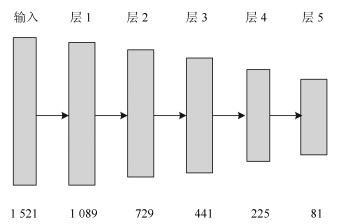
Polarimetric SAR Image Classification Based on Deep Learning and Hierarchical Semantic Model
-
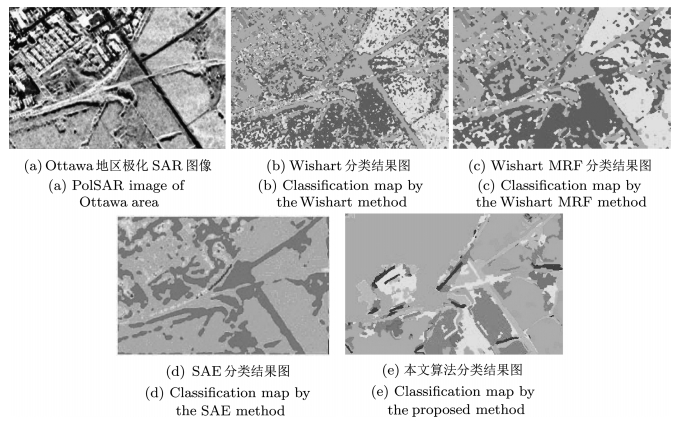
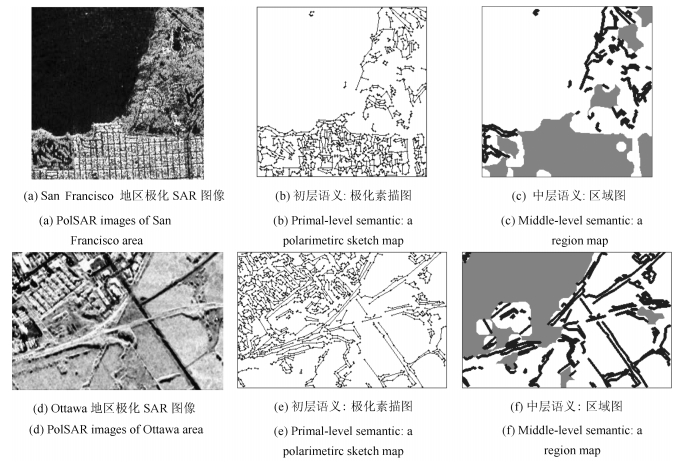
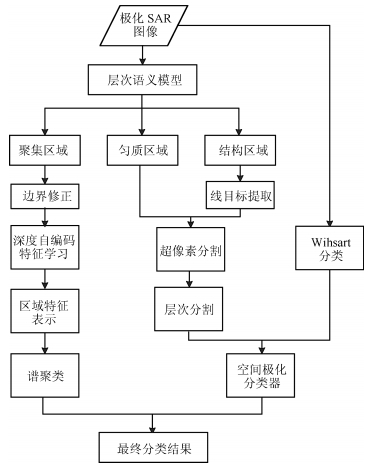
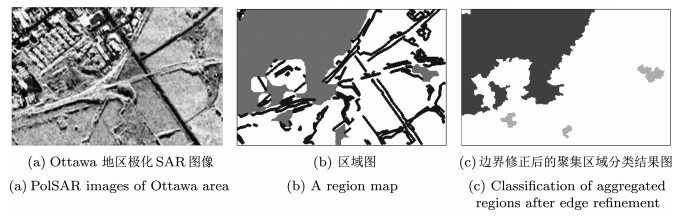
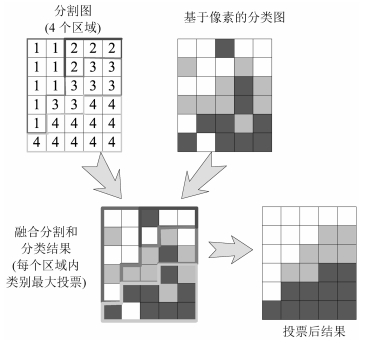
摘要: 针对复杂场景的极化合成孔径雷达(Synthetic aperture radar,SAR)图像,堆叠自编码模型能够自动学习高层特性,有效表示城区、森林等复杂地物的结构,然而,却难以保持图像的边界和细节.为了克服该缺点,本文结合深度自编码器和极化层次语义模型(Polarimetric hierarchical semantic model,PHSM),提出了新的无监督的极化SAR图像分类算法.该方法根据极化层次语义模型,将复杂的极化SAR图像划分为聚集、匀质和结构三大区域.对聚集区域,采用堆叠自编码模型进行高层特征表示,并构造字典得到稀疏特征进行分类;对匀质区域,采用层次模型进行分类;对于结构区域,进行线目标保留和边界定位.实验结果表明,该算法通过不同的分类策略优势互补,能够得到区域一致性好且边界保持的分类结果.Abstract: Stacked auto-encoder model can effectively represent the complex terrain structures, such as the urban and the forest, by automatically learning high-level features. However, it has difficulty in preserving details and edges. In order to overcome this shortcoming, a new unsupervised polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (PolSAR) classification method is proposed by combining the deep learning and the polarimetric hierarchical semantic model (PHSM). According to the PHSM, a PolSAR image is partitioned into aggregated, homogeneous and structural regions. For aggregated regions, a stacked auto-encoder model is applied to learn high-level features, and further the sparse representation and classification is constructed by learning a dictionary with high-level features. For homogeneous regions, hierarchical segmentation and classification is applied. In addition, edges are located and line objects are preserved for structural regions. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can obtain good performance in both region homogeneity and edge preservation.1) 本文责任编委 柯登峰
-
表 1 不同算法的分类结果统计(%)
Table 1 Classification accuracies for different algorithms (%)
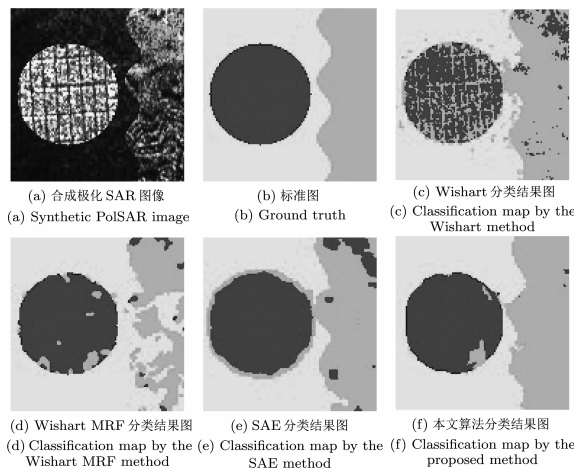
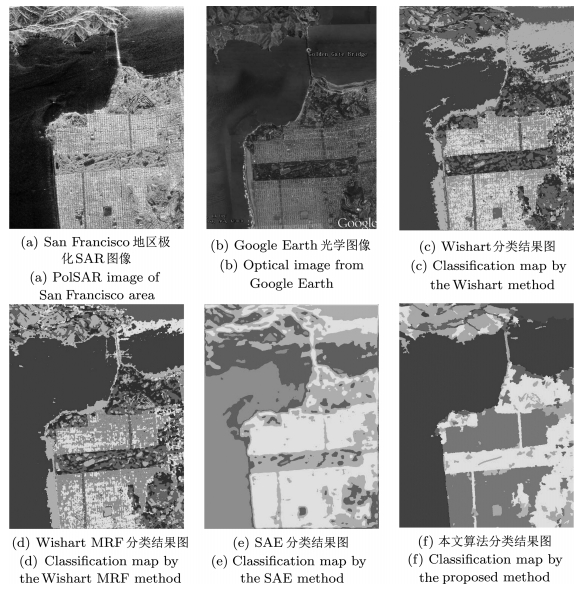
Wishart Wishart MRF SAE 本文算法 城区 61.33 92.47 96.11 92.94 海洋 96.05 99.23 93.64 97.09 森林 93.52 58.52 95.79 98.13 平均精度 83.63 83.41 95.18 96.05 Kappa系数 78.48 76.75 84.64 94.30 表 2 文中算法的混淆矩阵(%)
Table 2 Confusion matrix for the proposed method (%)
城区 海洋 森林 城区 92.94 2.70 4.36 海洋 0.40 97.09 2.51 森林 0.32 1.55 98.13 表 3 不同算法的运行时间(s)
Table 3 Running time for different algorithms (s)
Wishart Wishart MRF SAE 本文算法 时间 9.79 68.41 109.55 98.82 -
[1] Cloude S R, Pottier E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1):68-78 doi: 10.1109/36.551935 [2] Zhao L W, Zhou X G, Jiang Y M, Kuang G Y. Iterative classification of polarimetric SAR image based on the freeman decomposition and scattering entropy. In:Proceedings of the 1st Asian and Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, APSAR 2007. Huangshan, China:IEEE, 2007. 473-476 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/4418653/ [3] Lee J S, Grunes M R. Classification of multi-look polarimetric SAR data based on complex Wishart distribution. In:Proceedings of the National Telesystems Conference. Washington D.C., USA:IEEE, 1992. 7/21-7/24 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/267879/ [4] Beaulieu J M, Touzi R. Segmentation of textured polarimetric SAR scenes by likelihood approximation. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(10):2063-2072 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.835302 [5] Shan Z L, Wang C, Zhang H, Wu F. Change detection in urban areas with high resolution SAR images using second kind statistics based G0 distribution. In:Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). Honolulu, HI:IEEE, 2010. 4600-4603 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5654435/ [6] Bombrun L, Vasile G, Gay M, Totir F. Hierarchical segmentation of polarimetric SAR images using heterogeneous clutter models. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(2):726-737 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2060730 [7] Lee J S, Grunes M R, Ainsworth T L, Du L J, Schuler D L, Cloude S R. Unsupervised classification using polarimetric decomposition and the complex Wishart classifier. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5):2249-2258 doi: 10.1109/36.789621 [8] Zhang B, Ma G R, Zhang Z, Qin Q Q. Region-based classification by combining MS segmentation and MRF for POLSAR images. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 24(3):400-409 doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2013.00048 [9] Ersahin K, Cumming I, Yedlin M. Classification of polarimetric SAR data using spectral graph partitioning. In:Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. Denver, USA:IEEE, 2006. 1756-1759 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/4241601/ [10] Ersahin K, Cumming I G, Ward R K. Segmentation and classification of polarimetric SAR data using spectral graph partitioning. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(1):164-174 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2024303 [11] Niu X, Ban Y F. An adaptive contextual SEM algorithm for urban land cover mapping using multitemporal high-resolution polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2012, 5(4):1129-1139 doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2012.2201448 [12] Liu F, Shi J F, Jiao L C, Liu H Y, Yang S Y, Wu J, Hao H X, Yuan J L. Hierarchical semantic model and scattering mechanism based PolSAR image classiffication. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 59:325-342 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.02.020 [13] Bengio Y. Learning deep architectures for AI. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2009, 2(1):1-127 doi: 10.1561/2200000006 [14] Bengio Y, Courville A, Vincent P. Representation learning:a review and new perspectives. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(8):1798-1828 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.50 [15] Vincent P. A connection between score matching and denoising autoencoders. Neural Computation, 2011, 23(7):1661-1674 doi: 10.1162/NECO_a_00142 [16] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In:Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25. Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA:Curran Associates, Inc., 2012. 1097-1105 http://papers.nips.cc/paper/4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks [17] Salakhutdinov R, Hinton G. An efficient learning procedure for deep Boltzmann machines. Neural Computation, 2012, 24(8):1967-2006 doi: 10.1162/NECO_a_00311 [18] Yildirim S, Cemgil T A, Aktar M, Ozakin Y, Ertuzun A. A Bayesian deconvolution approach for receiver function analysis. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12):4151-4163 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2050327 [19] Lee H, Ekanadham C, Ng A Y. Sparse deep belief net model for visual area V2. In:Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 20. Cambridge, MA:MIT Press, 2008. 873-880 http://papers.nips.cc/paper/3313-sparse-deep-belief-net-model-for-visual-area-v2 [20] Hyvärinen A, Hoyer P O. A two-layer sparse coding model learns simple and complex cell receptive fields and topography from natural images. Vision Research, 2001, 41(18):2413-2423 doi: 10.1016/S0042-6989(01)00114-6 [21] Ito M, Komatsu H. Representation of angles embedded within contour stimuli in area V2 of macaque monkeys. The Journal of Neuroscience, 2004, 24(13):3313-3324 doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4364-03.2004 [22] Vincent P, Larochelle H, Lajoie I, Bengio Y, Manzagol P A. Stacked denoising autoencoders:Learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11:3371-3408 [23] Marr D. Vision:A Computational Investigation into the Human Representation and Processing of Visual Information. New York:W. H. Freeman and Company, 1982. [24] Guo C E, Zhu S C, Wu Y N. Primal sketch:integrating structure and texture. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2007, 106(1):5-19 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2005.09.004 [25] Comaniciu D, Meer P. Mean shift:a robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(5):603-619 doi: 10.1109/34.1000236 [26] Tirilly P, Claveau V, Gros P. Language modeling for bag-of-visual words image categorization. In:Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Content-based Image and Video Retrieval. New York, USA:ACM, 2008. 249-258 [27] Ning J F, Zhang L, Zhang D, Wu C K. Interactive image segmentation by maximal similarity based region merging. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(2):445-456 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.03.004 [28] Feng J L, Cao Z J, Pi Y M. Polarimetric contextual classification of PolSAR images using sparse representation and superpixels. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(8):7158-7181 doi: 10.3390/rs6087158 [29] Rignot E, Chellappa R. Segmentation of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar data. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1992, 1(3):281-300 doi: 10.1109/83.148603 -




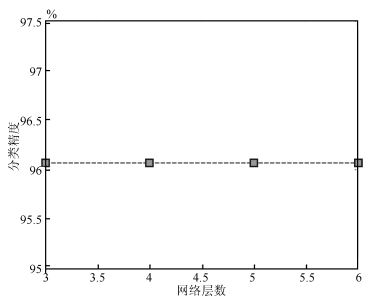
 下载:
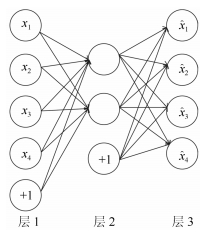
下载: