Multi-objective Evolutionary Optimization With Objective Space Partition Based on Online Perception of Pareto Front
-
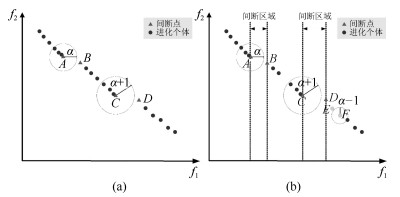
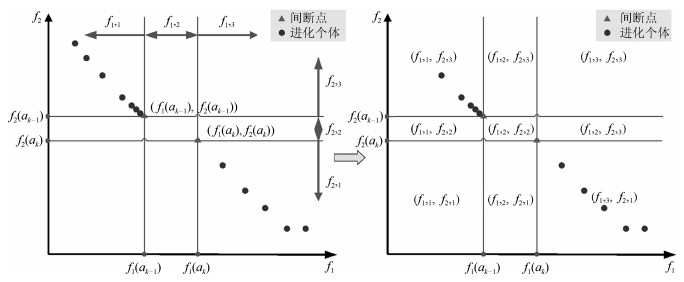
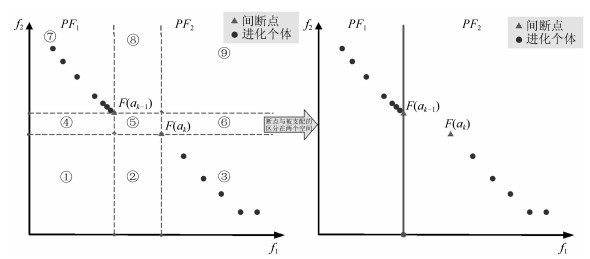
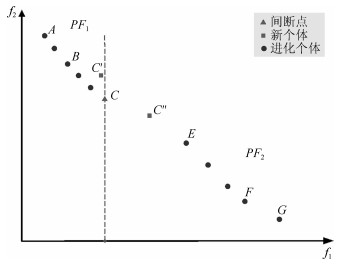
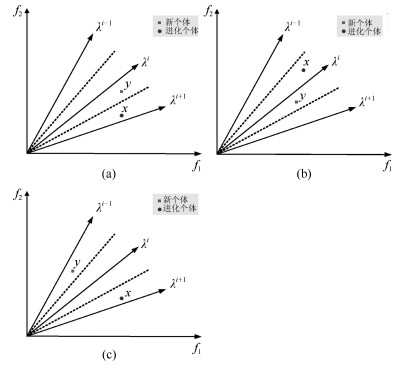
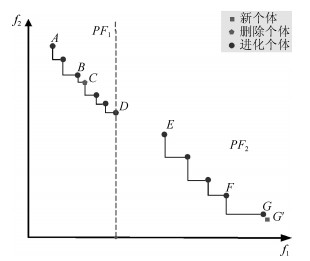
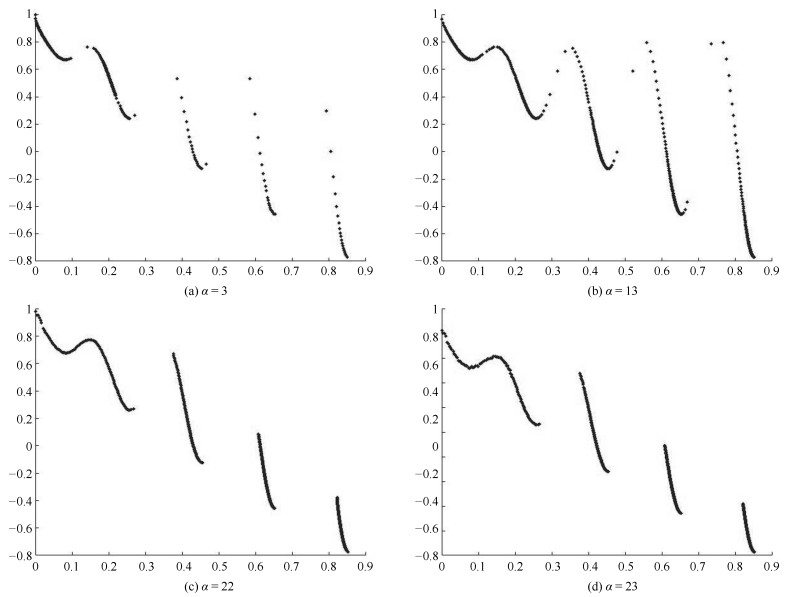
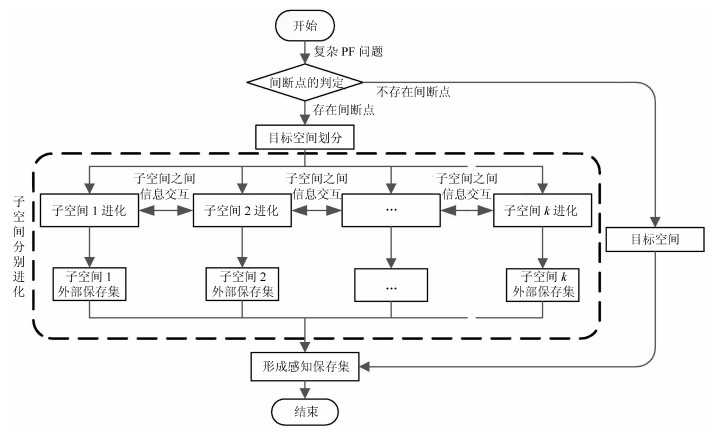
摘要: 多目标进化优化是求解多目标优化问题的可行方法.但是, 由于没有准确感知并充分利用问题的Pareto前沿, 已有方法难以高效求解复杂的多目标优化问题.本文提出一种基于在线感知Pareto前沿划分目标空间的多目标进化优化方法, 以利用感知的结果, 采用有针对性的进化优化方法求解多目标优化问题.首先, 根据个体之间的拥挤距离与给定阈值的关系感知优化问题的Pareto前沿上的间断点, 并基于此将目标空间划分为若干子空间; 然后, 在每一子空间中采用MOEA/D (Multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition)得到一个外部保存集; 最后, 基于所有外部保存集生成问题的Pareto解集.将提出的方法应用于15个基准数值函数优化问题, 并与NSGA-Ⅱ、RPEA、MOEA/D、MOEA/DPBI、MOEA/D-STM和MOEA/D-ACD等比较.结果表明, 提出的方法能够产生收敛和分布性更优的Pareto解集, 是一种非常有竞争力的方法.Abstract: Multi-objective evolutionary optimization is a feasible way to solve multi-objective optimization problems. However, previous methods have di–culties in e–ciently tackling a complex multi-objective optimization problem, since they cannot accurately perceive the shape of the Pareto front and take full advantages of it. A multi-objective evolutionary algorithm with objective space partition based on online perceiving the Pareto front of an optimization problem is proposed in this study. In the proposed method, a series of discontinuous points on a Pareto front which is getting from the relationship between the crowded distance of individuals and a given threshold are flrst detected. Then, the objective space is divided into a number of sub-spaces based on these points. In each sub-space, the multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition (MOEA/D) is employed to obtain an external archive set. Finally, the Pareto optimal set of the problem is formed based on all the external sets. The proposed method is compared with NSGA-Ⅱ, RPEA, MOEA/D, MOEA/D-PBI, MOEA/D-STM, and MOEA/D-ACD on 15 benchmark optimization problems. The results empirically demonstrate that the proposed method has capabilities in obtaining a Pareto optimal set with good performance in convergence and diversity, and is a competitive alternative for multi-objective optimization.
-
Key words:
- Multi-objective evolutionary optimization /
- Pareto front /
- discontinuous point /
- objective space division /
- MOEA/D
1) 本文责任编委 魏庆来 -
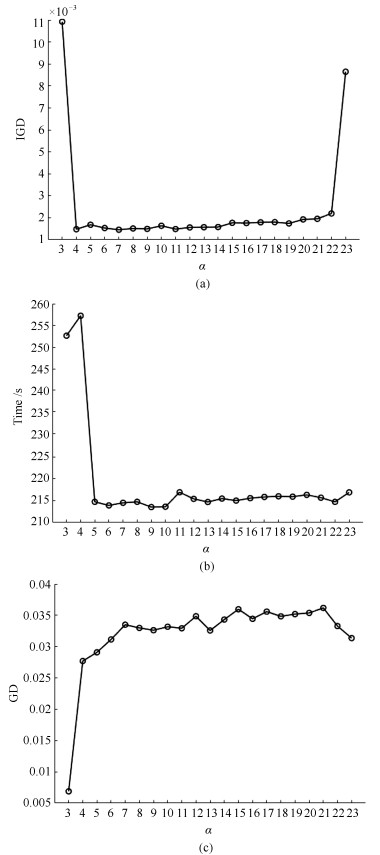
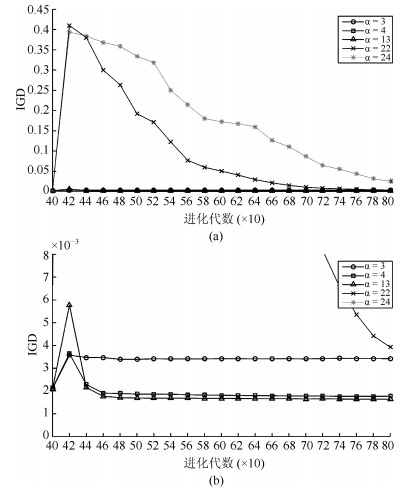
表 1 不同方法求解测试函数的IGD值
Table 1 The values of IGD obtained by different algorithms
优化问题 NSGA-Ⅱ RPEA MOEA/D MOEA/D-PBI MOEA/D-STM MOEA/D-ACD MOEA-PPF ZDT1 $6.546 \times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $2.260\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $8.708 \times 10^{-4}$ $1.608\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $7.637 \times10^{-4}\dagger$ ${\bf 7.629 \times 10^{-4}}\dagger$ $8.668 \times 10^{-4}$ ZDT2 $1.685\times 10^{-2}\dagger$ $4.700\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $8.392 \times 10^{-4}$ $1.110\times10^{-3}\dagger$ $7.507 \times 10^{-4}\dagger$ ${\bf 7.502 \times 10^{-4}}\dagger$ $8.368 \times 10^{-4}$ ZDT3 $2.647\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $3.534\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $2.038\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $3.978\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $2.060\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $2.050\times10^{-3}\dagger$ ${\bf 1.620 \times10^{-3}}$ ZDT4 $2.463\times 10^{-2}\dagger$ $2.198\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $7.791 \times 10^{-4}$ $1.277\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ ${\bf 7.637 \times 10^{-4}}\dagger$ $7.819 \times10^{-4}$ $7.719 \times10^{-4}$ ZDT6 $8.319 \times10^{-4}\dagger$ $1.177 \times10^{-1}\dagger$ $3.994 \times 10^{-4}$ $4.006 \times 10^{-4}$ ${\bf 3.811 \times10^{-4}}\dagger$ $5.225 \times 10^{-4}\dagger$ 3.988 $\times 10^{-4}$ KUR $3.962 \times10^{-1}$ $3.284\times 10^{-2}\dagger$ 1.012 $\times 10^{-2}$ $1.029 \times10^{-2}$ $9.779\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $9.853 \times 10^{-3}$ ${\bf 9.609 \times 10^{-3}}$ WFG1 $6.949 \times10^{-1}\dagger$ $4.685 \times10^{-1}\dagger$ $4.553 \times10^{-3}$ $3.248 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ $8.218 \times10^{-3}$ $4.680 \times10^{-1}\dagger$ ${\bf 3.940 \times 10^{-3}}$ WFG2 $3.968 \times 10^{-3}$ $1.049\times 10^{-3}\dagger$ $5.063 \times 10^{-3}$ $4.850 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ $4.805 \times 10^{-3}$ $5.241 \times 10^{-3}$ ${\bf 3.748 \times10^{-3}}$ WFG3 $3.198 \times10^{-3}$ $5.316 \times10^{-3}\dagger$ $2.953 \times10^{-3}$ $4.498 \times10^{-3}\dagger$ ${\bf 2.597 \times 10^{-3}}\dagger$ $2.747\times10^{-3}\dagger$ $2.951 \times10^{-3}$ WFG4 $2.665 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ $1.816 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ $5.724 \times10^{-3}$ $1.886 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ $8.427 \times10^{-3}\dagger$ $1.215 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ ${\bf 5.122 \times10^{-3}}$ WFG5 $6.206 \times10^{-3}\dagger$ $6.777 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ $6.326 \times10^{-2}$ $6.852 \times10^{-2}$ ${\bf 6.179\times10^{-2}}\dagger$ $6.287 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ $6.510 \times10^{-2}$ WFG6 $5.278 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ $7.205 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ $5.560 \times10^{-2}$ $5.597 \times10^{-2}$ $2.862 \times10^{-3}\dagger$ ${\bf 2.672\times10^{-3}}$ $5.287 \times10^{-2}$ WFG7 $3.186 \times10^{-3}\dagger$ $3.014 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ $2.663 \times10^{-3}$ $3.850 \times10^{-3}\dagger $ ${\bf 2.585\times10^{-3}}\dagger$ $2.666 \times10^{-3}$ $2.689 \times10^{-3}$ WFG8 $1.129 \times10^{-1}$ $1.017\times10^{-1}\dagger$ $1.033 \times10^{-1}\dagger$ $1.074 \times10^{-1}$ $9.793 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ ${\bf 8.302\times10^{-2}}\dagger$ $1.029 \times10^{-1}$ WFG9 $1.915 \times10^{-2}$ $1.272 \times10^{-2}\dagger$ $1.533 \times10^{-2}$ $2.155 \times10^{-2}$ $1.229 \times10^{-2}$ ${\bf 8.062\times10^{-3}}$ $1.522 \times10^{-2}$ †表示对比方法与本文方法的IGD指标具有显著差异(Mann-Whitney U分布检验, 置信水平为0.05) 表 2 不同方法获得的CR值
Table 2 Metric CR obtained by different algorithms
优化问题 NSGA-Ⅱ RPEA MOEA/D MOEA/D-PBI MOEA/D-STM MOEA/D-ACD MOEA-PPF ZDT1 0.9400 0.6860 0.9440 0.9360 0.9440 0.9440 0.9440 ZDT2 0.9260 0.6380 0.9960 0.9940 0.9960 0.9960 0.9960 ZDT3 0.6440 0.4340 0.5760 0.6460 0.5760 0.6720 0.7480 ZDT4 0.9340 0.6320 0.9440 0.9340 0.9440 0.9420 0.9440 ZDT6 0.9460 0.6640 0.9960 0.9960 0.9960 0.9960 0.9960 KUR 0.8020 0.6060 0.7800 0.9160 0.7780 0.8940 0.9140 WFG1 0.7320 0.3620 0.8700 0.8240 0.8480 0.4520 0.8720 WFG2 0.6100 0.3680 0.4880 0.6060 0.4860 0.6220 0.7360 WFG3 0.9460 0.8260 0.9920 0.9960 0.9960 0.9960 0.9960 WFG4 0.9280 0.5820 0.9500 0.9520 0.8440 0.8340 0.9560 WFG5 0.9020 0.5760 0.9180 0.9180 0.9540 0.9140 0.9200 WFG6 0.9000 0.5500 0.9460 0.9580 0.9620 0.9620 0.9580 WFG7 0.9240 0.5780 0.9660 0.9700 0.9680 0.9620 0.9680 WFG8 0.5400 0.3500 0.9060 0.9220 0.9140 0.9180 0.9000 WFG9 0.9220 0.6340 0.9260 0.9280 0.8920 0.9220 0.8980 -
[1] 左兴权, 王春露, 赵新超.一种结合多目标免疫算法和线性规划的双行设备布局方法.自动化学报, 2015, 41(3): 528-540 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140082Zuo Xing-Quan, Wang Chun-Lu, Zhao Xin-Chao. Combining multi-objective immune algorithm and linear programming for double row layout problem. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(3): 528-540 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140082 [2] Han Y Y, Gong D W, Jin Y C, Pan Q K. Evolutionary multi-objective blocking lot-streaming flow shop scheduling with interval processing time. Applied Soft Computing, 2016, 42: 229-245 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2016.01.033 [3] Li Y M, Tong S C. Adaptive fuzzy output-feedback stabilization control for a class of switched nonstrict-feedback nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(4): 1007-1016 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2536628 [4] 段凯蓉, 张功萱.基于多目标免疫系统算法的云任务调度策略.计算机应用, 2016, 36(2): 324-329 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsjyy201602007Duan Kai-Rong, Zhang Gong-Xuan. Multi-objective immune system algorithm for task scheduling in cloud computing. Journal of Computer Applications, 2016, 36(2): 324-329 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsjyy201602007 [5] Deb K. Multi-Objective Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithms. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2001. 277-293 [6] 刘元, 郑金华, 邹娟, 喻果.基于邻域竞赛的多目标优化算法.自动化学报, 2018, 44(7): 1304-1320 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160315Liu Yuan, Zheng Jin-Hua, Zou Juan, Yu Guo. An evolutionary algorithm through neighborhood competition for multi-objective optimization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(7): 1304-1320 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160315 [7] 乔俊飞, 韩改堂, 周红标.基于知识的污水生化处理过程智能优化方法.自动化学报, 2017, 43(6): 1038-1046 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c170088Qiao Jun-Fei, Han Gai-Tang, Zhou Hong-Biao. Knowledge-based intelligent optimal control for wastewater biochemical treatment process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(6): 1038-1046 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c170088 [8] 丁进良, 杨翠娥, 陈立鹏, 柴天佑.基于参考点预测的动态多目标优化算法.自动化学报, 2017, 43(2): 313-320 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150811Ding Jin-Liang, Yang Cui-E, Chen Li-Peng, Chai Tian-You. Dynamic multi-objective optimization algorithm based on reference point prediction. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(2): 313-320 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150811 [9] 巩敦卫, 刘益萍, 孙晓燕, 韩玉艳.基于目标分解的高维多目标并行进化优化方法.自动化学报, 2015, 41(8): 1438-1451 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140832Gong Dun-Wei, Liu Yi-Ping, Sun Xiao-Yan, Han Yu-Yan. Parallel many-objective evolutionary optimization using objectives decomposition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(8): 1438-1451 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c140832 [10] Li H, Zhang Q F. Multiobjective optimization problems with complicated Pareto sets, MOEA/D and NSGA-Ⅱ. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13(2): 284-302 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2008.925798 [11] Geoffrion A M. Proper efficiency and the theory of vector maximization. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 1968, 22(3): 618-630 doi: 10.1016/0022-247X(68)90201-1 [12] Zadeh L. Optimality and non-scalar-valued performance criteria. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1963, 8(1): 59-60 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1963.1105511 [13] Fonseca C M, Fleming P J. Genetic algorithms for multiobjective optimization: formulation, discussion and generalization. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Genetic Algorithms. San Mateo, USA: ACM, 1993. 416-423 [14] Srinivas N, Deb K. Muiltiobjective optimization using nondominated sorting in genetic algorithms. Evolutionary Computation, 1994, 2(3): 221-248 doi: 10.1162/evco.1994.2.3.221 [15] Horn J, Nafpliotis N, Goldberg D E. A niched Pareto genetic algorithm for multiobjective optimization. In: Proceedings of the 1st IEEE Conference on Evolutionary Computation. IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence. Orlando, USA: IEEE, 1994. 82-87 [16] Zitzler E, Laumanns M, Thiele L. SPEA2: improving the strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm. In: Proceedings of 2002 Evolutionary Methods for Design, Optimisation and Control with Application to Industrial Problems. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag, 2002. 95-100 [17] Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal A, Meyarivan T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-Ⅱ. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182-197 doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 [18] Corne D W, Jerram N R, Knowles J D, Oates M J. PESA-Ⅱ: region-based selection in evolutionary multiobjective optimization. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation. San Francisco, California, USA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2001. 283-290 [19] Bader J, Zitzler E. HypE: An algorithm for fast hypervolume-based many-objective optimization. Evolutionary Computation, 2011, 19(1): 45-76 doi: 10.1162/EVCO_a_00009 [20] Zitzler E, Künzli S. Indicator-based selection in multiobjective search. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature. Birmingham, UK: Springer-Verlag, 2004. 832-842 [21] Gu F Q, Liu H L. A novel weight design in multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security. Nanning, China: IEEE, 2010. 137-141 [22] Qi Y T, Ma X L, Liu F, Jiao L C, Sun J Y, Wu J S. MOEA/D with adaptive weight adjustment. Evolutionary Computation, 2014, 22(2): 231-264 doi: 10.1162/EVCO_a_00109 [23] Cheng R, Jin Y C, Olhofer M, Sendhoff B. A reference vector guided evolutionary algorithm for many-objective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2016, 20(5): 773-791 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2016.2519378 [24] Asafuddoula M, Singh H K, Ray T. An enhanced decomposition-based evolutionary algorithm with adaptive reference vectors. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(8): 2321-2334 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2737519 [25] Liu Y P, Gong D W, Sun X Y, Zhang Y. Many-objective evolutionary optimization based on reference points. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 50: 344-355 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2016.11.009 [26] Zhang Q F, Li H. MOEA/D: A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2007, 11(6): 712-731 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2007.892759 [27] Li K, Zhang Q F, Kwong S, Li M Q, Wang R. Stable matching-based selection in evolutionary multiobjective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2014, 18(6): 909-923 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2013.2293776 [28] Wang L P, Zhang Q F, Zhou A M, Gong M G, Jiao L C. Constrained subproblems in a decomposition-based multiobjective evolutionary algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2016, 20(3): 475-480 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2015.2457616 [29] Storn R, Price K. Differential evolution --- A simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. Journal of Global Optimization, 1997, 11(4): 341-359 doi: 10.1023/A:1008202821328 [30] Dorigo M, Maniezzo V, Colorni A. Ant system: Optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 1996, 26(1): 29-41 doi: 10.1109/3477.484436 [31] Branke J, Mostaghim S. About selecting the personal best in multi-objective particle swarm optimization. Parallel Problem Solving from Nature-PPSN IX. Berlin, Island: Springer, 2006. 52-532 [32] 雷德明, 吴智铭. Pareto档案多目标粒子群优化.模式识别与人工智能, 2006, 19(4): 475-480 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2006.04.008Lei De-Ming, Wu Zhi-Ming. Pareto archive multi-objective particle swarm optimization. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2006, 19(4): 475-480 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6059.2006.04.008 [33] Huang V L, Suganthan P N, Liang J J. Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for solving multiobjective optimization problems. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2006, 21(2): 209-226 doi: 10.1002/int.20128 [34] 公茂果, 程刚, 焦李成, 刘超.基于自适应划分的进化多目标优化非支配个体选择策略.计算机研究与发展, 2011, 48(4): 545-557 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsjyjyfz201104001Gong Mao-Guo, Cheng Gang, Jiao Li-Cheng, Liu Chao. Nondominated individual selection strategy based on adaptive partition for evolutionary multi-objective optimization. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2011, 48(4): 545-557 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsjyjyfz201104001 [35] Deng L Y, Lin V, Chen M. Hybrid ant colony optimization for the resource-constrained project scheduling problem. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 21(1): 67-71 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c215fe8cdf5ed804894cd3567dd3ab04&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [36] Zheng W, Wu X X, Yang X B, Cao S C, Liu W X, Lin J. Test suite minimization with mutation testing-based many-objective evolutionary optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Software Analysis, Testing and Evolution. Harbin, China: IEEE, 2017. 32-36 [37] Wang R, Ishibuchi H, Zhang Y, Zheng X K, Zhang T. On the effect of localized PBI method in MOEA/D for multi-objective optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI). Athens, Greece: IEEE, 2016. 1-8 [38] Jiang S Y, Yang S X. An improved multiobjective optimization evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition for complex Pareto fronts. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(2): 421-437 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2403131 [39] Deb K, Thiele L, Laumanns M, Zitzler E. Scalable test problems for evolutionary multiobjective optimization. Evolutionary Multiobjective Optimization: Theoretical Advances and Applications. London: Springer, 2005. 187-196 [40] Kursawe F. A variant of evolution strategies for vector optimization. In: Proceedings of the 1st Workshop Parallel Problem Solving from Nature. Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 1991. 193-197 [41] Huband S, Barone L, While L, Hingston P. A scalable multi-objective test problem toolkit. Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2005. 280-295 [42] Zhang Q, Zhou A, Zhao S, Suganthan P N, Liu W, Tiwari S. Multiobjective Optimization Test Instances for the CEC 2009 Special Session and Competition, Technical Report CES-487, University of Essex and Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 2008. -




 下载:
下载: