Development of Several Studies on Indirect Reciprocity and the Evolution of Cooperation
-
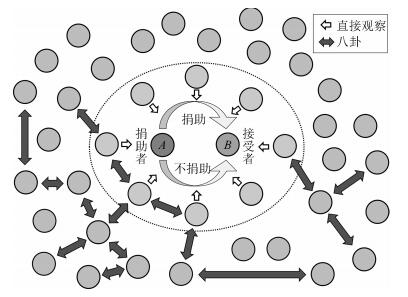
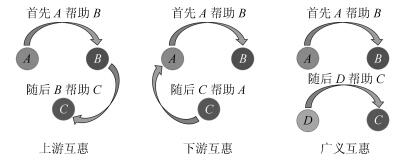
摘要: 2005年Science杂志指出"合作行为如何进化"是21世纪最关键的25个科学问题之一.间接互惠如何促进合作演化的研究已吸引了包括经济学家、社会学家和演化生物学家等众多学者的关注.这是由于:人类社会道德的形成、社会化分工、语言的出现、人类大脑的进化等都和间接互惠密不可分;随着经济全球化和网络时代的到来,依赖声望和信誉的陌生个体间的交易日益频繁,局部信息条件下个体的信任被利用的"道德风险"逐渐增大.本文所关注的间接互惠是以声望为核心的"下游互惠",具体而言,个体通过帮助他人建立自己在群体中的好声望,从而期待未来获得他人的帮助.可见,声望是"下游互惠"发挥作用的关键.声望的建立引发了两方面的研究:1)如何评价个体声望的好与坏,焦点是何种声望评估准则能够促进合作的演化;2)个体的声望如何在群体中快速、准确、广泛地传播,使得陌生个体间能够获得彼此的声望信息,其中八卦这种声望传播方式成为间接互惠的研究热点之一.基于声望的间接互惠研究前景广阔,未来可能的研究方向主要有复杂网络上的间接互惠、声望传播系统的鲁棒性、声望共享系统的建立和间接互惠在P2P网络中的应用.Abstract: How does cooperation evolve' has been considered as one of the most important scientific problems in the 21st century since 2005. The study about indirect reciprocity has attracted increasing attention from researchers such as economists, sociologists, and evolutionary biologists. There are mainly two reasons for this:Indirect reciprocity is closely related to the formation of human morality, socialized labor division, emergence of language, human brain evolution, and many other social developments; the deal among strangers, which mainly depends on reputation and credit, becomes more and more frequent with the economic globalization and the Internet era coming, thus the 'moral risk' of individual trust being exploited is increasing under local information conditions. In this paper, we focus on 'downstream reciprocity' which belongs to a form of indirect reciprocity and is based on reputation, specifically, individuals can obtain good reputation by helping others and then look forward to getting others' help in future. Obviously, reputation is the key factor for 'downstream reciprocity' to work. The establishment of reputation has motivated two studies:How do we define good reputation and bad reputation? Such studies aim to answer which reputation evaluation criterion can promote the evolution of cooperation; how does individual reputation information spread among strangers quickly, accurately, and widely so that individuals can know each other's reputation? Here, gossip, as one way of reputation dispersal, becomes one hot research topic. Indirect reciprocity based on reputation is a promising study, and the possible future research topics are indirect reciprocity in complex networks, robustness of reputation dispersal system, establishment of reputation sharing system, and application of indirect reciprocity in the P2P network.
-
Key words:
- Evolutionary game theory /
- indirect reciprocity /
- reputation evaluation criterion /
- gossip /
- P2P network
1) 本文责任编委 张化光 -
表 1 声望评估准则
Table 1 Reputation evaluation criterion
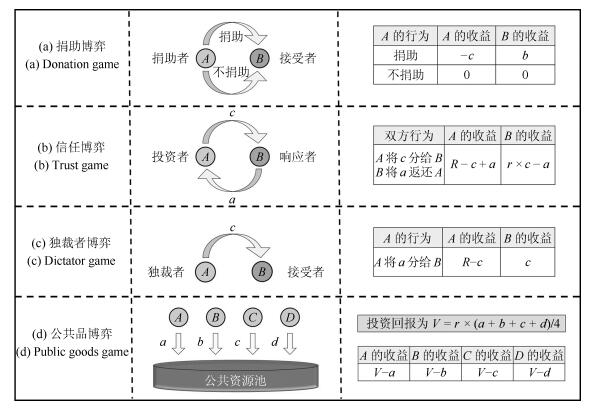
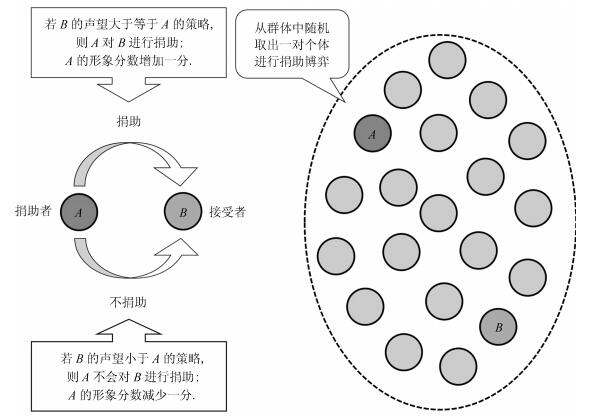
声望评估准则 定义 数量(种) 典型的例子 "一阶评估" 考虑捐助者行为 $2^2=4$ "形象分数" "二阶评估" 同时考虑捐助者行为和接受者声望 ${(2^2)}^2=16$ "温和准则"、"严苛准则" "三阶评估" 同时考虑捐助者行为和声望及接受者声望 ${({(2^2)}^2)}^2=256$ 表 2 典型的"二阶评估"
Table 2 Representative "second-order evaluation"
捐助者行为/接受者声望 捐助/好 捐助/坏 不捐助/好 不捐助/坏 "温和准则" 好 坏 坏 好 "严苛准则" 好 坏 坏 坏 表 3 8种促进合作演化的声望评估准则
Table 3 Eight reputation evaluation criterions which favor the evolution of cooperation
捐助者声望/接受者声望 好/好 好/坏 坏/好 坏/坏 捐助者捐助 好 未知 好 未知 捐助者不捐助 坏 好 坏 未知 -
[1] Darwin C. On the origin of species by means of natural selection. Science, 1963, 71(6):354-357 http://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/1228 [2] McDonald D B. Cooperation among animals:an evolutionary perspective. Lee Alan Dugatkin. The Quarterly Review of Biology, 1998, 73(3):387-388 doi: 10.1086/420391 [3] Nowak M A, Sigmund K. Evolutionary dynamics of biological games. Science, 2004, 303(5659):793-799 doi: 10.1126/science.1093411 [4] Clutton-Brock T. Cooperation between non-kin in animal societies. Nature, 2009, 462(7269):51-57 doi: 10.1038/nature08366 [5] Darwin C. The Works of Charles Darwin, Volume 15:On the Origin of Species 1859. New York:New York University Press, 2010. 69-83 [6] Axelrod R, Axelrod D E, Pienta K J. Evolution of cooperation among tumor cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(36):13474-13479 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606053103 [7] Smith E A. Communication and collective action:language and the evolution of human cooperation. Evolution and Human Behavior, 2010, 31(4):231-245 doi: 10.1016/j.evolhumbehav.2010.03.001 [8] Tuyls K, Parsons S. What evolutionary game theory tells us about multiagent learning. Artificial Intelligence, 2007, 171(7):406-416 doi: 10.1016/j.artint.2007.01.004 [9] Hardin G. The tragedy of the commons. Science, 1968, 162(3859):1243-1248 doi: 10.1126/science.162.3859.1243 [10] Milinski M, Sommerfeld R D, Krambeck H J, Reed F A, Marotzke J. The collective-risk social dilemma and the prevention of simulated dangerous climate change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(7):2291-2294 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709546105 [11] Requejo R J, Camacho J. Evolution of cooperation mediated by limiting resources:connecting resource based models and evolutionary game theory. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2011, 272(1):35-41 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.12.005 [12] Zhang Y, He J H. Research on the mobile net business knowledge sharing strategy of fraud evade. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 631-632:1171-1173 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272113750_Research_on_the_Mobile_Net_Business_Knowledge_Sharing_Strategy_of_Fraud_Evade [13] Pennisi E. How did cooperative behavior evolve? Science, 2005, 309(5731):93 doi: 10.1126/science.309.5731.93 [14] Smith J M, Price G R. The logic of animal conflict. Nature, 1973, 246(5427):15-18 doi: 10.1038/246015a0 [15] Fu F. Evolutionary Games and Evolution of Cooperation[Ph.D. dissertation], Peking University, China, 2009. [16] Chen X J. Evolutionary Dynamics of Cooperation in Complex Networks[Ph.D. dissertation], Peking University, China, 2010. [17] Wu B. Evolutionary Game Dynamics in Finite Populations[Ph.D. dissertation], Peking University, China, 2011. [18] Wang J. Evolutionary Game Dynamics in Populations[Ph.D. dissertation], Peking University, China, 2011. [19] Zhang C Y. Cooperation in Evolutionary Games on Networks of Agents[Ph.D. dissertation], Peking University, China, 2012. [20] Zhang J L. Cooperation Mechanisms in Evolutionary Games[Ph.D. dissertation], Peking University, China, 2013. [21] Wu T. Evolutionary Cooperation Dynamics[Ph.D. dissertation], Peking University, China, 2013. [22] Yang Z H. Evolutionary Games and Evolutionary Cooperation Dynamics in Complex Networks[Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, China, 2014. [23] Zhang Y L. Two Theoretical Methods upon the Evolution of Cooperation in Finite Populations and the Applications[Ph.D. dissertation], Peking University, China, 2015. [24] Cong R. Coevolutionary Games on Complex Networks[Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, China, 2014. [25] Du J M. Evolutionary Game Dynamics in Complex Systems[Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, China, 2016. [26] Li K. Evolutionary Dynamics in Collective Behavior[Ph.D. dissertation], Peking University, China, 2016. [27] 王龙, 伏锋, 陈小杰, 王靖, 李卓政, 谢广明, 楚天广.复杂网络上的演化博弈.智能系统学报, 2007, 2(2):1-10 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xdkjyc200702001Wang Long, Fu Feng, Chen Xiao-Jie, Wang Jing, Li Zhuo-Zheng, Xie Guang-Ming, Chu Tian-Guang. Evolutionary games on complex networks. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2007, 2(2):1-10 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xdkjyc200702001 [28] 王龙, 伏锋, 陈小杰, 王靖, 武斌, 楚天广, 谢广明.复杂网络上的群体决策.智能系统学报, 2008, 3(2):95-108 http://www.docin.com/p-1440573413.htmlWang Long, Fu Feng, Chen Xiao-Jie, Wang Jing, Wu Bin, Chu Tian-Guang, Xie Guang-Ming. Collective decision-making over complex networks. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2008, 3(2):95-108 http://www.docin.com/p-1440573413.html [29] 王龙, 王靖, 武斌.量子博弈:新方法与新策略.智能系统学报, 2008, 3(4):294-304 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JSJA201410056.htmWang Long, Wang Jing, Wu Bin. Quantum games:new methodologies and strategies. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2008, 3(4):294-304 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JSJA201410056.htm [30] 王龙, 吴特, 张艳玲.共演化博弈中的反馈机制.控制理论与应用, 2014, 31(7):823-836 https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/5b517652f12d2af90342e609.htmlWang Long, Wu Te, Zhang Yan-Ling. Feedback mechanism in coevolutionary games. Control Theory & Applications, 2014, 31(7):823-836 https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/5b517652f12d2af90342e609.html [31] Boccabella A, Natalini R, Pareschi L. On a continuous mixed strategies model for evolutionary game theory. Kinetic & Related Models, 2011, 4(1):187-213 https://arxiv.org/abs/1112.3663?context=cond-mat.stat-mech [32] Salimi Sartakhti J, Manshaei M H, Sadeghi M. MMP-TIMP interactions in cancer invasion:an evolutionary game-theoretical framework. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2017, 412:17-26 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2016.09.019 [33] Perc M, Jordan J J, Rand D G, Wang Z, Boccaletti S, Szolnoki A. Statistical physics of human cooperation. Physics Reports, 2017, 687:1-51 doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2017.05.004 [34] Wang Z, Jusup M, Wang R W, Shi L, Iwasa Y, Moreno Y, Kurths J. Onymity promotes cooperation in social dilemma experiments. Science Advances, 2017, 3(3):Article No.e1601444 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1601444 [35] Allen B, Lippner G, Chen Y T, Fotouhi B, Momeni N, Yau S T, Nowak M A. Evolutionary dynamics on any population structure. Nature, 2017, 544(7649):227-230 doi: 10.1038/nature21723 [36] Taylor C, Nowak M A. Transforming the dilemma. Evolution, 2007, 61(10):2281-2292 doi: 10.1111/evo.2007.61.issue-10 [37] Rand D G, Nowak M A. Human cooperation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2013, 17(8):413-425 doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2013.06.003 [38] Nowak M A. Five rules for the evolution of cooperation. Science, 2006, 314(5805):1560-1563 doi: 10.1126/science.1133755 [39] Zaggl M A. Eleven mechanisms for the evolution of cooperation. Journal of Institutional Economics, 2014, 10(2):197-230 doi: 10.1017/S1744137413000374 [40] Boyd R, Richerson P J. The evolution of indirect reciprocity. Social Networks, 1989, 11(3):213-236 doi: 10.1016/0378-8733(89)90003-8 [41] Wedekind C. Give and ye shall be recognized. Science, 1998, 280(5372):2070-2071 http://www.sciencemag.org/content/280/5372/2070.2.summary?related-urls=yes&legid=sci;280/5372/2070b [42] Ferriére R. Evolutionary biology:help and you shall be helped. Nature, 1998, 393(6685):517-519 doi: 10.1038/31102 [43] Nowak M A, Sigmund K. Evolution of indirect reciprocity by image scoring. Nature, 1998, 393(6685):573-577 doi: 10.1038/31225 [44] Nowak M A, Sigmund K. The dynamics of indirect reciprocity. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1998, 194(4):561-574 doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1998.0775 [45] Nowak M A, Sigmund K. Evolution of indirect reciprocity. Nature, 2005, 437(6685):1291-1298 https://www.unil.ch/files/live/sites/dee/files/shared/textes/Nowak_Sigmund_Nature_2005.pdf [46] Wedekind C, Braithwaite A V A. The long-term benefits of human generosity in indirect reciprocity. Current Biology, 2002, 12(12):1012-1015 doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00890-4 [47] Gardenfors P. Games, Actions and Social Software. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 2012. 164-183 [48] Resnick P, Kuwabara K, Zeckhauser R, Zeckhauser R, Friedman E. Reputation systems. Communications of the ACM, 2000, 43(12):45-48 doi: 10.1145/355112.355122 [49] Bolton G E, Katok E, Ockenfels A. How effective are electronic reputation mechanisms? An experimental investigation. Management Science, 2004, 50(11):1587-1602 doi: 10.1287/mnsc.1030.0199 [50] Resnick P, Zeckhauser R, Swanson J R, Lockwood K. The value of reputation on eBay:a controlled experiment. Experimental Economics, 2006, 9(2):79-101 doi: 10.1007/s10683-006-4309-2 [51] Geunes J, Akçali E, Pardalos P M, Romeijn H E, Shen Z J M. Applications of Supply Chain Management and E-Commerce Research. Boston:Springer-Verlag, 2005. 195-216 [52] Lucking-Reiley D, Bryan D, Prasad N, Reeves D. Pennies from eBay:the determinants of price in online auctions. The Journal of Industrial Economics, 2007, 55(2):223-233 doi: 10.1111/joie.2007.55.issue-2 [53] Greiner B, Levati M V. Indirect reciprocity in cyclical networks:an experimental study. Journal of Economic Psychology, 2003, 26(5):711-731 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167487005000334 [54] Pfeiffer T, Rutte C, Killingback T, Taborsky M, Bonhoeffer S. Evolution of cooperation by generalized reciprocity. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 2005, 272(1568):1115-1120 doi: 10.1098/rspb.2004.2988 [55] Chiong R, Kirley M. Promotion of cooperation in social dilemma games via generalised indirect reciprocity. Connection Science, 2015, 27(4):417-433 doi: 10.1080/09540091.2015.1080226 [56] Nowak M A, Roch S. Upstream reciprocity and the evolution of gratitude. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 2007, 274(1610):605-610 doi: 10.1098/rspb.2006.0125 [57] Iwagami A, Masuda N. Upstream reciprocity in heterogeneous networks. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2010, 265(3):297-305 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.05.010 [58] Roberts G. Partner choice drives the evolution of cooperation via indirect reciprocity. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6):Article No.e0129442 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129442 [59] Swakman V, Molleman L, Ule A, Egas M. Reputation-based cooperation:empirical evidence for behavioral strategies. Evolution and Human Behavior, 2016, 37(3):230-235 doi: 10.1016/j.evolhumbehav.2015.12.001 [60] dos Santos M, Plací S, Wedekind C. Stochasticity in economic losses increases the value of reputation in indirect reciprocity. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:Article No.18182 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286897806_Stochasticity_in_economic_losses_increases_the_value_of_reputation_in_indirect_reciprocity [61] Berger U, Grüne A. On the stability of cooperation under indirect reciprocity with first-order information. Games and Economic Behavior, 2016, 98:19-33 doi: 10.1016/j.geb.2016.05.003 [62] Tian L L, Li M C, Wang Z. Cooperation enhanced by indirect reciprocity in spatial prisoner's dilemma games for social P2P systems. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2016, 462:1252-1260 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2016.07.004 [63] Wedekind C, Milinski M. Cooperation through image scoring in humans. Science, 2000, 288(5467):850-852 doi: 10.1126/science.288.5467.850 [64] Leimar O, Hammerstein P. Evolution of cooperation through indirect reciprocity. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 2001, 268(1468):745-753 doi: 10.1098/rspb.2000.1573 [65] Milinski M, Semmann D, Bakker T C M, Krambeck H J. Cooperation through indirect reciprocity:image scoring or standing strategy? Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 2001, 268(1484):2495-2501 doi: 10.1098/rspb.2001.1809 [66] Panchanathan K, Boyd R. A tale of two defectors:the importance of standing for evolution of indirect reciprocity. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2003, 224(1):115-126 doi: 10.1016/S0022-5193(03)00154-1 [67] Fehr E, Gächter S. Altruistic punishment in humans. Nature, 2002, 415(6868):137-140 doi: 10.1038/415137a [68] Suzuki S, Akiyama E. Evolution of indirect reciprocity in groups of various sizes and comparison with direct reciprocity. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2007, 245(3):539-552 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.11.002 [69] Tanabe S, Suzuki H, Masuda N. Indirect reciprocity with trinary reputations. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2013, 317:338-347 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2012.10.031 [70] Berger U. Learning to cooperate via indirect reciprocity. Games and Economic Behavior, 2011, 72(1):30-37 doi: 10.1016/j.geb.2010.08.009 [71] Ohtsuki H, Iwasa Y, Nowak M A. Indirect reciprocity provides only a narrow margin of efficiency for costly punishment. Nature, 2009, 457(7225):79-82 doi: 10.1038/nature07601 [72] Whitaker R M, Colombo G B, Allen S M, Dunbar R I M. A dominant social comparison heuristic unites alternative mechanisms for the evolution of indirect reciprocity. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:Article No.31459 doi: 10.1038/srep31459 [73] Espín A M, Exadaktylos F, Neyse L. Heterogeneous motives in the trust game:a tale of two roles. Frontiers in Psychology, 2016, 7:Article No.728 doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00728/full [74] Burks S V, Carpenter J P, Verhoogen E. Playing both roles in the trust game. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 2003, 51(2):195-216 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167268102000938 [75] Wu J H, Balliet D, Van Lange P A M. Gossip versus punishment:the efficiency of reputation to promote and maintain cooperation. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:Article No.23919 doi: 10.1038/srep23919 [76] Eckel C C, Grossman P J. Altruism in anonymous dictator games. Games and Economic Behavior, 1996, 16(2):181-191 doi: 10.1006/game.1996.0081 [77] Bardsley N. Dictator game giving:altruism or artefact? Experimental Economics, 2008, 11(2):122-133 doi: 10.1007/s10683-007-9172-2 [78] Engel C. Dictator games:a meta study. Experimental Economics, 2011, 14(4):583-610 doi: 10.1007/s10683-011-9283-7 [79] Deng X Y, Liu Q, Sadiq R, Deng Y. Impact of roles assignation on heterogeneous populations in evolutionary dictator game. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4:Article No.6937 [80] Schank J C, Smaldino P E, Miller M L. Evolution of fairness in the dictator game by multilevel selection. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2015, 382:64-73 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.06.031 [81] Strang S, Grote X, Kuss K, Park S Q, Weber B. Generalized negative reciprocity in the dictator game-how to interrupt the chain of unfairness. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:Article No.22316 doi: 10.1038/srep22316 [82] Piazza J, Bering J M. Concerns about reputation via gossip promote generous allocations in an economic game. Evolution and Human Behavior, 2008, 29(3):172-178 doi: 10.1016/j.evolhumbehav.2007.12.002 [83] Milinski M, Semmann D, Krambeck H J. Reputation helps solve the 'tragedy of the commons'. Nature, 2002, 415(6870):424-426 doi: 10.1038/415424a [84] Hauert C, De Monte S, Hofbauer J, Sigmund K. Replicator dynamics for optional public good games. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2002, 218(2):187-194 doi: 10.1006/jtbi.2002.3067 [85] Brandt H, Hauert C, Sigmund K. Punishment and reputation in spatial public goods games. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 2003, 270(1519):1099-1104 doi: 10.1098/rspb.2003.2336 [86] Hauert C. Replicator dynamics of reward & reputation in public goods games. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2010, 267(1):22-28 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.08.009 [87] Li A M, Wu T, Cong R, Wang L. One step memory of group reputation is optimal to promote cooperation in public goods games. EPL, 2013, 103(3):Article No.30007 doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/103/30007 [88] Feinberg M, Willer R, Schultz M. Gossip and ostracism promote cooperation in groups. Psychological Science, 2014, 25(3):656-664 doi: 10.1177/0956797613510184 [89] Sigmund K. Moral assessment in indirect reciprocity. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2012, 299:25-30 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2011.03.024 [90] Fehr E, Fischbacher U. Social norms and human cooperation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2004, 8(4):185-190 doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2004.02.007 [91] Ohtsuki H, Iwasa Y. How should we define goodness?——reputation dynamics in indirect reciprocity. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2004, 231(1):107-120 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2004.06.005 [92] Brandt H, Sigmund K. The logic of reprobation:assessment and action rules for indirect reciprocation. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2004, 231(4):475-486 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2004.06.032 [93] Ohtsuki H, Iwasa Y. The leading eight:social norms that can maintain cooperation by indirect reciprocity. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2006, 239(4):435-444 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2005.08.008 [94] Ohtsuki H, Iwasa Y. Global analyses of evolutionary dynamics and exhaustive search for social norms that maintain cooperation by reputation. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2007, 244(3):518-531 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.08.018 [95] Pacheco J M, Santos F C, Chalub F A C C. Stern-judging:a simple, successful norm which promotes cooperation under indirect reciprocity. PLoS Computational Biology, 2007, 2(12):Article No.e178 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/6604852_Stern-Judging_A_Simple_Successful_Norm_Which_Promotes_Cooperation_under_Indirect_Reciprocity [96] Ohtsuki H. Reactive strategies in indirect reciprocity. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2004, 227(3):299-314 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2003.11.008 [97] Dawes R M, Messick D M. Social dilemmas. International Journal of Psychology, 2000, 35(2):111-116 doi: 10.1080/002075900399402 [98] Fehr E, Fischbacher U. The nature of human altruism. Nature, 2003, 425(6960):785-791 doi: 10.1038/nature02043 [99] Suzuki S, Akiyama E. Three-person game facilitates indirect reciprocity under image scoring. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2007, 249(1):93-100 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2007.07.017 [100] Berger U, Grüne A. Evolutionary Stability of Indirect Reciprocity by Image Scoring, Department of Economics Working Papers, WU Vienna University of Economics and Business, Vienna, 2014. 1-22 [101] Uchida S, Sigmund K. The competition of assessment rules for indirect reciprocity. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2010, 263(1):13-19 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2009.11.013 [102] Ding H, Cao L, Ren Y Z, Choo K K R, Shi B Y. Reputation-based investment helps to optimize group behaviors in spatial lattice networks. PLoS One, 2016, 11(9):Article No.e0162781 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162781 [103] Dunbar R I M. Gossip in evolutionary perspective. Review of General Psychology, 2004, 8(2):100-110 doi: 10.1037/1089-2680.8.2.100 [104] Foster E K. Research on gossip:taxonomy, methods, and future directions. Review of General Psychology, 2004, 8(2):78-99 doi: 10.1037/1089-2680.8.2.78 [105] Anderson C, Shirako A. Are individuals' reputations related to their history of behavior? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 2008, 94(2):320-333 doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.94.2.320 [106] Uchida S. Effect of private information on indirect reciprocity. Physical Review E, 2010, 82(2):Article No.036111 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960077913001598 [107] Nakamura M, Masuda N. Indirect reciprocity under incomplete observation. PLoS Computational Biology, 2011, 7(7):Article No.e1002113 doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002113 [108] Ohtsuki H, Iwasa Y, Nowak M A. Reputation effects in public and private interactions. PLoS Computational Biology, 2015, 11(11):Article No.e1004527 doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004527 [109] Brandt H, Sigmund K. Indirect reciprocity, image scoring, and moral hazard. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(7):2666-2670 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407370102 [110] Számadó S, Szalai F, Scheuring I. Deception undermines the stability of cooperation in games of indirect reciprocity. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1):Article No.e0147623 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147623 [111] Nakamaru M, Kawata M. Evolution of rumours that discriminate lying defectors. Evolutionary Ecology Research, 2004, 6(2):261-283 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/276295304_Evolution_of_rumours_that_discriminate_lying_defectors [112] Seki M, Nakamaru M. A model for gossip-mediated evolution of altruism with various types of false information by speakers and assessment by listeners. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2016, 407:90-105 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2016.07.001 [113] Franks H, Griffiths N. Robust reputation in decentralized markets. Computational Intelligence, 2015, 31(4):569-592 doi: 10.1111/coin.v31.4 [114] Suzuki S, Kimura H. Indirect reciprocity is sensitive to costs of information transfer. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3:Article No.1435 doi: 10.1038/srep01435 [115] Sommerfeld R D, Krambeck H J, Semmann D, Milinski M. Gossip as an alternative for direct observation in games of indirect reciprocity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(44):17435-17440 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704598104 [116] Sommerfeld R D, Krambeck H J, Milinski M. Multiple gossip statements and their effect on reputation and trustworthiness. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 2008, 275(1650):2529-2536 doi: 10.1098/rspb.2008.0762 [117] Lorenz J, Rauhut H, Schweitzer F, Helbing D. How social influence can undermine the wisdom of crowd effect. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108(22):9020-9025 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008636108 [118] Giardini F, Norling E. Multi-Agent-Based Simulation XV. Switzerland:Springer-Verlag, 2014. 104-118 [119] Wu J H, Balliet D, Van Lange P A M. Reputation management:why and how gossip enhances generosity. Evolution and Human Behavior, 2016, 37(3):193-201 doi: 10.1016/j.evolhumbehav.2015.11.001 [120] Wu J H, Balliet D, Van Lange P A M. When does gossip promote generosity? Indirect reciprocity under the shadow of the future. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 2015, 6(8):923-930 doi: 10.1177/1948550615595272 [121] Wu J H, Balliet D, Van Lange P A M. Reputation, gossip, and human cooperation. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 2016, 10(6):350-364 doi: 10.1111/spc3.v10.6 [122] Hess N H, Hagen E H. Psychological adaptations for assessing gossip veracity. Human Nature, 2006, 17(3):337-354 doi: 10.1007/s12110-006-1013-z [123] Giardini F, Vilone D. Evolution of gossip-based indirect reciprocity on a bipartite network. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:Article No.37931 doi: 10.1038/srep37931 [124] Giardini F. Deterrence and transmission as mechanisms ensuring reliability of gossip. Cognitive Processing, 2012, 13(S2):465-475 doi: 10.1007/s10339-011-0421-0 [125] Pfeiffer T, Tran L, Krumme C, Rand D G. The value of reputation. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2012, 9(76):2791-2797 doi: 10.1098/rsif.2012.0332 [126] Antonioni A, Sánchez A, Tomassini M. Cooperation survives and cheating pays in a dynamic network structure with unreliable reputation. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:Article No.27160 doi: 10.1038/srep27160 [127] Zhang Y L, Fu F, Wu T, Xie G M, Wang L. A tale of two contribution mechanisms for nonlinear public goods. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3:Article No.2021 doi: 10.1038/srep02021 [128] Zhang Y L, Wu T, Cheng X J, Xie G M, Wang L. Mixed strategy under generalized public goods games. Journal of Theoretical Biology 2013, 334:52-60 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2013.05.011 [129] Zhang Y L, Fu F, Wu T, Xie G M, Wang L. Inertia in strategy switching transforms the strategy evolution. Physical Review E, 2011, 84(6):Article No.066103 http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2011PhRvE..84f6103Z [130] Lieberman E, Hauert C, Nowak M A. Evolutionary dynamics on graphs. Nature, 2005, 433(7023):312-316 doi: 10.1038/nature03204 [131] Ohtsuki H, Hauert C, Lieberman E, Nowak M A. A simple rule for the evolution of cooperation on graphs and social networks. Nature, 2006, 441(7092):502-505 doi: 10.1038/nature04605 [132] Nowak M A, Tarnita C E, Antal T. Evolutionary dynamics in structured populations. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 2009, 365(1537):19-30 https://scholar.princeton.edu/sites/default/files/philtrans10_0.pdf [133] Hauert C, Imhof L A. Evolutionary games in deme structured, finite populations. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2012, 299:106-112 doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2011.06.010 [134] Vilone D, Giardini F, Paolucci M. Partner selection supports reputation-based cooperation in a Public Goods Game. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 2014. http://www.pnas.org/content/113/45/E7003.full [135] Efferson C, Lalive R, Fehr E. The coevolution of cultural groups and ingroup favoritism. Science, 2008, 321(5897):1844-1849 doi: 10.1126/science.1155805 [136] Perc M, Szolnoki A. Coevolutionary games——a mini review. Biosystems, 2010, 99(2):109-125 doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2009.10.003 [137] Fehl K, Van der Post D J, Semmann D. Co-evolution of behaviour and social network structure promotes human cooperation. Ecology Letters, 2011, 14(6):546-551 doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01615.x [138] Wang J, Suri S, Watts D J. Cooperation and assortativity with dynamic partner updating. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(36):14363-14368 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120867109 [139] Jordan J J, Rand D G, Arbesman S, Fowler J H, Christakis N A. Contagion of cooperation in static and fluid social networks. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6):Article No.e66199 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066199 [140] Zhang Y L, Liu A Z, Sun C Y. Impact of migration on the multi-strategy selection in finite group-structured populations. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:Article No.35114 doi: 10.1038/srep35114 [141] Zhang Y L, Su Q, Sun C Y. Intermediate-range migration furnishes a narrow margin of efficiency in the two-strategy competition. PLoS One, 2016, 11(5):Article No.e0155787 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155787 [142] Zhang Y L, Fu F, Chen X J, Xie G M, Wang L. Cooperation in group-structured populations with two layers of interactions. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5:Article No.17446 doi: 10.1038/srep17446 [143] Fu F, Hauert C, Nowak M A, Wang L. Reputation-based partner choice promotes cooperation in social networks. Physical Review E, 2008, 78(2):Article No.026117 https://dash.harvard.edu/handle/1/4686797?show=full [144] Peleteiro A, Burguillo J C, Chong S Y. Exploring indirect reciprocity in complex networks using coalitions and rewiring. In:Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-agent Systems. Paris, France:ACM, 2014. 669-676 [145] Ding H, Huang J Y, Chen Y F, Ren Y Z. Don't speak to strangers:the suspicious strategy can help to improve cooperation in spatial donation game. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology; Ubiquitous Computing and Communications; Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing; Pervasive Intelligence and Computing (CIT/IUCC/DASC/PICOM). Liverpool, Britain:IEEE, 2015. 1954-1959 [146] Phelps S. Emergence of social networks via direct and indirect reciprocity. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2013, 27(3):355-374 doi: 10.1007/s10458-012-9207-8.pdf [147] Han X, Shen Z S, Wang W X, Lai Y C, Grebogi C. Reconstructing direct and indirect interactions in networked public goods game. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:Article No.30241 doi: 10.1038/srep30241 [148] Kamvar S D, Schlosser M T, Garcia-Molina H. The eigentrust algorithm for reputation management in P2P networks. In:Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on World Wide Web. Budapest, Hungary:ACM, 2003. 640-651 [149] Xiong L, Liu L. PeerTrust:supporting reputation-based trust for peer-to-peer electronic communities. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2004, 16(7):843-857 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2004.1318566 [150] Yu Y L, Li K Q, Jin Y W, Zhang Y. A trust management model for service-oriented distributed networks. Concurrency and Computation:Practice and Experience, 2013, 25(14):2098-2111 doi: 10.1002/cpe.v25.14 [151] Resnick P, Zeckhauser R. Trust among strangers in internet transactions:empirical analysis of eBay's reputation system. The Economics of the Internet and E-Commerce. Amsterdam:Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 2002. 127-157 [152] Josang A, Ismail R. The beta reputation system. In:Proceedings of the 15th Bled Electronic Commerce Conference e-Reality:Constructing the e-Economy. Bled, Slovenia, 2002. 2502-2511 [153] Zhou R F, Hwang K. PowerTrust:a robust and scalable reputation system for trusted peer-to-peer computing. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2007, 18(4):460-473 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2007.1021 [154] Buragohain C, Agrawal D, Suri S. A game theoretic framework for incentives in P2P systems. In:Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Peer-To-Peer Computing. Washington DC, USA:IEEE, 2003. 48-56 [155] Feldman M, Lai K, Stoica I, Chuang J. Robust incentive techniques for peer-to-peer networks. In:Proceedings of the 5th ACM Conference on Electronic Commerce. New York, USA:ACM, 2004. 102-111 [156] Liu Y, Xiong N, Park J H, Yang C, Xu K. Fair incentive mechanism with pyramidal structure for peer-to-peer networks. IET Communications, 2010, 4(1):1-12 doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2008.0702 [157] Ma R T B, Lee S C M, Lui J C S, Yau D K Y. Incentive and service differentiation in P2P networks:a game theoretic approach. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2006, 14(5):978-991 doi: 10.1109/TNET.2006.882904 [158] Gupta R, Somani A K. Game theory as a tool to strategize as well as predict peers' behavior in peer-to-peer networks. In:Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems. Fukuoka, Japan:IEEE, 2005. 244-249 [159] Mortazavi B, Kesidis G. Cumulative reputation systems for peer-to-peer content distribution. In:Proceedings of the 40th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems. Princeton NJ, USA:IEEE, 2006. 1546-1552 [160] Mejia M, Peña N, Muñoz J L, Esparza O, Alzate M A. A game theoretic trust model for on-line distributed evolution of cooperation inMANETs. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2011, 34(1):39-51 doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2010.09.007 [161] Zhao B Q, Lui J C S, Chiu D M. Analysis of adaptive incentive protocols for P2P networks. In:Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE INFOCOM. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil:IEEE, 2009. 325-333 [162] Zuo F, Zhang W. An evolutionary game-based mechanism for routing P2P network flow among selfish peers. Journal of Networks, 2014, 9(1):10-17 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274663775_An_Evolutionary_Game-Based_Mechanism_for_Routing_P2P_Network_Flow_among_Selfish_Peers [163] Wang Y F, Nakao A, Vasilakos A V, Ma J H. P2P soft security:on evolutionary dynamics of P2P incentive mechanism. Computer Communications, 2011, 34(3):241-249 doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2010.01.021 [164] Cui G H, Li M C, Wang Z, Ren J K, Jiao D, Ma J H. Analysis and evaluation of incentive mechanisms in P2P networks:a spatial evolutionary game theory perspective. Concurrency and Computation:Practice and Experience, 2015, 27(12):3044-3064 doi: 10.1002/cpe.v27.12 [165] Lu K, Wang J L, Li M C. An Eigentrust dynamic evolutionary model in P2P file-sharing systems. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2016, 9(3):599-612 doi: 10.1007/s12083-015-0416-1 [166] Chen Z D, Qiu Y H, Liu J J, Xu L. Incentive mechanism for selfish nodes in wireless sensor networks based on evolutionary game. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2011, 62(9):3378-3388 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/220513393_Incentive_mechanism_for_selfish_nodes_in_wireless_sensor_networks_based_on_evolutionary_game [167] Zhu J, Jiang D D, Yuan Y H, Fang W L. An evolutionary game theory-based channel access mechanism for wireless multimedia sensor network with rate-adaptive applications. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2016, 75(22):14329-14349 doi: 10.1007/s11042-016-3403-5 [168] Zhao S S, Zhu Q, Zhu H B. Evolutionary game theoretical approach to dynamic spectrum sharing. Journal of Computational Information Systems, 2012, 8(10):4225-4232 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290229044_Evolutionary_game_theoretical_approach_to_dynamic_spectrum_sharing [169] Jiang C X, Chen Y, Gao Y, Liu K J R. Joint spectrum sensing and access evolutionary game in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12(5):2470-2483 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2013.031813.121135 [170] Wu D, Liu H, Bi Y R, Zhu H S. Evolutionary game theoretic modeling and repetition of media distributed shared in P2P-based VANET. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2014, 4(6):Article No.718639 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275065915_Evolutionary_Game_Theoretic_Modeling_and_Repetition_of_Media_Distributed_Shared_in_P2P-Based_VANET [171] 张慧, 王坤峰, 王飞跃.深度学习在目标视觉检测中的应用进展与展望.自动化学报, 2017, 43(8):1289-1305 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19104.shtmlZhang Hui, Wang Kun-Feng, Wang Fei-Yue. Advances and perspectives on applications of deep learning in visual object detection. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8):1289-1305 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19104.shtml [172] 游科友, 谢立华.网络控制系统的最新研究综述.自动化学报, 2013, 39(2):101-118 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17806.shtmlYou Ke-You, Xie Li-Hua. Survey of recent progress in networked control systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(2):101-118 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17806.shtml [173] 王丽媛, 郭戈, 庄严.网络控制系统发送功率分配问题研究.自动化学报, 2017, 43(8):1350-1357 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19109.shtmlWang Li-Yuan, Guo Ge, Zhuang Yan. Transmission power allocation for networked control systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8):1350-1357 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19109.shtml [174] 胡艳艳, 金增旺, 薛晓玲, 孙长银.基于异步IMM融合滤波的网络化系统故障诊断.自动化学报, 2017, 43(8):1329-1338 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19107.shtmlHu Yan-Yan, Jin Zeng-Wang, Xue Xiao-Ling, Sun Chang-Yin. Fault diagnosis for networked systems by asynchronous IMM fusion filtering. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(8):1329-1338 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19107.shtml -




 下载:
下载: