Sparse Bayesian Mixture of Experts and Its Application to Spectral Multivariate Calibration
-
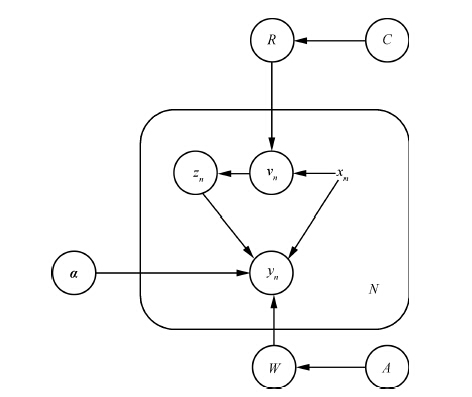
摘要: 在光谱数据的多元校正中, 光谱数据通常是在多种不同的环境条件下收集的. 为了建模来源于不同环境中的高维光谱数据, 本文提出了一种新的稀疏贝叶斯混合专家模型, 并将其用来选择多元校正模型的稀疏特征. 混合专家模型能够把训练数据划分到不同的子类, 之后使用不同的预测模型来分别对划分后的数据进行预测, 因此这种方法适合于建模来自于多种环境下的光谱数据. 本文提出的稀疏的混合专家模型利用稀疏贝叶斯的方法来进行特征选择, 不依赖于事先指定的参数; 同时利用probit模型作为门函数以得到解析的后验分布, 避免了在门函数分类模型中进行特征提取时需要的近似. 本文提出的模型与其他几种常用的回归模型在人工数据集和几个公开的光谱数据集上进行了比较, 比较结果显示本文提出的模型对多个来源的光谱数据进行浓度预测时精度比传统的回归方法有一定的提高.Abstract: In spectral multivariate calibration, high dimensional spectral data are often measured on different conditions. To predict the property value of a spectrum without knowing its source, a new sparse Bayesian mixture experts (ME) model is proposed and applied to the multivariate calibration model for selecting the sparse features. The technique of mixture of experts can divide the training data into some different classes and estimate the different predictive functions for each class. Therefore, ME is suitable for prediction of multiple-source spectral data. To analyze high dimensional spectral data, the new ME model employs the sparse Bayesian method to select certain features without tuning parameters. Moreover, the multinomial probit model is used as the gate function to obtain the analytic posterior distribution in this model. This new method is compared with some classical multivariate calibration methods on artificial and some real-world datasets. Experimental results show the advantage of proposed model for high dimensional spectral data.
-
Key words:
- Multivariate calibration /
- mixture of experts /
- feature selection /
- variational inference
-
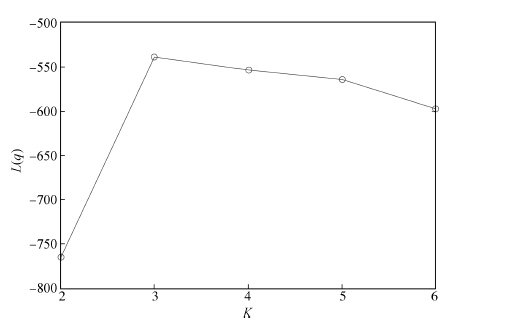
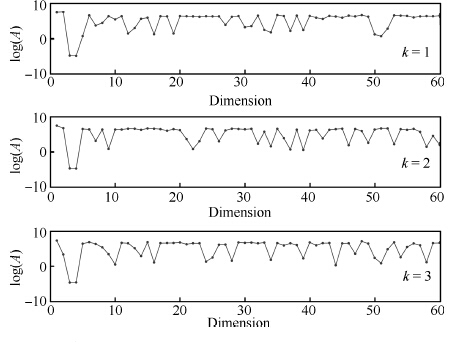
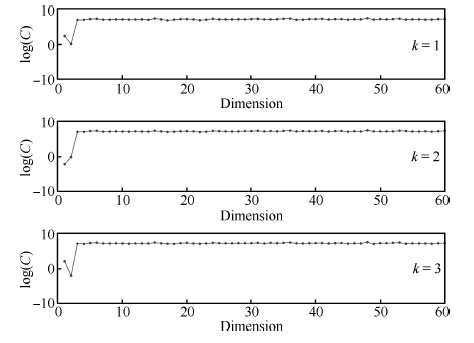
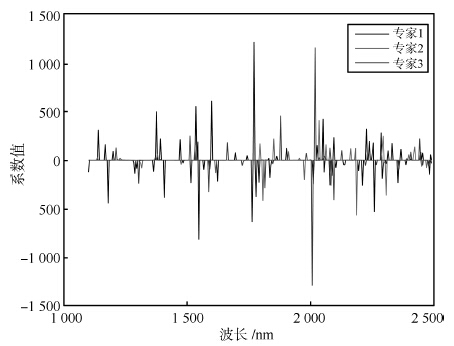
表 1 在人工数据集上的预测结果
Table 1 The prediction results in the arti-cial data set
Method RMSECV PLS 5.1617 ± 0.7679 SVR 4.9164 ± 0.5646 LASSO 5.2411 ± 0.4112 Ridge 5.0103 ± 0.5044 ME 10.236 ± 1.5720 SME 1.5130 ± 0.3117 表 2 玉米光谱数据集的预测结果
Table 2 The prediction results in corn data set
Method RMSECV PLS 0.1480±0.0093 SVR 0.1504±0.0084 LASSO 0.1510±0.0114 Ridge 0.1511±0.0083 Bagging-ridge 0.1239±0.0113 SME 0.1124±0.0034 Multi-task 0.1145±0.0094 表 3 温度数据集的预测结果
Table 3 The prediction results in temperature data set
Method RMSECV PLS 0.0148±0.0026 SVR 0.0180±0.0019 LASSO 0.0208±0.0031 Ridge 0.0345±0.0013 Bagging-ridge 0.0143±0.0018 SME 0.0106±0.0008 Multi-task 0.0225±0.0032 表 4 药片光谱数据集的预测结果
Table 4 The prediction results in pharmaceutical data set
Method RMSECV PLS 0.0148±0.0026 SVR 0.0180±0.0019 LASSO 0.0208±0.0031 Ridge 0.0345±0.0013 Bagging-ridge 0.0143±0.0018 SME 0.0106±0.0008 Multi-task 0.0225±0.0032 -
[1] Jacobs R A, Jordan M I, Nowlan S J, Hinton G E. Adaptive mixtures of local experts. Neural Computation, 1991, 3(1): 79-87 doi: 10.1162/neco.1991.3.1.79 [2] Bishop C M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. New York: Springer, 2006. http://www.oalib.com/references/17189298 [3] Yuksel S E, Wilson J N, Gader P D. Twenty years of mixture of experts. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(8): 1177-1193 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2200299 [4] Jordan M I, Jacobs R A. Hierarchical mixtures of experts and the EM algorithm. Neural Computation, 1994, 6(2): 181-214 doi: 10.1162/neco.1994.6.2.181 [5] Bo L F, Sminchisescu C, Kanaujia A, Metaxas D. Fast algorithms for large scale conditional 3D prediction. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Anchorage, AK: IEEE, 2008. 1-8 https://www.computer.org/csdl/proceedings/cvpr/2008/2242/00/index.html [6] Rasmussen C E, Ghahramani Z. Infinite mixtures of Gaussian process experts. In: Proceedings of the 2002 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge MA: MIT Press, 2002. 881-888 [7] Meeds E, Osindero S. An alternative infinite mixture of Gaussian process experts. In: Proceedings of the 2006 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge MA: MIT Press, 2006. 883-890 [8] Peralta B, Soto A. Embedded local feature selection within mixture of experts. Information Sciences, 2014, 269: 176-187 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.01.008 [9] Pan W, Shen X T. Penalized model-based clustering with application to variable selection. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2007, 8: 1145-1164 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2108435369&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [10] Khalili A. New estimation and feature selection methods in mixture-of-experts models. Canadian Journal of Statistics, 2010, 38(4): 519-539 doi: 10.1002/cjs.10083 [11] Tipping M E. Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2001, 1: 211-244 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1648445109&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [12] Ding Y F, Harrison R F. A sparse multinomial probit model for classification. Pattern Analysis and Applications, 2011, 14(1): 47-55 doi: 10.1007/s10044-010-0177-7 [13] 徐丹蕾, 杜兰, 刘宏伟, 洪灵, 李彦兵. 一种基于变分相关向量机的特征选择和分类结合方法. 自动化学报, 2011, 37(8): 932-943Xu Dan-Lei, Du Lan, Liu Hong-Wei, Hong Ling, Li Yan-Bing. Joint feature selection and classification design based on variational relevance vector machine. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(8): 932-943 [14] Bishop C M, Svensen M. Bayesian hierarchical mixtures of experts. In: Proceedings of the 19th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. Acapulco, Mexico: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 2003. 57-64 [15] Wülfert F, Kok W T, Smilde A K. Influence of temperature on vibrational spectra and consequences for the predictive ability of multivariate models. Analytical Chemistry, 1998, 70(9): 1761-1767 doi: 10.1021/ac9709920 [16] Feudale R N, Woody N A, Tan H W, Myles A J, Brown S D, Ferré J. Transfer of multivariate calibration models: a review. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2002, 64(2): 181-192 doi: 10.1016/S0169-7439(02)00085-0 [17] Thissen U, Üstün B, Melssen W J, Buydens L M C. Multivariate calibration with least-squares support vector machines. Analytical Chemistry, 2004, 76(11): 3099-3105 doi: 10.1021/ac035522m [18] Thissen U, Pepers M, Üstün B, Melssen W J, Buydens L M C. Comparing support vector machines to PLS for spectral regression applications. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2004, 73(2): 169-179 doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2004.01.002 [19] Hernández N, Talavera I, Biscay R J, Porro D, Ferreira M M C. Support vector regression for functional data in multivariate calibration problems. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2009, 642(1-2): 110-116 doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2008.10.063 [20] Barman I, Kong C R, Dingari N C, Dasari R R, Feld M S. Development of robust calibration models using support vector machines for spectroscopic monitoring of blood glucose. Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 82(23): 9719-9726 doi: 10.1021/ac101754n [21] Hernández N, Talavera I, Dago A, Biscay R J, Ferreira M M C, Porro D. Relevance vector machines for multivariate calibration purposes. Journal of Chemometrics, 2008, 22(11-12): 686-694 doi: 10.1002/cem.v22:11/12 [22] Pan S J, Yang Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2010, 22(10): 1345-1359 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191 [23] Chen J H, Tang L, Liu J, Ye J P. A convex formulation for learning a shared predictive structure from multiple tasks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(5): 1025-1038 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.189 [24] Ando R K, Zhang T. A framework for learning predictive structures from multiple tasks and unlabeled data. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2005, 6: 1817-1853 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2130903752&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [25] Romera-Paredes B, Argyriou A, Bianchi-Berthouze N, Pontil M. Exploiting unrelated tasks in multi-task learning. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. La Palma, Canary Islands, 2012. 951-959 [26] Caruana R. Multitask learning. Machine Learning, 1997, 28(1): 41-75 doi: 10.1023/A:1007379606734 [27] Argyriou A, Evgeniou T, Pontil M. Convex multi-task feature learning. Machine Learning, 2008, 73(3): 243-272 doi: 10.1007/s10994-007-5040-8 [28] Zhang W L, Li R J, Zeng T, Sun Q, Kumar S, Ye J P, Ji S W. Deep model based transfer and multi-task learning for biological image analysis. In: Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2015. 1475-1484 [29] Liu A A, Xu N, Su Y T, Hong L, Hao T, Yang Z X. Single/multi-view human action recognition via regularized multi-task learning. Neurocomputing, 2015, 151: 544-553 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.04.090 [30] Archambeau C, Guo S B, Zoeter O. Sparse Bayesian multi-task learning. In: Proceedings of the 2011 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge MA: MIT Press, 2011. 1755-1763 [31] Ueda N, Nakano R. Deterministic annealing EM algorithm. Neural Networks, 1998, 11(2): 271-282 doi: 10.1016/S0893-6080(97)00133-0 [32] Katahira K, Watanabe K, Okada M. Deterministic annealing variant of variational Bayes method. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2008, 95(1): 012015 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2108849983&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [33] Lin Z Z, Xu B, Li Y, Shi X Y, Qiao Y J. Application of orthogonal space regression to calibration transfer without standards. Journal of Chemometrics, 2013, 27(11): 406-413 doi: 10.1002/cem.2536 [34] Jun L, Ji S W, Ye J P. Multi-task feature learning via efficient L2, 1-norm minimization. In: Proceedings of the 25th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. Montreal, Canada, 2009. 339-348 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1871180460&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn -




 下载:
下载: