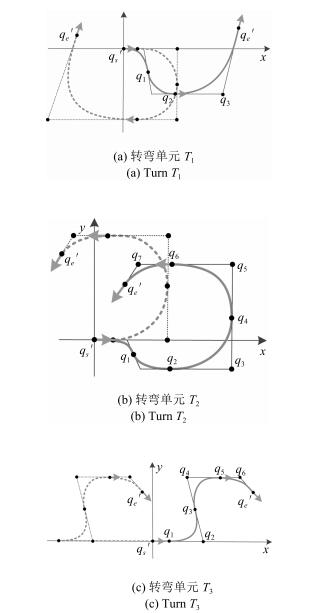
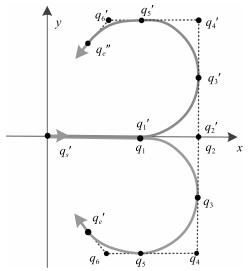
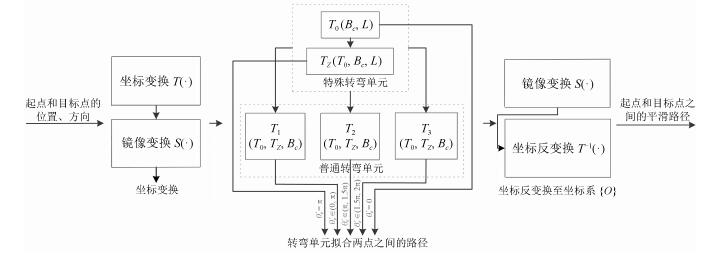
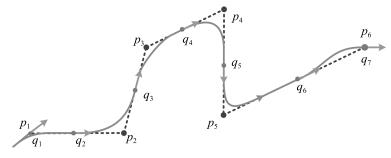
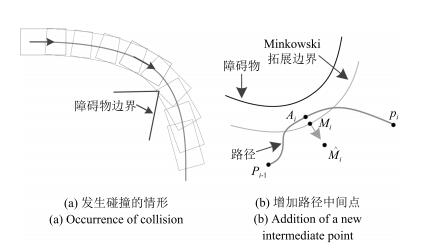
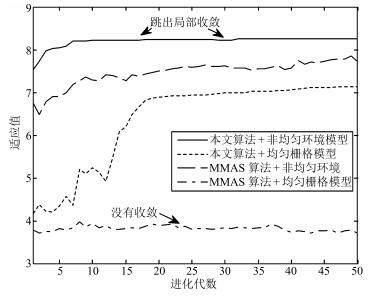
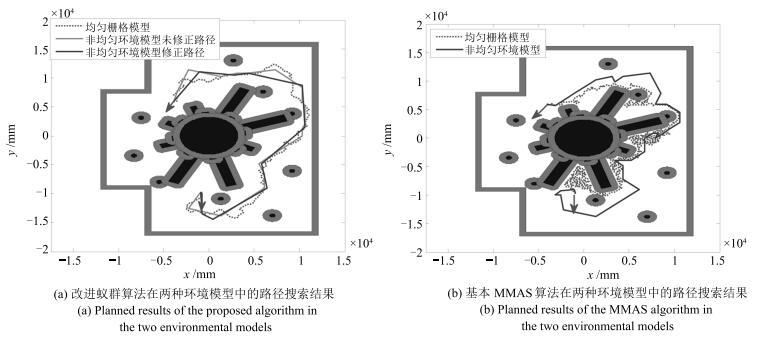
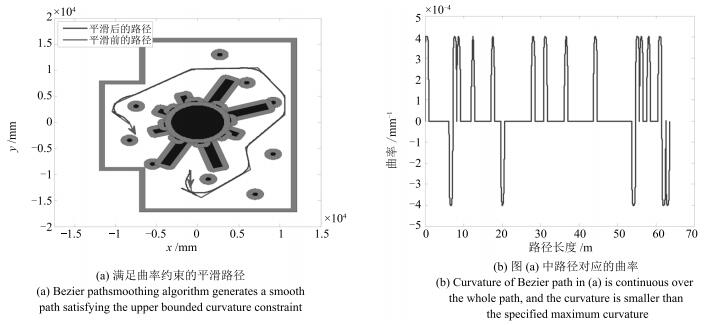
-
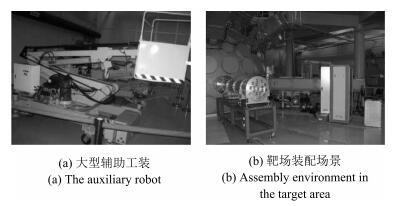
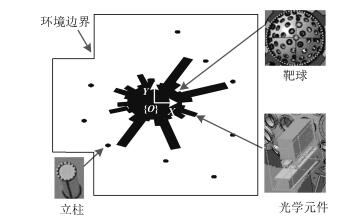
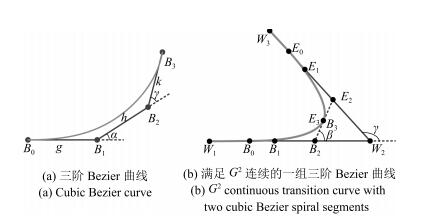
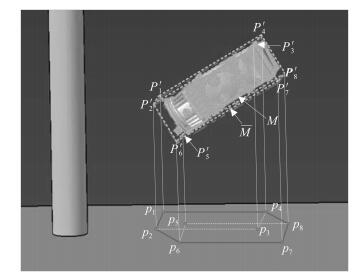
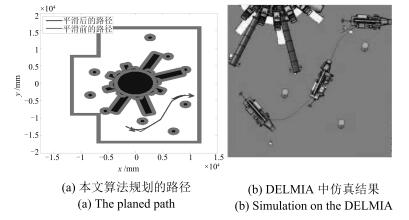
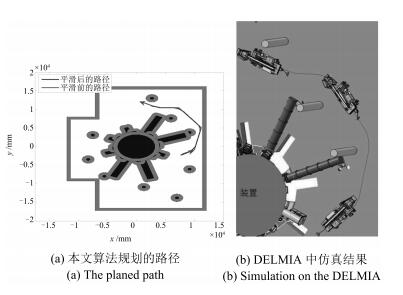
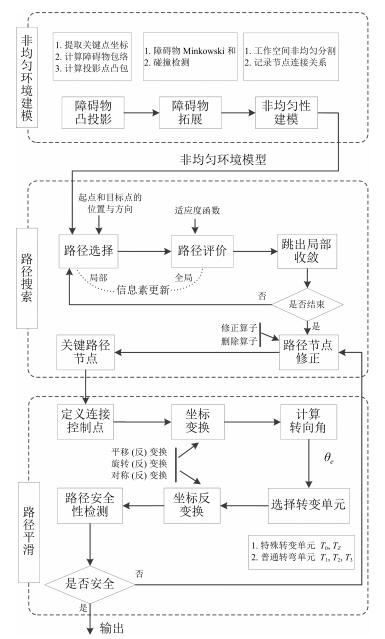
摘要: 针对工作于复杂环境下的大型工装,本文提出了一种基于非均匀环境建模与三阶Bezier曲线的平滑路径规划算法,以指导工装的运动.在环境建模方面,利用四叉树建立环境的非均匀模型,能够有效压缩环境信息,提高搜索效率;在路径搜索方面,以非均匀环境模型为基础,提出一种距离启发搜索和信息素混合更新的蚁群算法,能够得到工装的安全可行路径点;在路径平滑方面,基于三阶Bezier曲线,提出能够连接任意位置和任意方向两点的转弯单元的设计方法,利用转弯单元连接路径搜索算法得到的路径点,能够获得满足工装非完整性约束的平滑路径.最后,以大型激光驱动器的靶场环境为对象,对本文算法的有效性和可靠性进行验证,并利用DELMIA平台进一步验证了规划路径的运动平滑性和安全性.
-
关键词:
- 平滑路径规划 /
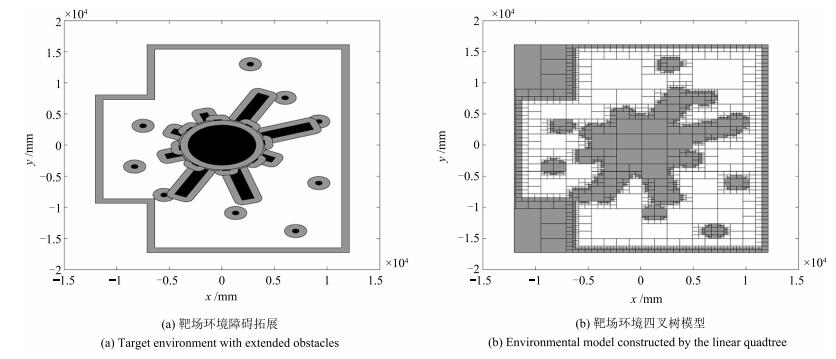
- 非均匀建模 /
- 蚁群算法 /
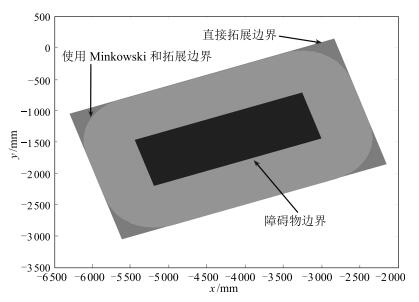
- Minkowski和 /
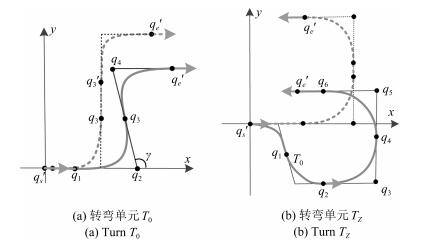
- Bezier曲线
Abstract: In this paper, a path planning algorithm is proposed to search feasible paths for an auxiliary robot working in complex environment. The movement of the robot could thus be guided by the planned result of the algorithm in assembly practice. In the process of environmental modeling, a quad tree method is employed to construct the non-uniform environmental model, which decreases the amount of environmental information to a minimum as needed. As a result, the searching efficiency is improved. In the process of path searching, on the basis of the predefined non-uniform environmental model, an improved ant colony algorithm is presented to search the path points for the robot, which adopts distance-based heuristic search method and fusion of two different pheromone updating mechanisms. In the process of path smoothing, Bezier turn is designed based on cubic Bezier curves to connect two arbitrary configurations. Bezier turns are used to fit a sequence of objective points offered by the improved ant colony algorithm, so that a smooth path satisfying the robot's nonholonomic constraints can be obtained. Finally, the method is experimentally demonstrated in target area with large laser facility. Furthermore, the feasibility and security of the planned path is verified based on the platform of DELMIA.1) 本文责任编委 王红卫 -
表 1 两种建模方法对比
Table 1 Comparison of the two modeling methods
自由栅格 障碍栅格 总数 四叉树法 1 219 1 377 2 596 均匀栅格法 11 839 9 071 20 910 表 2(a) 本文算法与基本MMAS在不同环境模型下对比(a)
Table 2(a) Comparison of the proposed algorithm with the MMAS in different environmental models (a)
序号 终点 改进算法+非均匀模型 改进算法+均匀栅格模型 Fw Lw Ew Bw Tw Fw Lw Ew Bw Tw 1 (−353, −7 548) 8.63 1 897 0.77 2 0.93 8.61 2 444 0.83 3.3 1.01 2 (4 572, −5 381) 8.63 22 717 0.54 6 1.21 8.04 15 082 1.03 24.7 2.99 3 (5 754, −259) 8.46 25 634 0.63 9.7 1.71 7.91 21 730 0.99 36.7 4.51 4 (5 557, 6 242) 8.15 41 289 1.00 16.8 4.32 7.50 44 339 1.26 89.3 13.15 5 (632, 10 182) 8.15 41 954 0.83 15.5 4.33 7.36 50 922 1.12 105.8 15.31 6 (2 602, 11 167) 8.26 43 852 0.82 16.7 4.70 7.33 51 068 1.26 108.3 14.69 7 (−3 899, 5 848) 8.26 53 701 0.79 18.4 5.34 6.98 65 284 1.24 147 2 185 8 (−6 066, 726) 8.18 65 815 0.78 24.8 6.53 6.75 74 028 1.12 175.1 32.27 9 (−10 203, −6 563) 8.21 70 886 0.77 22.8 7.73 6.32 93 157 1.27 240.2 49.75 10 (−5 278, −4 593) 8.14 71 386 0.80 27.1 7.72 6.40 90 830 1.44 227.4 51.42 表 2(b) 本文算法与基本MMAS在不同环境模型下对比(b)
Table 2(b) Comparison of the proposed algorithm with the MMAS in different environmental models (b)
序号 基本MMAS算法+非均匀模型 基本MMAS算法+均匀栅格模型 Fw Lw Ew Bw Tw Fw Lw Ew Bw Tw 1 8.63 1 897 0.77 2 0.57 8.61 2 411 0.90 2.3 0.31 2 8.56 20 341 0.55 6 1.66 7.65 12 711 1.67 27.5 2.09 3 8.46 25 320 0.65 9.2 1.77 7.23 23 016 1.70 61.2 3.93 4 8.04 38 956 1.15 18.4 6.62 6.14 50 406 2.09 152.5 13.14 5 8.13 46 588 0.98 19 7.47 5.36 85 489 2.01 266.8 20.03 6 8.17 44 814 0.93 17.8 6.53 5.67 65 877 2.21 204.4 16.22 7 7.76 66 983 1.26 36 10.46 4.02 200 854 2.38 672.7 38.22 8 7.36 83 167 1.58 56.1 12.96 3.82 1 151 948 2.36 3 925 51.51 9 7.03 116 137 1.63 83.05 15.72 3.88 1 304 770 2.49 4 450 61.40 10 6.95 113 584 1.71 87.1 16.40 3.87 1 418 617 2.61 4 835.9 60.16 表 3 次独立实验中本文算法和基本MMAS算法的对比
Table 3 Comparison of the planned results of the proposed algorithm and the MMAS algorithm in several independent experiments
本文算法 基本MMAS算法 适应度 8.21 7.33 路径长度(mm) 63453 86501 危险度 0.77 1.65 转弯次数(次) 23.1 56.3 耗时(s) 6.51 12.98 -
[1] Elbanhawi M, Simic M. Sampling-based robot motion planning: a review. IEEE Access, 2014, 2: 56-77 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2014.2302442 [2] Maekawa T, Noda T, Tamura S, Ozaki T, Machida K. Curvature continuous path generation for autonomous vehicle using B-spline curves. Computer-Aided Design, 2010, 42(4): 350-359 doi: 10.1016/j.cad.2009.12.007 [3] Jung D, Tsiotras P. On-line path generation for unmanned aerial vehicles using B-spline path templates. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2013, 36(6): 1642-1653 doi: 10.2514/1.60780 [4] O'Rourke J. Computational Geometry in C. London: Cambridge University Press, 1997. [5] Neus M, Maouche S. Motion planning using the modified visibility graph. In: Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics. Tokyo, Japan: IEEE, 1999. 651-655 [6] Brooks R A. Solving the find-path problem by good representation of free space. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1983, SMC-13(2): 190-197 [7] Alajlan M, Koubaa A, Chaari I, Bennaceur H, Ammar A. Global path planning for mobile robots in large-scale grid environments using genetic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Individual and Collective Behaviors in Robotics (ICBR). Sousse, Tunisia: IEEE, 2013. 1-8 [8] Takahashi O, Schilling R J. Motion planning in a plane using generalized voronoi diagrams. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1989, 5(2): 143-150 doi: 10.1109/70.88035 [9] Jan G E, Sun C C, Tsai W C, Lin T H. An O(n log n) shortest path algorithm based on Delaunay triangulation. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2014, 19(2): 660-666 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2013.2252076 [10] Stentz A. Optimal and efficient path planning for unknown and dynamic environments. International Journal of Robotics and Automation, 1995, 10(3): 89-100 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.15.3683 [11] Alexopoulos C, Griffin P M. Path planning for a mobile robot. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1992, 22(2): 318-322 doi: 10.1109/21.148404 [12] Fan D K, Shi P. Improvement of Dijkstra's algorithm and its application in route planning. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD). Yantai, China: IEEE, 2010. 1901-1904 [13] Hu Y R, Yang S X, Xu L Z, Meng M Q H. A knowledge based genetic algorithm for path planning in unstructured mobile robot environments. In: Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). Shenyang, China: IEEE, 2004. 767-772 [14] Dorigo M, Maniezzo V, Coloni A. Ant system: optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 1996, 26(1): 29-41 doi: 10.1109/3477.484436 [15] Juang C F, Hsu C H. Reinforcement ant optimized fuzzy controller for mobile-robot wall-following control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(10): 3931-3940 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2017557 [16] Dorigo M, Gambardella L M. Ant colony system: a cooperative learning approach to the traveling salesman problem. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 1997, 1(1): 53-66 doi: 10.1109/4235.585892 [17] Stützle T, Hoos H H. MAX-MIN ant system. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2000, 16(8): 889-914 doi: 10.1016/S0167-739X(00)00043-1 [18] Zeng D W, He Q, Leng B, Zheng W M, Xu H W, Wang Y Y, Guan G. An improved ant colony optimization algorithm based on dynamically adjusting ant number. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). Guangzhou, China: IEEE, 2012. 2039-2043 [19] Dubins L E. On curves of minimal length with a constraint on average curvature, and with prescribed initial and terminal positions and tangents. American Journal of Mathematics, 1957, 79(3): 497-516 doi: 10.2307/2372560 [20] Reeds J A, Shepp L A. Optimal paths for a car that goes both forwards and backwards. Pacific Journal of Mathematics, 1990, 145(2): 367-393 doi: 10.2140/pjm [21] Boissonnat J D, Cerezo A, Leblond J. Shortest paths of bounded curvature in the plane. In: Proceedings of the 1992 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Nice, France: IEEE, 1992. 2315-2320 [22] Scheuer A, Fraichard T. Collision-free and continuous-curvature path planning for car-like robots. In: Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA: IEEE, 1997. 867-873 [23] Scheuer A, Fraichard T. Planning continuous-curvature paths for car-like robots. In: Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Osaka, Japan: IEEE, 1996. 1304-1311 [24] Scheuer A, Fraichard T. Continuous-curvature path planning for car-like vehicles. In: Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Grenoble, France: IEEE, 1997. 997-1003 [25] Fraichard T, Scheuer A. From Reeds and Shepp's to continuous-curvature paths. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2004, 20(6): 1025-1035 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2004.833789 [26] Yang K, Sukkarieh S. An analytical continuous-curvature path-smoothing algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2010, 26(3): 561-568 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2010.2042990 [27] Walton D J, Meek D S, Ali J M. Planar G2 transition curves composed of cubic Bézier spiral segments. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2003, 157(2): 453-476 doi: 10.1016/S0377-0427(03)00435-7 [28] Škrjanc I, Klančar G. Optimal cooperative collision avoidance between multiple robots based on Bernstein-Bézier curves. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2010, 58(1): 1-9 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2009.09.003 [29] Lo Bianco C G, Piazzi A, Romano M. Smooth motion generation for unicycle mobile robots via dynamic path inversion. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2004, 20(5): 884-891 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2004.832827 [30] Piazzi A, Lo Bianco C G, Romano M. η3-spline for the smooth path generation of wheeled mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2007, 23(5): 1089-1095 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2007.903816 [31] Lai X C, Al Mamun A, Ge S S. Polar polynomial curve for smooth, collision-free path generation between two arbitrary configurations for nonholonomic robots. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Symposium on Intelligent Control. Singapore, Singapore: IEEE, 2007. 59-64 [32] Sahni S. Data Structures, Algorithms, and Applications in C++. Boston: McGraw Hill, 1998. [33] Duan H B, Ma G J, Liu S Q. Experimental study of the adjustable parameters in basic ant colony optimization algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. Singapore, Singapore: IEEE, 2007. 149-156 -




 下载:
下载: