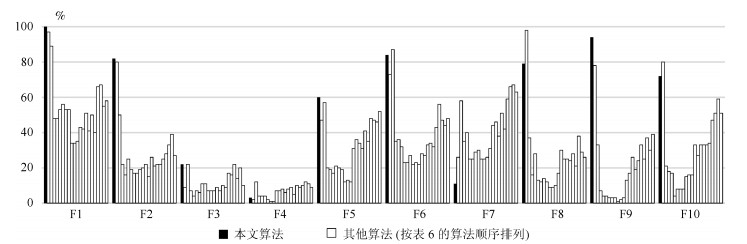
Techniques Functions F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 本文算法 ${\bf 100 }$ ${\bf 82}$ ${\bf 22}$ 3 ${\bf 60}$ 84 11 79 ${\bf 94}$ 72 AFSA 97 80 9 2 47 73 26 ${\bf 98}$ 78 ${\bf 80}$ ABCP 89 50 ${\bf 22}$ ${\bf 12}$ 57 ${\bf 87}$ 58 37 33 21 SC 48 22 7 4 20 35 35 16 7 18 NSM 48 16 4 4 19 36 40 28 4 17 SAC2 53 25 7 4 17 32 25 13 4 4 SAC3 56 19 6 2 21 23 25 12 3 8 SAC4 53 17 11 1 20 23 29 14 3 8 SAC5 53 17 11 1 19 27 30 12 3 8 CAC1 34 19 7 7 12 22 25 9 1 15 CAC2 34 20 7 7 13 23 25 9 2 16 CAC4 35 22 7 8 12 22 26 10 3 16 SBS31 43 15 9 6 31 28 31 17 13 33 SBS32 42 26 7 8 36 27 44 30 17 27 SBS34 51 21 10 9 34 33 46 25 26 33 SBS41 41 22 9 5 31 34 38 25 19 33 SBS42 50 22 17 10 41 32 51 24 24 33 SBS44 40 25 16 9 35 43 42 28 33 34 SSC8 66 28 ${\bf 22}$ 10 48 56 59 21 25 47 SSC12 67 33 14 ${\bf 12}$ 47 47 66 38 37 51 SSC16 55 39 20 11 46 44 ${\bf 67}$ 29 30 59 SSC20 58 27 10 9 52 48 63 26 39 51 表 7 平均最佳适应值(%)
Table 7 Mean best fitness values (%)
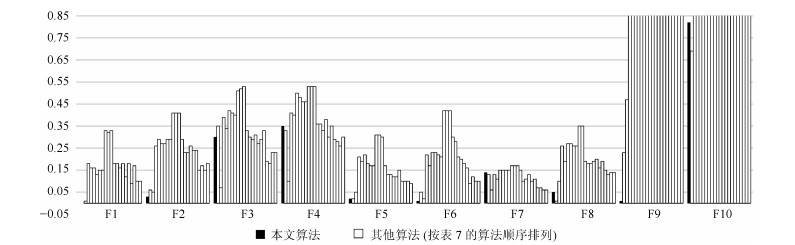
Techniques Functions F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 本文算法 ${\bf 0.00}$ ${\bf 0.03}$ 0.30 0.35 ${\bf 0.02}$ ${\bf 0.01}$ 0.14 0.05 ${\bf 0.01}$ 0.82 AFSA ${\bf 0.00}$ 0.06 0.35 0.33 ${\bf 0.02}$ 0.05 0.13 ${\bf 0.01}$ 0.23 ${\bf 0.69}$ ABCP 0.01 0.05 ${\bf 0.07}$ ${\bf 0.10}$ 0.05 0.02 ${\bf 0.06}$ 0.10 0.47 1.06 SC 0.18 0.26 0.39 0.41 0.21 0.22 0.13 0.26 5.54 2.26 NSM 0.16 0.29 0.34 0.40 0.19 0.17 0.11 0.19 5.44 2.16 SAC2 0.16 0.27 0.42 0.50 0.22 0.23 0.15 0.27 5.99 3.19 SAC3 0.13 0.27 0.41 0.48 0.18 0.23 0.15 0.27 5.77 3.13 SAC4 0.15 0.29 0.40 0.46 0.17 0.22 0.15 0.26 5.77 3.03 SAC5 0.15 0.29 0.51 0.46 0.17 0.21 0.15 0.26 5.77 2.98 CAC1 0.33 0.41 0.52 0.53 0.31 0.42 0.17 0.35 7.83 4.40 CAC2 0.32 0.41 0.53 0.53 0.31 0.42 0.17 0.35 7.38 4.30 CAC4 0.33 0.41 0.33 0.53 0.30 0.42 0.17 0.19 7.80 4.32 SBS31 0.18 0.29 0.30 0.36 0.17 0.30 0.15 0.18 4.78 2.75 SBS32 0.18 0.23 0.29 0.36 0.13 0.28 0.10 0.18 4.47 2.77 SBS34 0.16 0.23 0.31 0.33 0.13 0.21 0.11 0.19 4.17 2.90 SBS41 0.18 0.26 0.27 0.38 0.12 0.20 0.13 0.20 4.40 2.75 SBS42 0.12 0.24 0.29 0.30 0.12 0.18 0.10 0.16 3.95 2.76 SBS44 0.18 0.24 0.33 0.35 0.15 0.16 0.11 0.19 2.85 1.75 SSC8 0.09 0.15 0.19 0.29 0.10 0.09 0.07 0.15 3.91 1.53 SSC12 0.17 0.17 0.18 0.28 0.10 0.12 0.07 0.13 3.54 1.45 SSC16 0.10 0.15 0.23 0.26 0.10 0.10 ${\bf 0.06}$ 0.14 3.11 1.22 SSC20 0.10 0.18 0.23 0.30 0.09 0.10 ${\bf 0.06}$ 0.14 2.64 1.23 表 8 "Ⅴ"型函数建模的算法参数
Table 8 Algorithm parameters for "V" function
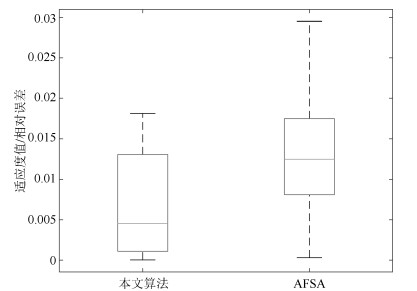
参数 参数取值 迭代次数 50 000 种群数量 300 首段长度 25 约束长度 35 罚因子 0.05 环状结构邻域大小 $2r+1, r=2$ 终止符 $x, 1, 0.2, 2, 4, 0.7, 0.1, 0.1415, 0.01, 3$ 函数及运算符 $+, -, \times, /, \sqrt{~~}, \sin, \cos, {\rm e}^x, \ln, x^2$ 测试次数 100 算法 评价指标 F1 F2 F3 F11 TSO Average fitness 0 0.09 0.63 0.26 Standard deviation 0 0.35 0.79 0.36 Perfect hits in % 100 92 57 52 Number of evaluations 1 220 4 660 7 000 9 020 本文算法 Average fitness 0 0 0.04 0.23 Standard deviation 0 0 0.26 0.30 Perfect hits in % 100 100 97 73 Number of evaluations 692 1 589 6 645 8 350 表 10 观测数据
Table 10 Observation data
$x$ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20 $y$ 0.250841, $-$0.373517, $-$1.957016, $-$2.699129, 1.619885 4.684452, 2.686799, $-$0.501882, $-$4.718648, $-$7.787834 0.056755, 9.363730, 6.761007, 0.824883, $-$5.821076 $ -$12.512195, $-$5.349206, 12.234454, 12.324229, 3.656108 表 11 不同约束长度下的函数模型
Table 11 Function models with different constrained length
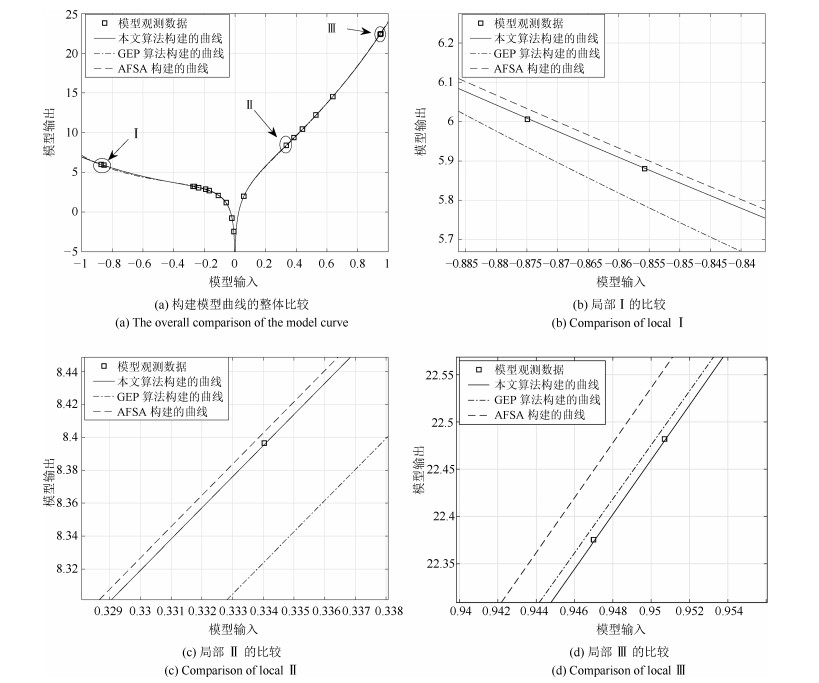
约束长度 有效长度 编码 模型表达式 25 24 $\times, \cos, \times, x, /, \cos, x, \sqrt{~~}, \cos, \exp, \cos, \sin, \sin, x, \sqrt{~~}, \cos, $ $\dfrac{x\cdot \cos x}{\sqrt {{\rm e}^{\sin x}}}\cdot \cos(\cos(\cos(\sin(\sqrt{\cos(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-x}{x^2})}))))$ $/, -, \times, \sqrt{~~}, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x$ 22 21 $\times, \cos, /, x, x, \sqrt{~~}, \exp, +, \sin, \sin, \sin, x, \cos, /, \ln, \cos, \sqrt{~~}, $ $\dfrac{x\cdot \cos x}{\sqrt{{\rm exp}({\sin x}+ \sin(\sin(\cos(\dfrac{\ln{\sqrt {{\rm e}^{\cos x}}}}{\cos x}))))}}$ $x, \exp, \cos, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x$ 20 19 $\times, /, x, \cos, \sqrt{~~}, x, \exp, +, \cos, \sin, \sin, x, \sqrt{~~}, \cos, /, x, +, $ $\dfrac{x\cdot \cos x}{\sqrt{{\rm exp}({\sin x}+ \cos(\sin(\sqrt{\cos(\dfrac{x}{2x})})))}}$ $/x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x$ 18 18 $ /, \cos, /, x, \sqrt{~~}, x, +, \exp, -, \sin, \exp, \ln, x, \sin, /, x, x, $ $\dfrac{x\cdot \cos x}{\sqrt{{\rm e}^{\sin x}+{\rm e}^{\sin x}-\ln{(\dfrac{x}{x})}}}$ $x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x$ 15 13 $/, \cos, /, x, \sqrt{~~}, x, +, \exp, \exp, \sin, \sin, x, x, x, x, x, \times, $ $\dfrac{x\cdot \cos x}{\sqrt{{\rm e}^{\sin x}+{\rm e}^{\sin x}}}$ $x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x, x$ 表 12 预测值(百万)
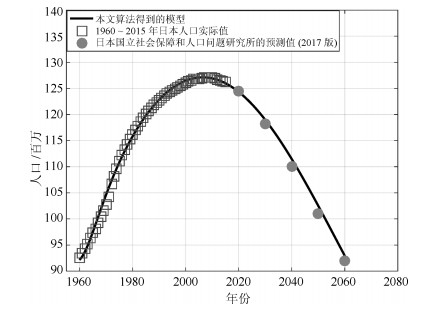
Table 12 Predicted values (million)
年份 文献[31] 本文算法 二者之差 2020 125.325 125.238 0.087 2030 119.125 119.902 0.777 2040 110.919 112.385 1.466 2050 101.923 103.425 1.502 2060 92.840 93.845 1.005 -
[1] 刘强, 秦泗钊.过程工业大数据建模研究展望.自动化学报, 2016, 42(2): 161-171 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150510Liu Qiang, Qin S. Joe. Perspectives on big data modeling of process industries. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(2): 161-171 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150510 [2] 司小胜, 胡昌华, 周东华.带测量误差的非线性退化过程建模与剩余寿命估计.自动化学报, 2013, 39(5): 530-541 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00530Si Xiao-Sheng, Hu Chang-Hua, Zhou Dong-Hua. Nonlinear degradation process modeling and remaining useful life estimation subject to measurement error. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(5): 530-541 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.00530 [3] Yao X, Liu Y, Li J, He J. Current developments and future directions of bio-inspired computation and implications for ecoinformatics. Ecological informatics, 2006, 1(1): 9-22 doi: 10.1016/j.ecoinf.2005.07.001 [4] Koza J R. Genetic Programming: On the Programming of Computers by Means of Natural Selection. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1992. [5] Ferreira C. Gene Expression Programming: A New Adaptive Algorithm for Solving Problems. Computer Science, 2001, 21(2): 87-129 [6] Yassin M A, Alazba A A, Mattar M A. A new predictive model for furrow irrigation infiltration using gene expression programming. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2016, 122: 168-175 doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2016.01.035 [7] Mohamed M. Mostafa, Ahmed A. El-Masry. Oil price forecasting using gene expression programming and artificial neural networks. Economic Modelling, 2016, 54(1): 40-53 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264999315004101 [8] Weatheritt J, Sandberg R. A novel evolutionary algorithm applied to algebraic modifications of the RANS stress-strain relationship. Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 325: 22-37 doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2016.08.015 [9] Phukoetphim P, Shamseldin A Y, Adams K. Multimodel approach using neural networks and symbolic regression to combine the estimated discharges of rainfall-runoff models. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 2016, 21(8): 04016022 doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001332 [10] Razaq S A, Shahid S, Ismail T, et al. Prediction of flow duration curve in ungauged catchments using genetic expression programming. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 154: 1431-1438 doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.07.516 [11] Soule T. Code growth in genetic programming. In: Proceedings of the 1995 Conference Genetic Programming. Atlanta, GA, USA: ACM, 1995. 148-159 [12] Ragalo A W, Pillay N. A building block conservation and extension mechanism for improved performance in polynomial symbolic regression tree-based genetic programming. In: Proceedings of the 2012 Nature and Biologically Inspired Computing. New York, USA: IEEE, 2012. 123-129 [13] Sotto L F D P, de Melo V V. Investigation of linear genetic programming techniques for symbolic regression. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems. New York, USA: IEEE, 2014. 146-151 [14] Peng Y Z, Yuan C A, Qin X, et al. An improved gene expression programming approach for symbolic regression problems. Neurocomputing, 2014, 137(15): 293-301 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9b3fe6fd0d6560aabb8e480a7ce4be02 [15] Zhong J, Ong Y S, Cai W. Self-learning gene expression programming. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2016, 20(1): 65-80 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=13200aa4d92c48a51b9eb60989f98571 [16] Olmo J L, Romero J R, Ventura S. Swarm-based metaheuristics in automatic programming: A survey. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2014, 4(6): 445-469 doi: 10.1002/widm.1138 [17] Karaboga D, Ozturk C, Karaboga N, et al. Artificial bee colony programming for symbolic regression. Information Sciences, 2012, 209: 1-15 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2012.05.002 [18] Liu Q, Odaka T, Kuroiwa J, et al. Application of an artificial fish swarm algorithm in symbolic regression. IEICE Transactions on Information & Systems, 2013, E96. D(4): 872-885 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/274462480_Application_of_an_Artificial_Fish_Swarm_Algorithm_in_Symbolic_Regression [19] Qi F, Ma Y H, Liu X Y, Ji G Y. A hybrid genetic programming with particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference in Swarm Intelligence. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag, 2013. 11-18 [20] Veenhuis C, Koppen M, Kruger J, Nickolay B. Tree swarm optimization: An approach to PSO-based tree discovery. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. New York, USA: IEEE, 2005. 1238-1245 [21] Kennedy J, Eberhart R C. Particle swam optimization. In: Proceedings of the 1995 Neural Networks. Picataupy, USA: IEEE, 1995. 1942-1948 [22] Zhang S, Xu J, Lee L H, et al. Optimal computing budget allocation for particle swarm optimization in stochastic optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2017, 21(2): 206-219 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2016.2592185 [23] Wu H Y, Nie C H, Kuo F C, Leung H, Colbourn C J. A discrete particle swarm optimization for covering array generation. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2015, 19(4): 575-591 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2014.2362532 [24] Gong Y J, Zhang J, Chung H S H, et al. An efficient resource allocation scheme using particle swarm optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2012, 16(6): 801-816 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2012.2185052 [25] Lee K B, Kim J H. Multiobjective particle swarm optimization with preference-based sort and its application to path following footstep optimization for humanoid robots. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2013, 17(6): 755-766 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2013.2240688 [26] Thongchart Kerdphol, Kiyotaka Fuji, Yasunori Mitani, Yaser Qudaih. Optimization of a battery energy storage system using particle swarm optimization for stand-alone microgrid. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2016, 81: 32-39 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=03d5dc3e6af2f9033ef9603d73ebbbc0 [27] Iba H, Garis H D, Sato T. Genetic programming using a minimum description length principle. Advances in Genetic Programming, 1994: 265-284 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1611327e61e1eed6ae6e76abb3a46aa1 [28] Liu Q F, Wei W H, Yuan H Q, Li Y. Topology selection for particle swarm optimization. Information Sciences, 2016, 363: 154-173 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.04.050 [29] 周晓君, 阳春华, 桂卫华, 董天雪.带可变随机函数和变异算子的粒子群优化算法.自动化学报, 2014, 40(7): 1339-1347 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.01339Zhou Xiao-Jun, Yang Chun-Hua, Gui Wei-Hua, Dong Tian-Xue. A particle swarm optimization algorithm with variable random functions and mutation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(7): 1339-1347 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.01339 [30] Uy N Q, Hoai N X, O'Neill M, et al. Semantically-based crossover in genetic programming: Application to real-valued symbolic regression. Genetic Programming and Evolvable Machines, 2011, 12(2): 91-119 doi: 10.1007/s10710-010-9121-2 [31] Population Statistics of Japan 2017[Online], available: http://www.ipss.go.jp/p-info/e/psj2017/PSJ2017.asp, October 9, 2018 -




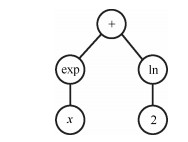
 下载:
下载: