Edge Dynamic Event-triggered-based Online Distributed Composite Bandit Optimization Algorithm
-
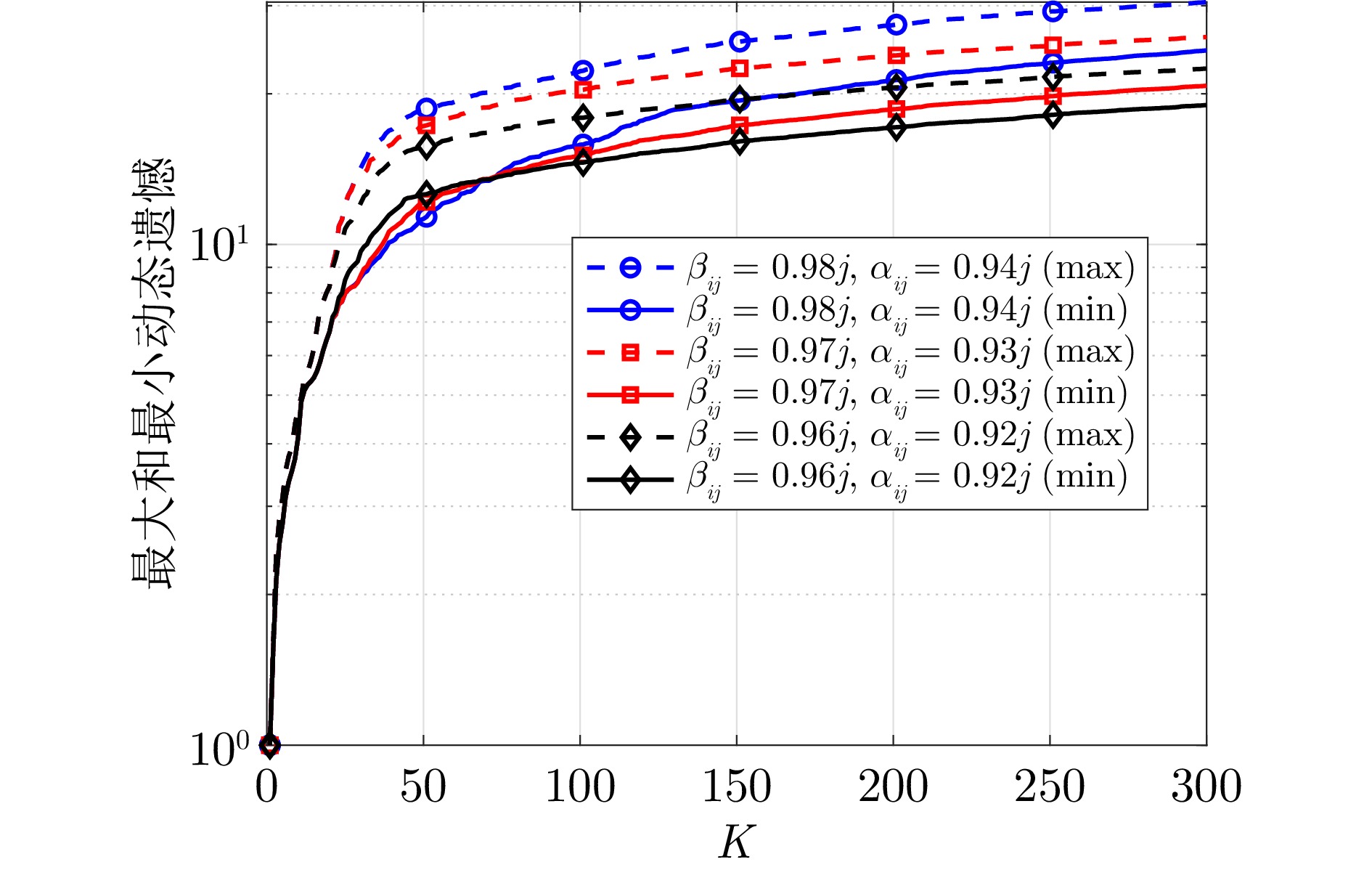
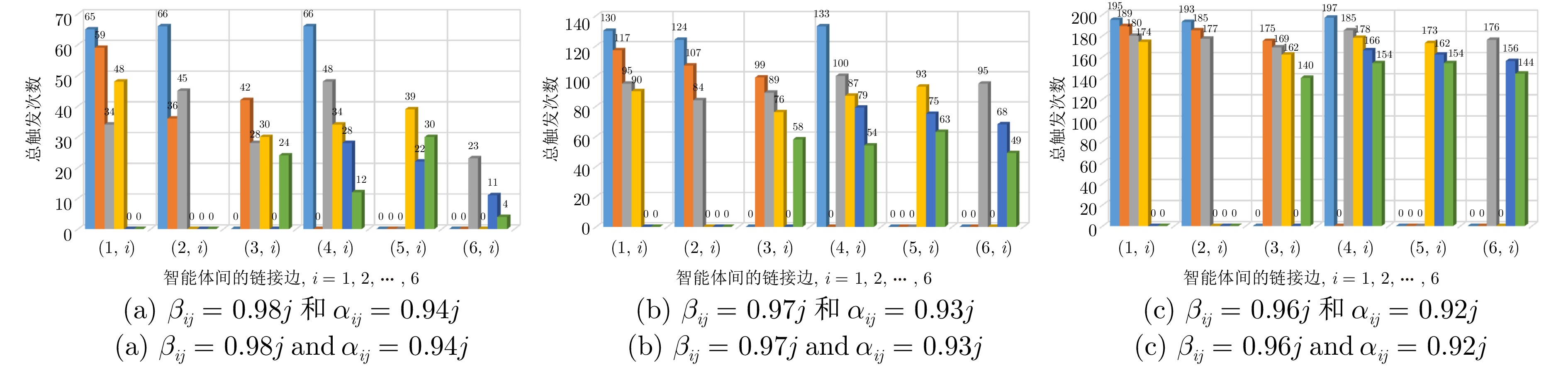
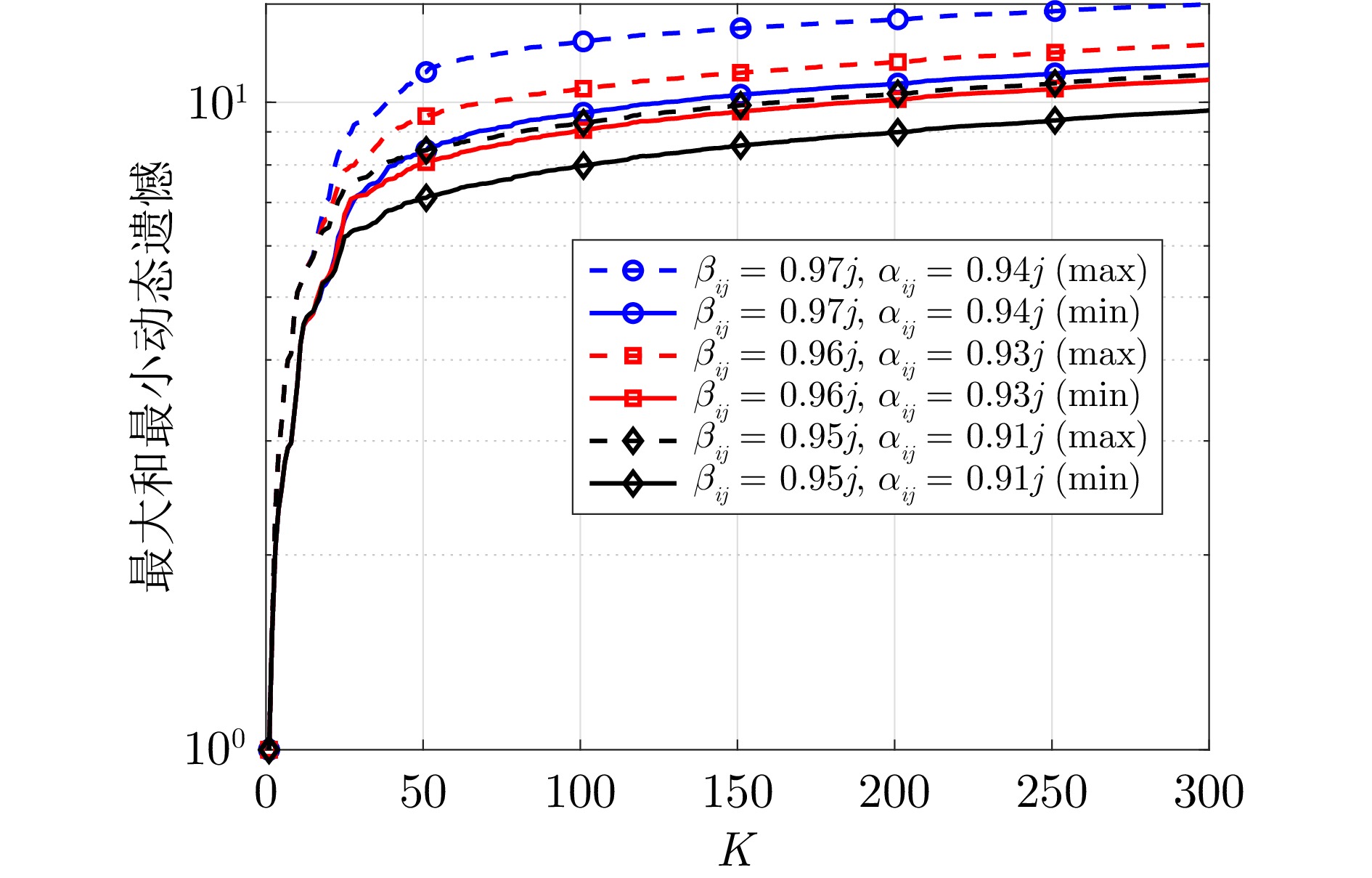
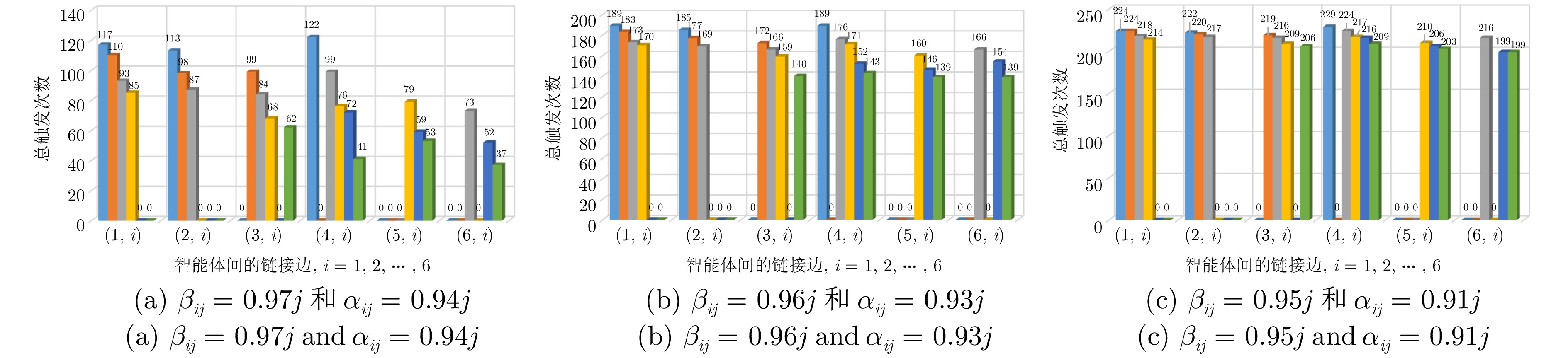
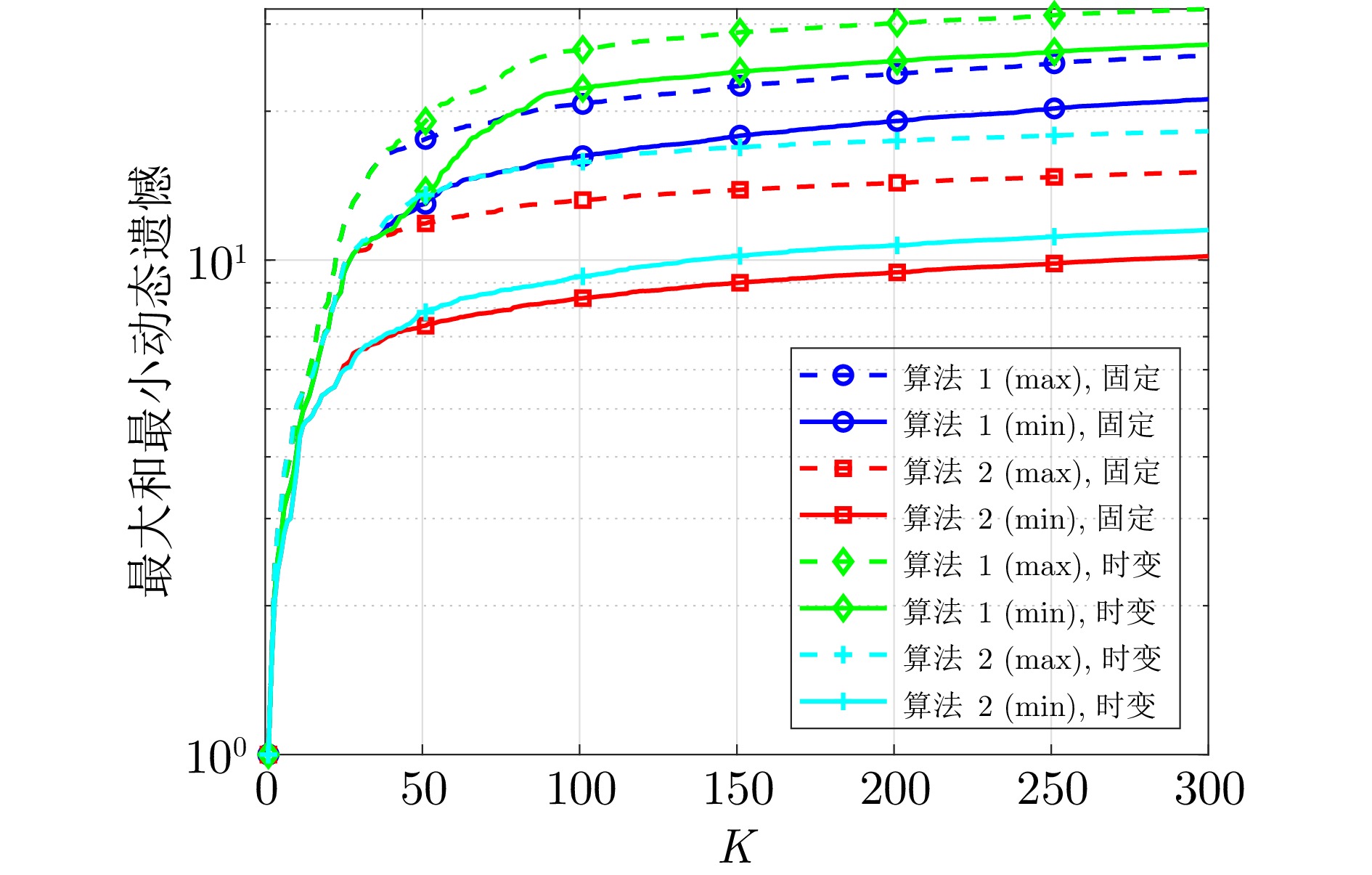
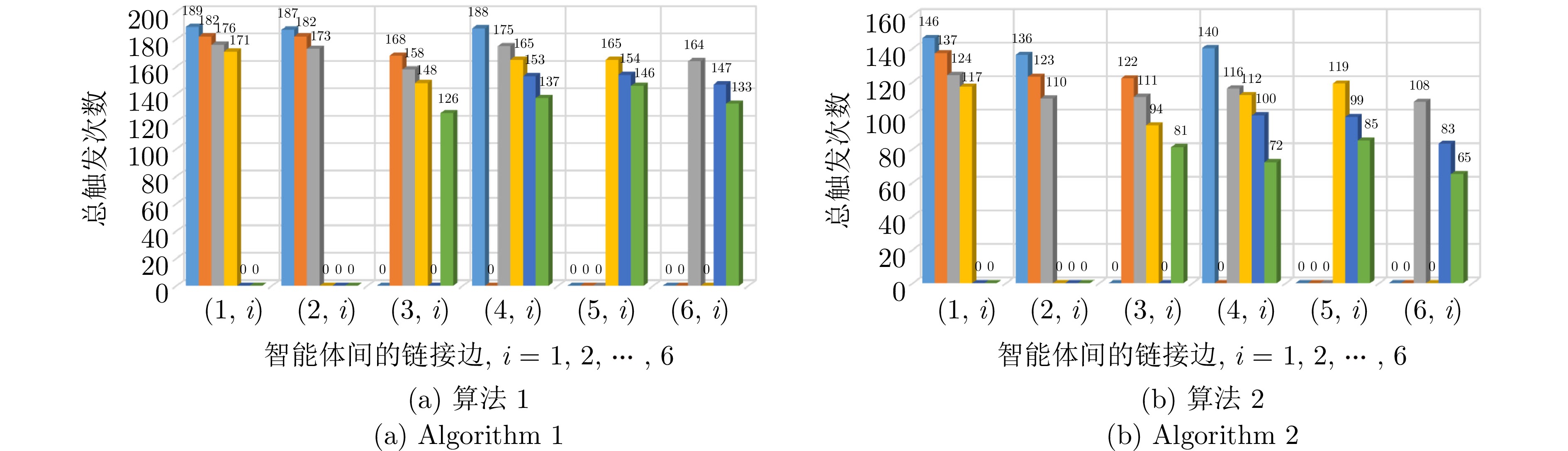
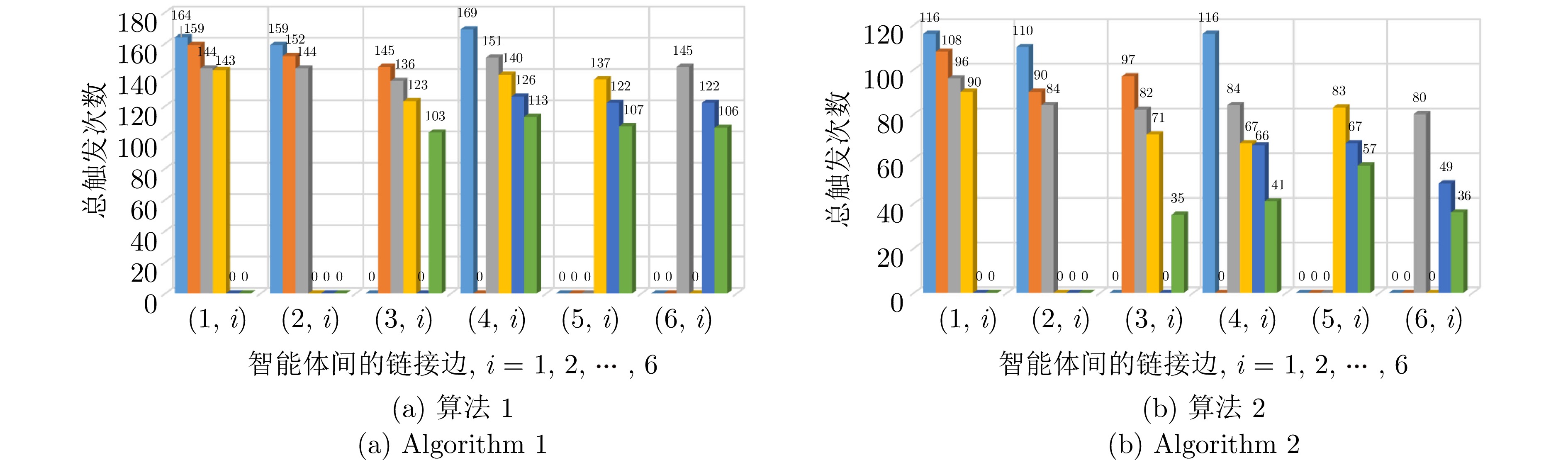
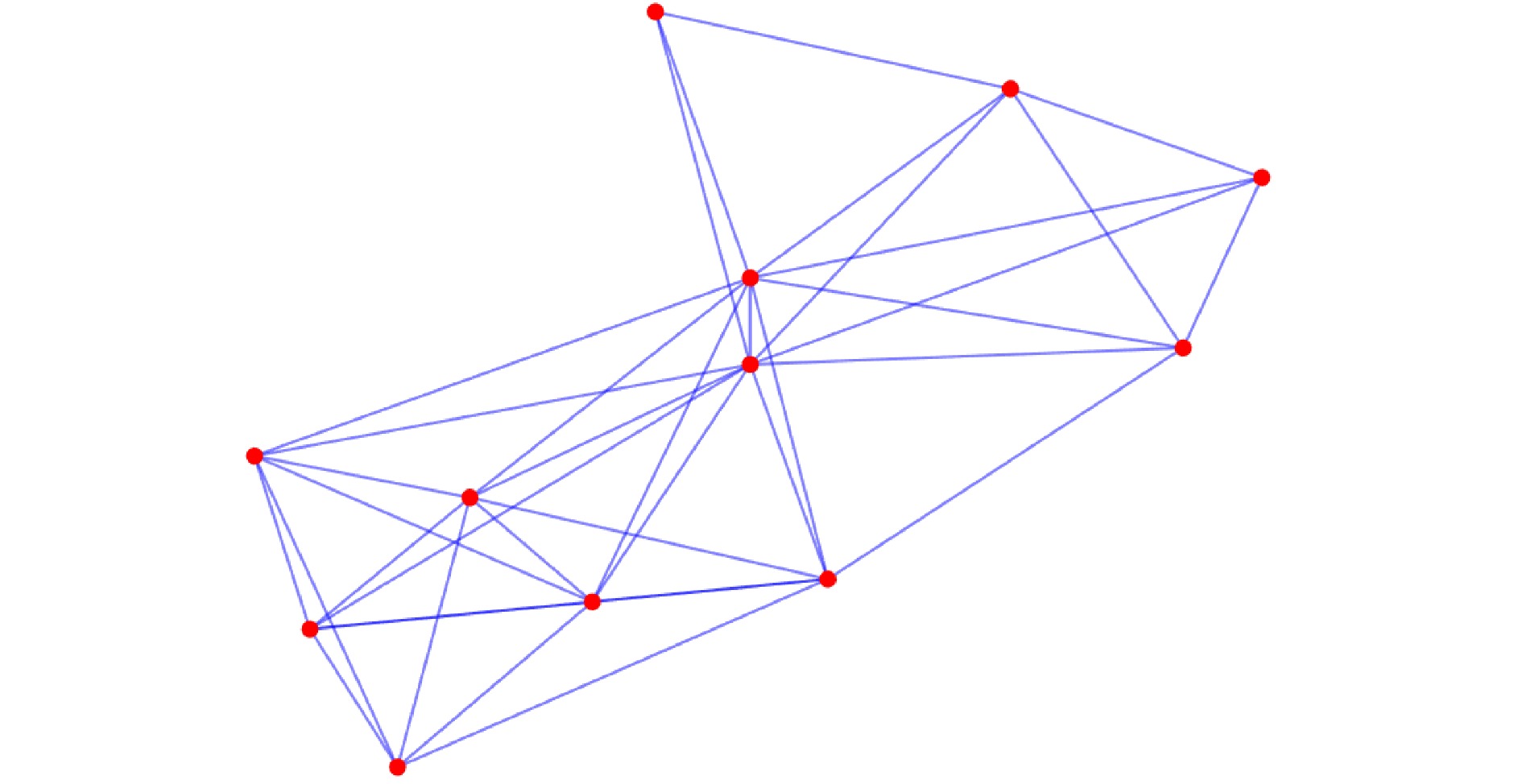
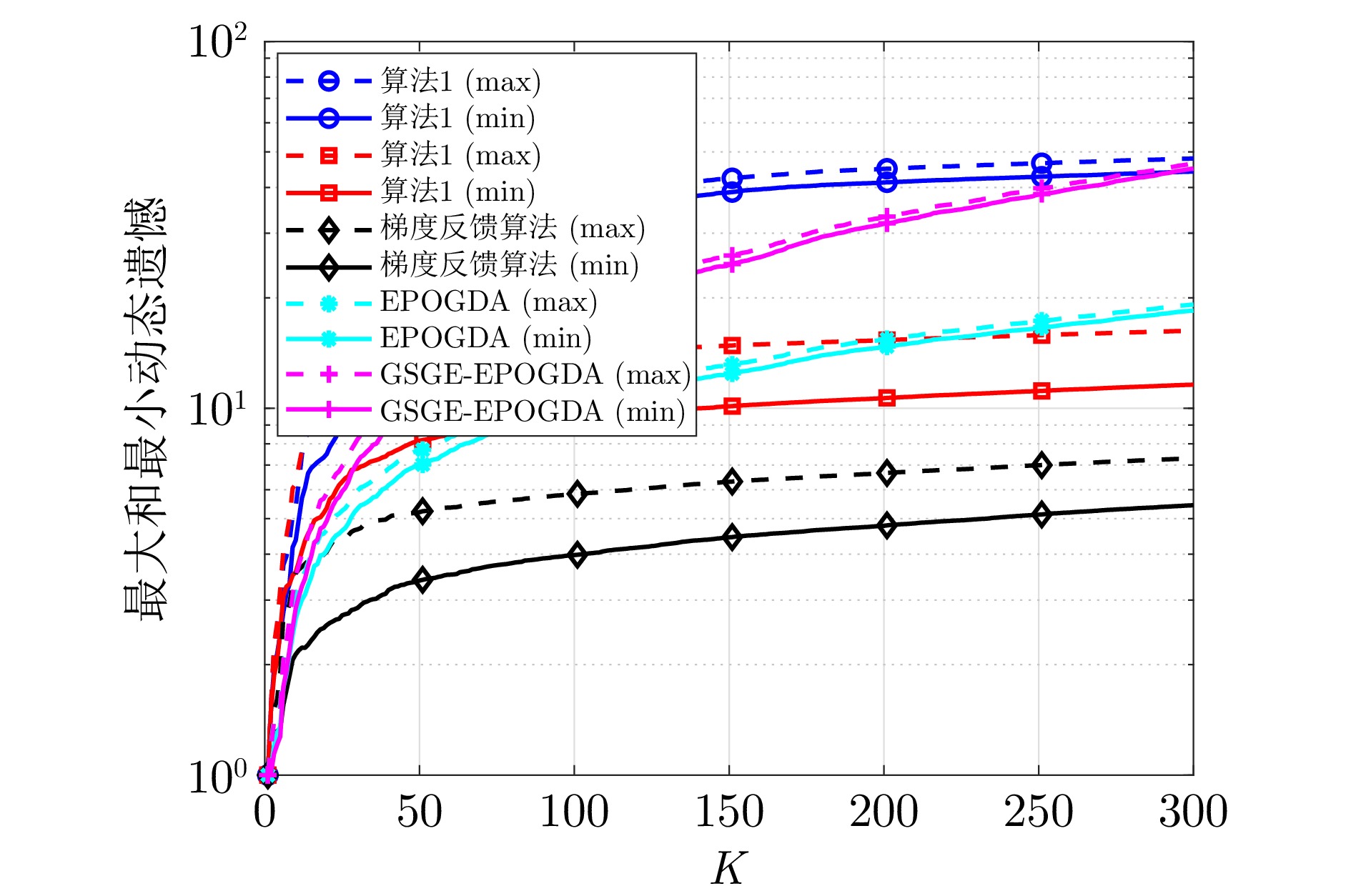
摘要: 研究带宽受限的非平衡有向多智能体网络环境下的在线分布式复合Bandit优化问题. 该问题中每个智能体的局部目标函数具有复合结构: 其一为梯度信息不可获取的时变损失函数, 其二为具有特定结构的正则化项. 为应对网络带宽的受限, 设计具有控制因子的边缘动态事件触发通信协议, 以降低通信开销. 同时, 针对局部损失函数梯度信息难以获取的挑战, 分别引入单点和两点梯度估计方法, 以支撑损失函数梯度信息的获取. 基于此, 结合近端算子, 分别设计仅要求加权邻接矩阵满足行随机性质的在线分布式复合单点和两点Bandit优化算法, 并使用动态遗憾指标分析两种算法的收敛性. 结果表明, 在合理的假设和参数设定下, 两种算法在期望意义下分别可获得${\cal{O}}({K^\frac{3}{4}}(1+{{\cal{P}}_K}))$和${\cal{O}}({K^\frac{1}{2}}(1+{{\cal{P}}_K}))$的动态遗憾上界, 其中$K$是总迭代次数, ${\cal{P}}_K$是路径变差度量. 进一步, 当${\cal{P}}_K$能够被提前估计时, 两种算法分别可获得${\cal{O}}({K^\frac{3}{4}}\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}})$和${\cal{O}}({K^\frac{1}{2}}\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}})$的期望动态遗憾上界. 最后, 通过对在线分布式岭回归问题的仿真实验, 验证了算法的收敛性以及理论结果的正确性.Abstract: This paper investigates an online distributed composite Bandit optimization problem on an unbalanced directed multi-agent network environment with limited bandwidth. The local objective function of each agent in such a problem has a composite structure: One is a time-varying loss function with inaccessible gradient information, and the other is a regularization with a specific structure. To cope with the limited network bandwidth, an edge dynamic event-triggered communication protocol with a control factor is designed to reduce the communication overhead. Meanwhile, to address the challenge of difficulty in obtaining the gradient information of local loss function, single-point and two-point gradient estimation methods are introduced to support the acquisition of the gradient information of the loss function, respectively. Based on this, combined with the proximal operator, the online distributed composite single-point and two-point Bandit optimization algorithms that only require the weighted adjacency matrix to be row-stochastic are designed, and the convergence of two algorithms is analyzed using the dynamic regret index. The results show that under reasonable assumptions and parameter settings, two algorithms respectively achieve the dynamic regret upper bounds of order ${\cal{O}}({K^\frac{3}{4}}(1+{{\cal{P}}_K}))$ and ${\cal{O}}({K^\frac{1}{2}}(1+{{\cal{P}}_K}))$ in the expectation sense, where $K$ is the total number of iterations, and ${\cal{P}}_K$ is path-variation measure. Furthermore, if ${\cal{P}}_K$ can be estimated a priori, two algorithms achieve the expected dynamic regret upper bounds of order ${\cal{O}}({K^\frac{3}{4}}\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}})$ and ${\cal{O}}({K^\frac{1}{2}}\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}})$, respectively. Finally, the convergence of the algorithms and the correctness of the theoretical results are validated through simulation experiments on an online distributed ridge regression problem.1)
1 1 $ 0.97j = 0.97 + 0.001\times j $ -
表 1 算法1和2的动态遗憾界
Table 1 Dynamic regret bounds of algorithms 1 and 2
步长$ \eta(k) $ 缩减参数$ \varpi_k $ 算法1 算法2 $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_1}k^{-\varepsilon} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_2}{k^{-\frac{1}{4}}} $ $ {\cal{O}}_1 $ — $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_1}k^{-\frac{3}{4}} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_2}{k^{-\frac{1}{4}}} $ $ {\cal{O}}({K^\frac{3}{4}}(1+{{\cal{P}}_K})) $ — $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_3}k^{-\frac{3}{4}}{\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}}} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_2}{k^{-\frac{1}{4}}} $ $ {\cal{O}}(K^{\frac{3}{4}}{\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}}}) $ — $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_3}K^{-\frac{3}{4}}{\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}}} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_2}{k^{-\frac{1}{4}}} $ $ {\cal{O}}(K^{\frac{3}{4}}{\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}}}) $ — $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_1}k^{-\delta} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_2}{k^{-\frac{1}{2}}} $ — $ {\cal{O}}_2 $ $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_1}k^{-\frac{1}{2}} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_2}{k^{-\frac{1}{2}}} $ — $ {\cal{O}}({K^\frac{1}{2}}(1+{{\cal{P}}_K})) $ $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_3}k^{-\frac{1}{2}}{\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}}} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_2}{k^{-\frac{1}{2}}} $ — $ {\cal{O}}(K^{\frac{1}{2}}{\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}}}) $ $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_3}K^{-\frac{1}{2}}{\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}}} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{a}}_2}{k^{-\frac{1}{2}}} $ — $ {\cal{O}}(K^{\frac{1}{2}}{\sqrt{1+{{\cal{P}}_K}}}) $ 注: $\; {\boldsymbol{a}}_1 >0 $, $ 0<{\boldsymbol{a}}_2<1 $, $ {\boldsymbol{a}}_3 >0 $, $ \frac{1}{2}<\varepsilon<1 $, $ 0<\delta<1 $
$ {\cal{O}}_1 = {\cal{O}}(\max\{{K^\varepsilon}(1+{{\cal{P}}_K}),\; K^{\frac{3}{2}-\varepsilon},\; K^{\frac{3}{4}}\}) $
$ {\cal{O}}_2 = {\cal{O}}(\max\{{K^\delta}(1+{{\cal{P}}_K}),\; K^{1-\delta}\}) $ -
[1] Olfati-Saber R, Murray R M. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(9): 1520−1533 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.834113 [2] Ren W, Beard R W. Consensus seeking in multiagent systems under dynamically changing interaction topologies. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2005, 50(5): 655−661 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2005.846556 [3] Zhang Y Q, Lou Y C, Hong Y G, Xie L H. Distributed projection-based algorithms for source localization in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(6): 3131−3142 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2402672 [4] Yang T, Wu D, Fang H Z, Ren W, Wang H, Hong Y G, et al. Distributed energy resource coordination over time-varying directed communication networks. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2019, 6(3): 1124−1134 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2019.2921284 [5] Nedic A. Distributed gradient methods for convex machine learning problems in networks: Distributed optimization. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(3): 92−101 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.2975210 [6] 滕菲, 单麒赫, 李铁山. 智能船舶综合能源系统及其分布式优化调度方法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(9): 1809−1817Teng Fei, Shan Qi-He, Li Tie-Shan. Intelligent ship integrated energy system and its distributed optimal scheduling algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(9): 1809−1817 [7] Tsitsiklis J, Bertsekas D, Athans M. Distributed asynchronous deterministic and stochastic gradient optimization algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1986, 31(9): 803−812 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1986.1104412 [8] Nedic A, Ozdaglar A. Distributed subgradient methods for multi-agent optimization. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(1): 48−61 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2008.2009515 [9] Nedic A, Ozdaglar A, Parrilo P A. Constrained consensus and optimization in multi-agent networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010, 55(4): 922−938 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2041686 [10] Duchi J C, Agarwal A, Wainwright M J. Dual averaging for distributed optimization: Convergence analysis and network scaling. IEEE Transactions on Automatic control, 2011, 57(3): 592−606 [11] Yuan D M, Hong Y G, Ho D W C, Jiang G P. Optimal distributed stochastic mirror descent for strongly convex optimization. Automatica, 2018, 90: 196−203 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.12.053 [12] 谢佩, 游科友, 洪奕光, 谢立华. 网络化分布式凸优化算法研究进展. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35(7): 918−927 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.80205Xie Pei, You Ke-You, Hong Yi-Guang, Xie Li-Hua. A survey of distributed convex optimization algorithms over networks. Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 35(7): 918−927 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.80205 [13] 王龙, 卢开红, 关永强. 分布式优化的多智能体方法. 控制理论与应用, 2019, 36(11): 1820−1833 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90502Wang Long, Lu Kai-Hong, Guan Yong-Qiang. Distributed optimization via multi-agent systems. Control Theory & Applications, 2019, 36(11): 1820−1833 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.90502 [14] Yang T, Yi X L, Wu J F, Yuan Y, Wu D, Meng Z Y, et al. A survey of distributed optimization. Annual Reviews in Control, 2019, 47: 278−305 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2019.05.006 [15] Zinkevich M. Online convex programming and generalized infinitesimal gradient ascent. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Washington, USA: AAAI Press, 2003. 928−936 [16] Hazan E. Introduction to online convex optimization. Foundations and Trends® in Optimization, 2016, 2(3−4): 157−325 [17] Li X X. Recent advances on distributed online optimization. Control Theory and Technology, 2021, 19: 153−156 doi: 10.1007/s11768-021-00041-3 [18] Li X X, Xie L H, Li N. A survey on distributed online optimization and online games. Annual Reviews in Control, 2023, 56: Article No. 100904 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2023.100904 [19] Yuan D M, Proutiere A, Shi G D. Multi-agent online optimization. Foundations and Trends® in Optimization, 2024, 7(2−3): 81−263, 2024 [20] Yuan D M, Hong Y G, Ho D W C, Xu S Y. Distributed mirror descent for online composite optimization. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 66(2): 714−729 [21] Dixit R, Bedi A S, Rajawat K. Online learning over dynamic graphs via distributed proximal gradient algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 66(11): 5065−5079 [22] Hou R J, Yu Y, Li X X. Dynamic regret for distributed online composite optimization. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2025, 70(5): 3056−3071 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3489222 [23] 侯瑞捷, 李修贤, 易新蕾, 洪奕光, 谢立华. 具有反馈延迟分布式在线复合优化的动态遗憾性能. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(4): 835−856Hou Rui-Jie, Li Xiu-Xian, Yi Xin-Lei, Hong Yi-Guang, Xie Li-Hua. Dynamic regret for distributed online composite convex optimization with delayed feedbacks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(4): 835−856 [24] Zhou Y Y, Chen G. Event-triggered proximal online gradient descent algorithm for parameter estimation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024, 72: 2594−2606 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2024.3400453 [25] Yuan D M, Zhang B Y, Xu S Y, Zhao H Y. Distributed regularized online optimization using forward-backward splitting. Control Theory and Technology, 2023, 21(2): 212−221 doi: 10.1007/s11768-023-00134-1 [26] Yi X L, Li X X, Yang T, Xie L H, Chai T Y, Johansson K H. Distributed bandit online convex optimization with time-varying coupled inequality constraints. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(10): 4620−4635 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3030883 [27] 张文韬, 张保勇, 袁德明, 徐胜元. 分布式在线鞍点问题的Bandit反馈优化算法. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(4): 857−874Zhang Wen-Tao, Zhang Bao-Yong, Yuan De-Ming, Xu Sheng-Yuan. Bandit feedback optimization algorithm for distributed online saddle point problem. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(4): 857−874 [28] Peng C, Li F Q. A survey on recent advances in event-triggered communication and control. Information Sciences, 2018, 457: 113−125 [29] Ding L, Han Q L, Ge X H, Zhang X M. An overview of recent advances in event-triggered consensus of multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2018, 48(4): 1110−1123 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2771560 [30] Ge X H, Han Q L, Zhang X M, Ding D R. Dynamic event-triggered control and estimation: A survey. International Journal of Automation and Computing, 2021, 18(6): 857−886 doi: 10.1007/s11633-021-1306-z [31] Cao X Y, Basar T. Decentralized online convex optimization with event-triggered communications. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 69: 284−299 [32] Xiong M H, Zhang B Y, Yuan D M, Zhang Y J, Chen J. Event-triggered distributed online convex optimization with delayed bandit feedback. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2023, 445: Article No. 127865 doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2023.127865 [33] Zhang K P, Yi X L, Li Y Z, Cao M, Chai T Y, Yang T. Distributed online constrained convex optimization with event-triggered communication. European Journal of Control, 2024, 80: Article No. 101042 doi: 10.1016/j.ejcon.2024.101042 [34] Xiong M H, Ho D W C, Zhang B Y, Yuan D M, Xu S Y. Distributed online mirror descent with delayed subgradient and event-triggered communications. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2024, 11(2): 1702−1715 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2023.3329523 [35] Zhang D F, Feng Z C, Xu W Y, Yang S F, Cao J D. Distributed online optimization subject to long-term constraints and time-varying topology: An event-triggered and bandit feedback approach. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2024, 361(16): Article No. 107132 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2024.107132 [36] Okamoto K, Hayashi N, Takai S. Distributed online adaptive gradient descent with event-triggered communication. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2023, 11(2): 610−622 [37] 杨涛, 徐磊, 易新蕾, 张圣军, 陈蕊娟, 李渝哲. 基于事件触发的分布式优化算法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 133−143Yang Tao, Xu Lei, Yi Xin-Lei, Zhang Sheng-Jun, Chen Rui-Juan, Li Yu-Zhe. Event-triggered distributed optimization algorithms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 133−143 [38] Yuan Y, He W L, Du W L, Tian Y C, Han Q L, Qian F. Distributed gradient tracking for differentially private multi-agent optimization with a dynamic event-triggered mechanism. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(5): 3044−3055 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3357253 [39] Flaxman A D, Kalai A T, McMahan B H. Online convex optimization in the bandit setting: Gradient descent without a gradient. In: Proceedings of the 16th Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms. Vancouver, Canada: SIAM Press, 2005. 385−394 [40] Duchi J C, Shalev-Shwartz S, Singer Y, Tewari A. Composite objective mirror descent. In: Proceedings of the 23rd Conference on Learning Theory (COLT). Haifa, Israel: Omnipress, 2010. 14−26 [41] Beck A. First-order Methods in Optimization. Philadelphia: SIAM and Mathematical Optimization Society Press, 2017. [42] Xie P, You K Y, Tempo R, Song S J, Wu C. Distributed convex optimization with inequality constraints over time-varying unbalanced digraphs. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(12): 4331−4337 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2816104 [43] Mai V S, Abed E H. Distributed optimization over directed graphs with row stochasticity and constraint regularity. Automatica, 2019, 102: 94−104 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.07.020 -




 下载:
下载: