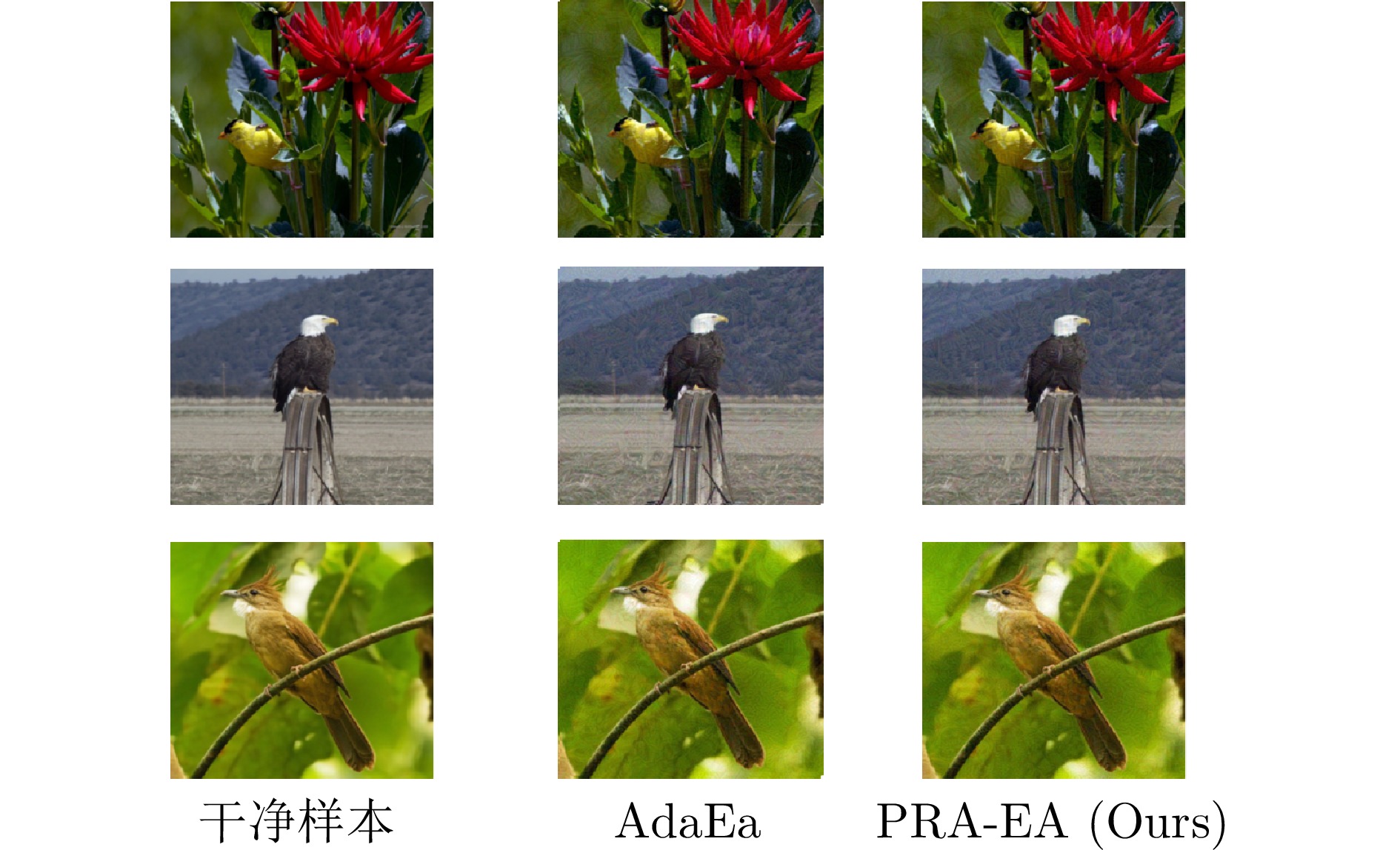
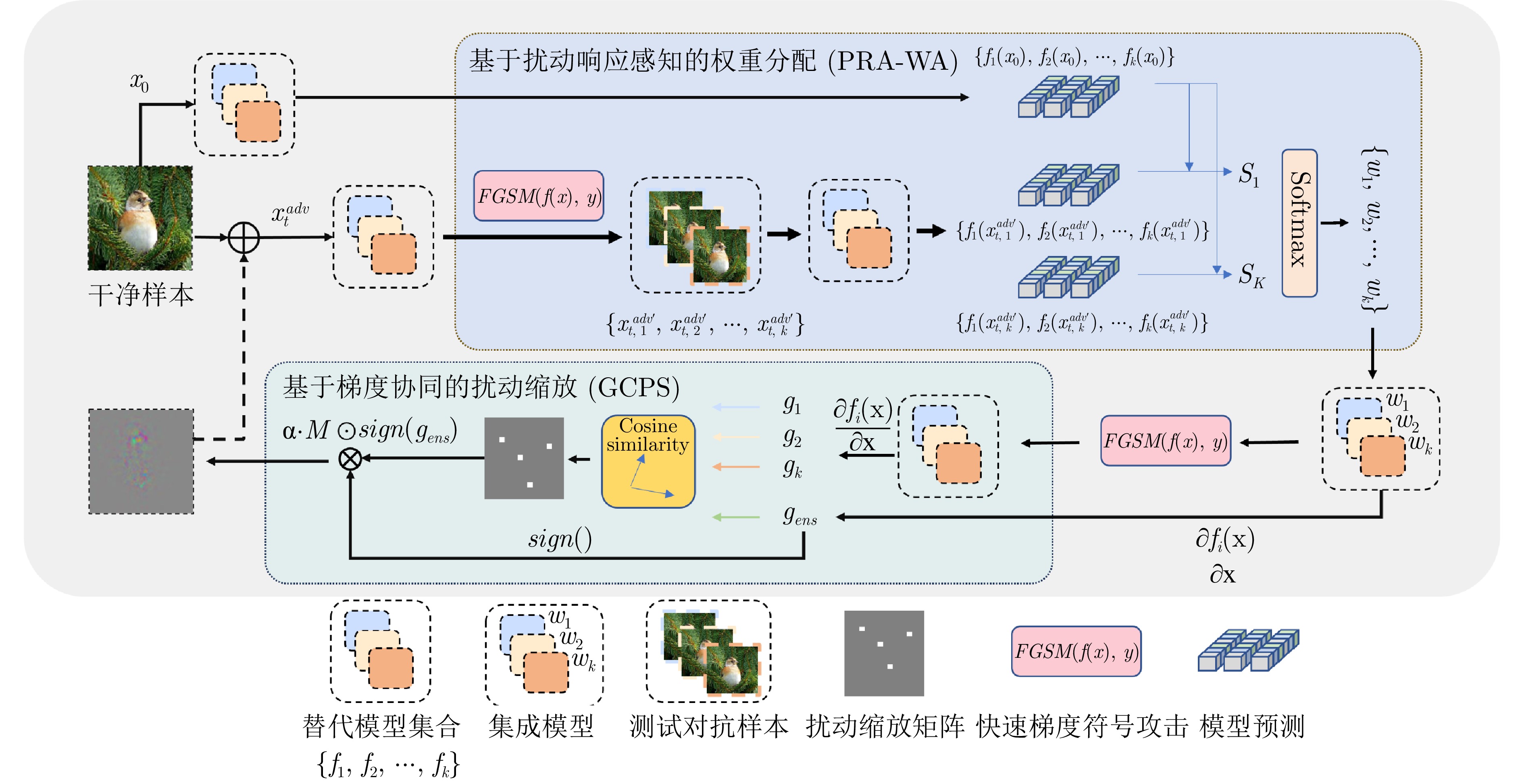
Perturbation Response-based Adaptive Ensemble Black-box Adversarial Attack Algorithm
-
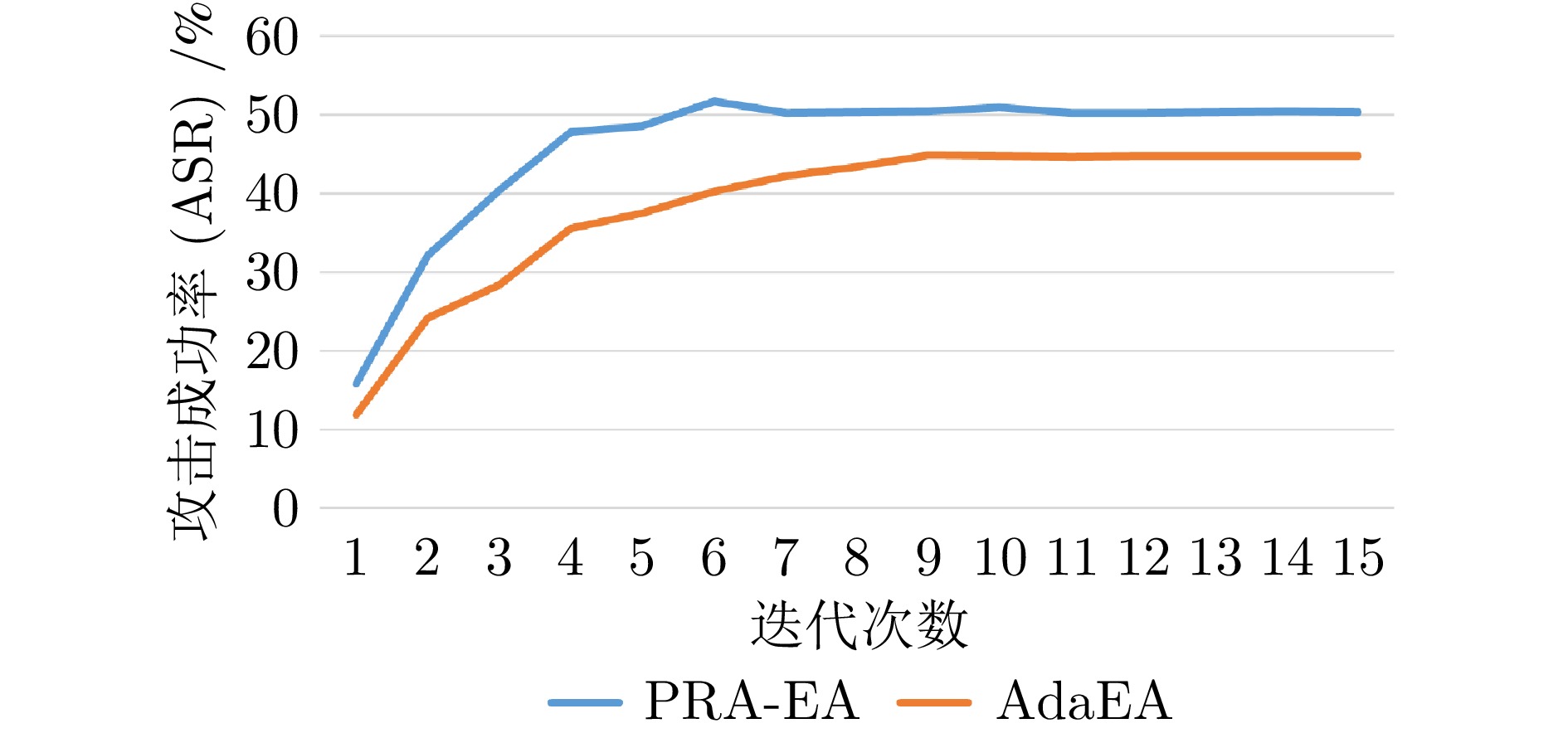
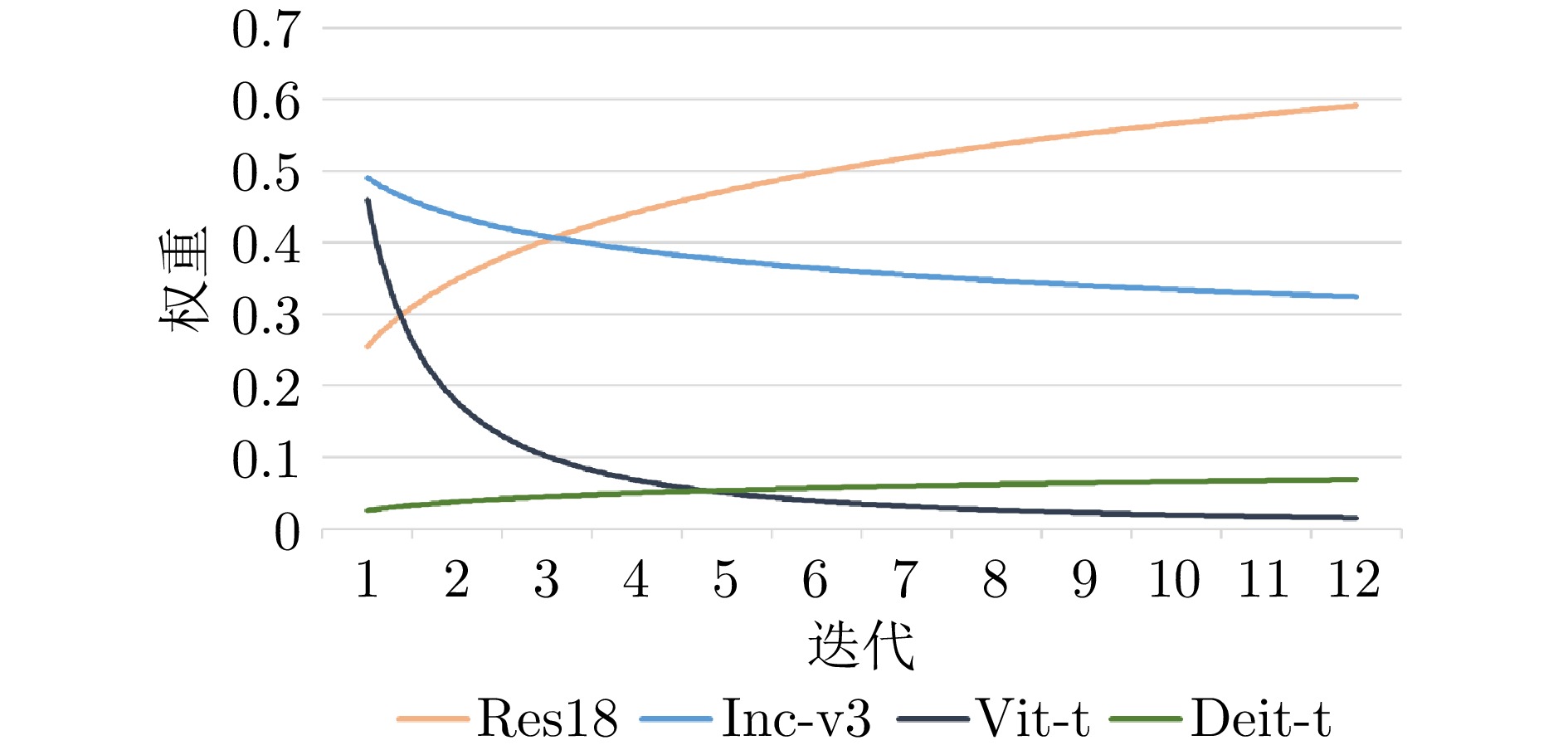
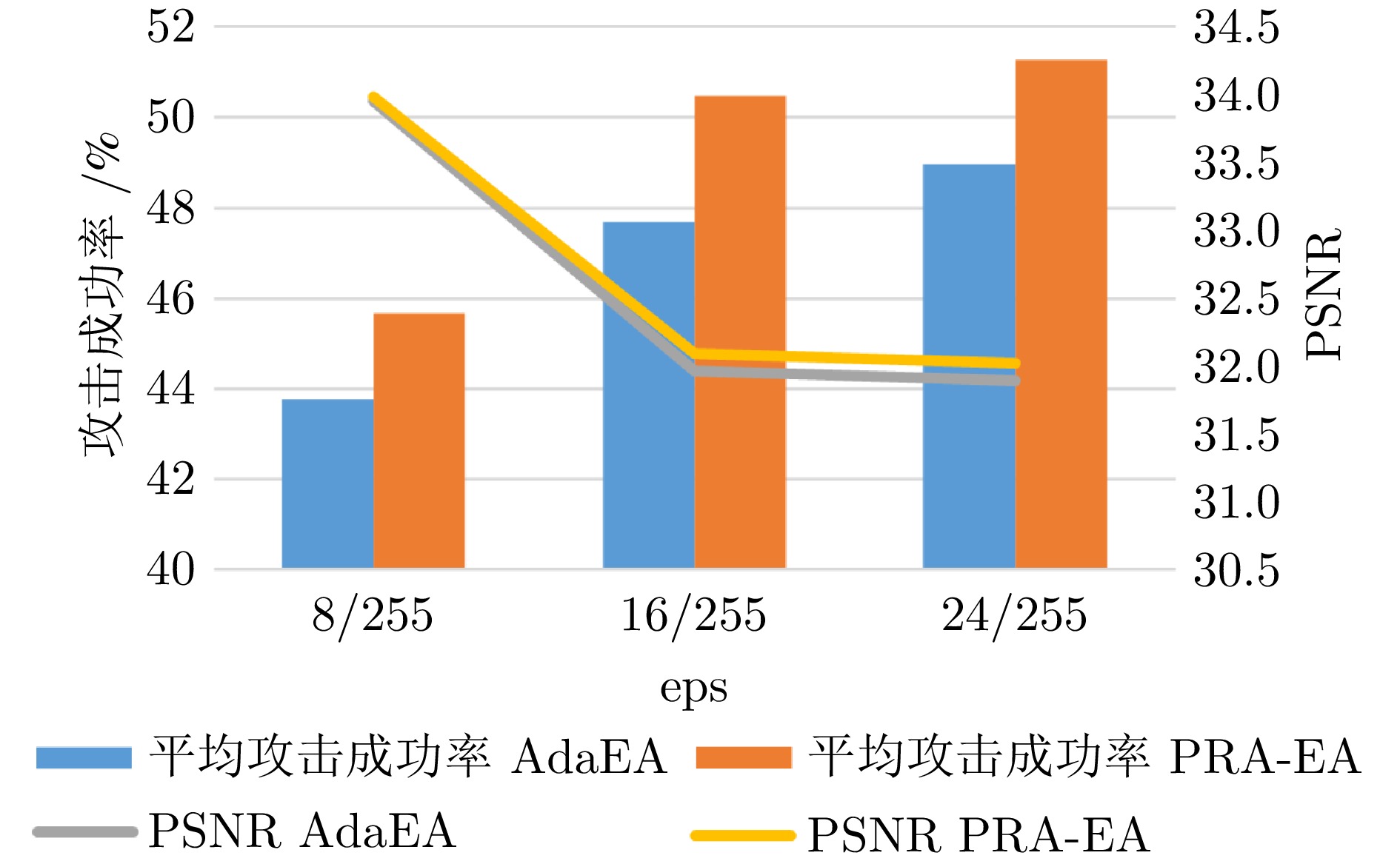
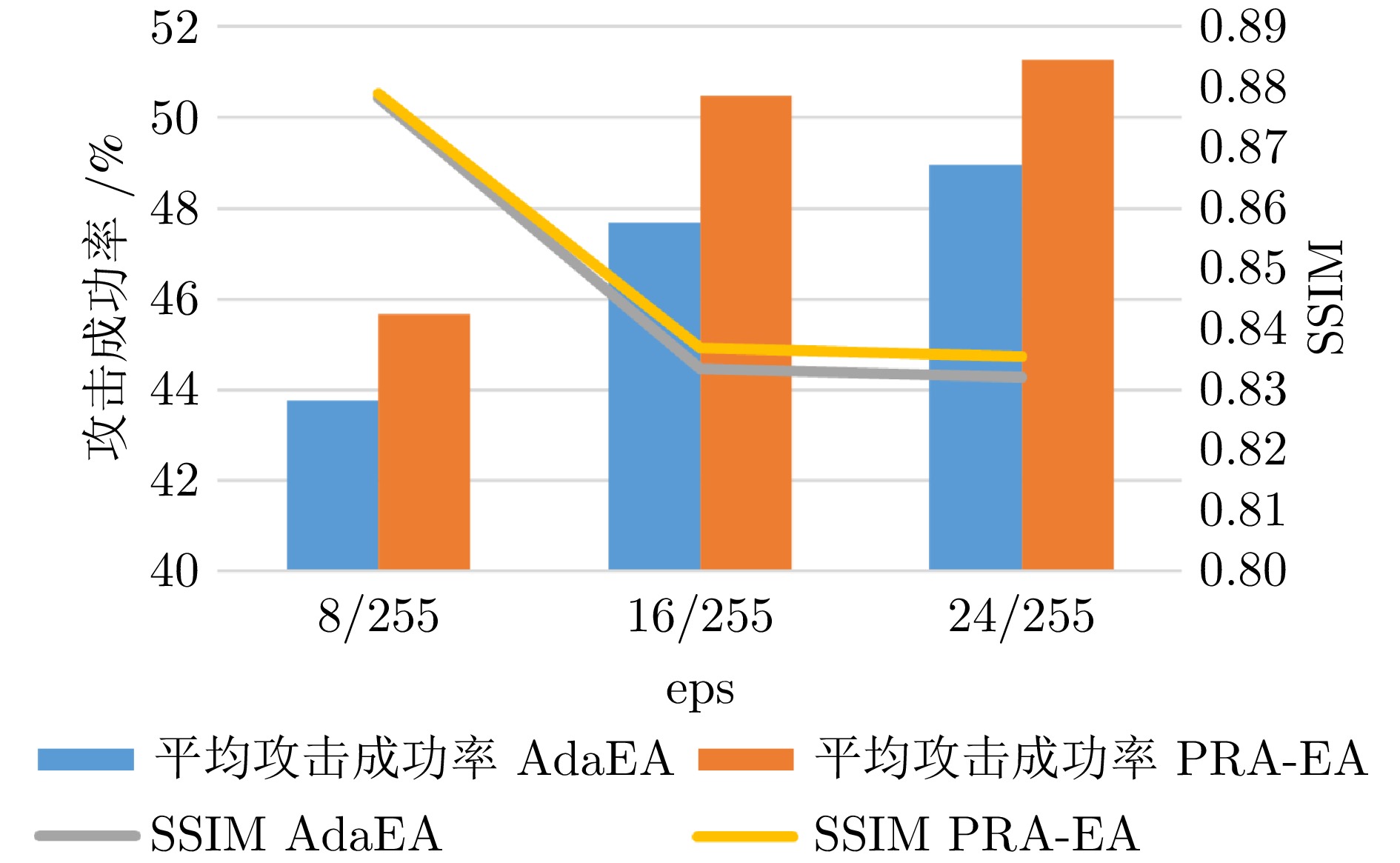
摘要: 模型集成对抗攻击通过整合多个替代模型的梯度信息, 能够显著增强对抗样本的跨模型迁移能力, 是当前黑盒攻击中最具潜力的策略之一. 然而, 现有集成方法在动态加权过程中通常依赖扰动引起的预测误差作为权重依据, 未能有效区分扰动作用与模型自身固有误差. 由此可能高估低质量模型对扰动优化的贡献, 干扰攻击方向, 进而削弱对抗样本的实际迁移效果. 提出了基于扰动响应的自适应集成黑盒对抗攻击算法(Perturbation response-based adaptive ensemble black-box adversarial attack algorithm, PRA-EA). 首先, 设计了扰动响应感知的权重分配策略(Perturbation response-aware weight allocation, PRA-WA), 通过引入KL散度与集成相似度指标来衡量扰动对模型输出的真实影响, 避免低质量模型对集成过程的负面干扰. 其次, 提出梯度协同扰动缩放策略(Gradient-collaborative based perturbation scaling, GCPS), 结合像素级梯度一致性度量, 动态调整扰动幅度, 缓解集成过程中的局部过拟合现象, 增强对抗样本在多模型间的泛化能力. 最后, 在多个黑盒攻击任务中进行系统评估, 实验结果表明所提出的基于扰动响应的自适应集成黑盒对抗攻击算法在迁移性能、攻击成功率与扰动效率方面均显著优于现有方法.Abstract: Model integration adversarial attacks enhance the cross-model transferability of adversarial samples by aggregating the gradient information of multiple substitute models, and are among the most promising strategies in current black-box attacks. However, existing methods typically use prediction errors caused by perturbations as weights during dynamic integration, failing to distinguish the impact of perturbations from models' inherent errors. This may overestimate the contribution of low-quality models, mislead the attack direction, and weaken actual transferability. We propose a perturbation response-based adaptive ensemble black-box adversarial attack algorithm (PRA-EA). First, we introduce a perturbation response-aware weight allocation strategy (PRA-WA), which leverages KL divergence and an ensemble similarity metric to assess the true effect of perturbations on model outputs, avoiding interference from low-quality models. Second, we propose a gradient-collaborative perturbation scaling strategy (GCPS), which uses pixel-level gradient consistency to dynamically adjust perturbation magnitude, mitigating local overfitting and improving adversarial generalization across models. Finally, comprehensive evaluations on multiple black-box attack tasks show that our proposed PRA-EA algorithm significantly outperforms existing methods in transferability, success rate, and perturbation efficiency.
-
Key words:
- Adversarial examples /
- ensemble attacks /
- gradient /
- black-box model
-
表 1 7个在CIFAR-10上自然训练模型在黑盒攻击下的分类准确率(%)
Table 1 Classification accuracy (%) of 7 naturally trained models on CIFAR-10 under black-box attacks
数据集 攻击算法 Res-50 WRN101-2 BiT-50 BiT-101 ViT-B DeiT-B Swin-B Avg NoAttack 97.56 97.58 94.34 94.24 98.61 98.39 98.86 97.08 CIFAR-10 AdaEA 42.13 65.09 67.99 71.85 74.37 50.24 61.13 61.83 PRA-EA 37.76 61.37 64.35 68.19 64.36 39.9 50.01 55.13 表 3 9个在ImageNet上自然训练模型在黑盒攻击下的分类准确率(%)
Table 3 Classification Accuracy (%) of 9 naturally trained models on ImageNet under black-box attacks
数据集 攻击算法 Res-50 WRN101-2 BiT-50 BiT-101 ViT-B DeiT-B Swin-B Conv Effi Avg NoAttack 74.55 77.92 72.76 74.89 84.8 81.26 84.29 83.64 76.93 79.01 ImageNet AdaEA 26.97 39.51 35.97 43.43 55.18 42.13 63.16 53.65 38.41 44.26 PRA-EA 25.82 32.55 30.07 37.24 48.48 34.28 60.04 52.84 37.59 39.88 表 4 4个在ImageNet-21K上自然训练模型在黑盒攻击下的分类准确率(%)
Table 4 Classification accuracy (%) of 4 naturally trained models on ImageNet-21K under black-box attacks
数据集 集成模型 攻击算法 BiT-101 ViT-B Swin-B Conv Avg ImageNet-21K BiT-50, Effi Vit-T, Swin-S NoAttack 73.28 82.65 83.43 82.88 80.56 AdaEA 42.57 53.77 64.08 52.97 53.35 PRA-EA 36.58 47.32 59.67 52.64 49.05 表 5 在目标识别任务下的黑盒攻击效果
Table 5 The effectiveness of black - box attacks in the object recognition task
数据集 集成模型 攻击算法 mP mR mAp50 mAp CoCo yolo5s yolo5m NoAttack 0.725 0.607 0.657 0.475 AdaEA 0.112 0.109 0.0549 0.0290 PRA-EA 0.106 0.105 0.0554 0.0287 表 2 7个在CIFAR-100上自然训练模型在黑盒攻击下的分类准确率(%)
Table 2 Classification accuracy (%) of 7 naturally trained models on CIFAR-100 under black-box attacks
数据集 攻击算法 Res-50 WRN101-2 BiT-50 BiT-101 ViT-B DeiT-B Swin-B Avg NoAttack 85.87 71.95 75.41 72.4 88.4 89.8 92.56 82.34 CIFAR-100 AdaEA 20.63 26.43 33.21 43.1 53.54 34.74 40.03 35.95 PRA-EA 20.53 25.12 30.23 39.64 46.01 29.36 35.02 32.27 表 6 集成模型配置
Table 6 Ensemble model configuration
集成模型 配置1 Res-18 Inc-v3 DeiT-T Vit-T 69.01 67.3 69.95 72.96 配置2 EfficientNet Inc-v3 DeiT-T Vit-T 76.93 67.3 69.95 72.96 配置3 ConvNeXt Inc-v3 DeiT-T Vit-T 83.64 67.3 69.95 72.96 表 7 在Imagenet上对比集成模型预测准确率和黑盒攻击成功率(%)
Table 7 Comparison of ensemble model prediction accuracy and black-box attack success rate (%) on ImageNet
集成模型 攻击算法 CNNs ViTs Res-50 WRN101-2 BiT-101 Avg ViT-B DeiT-B Swin-S Avg 配置1 AdaEA 63.82 49.30 42.01 51.71 34.93 48.15 25.07 36.05 PRA-EA 65.37 58.23 50.28 57.96 42.83 57.81 28.77 43.14 配置2 AdaEA 63.58 49.66 42.57 52.94 36.57 49.77 25.79 37.38 PRA-EA 66.15 59.07 52.16 59.13 45.52 58.15 29.04 44.24 配置3 AdaEA 64.63 51.41 42.82 52.95 38.88 50.15 28.13 39.05 PRA-EA 66.84 60.01 52.98 59.94 46.59 59.37 30.28 45.41 表 8 在CIFAR-10上比较不同集成模型类型和数量下AdaEA与本文PRA-EA的平均攻击成功率(%)
Table 8 Comparison of attack success rate (%) of AdaEA and PRA-EA under different ensemble models on CIFAR-10
集成模型 CNNS ViTS 攻击算法 CNNS ViTS Res-50 WRN101-2 BiT-101 Avg ViT-B DeiT-B Swin-S Avg 配置1 Inc-v3 DeiT-T 1 1 AdaEA 22.69 13.28 12.82 16.26 12.48 24.39 15.14 17.34 PRA-EA 23.58 14.85 14.07 17.50 13.56 25.67 17.09 18.77 配置2 Resnet18 Inc-v3 DeiT-T 2 1 AdaEA 46.00 26.14 17.88 30.01 12.35 24.31 18.83 18.50 PRA-EA 48.00 26.33 19.76 31.36 12.7 26.22 20.59 19.84 配置3 Inc-v3 DeiT-T ViT-T 1 2 AdaEA 29.28 17.34 15.03 20.55 21.47 42.66 27.34 30.49 PRA-EA 35.85 21.85 20.35 26.02 34.37 59.84 41.60 45.27 配置4 Resnet18 Inc-v3 2 0 AdaEA 33.63 17.07 9.63 20.11 1.44 2.85 5.18 3.16 PRA-EA 34.06 18.2 11.00 21.09 2.91 4.49 6.13 4.51 配置5 ViT-T DeiT-T 0 2 AdaEA 35.94 24.41 24.87 28.41 43.25 69.67 50.20 54.37 PRA-EA 39.96 26.20 25.98 30.71 46.64 74.84 53.41 58.30 表 9 PRA-EA在一些防御方法中的平均攻击成功率(%)
Table 9 The average attack success rate (%) of PRA-EA in some defense methods
防御方法 攻击方法 Inv-3 Resnet101 avg R&P AdaEA 21.63 19.51 20.57 PRA-EA 21.47 21.39 21.43 JPEG AdaEA 36.58 33.92 35.25 PRA-EA 36.72 37.42 37.07 AdvTrain AdaEA 0.77 0.70 0.74 PRA-EA 0.79 0.72 0.76 表 10 PRA-EA中组件消融的平均攻击成功率(%)实验结果
Table 10 The average attack success rate (%) of component ablation experiments in PRA-EA
集成模型 攻击方法 CNNS ViTs All Res-18 Ens 30.58 23.51 27.55 Inc-v3 +PRA-WA 43.76 37.82 40.79 ViT-T +GCPS 38.68 37.92 38.3 DeiT-T PRA-EA 57.96 43.14 50.55 -
[1] Wen L, Wang X, Liu J, Xu Z. Mveb: Self-supervised learning with multi-view entropy bottleneck. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(9): 6097−6108 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3380065 [2] Li Z, Guo Y, Liu H, Zhang C. A theoretical view of linear backpropagation and its convergence. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(5): 3972−3980 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3353919 [3] Kolesnikov A, Beyer L, Zhai X, Puigcerver J, Yung J, Gelly S, et al. Big transfer (bit): General visual representation learning. In: Proceedings of 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 491−507 [4] 王辉, 黄宇廷, 夏玉婷, 范自柱, 罗国亮, 杨辉. 基于视觉属性的多模态可解释图像分类方法. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(2): 445−456Wang Hui, Huang Yu-Ting, Xia Yu-Ting, Fan Zi-Zhu, Luo Guo-Liang, Yang Hui. Multimodal interpretable image classification method based on visual attributes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(2): 445−456 [5] Xu Z, Wu D, Yu C, Chu X, Sang N, Gao C. Sctnet: Single-branch cnn with transformer semantic information for real-time segmentation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada: AAAI, 2024. 6378−6386 [6] Zong Y, Zuo Q, Ng M K P, Lei B, Wang S. A new brain network construction paradigm for brain disorder via diffusion-based graph contrastive learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(12): 10389−10403 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3442811 [7] Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event: 2020. 1−21 [8] Xia C, Wang X, Lv F, Hao X, Shi Y. Vit-comer: Vision transformer with convolutional multi-scale feature interaction for dense predictions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, Washington, USA: IEEE, 2024. 5493−5502 [9] Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Guo B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 10012−10022 [10] 潘雨辰, 贾克斌, 张铁林. 前额叶皮层启发的Transformer模型应用及其进展. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(5): 1−20Pan Yu-Chen, Jia Ke-Bin, Zhang Tie-Lin. The application and progress of prefrontal cortex-inspired transformer model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(5): 1−20 [11] Zhou M, Wang L, Niu Z, Zhang Q, Zheng N, Hua G. Adversarial attack and defense in deep ranking. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(8): 5306−5324 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3365699 [12] 王璐瑶, 曹渊, 刘博涵, 曾恩, 刘坤, 夏元清. 时间序列分类模型的集成对抗训练防御方法. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(1): 144−160Wang Lu-Yao, Cao Yuan, Liu Bo-Han, Zeng En, Liu Kun, Xia Yuan-Qing. Ensemble adversarial training defense for time series classification models. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(1): 144−160 [13] Chen P, Zhang H, Sharma Y, Yi J, Hsieh C J. Zoo: Zeroth order optimization based black-box attacks to deep neural networks without training substitute models. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security. Dallas, Texas, USA: ACM, 2017. 15−26 [14] Xiaosen W, Tong K, He K. Rethinking the backward propagation for adversarial transferability. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: 2023. 1905−1922 [15] Huang H, Chen Z, Chen H, Wang Y, Zhang K. T-sea: Transfer-based self-ensemble attack on object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2023. 20514−20523 [16] Chen B, Yin J, Chen S, Chen B, Liu X. An adaptive model ensemble adversarial attack for boosting adversarial transferability. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Paris, France: IEEE, 2023. 4489−4498 [17] Tang B, Wang Z, Bin Y, Dou Q, Yang Y, Shen H T. Ensemble diversity facilitates adversarial transferability. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, Washington, USA: IEEE, 2024. 24377−24386 [18] Liu Y, Chen X, Liu C, Song D. Delving into transferable adversarial examples and black-box attacks. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon, France: 2017. 2235−2248 [19] Szegedy C, Zaremba W, Sutskever I, Bruna J, Erhan D, Goodfellow I, et al. Intriguing properties of neural networks. In: Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA: JMLR, 2014. 1−10 [20] Goodfellow I J, Shlens J, Szegedy C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations. Lille, France: JMLR, 2015. 1−11 [21] Kurakin A, Goodfellow I J, Bengio S. Adversarial examples in the physical world. Artificial Intelligence Safety and Security. Toulon, France: Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2018. 99−112 [22] Dong Y, Pang T, Su H, Zhu J. Evading defenses to transferable adversarial examples by translation-invariant attacks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, California, USA: IEEE, 2019. 4312−4321 [23] Carlini N, Wagner D. Towards evaluating the robustness of neural networks. In: Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. San Jose, USA: IEEE, 2017. 39−57 [24] Dong Y, Liao F, Pang T, Su H, Zhu J, Hu X, et al. Boosting adversarial attacks with momentum. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 9185−9193 [25] Madry A, Makelov A, Schmidt L, Tsipras D, Vladu A. Towards Deep Learning Models Resistant to Adversarial Attacks. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations. Vancouver, Canada: 2018. 4138−4160 [26] Papernot N, McDaniel P, Goodfellow I. Transferability in machine learning: from phenomena to black-box attacks using adversarial samples. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1605.07277, 2016. [27] Zhang H, Yu Y, Jiao J, Xing E, El Ghaoui L, Jordan M. Theoretically principled trade-off between robustness and accuracy. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach, California: PMLR, 2019. 7472−7482 [28] Xie C, Zhang Z, Zhou Y, Bai S, Wang J, Ren Z, et al. Improving transferability of adversarial examples with input diversity. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, California, USA: IEEE, 2019. 2730−2739. [29] 丁佳, 许智武. 基于 Rectified Adam 和颜色不变性的对抗迁移攻击. 软件学报, 2022, 33(7): 2525−2537Ding Jia, Xu Zhiwu. Transfer-based adversarial attack with rectified adam and color invariance. Journal of Software, 2022, 33(7): 2525−2537 [30] Moosavi-Dezfooli S M, Fawzi A, Frossard P. Deepfool: a simple and accurate method to fool deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2574−2582. [31] Tramèr F, Papernot N, Goodfellow I, Boneh D, McDaniel P. The space of transferable adversarial examples. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1704.03453, 2017. [32] Fu Y, Liu Z, Lyu J. Transferable adversarial attacks for remote sensing object recognition via spatial-frequency co-transformation. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 1−12 [33] Ilyas A, Engstrom L, Athalye A, Lin J. Black-box adversarial attacks with limited queries and information. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: 2018. 2137−2146. [34] Xiong Y, Lin J, Zhang M, Hopcroft J E, He K. Stochastic variance reduced ensemble adversarial attack for boosting the adversarial transferability. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 14983−14992 [35] Ji S, Zhang Z, Ying S, Wang L, Zhao X, Gao Y. Kullback–Leibler divergence metric learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 52(4): 2047−2058 [36] Zhang B, Li L, Wang S, Cai S, Zha Z, Tian Q, et al. Inductive state-relabeling adversarial active learning with heuristic clique rescaling. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(12): 9780−9796 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3432099 [37] Liu J, Yang H, Zhou H, Xi Y, Yu L, Li C, et al. Swin-umamba: Mamba-based unet with imagenet-based pretraining. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Marrakesh, Morocco: Spring, 2024. 615−625 [38] Liu Z, Mao H, Wu C, Feichtenhofer C, Darrell T, Xie S. A convnet for the 2020s. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 11976−11986 [39] Tan M, Le Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach, California, USA: PMLR, 2019. 6105−6114 [40] Zhang J, Huang Y, Xu Z, Wu W, Lyu M R. Improving the adversarial transferability of vision transformers with virtual dense connection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI, 2024. 7133−7141 [41] 徐昌凯, 冯卫栋, 张淳杰, 郑晓龙, 张辉, 王飞跃. 针对身份证文本识别的黑盒攻击算法研究. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(1): 103−120Xu Chang-Kai, Feng Wei-Dong, Zhang Chun-Jie, Zheng Xiao-Long, Zhang Hui, Wang Fei-Yue. Research on black-box attack algorithm by targeting ID card text recognition. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(1): 103−120 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 12
- HTML全文浏览量: 8
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: