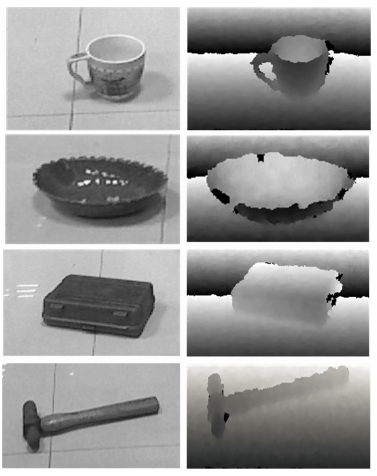
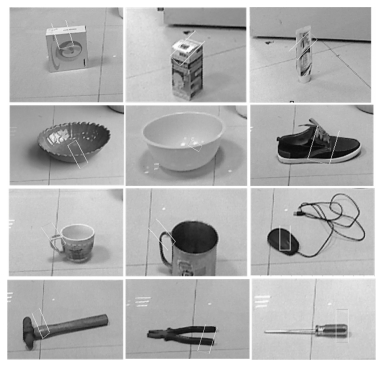
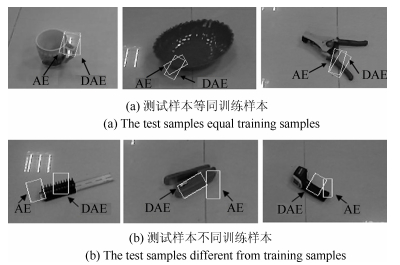
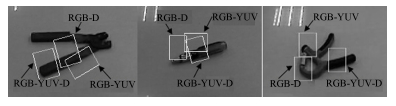
-
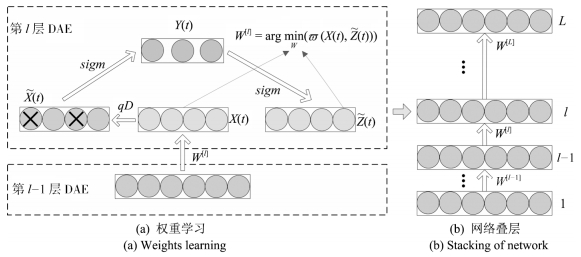
摘要: 针对智能机器人抓取判别问题,研究多模特征深度学习与融合方法.该方法将测试特征分布偏离训练特征视为一类噪化,引入带稀疏约束的降噪自动编码(Denoising auto-encoding, DAE),实现网络权值学习;并以叠层融合策略,获取初始多模特征的深层抽象表达,两种手段相结合旨在提高深度网络的鲁棒性和抓取判别精确性.实验采用深度摄像机与6自由度工业机器人组建测试平台,对不同类别目标进行在线对比实验.结果表明,设计的多模特征深度学习依据人的抓取习惯,实现最优抓取判别,并且机器人成功实施抓取定位,研究方法对新目标具备良好的抓取判别能力.Abstract: In this paper, a multimodal features deep learning and a fusion approach are proposed to address the problem of robotic potential grasp recognition. In our thinking, the test features which diverge from training are presented as noise-processing, then the denoising auto-encoding (DAE) and sparse constraint conditions are introduced to realize the network's weights training. Furthermore, a stacked DAE with fusion method is adopted to deal with the multimodal vision dataset for its high-level abstract expression. These two strategies aim at improving the network's robustness and the precision of grasp recognition. A six-degree-of-freedom robotic manipulator with a stereo camera configuration is used to demonstrate the robotic potential grasp recognition. Experimental results show that the robot can optimally localizate the target by simulating human grasps, and that the proposed method is robust to a variety of new target grasp recognition.
-
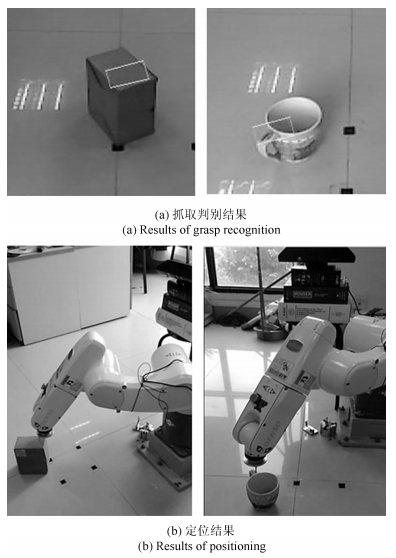
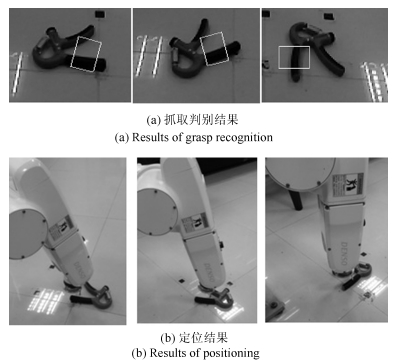
表 1 机器人对不同物体、不同摆放方向抓取定位统计结果
Table 1 Results of robot grasp positioning for different targets with different poses
矩形盒 杯子 盘子 工具 总计 实验总次数 23 21 27 25 96 成功次数 22 18 25 23 88 成功率(%) 95.7 85.7 92.6 92 91.7 -
[1] Paolini R, Rodriguez A, Srinivasa S S, Mason M T. A data-driven statistical framework for post-grasp manipulation. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2014, 33(4):600-615 doi: 10.1177/0278364913507756 [2] 贾丙西, 刘山, 张凯祥, 陈剑.机器人视觉伺服研究进展:视觉系统与控制策略.自动化学报, 2015, 41(5):861-873 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18661.shtmlJia Bing-Xi, Liu Shan, Zhang Kai-Xiang, Chen Jian. Survey on robot visual servo control:vision system and control strategies. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(5):861-873 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18661.shtml [3] Droniou A, Ivaldi S, Sigaud O. Deep unsupervised network for multimodal perception, representation and classification. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2015, 71(9):83-98 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2009841905&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [4] 高莹莹, 朱维彬.深层神经网络中间层可见化建模.自动化学报, 2015, 41(9):1627-1637 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18736.shtmlGao Ying-Ying, Zhu Wei-Bin. Deep neural networks with visible intermediate layers. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(9):1627-1637 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18736.shtml [5] 乔俊飞, 潘广源, 韩红桂.一种连续型深度信念网的设计与应用.自动化学报, 2015, 41(12):2138-2146 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18786.shtmlQiao Jun-Fei, Pan Guang-Yuan, Han Hong-Gui. Design and application of continuous deep belief network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(12):2138-2146 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18786.shtml [6] Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 2006, 313(5786):504-507 doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 [7] Bengio Y. Learning deep architectures for AI. Foundations and TrendsoledR in Machine Learning, 2009, 2(1):1-127 doi: 10.1561/2200000006 [8] Längkvist M, Karlsson L, Loutfi A. A review of unsupervised feature learning and deep learning for time-series modeling. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2014, 42:11-24 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2014.01.008 [9] Erhan D, Bengio Y, Courville A, Manzagol P A, Vincent P, Bengio S. Why does unsupervised pre-training help deep learning? Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11:625-660 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2138857742&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [10] Salakhutdinov R, Hinton G. Deep Boltzmann machines. In:Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS) 2009. Florid, USA, 2009. 448-455 [11] Ngiam J, Khosla A, Kim M, Nam J, Lee H, Ng A Y. Multimodal deep learning. In:Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning. Bellevue, USA, 2011. 689-696 [12] Baldi P, Lu Z Q. Complex-valued autoencoders. Neural Networks, 2012, 33:136-147 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2012.04.011 [13] Wu P C, Hoi S C H, Xia H, Zhao P L, Wang D Y, Miao C Y. Online multimodal deep similarity learning with application to image retrieval. In:Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Barcelona, Spain:ACM, 2013. 153-162 [14] 耿杰, 范剑超, 初佳兰, 王洪玉.基于深度协同稀疏编码网络的海洋浮筏SAR图像目标识别.自动化学报, 2016, 42(4):593-604 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18846.shtmlGeng Jie, Fan Jian-Chao, Chu Jia-Lan, Wang Hong-Yu. Research on marine floating raft aquaculture SAR image target recognition based on deep collaborative sparse coding network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4):593-604 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18846.shtml [15] Mohamed A R, Dahl G E, Hinton G. Acoustic modeling using deep belief networks. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2012, 20(1):14-22 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2011.2109382 [16] Sarikaya R, Hinton G E, Deoras A. Application of deep belief networks for natural language understanding. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2014, 22(4):778-784 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2014.2303296 [17] Humphrey E J, Bello J P, LeCun Y. Feature learning and deep architectures:new directions for music informatics. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 2013, 41(3):461-481 doi: 10.1007/s10844-013-0248-5 [18] Yu J C, Weng K J, Liang G Y, Xie G H. A vision-based robotic grasping system using deep learning for 3D object recognition and pose estimation. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics. Shenzhen, China:IEEE, 2013. 1175-1180 [19] Noda K, Arie H, Suga Y, Ogata T. Multimodal integration learning of object manipulation behaviors using deep neural networks. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Tokyo, Japan:IEEE, 2013. 1728-1733 [20] Lenz I, Lee H, Saxena A. Deep learning for detecting robotic grasps. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2015, 34(4-5):705-724 doi: 10.1177/0278364914549607 [21] El-Khoury S, Sahbani A. A new strategy combining empirical and analytical approaches for grasping unknown 3D objects. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2010, 58(5):497-507 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2010.01.008 [22] Pelossof R, Miller A, Allen P, Jebara T. An SVM learning approach to robotic grasping. In:Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. New Orleans, USA:IEEE, 2004. 3512-3518 [23] Boularias A, Kroemer O, Peters J. Learning robot grasping from 3-D images with Markov random fields. In:Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. San Francisco, USA:IEEE, 2011. 1548-1553 [24] Papazov C, Haddadin S, Parusel S, Krieger K, Burschka D. Rigid 3D geometry matching for grasping of known objects in cluttered scenes. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2012, 31(4):538-553 doi: 10.1177/0278364911436019 [25] 刘建伟, 孙正康, 罗雄麟.域自适应学习研究进展.自动化学报, 2014, 40(8):1576-1600 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18427.shtmlLiu Jian-Wei, Sun Zheng-Kang, Luo Xiong-Lin. Review and research development on domain adaptation learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(8):1576-1600 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18427.shtml [26] Shin H C, Orton M R, Collins D J, Doran S J, Leach M O. Stacked autoencoders for unsupervised feature learning and multiple organ detection in a pilot study using 4D patient data. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(8):1930-1943 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.277 [27] Vincent P, Larochelle H, Bengio Y, Manzagol P A. Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In:Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning. Helsinki, Finland:ACM, 2008. 1096-1103 [28] Jiang Y, Moseson, Saxena A. Efficient grasping from RGBD images:learning using a new rectangle representation. In:Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Shanghai, China:IEEE, 2011. 3304-3311 -




 下载:
下载: