Independent Slow Feature Analysis Modelling Method and Its Application in Dynamic Fault Detection
-
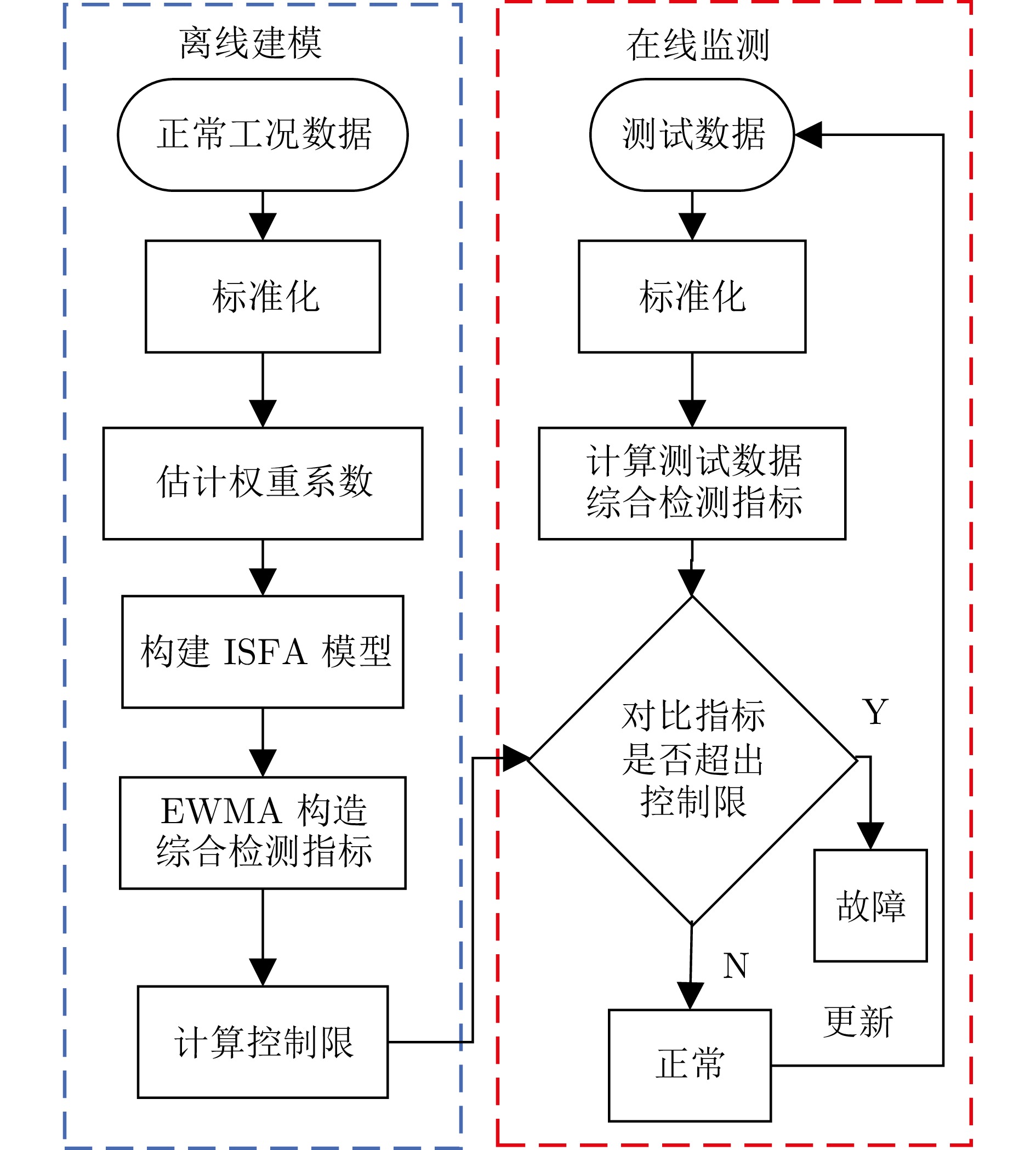
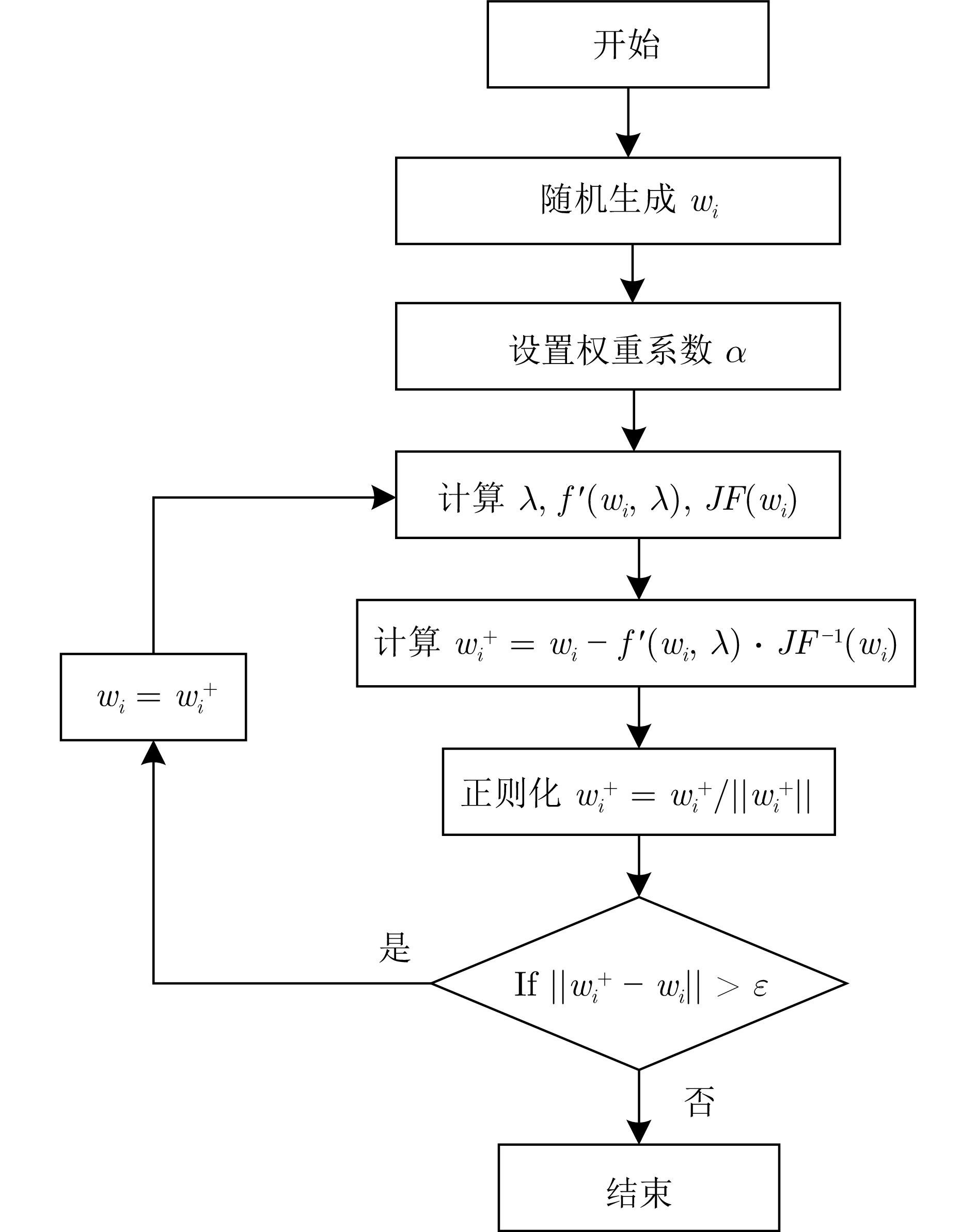
摘要: 故障检测与诊断技术是保证复杂装备或工业过程正常运行的技术支撑和有效手段, 独立成分分析(Independent component analysis, ICA)作为一种典型的多元统计过程监测(Multivariate statistical process monitoring, MSPM)方法, 可充分挖掘数据的高阶统计信息. 传统ICA方法在预处理阶段采用主成分分析(Principle component analysis, PCA)进行白化和降维, 但PCA的静态性质导致ICA在动态过程监测中的效果不太理想. 为解决这一问题, 提出一种独立慢特征分析(Independent-slow feature analysis, ISFA)建模方法. ISFA以原始观测矩阵和白化矩阵为自变量构造双目标优化函数, 基于牛顿迭代法求解目标函数, 使用网格搜索优化权重系数, 利用指数加权移动平均(Exponentially weighted moving average, EWMA)修正统计量并构建综合检测指标; 最后, 利用数值仿真和电动伺服机构实验验证所提方法的有效性.Abstract: Fault detection and diagnosis technologies serve as critical technical supports and effective means to ensure the normal operation of complex equipment or industrial processes. As a typical multivariate statistical process monitoring (MSPM) method, independent component analysis (ICA) can fully exploit high-order statistical information from data. Conventional ICA methods employ principal component analysis (PCA) for whitening and dimensionality reduction during the pre-processing stage. However, the static nature of PCA compromises ICA's effectiveness in dynamic process monitoring. To address this issue, an independent-slow feature analysis (ISFA) modelling method is approached. Specifically, ISFA constructs a dual-objective optimization function using the original observation matrix and whitening matrix as independent variables, solves the objective function via Newton's iteration method, optimizes weight coefficients through grid search, modifies statistical metrics using exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA), and establishes a comprehensive detection index. Finally, numerical simulations and electric servo mechanism experiments are conducted to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
Key words:
- Independent-slow feature /
- dynamic process /
- fault detection /
- grid search
-
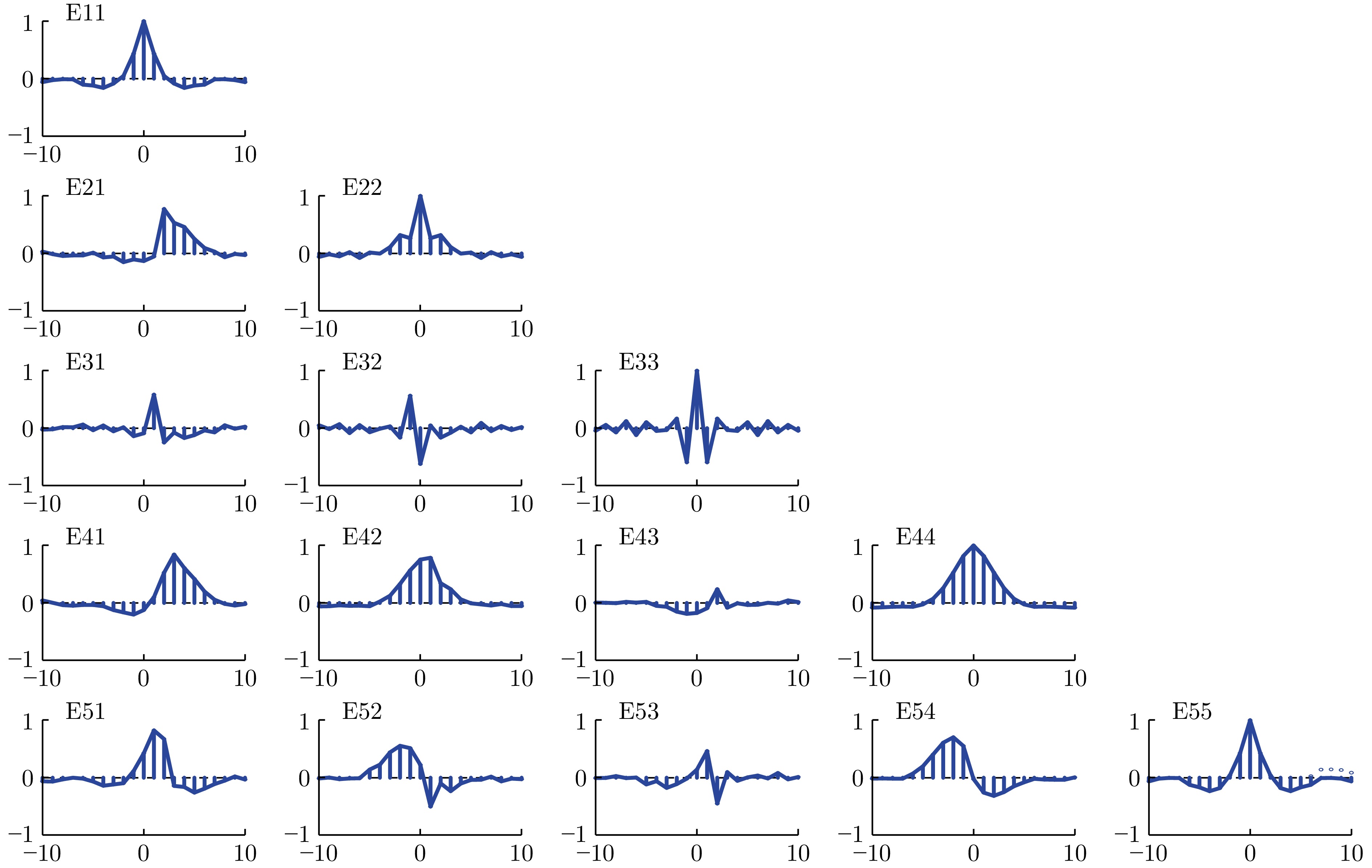
表 1 各变量零延迟相关系数表
Table 1 Zero delay correlation coefficient table for each variable
变量 $ E_1 $ $ E_2 $ $ E_3 $ $ E_4 $ $ E_5 $ $ E_1 $ 1 — — — — $ E_2 $ −0.13 1 — — — $ E_3 $ −0.09 −0.62 1 — — $ E_4 $ −0.12 0.76 −0.17 1 — $ E_5 $ 0.43 0.22 0.14 −0.02 1 表 2 数值仿真故障检测的FARs和FDRs (%)
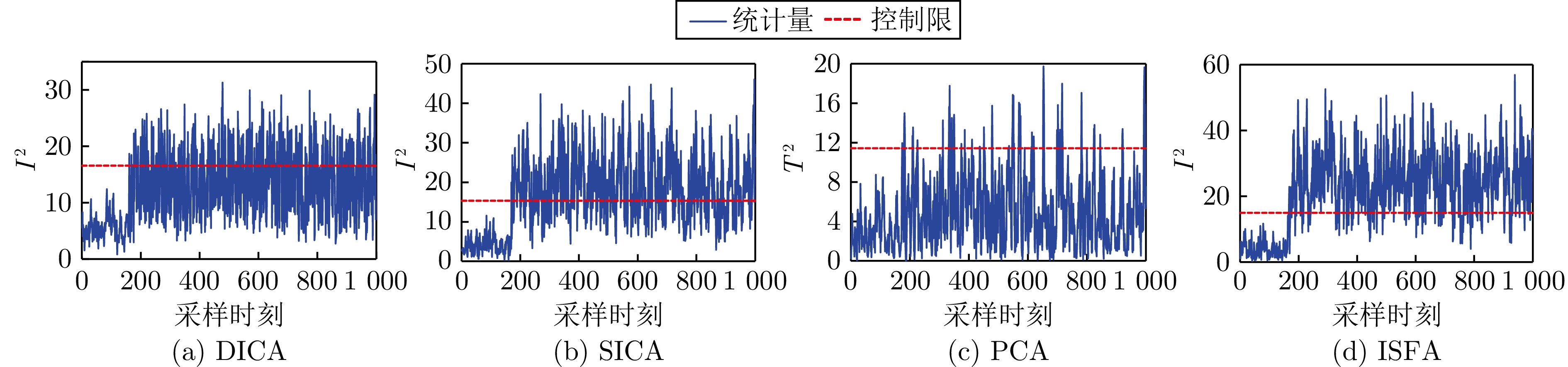
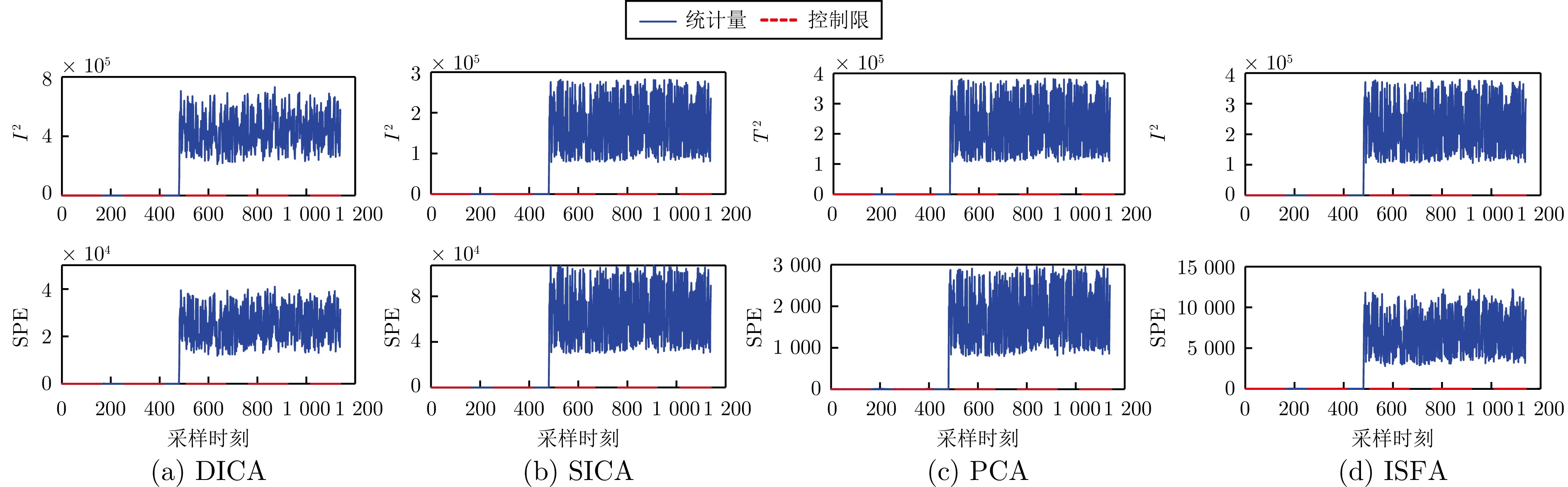
Table 2 FARs and FDRs for fault detection of numerical simulation (%)
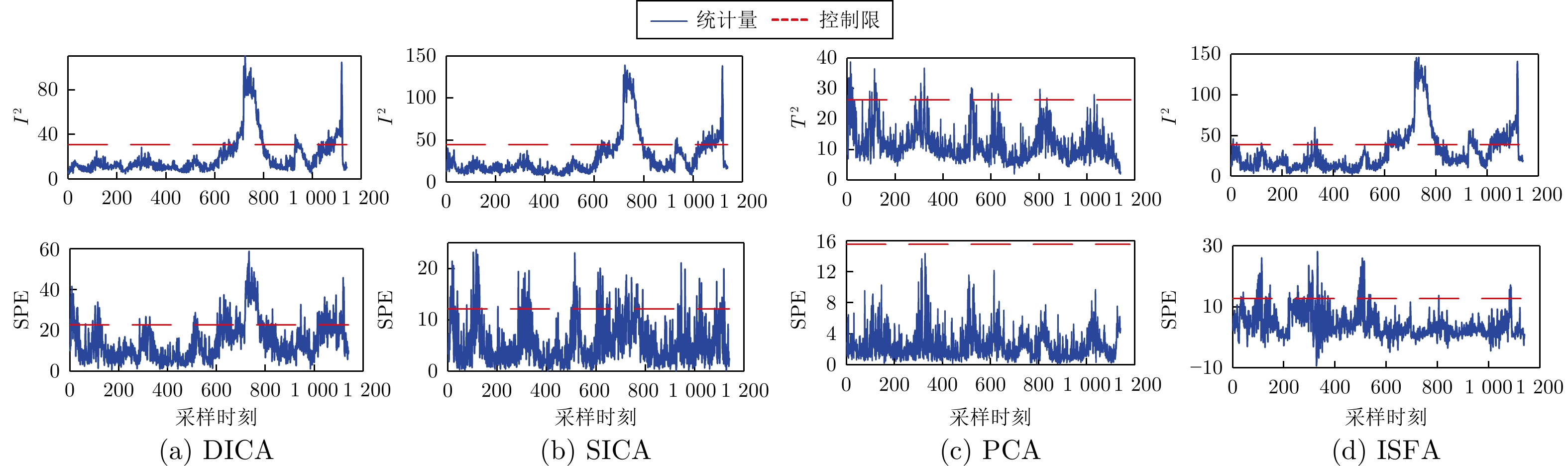
算法 DICA SICA PCA ISFA 故障 FAR FDR FAR FDR FAR FDR FAR FDR 1 0.00 33.69 0.00 63.33 0.00 7.97 0.00 83.81 2 0.00 91.19 0.00 97.02 0.00 93.45 0.00 98.81 3 0.00 96.78 0.00 99.88 0.00 99.40 0.00 99.76 平均 0.00 73.89 0.00 86,74 0.00 66.94 0.00 94.13 表 3 电动伺服机构变量表
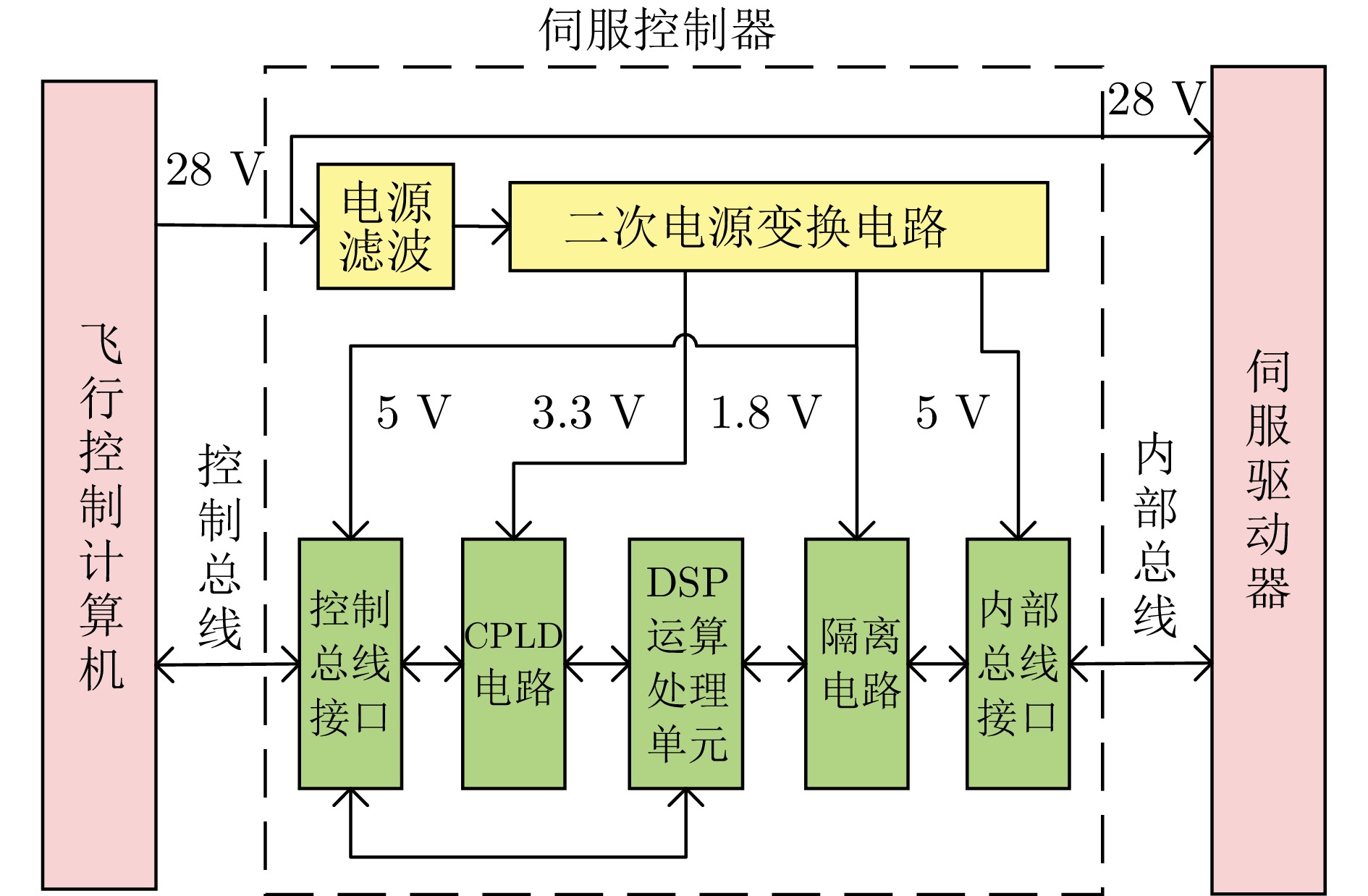
Table 3 Variable table of electric servo mechanism
序号 变量描述 序号 变量描述 1 时标(高字) 2 时标(低字) 3 A通道位置反馈 4 B通道位置反馈 5 A通道速度反馈 6 B通道速度反馈 7 A通道q轴电流反馈 8 B通道q轴电流反馈 9 A通道d轴电流反馈 10 B通道d轴电流反馈 11 A通道喷管摆角 12 B通道喷管摆角 13 A通道电机转角 14 B通道电机转角 15 +10 V供电状态 16 −10 V供电状态 17 +15 V供电状态 18 −15 V供电状态 19 +5 V供电状态 20 28 V电压 21 28 V电流 表 4 电动伺服机构故障检测的FARs和FDRs (%)
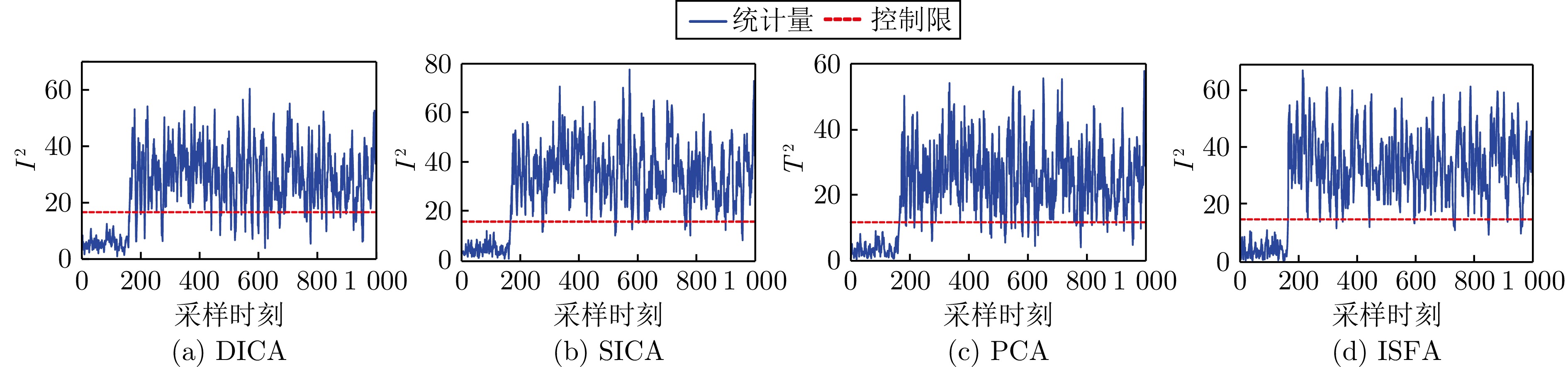
Table 4 FARs and FDRs for fault detection of electric servo mechanisms (%)
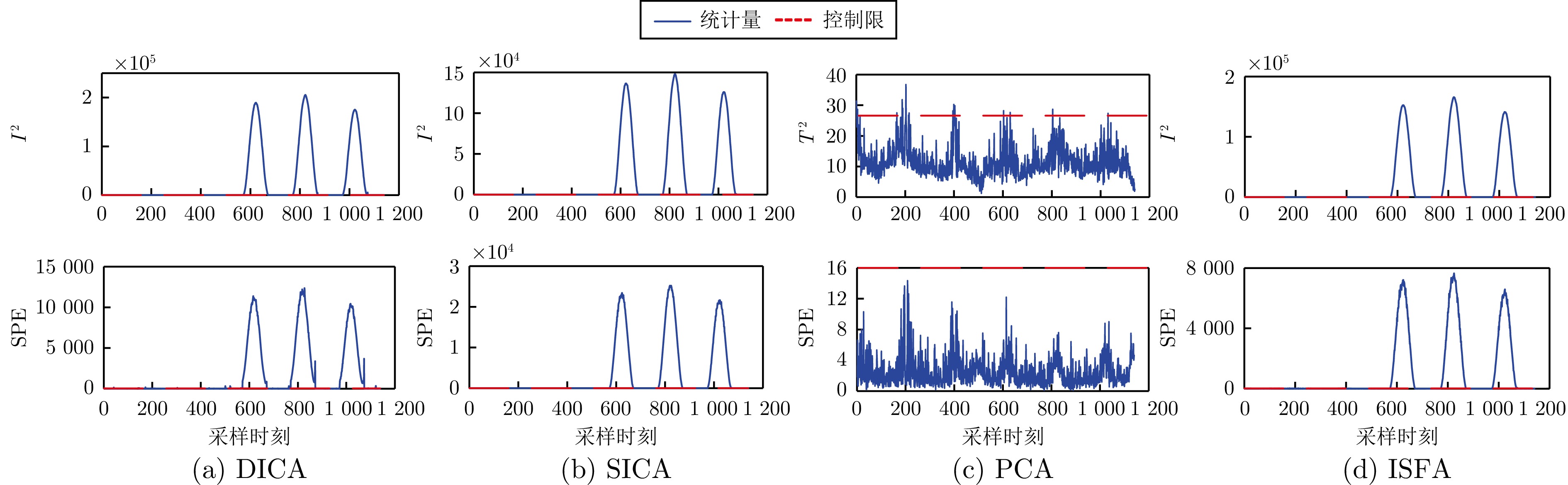
算法 DICA SICA PCA ISFA 故障 FAR FDR FAR FDR FAR FDR FAR FDR 1 0.21 99.85 0.89 100.00 2.50 99.85 0.00 100.00 2 0.72 99.01 0.24 97.69 1.44 1.32 0.00 98.69 3 0.00 36.18 0.00 4.67 0.93 33.89 0.84 53.33 平均 0.31 78.35 0.38 77.19 2.87 34.03 0.28 84.01 -
[1] 刘美枝, 孔祥玉, 胡昌华. 基于质量关联虚拟变量的质量相关变量划分及故障检测. 自动化学报, 2024, 51(5): 1−13Liu Mei-Zhi, Kong Xiang-Yu, Hu Chang-Hua. Quality-related variable division and fault detection based on quality-related virtual variable. Acta Automation Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1−13 [2] 董洁, 张伟, 彭开香, 等. 一种面向工业过程的质量异常检测与故障量化评估方法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(10): 2406−2415Dong Jie, Zhang Wei, Peng Kai-Xiang, Ma Liang. A novel method of quality abnormality detection and fault quantitative assessment for industrial processes. Acta Automation Sinica, 2022, 48(10): 2406−2415 [3] Obanya P O, Coetzer R L J, Olivier C P, Verster T. Variable contribution analysis in multivariate process monitoring using permutation entropy. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 2024, 190: Article No. 110064 doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2024.110064 [4] Li Z C, Yan X F. Fault-relevant optimal ensemble ICA model for non-Gaussian process monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2024, 28(6): 2581−2590 [5] Xu Y, Shen S Q, He Y L, Zhu Q X. A novel hybrid method integrating ICA-PCA with relevant vector machine for multivariate process monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2019, 27(4): 1780−1787 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2018.2816903 [6] Yang N C, Ismail H. Robust intelligent learning algorithm using random forest and modified-independent component analysis for pv fault detection: in case of imbalanced data. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 41119−41130 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3166477 [7] Zhang S M, Wang S J, Zhao C H. Vertices packaging-based interval independent component analysis for fault detection with process uncertainty. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(1): 919−930 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3271737 [8] Odiowei P P, Cao Y. State-space independent component analysis for nonlinear dynamic process monitoring. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2010, 103(1): 59−65 doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2010.05.014 [9] Huang J, Yan X F. Dynamic process fault detection and diagnosis based on dynamic principal component analysis, dynamic independent component analysis and Bayesian inference. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2015, 148: 115−127 doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2015.09.010 [10] Zhang C, Zheng X F, Li Y. A novel fault detection and diagnosis scheme based on independent component analysis-statistical characteristics: application on the Tennessee Eastman benchmark process. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 54(6): 304−312 [11] Wiskott L, Sejnowski T. Slow feature analysis: unsupervised learning of invariances. Neural Computation, 2002, 14(4): 715−770 doi: 10.1162/089976602317318938 [12] Ji H Q. Data-driven sensor fault diagnosis under closed-loop control with slow feature analysis. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(24): 24299−24308 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3221282 [13] Zhang H Y, Li C D, Wei Q L, Zhang Y C. Fault detection and diagnosis of the air handling unit via combining the feature sparse representation based dynamic SFA and the LSTM network. Energy and Buildings, 2022, 269: Article No. 112241 doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2022.112241 [14] Saafan H, Zhu Q Q. Improved manifold sparse slow feature analysis for process monitoring. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 2022, 164: Article No. 107905 doi: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2022.107905 [15] Feng L J, Zhao C H, Huang B. A slow independent component analysis algorithm for time series feature extraction with the concurrent consideration of high-order statistic and slowness. Journal of Process Control, 2019, 84: 1−12 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2019.09.005 [16] Li C, Wen C L, Zhou Z. An industrial process fault diagnosis method based on independent slow feature analysis and stacked sparse autoencoder network. Journal ofthe Franklin Institute, 2024, 361: 234−247 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2023.10.004 [17] Li C, Zhou Z, Wen C L, Li Z X. Fault detection of non-Gaussian and nonlinear processes based on independent slow feature analysis. ACS Omega, 2022, 7(8): 6978−6990 doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c06649 [18] Shang C, Yang F, Gao X Q, Huang X L, Suykens J A K, Huang D X. Concurrent monitoring of operating condition deviations and process dynamics anomalies with slow feature analysis. AIChE Journal, 2015, 61(11): 3666−3682 doi: 10.1002/aic.14888 [19] Zhang Y W, Wang W, Deng Y K, Wang R. Signal reconstruction algorithm for azimuth multichannel SAR system based on a multiobjective optimization model. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience And Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(6): 3881−3893 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2959217 [20] Lupu D, Necoara I, Garrett J L L, Johansen T A. Stochastic higher-order independent component analysis for hyperspectral dimensionality reduction. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2022, 8: 1184−1194 doi: 10.1109/TCI.2022.3230584 [21] Gao H M, Diao R S, Huang Z, Zhong Y, Mao Y F, Tang W B. Parameter identification of SVG using multilayer coarse-to-fine grid searching and particle swarm optimization. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 77137−77146 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3192538 [22] Fan S K S, Jen C H, Hsu C Y, Liao Y L. A new double exponentially weighted moving average run-to-run control using a disturbance-accumulating strategy for mixed-product mode. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(4): 1846−1860 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2020.3021949 [23] Oja E, Yuan Z J. The FastICA Algorithm Revisited: Convergence Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2006, 17(6): 1370−1381 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2006.880980 [24] Cui Y Y, Zhu Y K, Liu J, Wang C L, Zhao L. Analysis, estimation, and rejection of multi-frequency unknown disturbances in CMG gimbal servo systems. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2024, 71(10): 4501−4505 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2024.3398066 [25] Shi Z H, Xiao J, Jiang J H, Zhang Y, Zhou Y H. Identifying reliability high-correlated gates of logic circuits with Pearson correlation coefficient. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2024, 71(4): 2319−2323 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2023.3334390 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 19
- HTML全文浏览量: 11
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: