Bidirectional Modeling-enhanced TKAN and Global Attention Mechanism Fusion for Rolling Bearing Remaining Useful Life Prediction
-
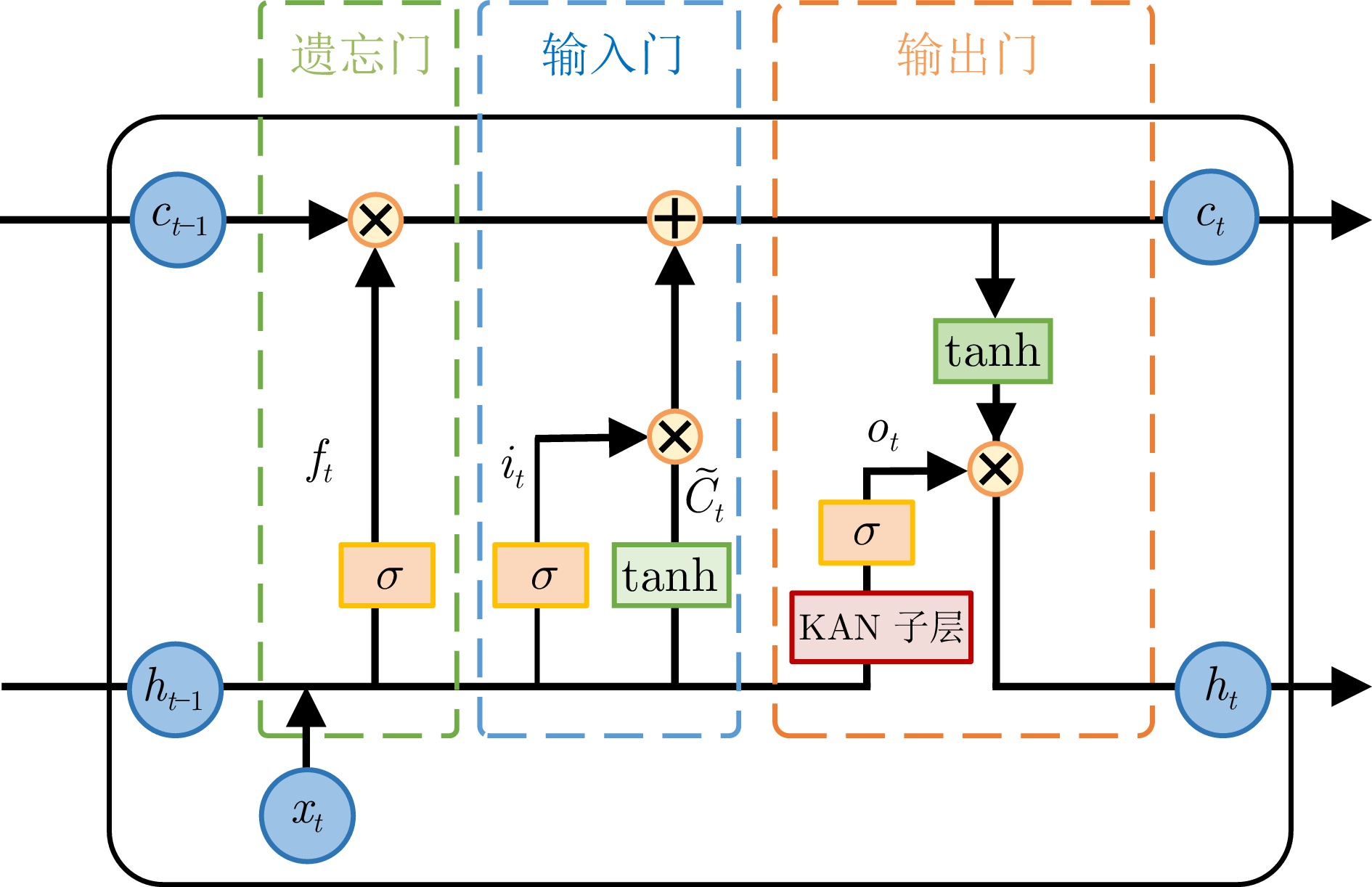
摘要: 滚动轴承剩余使用寿命(RUL)的精准预测是确保设备或系统安全可靠运行的关键. 针对滚动轴承RUL预测中多维退化特征的长期依赖关系难以有效建模的问题, 提出一种双向时间序列建模与注意力机制融合的预测模型——双向时序科尔莫戈洛夫−阿诺尔德注意力网络(Bi-TKAN-Att). 该模型兼具了时序科尔莫戈洛夫−阿诺尔德网络的强时序建模能力和全局注意力机制的关键特征提取能力, 采用双向建模的方式捕捉前后向信息, 最终实现了具有长期依赖多维退化特征的滚动轴承RUL预测. 所提方法在滚动轴承数据集上进行实验验证, 结果表明Bi-TKAN-Att模型在捕获滚动轴承退化特性和提升RUL预测精度方面具有显著优势, 并通过消融实验证明了模型各组件的合理性和有效性, 为滚动轴承的寿命预测提供了全新可行的解决方案.
-
关键词:
- 剩余使用寿命预测 /
- 滚动轴承 /
- 时序科尔莫戈洛夫−阿诺尔德网络 /
- 双向建模 /
- 全局注意力机制
Abstract: The accurate prediction of the remaining useful life (RUL) of rolling bearings is crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of equipment or system. To address the challenge of effectively modeling the long-term dependencies of multi-dimensional degradation features in RUL prediction, this paper proposes a prediction model that integrates bidirectional time-series modeling and attention mechanisms——Bidirectional temporal Kolmogorov-Arnold attention networks (Bi-TKAN-Att). This model combines the powerful time-series modeling capability of temporal Kolmogorov-Arnold networks with the key feature extraction capability of global attention mechanisms. It uses a bidirectional modeling approach to capture both forward and backward information, ultimately achieving RUL prediction for rolling bearings with long-term dependent multi-dimensional degradation features. The proposed method is experimentally validated on the rolling bearing dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that the Bi-TKAN-Att model has significant advantages in capturing rolling bearing degradation features and improving RUL prediction accuracy. Ablation experiments further confirm the rationality and effectiveness of each component of the model, providing a novel and feasible solution for the lifetime prediction of rolling bearing. -
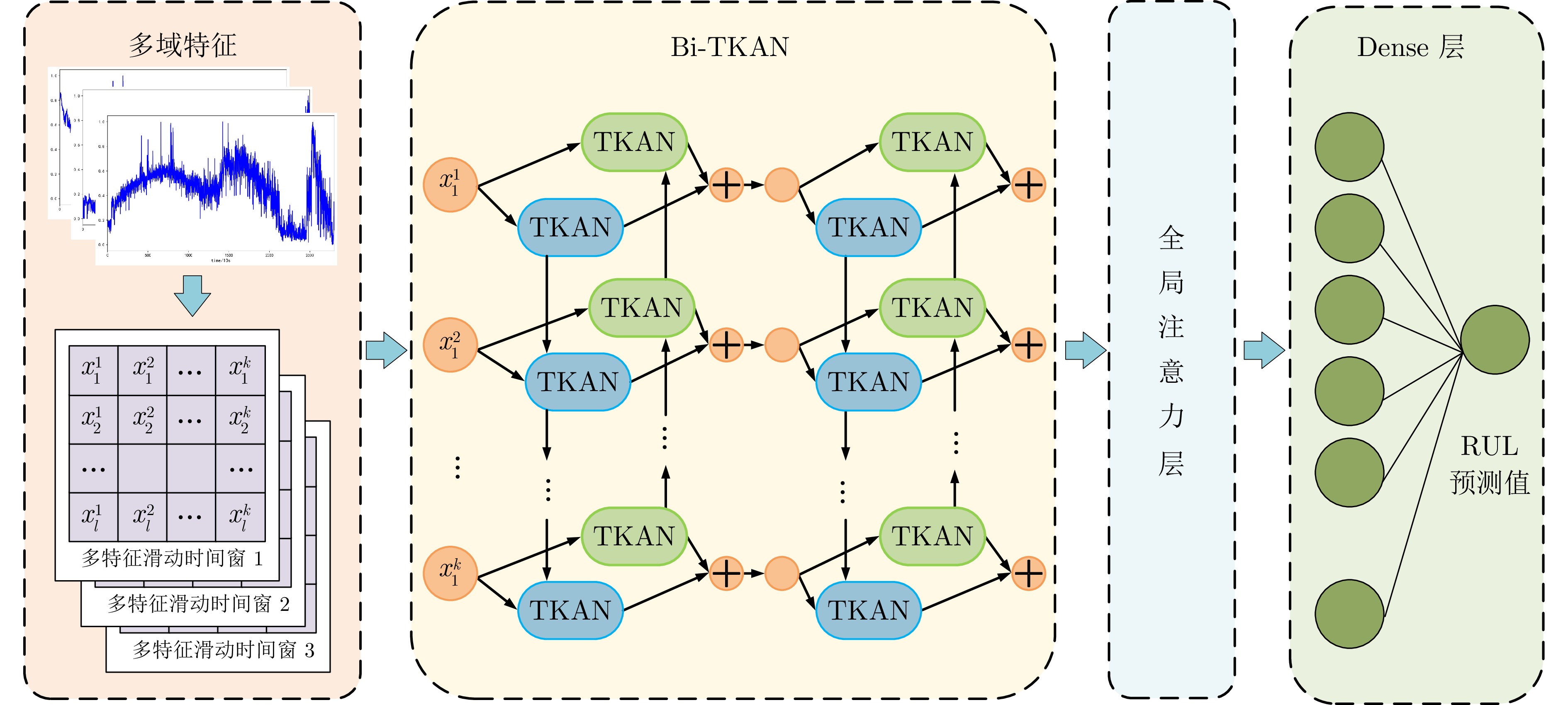
表 1 Bi-TKAN-Att的结构参数
Table 1 Structural parameters of Bi-TKAN-Att
网络结构超参数 最优值 Bi-TKAN层 2 Bi-TKAN层1 32 Bi-TKAN层2 40 全连接层 (40, 1) 批次大小 128 训练周期 100 学习率 0.0008 滑动窗口大小 300 表 2 消融实验预测结果评价指标对比
Table 2 Comparison of evaluation metrics for ablation experiment prediction results
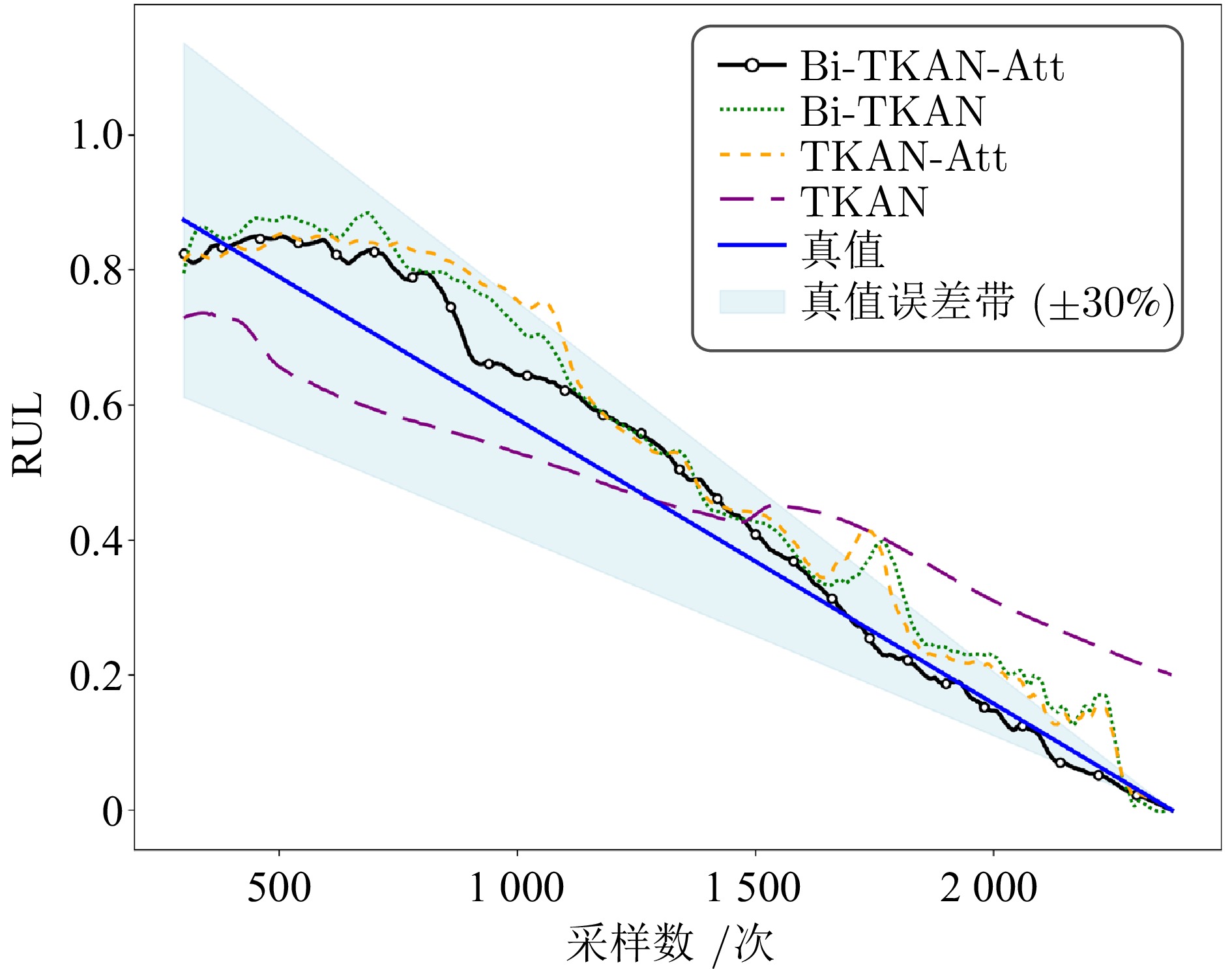
评价指标 Bi-TKAN-Att Bi-TKAN TKAN-Att TKAN R2 0.9373 0.8601 0.8464 0.7796 RMSE (%) 6.3199 9.4381 9.8893 11.8460 MAE (%) 5.0744 8.1298 8.1888 10.5069 表 3 Bi-TKAN-Att与其他方法预测结果评价指标对比
Table 3 Comparison of evaluation metrics of prediction results between Bi-TKAN-Att and other methods
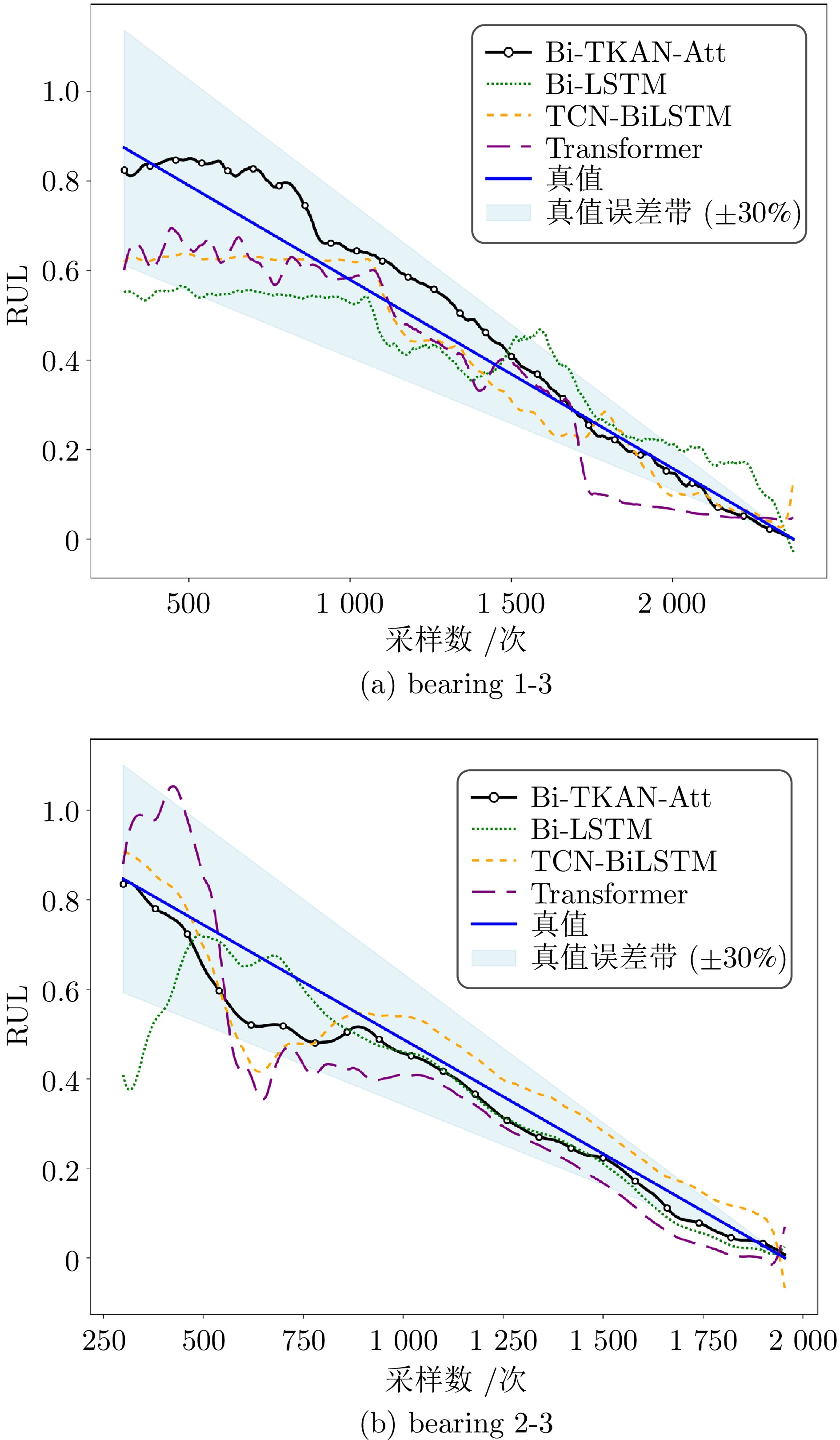
轴承编号 评价指标 Bi-TKAN-Att Bi-LSTM TCN-BiLSTM Transformer R2 0.9373 0.7390 0.8898 0.8667 bearing1-3 RMSE (%) 6.3199 12.8902 8.3768 9.2119 MAE (%) 5.0744 10.0602 6.0953 6.9968 R2 0.9270 0.8223 0.8708 0.7084 bearing2-3 RMSE (%) 6.6083 10.3079 8.7897 13.2034 MAE (%) 4.9011 5.7579 6.8132 10.9906 表 4 Bi-TKAN-Att与其他预测方法的结果对比
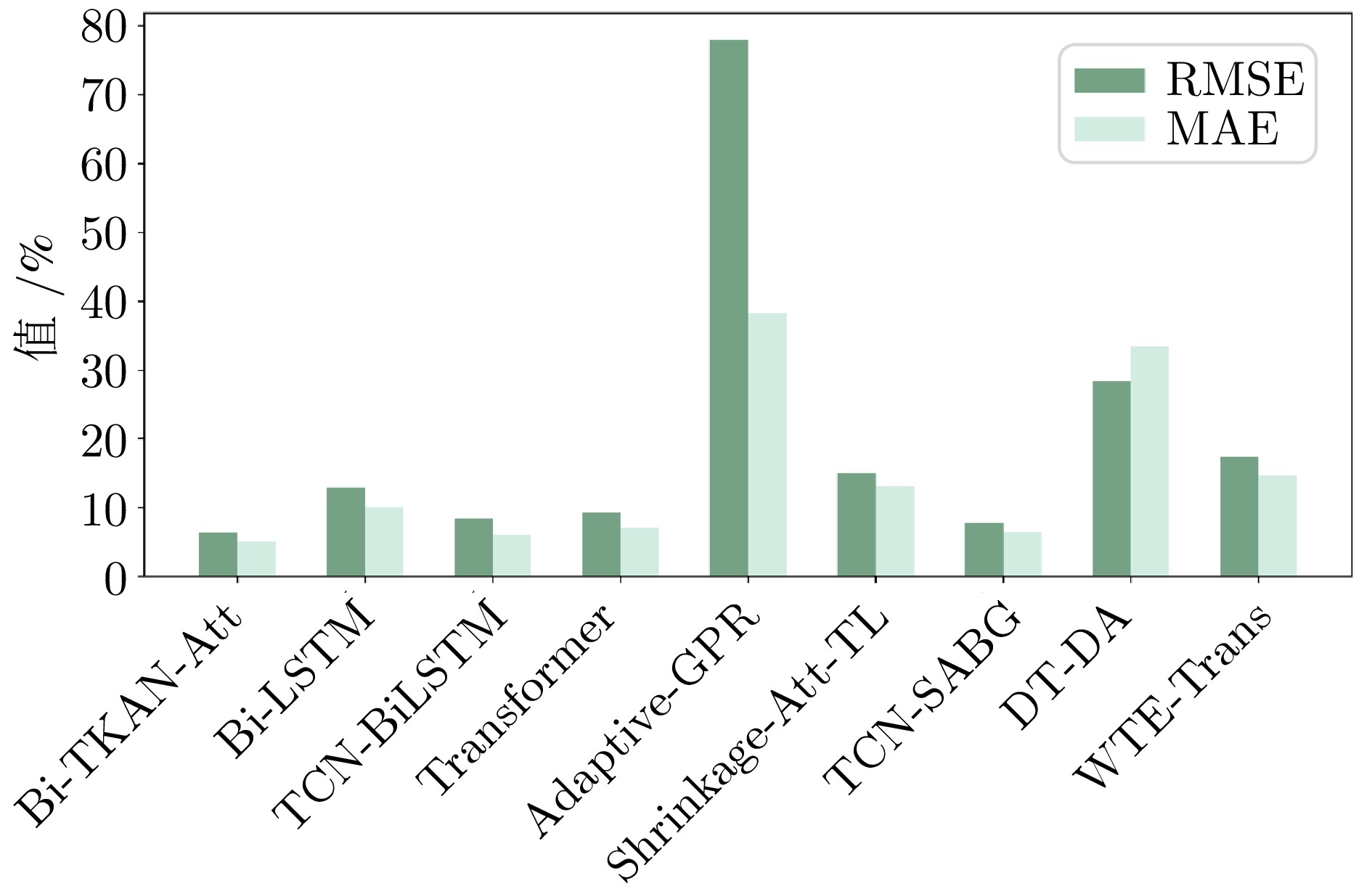
Table 4 Comparison of the results of Bi-TKAN-Att with other prediction methods
表 5 工作条件1下预测结果评价指标
Table 5 Evaluation metrics of prediction results under working condition 1
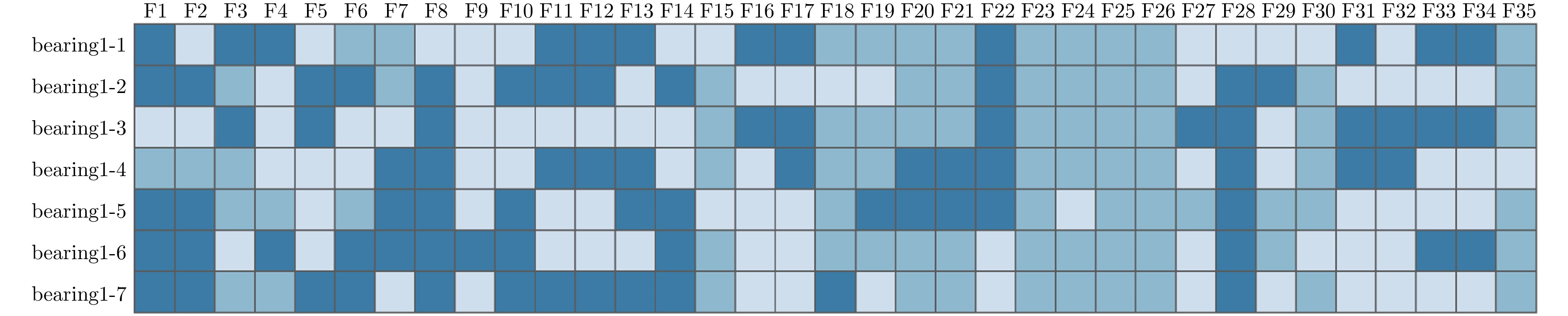
轴承编号 R2 RMSE (%) MAE (%) bearing1-1 0.9231 7.7832 4.6578 bearing1-2 0.8976 9.8970 8.9352 bearing1-3 0.9378 6.3178 5.0723 bearing1-4 0.9047 8.4254 7.6311 bearing1-5 0.9207 7.7601 4.5507 -
[1] 董青, 郑建飞, 胡昌华, 李冰, 牟含笑. 基于两阶段自适应Wiener过程的剩余寿命预测方法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(2): 539−553Dong Qing, Zheng Jian-Fei, Hu Chang-Hua, Li Bing, Mu Han-Xiao. Remaining useful life prognostic method based on two-stage adaptive Wiener process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(2): 539−553 [2] Ye Z S, Revie M, Walls L. A load sharing system reliability model with managed component degradation. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2014, 63(3): 721−730 doi: 10.1109/TR.2014.2315965 [3] Kong Y N, Ye Z S. Goodness-of-fit tests in the multi-state Markov model. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2017, 166: 16−24 [4] Cubillo A, Perinpanayagam S, Esperon-Miguez M. A review of physics-based models in prognostics: Application to gears and bearings of rotating machinery. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 8(8): 1−21 [5] Wang T, Liu Z, Mrad N. A probabilistic framework for remaining useful life prediction of bearings. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: Article No. 3503412 [6] Liu L, Song X, Chen K, Hou B C, Chai X D, Ning H S. An enhanced encoder-decoder framework for bearing remaining useful life prediction. Measurement, 2021, 170: Article No. 108753 doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108753 [7] Zhao R, Yan R Q, Chen Z H, Mao K Z, Wang P, Gao R X. Deep learning and its applications to machine health monitoring: A survey. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 115: 213−237 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.05.050 [8] 莫仁鹏, 李天梅, 司小胜, 朱旭. 采用残差网络与卷积注意力机制的设备剩余使用寿命预测方法. 西安交通大学学报, 2022, 56(4): 194−202 doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202204021Mo Ren-Peng, Li Tian-Mei, Si Xiao-Sheng, Zhu Xu. Remaining useful life prediction for equipment using residual network and convolutional attention mechanism. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2022, 56(4): 194−202 doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202204021 [9] Guo L, Lei Y G, Li N P, Yan T, Li N B. Machinery health indicator construction based on convolutional neural networks considering trend burr. Neurocomputing, 2018, 292: 142−150 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.02.083 [10] Guo L, Li N P, Jia F, Lei Y G, Lin J. A recurrent neural network based health indicator for remaining useful life prediction of bearings. Neurocomputing, 2017, 240: 98−109 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.02.045 [11] 郑建飞, 牟含笑, 胡昌华, 赵瑞星, 张博玮. 考虑多性能指标相关性的退化设备剩余寿命预测. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2022, 43(5): 620−629 doi: 10.11990/jheu.202109032Zheng Jian-Fei, Mu Han-Xiao, Hu Chang-Hua, Zhao Rui-Xing, Zhang Bo-Wei. Remaining useful life prediction of degradation equipment considering multiple performance indexes correlation. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2022, 43(5): 620−629 doi: 10.11990/jheu.202109032 [12] Lin R G, Wang H W, Xiong M L, Hou Z G, Che C C. Attention-based gate recurrent unit for remaining useful life prediction in prognostics. Applied Soft Computing, 2023, 143: Article No. 110419 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110419 [13] Xu Z Q, Zhang Y J, Miao Q. An attention-based multi-scale temporal convolutional network for remaining useful life prediction. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2024, 250: Article No. 110288 [14] Zhou J H, Qin Y, Chen D L, Liu F Q, Qian Q. Remaining useful life prediction of bearings by a new reinforced memory GRU network. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2022, 53: Article No. 101682 doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2022.101682 [15] Zhao B, Zhang W G, Zhang Y R, Zhang C P, Zhang C, Zhang J W. Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction based on interpretable deep learning and network parameter optimization. Applied Energy, 2025, 379: Article No. 124713 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.124713 [16] 康守强, 周月, 王玉静, 谢金宝. 基于改进SAE和双向LSTM的滚动轴承RUL预测方法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(9): 2327−2336Kang Shou-Qiang, Zhou Yue, Wang Yu-Jing, Xie Jin-Bao. RUL prediction method of a rolling bearing based on improved SAE and Bi-LSTM. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(9): 2327−2336 [17] 夏然, 苏春. 基于健康因子和混合Bi-LSTM-NAR模型的锂离子电池剩余寿命预测. 中国机械工程, 2024, 35(5): 851−859 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2024.05.010Xia Ran, Su Chun. Remaining useful life prediction for lithium-ion batteries based on health indicators and hybrid Bi-LSTM-NAR model. China Mechanica Engineering, 2024, 35(5): 851−859 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2024.05.010 [18] Liu Z M, Wang Y X, Vaidya S, Ruehle F, Halverson J, Soljacic M. KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2404.19756, 2024. [19] Genet R, Inzirillo H. TKAN: Temporal Kolmogorov-Arnold networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2405.07344v2, 2024. [20] He J, Xiao Z G, Zhang C F. Predicting the remaining useful life of rails based on improved deep spiking residual neural network. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024, 188: 1106−1117 doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2024.06.008 [21] Lei Y G, Li N P, Guo L, Li N B, Yan T, Lin J. Machinery health prognostics: A systematic review from data acquisition to RUL prediction. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 104: 799−834 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.11.016 [22] 梁浩鹏, 曹洁, 赵小强. 基于并行双向时间卷积网络和双向长短期记忆网络的轴承剩余使用寿命预测方法. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(4): 1288−1296Liang Hao-Peng, Cao Jie, Zhao Xiao-Qiang. Remaining useful life prediction method for bearing based on parallel bidirectional temporal convolutional network and bidirectional long and short-term memory network. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(4): 1288−1296 [23] 刘业峰, 王帅, 刘晶晶, 马祎航. 基于TCN-SA和Bi-GRU的轴承剩余寿命预测. 计算机集成制造系统, DOI: 10.13196/j.cims.2024.0260Liu Ye-Feng, Wang Shuai, Liu Jing-Jing, Ma Yi-Hang. Bearing remaining life prediction based on TCN-SA and Bi-GRU. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, DOI: 10.13196/j.cims.2024.0260 [24] Li X, Zhang W, Ma H, Luo Z, Li X. Data alignments in machinery remaining useful life prediction using deep adversarial neural networks. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 197: Article No. 105843 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105843 [25] Li W X, Shang Z W, Gao M S, Qian S Q, Feng Z H. Remaining useful life prediction based on transfer multi-stage shrinkage attention temporal convolutional network under variable working conditions. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2022, 226: Article No. 108722 doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2022.108722 [26] Hou W J, Peng Y Z. Adaptive ensemble Gaussian process regression-driven degradation prognosis with applications to bearing degradation. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2023, 239: Article No. 109479 doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2023.109479 [27] Zhang M Y, He C, Huang C X, Yang J H. A weighted time embedding Transformer network for remaining useful life prediction of rolling bearing. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2024, 251: Article No. 110399 doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2024.110399 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 16
- HTML全文浏览量: 10
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: