-
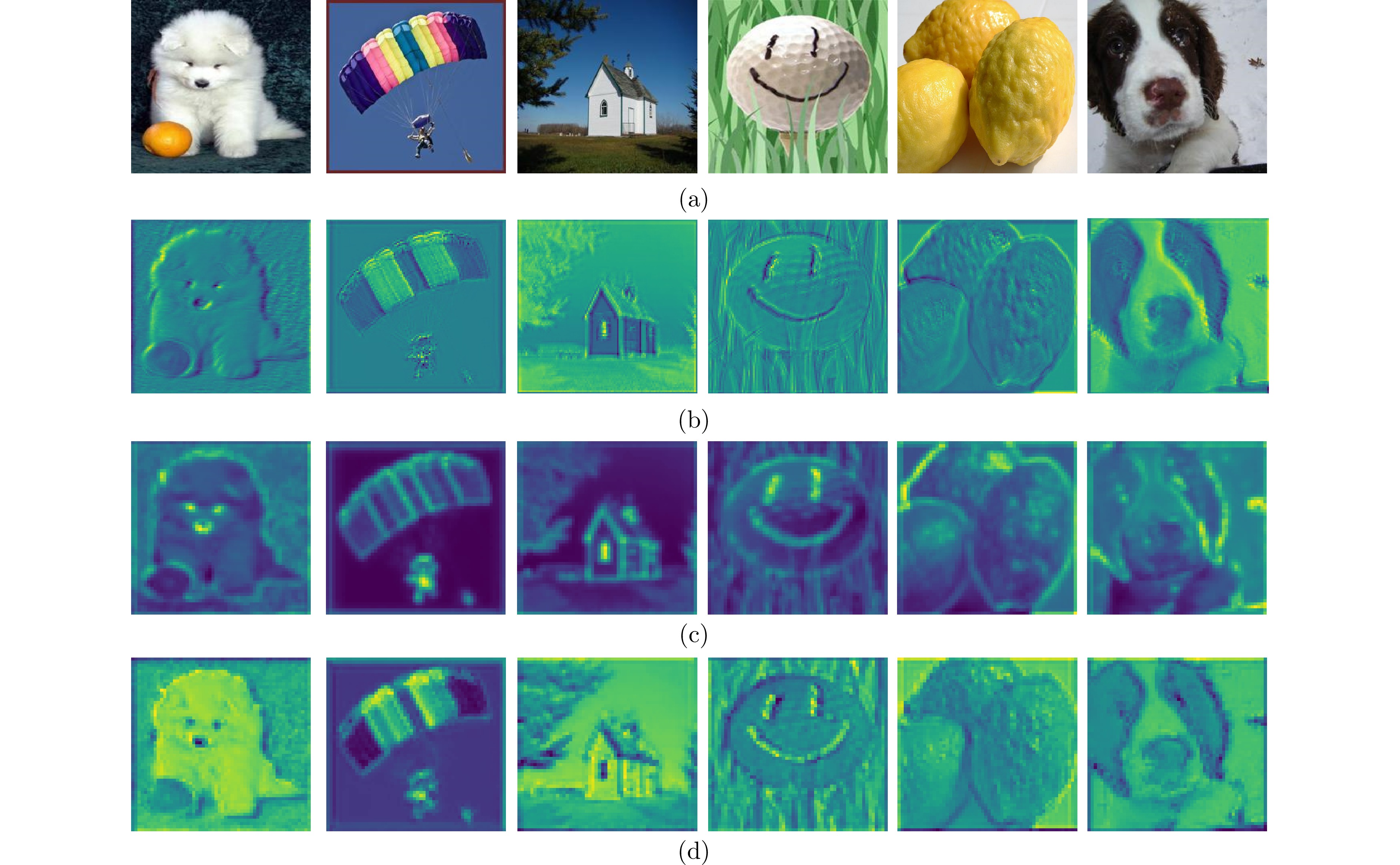
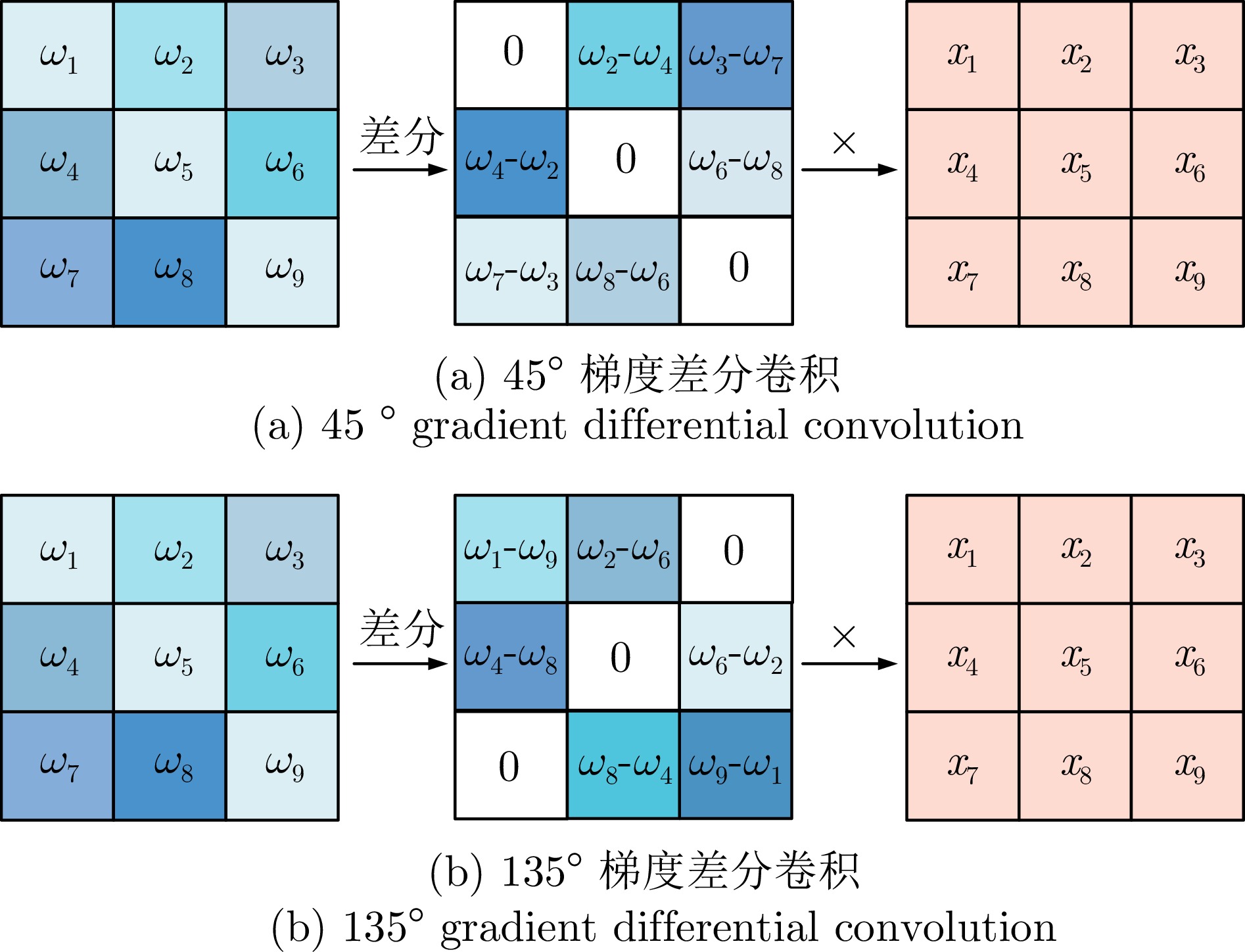
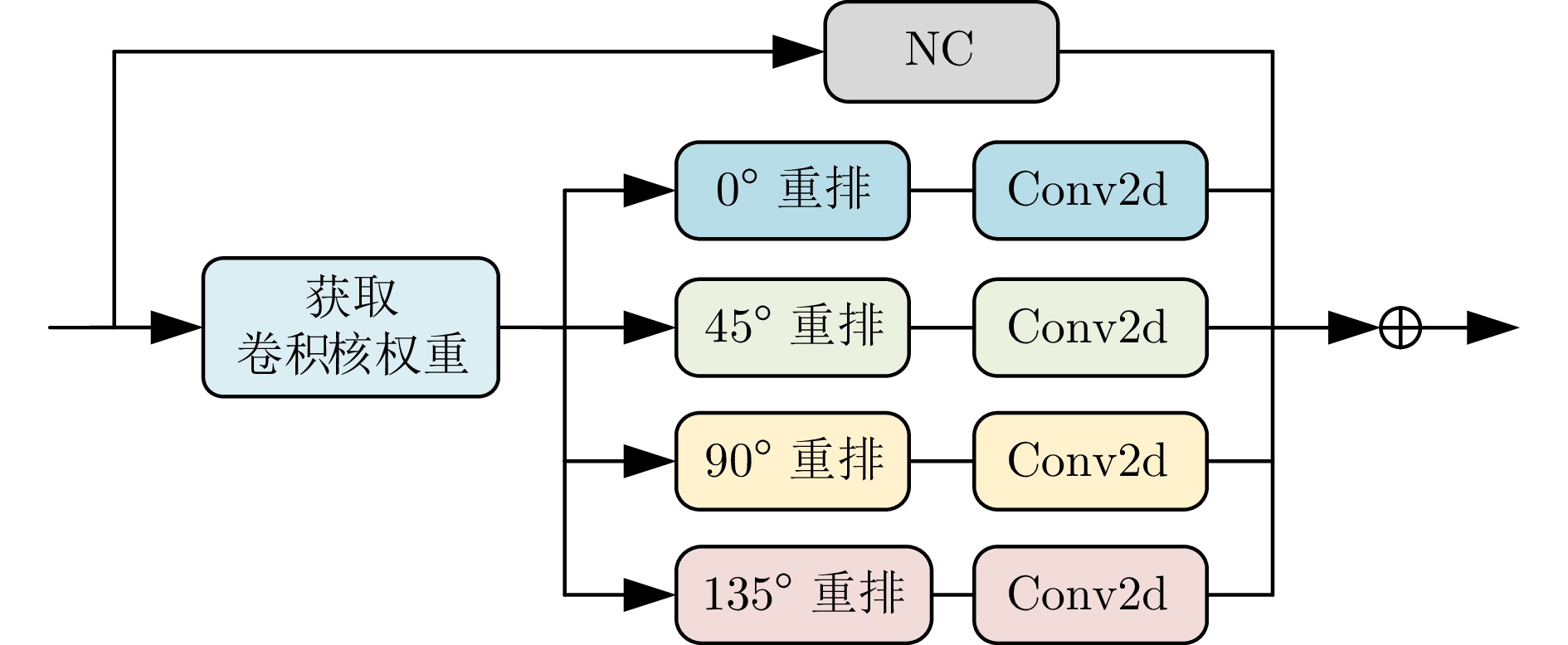
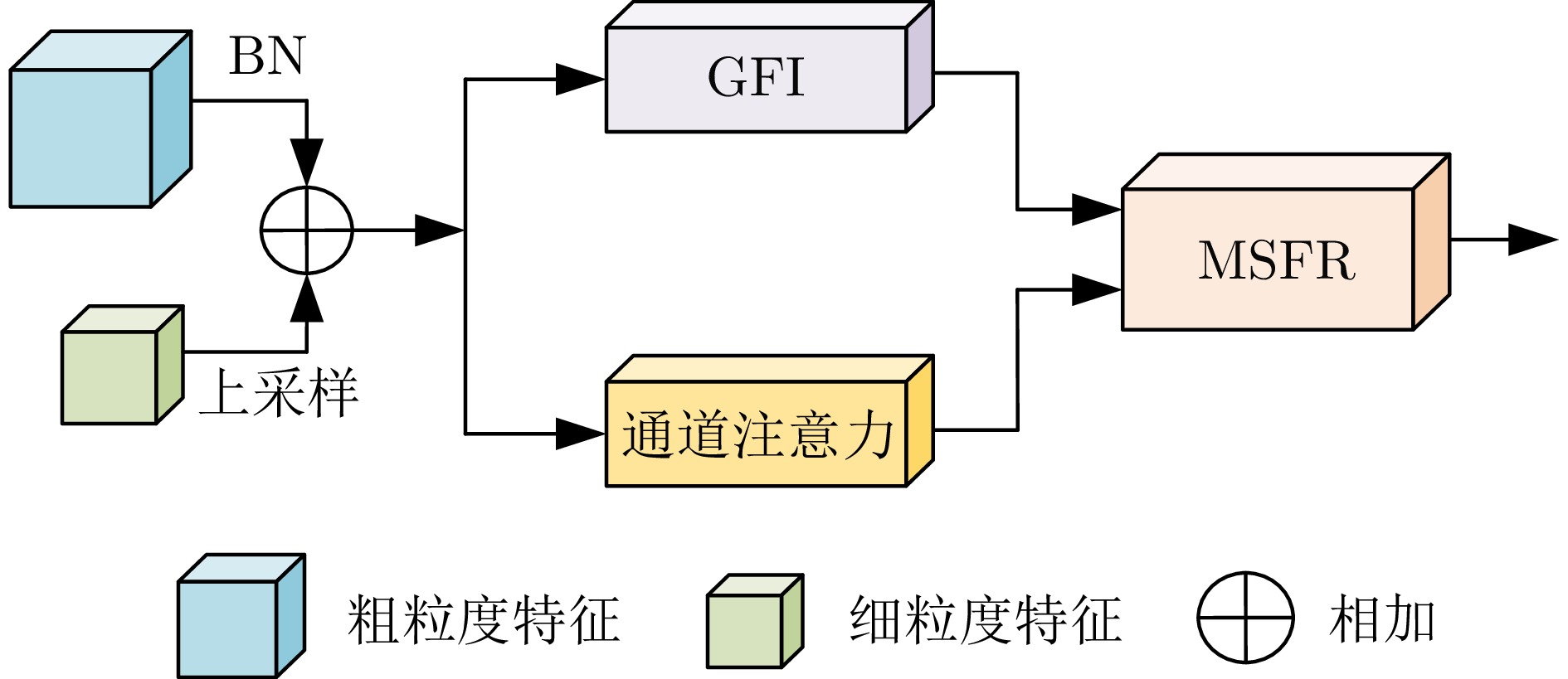
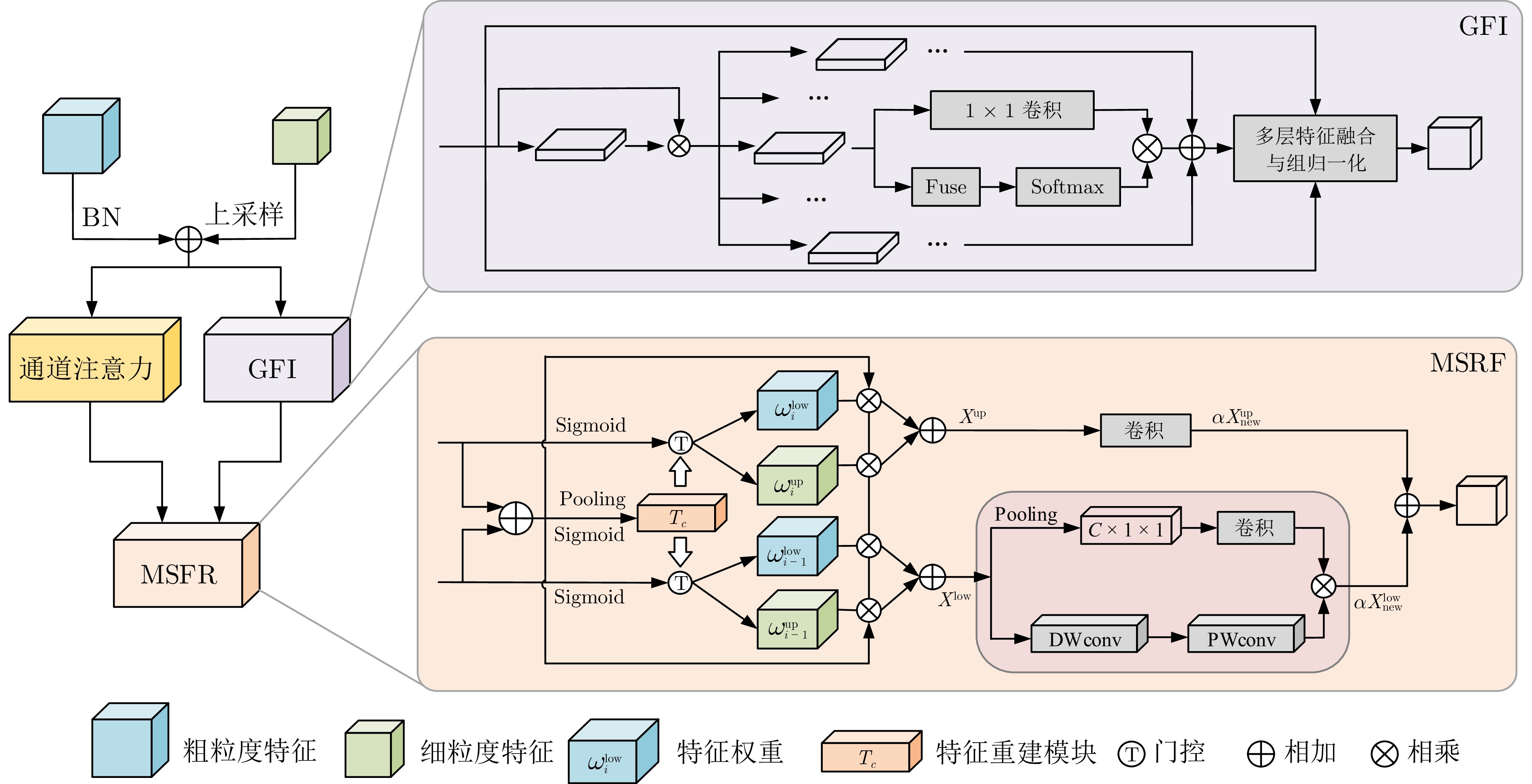
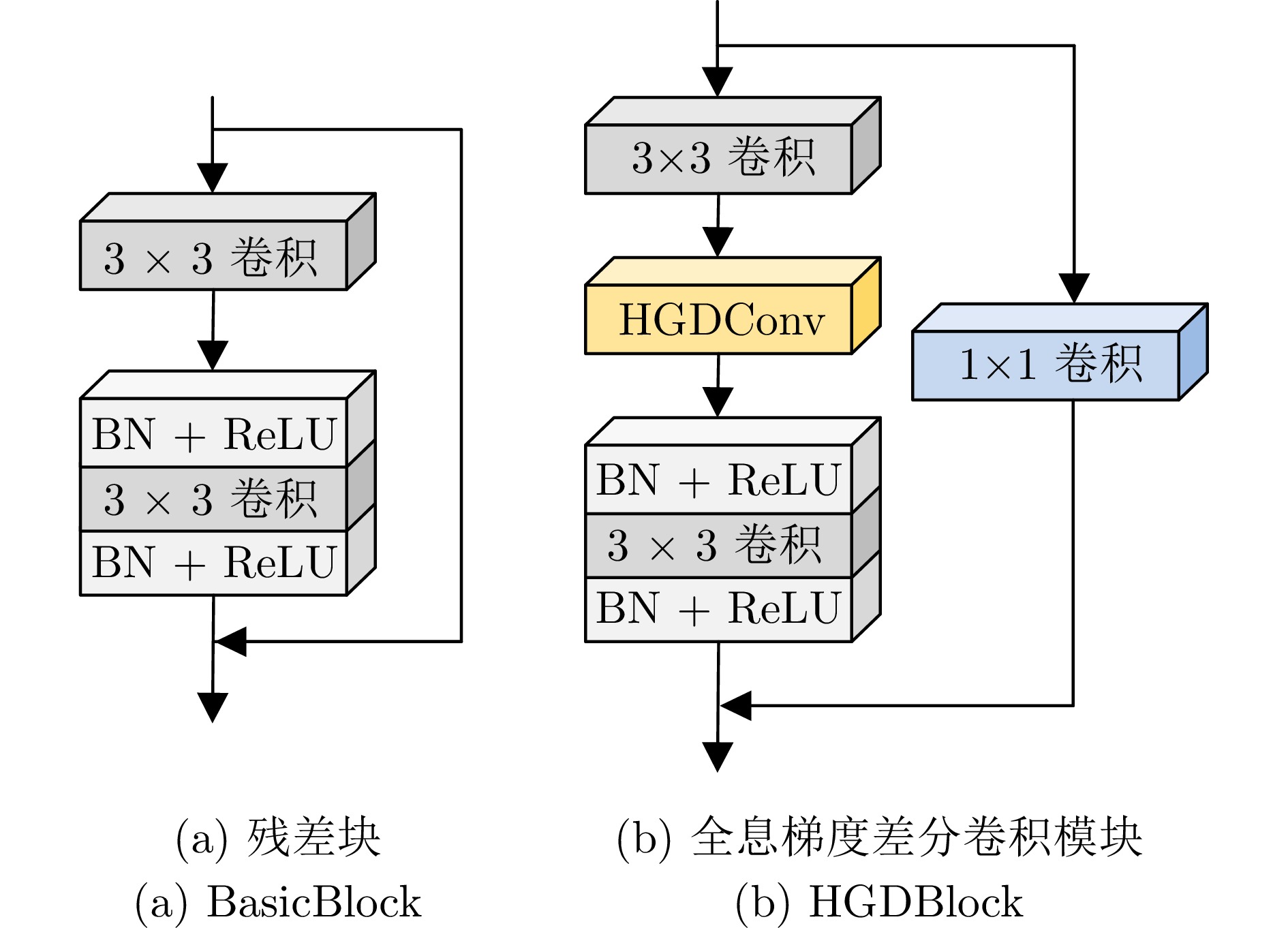
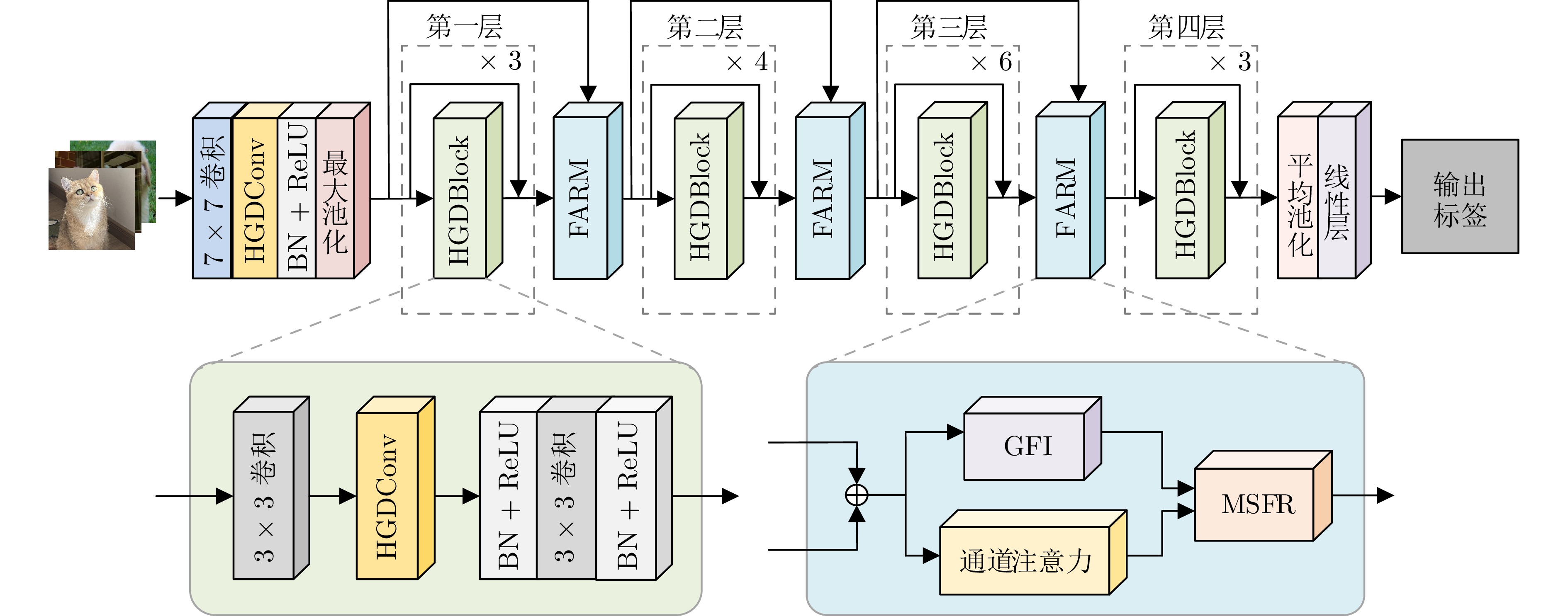
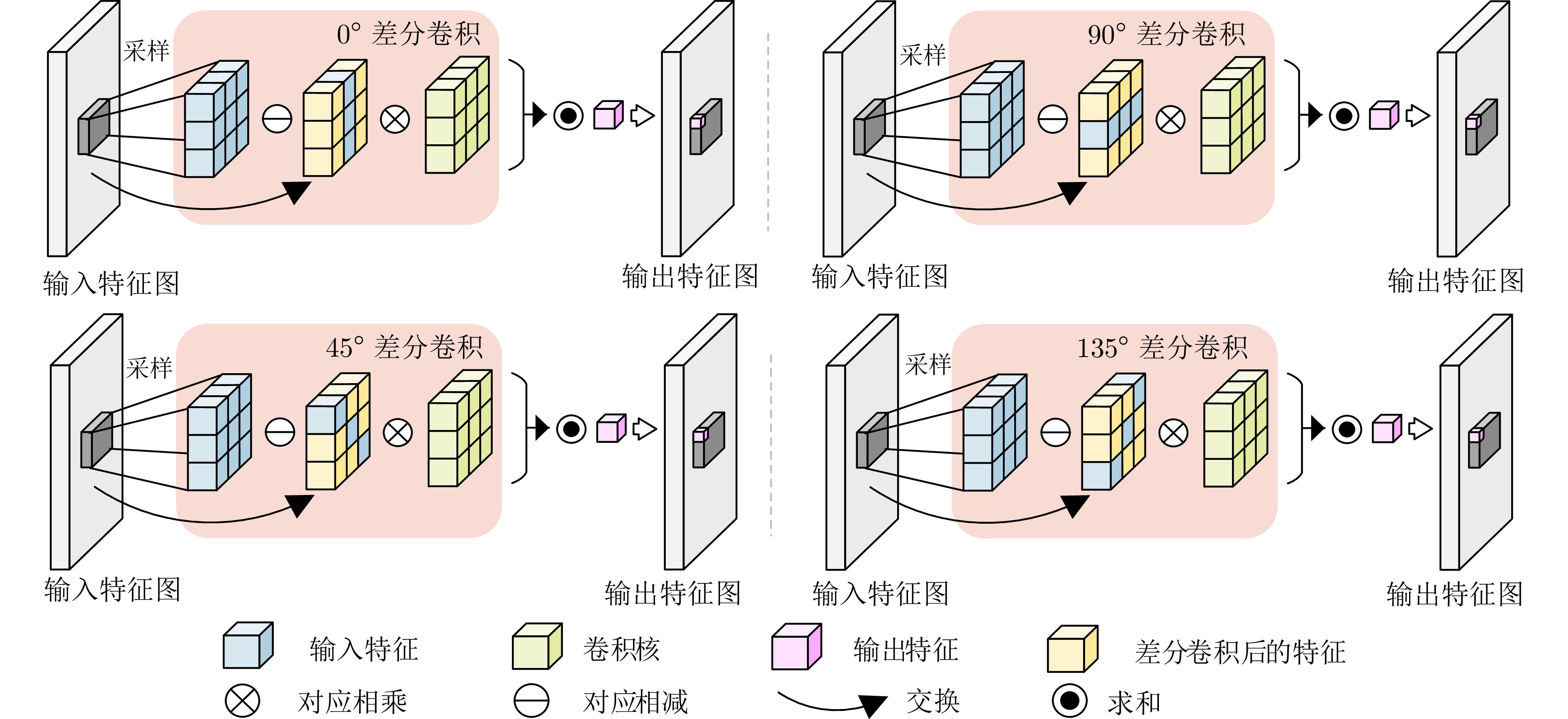
摘要: 为解决传统图像分类方法边缘信息提取模糊、多尺度特征聚合不充分的问题, 提出全息梯度差分卷积的图像分类网络(HGDNet). HGDNet以ResNet-34为基础网络, 通过设计全息梯度差分卷积(HGDConv)与多尺度特征聚合模块(FARM)实现对图像特征的高效提取与精细聚合. HGDConv通过设计$0^{\circ}$、$45^{\circ}$、$90^{\circ}$、$135^{\circ}$四种角度的梯度差分操作, 结合传统卷积的特性, 有效拓宽感受野, 提高对图像多角度特征的捕获能力, 显著增强网络在细节特征和边缘信息上的表达能力. FARM通过通道注意力机制动态调整特征通道的重要性, 提升特征选择的精准性, 进一步优化了特征提取与融合; 同时, FARM结合全局特征集成和多尺度特征细化, 在捕捉全局语义信息的同时, 对关键区域进行细化处理, 有效减少冗余信息并增强重要特征表达. 实验结果表明, HGDNet在CIFAR-10、CIFAR-100、SVHN、STL-10、Imagenette和Imagewoof上均表现出优异的分类性能, 相较于当前先进方法准确率显著提升. 此外, HGDConv作为一个即插即用的卷积, 与其他卷积相比也展现出更好的特征表示能力.Abstract: In order to solve the problems of blurred edge information extraction and insufficient multi-scale feature aggregation in traditional image classification methods. A image classification network of holographic gradient differential convolution (HGDNet) is proposesd. Based on the ResNet-34 backbone, HGDNet achieves efficient extraction and fine aggregation of image features by designing holographic gradient differential convolution (HGDConv) and multi-scale feature aggregation refinement module (FARM). By designing gradient difference operations at four angles of $0^{\circ},\; 45^{\circ},\; 90^{\circ}$, and $135^{\circ}$, HGDConv effectively broadens the receptive field by combining the characteristics of traditional convolution, improves the ability to capture multi-angle features of images, and significantly enhances the network's ability to express detailed features and edge information. FARM dynamically adjusts the importance of feature channels through channel attention mechanism, improves the accuracy of feature selection, and further optimizes feature extraction and fusion. At the same time, FARM combines global feature integration and multi-scale feature refiner to refine key regions while capturing global semantic information, effectively reducing redundant information and enhancing important feature expression. The experimental results show that HGDNet has excellent classification performance on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, SVHN, STL-10, Imagenette and Imagewoof, and the accuracy is significantly improved compared with the current advanced methods. In addition, HGDConv, as a plug-and-play convolution, also shows better feature representation ability than other convolutions.
-
表 1 实验数据集
Table 1 Experimental data set
名称 图像尺寸 分类数 训练集数量 测试集数量 CIFAR-10 $ 32\times32 $ 10 50 000 10 000 CIFAR-100 $ 32\times32 $ 100 50 000 10 000 SVHN $ 32\times32 $ 10 73 257 26 032 STL10 $ 96\times96 $ 10 5 000 8 000 Imagenette $ 224\times224 $ 10 9 469 3 925 Imagewoof $ 224\times224 $ 10 9 025 3 929 COVID-19 $ 224\times224 $ 4 36 721 15 737 RSOD $ 224\times224 $ 10 700 300 UC Merced Land-Use $ 256\times256 $ 21 1 470 630 表 2 各网络在5个密集性数据集上的分类准确率(%)
Table 2 Classification accuracy of each network on 5 dense datasets (%)
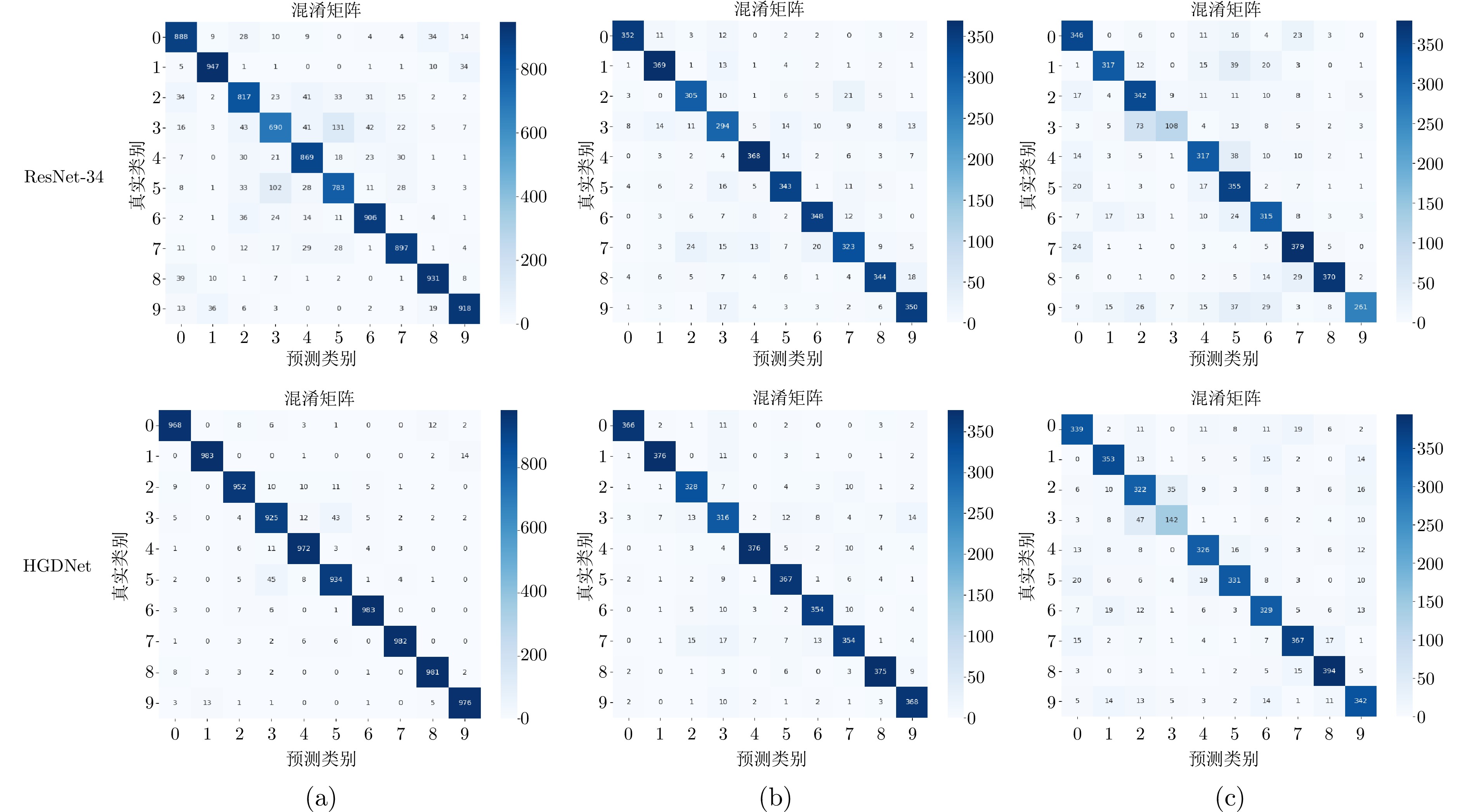
网络 分类准确率 CIFAR-10 CIFAR-100 SVHN Imagenette Imagewoof HGDNet 96.80 80.09 97.60 91.21 83.99 ResNet-34 95.23 77.98 95.51 87.46 77.93 WideResnet-28-10 95.83 79.45 95.21 88.34 78.71 Efficient-Nets 94.04 75.96 93.32 88.03 77.95 GhostNet 94.95 77.15 93.86 87.83 78.22 Couplformer 93.54 73.92 94.26 87.91 79.08 HO-ResNet 96.32 77.12 95.69 86.23 79.64 CAPR-DenseNet 94.24 78.84 94.94 87.56 80.79 Multi-ResNet 94.56 78.68 94.58 87.69 81.21 ATONet 94.51 78.54 95.21 86.67 80.19 FAVOR+ 91.45 72.56 93.21 88.16 77.57 TLENet 95.46 78.42 96.83 87.62 80.57 SSLLNet 95.51 79.23 96.91 87.93 80.89 表 3 各网络在3个稀疏型数据集上的分类准确率(%)
Table 3 Classification accuracy of each network on 3 sparse datasets (%)
网络 分类准确率 COVID-19 UC Merced Land-Use RSOD HGDNet 89.56 71.27 96.55 ResNet-34 88.23 65.56 88.62 WideResnet-28-10 89.37 70.23 88.37 MobileNet-v2 85.69 70.35 95.17 GhostNet 86.35 68.55 92.54 ATONet 88.97 71.72 92.54 CLMGNet 85.03 71.93 96.39 MEGANet 89.29 68.38 87.77 表 4 各网络的参数量、运行速度及浮点运算次数
Table 4 The parameter count, running speed, and floating-point operation count of each network
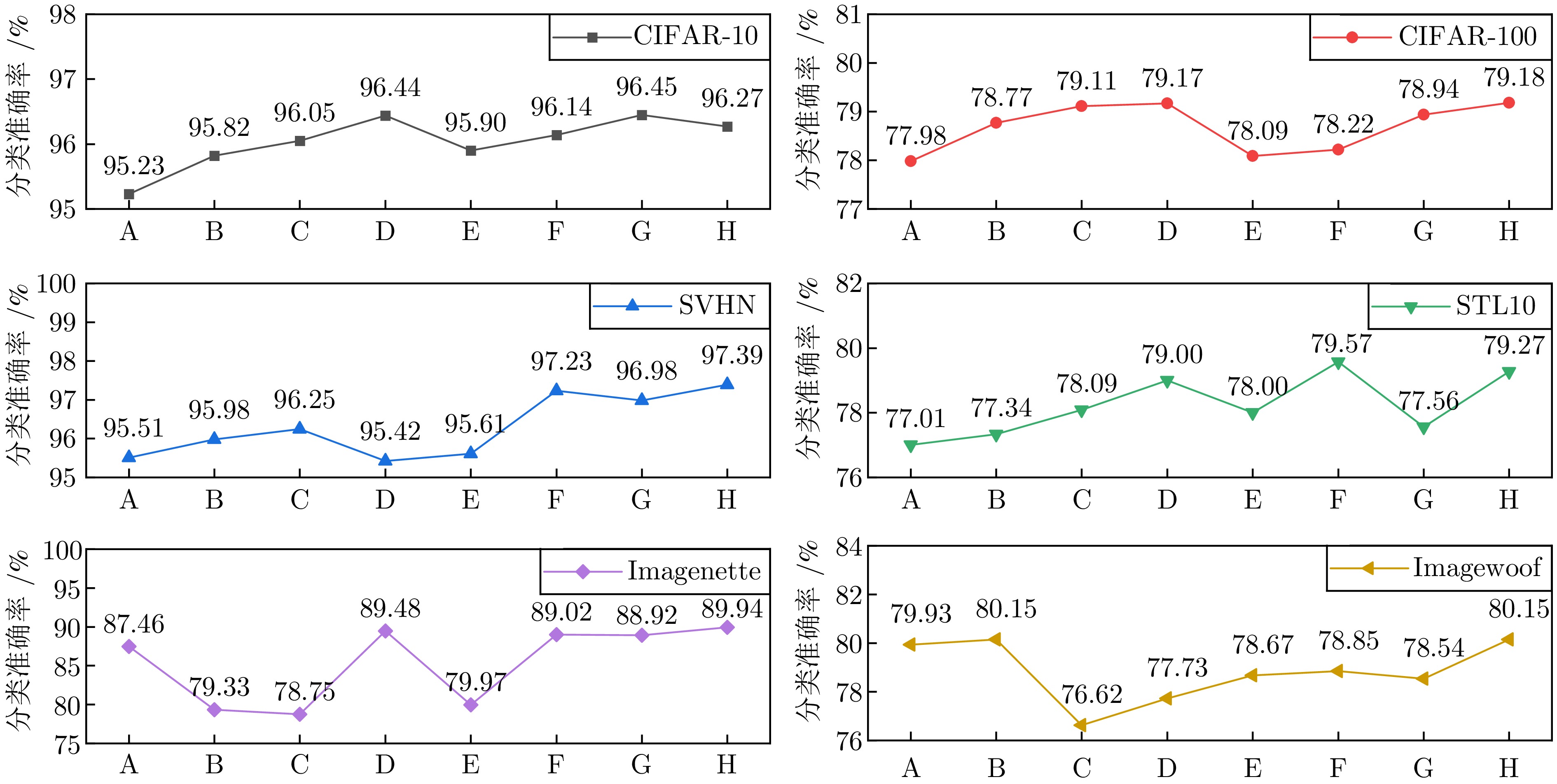
网络 参数量(M) Speed$ ({f} / {s}) $ FLOPs(G) HGDNet 21.85 1.82 6.49 ResNet-34 21.29 3.02 3.60 Efficient-Nets 52.98 — 4.61 WideResnet-28-10 37.16 — 5.96 Couplformer 27.63 2.73 4.42 HO-ResNet 50.26 1.93 11.05 CAPRDenseNet 25.51 2.86 5.50 Multi-ResNet 51.23 1.62 11.73 ATONet 30.12 2.88 5.24 TLENet 46.67 2.19 9.46 SSLLNet 31.57 2.57 6.47 表 5 不同角度的组合方式
Table 5 Combination of different angles
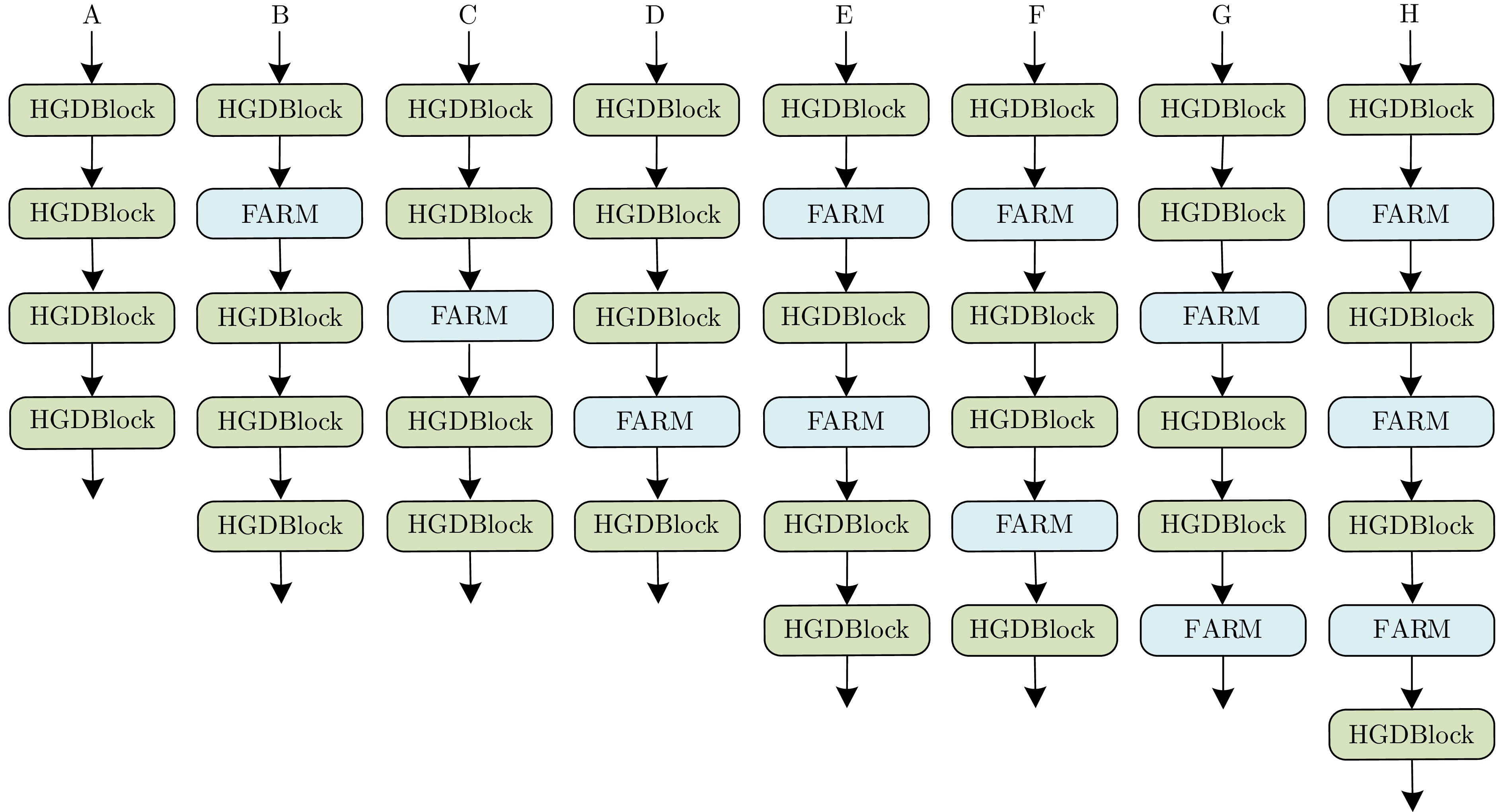
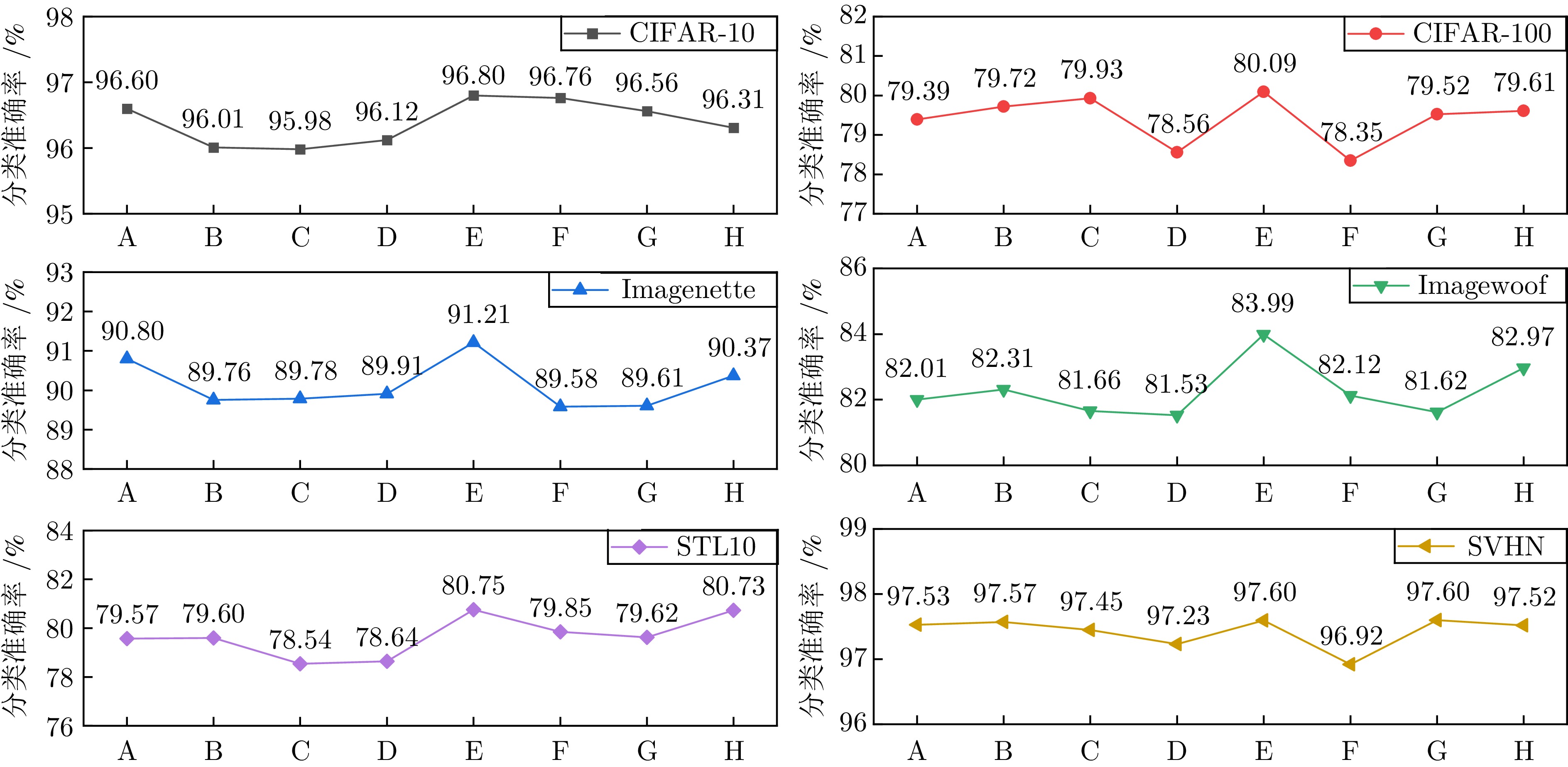
角度\方法 A B C D E F G H 0° — — √ — — √ — √ 45° — — — — √ — √ √ 90° — √ — — — √ — √ 135° — — — √ — — √ √ 表 6 消融实验结果
Table 6 Ablation experimental results
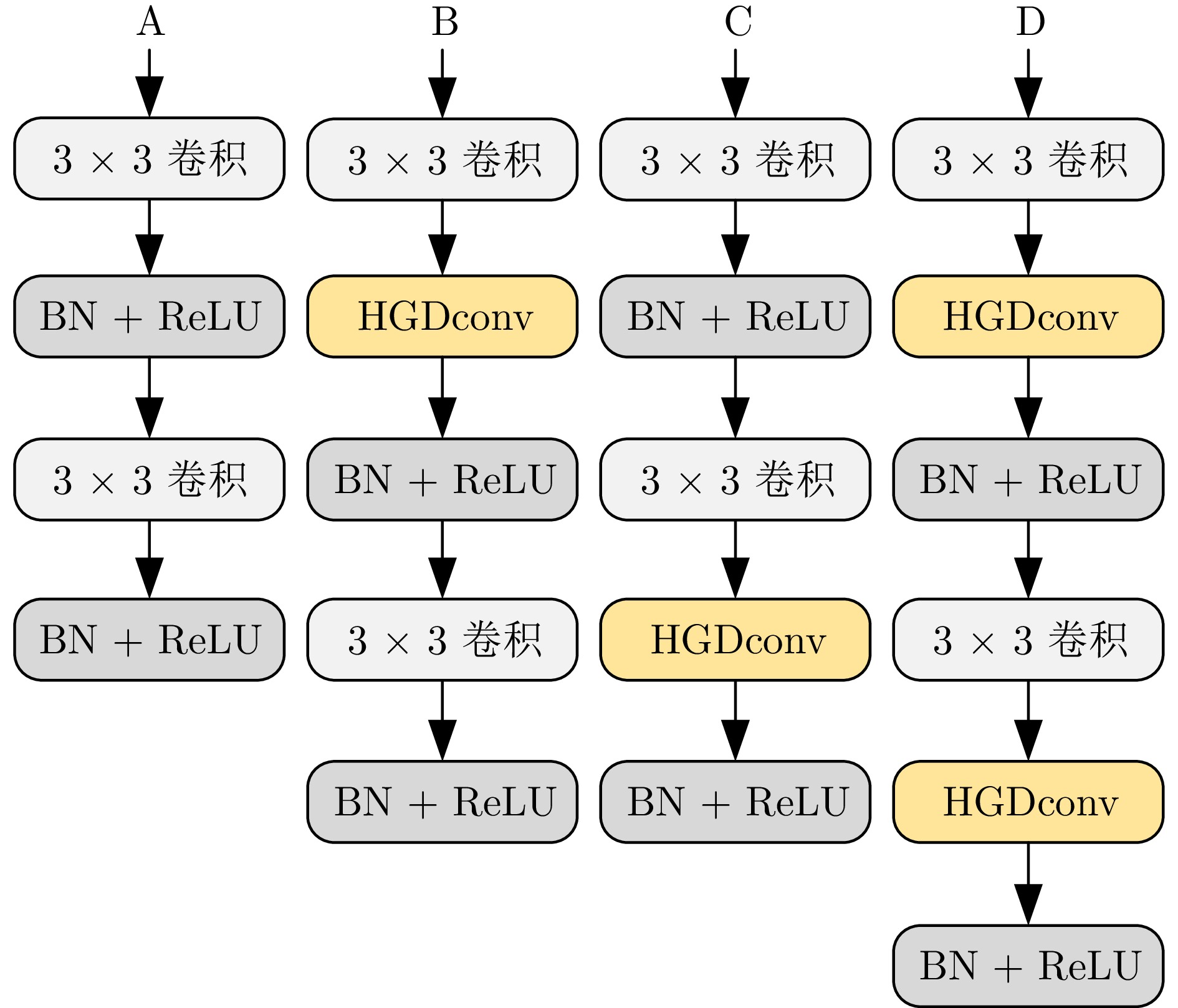
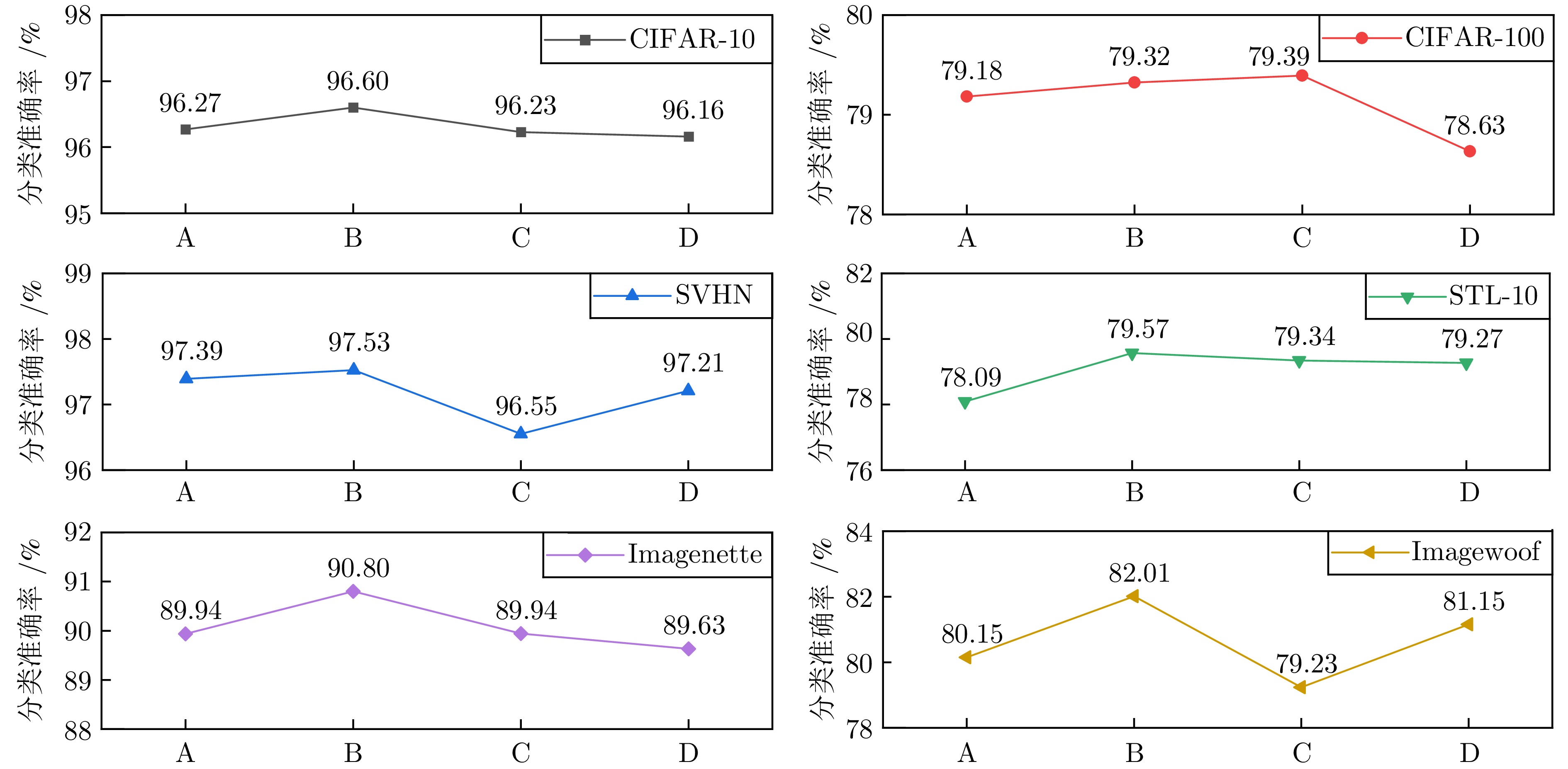
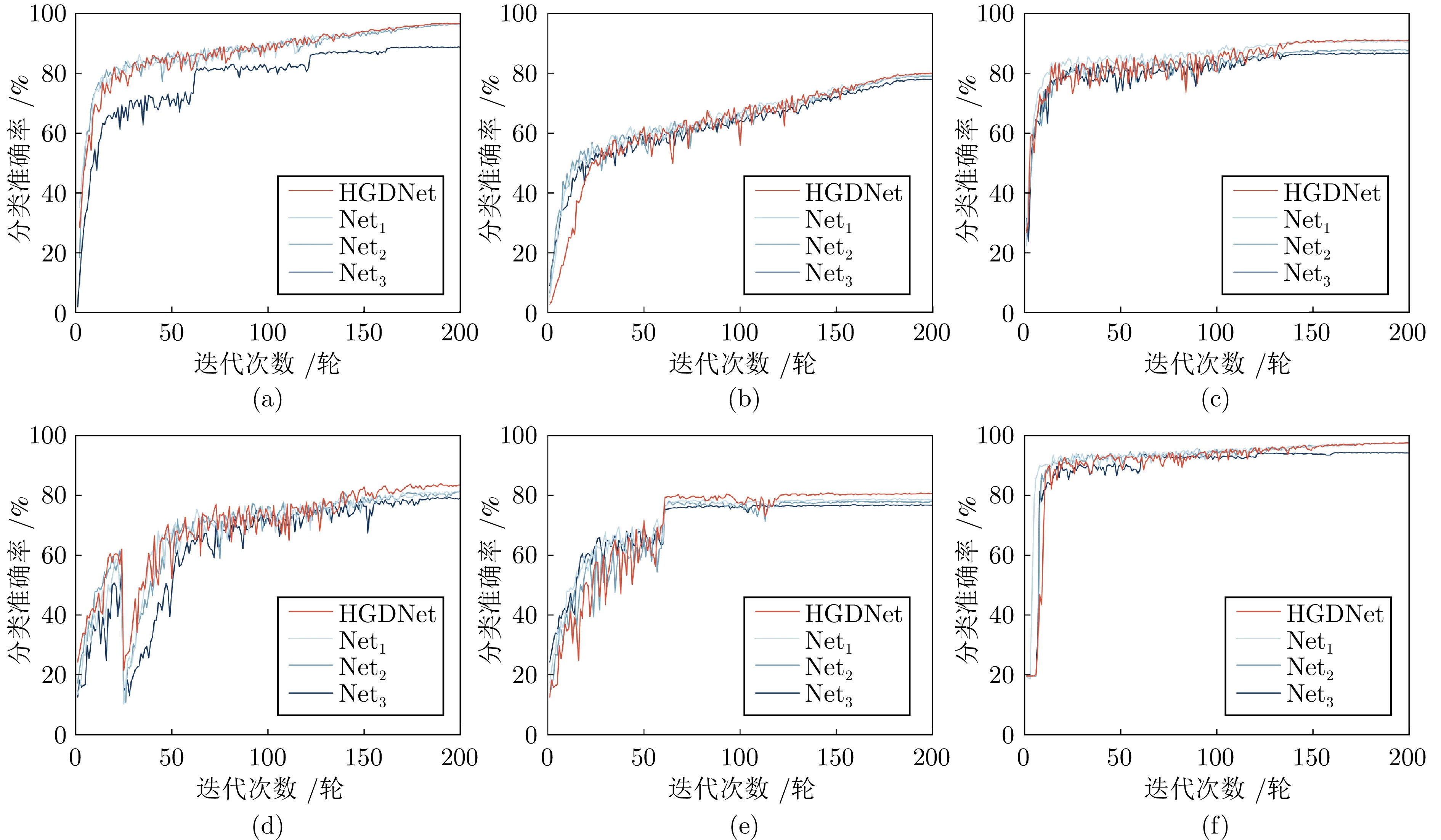
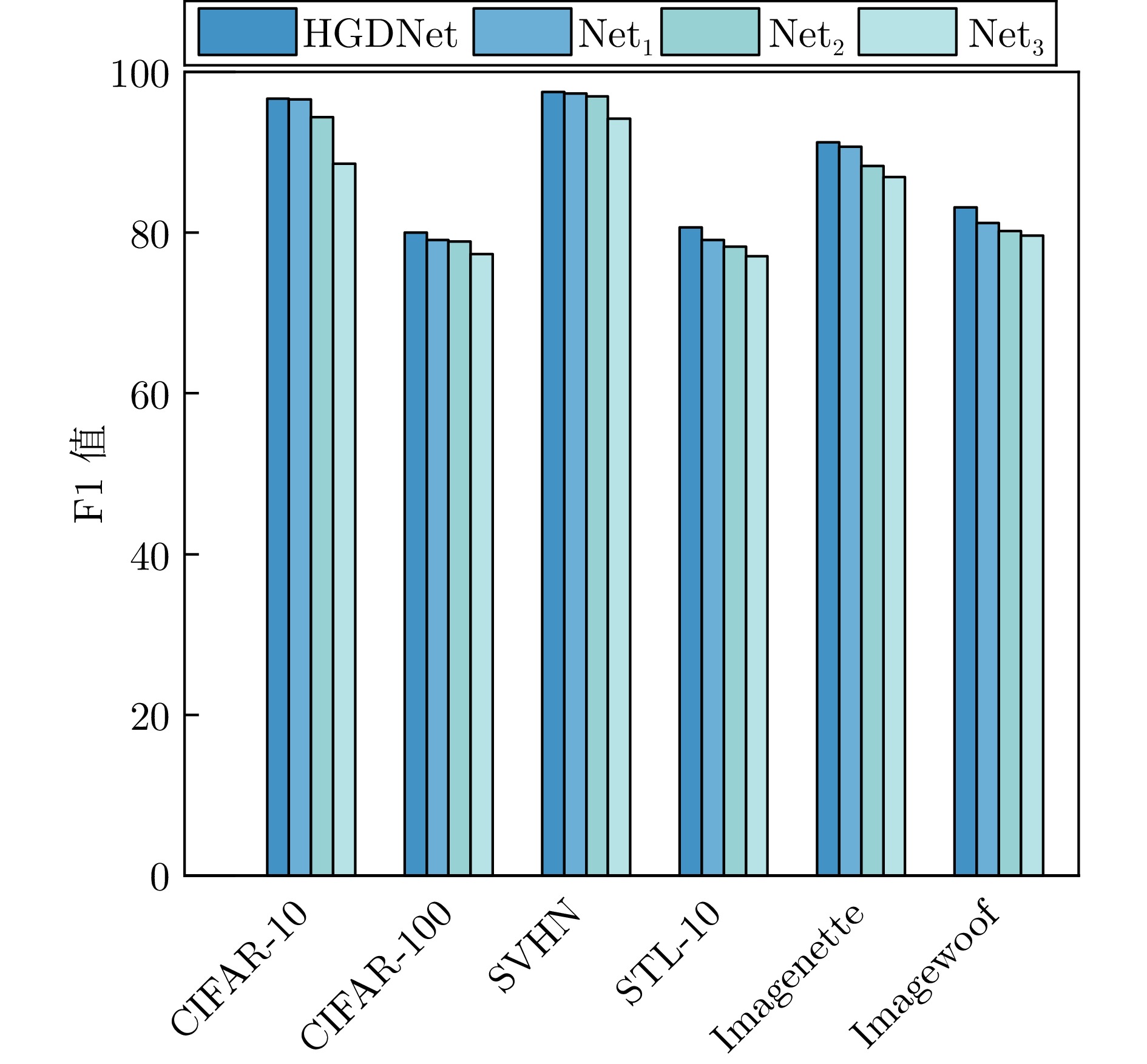
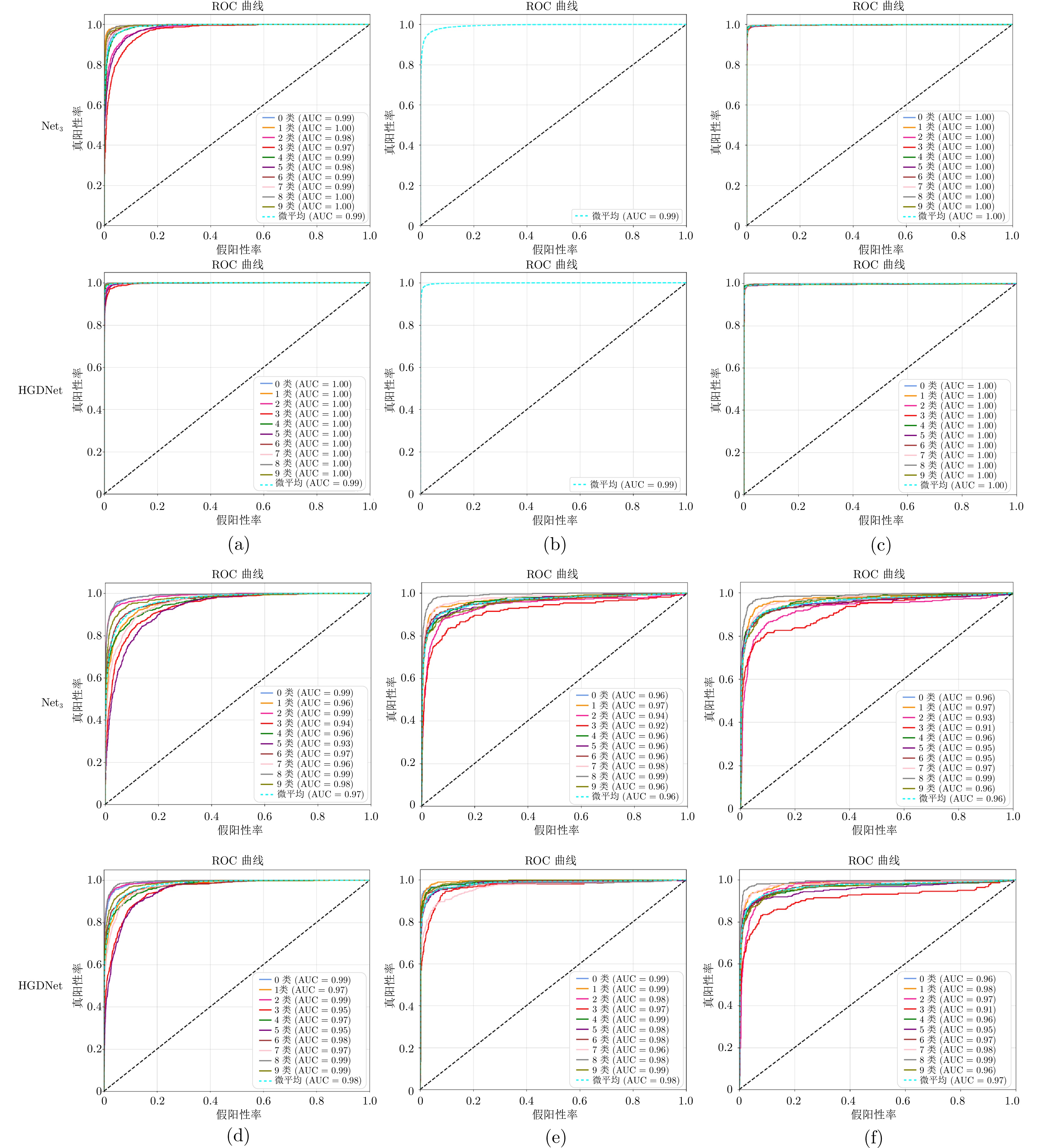
网路 分类准确率(%) CIFAR-10 CIFAR-100 SVHN STL-10 Imagenette Imagewoof HGDNet 96.80 80.09 97.60 80.73 91.21 83.99 $ \text{Net}_{1} $ 96.60 79.39 97.53 78.99 90.80 82.01 $ \text{Net}_{2} $ 96.27 79.18 97.39 78.09 88.10 81.24 $ \text{Net}_{3} $ 88.90 78.02 94.33 77.01 86.90 79.71 表 7 各模型嵌入HGDConv前后的分类准确率(%)
Table 7 Classification accuracy of each model before and after embedding HGDConv (%)
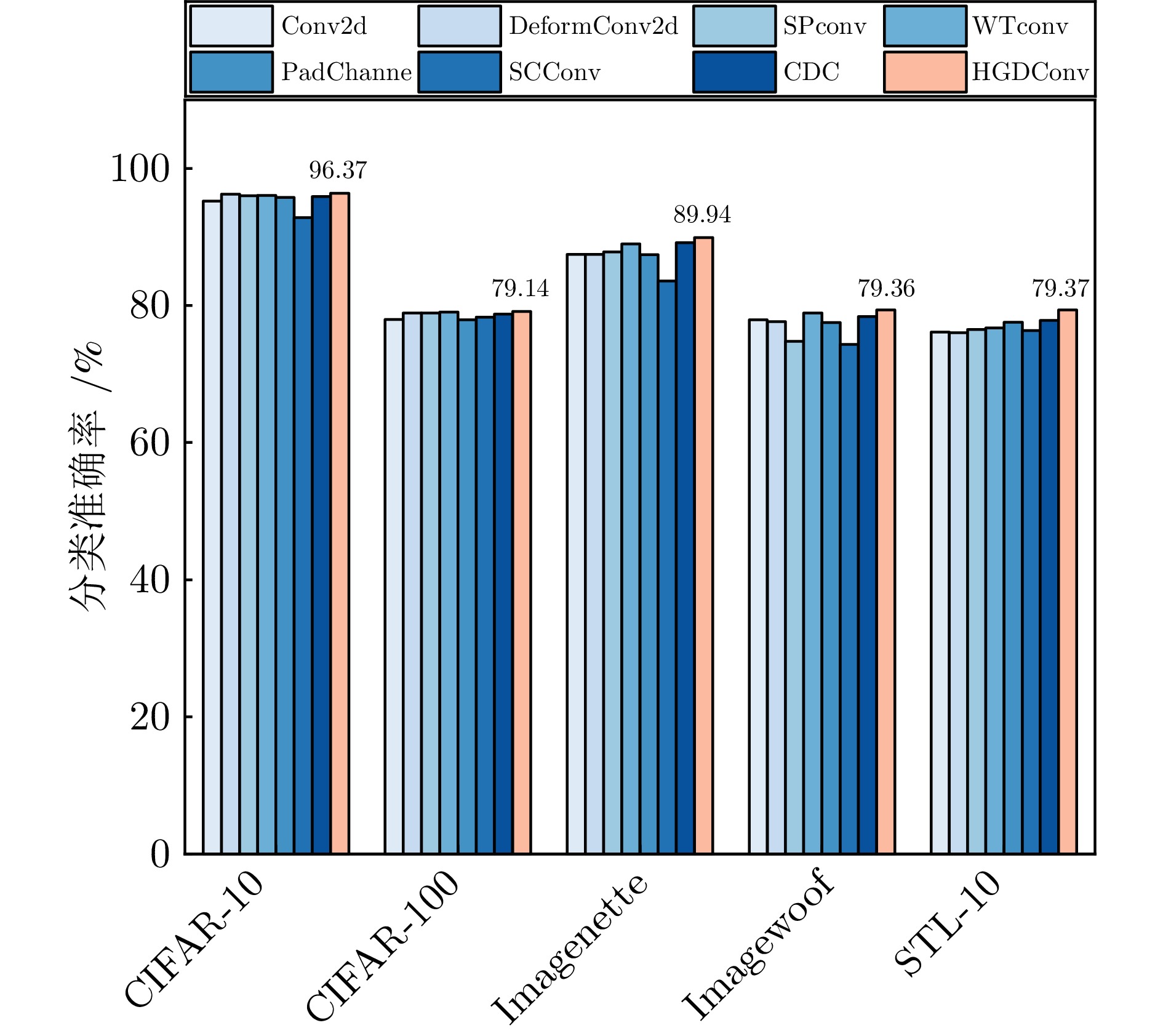
网络 分类准确率 CIFAR-10 CIFAR-100 SVHN Imagenette Imagewoof AlexNet — — 88.01 82.73 67.96 AlexNet- HGDConv — — 84.36 84.36 70.32 ShuffleNet 81.48 69.53 80.76 80.76 63.22 ShuffleNet- HGDConv 83.56 71.35 81.07 81.07 63.63 DenseNet201 83.67 75.45 97.86 83.46 77.48 DenseNet201- HGDConv 83.71 75.86 98.03 88.87 78.98 DenseNet169 83.88 76.21 97.99 83.90 77.86 DenseNet169- HGDConv 84.04 76.53 98.18 88.43 78.43 DenseNet121 83.73 76.58 98.21 86.55 78.32 DenseNet121- HGDConv 84.54 77.96 98.33 89.99 76.28 -
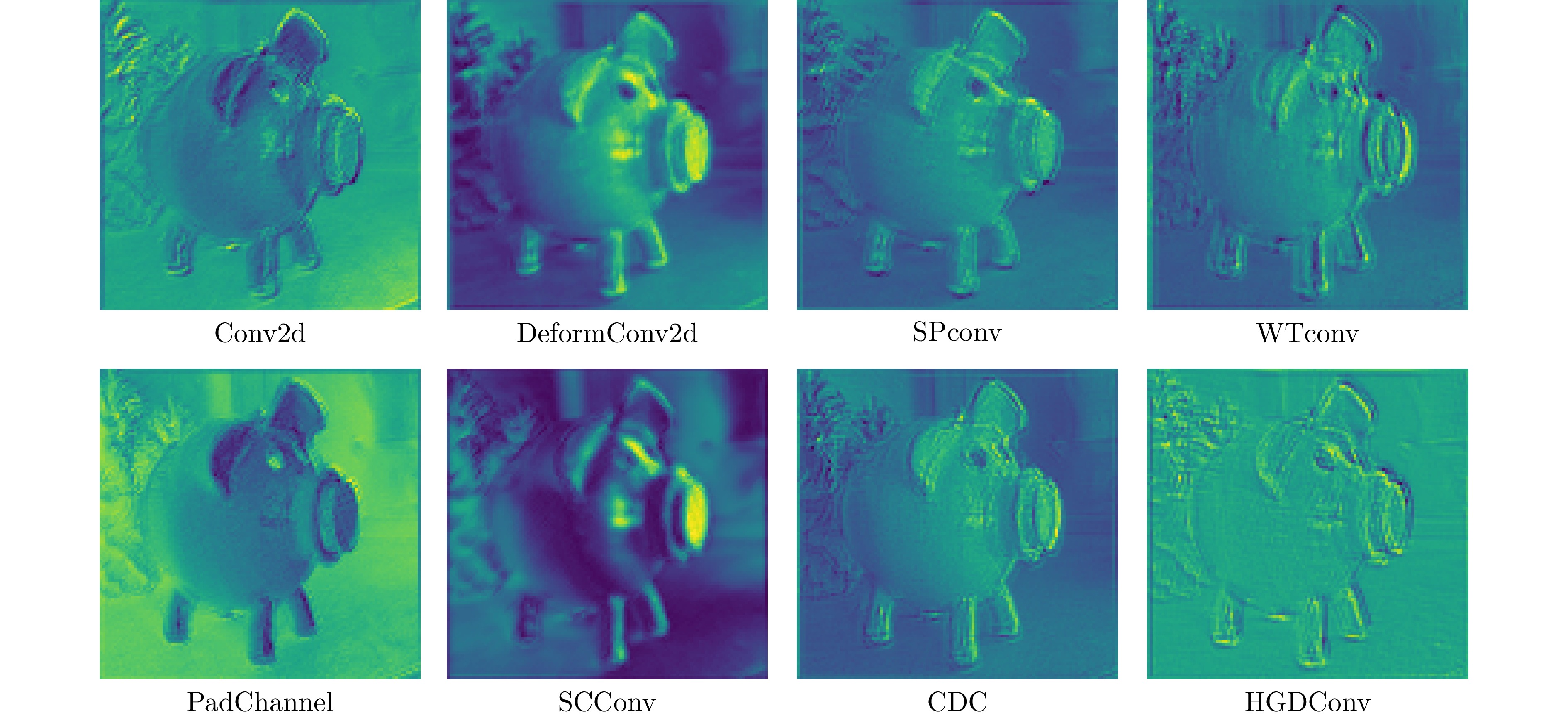
[1] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25. Lake Tahoe, NV, USA: Curran Associates, 2012. 1097−1105. [2] Simonyan K, Zissweman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, USA: ICLR, 2015. 1−14 [3] Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, et al. Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1−9 [4] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [5] Aldin S S, Aldin N B, Ayka M. Enhanced image classification using edge CNN (E-CNN). The Visual Computer, 2023, 40(1): 319−332 [6] Ye Z, Cao Z, Liu H, Liu H, Li W, Bai L, et al. Self-supervised learning with multiscale densely connected network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3424394 [7] Feng C, Jie Z, Zhong Y, Chu X, Ma L. AeDet: Azimuth-invariant multi-view 3-D object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2023. 21580−21588 [8] Kristiani E, Yang C T, Huang C Y. iSEC: An optimized deep learning model for image classification on edge computing. IEEE Access, DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2971566 [9] Huang G, Liu Z, van Der Maaten L, Weinberger K Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2261−2269 [10] Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, He K M, Hariharan B, Belongie S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1612.03144, 2016. [11] Fei Z, Fan M, Zhu L, Huang J, Wei X M, Wei X L. Masked auto-encoders meet generative adversarial networks and beyond. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2023. 24449−24459 [12] Xiao Y, Xu T, Yu X, Fang Y, Li J. A lightweight fusion strategy with enhanced interlayer feature correlation for small object detection. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3457155 [13] Ojala T, Pietikäinen M, Harwood D. Performance evaluation of texture measures with classification based on Kullback discrimination of distributions. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Jerusalem, Israel: IEEE, 1994. 582−585 [14] Juefei-Xu F, Boddeti V N, Savvides M. Local binary convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4284−4293 [15] Yu Z, Zhao C, Wang Z, Qin Y, Su Z, Li X, et al. Searching central difference convolutional networks for face anti-spoofing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2020. 5295−5305 [16] Chaple G, Daruwala R D. Design of Sobel-operator-based image edge detection algorithm on FPGA. In: Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Communications and Signal Processing. Melmaruvathur, India: IEEE, 2014. 788−792 [17] Chollet F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1800−1807 [18] Zagoruyko S, Komodakis N. Wide residual networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1605.07146, 2016. [19] Tan M, Le Q V. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Los Angeles, USA: PMLR, 2019.6105−6114 [20] Han K, Wang Y, Tian Q, Guo J, Xu C J, Xu C. GhostNet: More features from cheap operations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 165−174 [21] Lan H, Wang X, Wei X. Couplformer: Rethinking vision transformer with coupling attention map. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2112.05425, 2021. [22] Luo Z, Sun Z, Zhou W, Wu Z, Kamata S. Rethinking ResNets: Improved stacking strategies with high-order schemes for image classification. Complex and Intelligent Systems, 2022, 8(4): 3395−3407 doi: 10.1007/s40747-022-00671-3 [23] Abdi M, Nahavandi S. Multi-residual networks: improving the speed and accuracy of residual networks. arXiv: 1609.05672, 2016. [24] Wu X, Gao S, Zhang Z, Li Z, Bao R, Zhang Y, et al. Auto-train-once: Controller network guided automatic network pruning from scratch. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2024. 16163−16173 [25] Choromanski K M, Likhosherstov V, Dohan D, Song X Y, Gane A, Sarlás T, et al. Rethinking attention with performers. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2021. [26] Shin H, Choi D-W. Teacher as a lenient expert: Teacher-agnostic data-free knowledge distillation. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI, 2024. 14991−14999. [27] Zhang Y, Zhang S, Wang P, Zhu F, Guan D, Su J, et al. MLAAN: Scaling supervised local learning with augmented auxiliary networks. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Washington, USA: AAAI, 2025. 22686−22694 [28] Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M L, Zhmoginov A, Chen L C. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4510−4520 [29] Fu Y, Liu H, Zou Y, Wang S, Li Z, Zheng D, et al. Category-level band learning-based feature extraction for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3340517 [30] Bui N T, Hoang D H, Nguyen Q T, Tran M T, Le N. MEGANet: Multi-scale edge-guided attention network for weak-boundary polyp segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Waikoloa, HI, USA: IEEE, 2024. 7970−7979. [31] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 26th Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2012. 1097−1105 [32] Zhang X Y, Zhou X Y, Lin M X, Sun J. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 6848−6856 [33] Dai J F, Qi H Z, Xiong Y W, Li Y, Zhang G D, Hu H, et al. Deformable convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 764−773 [34] Zhang Q, Jiang Z, Lu Q, Han J, Zeng Z, Gao S, et al. Split to be slim: An overlooked redundancy in vanilla convolution. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2006.12085, 2020. [35] Finder S E, Amoyal R, Treister E, Freifeld O. Wavelet convolutions for large receptive fields. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2407.05848, 2024. [36] Kim J. PadChannel: Improving CNN performance through explicit padding encoding. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2311.07623, 2023. [37] Li J, Wen Y, He L. SCConv: Spatial and channel reconstruction convolution for feature redundancy. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Vancouver, BC, Canada: IEEE, 2023. 6153−6162 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 65
- HTML全文浏览量: 153
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: