Construction of Lower Limb's Functional Muscle Network and Its Application Based on Surface EMG
-
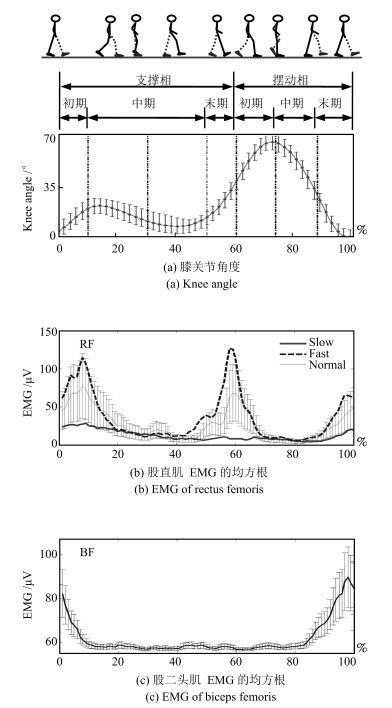
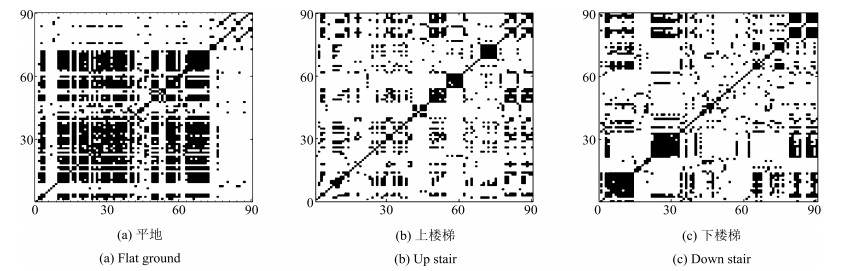
摘要: 在肌电控制下肢康复辅具研究中,合适的肌电采集位置是运动模式识别的前提与基础.针对目前肌电采集位置缺乏成熟理论依据和统一标准的问题,选取90个下肢肌电采集点作为节点,通过计算节点间的肌电相关性,构建下肢肌肉功能网络,证明其具有小世界特性.实验结果表明:不同运动模式的网络具有明显的拓扑结构差异,通过网络特性分析可以确定与模式关联度大的肌电采集位置,取得较好的运动模式识别结果.通过构建及分析下肢肌肉功能网络,深入了解下肢运动模式更替过程中的肌肉协同工作机制,为下肢康复辅具控制中肌电采集位置的确定提供了理论支持.Abstract: For myoelectric control study on lower limb rehabilitation aids, suitable electrode placements are the premise and foundation of movement pattern recognition. In response to the lack of mature theoretical basis and uniform standards for electrode placement, 90 acquisition points of lower limb are chosen as nodes, and a functional muscle network of lower limb is established by calculating correlations among those nodes. The characteristic of small work is also proved. The results show that there are obvious topology structure differences among different movement patterns. The collection locations which have close relationship with movement patterns can be selected through analysis of network features, and they may provide considerable precision for identification of movement patterns. Constructing and analyzing the functional muscle network may help to explore the collaborative work mechanism of muscles in transformation process, and provide theoretical support for selection of electromyography acquisition location.1) 本文责任编委 赵新刚
-
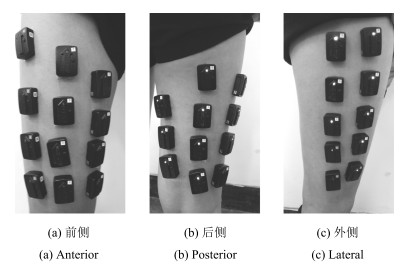
表 1 肌电电极分区与分布情况
Table 1 The partition and distribution of EMG electrodes
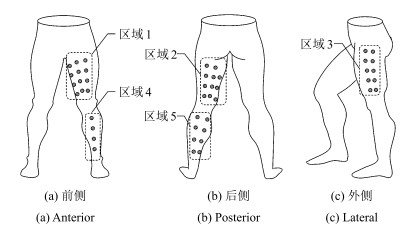
区域 个数 节点 名称 位置 分布情况 1 12 V01~V12 LTF1~LTF12 左侧大腿前侧 四排三列 2 11 V13~V23 LTP1~LTP12 左腿大腿后侧 三列 (三排一列+四排两列) 3 10 V24~V33 LTL1~LTL10 左腿大腿外侧 五排两列 4 4 V34~V37 LCF1~LCF4 左侧小腿前侧 纵向排列 5 8 V38~V45 LCP1~LCP8 左腿小腿后侧 四排两列 6 12 V46~V57 RTF1~RTF12 右侧大腿前侧 四排三列 7 11 V58~V68 RTP1~RTP12 右腿大腿后侧 三列 (三排一列+四排两列) 8 10 V69~V78 RTL1~RTL10 右腿大腿外侧 五排两列 9 4 V79~V82 RCF1~RCF4 右侧小腿前侧 纵向排列 10 8 V83~V90 RCP1~RCP8 右腿小腿后侧 四排两列 表 2 受试者信息
Table 2 The information of subjects
实验对象 性别 年龄 身高 (cm) 体重 (kg) S1 女 24 165 48 S2 女 24 170 54 S3 女 45 162 65 S4 女 65 155 73 S5 男 23 172 80 S6 男 27 180 95 S7 男 42 175 70 S8 男 62 170 72 表 3 三种模式复杂网络的小世界特性参量统计
Table 3 Three models of complex networks of small world characteristic parameter statistics
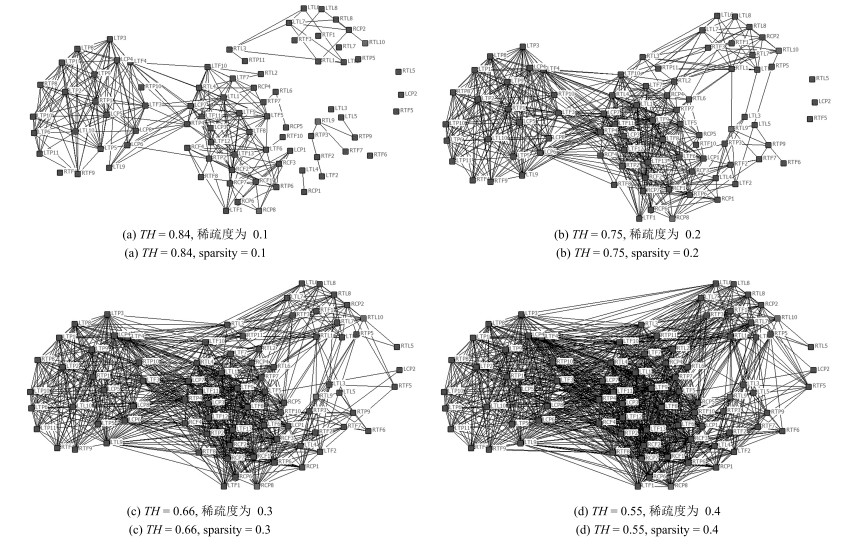
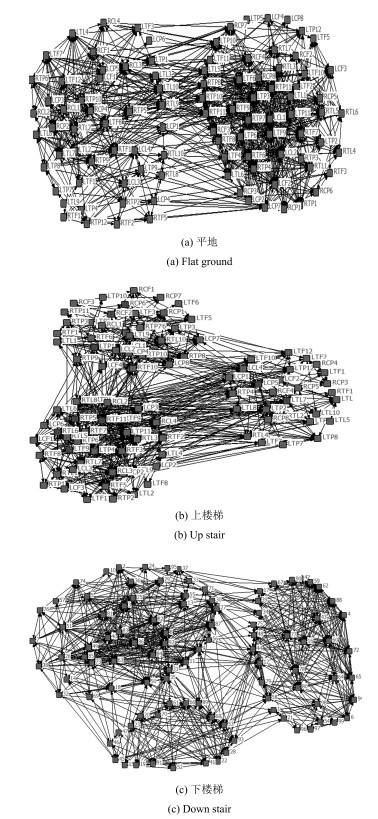
运动模式 $n$ $langlekrangle$ $edges$ $CC$ $L$ $C_{nc}$ $L_{nc}$ $C_{ER}$ $L_{ER}$ $gamma=C/{C_{ER}}$ $lambda=L/{L_{ER}}$ $sigma=gamma/lambda$ 平地 90 30.0 2487 0.8883 1.7857 0.7241 1.3833 0.3659 1.2992 2.4277 1.3745 1.7662 上楼梯 90 13.1 1091 0.8874 2.3736 0.6880 3.1679 0.1598 1.7129 5.5532 1.3857 4.0075 下楼梯 90 16.1 1337 0.8318 2.0372 0.7003 2.5776 0.1963 1.5902 4.2374 1.2811 3.3076 表 4 不同阈值下的网络统计特性
Table 4 Network statistical characteristics under different threshold
$TH$ 稀疏度$S_p$ 平均度$langlekrangle$ 聚类系数$CC$ 0.5 0.4916 40.81 0.7527 0.55 0.4266 35.41 0.7665 0.6 0.3648 30.28 0.7708 0.65 0.3024 25.10 0.7899 0.7 0.2472 20.52 0.7945 0.75 0.1941 16.11 0.8318 0.8 0.1418 11.77 0.8250 0.85 0.0910 7.55 0.8193 0.9 0.0565 4.69 0.7194 0.95 0.0344 2.86 0.5770 表 5 不同模式下节点介数特性统计
Table 5 Node betweenness under different model
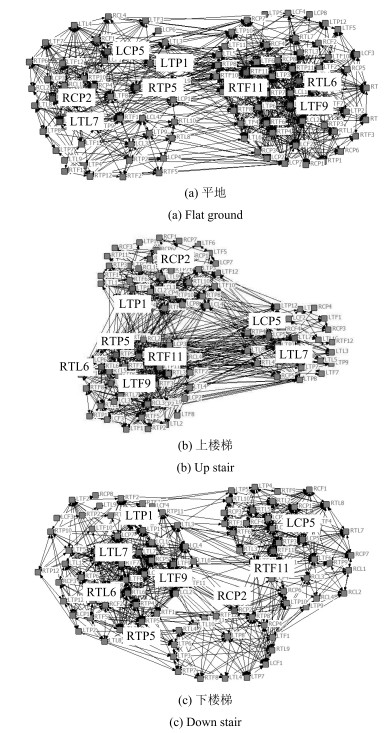
排序 平地 下楼 上楼 1 RTL4h 280.1 LCP6h 1644.4 RCP4h 557.2 2 RTF9h 277.7 RTP6h 1473.8 RCP8h 366.5 3 RTL10h 267.0 RCP3h 1369.9 RCP6h 344.4 4 LTP5h 236.4 LTL4h 1304.2 RCP5h 327.2 5 RTF10h 208.8 RTP3h 1216.6 RTP6h 318.2 6 RTF7h 180.6 RCP2h 1212.6 LTP3h 301.6 7 LTF10h 161.4 RTL1h 1198.6 RTF8h 287.5 8 LCP3h 151.1 RTL9h 1141.3 RTP3h 221.2 9 RTF1h 135.9 RTP2h 1048.7 RTP1h 218.5 10 LCP5h 128.4 RTL2h 932.4 RTL8h 193.0 表 6 不同模式下节点介数特性统计
Table 6 Node betweenness under different model
排序 节点标号 位置 1 RTP5 右腿大腿后侧 2 LTP1 左腿大腿后侧 3 LTL7 左腿大腿后侧 4 LTF9 左腿大腿前侧 5 RTL6 右腿大腿外侧 6 RCP2 右腿小腿后侧 7 LCP5 左腿小腿后侧 8 RTF11 右腿大腿前侧 表 7 不同特征提取方法的模式识别比较
Table 7 Comparison of pattern recognition based on different methods of feature extraction
序号 单侧肌肉数目 肌肉采集点 识别率 (%) LDA SVM NN S1 12 大腿:RF, VL, BF, VM, ST, SM, AL, KTF小腿:TA, PL, GM, SM 78.1 82.3 80.2 S2 8 大腿:RF, VL, BF, VM, ST小腿:TA, GM, SM 91.4 93.1 92.2 S3 6 大腿:RF, VL, BF, VM小腿:TA, GM 95.6 97.6 97.3 S4 3 大腿:RF, VL小腿:SM[6] 84.4 85.7 86.4 S5 4 大腿:VM, SM, AL, KTF[7] 87.4 90.6 89.9 S6 4 下肢肌肉功能网络分析结果 95.3 98.4 97.9 -
[1] Fan Y J, Yin Y H. Active and progressive exoskeleton rehabilitation using multisource information fusion from EMG and force-position EPP. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2013, 60(12): 3314-3321 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2013.2267741 [2] Tsai A C, Luh J J, Lin T T. A novel STFT-ranking feature of multi-channel EMG for motion pattern recognition. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(7): 3327-3341 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2014.11.044 [3] Hoover C D, Fulk G D, Fite K B. Stair ascent with a powered transfemoral prosthesis under direct myoelectric control. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2013, 18(3): 1191-1200 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2012.2200498 [4] 丁其川, 熊安斌, 赵新刚, 韩建达.基于表面肌电的运动意图识别方法研究及应用综述.自动化学报, 2016, 42(1): 13-25 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18792.shtmlDing Qi-Chuan, Xiong An-Bin, Zhao Xin-Gang, Han Jian-Da. A review on researches and applications of sEMG-based motion intent recognition methods. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(1): 13-25 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18792.shtml [5] 胡进, 侯增广, 陈翼雄, 张峰, 王卫群.下肢康复机器人及其交互控制方法.自动化学报, 2014, 40(11): 2377-2390 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18514.shtmlHu Jin, Hou Zeng-Guang, Chen Yi-Xiong, Zhang Feng, Wang Wei-Qun. Lower limb rehabilitation robots and interactive control methods. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(11): 2377-2390 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18514.shtml [6] 佟丽娜, 侯增广, 彭亮, 王卫群, 陈翼雄, 谭民.基于多路sEMG时序分析的人体运动模式识别方法.自动化学报, 2014, 40(5): 810-821 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18349.shtmlTong Li-Na, Hou Zeng-Guang, Peng Liang, Wang Wei-Qun, Chen Yi-Xiong, Tan Min. Multi-channel sEMG time series analysis based human motion recognition method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(5): 810-821 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18349.shtml [7] 佘青山, 高云园, 孟明, 罗志增.下肢EMG的小波支持向量机多类识别方法.华中科技大学学报 (自然科学版), 2010, 38(10): 75-79 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG201010022.htmShe Qing-Shan, Gao Yun-Yuan, Meng Ming, Luo Zhi-Zeng. Multiclass recognition of lower limb EMG using wavelet SVM. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(10): 75-79 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG201010022.htm [8] He H, Kiguchi K, Horikawa E. A study on lower-limb muscle activities during daily lower-limb motions. International Journal of Bioelectromagnetism, 2007, 9(2): 79-84 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228896722_A_Study_on_Lower-Limb_Muscle_Activities_during_Daily_Lower-Limb_Motions [9] Chen B J, Zheng E H, Wang Q N, Wang L. A new strategy for parameter optimization to improve phase-dependent locomotion mode recognition. Neurocomputing, 2015, 149: 585-593 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.08.016 [10] Ambrozic L, Gorsic M, Geeroms J, Flynn L, Lova R M, Kamnik R, Munih M, Vitiello N. CYBERLEGs: a user-oriented robotic transfemoral prosthesis with whole-body awareness control. IEEE Robotics and Automation Magazine, 2014, 21(4): 82-93 doi: 10.1109/MRA.2014.2360278 [11] Spanias J A, Perreault E J, Hargrove L J. Detection of and compensation for EMG disturbances for powered lower limb prosthesis control. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2016, 24(2): 226-234 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2015.2413393 [12] Zhang D H, Zhao X G, Han J D, Zhao Y W. A comparative study on PCA and LDA based EMG pattern recognition for anthropomorphic robotic hand. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Hong Kong, China, IEEE, 2014. 4850-4855 [13] Watts D J, Strogatz S H. Collective dynamics of "small-world" networks. Nature, 1998, 393(6684): 440-442 doi: 10.1038/30918 [14] Barabási A L, Albert R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science, 1999, 286(5439): 509-512 doi: 10.1126/science.286.5439.509 [15] 郝崇清, 王江, 邓斌, 魏熙乐.基于复杂网络的脑电信号分析.计算机应用研究, 2012, 29(10): 3870-3872 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYJ201210070.htmHao Chong-Qing, Wang Jiang, Deng Bin, Wei Xi-Le. Electroencephalograph analysis based on complex networks. Application Research of Computers, 2012, 29(10): 3870-3872 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYJ201210070.htm [16] Caciagli L, Bernhardt B C, Hong S J, Bernasconi A, Bernasconi N. Functional network alterations and their structural substrate in drug-resistant epilepsy. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2014, 8: 411 [17] 胡赛, 熊慧军, 李学勇, 赵碧海, 倪问尹, 杨品红, 刘臻.多关系蛋白质网络构建及其应用研究.自动化学报, 2015, 41(12): 2155-2163 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18788.shtmlHu Sai, Xiong Hui-Jun, Li Xue-Yong, Zhao Bi-Hai, Ni Wen-Yin, Yang Pin-Hong, Liu Zhen. Construction of multi-relation protein networks and its application. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(12): 2155-2163 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18788.shtml [18] Karbasi A, Ioannidis S, Massoulié L. From small-world networks to comparison-based search. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2015, 61(6): 3056-3074 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2015.2418284 [19] Saniee I. Scalable algorithms for large and dynamic networks: reducing big data for small computations. Bell Labs Technical Journal, 2015, 20: 23-33 doi: 10.15325/BLTJ.2015.2437465 [20] 陈俊杰, 李海芳, 相洁, 郭浩.脑网络组学构建分析及应用研究.太原理工大学学报, 2012, 43(3): 329-333, 343 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYGY201203019.htmChen Jun-Jie, Li Hai-Fang, Xiang Jie, Guo Hao. Human connectome research: construction, analysis and application. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2012, 43(3): 329-333, 343 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYGY201203019.htm [21] Zheng E H, Wang L, Wei K L, Wang Q N. A noncontact capacitive sensing system for recognizing locomotion modes of transtibial amputees. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2014, 61(12): 2911-2920 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2014.2334316 -




 下载:
下载: