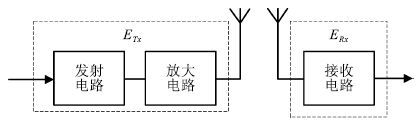
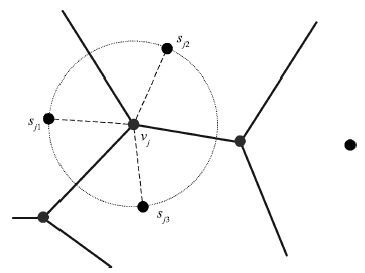
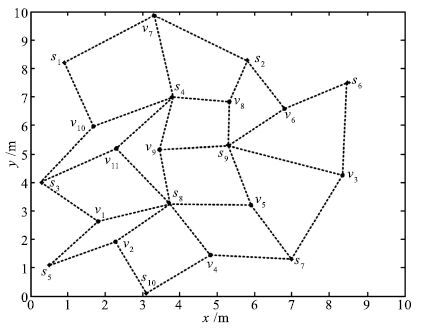
A Path Planning Method for Water Surface Mobile Sink Based on Voronoi Diagram and Bipartite Graph
-
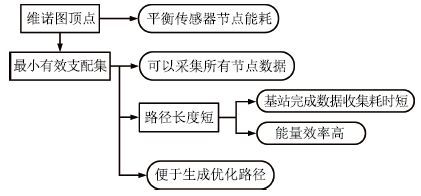
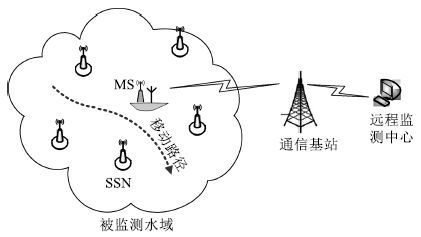
摘要: 水面传感器网络(Surface sensor networks,SSNs)具有节点稀疏布置的特点(节点间距离通常大于节点通信半径),因此难以通过节点间的多跳路由汇聚数据,目前主要采用移动基站(Mobile sink,MS)收集网络中的数据,其中移动基站的路径规划是一个关键问题.该文提出一种基于维诺图和二分图的水面移动基站路径规划方法,首先利用维诺图理论生成数据收集“候选点”;然后以二分图描述候选点对网络中传感器节点的支配关系,并基于支配集理论求解出“最小有效支配集”,即可以收集网络中所有节点数据的最小的候选点集合;最后针对最小有效支配集形成最优路径.大量实验结果表明该方法可以有效地规划出水面传感器网络中移动基站的路径,不仅可以完成全网数据收集任务,而且具有路径长度短、能量效率高和节点能耗均衡的优点.Abstract: In surface sensor networks with sparsely deployed sensors, the distance between sensors is usually larger than the communication radius of sensors. So, it is difficult for sensors to gather their data by multi-hop routing. At present, an effective data gathering method is to use a mobile sink travelling in the network, and the path planning for the mobile sink becomes a key problem. In this paper, a path planning method based on Voronoi diagram and bipartite graph is proposed. Firstly, the data gathering "candidate vertexes" are generated using the Voronoi diagram theory. Secondly, a bipartite graph is constructed to describe the dominating relationship between candidate vertexes and sensors, and the "minimum effective dominating set", which includes the least candidate vertexes gathering all sensors data, can be computed by dominating set theory. Lastly, the optimal path is formed based on the minimum effective dominating set. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that the proposed method can effectively plan the path for mobile sink to gather all sensors' data with advantages such as short path, high energy efficiency, and balanced energy consumption among sensors.
-
Key words:
- Surface sensor networks (SSNs) /
- mobile sink (MS) /
- path planning /
- Voronoi diagram /
- bipartite graph /
- dominating set
-
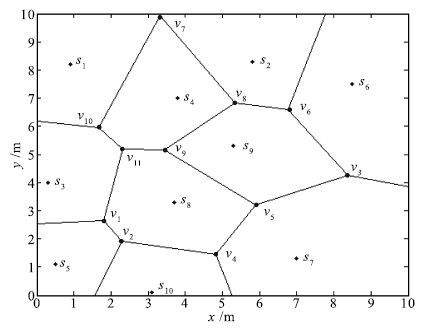
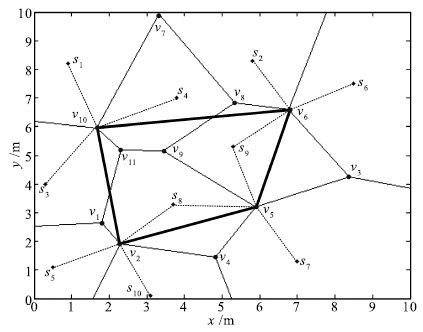
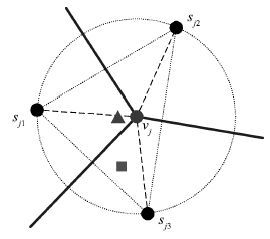
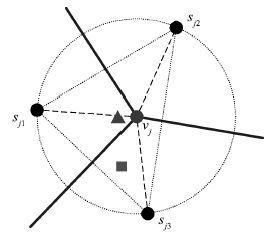
表 1 传感器节点与维诺图顶点间的支配关系
Table 1 Dominating relationship between sensor nodes and Voronoi vertexes
节点 顶点 节点 顶点 s1 v7 ,v10 s2 v6 ,v7 ,v8 s3 v1 ,v10 ,v11 s4 v7 ,v8 ,v9 ,v10 ,v11 s5 v1 ,v2 s6 v3 ,v6 s7 v3 ,v4 ,v5 s8 v1 ,v2 ,v4 ,v5 ,v9 ,v11 s9 v3 ,v5 ,v6 ,v8 ,v9 s10 v2 ,v4 表 2 通信模型参数值
Table 2 Parameter value of communication model
参数 值 节点发射或接收电路能耗系数es (nJ/bit) 50 节点功率放大能耗系数εs (pJ/bit m2) 100 移动基站广播数据量k1 (bit) 100 传感器节点发送数据量k2 (bit) 10000 基站航行速v (m/s) 5 表 3 分组实验所得结果
Table 3 Grouping experiment results
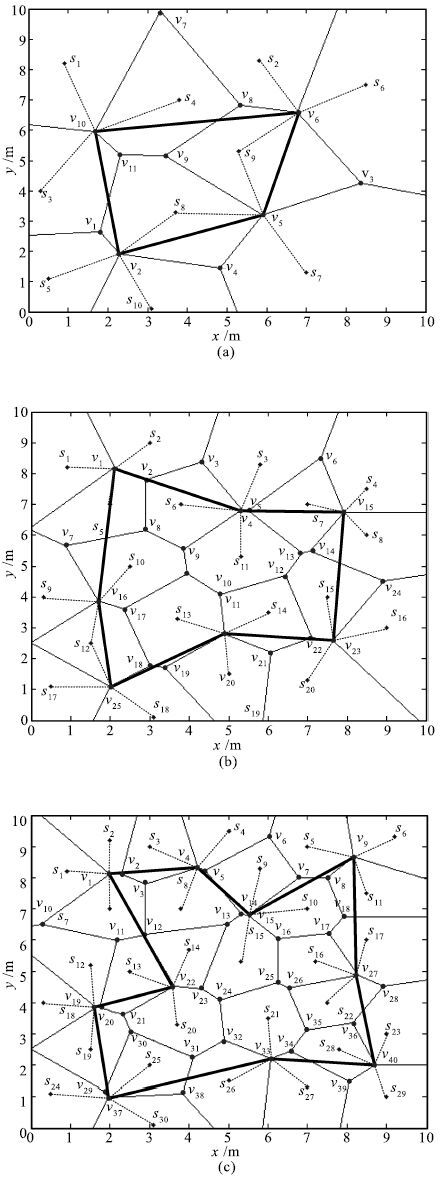
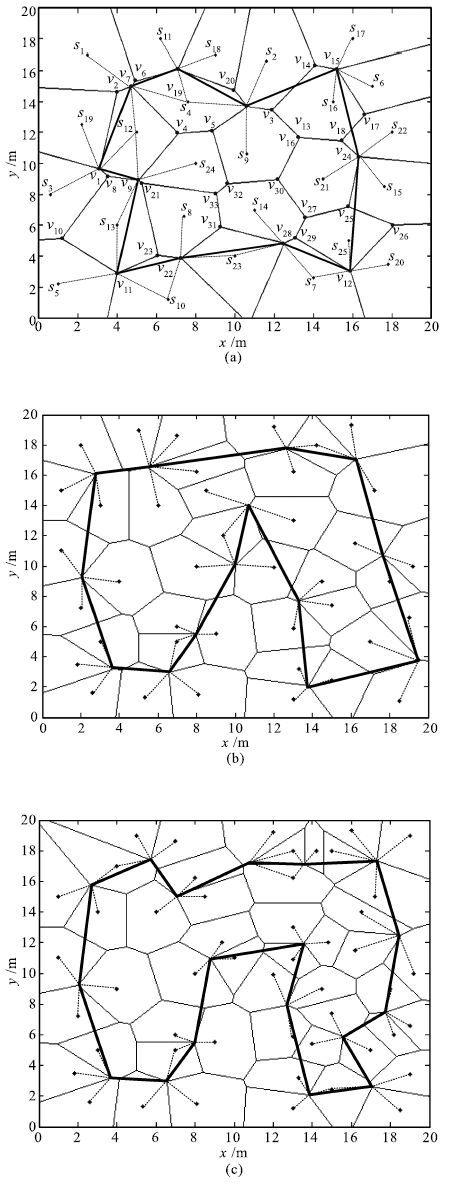
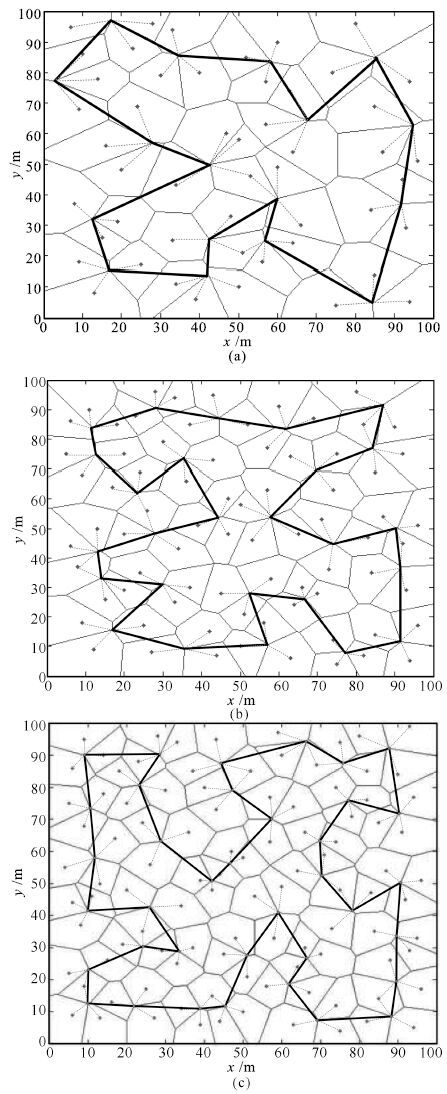
实验分组 路径长度(m) 网络总能耗(10-3J) 能量效率(J-1) (a) 16.559 5.076 7.181 实验1 (b) 23.507 10.124 0.897 (c) 29.993 15.174 0.164 (a) 51.492 12.751 2.642 × 10-3 实验2 (b) 69.923 20.302 4.159 × 10-5 (c) 75.293 25.348 1.138 × 10-5 (a) 409.118 27.05 1.077 × 10-34 实验3 (b) 456.700 39.75 5.398 × 10-39 (c) 532.231 52.525 1.124 × 10-45 表 4 三种方法所规划路径的长度比较
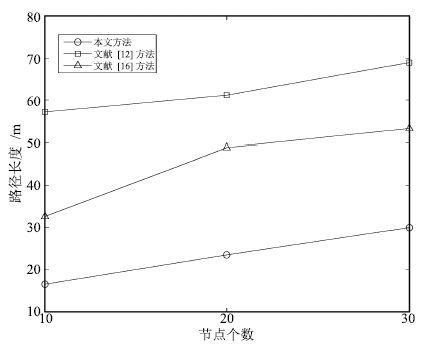
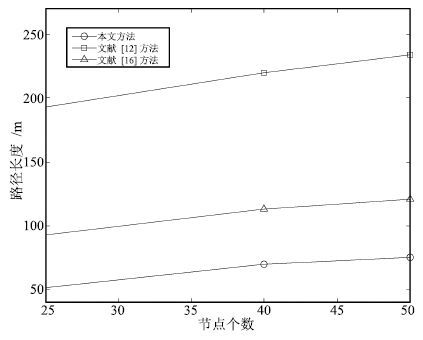
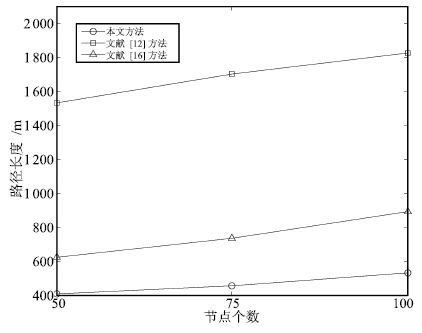
Table 4 Comparison of path length by three methods
表 5 三种方法所规划路径的网络总能耗比较
Table 5 Comparison of total energy consumption by three methods
表 6 三种方法所规划路径的能量效率比较
Table 6 Comparison of total energy efficiency by three methods
实验分组 能量效率(J-1) 本文方法 文献[12]方法 文献[16]方法 (a) 7.181 2.127 × 10-3 0.288 实验1 (b) 0.897 4.821 × 10-4 5.634 × 10-3 (c) 0.164 6.789 × 10-5 1.556 × 10-3 (a) 2.642 × 10-3 1.441 × 10-15 6.675 × 10-7 实验2 (b) 4.159 × 10-5 4.117 × 10-18 7.247 × 10-9 (c) 1.138 × 10-5 1.966 × 10-19 1.218 × 10-9 (a) 1.077 × 10-34 0 2.206 × 10-53 实验3 (b) 5.398 × 10-39 0 3.009 × 10-63 (c) 1.124 × 10-45 0 5.642 × 10-77 表 7 实验1(a)中,传感器节点的能耗及方差值
Table 7 Energy consumption and variance of sensor nodes in Experiment 1(a)
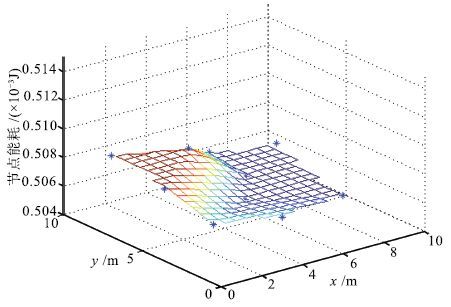
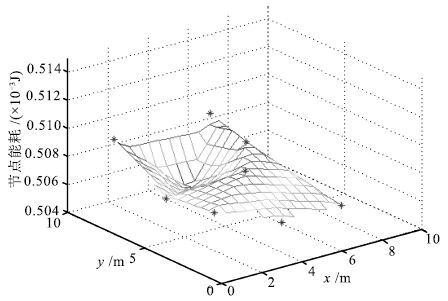
实验1(a) 能耗(10-3J) 方差(10-12J2) s1 s2 s3 s4 s5 s6 s7 s8 s9 s10 ∑ 本文方法的维诺图顶点 0.5087 0.5070 0.5087 0.5087 0.5076 0.5070 0.5070 0.5070 0.5070 0.5076 5.076 0.543 Delaunay三角形重心 0.5081 0.5062 0.5093 0.5083 0.5079 0.5073 0.5060 0.5079 0.5072 0.5071 5.075 0.879 Delaunay三角形内随机点 0.5098 0.5097 0.5079 0.5058 0.5083 0.5051 0.5062 0.5089 0.5094 0.5071 5.078 2.198 -
[1] Gkikopouli A, Nikolakopoulos G, Manesis S. A survey on underwater wireless sensor networks and applications. In:Proceedings of the 20th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation. Barcelona, Spain:IEEE, 2012.1147-1154 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281716899_Multihops_Fitting_Approach_for_Node_Localization_in_Underwater_Wireless_Sensor_Networks [2] Davis A, Chang H. Underwater wireless sensor networks. In:Proceedings of the 2012 Oceans Conference. Virginia, USA:IEEE, 2012.1-5 http://eprints.qut.edu.au/view/types/conference=5Fpaper/2012.default.html [3] Tunca C, Isik S, Donmez M Y, Ersoy C. Distributed mobile sink routing for wireless sensor networks:a survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2014, 16(2):877-897 doi: 10.1109/SURV.2013.100113.00293 [4] 罗旭, 柴利, 杨君. 无线传感器网络下静态水体中的近岸污染源定位. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(5):849-861 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18353.shtmlLuo Xu, Chai Li, Yang Jun. Offshore pollution source localization in static water using wireless sensor networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(5):849-861 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18353.shtml [5] Wang J, Yang X Q, Li B, Lee S Y, Jeon S K. A mobile sink based uneven clustering algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Journal of Internet Technology, 2013, 14(6):895-902 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2261891850&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [6] Nizhamudong Y, Nakaya N, Hagihara Y, Koui Y. Performance evaluation of route cost for wireless sensor networks with a mobile sink. In:Proceedings of the 2011 SICE Annual Conference. Tokyo, Japan:IEEE, 2011.2029-2031 [7] Liang W F, Schweitzer P, Xu Z C. Approximation algorithms for capacitated minimum forest problems in wireless sensor networks with a mobile sink. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2013, 62(10):1932-1944 doi: 10.1109/TC.2012.124 [8] Saad E M, Awadalla M H, Darwish R R. A data gathering algorithm for a mobile sink in large-scale sensor networks. In:Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Communications. Athens, Greece:IEEE, 2008.207-213 [9] Liang W F, Luo J. Network lifetime maximization in sensor networks with multiple mobile sinks. In:Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Local Computer Networks. Bonn, Germany:IEEE, 2011.350-357 http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2195216.2195437 [10] Nagamalar T, Rangaswamy T R. Energy efficient cluster based approach for data collection in wireless sensor networks with multiple mobile sink. In:Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Industrial Instrumentation and Control. Pune, India:IEEE, 2015.348-353 [11] Shah R C, Roy S, Jain S, Brunette W. Data MULEs:modeling and analysis of a three-tier architecture for sparse sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 2003, 1(2-3):215-233 doi: 10.1016/S1570-8705(03)00003-9 [12] Chatzigiannakis I, Kinalis A, Nikoletseas S. Efficient data propagation strategies in wireless sensor networks using a single mobile sink. Computer Communications, 2008, 31(5):896-914 doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2007.12.011 [13] Ma M, Yang Y Y. Data gathering in wireless sensor networks with mobile collectors. In:Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing. Miami, USA:IEEE, 2008.1-9 http://dsn.sagepub.com/content/10/9/698452.full [14] Luo J, Hubaux J P. Joint mobility and routing for lifetime elongation in wireless sensor networks. In:Proceedings of the 24th Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies. Miami, USA:IEEE, 2005.1735-1746 [15] 石高涛, 廖明宏. 传感器网络中具有负载平衡的移动协助数据收集模式. 软件学报, 2007, 18(9):2235-2244 doi: 10.1360/jos182235Shi Gao-Tao, Liao Ming-Hong. Movement-assisted data gathering scheme with load-balancing for sensor networks. Journal of Software, 2007, 18(9):2235-2244 doi: 10.1360/jos182235 [16] Zhu R B, Qin Y Y, Wang J Q. Energy-aware distributed intelligent data gathering algorithm in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2011, 2011:Article ID 235724 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1998032303&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [17] Salarian H, Chin K W, Naghdy F. An energy-efficient mobile-sink path selection strategy for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2014, 63(5):2407-2419 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2013.2291811 [18] Heinzelman W R, Chandrakasan A, Balakrishnan H. Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In:Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. Hawaii, USA:IEEE, 2000. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1966877298&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [19] Voronoi G M. Nouvelles applications des paramétres continus á la théorie des formes quadratiques deuxiéme memoire:recherches sur les parallélloédres primitifs. Journal Für Die Reine und Angewandte Mathematik, 1908, 1908(134):198-287 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1520127302&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [20] Mirzargar M, Entezari A. Voronoi splines. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(9):4572-4582 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2051808 [21] Garrido S, Moreno L, Blanco D, Jurewicz P P. Path planning for mobile robot navigation using Voronoi diagram and fast marching. International Journal of Robotics and Automation, 2011, 2(1):42-64 http://yadda.icm.edu.pl/yadda/element/bwmeta1.element.ieee-000004058742 [22] Ok K, Ansari S, Gallagher B, Sica W, Dellaert F, Stilman M. Path planning with uncertainty:Voronoi uncertainty fields. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Karlsruhe:IEEE, 2013.4596-4601 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2368403481&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [23] 夏娜, 倪成春, 徐朝农, 丁胜, 郑榕. 逆向捕获时间差的Voronoi声源定位机制. 通信学报, 2013, 34(11):140-152 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TXXB201311016.htmXia Na, Ni Cheng-Chun, Xu Chao-Nong, Ding Sheng, Zheng Rong. Voronoi acoustic source localization mechanism based on counter captured time difference. Journal on Communications, 2013, 34(11):140-152 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TXXB201311016.htm [24] 郭帅, 马书根, 李斌, 王明辉, 王越超. 基于Voronoi地图表示方法的同步定位与地图创建. 自动化学报, 2011, 37(9):1095-1104 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17532.shtmlGuo Shuai, Ma Shu-Gen, Li Bin, Wang Ming-Hui, Wang Yue-Chao. Simultaneous localization and mapping through a Voronoi-diagram-based map representation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(9):1095-1104 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17532.shtml [25] Bourgeois N, Croce F D, Escoffier B, Paschos V T. Fast algorithms for min independent dominating set. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 2013, 161(4-5):558-572 doi: 10.1016/j.dam.2012.01.003 [26] 路纲, 周明天, 唐勇, 吴振强, 裘国永, 袁柳. 任意图支配集精确算法回顾. 计算机学报, 2010, 33(6):1073-1087 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2010.01073Lu Gang, Zhou Ming-Tian, Tang Yong, Wu Zhen-Qiang, Qiu Guo-Yong, Yuan Liu. A survey on exact algorithms for dominating set related problems in arbitrary graphs. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2010, 33(6):1073-1087 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2010.01073 [27] Chen S M, Chien C Y. Solving the traveling salesman problem based on the genetic simulated annealing ant colony system with particle swarm optimization techniques. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(12):14439-14450 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.04.163 [28] 饶卫振, 金淳. 基于求解TSP问题的改进贪婪算法. 运筹与管理, 2012, 21(6):1-9 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YCGL201206003.htmRao Wei-Zhen, Jin Chun. An improved greedy heuristic based on solving traveling salesman problem. Operations Research and Management Science, 2012, 21(6):1-9 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YCGL201206003.htm [29] Hassin R, Keinan A. Greedy heuristics with regret, with application to the cheapest insertion algorithm for the TSP. Operations Research Letters, 2008, 36(2):243-246 doi: 10.1016/j.orl.2007.05.001 [30] Qin H S, Zhou S L, Huo L, Luo J. A new ant colony algorithm based on dynamic local search for TSP. In:Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies. Gwalior, India:IEEE, 2015.913-917 [31] Wang P D, Tang Y L, Li Y, Yang X X. Improved ant colony algorithm for traveling salesman problems. In:Proceedings of the 24th Chinese Control and Decision Conference. Taiyuan, China:IEEE, 2012.660-664 -




 下载:
下载: