|
[1]
|
Rubenstein M, Cornejo A, Nagpal R. Programmable self-assembly in a thousand-robot swarm. Science, 2014, 345(6198): 795−799 doi: 10.1126/science.1254295
|
|
[2]
|
Wang Y D, He H B, Sun C Y. Learning to navigate through complex dynamic environment with modular deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Games, 2018, 10(4): 400−412 doi: 10.1109/TG.2018.2849942
|
|
[3]
|
郑南宁. 人工智能面临的挑战. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(5): 641−642Zheng Nan-Ning. On challenges in artificial intelligence. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5): 641−642
|
|
[4]
|
Nguyen T T, Nguyen N D, Nahavandi S. Deep reinforcement learning for multiagent systems: a review of challenges, solutions, and applications. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2977374
|
|
[5]
|
赵冬斌, 邵坤, 朱圆恒, 李栋, 陈亚冉, 王海涛, 等. 深度强化学习综述: 兼论计算机围棋的发展. 控制理论与应用, 2016, 33(6): 701−717 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2016.60173Zhao Dong-Bin, Shao Kun, Zhu Yuan-Heng, Li Dong, Chen Ya-Ran, Wang Hai-Tao, et al. Review of deep reinforcement learning and discussions on the development of computer Go. Control Theory & Applications, 2016, 33(6): 701−717 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2016.60173
|
|
[6]
|
周志华. AlphaGo专题介绍. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(5): 670Zhou Zhi-Hua. AlphaGo special session: an introduction. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5): 670
|
|
[7]
|
Silver D, Huang A, Maddison C J, Guez A, Sifre L, van den Driessche G, et al. Mastering the game of go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature, 2016, 529(7587): 484−489 doi: 10.1038/nature16961
|
|
[8]
|
Silver D, Schrittwieser J, Simonyan K, Antonoglou I, Huang A, Guez A, et al. Mastering the game of go without human knowledge. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 354−359 doi: 10.1038/nature24270
|
|
[9]
|
Berner C, Brockman G, Chan B, Cheung V, Dębiak P, Denniso C, et al. Dota 2 with large scale deep reinforcement learning. arXiv: 1912.06680, 2019.
|
|
[10]
|
Hung S M, Givigi S N. A Q-learning approach to flocking with UAVs in a stochastic environment. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(1): 186−197 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2509646
|
|
[11]
|
Schwab D, Zhu Y F, Veloso M. Zero shot transfer learning for robot soccer. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2018). Stockholm, Sweden: ACM, 2018. 2070−2072
|
|
[12]
|
王云鹏, 郭戈. 基于深度强化学习的有轨电车信号优先控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(12): 2366−2377Wang Yun-Peng, Guo Ge. Signal priority control for trams using deep reinforcement learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(12): 2366−2377
|
|
[13]
|
Rahman M S, Mahmud M A, Pota H R, Hossain M J, Orchi T F. Distributed multi-agent-based protection scheme for transient stability enhancement in power systems. International Journal of Emerging Electric Power Systems, 2015, 16(2): 117−129 doi: 10.1515/ijeeps-2014-0143
|
|
[14]
|
He J, Peng J, Jiang F, Qin G R, Liu W R. A distributed Q learning spectrum decision scheme for cognitive radio sensor network. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2015, 2015: 7
|
|
[15]
|
Leibo J Z, Zambaldi V, Lanctot M, Marecki J, Graepel T. Multi-agent reinforcement learning in sequential social dilemmas. In: Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. Sao Paulo, Brazil: ACM, 2017. 464−473
|
|
[16]
|
吴国政. 从F03项目资助情况分析我国自动化学科的发展现状与趋势. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(9): 1611−1619Wu Guo-Zheng. Analysis of the status and trend of the development of China's automation discipline from F03 funding of NSFC. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(9): 1611−1619
|
|
[17]
|
Hernandez-Leal P, Kartal B, Taylor M E. A survey and critique of multiagent deep reinforcement learning. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2019, 33(6): 750−797 doi: 10.1007/s10458-019-09421-1
|
|
[18]
|
Mu C X, Ni Z, Sun C Y, He H B. Air-breathing hypersonic vehicle tracking control based on adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(3): 584−598 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2516948
|
|
[19]
|
Mu C, Zhao Q, Sun C, Gao Z. A novel Q-learning algorithm for optimal tracking control of linear discrete-time systems with unknown dynamics. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 82: 1−13
|
|
[20]
|
Wang Y D, Sun J, He H B, Sun C Y. Deterministic policy gradient with integral compensator for robust quadrotor control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2884725
|
|
[21]
|
Sutton R S, McAllester D, Singh S, Mansour Y. Policy gradient methods for reinforcement learning with function approximation. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Denver, USA: MIT Press, 1999. 1057−1063
|
|
[22]
|
Silver D, Lever G, Heess N, Degris T, Wierstra D, Riedmiller M. Deterministic policy gradient algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing, China: ACM, 2014. 387−395
|
|
[23]
|
Wei Q L, Wang L X, Liu Y, Polycarpou M M. Optimal elevator group control via deep asynchronous actor-critic learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2965208
|
|
[24]
|
Dong L, Zhong X N, Sun C Y, He H B. Adaptive event-triggered control based on heuristic dynamic programming for nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(7): 1594−1605 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2541020
|
|
[25]
|
Arulkumaran K, Deisenroth M P, Brundage M, Bharath A A. Deep reinforcement learning: a brief survey. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34(6): 26−38 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2743240
|
|
[26]
|
Li Y X. Deep reinforcement learning: an overview. arXiv: 1701.07274, 2017.
|
|
[27]
|
Nguyen N D, Nguyen T, Nahavandi S. System design perspective for human-level agents using deep reinforcement learning: a survey. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 27091−27102 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2777827
|
|
[28]
|
Nguyen T T. A multi-objective deep reinforcement learning framework. arXiv: 1803.02965, 2018.
|
|
[29]
|
Tsitsiklis J N, van Roy B. Analysis of temporal-difference learning with function approximation. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Denver, USA: MIT Press, 1996. 1075−1081
|
|
[30]
|
Van Hasselt H. Double Q-learning. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: MIT Press, 2010. 2613−2621
|
|
[31]
|
Van Hasselt H, Guez A, Silver D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning. arXiv: 1509.06461, 2015.
|
|
[32]
|
Schaul T, Quan J, Antonoglou I, Silver D. Prioritized experience replay. arXiv: 1511.05952, 2015.
|
|
[33]
|
Wang Z Y, Schaul T, Hessel M, van Hasselt H, Lanctot M, de Freitas N. Dueling network architectures for deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: ACM, 2016. 1995−2003
|
|
[34]
|
Hausknecht H, Stone P. Deep recurrent Q-learning for partially observable MDPs. arXiv: 1507.06527, 2017.
|
|
[35]
|
Lample G, Chaplot D S. Playing FPS games with deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, USA: AIAA, 2017.
|
|
[36]
|
Sorokin I, Seleznev A, Pavlov M, Fedorov A, Ignateva A. Deep attention recurrent Q-network. arXiv: 1512.01693, 2015.
|
|
[37]
|
Lillicrap T P, Hunt J J, Pritzel A, Heess N, Erez T, Tassa Y, et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv: 1509.02971, 2015.
|
|
[38]
|
Mnih V, Badia A P, Mirza M, Graves A, Harley T, Lillicrap T P, et al. Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: ACM, 2016. 1928−1937
|
|
[39]
|
Haarnoja T, Zhou A, Abbeel P, Levine S. Soft actor-critic: off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor. arXiv: 1801.01290, 2018.
|
|
[40]
|
Schulman J, Levine S, Abbeel P, Jordan M I, Moritz P. Trust region policy optimization. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: ACM, 2015. 1889−1897
|
|
[41]
|
Jadid O A, Hajinezhad D. A review of cooperative multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. arXiv: 1908.03963, 2019.
|
|
[42]
|
Tan M. Multi-agent reinforcement learning: independent vs. cooperative agents. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Machine Learning. Amherst, USA: ACM, 1993. 330−337
|
|
[43]
|
Matignon L, Laurent G J, Le Fort-Piat N. Independent reinforcement learners in cooperative markov games: a survey regarding coordination problems. The Knowledge Engineering Review, 2012, 27(1): 1−31 doi: 10.1017/S0269888912000057
|
|
[44]
|
Tampuu A, Matiisen T, Kodelja D, Kuzovkin I, Korjus K, Aru J, et al. Multiagent cooperation and competition with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv: 1511.08779, 2015.
|
|
[45]
|
Usunier N, Synnaeve G, Lin Z M, Chintala S. Episodic exploration for deep deterministic policies: an application to starcraft micromanagement tasks. arXiv: 1609.02993, 2016.
|
|
[46]
|
Cui L L, Wang X W, Zhang Y. Reinforcement learning-based asymptotic cooperative tracking of a class multi-agent dynamic systems using neural networks. Neurocomputing, 2016, 171: 220−229 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.06.066
|
|
[47]
|
Kraemer L, Banerjee B. Multi-agent reinforcement learning as a rehearsal for decentralized planning. Neurocomputing, 2016, 190: 82−94 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.01.031
|
|
[48]
|
Lowe R, Wu Y, Tamar A, Harb J, Abbeel P, Mordatch I. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: MIT Press, 2017. 6379−6390
|
|
[49]
|
Ryu H, Shin H, Park J. Multi-agent actor-critic with generative cooperative policy network. arXiv: 1810.09206, 2018.
|
|
[50]
|
Chu X X, Ye H J. Parameter sharing deep deterministic policy gradient for cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning. arXiv: 1710.00336, 2017.
|
|
[51]
|
Foerster J N, Farquhar G, Afouras T, Nardelli N, Whiteson S. Counterfactual multi-agent policy gradients. arXiv: 1705.08926, 2017.
|
|
[52]
|
Zhang K Q, Yang Z R, Liu H, Zhang T, Basar T. Fully decentralized multi-agent reinforcement learning with networked agents. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: ACM, 2018. 5872−5881
|
|
[53]
|
Jiang J C, Dun C, Huang T J, Lu Z Q. Graph convolutional reinforcement learning. arXiv: 1810.09202, 2018.
|
|
[54]
|
Wang Q L, Psillakis H E, Sun C Y. Cooperative control of multiple agents with unknown high-frequency gain signs under unbalanced and switching topologies. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(6): 2495−2501 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2867161
|
|
[55]
|
Hernandez-Leal P, Kaisers M, Baarslag T, de Cote E M. A survey of learning in multiagent environments: dealing with non-stationarity. arXiv: 1707.09183, 2017.
|
|
[56]
|
Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, Rusu A A, Veness J, Bellemare M G, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529−533 doi: 10.1038/nature14236
|
|
[57]
|
Abdallah S, Kaisers M. Addressing the policy-bias of Q-learning by repeating updates. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-agent Systems. Saint Paul, USA: ACM, 2013. 1045−1052
|
|
[58]
|
Abdallah S, Kaisers M. Addressing environment non-stationarity by repeating Q-learning updates. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2016, 17(1): 1582−1612
|
|
[59]
|
Yu C, Zhang M J, Ren F H, Tan G Z. Emotional multiagent reinforcement learning in spatial social dilemmas. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(12): 3083−3096 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2403394
|
|
[60]
|
Diallo E A O, Sugiyama A, Sugawara T. Learning to coordinate with deep reinforcement learning in doubles pong game. In: Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications. Cancun, Mexico: IEEE, 2017. 14−19
|
|
[61]
|
Foerster J N, Nardelli N, Farquhar G, Afouras T, Torr P H S, Kohli P. Stabilising experience replay for deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: ACM, 2017. 1146−1155
|
|
[62]
|
Palmer G, Tuyls K, Bloembergen D, Savani R. Lenient multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. Stockholm, Sweden: ACM, 2018. 443−451
|
|
[63]
|
Omidshafiei S, Pazis J, Amato C, How J P, Vian J. Deep decentralized multi-task multi-agent reinforcement learning under partial observability. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: ACM, 2017. 2681−2690
|
|
[64]
|
Zheng Y, Meng Z P, Hao J Y, Zhang Z Z. Weighted double deep multiagent reinforcement learning in stochastic cooperative environments. In: Proceedings of the 15th Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Nanjing, China: ACM, 2018. 421−429
|
|
[65]
|
Mu C X, Zhao Q, Sun C Y. Optimal model-free output synchronization of heterogeneous multi-agent systems under switching topologies. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2958277
|
|
[66]
|
Foerster J N, Assael Y M, de Freitas N, Whiteson S. Learning to communicate to solve riddles with deep distributed recurrent Q-networks. arXiv: 1602.02672, 2016.
|
|
[67]
|
Hong Z W, Su S Y, Shann T Y, Chang Y H, Lee C Y. A deep policy inference Q-network for multi-agent systems. In: Proceedings of the 17th Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. Stockholm, Sweden: Springer, 2018. 1388−1396
|
|
[68]
|
Kasai T, Tenmoto H, Kamiya A. Learning of communication codes in multi-agent reinforcement learning problem. In: Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Conference on Soft Computing in Industrial Applications. Muroran, Japan: IEEE, 2008. 1−6
|
|
[69]
|
Foerster J N, Assael Y M, de Freitas N, Whiteson S. Learning to communicate with deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2016. 2137−2145
|
|
[70]
|
Sukhbaatar S, Szlam A, Fergus R. Learning multiagent communication with backpropagation. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2016. 2252−2260
|
|
[71]
|
Zhang H G, Jiang H, Luo Y H, Xiao G Y. Data-driven optimal consensus control for discrete-time multi-agent systems with unknown dynamics using reinforcement learning method. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(5): 4091−4100 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2542134
|
|
[72]
|
Zhang Y, Zavlanos M M. Distributed off-policy actor-critic reinforcement learning with policy consensus. arXiv: 1903.09255, 2019.
|
|
[73]
|
Wei Q L, Liu D R, Lewis F L, Liu Y, Zhang J. Mixed iterative adaptive dynamic programming for optimal battery energy control in smart residential microgrids. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(5): 4110−4120 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2650872
|
|
[74]
|
Yang X D, Wang Y D, He H B, Sun C Y, Zhang Y B. Deep reinforcement learning for economic energy scheduling in data center microgrids. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting. Atlanta, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1−5
|
|
[75]
|
Prasad A, Dusparic I. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for zero energy communities. arXiv: 1810.03679, 2018.
|
|
[76]
|
徐昕. 增强学习与近似动态规划. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010Xu Xin. Reinforcement Learning and Approximate Dynamic Programming. Beijing: Science Press, 2010
|
|
[77]
|
Wan Z Q, Jiang C, Fahad M, Ni Z, Guo Y, He H B. Robot-assisted pedestrian regulation based on deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(4): 1669−1682 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2878977
|
|
[78]
|
Lin K X, Zhao R Y, Xu Z, Zhou J Y. Efficient large-scale fleet management via multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. London, UK: ACM, 2018. 1774−1783
|
|
[79]
|
Ben Noureddine D, Gharbi A, Ben Ahmed S. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for task allocation in dynamic environment. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Software Technologies. Madrid, Spain: SciTePress, 2017. 17−26
|
|
[80]
|
Hüttenrauch M, Šošić A, Neumann G. Guided deep reinforcement learning for swarm systems. arXiv: 1709.06011, 2017.
|
|
[81]
|
Kurek M, Jaśkowski W. Heterogeneous team deep Q-learning in low-dimensional multi-agent environments. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence and Games (CIG). Santorini, Greece: IEEE, 2016. 1−8
|
|
[82]
|
Perolat J, Leibo J Z, Zambaldi V, Beattie C, Tuyls K, Graepel T. A multi-agent reinforcement learning model of common-pool resource appropriation. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: ACM, 2017. 3643−3652
|
|
[83]
|
Piot B, Geist M, Pietquin O. Bridging the gap between imitation learning and inverse reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(8): 1814−1826 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2543000
|
|
[84]
|
Hadfield-Menell D, Russell S J, Abbeel P, Dragan A. Cooperative inverse reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2016. 3909−3917
|
|
[85]
|
Hadfield-Menell D, Milli S, Abbeel P, Russell S, Dragan A D. Inverse reward design. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: ACM, 2017. 6765−6774
|
|
[86]
|
Levine S, Finn C, Darrell T, Abbeel P. End-to-end training of deep visuomotor policies. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2016, 17(1): 1334−1373
|
|
[87]
|
Nagabandi A, Kahn G, Fearing R S, Levine S. Neural network dynamics for model-based deep reinforcement learning with model-free fine-tuning. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane, Australia: IEEE, 2018. 7559−7566
|
|
[88]
|
Gu S X, Lillicrap T P, Sutskever I, Levine S. Continuous deep Q-learning with model-based acceleration. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: ACM, 2016. 2829−2838
|
|
[89]
|
Finn C, Levine S. Deep visual foresight for planning robot motion. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Singapore: IEEE, 2017. 2786−2793
|
|
[90]
|
Serban I V, Sankar C, Pieper M, Pineau J, Bengio Y. The bottleneck simulator: a model-based deep reinforcement learning approach. arXiv: 1807.04723, 2018.
|
|
[91]
|
Rashid T, Samvelyan M, de Witt C S, Farquhar G, Foerster J, Whiteson S. QMIX: monotonic value function factorisation for deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. arXiv: 1803.11485, 2018.
|
|
[92]
|
Foerster J N, Chen R Y, Al-Shedivat M, Whiteson S, Abbeel P, Mordatch I. Learning with opponent-learning awareness. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. Stockholm, Sweden: ACM, 2018. 122−130
|
|
[93]
|
Yuan X, Dong L, Sun C Y. Solver-critic: a reinforcement learning method for discrete-time constrained-input systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2978088
|
|
[94]
|
He W, Li Z J, Chen C L P. A survey of human-centered intelligent robots: issues and challenges. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2017, 4(4): 602−609 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510604
|
|
[95]
|
Nahavandi S. Trusted autonomy between humans and robots: toward human-on-the-loop in robotics and autonomous systems. IEEE Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Magazine, 2017, 3(1): 10−17 doi: 10.1109/MSMC.2016.2623867
|




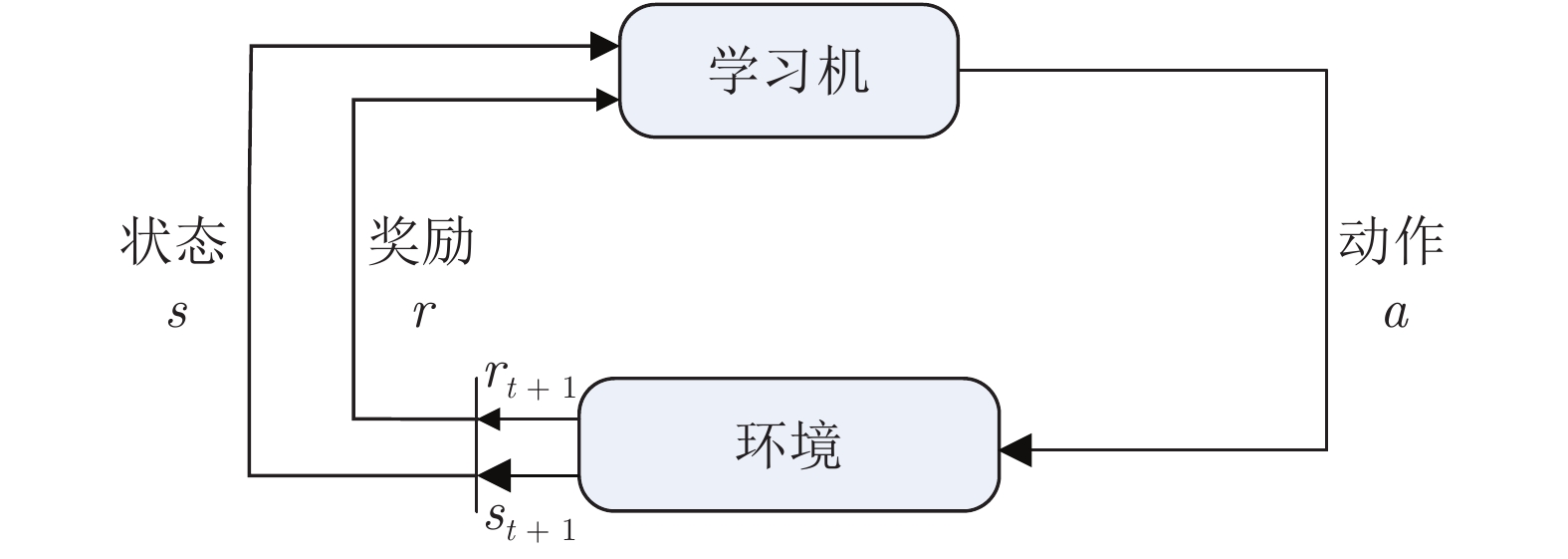
 下载:
下载: