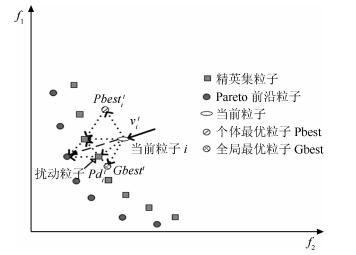
-
摘要: 高维多目标优化问题由于具有巨大的目标空间使得一些经典的多目标优化算法面临挑战.提出一种基于自适应模糊支配的高维多目标粒子群算法MAPSOAF,该算法定义了一种自适应的模糊支配关系,通过对模糊支配的阈值自适应变化若干步长,在加强个体间支配能力的同时实现对种群选择压力的精细化控制,以改善算法的收敛性;其次,通过从外部档案集中选取扰动粒子,并在粒子速度更新公式中新增一扰动项以克服粒子群早熟收敛并改善个体分布的均匀性;另外,算法利用简化的Harmonic归一化距离评估个体的密度,在改善种群分布性的同时降低算法的计算代价.该算法与另外五种高性能的多目标进化算法在标准测试函数集DTLZ{1,2,4,5}上进行对比实验,结果表明该算法在收敛性和多样性方面总体上具有较显著的性能优势.
-
关键词:
- 自适应模糊支配 /
- 精英个体扰动 /
- 粒子群算法 /
- 高维多目标优化问题 /
- 高维多目标粒子群优化算法
Abstract: The huge objective space makes some representative multiobjective optimization algorithms face challenges. A many-objective particle swarm optimization based on adaptive fuzzy dominance (MAPSOAF) is proposed. An adaptive fuzzy dominance relation is defined to adjust the threshold of fuzzy dominance adaptively to improve the convergence of MAPSOAF. Second, a perturbation term is added to the particle's velocity formula by selecting an elite member from the external archive to conquer premature convergence and to enhance the diversity of population. In addition, a method of simplified Harmonic normalized distance is utilized to evaluate the density of individuals and reduce the computational cost when while improving the population diversity. MAPSOAF is compared with other five high-performance multiobjective evolutionary algorithms on the benchmark test set DTLZ {1, 2, 4, 5}, and the results show that the proposed MAPSOAF has more significant performance advantages in convergence and diversity over the peering algorithms.1) 本文责任编委 魏庆来 -
表 1 5种对比算法的参数设置
Table 1 Parameter settings of all the algorithms compared
Algorithm Parameter settings NSGA-II ${N}=100, P_{c}=0.9, P_{m}=1/n, \eta_{c}=20, \eta_{m}=20$ SPEA2 ${N}=100, P_{c}=0.9, P_{m}=1/n, \eta_{c}=20, \eta_{m}=20$ SMPSO ${C}_1\in[1.5, 2.5], C_2\in[1.5, 2.5], P_{m}=1/n, \eta_{m}=20$ AbYSS ${N}=100, N_{RefSet1}=10, N_{RefSet2}=10, P_{c}=0.9, P_{m}=1/n, \eta_{c}=20, \eta_{m}=20$ MOEA/D-ACD ${N}=100, CR=1.0, F=0.5, P_{m}=1/n, \eta_{m}=20, \delta=0.9, n_{r}=2$ 表 2 各算法在DTLZ1函数上获得IGD值的比较
Table 2 Results of IGD for algorithms compared based on DTLZ1
各项指标 算法 NSGA-II AbYSS SPEA2 SMPSO MOEA$/$D-ACD MAPSOAF 目标个数 4目标 mean 2.0458E-01 9.5918E-02 1.7712E-01 7.8417E-02 3.4736E-01 8.2288E-02 std 5.6012E-04 5.5421E-04 1.1871E-04 4.0001E-04 5.8170E-05 8.4901E-04 rank 5 $-$ 3 $-$ 4 $-$ 1 + 6 $-$ 2 10目标 mean 6.7936E-01 5.9651E-01 6.1816E-01 5.0051E-01 6.9881E-01 4.9810E-01 std 4.9647E-04 7.5481E-04 3.6454E-04 4.7007E-04 4.4327E-05 7.5541E-04 rank 5 $-$ 3 $-$ 4 $-$ 2 $\approx$ 6 $-$ 1 30目标 mean 7.9579E-01 7.8171E-01 7.7545E-01 7.4014E-01 8.0986E-01 6.5187E-01 std 2.1294E-04 4.5699E-03 6.5441E-04 0.00E+00 2.9857E-04 5.3458E-03 rank 5 $-$ 3 $-$ 4 $-$ 2 $\approx$ 6 $-$ 1 rank sum 15 10 11 5 18 4 final rank 5 3 4 2 6 1 better$/$worst$/$similar 0$/3/$0 0$/3/$0 0$/3/$0 1$/1/$1 0$/3/$0 $/$ 表 3 各算法在DTLZ2函数上获得IGD值的比较
Table 3 Results of IGD for algorithms compared based on DTLZ2
各项指标 算法 NSGA-II AbYSS SPEA2 SMPSO MOEA$/$D-ACD MAPSOAF 目标个数 4目标 mean 7.0109E-02 2.8412E-01 3.5341E-01 1.5415E-01 4.1627E-01 8.9241E-02 std 5.1015E-04 7.1918E-04 6.8418E-04 4.5159E-04 1.8748E-04 4.6174E-04 rank 1+ 4 $-$ 5 $-$ 3 $-$ 6 $-$ 2 10目标 mean 5.2851E-01 5.6171E-01 6.0151E-01 5.5241E-01 6.9741E-01 4.8169E-01 std 5.6740E-04 6.9151E-04 5.9871E-04 5.1762E-04 3.5061E-04 5.5651E-04 rank 2 $\approx$ 4 $-$ 5 $-$ 3 $-$ 6 $-$ 1 30目标 mean 7.5548E-01 7.8851E-01 7.8158E-01 7.7941E-01 7.9967E-01 6.9181E-01 std 6.5141E-03 5.9210E-04 4.2225E-04 6.2131E-03 5.1101E-04 3.6518E-03 rank 2 $-$ 5 $-$ 4 $-$ 3 $-$ 6 $-$ 1 rank sum 5 13 14 9 18 4 final rank 2 4 5 3 6 1 better$/$worst$/$similar 1$/1/$1 0$/3/$0 0$/3/$0 0$/0/$0 0$/3/$0 $/$ 表 4 各算法在DTLZ4函数上获得IGD值的比较
Table 4 Results of IGD for algorithms compared based on DTLZ4
各项指标 算法 NSGA-II AbYSS SPEA2 SMPSO MOEA$/$D-ACD MAPSOAF 目标个数 4目标 mean 8.3841E-02 2.1541E-01 2.6114E-01 1.5116E-01 7.1981E-02 7.9141E-02 std 3.2987E-04 4.1123E-04 5.6101E-04 6.8917E-04 3.3176E-04 4.5005E-04 rank 3 $\approx$ 5 $-$ 6 $-$ 4 $-$ 1+ 2 10目标 mean 5.8584E-01 6.5141E-01 6.9184E-01 6.6810E-01 5.4214E-01 5.9515E-01 std 5.8771E-04 4.4414E-04 6.6516E-04 7.0151E-04 3.6011E-04 4.6001E-04 rank 2 $\approx$ 4 $-$ 6 $-$ 5 $-$ 1+ 3 30目标 mean 7.5541E-01 8.2994E-01 8.0441E-01 8.1945E-01 7.0713E-01 7.9541E-01 std 8.8151E-03 8.5104E-04 2.9414E-03 4.6054E-03 5.6807E-03 5.1112E-03 rank 2 $-$ 6 $-$ 4 $-$ 5 $-$ 1+ 3 rank sum 7 15 16 14 3 8 final rank 2 5 6 4 1 3 better$/$worst$/$similar 0$/2/$1 0$/3/$0 0$/3/$0 0$/3/$0 3$/0/$0 $/$ 表 5 各算法在DTLZ5函数上获得IGD值的比较
Table 5 Results of IGD for algorithms compared based on DTLZ5
各项指标 算法 NSGA-II AbYSS SPEA2 SMPSO MOEA$/$D-ACD MAPSOAF 目标个数 4目标 mean 1.38121E-01 1.6051E-01 1.7717E-01 9.5651E-02 1.8678E-01 9.1410E-02 std 5.6012E-04 5.5421E-04 1.1871E-04 4.0001E-04 5.8170E-05 8.4901E-04 rank 3 $-$ 4 $-$ 5 $-$ 2 $\approx$ 6 $-$ 1 10目标 mean 6.5172E-01 7.1141E-01 7.0914E-01 6.9241E-01 7.2661E-01 5.0941E-01 std 7.5615E-04 5.5551E-04 4.1191E-04 6.4101E-04 5.5827E-04 5.9151E-04 rank 2 $\approx$ 5 $-$ 4 $-$ 3 $-$ 6 $-$ 1 30目标 mean 7.7141E-01 7.8810E-01 7.6585E-01 7.6151E-01 7.9841E-01 6.9510E-01 std 3.4287E-03 8.8140E-04 3.9410E-03 4.6415E-03 8.2662E-04 4.6519E-03 rank 4 $-$ 5 $-$ 3 $-$ 2 $-$ 6 $-$ 1 rank sum 9 14 13 7 18 3 final rank 3 5 4 2 6 1 better$/$worst$/$similar 0$/2/$1 0$/3/$0 0$/3/$0 0$/3/$1 0$/3/$0 $/$ -
[1] Adra S F, Fleming P J. A diversity management operator for evolutionary many-objective optimisation. In: International Conference on Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization. Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany: Springer-Verlag, 2009. 81-94 [2] Wagner T, Beume N, Naujoks B. Pareto-, aggregation-, and indicator-based methods in many-objective optimization. In: International Conference on Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization. Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany: Springer-Verlag, 2007. 742-756 [3] Li M Q, Yang S X, Liu X H. Shift-based density estimation for Pareto-based algorithms in many-objective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2014, 18(3):348-365 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2013.2262178 [4] 陈振兴, 严宣辉, 吴坤安, 白猛.融合张角拥挤控制策略的高维多目标优化.自动化学报, 2015, 41(6):1145-1158 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18689.shtmlChen Zhen-Xing, Yan Xuan-Hui, Wu Kun-An, Bai Meng. Many-objective optimization integrating open angle based congestion control strategy. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(6):1145-1158 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18689.shtml [5] 巩敦卫, 刘益萍, 孙晓燕, 韩玉艳.基于目标分解的高维多目标并行进化优化方法.自动化学报, 2015, 41(8):1438-1451 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2015/V41/I8/1438Gong Dun-Wei, Liu Yi-Ping, Sun Xiao-Yan, Han Yu-Yan. Parallel many-objective evolutionary optimization using objectives decomposition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(8):1438-1451 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2015/V41/I8/1438 [6] Drechsler D, Drechsler R, Becker B. Multi-objective optimisation based on relation favour. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization. London, UK: Springer-Verlag, 2001. 154-166 [7] Di Pierro F, Djordjević S, Kapelan Z, Khu S T, Savić D, Walters G A. Automatic calibration of urban drainage model using a novel multi-objective genetic algorithm. Water Science and Technology, 2005, 52(5):43-52 doi: 10.2166/wst.2005.0105 [8] Sato H, Aguirre H E, Tanaka K. Controlling dominance area of solutions and its impact on the performance of MOEAs. In: International Conference on Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol.4403. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2007. 5-20 [9] Hernández-Díaz A, Santana-Quintero L, Coello-Coello C, Molina J. Pareto-adaptive ε-dominance. Evolutionary Computation, 2007, 15(4):493-517 doi: 10.1162/evco.2007.15.4.493 [10] Kang Z, Kang L S, Zou X F, Liu M Z, Li C H, Yang M, et al. A new evolutionary decision theory for many-objective optimization problems. In: Advances in Computation and Intelligence. Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 2007. 1-11 [11] Zou X F, Chen Y, Liu M Z, Kang L S. A new evolutionary algorithm for solving many-objective optimization problems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part B:Cybernetics, 2008, 38(5):1402-1412 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2008.926329 [12] Farina M, Amato P. A fuzzy definition of "optimality" for many-criterion optimization problems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A:Systems and Humans, 2004, 34(3):315-326 doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2004.824873 [13] 毕晓君, 张永建, 陈春雨.基于模糊支配的高维多目标进化算法MFEA.电子学报, 2014, 42(8):1653-1659 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2014.08.031Bi Xiao-Jun, Zhang Yong-Jian, Chen Chun-Yu. A many-objective evolutionary algorithm based on fuzzy dominance:MFEA. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2014, 42(8):1653-1659 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2014.08.031 [14] Kennedy J, Eberhart R C. Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks. Perth, WA, Australia: IEEE, 1995. 1942-1948 [15] 肖婧, 毕晓君, 王科俊.基于全局排序的高维多目标优化研究.软件学报, 2015, 26(7):1574-1583 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb201507002Xiao Jing, Bi Xiao-Jun, Wang Ke-Jun. Research of global ranking based many-objective optimization. Journal of Software, 2015, 26(7):1574-1583 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb201507002 [16] Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm:NSGA-Ⅱ. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2):182-197 doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 [17] Nebro A J, Luna F, Alba E, Dorronsoro B, Durillo J J, Beham A. AbYSS:adapting scatter search to multiobjective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2008, 12(4):439-457 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2007.913109 [18] Zitzler E, Laumanns M, Thiele L. SPEA2: Improving the Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm, TIK-Report 103, 2001. [19] Nebro A J, Durillo J J, Garcia-Nieto J, Coello Coello C A, Luna F, Alba E. SMPSO: a new PSO-based metaheuristic for multi-objective optimization. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM). Nashville, TN, USA, 2009, 66-73 [20] Wang L P, Zhang Q F, Zhou A M, Gong M G, Jiao L C. Constrained subproblems in a decomposition-based multiobjective evolutionary algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2016, 20(3):475-480 doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2015.2457616 [21] Deb K, Thiele L, Laumanns M, Zitzler E. Scalable multi-objective optimization test problems. In: Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2002. 825-830 [22] Zhang Q F, Zhou A M, Zhao S Z, Suganthan P N, Liu W D, Tiwari S. Multiobjective Optimization Test Instances for the CEC 2009 Special Session and Competition, Technical Report CES-487, 2009. -




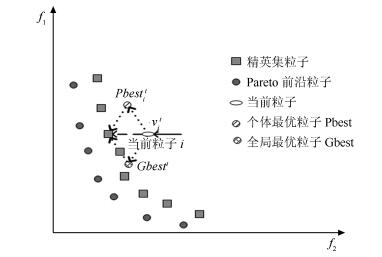
 下载:
下载: