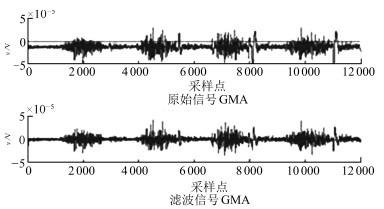
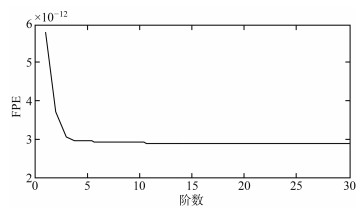
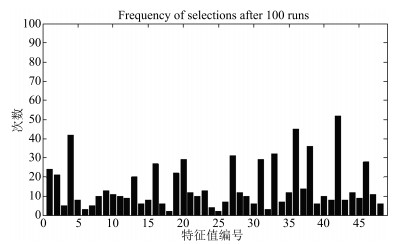
-
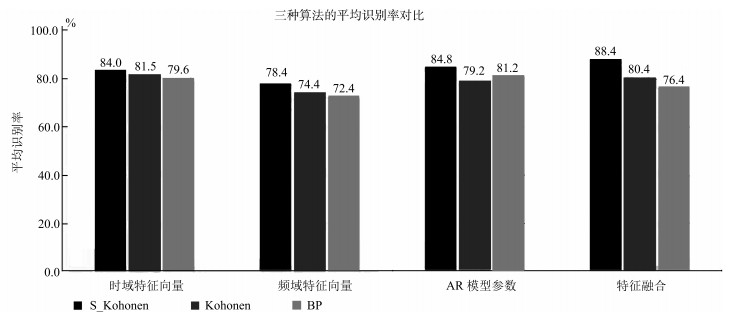
摘要: 表面肌电信号随着时间的变化而改变,这将影响运动模式的分类精度.传统人体下肢假肢运动模式的识别算法不能保证在整个肌电控制时间内达到对运动模式的有效识别.为了解决这些问题,本文提取步态初期200ms的信号的特征值,将无监督和有监督的Kohonen神经网络算法应用到大腿截肢者残肢侧的步态识别中,并与传统BP神经网络进行了对比.结果表明,有监督的Kohonen神经网络算法将五种路况下步态的平均识别率提高到88.4%,优于无监督的Kohonen神经网络算法和BP神经网络.
-
关键词:
- 表面肌电信号 /
- 智能假肢 /
- 特征提取 /
- 有监督Kohonen神经网络 /
- 步态识别
Abstract: Surface electromyography (sEMG) is changeable with time, which will affect the classification accuracy. The traditional recognition method cannot guarantee its effectiveness within whole control cycle for lower limb movement. This paper extracts the feature from initial 200ms EMG, applies Kohonen and supervised Kohonen neural networks, and compares the result with BP neural network. Experimental results show that supervised Kohonen neural network is superior to the other two algorithms. The average recognition rate can be increased to 88.4% for five kinds of terrains. -
表 1 大腿截肢者5种步态的功率谱比值
Table 1 Power spectrum ratio of five gaits
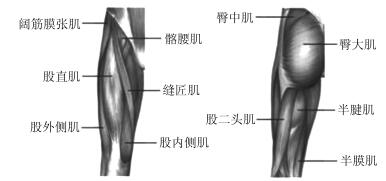
平地 上楼梯 下楼梯 上斜坡 下斜坡 股直肌 6.7530 5.2074 4.2859 3.7062 2.0640 股外侧肌 2.6390 3.0697 2.8058 3.5630 3.0875 股二头肌 1.5962 2.4860 3.5804 2.2074 3.6307 半腱肌 4.8403 5.2830 4.7083 5.0642 4.0974 阔筋膜张肌 2.3746 3.4390 5.0261 5.9803 6.7549 臀大肌 3.9827 3.7650 3.0548 3.2769 2.9067 表 2 大腿截肢者股外侧肌的4阶模型参数
Table 2 The 4th order model parameters of vastus
${\boldsymbol A\boldsymbol R}_1$ ${\boldsymbol A\boldsymbol R}_2$ ${\boldsymbol A\boldsymbol R}_3$ ${\boldsymbol {AR}}_4$ 平地 4.3927 4.2654 4.3761 4.1862 上楼梯 -2.9846 -2.7062 -2.6873 -2.8306 下楼梯 4.6834 4.7635 4.5980 2.2074 上斜坡 3.1370 3.2537 3.3207 3.1752 下斜坡 -0.8349 -0.7859 -0.8263 -0.7952 表 3 步态识别结果
Table 3 The results of gait recognition
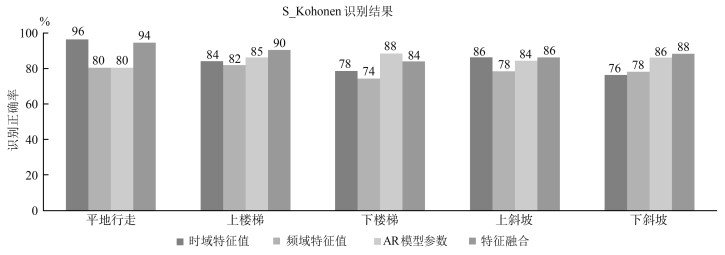
平地 上楼梯 下楼梯 上斜坡 下斜坡 训练样本数 100 100 100 100 100 测试样本数 50 50 50 50 50 识别样本数 47 45 42 43 44 识别率 (%) 94 90 84 86 88 平均识别率 (%) 88.4 -
[1] Chen B J, Wang Q N. Combining human volitional control with intrinsic controller on robotic prosthesis: a case study on adaptive slope walking. In: Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Milan, Italy: IEEE, 2015. 4777-4780 [2] Cherelle P, Mathijssen G, Wang Q N, Vanderborght B, Lefeber D. Advances in propulsive bionic feet and their actuation principles. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 2014: 984046 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266384382_Review_Article_Advances_in_Propulsive_Bionic_Feet_and_Their_Actuation_Principles [3] Meier M R, Hansen A H, Gard S A, McFadyen A K. Obstacle course: users' maneuverability and movement efficiency when using Otto Bock C-Leg, Otto Bock 3R60, and the CaTech SNS prosthetic knee joints. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development, 2012, 49(4): 583-596 doi: 10.1682/JRRD.2010.05.0094 [4] Hoover C D, Fulk G D, Fite K B. The design and initial experimental validation of an active myoelectric transfemoral prosthesis. Journal of Medical Devices, 2012, 6(1): 011005 doi: 10.1115/1.4005784 [5] 田彦涛, 孙中波, 李宏扬, 王静.动态双足机器人的控制与优化研究进展.自动化学报, 2016, 42(8): 1143-1157 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18904.shtmlTian Yan-Tao, Sun Zhong-Bo, Li Hong-Yang, Wang Jing. A review of optimal and control strategies for dynamic walking bipedal robots. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(8): 1143-1157 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18904.shtml [6] Hoover C D, Fulk G D, Fite K B. Stair ascent with a powered transfemoral prosthesis under direct myoelectric control. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2013, 18(3): 1191-1200 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2012.2200498 [7] Kim D H, Cho C H, Ryu J. Real-time locomotion mode recognition employing correlation feature analysis using EMG pattern. ETRI Journal, 2014, 36(1): 99-105 doi: 10.4218/etrij.14.0113.0064 [8] Zhang F, Huang H. Source selection for real-time user intent recognition toward volitional control of artificial legs. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2013, 17(5): 907-914 doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2012.2236563 [9] Huang H, Zhang F, Hargrove L J, Dou Z, Rogers D R, Englehart K B. Continuous locomotion-mode identification for prosthetic legs based on neuromuscular-mechanical fusion. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2011, 58(10): 2867-2875 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2011.2161671 [10] 陈国兴, 耿艳利, 刘作军, 杨鹏.假肢跌倒预警中基于相关性分析的模糊自适应反馈调节.机器人, 2015, 37(6): 732-737, 747 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JQRR201506012.htmChen Guo-Xing, Geng Yan-Li, Liu Zuo-Jun, Yang Peng. Fuzzy adaptive feedback regulation for stumble pre-warning of lower limb prosthesis based on the correlation analysis. Robot, 2015, 37(6): 732-737, 747 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JQRR201506012.htm [11] 赵丽娜, 刘作军, 苟斌, 杨鹏.基于隐马尔可夫模型的动力型下肢假肢步态预识别.机器人, 2014, 36(3): 337-341 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JQRR201403012.htmZhao Li-Na, Liu Zuo-Jun, Gou Bin, Yang Peng. Gait pre-recognition of dynamic lower limb prosthesis based on hidden Markov model. Robot, 2014, 36(3): 337-341 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JQRR201403012.htm [12] Peng L, Hou Z G, Kasabov K, Hu J, Peng L, Wang W Q. sEMG-based torque estimation for robot-assisted lower limb rehabilitation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Ireland, County Kerry: IEEE, 2015. DOI: 10.1109/IJCNN.2015.7280449. [13] 丁其川, 熊安斌, 赵新刚, 韩建达.基于表面肌电的运动意图识别方法研究及应用综述.自动化学报, 2016, 42(1): 13-25 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18792.shtmlDing Qi-Chuan, Xiong An-Bin, Zhao Xin-Gang, Han Jian-Da. A review on researches and applications of sEMG-based motion intent recognition methods. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(1): 13-25 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18792.shtml [14] Vallery H, Burgkart R, Hartmann C, Mitternacht J, Riener R, Buss M. Complementary limb motion estimation for the control of active knee prostheses. Biomedizinische Technik. Biomedical Engineering, 2011, 56(1): 45-51 doi: 10.1515/bmt.2010.057 [15] 刘洪涛, 曹玉珍, 谢小波, 胡勇.表面肌电信号的时变AR模型参数评估肌疲劳程度的研究.中国生物医学工程学报, 2007, 26(4): 493-497 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSWY200704002.htmLiu Hong-Tao, Cao Yu-Zhen, Xie Xiao-Bo, Hu Yong. Estimation of muscle fatigue degree using time-varying autoregressive model parameter estimation of surface electromyography. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2007, 26(4): 493-497 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSWY200704002.htm [16] 张培林, 李胜.基于小波包变换和GA-PLS算法的故障特征选择方法.振动、测试与诊断, 2014, 34(2): 385-391 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCS201402035.htmZhang Pei-Lin, Li Sheng. Fault feature selection method based on wavelet and GA-PLS algorithm. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2014, 34(2): 385-391 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCS201402035.htm [17] Zhou S, Lawson D L, Morrison W E, Fairweather I. Electromechanical delay in isometric muscle contractions evoked by voluntary, reflex and electrical stimulation. European Journal of Applied Physiology and Occupational Physiology, 1995, 70(2): 138-145 doi: 10.1007/BF00361541 [18] Lawson B E, Varol H A, Huff A, Erdemir E, Goldfarb M. Control of stair ascent and descent with a powered transfemoral prosthesis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2012, 21(3): 466-473 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232699496_Control_of_Stair_Ascent_and_Descent_With_a_Powered_Transfemoral_Prosthesis [19] Huang S, Ferris D P. Muscle activation patterns during walking from transtibial amputees recorded within the residual limb-prosthetic interface. Journal of Neuroengineering and Rehabilitation, 2012, 9: 55. DOI: 10.1186/1743-0003-9-55 [20] Hargrove L J, Simon A M, Lipschutz R D, Finucane S B, Kuiken T A. Real-time myoelectric control of knee and ankle motions for transfemoral amputees. JAMA, 2011, 305(15): 1542-1544 doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.465 [21] Sagawa Y Jr, Turcot K, Armand S, Thevenon A, Vuillerme N, Watelain E. Biomechanics and physiological parameters during gait in lower-limb amputees: a systematic review. Gait & Posture, 2011, 33(4): 511-526 http://www.academia.edu/17420300/Biomechanics_and_physiological_parameters_during_gait_in_lower-limb_amputees_A_systematic_review -




 下载:
下载: