Adaptive Ensemble Modelling Approach Based on Updating Sample Intelligent Identification
-
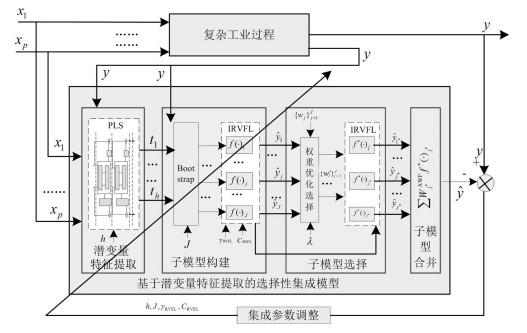
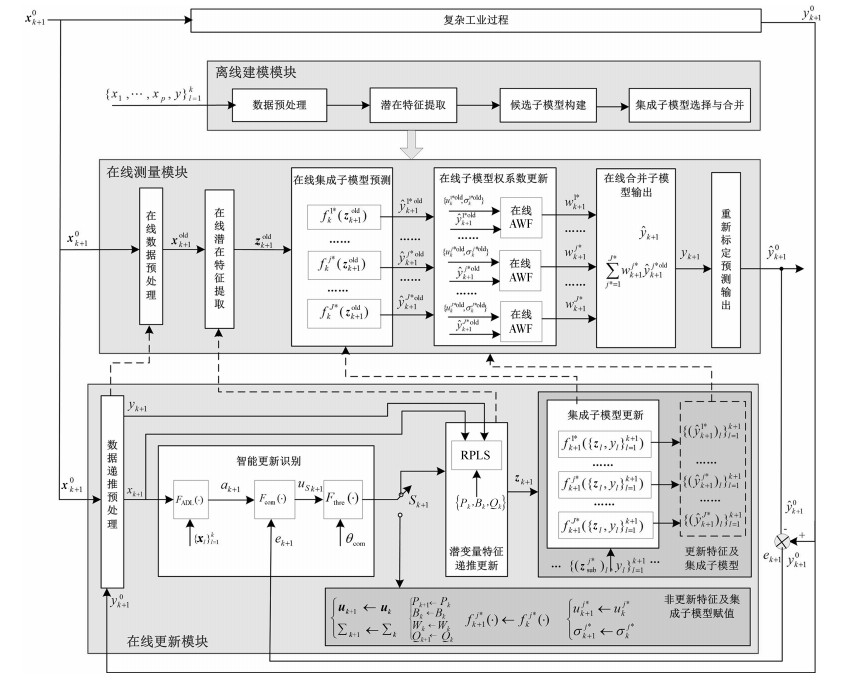
摘要: 选择表征建模对象特性漂移的新样本对软测量模型进行自适应更新,能够降低模型复杂度和运行消耗,提高模型可解释性和预测精度.针对新样本近似线性依靠程度(Approximate linear dependence, ALD)和预测误差(Prediction error, PE)等指标只能片面反映建模对象的漂移程度,领域专家结合具体工业过程需要依据上述指标和自身积累经验进行更新样本的有效识别等问题,本文提出了基于更新样本智能识别算法的自适应集成建模策略.首先,基于历史数据离线建立基于改进随机向量泛函连接网络(Improved random vector functional-link networks, IRVFL)的选择性集成模型;然后,基于集成子模型对新样本进行预测输出后采用在线自适应加权算法(On-line adaptive weighting fusion, OLAWF)对集成子模型权重进行更新,实现在线测量阶段对建模对象特性变化的动态自适应;接着基于领域专家知识构建模糊推理模型对新样本相对ALD(Relative ALD, RALD)值和相对PE(Relative PE, RPE)值进行融合,实现更新样本智能识别,构建新的建模样本库;最后实现集成模型的在线自适应更新.采用合成数据仿真验证了所提算法的合理性和有效性.Abstract: Some new samples can represent concept drift of the modeling plant. Adaptive updating soft sensor model with these new samples can reduce model complexity and running consumption, improve model interpretation and prediction performance. Concept drift embodies on both approximate linear dependence (ALD) and prediction error (PE). In industrial practice, whether to update the old soft measuring models should be decided by the domain experts. Aimmed at these problems, a new online ensemble modeling approach based on updating sample intelligent identification is proposed in this paper. At first, the offline ensemble model based on improved random vector functional-link networks (IRVFL) algorithm is used for online prediction using the new sample. Then, relative ALD (RALD) and relative PE (RPE) values of the new sample are fed into the fuzzy inference model based on domain expert's knowledge, whose output is used to identify whether this new sample is taken to updating the model. At last, the ensemble model is updated with the re-training strategy. Simulation results based on synthetic data show that the proposed method is valid and effective.
-
表 1 更新样本模糊推理规则
Table 1 Fuzzy inference rulers of the updating sample
Us RALD NB NM NS Z PS PM PB R NB NB NB NM NM NS NS Z P NM NB NM NM NS NS Z PS E NS NM NM NS NS Z PS PS Z NM NS NS Z PS PS PM PS NS NS Z PS PS PM PM PM NS Z PS PS PM PM PB PB Z PS PS PM PM PB PB 表 2 仿真数据的方差贡献率(%)
Table 2 Percent variance contribution of the simulation data(%)
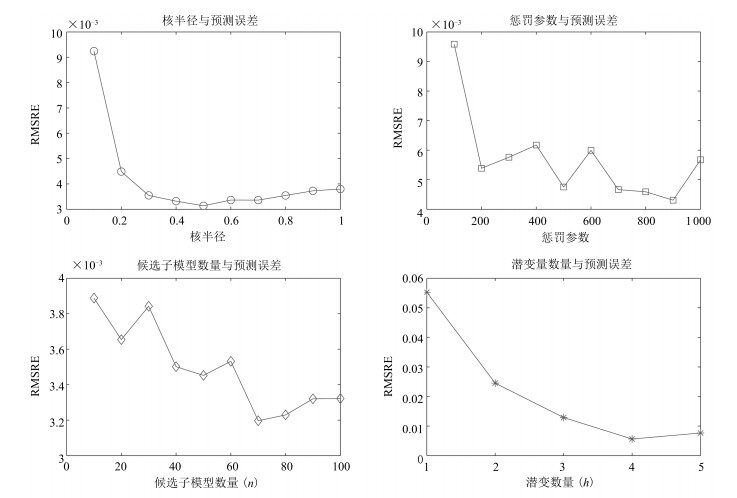
LV 输入数据(X-Block) 输出数据(Y-Block) 潜变量贡献率 累计贡献率 潜变量贡献率 累计贡献率 1 69.79 69.79 66 66 2 28.33 98.11 25.66 91.65 3 1.62 99.73 7.86 99.51 4 0.16 99.89 0.05 99.56 5 0.11 100 0 99.57 表 3 仿真数据在线更新模型重复20次的统计结果
Table 3 Statistical results of the online updating model with repeated 20 times for the simulation data
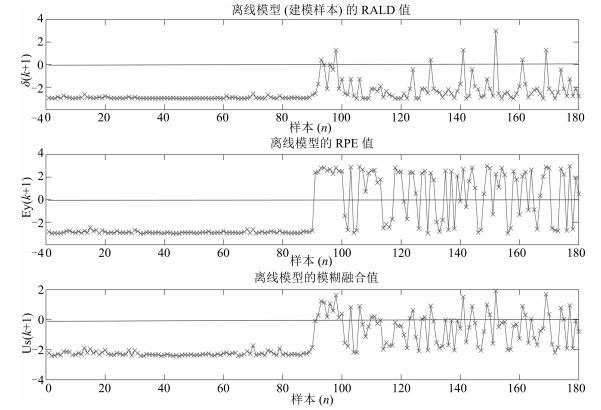
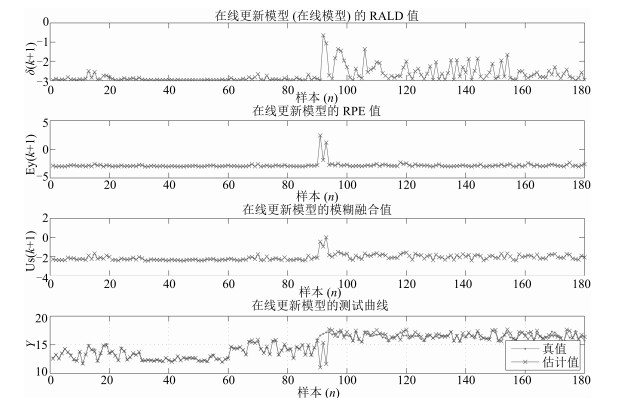
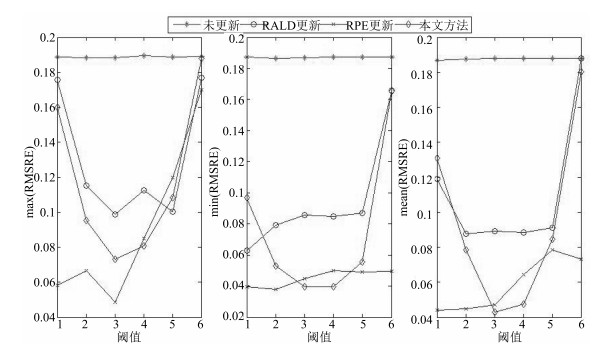
更新样本识别方法 统计项 更新样本预设定阈值 –2.5 –2 –1.5 –1 0 1 非更新方法 最大误差 0.1886 0.1885 0.1884 0.1894 0.1887 0.1892 最小误差 0.1875 0.1865 0.187 0.1872 0.1872 0.1871 误差均值 0.1868 0.1876 0.1878 0.1879 0.1878 0.1879 误差方差 0.0004 0.0004 0.0004 0.0005 0.0004 0.0005 基于RALD的更新样本识别方法 最大误差 0.1758 0.1152 0.0989 0.1127 0.1004 0.1767 最小误差 0.0628 0.0794 0.0856 0.085 0.087 0.1658 误差均值 0.119 0.0876 0.0892 0.0886 0.0911 0.1878 误差方差 0.0376 0.0094 0.0044 0.006 0.0033 0.0071 更新次数最多的样本编号 92, 94, 96, 118, 119, 141 99, 100, 106, 98, 100, 103 99, 106, 118, 124 99, 106 99, 123, 149, 154 - 平均更新次数 11 5 2 2 2 0 基于RPE的更新样本识别方法 最大误差 0.058 0.0665 0.0486 0.085 0.1198 0.1701 最小误差 0.0396 0.038 0.0449 0.05 0.0492 0.0494 误差均值 0.044 0.0446 0.0469 0.0642 0.0785 0.0731 误差方差 0.0042 0.007 0.0008 0.012 0.0231 0.0284 更新次数最多的样本编号 91, 92, 93, 118, 124 91, 93, 92, 97, 95 91, 93, 1 91, 93, 8, 1, 119 91, 93, 8, 16, 11 93, 91, 92, 11 平均更新次数 10.3 4.1 2.05 2.6 2.2 1.9 本文方法 最大误差 0.16 0.0953 0.0733 0.0808 0.1082 0.1878 最小误差 0.0967 0.0529 0.0397 0.0395 0.0556 0.1653 误差均值 0.1309 0.0784 0.0429 0.0474 0.0847 0.1804 误差方差 0.0199 0.0116 0.0078 0.0101 0.0117 0.0066 更新次数最多的样本编号 1180 91, 91, 93, 95, 97, 76 91, 92, 93, 97, 124 93, 91, 92 92, 94, 93, 99 – 平均更新次数 180 72.95 3.4 2.55 1.7 0 -
[1] Tsymbal A. The Problem of Concept Drift:Definitions and Related Work, Technical Report, The University of Dublin, Trinity College, Department of Computer Science, Dublin, Ireland, 2004. [2] Soares S G, Araújo R. An on-line weighted ensemble of regressor models to handle concept drifts. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2015, 37:392-406 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2014.10.003 [3] (汤健, 田福庆, 贾美英, 李东.基于频谱数据驱动的旋转机械设备负荷软测量.北京:国防工业出版社, 2015. 167-173)Tang Jian, Tian Fu-Qing, Jia Mei-Ying, Li Dong. Load Soft Sensor of Rotating Mechanical Device based on Frequency Spectral Data-driven. Beijing:National Defense Industrial Press, 2015. 167-173 [4] Liu J L. On-line soft sensor for polyethylene process with multiple production grades. Control Engineering Practice, 2007, 15(7):769-778 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2005.12.005 [5] Engel Y, Mannor S, Meir R. The kernel recursive least-squares algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(8):2275-2285 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.830985 [6] Yu W. Fuzzy modelling via on-line support vector machines. International Journal of Systems Science, 2010, 41(11):1325-1335 doi: 10.1080/00207720903045775 [7] Liu Y, Wang H Q, Yu J, Li P. Selective recursive kernel learning for online identification of nonlinear systems with NARX form. Journal of Process Control, 2001, 20(2):181-194 [8] Tang J, Yu W, Chai T Y, Zhao L J. On-line principal component analysis with application to process modeling. Neurocomputing, 2012, 82:167-168 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2011.10.026 [9] (汤健, 柴天佑, 余文, 赵立杰.在线KPLS建模方法及在磨机负荷参数集成建模中的应用.自动化学报, 2013, 39(5):471-486) http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17934.shtmlTang Jian, Chai Tian-You, Yu Wen, Zhao Li-Jie. On-line KPLS algorithm with application to ensemble modeling parameters of mill load. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(5):471-486 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17934.shtml [10] Kadlec P, GrbićR, Gabrys B. Review of adaptation mechanisms for data-driven soft sensors. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 2011, 35(1):1-24 doi: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2010.07.034 [11] Tang K, Lin M L, Minku F, Yao X. Selective negative correlation learning approach to incremental learning. Neurocomputing, 2009, 72(13-15):2796-2805 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2008.09.022 [12] van Heeswijk M, Miche Y, Lindh-Knuutila T, Hilbers P A, Honkela T, Oja E, Lendasse A. Adaptive ensemble models of extreme learning machines for time series prediction. In:Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Limassol, Cyprus:Springer-Verlag, 2009. 305-314 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2158286838&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [13] Tian H X, Mao Z Z. An ensemble ELM based on modified AdaBoost.RT algorithm for predicting the temperature of molten steel in ladle furnace. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2010, 7(1):73-80 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2008.2005640 [14] (郝红卫, 王志彬, 殷绪成, 陈志强.分类器的动态选择与循环集成方法.自动化学报, 2011, 37(11):1290-1295) http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2011/V37/I11/1290Hao Hong-Wei, Wang Zhi-Bin, Yin Xu-Cheng, Chen Zhi-Qiang. Dynamic selection and circulating combination for multiple classifier systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(11):1290-1295 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2011/V37/I11/1290 [15] Soares S G, Araújo R. A dynamic and on-line ensemble regression for changing environments. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(6):2935-2948 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2014.11.053 [16] Pao Y H, Takefuji Y. Functional-link net computing:theory, system architecture, and functionalities. Computer, 1992, 25(5):76-79 doi: 10.1109/2.144401 [17] Igelnik B, Pao Y H. Stochastic choice of basis functions in adaptive function approximation and the functional-link net. IEEE Transactions on Neural Network, 1995, 6(6):1320-1329 doi: 10.1109/72.471375 [18] Comminiello D, Scarpiniti M, Azpicueta-Ruiz L A, Arenas-García J, Uncini A. Functional link adaptive filters for nonlinear acoustic echo cancellation. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2013, 21(7):1502-1512 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2013.2255276 [19] Alhamdoosh M, Wang D H. Fast decorrelated neural network ensembles with random weights. Information Sciences, 2014, 264(6):104-117 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1967165756&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [20] Cao F L, Wang D H, Zhu H Y, Wang Y G. An iterative learning algorithm for feedforward neural networks with random weights. Information Sciences, 2016, 328:546-557 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.09.002 [21] Tang J, Jia M Y, Li D. Selective ensemble simulate metamodeling approach based on latent features extraction and kernel learning. In:Proceedings of the 27th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (2015 CCDC). Qingdao, China:IEEE, 2015. 6503-6508 [22] Fukunaga K, Hayes R R. Effects of sample size in classifier design. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1989, 11(8):873-885 doi: 10.1109/34.31448 [23] (汤健, 柴天佑, 丛秋梅, 苑明哲, 赵立杰, 刘卓, 余文.基于EMD和选择性集成学习算法的磨机负荷参数软测量.自动化学报, 2014, 40(9):1853-1866) http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2014/V40/I9/1853Tang Jian, Chai Tian-You, Cong Qiu-Mei, Yuan Ming-Zhe, Zhao Li-Jie, Liu Zhuo, Yu Wen. Soft sensor approach for modeling mill load parameters based on EMD and selective ensemble learning algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(9):1853-1866 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2014/V40/I9/1853 [24] Tang J, Yu W, Chai T Y, Liu Z, Zhou X J. Selective ensemble modeling load parameters of ball mill based on multi-scale frequency spectral features and sphere criterion. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 66-67:485-504 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.04.028 [25] Tang J, Chai T Y, Liu Z, Yu W. Selective ensemble modeling based on nonlinear frequency spectral feature extraction for predicting load parameter in ball mills. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2015, 23(12):2020-2028 doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2015.10.006 [26] (余建波, 卢笑蕾, 宗卫周.基于局部与非局部线性判别分析和高斯混合模型动态集成的晶圆表面缺陷探测与识别.自动化学报, 2016, 42(1):47-59) http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2016/V42/I1/47Yu Jian-Bo, Lu Xiao-Lei, Zong Wei-Zhou. Wafer defect detection and recognition based on local and nonlocal linear discriminant analysis and dynamic ensemble of Gaussian mixture models. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(1):47-59 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2016/V42/I1/47 [27] Dhanjal C, Gunn S R, Shawe-Taylor J. Efficient sparse kernel feature extraction based on partial least squares. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 31(8):1347-1361 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.171 [28] Qin S J. Recursive PLS algorithms for adaptive data modeling. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 1998, 22(4-5):503-514 doi: 10.1016/S0098-1354(97)00262-7 [29] Yue H H, Qin S J. Reconstruction-based fault identification using a combined index. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2001, 40(20):4403-4414 doi: 10.1021/ie000141+ -




 下载:
下载: