Background Modeling of Infrared Image in Dynamic Scene With Gaussian Mixture Model in Compressed Sensing Domain
-
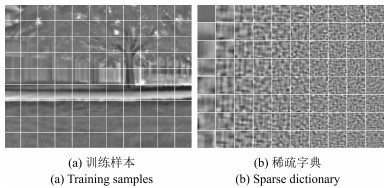
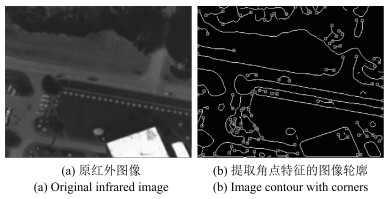
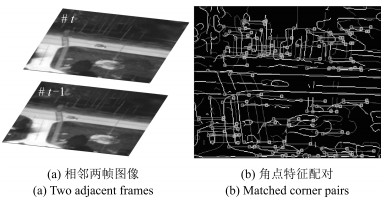
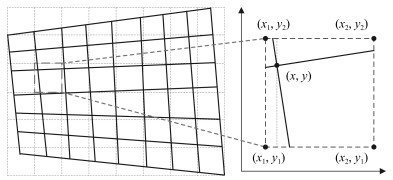
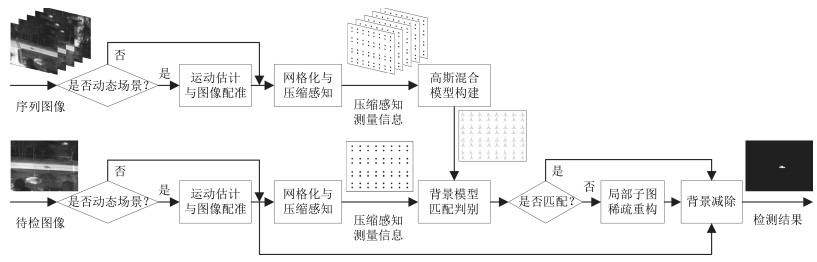
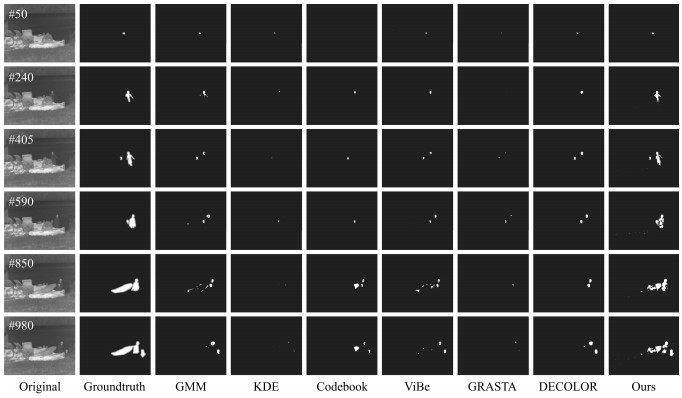
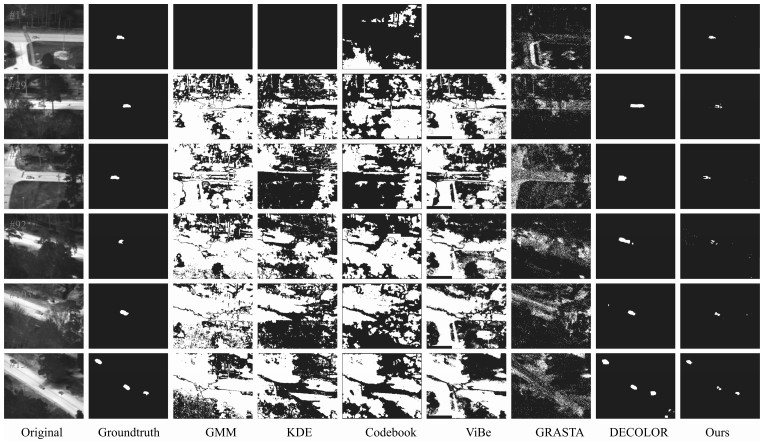
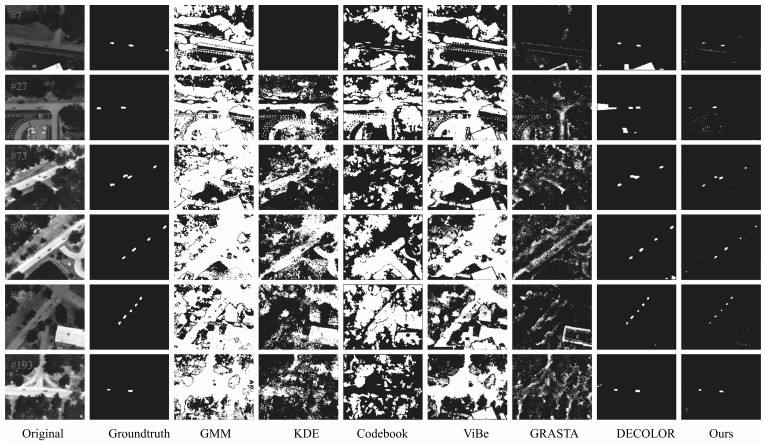
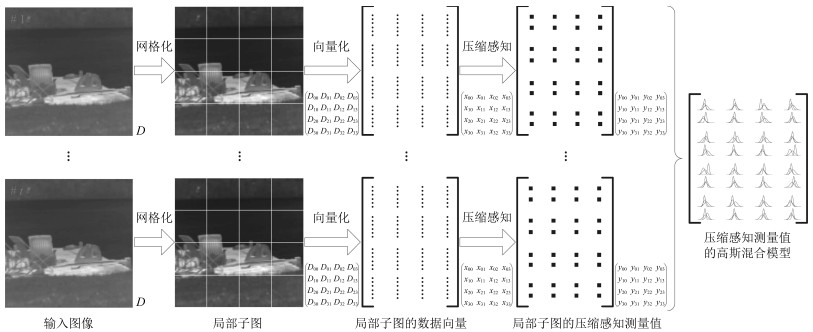
摘要: 针对动态场景下红外图像的背景模型构建问题,提出一种基于压缩感知(Compressed sensing,CS)域高斯混合模型(Gaussian mixture model,GMM)的背景建模方法.该方法不是对图像中的每个像素建立高斯混合模型,而是对图像局部区域的压缩感知测量值建立高斯混合模型.1)通过提取红外图像轮廓的角点特征,估计相邻帧图像间的相对运动参数以对图像进行校正与配准;2)将每帧图像网格化为适当数目的局部子图,利用序列图像构建每个局部子图的压缩感知域高斯混合背景模型;3)采用子空间学习训练稀疏字典,通过子空间追踪对可能含有目标的局部子图进行选择性稀疏重构;4)通过背景减除实现前景目标检测.以红外图像数据集CDnet2014和VIVID PETS2005进行实验验证,结果表明:该方法能建立有效的动态场景红外图像背景模型,对成像过程中所受到的场景动态变化、背景扰动等具有较强的鲁棒性,其召回率、精确率、F-measure等性能指标及处理速度较之于同类算法具有明显优势.Abstract: For the problem in background modeling of infrared image in dynamic scene, a new approach to background modeling based on Gaussian mixture model (GMM) in the compressed sensing (CS) domain is presented. The Gaussian mixture model is not for each pixel in the image but for the compression sensing measurement of local regions in the image. Firstly, correction and registration of images are carried out with the motion parameters between adjacent frames estimated by utilizing corner feature of image contour. Then, each frame in the infrared image sequence is meshed into an appropriate number of local sub-images, and the background model of each local sub-image is constructed with Gaussian mixture model in the compressed sensing domain. Furthermore, the local sub-images which may contain target are selectively reconstructed by employing subspace pursuit algorithm with sparse dictionary trained by the subspace learning method. Finally, the foreground targets are detected by background subtraction. Experiments on two datasets of infrared images, CDnet2014 and VIVID PETS2005, are conducted to verify the performance of the proposed algorithm. The results show that the proposed algorithm can establish efficient background model for infrared image in dynamic scene, and has strong robustness to dynamic changes of scene and background disturbance during imaging. The performance evaluations such as recall, precision and F-measure as well as processing speed have obvious advantages over the comparison algorithms.1) 本文责任编委 胡清华
-
表 1 固定场景图像序列下各算法的F-measure指标
Table 1 The F-measure index of different algorithms in fixed scene image sequences
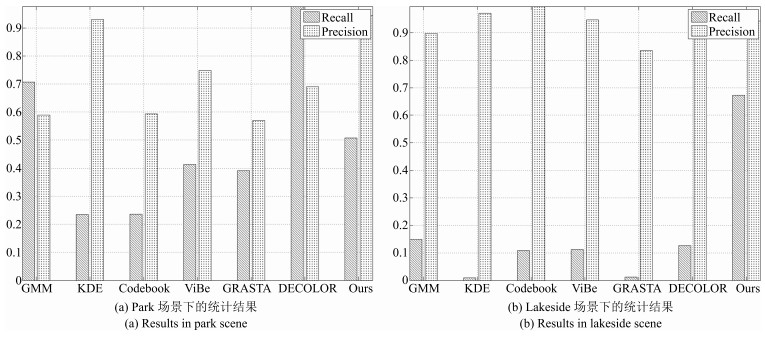
GMM KDE Codebook ViBe GRASTA DECOLOR Ours CDnet2014 park 0.6429 0.3761 0.3379 0.5335 0.4645 0.8098 0.6607 CDnet2014 lakeside 0.2561 0.0185 0.1943 0.2 0.0238 0.224 0.7848 表 2 处理固定场景中一帧红外图像的平均时间消耗(s)
Table 2 The average time consumption of each infrared image in fixed scenes (s)
压缩感知 模型构建 稀疏重构 背景减除 CDnet2014 park 0.0065 0.1352 0.4938 0.0003 CDnet2014 lakeside 0.0043 0.0827 0.5594 0.0003 表 3 动态场景图像序列下各算法的F-measure指标
Table 3 The F-measure index of different algorithms in dynamic scene image sequences
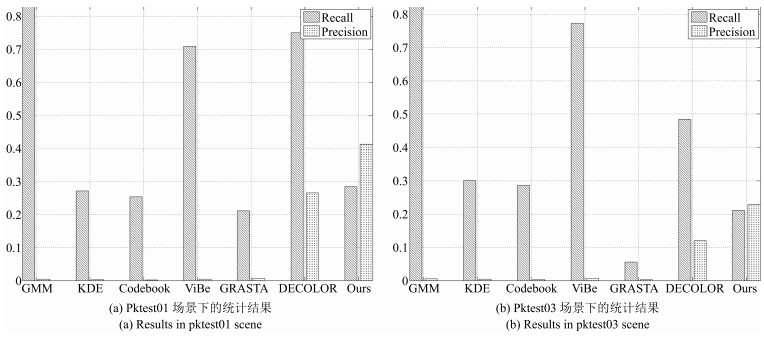
GMM KDE Codebook ViBe GRASTA DECOLOR Ours PETS2005 pktest01 0.0089 0.0052 0.0040 0.0086 0.0125 0.3927 0.3369 PETS2005 pktest03 0.0099 0.0086 0.0062 0.0123 0.0047 0.1929 0.2198 表 4 处理动态场景中一帧红外图像的平均时间消耗(s)
Table 4 The average time consumption of each infrared image in dynamic scenes (s)
图像校正与配准 背景建模与重构 DECOLOR Ours DECOLOR Ours PETS2005 pktest01 0.6610 1.4632 0.6053 0.5509 PETS2005 pktest03 0.7608 1.1273 0.6942 0.6454 -
[1] Cao Y, Liu R M, Yang J. Small target detection using two-dimensional least mean square (TDLMS) filter based on neighborhood analysis. International Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2008, 29(2):188-200 doi: 10.1007/s10762-007-9313-x [2] Bae T W, Kim Y C, Ahn S H, Sohng K I. An efficient two-dimensional least mean square (TDLMS) based on block statistics for small target detection. Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, 2009, 30(10):1092-1101 doi: 10.1007/s10762-009-9530-6 [3] Kim S. Double layered-background removal filter for detecting small infrared targets in heterogenous backgrounds. Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, 2011, 32(1):79-101 doi: 10.1007/s10762-010-9742-9 [4] Stauffer C, Grimson W E L. Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking. In: Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Fort Collins, Colorado, USA: IEEE, 1999, 2: 252 [5] Lee D S. Effective Gaussian mixture learning for video background subtraction. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(5):827-832 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.102 [6] Haines T S F, Xiang T. Background subtraction with dirichlet process mixture models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(4):670-683 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.239 [7] Elgammal A, Harwood D, Davis L. Non-parametric model for background subtraction. In: Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 2000. 751-767 [8] Kim K, Chalidabhongse T H, Harwood D, Davis L. Real-time foreground-background segmentation using codebook model. Real-Time Imaging, 2005, 11(3):172-185 doi: 10.1016/j.rti.2004.12.004 [9] Barnich O, Van Droogenbroeck M. ViBe:a universal background subtraction algorithm for video sequences. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(6):1709-1724 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2101613 [10] Wang L, Wang L, Wen M, Zhuo Q, Wang W Y. Background subtraction using incremental subspace learning. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. San Antonio, Texas, USA: IEEE, 2007. V-45-V-48 [11] Seo J W, Kim S D. Recursive on-line (2D)2PCA and its application to long-term background subtraction. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2014, 16(8):2333-2344 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2014.2353772 [12] He J, Balzano L, Szlam A. Incremental gradient on the grassmannian for online foreground and background separation in subsampled video. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Providence, Rhode Island, USA: IEEE, 2012. 1568-1575 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.662.1791&rep=rep1&type=pdf [13] Zhou X W, Yang C, Yu W C. Moving object detection by detecting contiguous outliers in the low-rank representation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(3):597-610 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.132 [14] 沈燕飞, 李锦涛, 朱珍民, 张勇东, 代锋.基于非局部相似模型的压缩感知图像恢复算法.自动化学报, 2015, 41(2):261-272 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18605.shtmlShen Yan-Fei, Li Jin-Tao, Zhu Zhen-Min, Zhang Yong-Dong, Dai Feng. Image reconstruction algorithm of compressed sensing based on nonlocal similarity model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(2):261-272 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18605.shtml [15] Candés E J. The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing. Comptes Rendus Mathematique, 2008, 346(9-10):589-592 doi: 10.1016/j.crma.2008.03.014 [16] Baraniuk R. Compressive sensing. In: Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems. Princeton, NJ, USA: IEEE, 2008. 4-5 [17] Szabó Z, Lñrincz A. Distributed high dimensional information theoretical image registration via random projections. Digital Signal Processing, 2012, 22(6):894-902 doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2012.04.018 [18] Amador J. Random projection and orthonormality for lossy image compression. Image and Vision Computing, 2007, 25(5):754-766 doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2006.05.018 [19] Liu L, Fieguth P W. Texture classification from random features. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(3):574-586 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.145 [20] Liu L, Fieguth P W, Clausi D, Kuang G Y. Sorted random projections for robust rotation-invariant texture classification. Pattern Recognition, 2012, 45(6):2405-2418 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2011.10.027 [21] Liu L, Fieguth P W, Hu D W, Wei Y M, Kuang G Y. Fusing sorted random projections for robust texture and material classification. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2015, 25(3):482-496 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2014.2359098 [22] Johnson W, Lindenstrauss J. Extensions of lipschitz mappings into a Hilbert space. Contemporary Mathematics, 1984, 26:189-206 doi: 10.1090/conm/026 [23] Diaconis P, Freedman D. Asymptotics of graphical projection pursuit. The Annals of Statistics, 1984, 12(3):793-815 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5ece6b6fde4df69c965412100d9e9b9b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [24] 朱碧婷, 郑世宝.基于高斯混合模型的空间域背景分离法及阴影消除法.中国图象图形学报, 2008, 13(10):1906-1909 doi: 10.11834/jig.20081022Zhu Bi-Ting, Zheng Shi-Bao. Space-domain background subtraction and shadow elimination based on Gaussian mixture model. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2008, 13(10):1906-1909 doi: 10.11834/jig.20081022 [25] Gowreesunker B V, Tewfik A H. Learning sparse representation using iterative subspace identification. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(6):3055-3065 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2044251 [26] 荆楠, 毕卫红, 胡正平, 王林.动态压缩感知综述.自动化学报, 2015, 41(1):22-37 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18580.shtmlJing Nan, Bi Wei-Hong, Hu Zheng-Ping, Wang Lin. A survey on dynamic compressed sensing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(1):22-37 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18580.shtml [27] Dai W, Milenkovic O. Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing signal reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(5):2230-2249 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2009.2016006 [28] He X C, Yung N H C. Corner detector based on global and local curvature properties. Optical Engineering, 2008, 47(5):Article No.057008 [29] Zhao Y, Hong R C, Jiang J G. Visual summarization of image collections by fast RANSAC. Neurocomputing, 2016, 172:48-52 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.09.095 [30] Wang Y, Jodoin P M, Porikli F, Konrad J, Benezeth Y, Ishwar P. CDnet 2014: an expanded change detection benchmark dataset. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Columbus, Ohio, USA: IEEE, 2014. 393-400 https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/CDnet-2014%3A-An-Expanded-Change-Detection-Benchmark-Wang-Jodoin/45790b5bf6a3ad7c641809035661d14d73d6361b [31] Collins R, Zhou X, Teh S K. An open source tracking testbed and evaluation web site. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Workshop on Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance (PETS). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2005. 1-8 [32] 秦明, 陆耀, 邸慧军, 吕峰.基于误差补偿的复杂场景下背景建模方法.自动化学报, 2016, 42(9):1356-1366 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18924.shtmlQin Ming, Lu Yao, Di Hui-Jun, Lv Feng. An error compensation based background modeling method for complex scenarios. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(9):1356-1366 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18924.shtml [33] Sobral A. BGSLibrary: an openCV C++ background subtraction library. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IX Workshop de Visão Computacional. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013. 1-6 -




 下载:
下载: