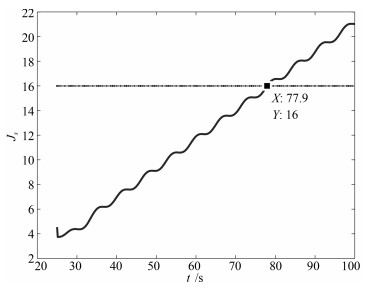
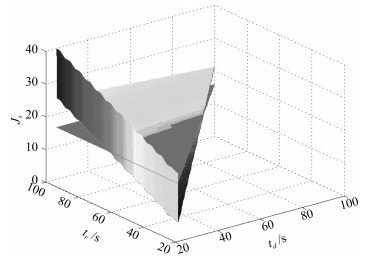
|
[1]
|
Gao Z W, Ding S X, Cecati C. Real-time fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(6):3752-3756 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2417511
|
|
[2]
|
李文博, 王大轶, 刘成瑞.动态系统实际故障可诊断性的量化评价研究.自动化学报, 2015, 41(3):497-507 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18628.shtmlLi Wen-Bo, Wang Da-Yi, Liu Cheng-Rui. Quantitative evaluation of actual fault diagnosability for dynamic systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(3):497-507 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18628.shtml
|
|
[3]
|
段文杰, 王大轶, 刘成瑞.卫星控制系统离散积分滑模容错控制.控制理论与应用, 2015, 32(2):133-141 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kzllyyy201502001Duan Wen-Jie, Wang Da-Yi, Liu Cheng-Rui. Discrete-time integral sliding-mode fault-tolerant controller for satellite control system. Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 32(2):133-141 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kzllyyy201502001
|
|
[4]
|
Wu N E, Zhou K M, Salomon G. Control reconfigurability of linear time-invariant systems. Automatica, 2000, 36(11):1767-1771 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(00)00080-7
|
|
[5]
|
关守平, 杨飞生.面向重构目标的控制系统可重构性.信息与控制, 2010, 39(4):391-396 http://www.oalib.com/paper/4719569Guan Shou-Ping, Yang Fei-Sheng. Reconfiguration-goal-oriented control system reconfigurability. Information and Control, 2010, 39(4):391-396 http://www.oalib.com/paper/4719569
|
|
[6]
|
Staroswiecki M. On reconfigurability with respect to actuator failures. In:Proceedings of the 15th Triennial World Congress of the International Federation of Automatic Control. Barcelona, Spanish:IFAC, 2002. 775-780
|
|
[7]
|
Du G X, Quan Q, Yang B X, Cai K Y. Controllability analysis for multirotor helicopter rotor degradation and failure. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2015, 38(5):978-985 doi: 10.2514/1.G000731
|
|
[8]
|
Khelassi A, Theilliol D, Weber P. Reconfigurability analysis for reliable fault-tolerant control design. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science, 2011, 21(3):431-439 doi: 10.2478/v10006-011-0032-z
|
|
[9]
|
Wu N E, Busch T. Operational reconfigurability in command and control. In:Proceedings of the 2004 American Control Conference. Boston, USA:IEEE, 2004. 4426-4431
|
|
[10]
|
Gehin A L, Staroswiecki M. Reconfiguration analysis using generic component models. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A:Systems and Humans, 2008, 38(3):575-583 doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2008.918608
|
|
[11]
|
段文杰, 王大轶, 刘成瑞.一种线性系统可重构控制分析方法.自动化学报, 2014, 40(12):2726-2736 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18552.shtmlDuan Wen-Jie, Wang Da-Yi, Liu Cheng-Rui. An analysis method for reconfigurable control of linear systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(12):2726-2736 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18552.shtml
|
|
[12]
|
项昌毅, 杨浩, 程月华, 姜斌, 刘成瑞.卫星姿态控制系统的可重构性指标分配.航天控制, 2014, 32(2):46-52, 59 http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/HTKZ201402009.htmXiang Chang-Yi, Yang Hao, Cheng Yue-Hua, Jiang Bin, Liu Cheng-Rui. Reconfigurable allocation of satellite attitude control system. Aerospace Control, 2014, 32(2):46-52, 59 http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/HTKZ201402009.htm
|
|
[13]
|
Staroswiecki M, Cazaurang F. Fault recovery by nominal trajectory tracking. In:Proceedings of the 2008 American Control Conference. Seattle, Washington, USA:IEEE, 2008. 1070-1075
|
|
[14]
|
Zhang Y M, Jiang J. Issues on integration of fault diagnosis and reconfigurable control in active fault-tolerant control systems. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2006, 39(13):1437-1448 doi: 10.3182/20060829-4-CN-2909.00240
|
|
[15]
|
Hamdaoui R, Abdelkrim M N. Conditions on diagnosis and accommodation delays for actuator fault recoverability. In:Proceedings of the 8th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals and Devices. Sousse, Tunisia:IEEE, 2011. 1-6
|
|
[16]
|
Joshi S M, González O R, Upchurch J M. Identifiability of additive actuator and sensor faults by state augmentation. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2014, 37(3):941-946 doi: 10.2514/1.62523
|
|
[17]
|
Upchurch J M, González O R, Joshi S M. Identifiability of additive, time-varying actuator and sensor faults by state augmentation, Technical Report NASA/TM-2014-218669, NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA, USA, 2014.
|
|
[18]
|
Hamdaoui R, Guesmi S, El Harabi R. UIO based robust fault detection and estimation. In:Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies. Hammamet, Tunisia:IEEE, 2013. 76-81
|
|
[19]
|
胡志坤, 孙岩, 姜斌, 何静, 张昌凡.一种基于最优未知输入观测器的故障诊断方法.自动化学报, 2013, 39(8):1225-1230 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18153.shtmlHu Zhi-Kun, Sun Yan, Jiang Bin, He Jing, Zhang Chang-Fan. An optimal unknown input observer based fault diagnosis method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(8):1225-1230 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18153.shtml
|
|
[20]
|
Jiang B, Staroswiecki M. Adaptive observer design for robust fault estimation. International Journal of Systems Science, 2002, 33(9):767-775 doi: 10.1080/00207720210144776
|
|
[21]
|
Collins E G, Song T L. Robust H∞ estimation and fault detection of uncertain dynamic systems. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2000, 23(5):857-864 doi: 10.2514/2.4615
|
|
[22]
|
Tang G Y, Li J. Optimal fault diagnosis for systems with delayed measurements. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2008, 2(11):990-998 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224347343_Optimal_fault_diagnosis_for_systems_with_delayed_measurements
|
|
[23]
|
Chen W, Saif M. Observer-based fault diagnosis of satellite systems subject to time-varying thruster faults. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2007, 129(3):352-356 doi: 10.1115/1.2719773
|




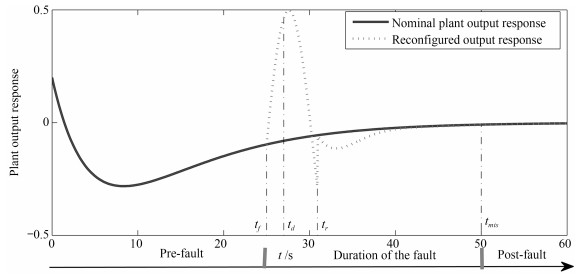
 下载:
下载: