Pseudospectral Method Based Time Optimal Anti-swing Trajectory Planning for Double Pendulum Crane Systems
-
摘要: 在工业生产过程中,桥式吊车系统经常会体现出双摆系统的特性,导致更多欠驱动状态量的出现,增大控制难度.基于此,论文提出了一种针对双摆桥式吊车系统的时间最优轨迹规划方法,可以得到全局时间最优且具有消摆能力的轨迹.具体而言,为方便地构造以时间为代价函数的优化问题,首先对系统运动学模型进行相应的变换;在此基础上,考虑包括两级摆角及台车速度和加速度上限值在内的多种约束,构造出相应的优化问题;然后,利用高斯伪谱法(Gauss-pseudospectral method, GPM)将该带约束的优化问题转化为更易于求解的非线性规划问题,且在转化过程中,可以非常方便地考虑轨迹约束.求解该非线性规划问题,即可得到时间最优的台车轨迹.不同于已有的大多数方法,该方法可获得全局时间最优的结果.最后,通过仿真与实验结果验证了这种时间最优轨迹规划方法具有满意的控制性能.Abstract: In practice, an overhead crane system may behave like a double pendulum, which has more unactuated states and is more difficult to be controlled properly. Motivated by this observation, we present a time optimal trajectory planning scheme for double pendulum crane systems, which can yield a global time-optimal swing-free trajectory. Specifically, to facilitate the optimization problem creation process, we first implement some basic transformations on the system kinematics. Then, various constraints, including upper and lower bounds of the two pendulum angles and upper bounds of the trolley velocity and acceleration, are taken into consideration to set up the optimization problem. After that, the Gauss-pseudospectral method(GPM) is utilized to convert the constrained optimization problem into a nonlinear programming problem, which can be solved more conveniently, while the trajectory constraints are also considered during the transformation. By solving the constructed nonlinear programming problem, a global time-optimal result is obtained, which is different from most existing methods. Finally, numerical simulation and experimental results are given to illustrate the satisfactory performance of the proposed method.
-
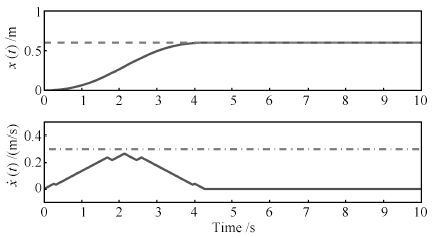
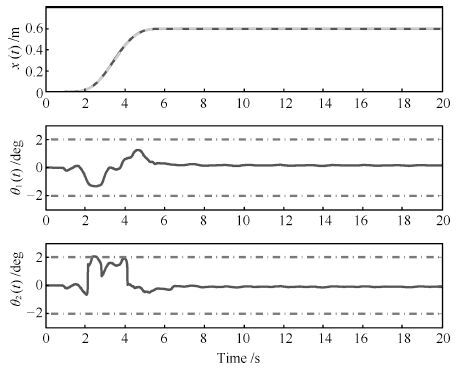
图 3 本文方法仿真结果(台车位置以及速度) (实线:仿真结果; 虚线: 目标位置 $x_f=0. 6~{\rm{m}}$ ; 点画线:台车速度约束 $v_{\max}=0. 3~{\rm{m/s}})$
Fig. 3 Simulation results (trolley position and velocity)(Solid line: simulation results; Dashed line: target position $x_f=0. 6~{\rm{m}}$ ; Dotted-dashed line: trolley velocity constraint $v_{\max}=0. 3~{\rm{m/s}}$ )
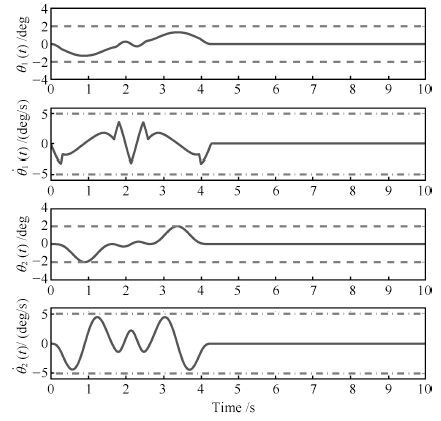
图 4 本文方法仿真结果(两级摆动对应的摆角及角速度) (实线: 仿真结果;虚线: 摆角约束 $\theta_{1\max}=\theta_{2\max}=2~{\rm{deg}}$ ;点画线: 角速度约束 $\omega_{1\max}=\omega_{2\max}=5~{\rm{deg/s}})$
Fig. 4 Simulation results (first and second order swing angles and angular velocities) (Solid line: simulation results;Dashed line: swing angle constraint $\theta_{1\max}=\theta_{2\max}=2~{\rm{deg}}$ ; Dotted-dashed line:angular velocity constraint $\omega_{1\max}=\omega_{2\max}=5~{\rm{deg/s})}$
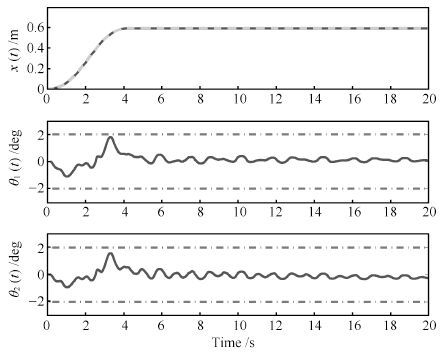
图 6 本文方法实验结果(台车位置、 一级摆角、二级摆角) (实线: 实验结果; 虚线: 待跟踪最优轨迹; 点画线:摆角约束 $\theta_{1\max}=\theta_{2\max}=2~{\rm{deg})}$
Fig. 6 Experimental results of proposed method (trolley position,first and second order swing angles) (Solid line:experimental results; Dashed line: planned trajectory; Dotted-dashed line: swing angle constraint $\theta_{1\max}=\theta_{2\max}=2~{\rm{deg}}$ )
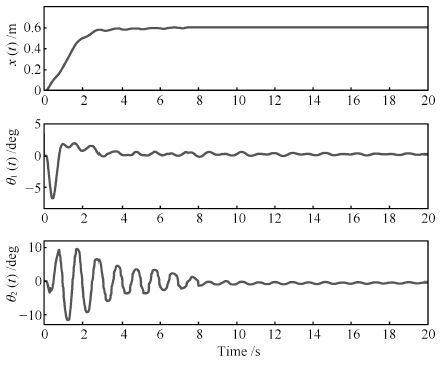
图 8 文献[21]方法实验结果(台车位置、一级摆角、 二级摆角) (实线: 实验结果; 虚线: 待跟踪轨迹; 点画线:摆角约束 $\theta_{1\max}=\theta_{2\max}=2~{\rm{deg}}$ )
Fig. 8 Experimental results of the method in [21] (trolley position,first and second order swing angles) (Solid line:experimental results; Dashed line: planned trajectory; Dotted-dashed line: swing angle constraint$\theta_{1\max}=\theta_{2\max}=2~{\rm{deg})
-
[1] Liu Y, Yu H N. A survey of underactuated mechanical systems. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2013, 7(7):921-935 https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Hongnian_Yu/publication/260586292_A_survey_of_underactuated_mechanical_systems/links/02e7e535974fe51e60000000.pdf [2] Tuan L A, Lee S G, Dang V H, Moon S, Kim B. Partial feedback linearization control of a three-dimensional overhead crane. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2013, 11(4):718-727 doi: 10.1007/s12555-012-9305-z [3] Tuan L A, Kim G H, Kim M Y, Lee S G. Partial feedback linearization control of overhead cranes with varying cable lengths. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2012, 13(4):501-507 doi: 10.1007/s12541-012-0065-8 [4] Singhose W, Kim D, Kenison M. Input shaping control of double-pendulum bridge crane oscillations. ASME Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2008, 130(3):034504 doi: 10.1115/1.2907363 [5] Blackburn D, Singhose W, Kitchen J, Patrangenaru V, Lawrence J, Kamoi T, Taura A. Command shaping for nonlinear crane dynamics. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2010, 16(4):477-501 doi: 10.1177/1077546309106142 [6] 王伟, 易建强, 赵冬斌, 刘殿通. 桥式吊车系统的分级滑模控制方法. 自动化学报, 2004, 30(5):784-788 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract16252.shtmlWang Wei, Yi Jian-Qiang, Zhao Dong-Bin, Liu Dian-Tong. Hierarchical sliding-mode control method for overhead cranes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2004, 30(5):784-788 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract16252.shtml [7] Xi Z, Hesketh T. Discrete time integral sliding mode control for overhead crane with uncertainties. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2010, 4(10):2071-2081 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?reload=true&arnumber=5611727&contentType=Journals+%26+Magazines [8] 胡洲, 王志胜, 甄子洋. 带输入饱和的欠驱动吊车非线性信息融合控制. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(7):1522-1527 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18422.shtmlHu Zhou, Wang Zhi-Sheng, Zhen Zi-Yang. Nonlinear information fusion control for underactuated cranes with input saturation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(7):1522-1527 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18422.shtml [9] Sun N, Fang Y C, Zhang X B. Energy coupling output feedback control of 4-DOF underactuated cranes with saturated inputs. Automatica, 2013, 49(5):1318-1325 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.01.039 [10] Sun N, Fang Y C. New energy analytical results for the regulation of underactuated overhead cranes:an end-effector motion-based approach. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(12):4723-4734 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2012.2183837 [11] Nakazono K, Ohnishi K, Kinjo H, Yamamoto T. Load swing suppression for rotary crane system using direct gradient descent controller optimized by genetic algorithm. Transactions of the Institute of Systems, Control and Information Engineers, 2011, 22(8):303-310 [12] Zhao Y, Gao H J. Fuzzy-model-based control of an overhead crane with input delay and actuator saturation. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2012, 20(1):181-186 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2011.2164083 [13] Uchiyama N, Ouyang H M, Sano S. Simple rotary crane dynamics modeling and open-loop control for residual load sway suppression by only horizontal boom motion. Mechatronics, 2013, 23(8):1223-1236 doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2013.09.001 [14] Sun N, Fang Y, Zhang X, Yuan Y. Transportation task-oriented trajectory planning for underactuated overhead cranes using geometric analysis. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2012, 6(10):1410-1423 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/iel5/4079545/6257070/06257077.pdf [15] 孙宁, 方勇纯, 王鹏程, 张雪波. 欠驱动三维桥式吊车系统自适应跟踪控制器设计. 自动化学报, 2010, 36(9):1287-1294 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.01287Sun Ning, Fang Yong-Chun, Wang Peng-Cheng, Zhang Xue-Bo. Adaptive trajectory tracking control of underactuated 3-dimensional overhead crane systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(9):1287-1294 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.01287 [16] Sun N, Fang Y C, Zhang Y D, Ma B J. A novel kinematic coupling-based trajectory planning method for overhead cranes. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2012, 17(1):166-173 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2010.2103085 [17] Wang P C, Fang Y C, Jiang Z Y. A direct swing constraint-based trajectory planning method for underactuated overhead cranes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(11):2414-2419 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(14)60397-9 [18] Vaughan J, Kim D, Singhose W. Control of tower cranes with double-pendulum payload dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2010, 18(6):1345-1358 [19] Singhose W, Kim D. Manipulation with tower cranes exhibiting double-pendulum oscillations. In:Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Roma, Italy:IEEE, 2007. 4550-4555 [20] Masoud Z, Alhazza K, Abu-Nada E, Majeed M. A hybrid command-shaper for double-pendulum overhead cranes. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2014, 20(1):24-37 doi: 10.1177/1077546312461371 [21] 孙宁, 方勇纯, 钱彧哲. 带有状态约束的双摆效应吊车轨迹规划. 控制理论与应用, 2014, 31(7):974-980 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201407019.htmSun Ning, Fang Yong-Chun, Qian Yu-Zhe. Motion planning for cranes with double pendulum effects subject to state constraints. Control Theory and Applications, 2014, 31(7):974-980 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201407019.htm [22] 郭卫平, 刘殿通. 二级摆型吊车系统动态及基于无源的控制. 系统仿真学报, 2008, 20(18):4945-4948 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200818045.htmGuo Wei-Ping, Liu Dian-Tong. Double-pendulum-type crane dynamics and passivity based control. Journal of System Simulation, 2008, 20(18):4945-4948 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ200818045.htm [23] Xu B, Huang X Y, Wang D W, Sun F C. Dynamic surface control of constrained hypersonic flight models with parameter estimation and actuator compensation. Asian Journal of Control, 2014, 16(1):162-174 doi: 10.1002/asjc.2014.16.issue-1 [24] Xu B. Robust adaptive neural control of flexible hypersonic flight vehicle with dead-zone input nonlinearity. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2015, 80(3):1509-1520 doi: 10.1007/s11071-015-1958-8 [25] Garg D, Patterson M, Hager W W, Rao A V, Benson D A, Huntington G T. A unified framework for the numerical solution of optimal control problems using pseudospectral methods. Automatica, 2010, 46(11):1843-1851 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2010.06.048 [26] Gill P E, Murray W, Saunders M A. SNOPT:an SQP algorithm for large-scale constrained optimization. SIAM Review, 2005, 47:99-131 doi: 10.1137/S0036144504446096 -




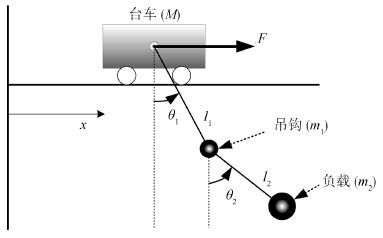
 下载:
下载: