-
摘要: 针对具有Snapback层间耦合框架的多层网络化数据采样系统的状态能控性展开研究. 首先构建出多层Snapback网络化数据采样系统的数学模型, 并推导出通用三层Snapback网络化数据采样系统能控性的充要条件, 揭示了层内网络拓扑结构, 节点动力学, 外部控制输入, 数据采样及层间耦合框架等因素对能控性的影响. 然后, 针对层内耦合矩阵为可对角化矩阵的基本Snapback网络化数据采样系统, 进一步简化了其能控性条件, 并将其结论进行了推广. 最后, 考虑由简单Snapback结构叠加而成的复合Snapback多层网络, 给出网络化数据采样系统能控性的充分条件. 通过例子验证了本文给出的结论.Abstract: This study investigates the state controllability of multilayer networked sampled-data systems with a snapback inter-layer coupling framework. Firstly, a mathematical model for multilayer snapback networked sampled-data systems is constructed, and the necessary and sufficient conditions for controllability of general three-layer snapback networked sampled-data systems are derived. These conditions reveal the influences of intra-layer network topology, nodal dynamics, external control inputs, data sampling, and inter-layer coupling frameworks on system controllability. For fundamental snapback networked sampled-data systems with diagonalizable intra-layer coupling matrices, the controllability conditions are further simplified and extended. Subsequently, considering composite multilayer networks formed by superposition of simple snapback structures, sufficient conditions for controllability of such networked sampled-data systems are established. Finally, numerical examples are provided to validate the theoretical conclusions presented in this paper.
-
Key words:
- Network controllability /
- sampled-data systems /
- multilayer network /
- interlayer coupling
-
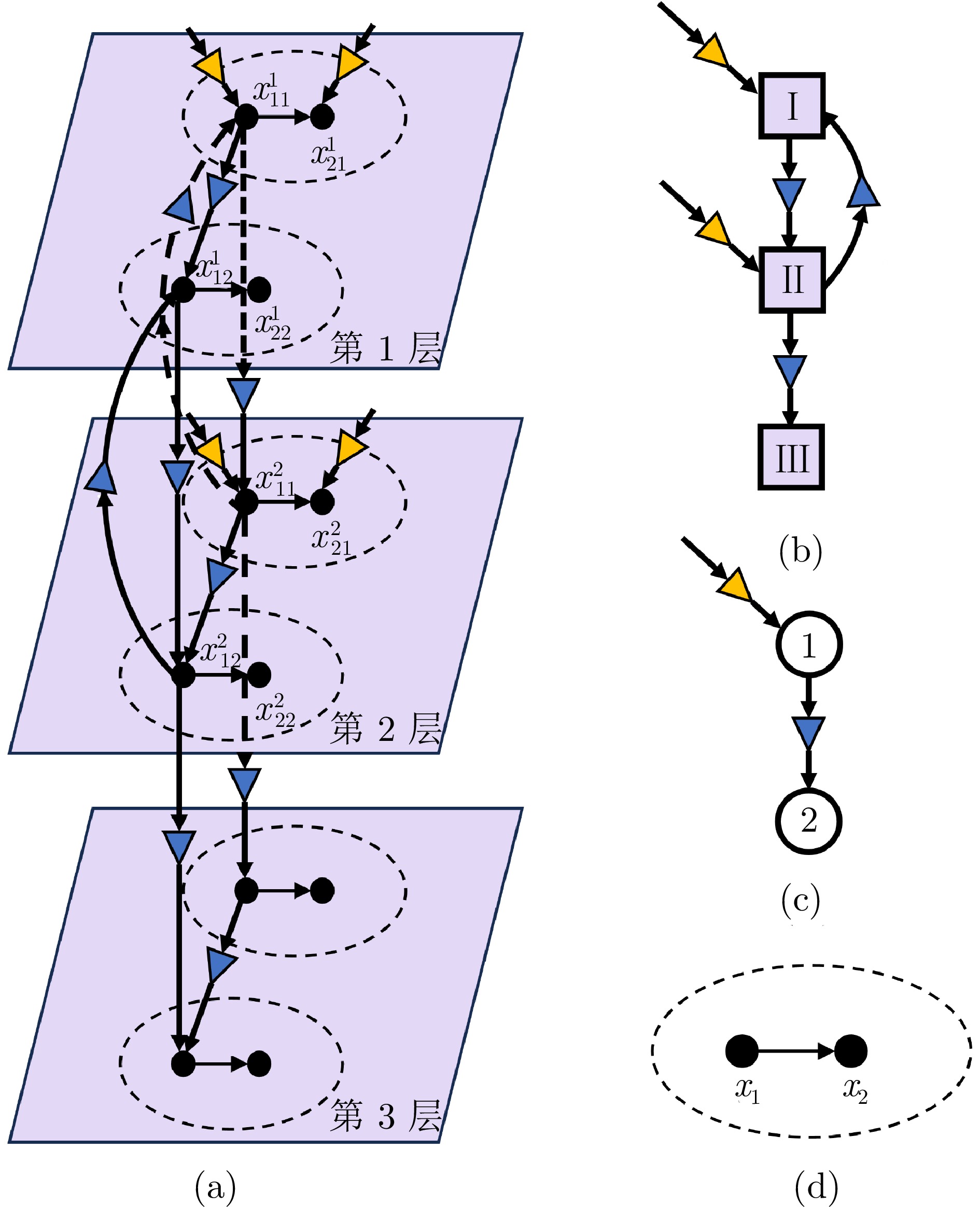
图 2 三层Snapback网络化采样数据系统实例(黄色和蓝色的三角形, 分别表示外界输入的控制采样和系统内部的传输采样) ((a) 整个网络化数据采样系统; (b) 层间耦合拓扑结构; (c) 层内耦合拓扑结构; (d) 单个节点系统)
Fig. 2 Example of a three-layer Snapback networked sampled-data system(The yellow and blue triangles represent the control sampling from external inputs and the transmission sampling within the system, respectively) ((a) Entire networked; sampled-data system; (b) Inter-layer coupling topology; (c) Intra-layer coupling topology; (d) Single-node system)
-
[1] Kalman R E. Canonical structure of linear dynamical systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1962, 48(4): 596−597 [2] Liu Y Y, Slotine J J, Barabási, et al. Controllability of complex networks. Nature, 2011, 473(7346): 167 doi: 10.1038/nature10011 [3] Ding J, Wen C, Li G, et al. Target controllability in multilayer networks via minimum-cost maximum-flow method. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(5): 1949−1962 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2995596 [4] Klickstein I, Sorrentino F. The controllability gramian of lattice graphs. Automatica, 2020, 114(3): Article No. 108833 [5] Zhang Y, Ding J, Li X. Network controllability robustness learning via spatial graph neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2024, 11(2): 4045−4058 [6] Wang L F, Li Z F, Zhao G T, et al. Input structure design for structural controllability of complex networks. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(7): 1571−1581 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123504 [7] Chen C, Surana A, Bloch A M, et al. Controllability of hypergraphs. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(2): 1646−1657 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2021.3068203 [8] Song K, Li G, Chen X, et al. Target controllability of two-layer multiplex networks based on network flow theory. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(5): 2699−2711 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2906700 [9] Wu J, Li X, Chen G. Controllability of deep-coupling dynamical networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2020, 67(12): 5211−5222 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.2999451 [10] Jiang L X, Tang L K, Lü J H. Controllability of multilayer networks. Asian Journal of Control, 2021, 10(1): 1−11 [11] Wang L, Li Z, Guo G. Target controllability of multi-layer networks with high-dimensional nodes. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(9): 1999−2010 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.124152 [12] Lou Y, Wang L, Chen G. Enhancing controllability robustness of q-snapback networks through redirecting edges. Research, 2020Article No. 7857534 [13] Chen G, Lou Y, Wang L. A comparative study on controllability robustness of complex networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Ⅱ: Exp. Briefs, 2020, 66(5): 828−832 [14] Lou Y, Wang L, Chen G. Local diversity-stability of the q-snapback network model. Physica, A. Statistical mechanics and its applications, 2020, 536: Article No. 121020 [15] Cohen J E, Newman C M. A stochastic theory of community food webs I. models and aggregated data. Proceedings of the Royal society of London, 1985, 224(1237): 421−448 [16] Cohen R, Erez K, Ben-Avraham D. Resilience of the internet to random breakdowns. Physical review letters, 2000, 85(21): 462−470 [17] Sun J, Chen G, Chen J. Stability analysis of aperiodic sampled-data systems: A switched polytopic system method. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2023, 67(6): 1054−1058 [18] Zhu H, Lu J, Liu Y, et al. Sampled-data consensus for multiagent systems with open topology and packet loss. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2025, 62(6): 1568−1578 [19] Zhuang X, Tian Y, Abdl Ghani H, et al. Sampled-data neural network observer for motion state estimation of full driving automation vehicle. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(2): 2726−2738 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3479416 [20] Yu L, Wang Z, Liu Y. Sampled-data nonfragile bipartite tracking consensus for nonlinear multiagent systems: Dealing with denial-of-service attacks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2025, 5(2): 1202−1214 [21] Lu Z H, Ji Z J, Zhang Z Q. Sampled-data based structural controllability of multi-agent systems with switching topology. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2020, 375(15): 10886−10899 [22] Yang Z, Wang X, Wang L. Controllability of networked sampled-data systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(8): 5081−2093 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3344692 [23] Yang Z, Wang X, Wang L. Controllability of multilayer networked sampled-data systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 5(3): 1287−1299 [24] Roman S, Axler S, Gehring F. Advanced Linear Algebra. Springer, 2005 [25] Hao Y, Duan Z, Chen G. New controllability conditions for networked identical LTI systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(10): 1525−1532 [26] Hao Y, Wang Q, Duan Z. Some necessary and sufficient conditions on the controllability of star networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2020, 67(11): 2582−2586 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2019.2953667 [27] Lou Y, Wang L, Chen G. Toward stronger robustness of network controllability: a snapback network model. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2018, 65(9): 2983−2991 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2018.2821124 [28] Wu J N, Li X, Chen G. Controllability of multilayer snapback networks. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2023, 10(1): 15−25 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2022.3185153 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 3
- HTML全文浏览量: 1
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: