-
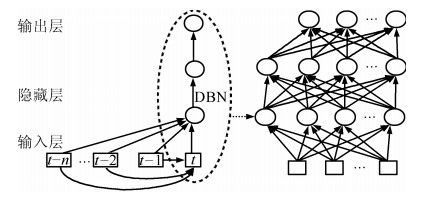
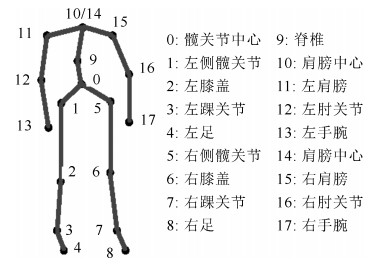
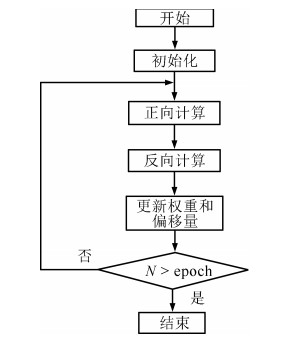
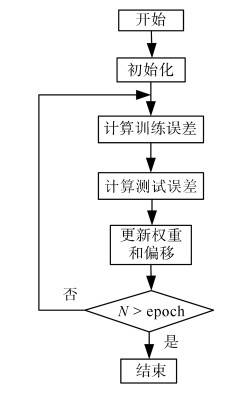
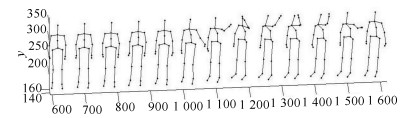
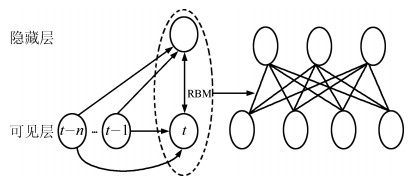
摘要: 在线人体动作识别是人体动作识别的最终目标,但由于如何分割动作序列是一个待解决的难点问题,因此目前大多数人体动作识别方法仅关注在分割好的动作序列中进行动作识别,未关注在线人体动作识别问题.本文针对这一问题,提出了一种可以完成在线人体动作识别的时序深度置信网络(Temporal deep belief network, TDBN)模型.该模型充分利用动作序列前后帧提供的上下文信息,解决了目前深度置信网络模型仅能识别静态图像的问题,不仅大大提高了动作识别的准确率,而且由于该模型不需要人为对动作序列进行分割,可以从动作进行中的任意时刻开始识别,实现了真正意义上的在线动作识别,为实际应用打下了较好的理论基础.Abstract: Online human action recognition is the ultimate goal of human action recognition. However, how to segment the action sequence is a difficult problem to be solved. So far, most human action recognition algorithms are only concerned with the action recognition within a segmented action sequences. In order to solve this problem, a deep belief network (DBN) model is proposed which can handle sequential time series data. This model makes full use of the action sequences and frames to provide contextual information so that it can handle video data. Moreover, this model not only greatly improves the action recognition accuracy, but also realizes online action recognition. So it lays a good theoretical foundation for practical applications.
-
表 1 测试1和测试2中整个序列的识别结果(%)
Table 1 Results of the sequences (%)
表 2 测试3中本文算法与其他算法的比较(%)
Table 2 Comparisons between our method
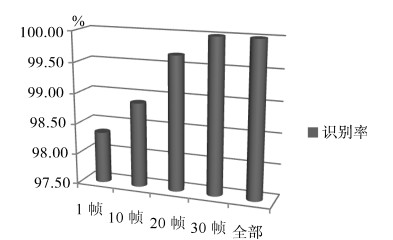
表 3 前5帧的识别结果(%)
Table 3 Recognition results of the first 5 sequences (%)
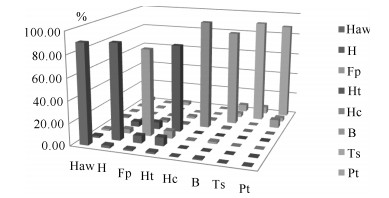
ASl1 AS21 AS31 AS12 AS22 AS32 本文 79.84 79.35 82.93 90.78 92.76 94.66 Yang等[3] 67±1 67±1 74±1 77±1 75±1 82±1 表 4 全部实验识别结果(%)
Table 4 All recognition results (%)
1 5 整个动作 ASl1 77.55 79.84 96.67 AS21 78.01 79.35 92.81 AS31 81.60 82.93 96.68 平均 79.05 80.71 95.39 ASl2 89.74 90.78 99.33 AS22 90.78 92.76 97.44 AS32 93.00 94.66 99.87 平均 91.17 92.73 98.88 表 5 不同阶数的识别时间(ms)
Table 5 Recognition time with different orders (ms)
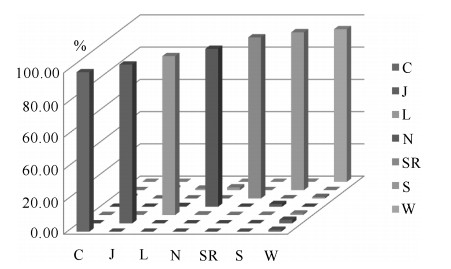
Action n 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Horizontal arm wave 4.45 9.78 12.56 14.61 17.21 19.45 23.51 Hammer 3.67 9.89 11.89 14.39 17.12 19.78 22.13 Forward punch 3.79 10.03 12.54 14.48 17.49 20.01 22.56 High throw 3.96 9.92 12.48 14.68 17.73 19.21 22.67 Hand clap 4.13 9.99 12.49 14.63 17.62 19.84 22.78 Bend 4.78 9.79 12.34 14.61 17.94 19.47 21.87 Tennis serve 4.56 9.67 12.52 14.65 17.56 19.49 22.46 Pickup and throw 3.71 9.97 12.67 14.51 17.83 19.92 22.81 表 6 不同阶数的识别率(%)
Table 6 Recognition rates with different orders (%)
Action n 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Horizontal arm wave 81.56 85.39 89.12 90.03 91.45 89.97 87.68 Hammer 82.56 86.48 85.34 87.50 86.84 88.10 87.98 Forward punch 73.67 76.45 78.78 79.19 77.87 78.16 78.45 High throw 72.78 73.46 76.98 79.92 79.23 78.89 76.75 Hand clap 87.65 93.78 98.34 98.65 97.85 96.12 96.23 Bend 80.13 81.35 84.56 86.43 86.72 85.97 83.85 Tennis serve 88.74 91.67 92.89 93.67 93.35 92.89 92.54 Pickup and throw 83.81 86.34 86.94 88.34 87.13 87.67 97.56 Average 81.36 84.37 86.62 87.97 87.56 87.22 87.63 -
[1] (佟丽娜, 侯增广, 彭亮, 王卫群, 陈翼雄, 谭民.基于多路sEMG时序分析的人体运动模式识别方法.自动化学报, 2014, 40(5):810-821) http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18349.shtmlTong Li-Na, Hou Zeng-Guang, Peng Liang, Wang Wei-Qun, Chen Yi-Xiong, Tan Min. Multi-channel sEMG time series analysis based human motion recognition method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(5):810-821 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18349.shtml [2] Li W Q, Zhang Z Y, Liu Z C. Action recognition based on a bag of 3D points. In:Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. San Francisco, CA:IEEE, 2010. 9-14 http://www.oalib.com/references/17186320 [3] Yang X D, Zhang C Y, Tian Y L. Recognizing actions using depth motion maps-based histograms of oriented gradients. In:Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Nara, Japan:ACM, 2012. 1057-1060 http://www.oalib.com/paper/4237135 [4] Ofli F, Chaudhry R, Kurillo G, Vidal R, Bajcsy R. Sequence of the most informative joints (SMIJ):a new representation for human skeletal action recognition. Journal of Visual Communication & Image Representation, 2014, 25(1):24-38 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2125073690&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] Theodorakopoulos I, Kastaniotis D, Economou G, Fotopoulos S. Pose-based human action recognition via sparse representation in dissimilarity space. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2014, 25(1):12-23 doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2013.03.008 [6] (王斌, 王媛媛, 肖文华, 王炜, 张茂军.基于判别稀疏编码视频表示的人体动作识别.机器人, 2012, 34(6):745-750) doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1218.2012.00745Wang Bin, Wang Yuan-Yuan, Xiao Wen-Hua, Wang Wei, Zhang Mao-Jun. Human action recognition based on discriminative sparse coding video representation. Robot, 2012, 34(6):745-750 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1218.2012.00745 [7] (田国会, 尹建芹, 韩旭, 于静.一种基于关节点信息的人体行为识别新方法.机器人, 2014, 34(3):285-292) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JQRR201403005.htmTian Guo-Hui, Yin Jian-Qin, Han Xu, Yu Jing. A novel human activity recognition method using joint points information. Robot, 2014, 34(3):285-292 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JQRR201403005.htm [8] (乔俊飞, 潘广源, 韩红桂.一种连续型深度信念网的设计与应用.自动化学报, 2015, 41(12):2138-2146) http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2015/V41/I12/2138Qiao Jun-Fei, Pan Guang-Yuan, Han Hong-Gui. Design and application of continuous deep belief network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(12):2138-2146 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/Y2015/V41/I12/2138 [9] Zhao S C, Liu Y B, Han Y H, Hong R C. Pooling the convolutional layers in deep convnets for action recognition[Online], available:http://120.52.73.77/arxiv.org/pdf/1511.02126v1.pdf, November 1, 2015. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1969767174&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [10] Liu C, Xu W S, Wu Q D, Yang G L. Learning motion and content-dependent features with convolutions for action recognition. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2015, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2550-4. [11] Baccouche M, Mamalet F, Wolf C, Garcia C, Baskurt A. Sequential deep learning for human action recognition. Human Behavior Understanding. Berlin:Springer, 2011. 29-39 [12] Lefebvre G, Berlemont S, Mamalet F, Garcia C. BLSTM-RNN based 3d gesture classification. Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning. Berlin:Springer, 2013. 381-388 [13] Du Y, Wang W, Wang L. Hierarchical recurrent neural network for skeleton based action recognition. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA:IEEE, 2015. 1110-1118 [14] Taylor G W, Hinton G E, Roweis S. Modeling human motion using binary latent variables. In:Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA:MIT Press, 2007. 1345-1352 [15] Hinton G E, Osindero S. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 2006, 18:1527-1554 doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 [16] Bengio Y, Lamblin P, Popovici D, Larochelle H. Personal communications with Will Zou. learning optimization Greedy layerwise training of deep networks. In:Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA:MIT Press, 2007. [17] Rumelhart D E, Hinton G E, Williams R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 1986, 323(6088):533-536 doi: 10.1038/323533a0 [18] Hsu E, Pulli K, PopovićJ. Style translation for human motion. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2005, 24(3):1082-1089 doi: 10.1145/1073204 [19] Xia L, Chen C C, Aggarwal J K. View invariant human action recognition using histograms of 3D joints. In:Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Providence, USA:IEEE, 2012. 20-27 http://www.oalib.com/references/16301407 [20] Ellis C, Masood S Z, Tappen M F, LaViola J J Jr, Sukthankar R. Exploring the trade-off between accuracy and observational latency in action recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 101(3):420-436 doi: 10.1007/s11263-012-0550-7 [21] Chen C, Liu K, Kehtarnavaz N. Real-time human action recognition based on depth motion maps. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 2016, 12(1):155-163 doi: 10.1007/s11554-013-0370-1 [22] Gowayyed M A, Torki M, Hussein M E, El-Saban M. Histogram of oriented displacements (HOD):describing trajectories of human joints for action recognition. In:Proceedings of the 2013 International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Beijing, China, AAAI Press, 2013. 1351-1357 [23] Vemulapalli R, Arrate F, Chellappa R. Human action recognition by representing 3D skeletons as points in a lie group. In:Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA:IEEE, 2014. 588-595 -




 下载:
下载: