Stochastic Optimal Control of a Class of Linear Systems with Input Delay and Multiplicative Noise
-
摘要: 研究存在未知系统动力学和输入时滞的乘性噪声系统线性二次最优控制问题. 当系统动力学完全已知时, 可以通过离线求解Riccati-ZXL方程获得最优反馈策略. 而当系统动力学不完全已知时, 离线求解Riccati-ZXL方程不再可行. 为此, 拟设计一种值迭代(value iteration, VI)算法来求解Riccati-ZXL方程, 该算法仅依赖可量测的状态和输入信息, 而不要求完全的系统动力学. 与策略迭代(policy iteration, PI)算法不同, 该算法消除了对初始策略稳定性的要求, 具有更强的适应性. 最后, 通过一个例子验证了所提算法的有效性.Abstract: The problem of linear quadratic optimal control for multiplicative noisy systems with unknown system dynamics and input time lags is investigated. When the system dynamics are completely known, the optimal feedback policy can be obtained by solving the Riccati-ZXL equations offline. However, when the system dynamics are not fully known, it is no longer feasible to solve the Riccati-ZXL equations offline. To this end, a value iteration (VI) algorithm is proposed to solve the Riccati-ZXL equations, which relies only on measurable states and inputs information and does not require full system dynamics. Unlike the policy iteration (PI) algorithm, this algorithm eliminates the requirement of initial policy stability and is more adaptable. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is verified by an example.
-
Key words:
- Optimal control /
- input delay /
- multiplicative noise /
- stochastic system
-
表 1 手臂运动模型参数
Table 1 Parameters of the arm movement model
参数 值 单位 $m$ 1.3 kg $b$ 10 Ns/m $\lambda$ 0.05 S $c_1$ 0.075 - $c_2$ 0.025 - $\chi$ 0.7 - 表 2 初始策略为(54)时, 时滞$d=2$时不同噪声强度VI与PI算法性能对比
Table 2 Performance comparison of the VI and PI algorithms for different noise levels but the delay $d=2$ and the initial strategy (54)
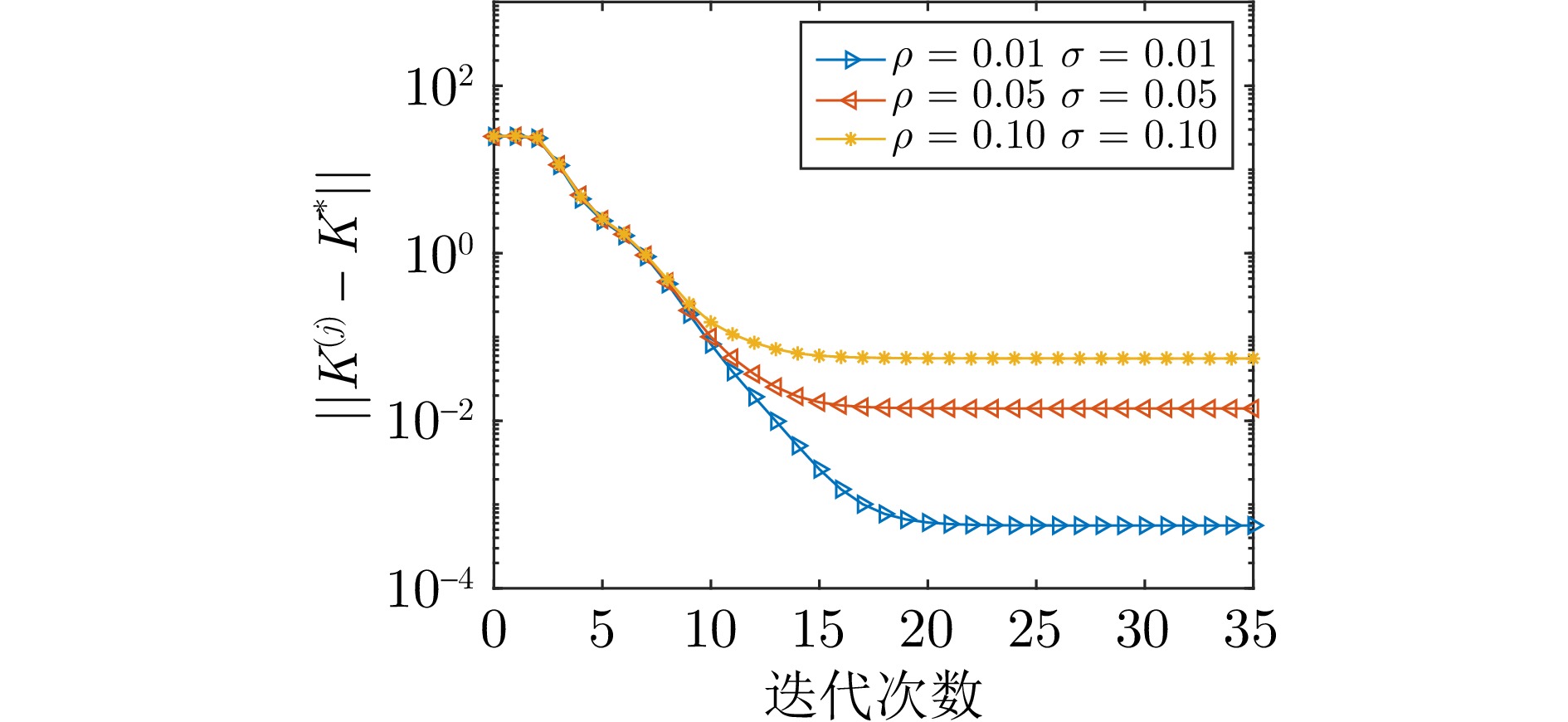
算法 噪声强度 收敛迭代次数 稳态误差$(||{{K}^{(j)}}-{{K}^*}||)$ VI算法 $\rho =0.01$,$\sigma =0.01$ 23 $5.7273\times10^{-4}$ PI算法 $\rho =0.01$,$\sigma =0.01$ 不收敛 不收敛 VI算法 $\rho =0.05$,$\sigma =0.05$ 24 0.0141 PI算法 $\rho =0.05$,$\sigma =0.05$ 不收敛 不收敛 VI算法 $\rho =0.10$,$\sigma =0.10$ 26 0.0559 PI算法 $\rho =0.10$,$\sigma =0.10$ 不收敛 不收敛 表 5 初始策略为(55)时, 噪声强度$\rho =0.01$, $\sigma =0.01$时不同时滞VI与PI算法性能对比
Table 5 Performance comparison of the VI and PI algorithms for different delays but the same noise intensities $\rho = 0.01$ and $\sigma = 0.01$ and the initial strategy (55)
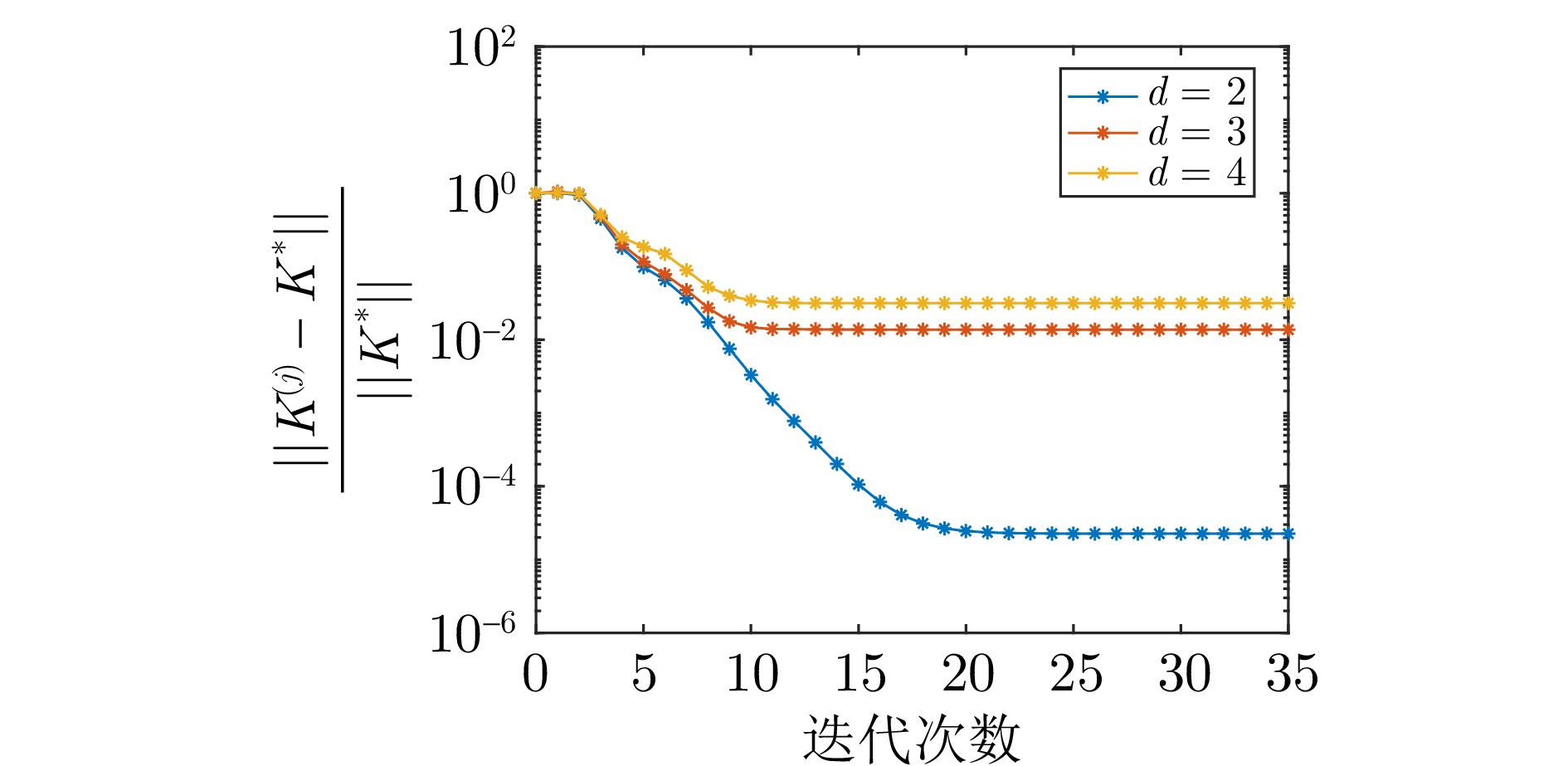
算法 噪声强度 收敛迭代次数 稳态误差$\big(\frac{||{{K}^{(j)}}-{{K}^*}||}{||{{K}^*}||}\big)$ VI算法 $d=2$ 29 $2.3014\times10^{-5}$ PI算法 $d=2$ 6 $7.8698\times10^{-6}$ VI算法 $d=3$ 29 0.0137 PI算法 $d=3$ 6 $1.4426\times10^{-5}$ VI算法 $d=4$ 45 0.0316 PI算法 $d=4$ 6 $1.7322\times10^{-5}$ 表 3 初始策略为(54)时, 噪声强度$\rho =0.01$,$\sigma =0.01$时不同时滞VI与PI算法性能对比
Table 3 Performance comparison of the VI and PI algorithms for different delays but the same noise intensities $\rho = 0.01$ and $\sigma = 0.01$ and the initial strategy (54)
算法 噪声强度 收敛迭代次数 稳态误差$\big(\frac{||{{K}^{(j)}}-{{K}^*}||}{||{{K}^*}||}\big)$ VI算法 $d=2$ 23 $2.3014\times10^{-4}$ PI算法 $d=2$ 不收敛 不收敛 VI算法 $d=3$ 23 0.0137 PI算法 $d=3$ 不收敛 不收敛 VI算法 $d=4$ 24 0.0316 PI算法 $d=4$ 不收敛 不收敛 表 4 初始策略为(55)时, 时滞$d=2$时不同噪声强度VI与PI算法性能对比
Table 4 Performance comparison of the VI and PI algorithms for different noise levels but the delay $d=2$ and the initial strategy (55)
算法 噪声强度 收敛迭代次数 稳态误差$(||{{K}^{(j)}}-{{K}^*}||)$ VI算法 $\rho =0.01$,$\sigma =0.01$ 37 $5.7273\times10^{-4}$ PI算法 $\rho =0.01$,$\sigma =0.01$ 6 $1.9585\times10^{-4}$ VI算法 $\rho =0.05$,$\sigma =0.05$ 37 0.0140 PI算法 $\rho =0.05$,$\sigma =0.05$ 6 0.0011 VI算法 $\rho =0.10$,$\sigma =0.10$ 40 0.0555 PI算法 $\rho =0.10$,$\sigma =0.10$ 6 0.0029 -
[1] Gershon E, Shaked U, Yaesh I. ${H_\infty}$ control and filtering of discrete-time stochastic systems with multiplicative noise. Automatica, 2001, 37(3): 409−417 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(00)00164-3 [2] El Ghaoui L. State-feedback control of systems with multiplicative noise via linear matrix inequalities. Systems & Control Letters, 1995, 24(3): 223−228 [3] 赵明旺. 乘性随机离散系统的最优控制. 自动化学报, 2003, 29(4): 633−640Zhao Ming-Wang. Optimal Control for Multiness Stochastic Discrete Systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2003, 29(4): 633−640 [4] Xing G J, Zhang C H, Cui P, Zhang H H. Indefinite LQ optimal control for systems with multiplicative noises: The incomplete information case. Advances in Computer Science, Intelligent System and Environment, 2011363−370 [5] Gravell B J, Esfahani P M, Summers T H. Robust control design for linear systems via multiplicative noise. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2020, 53(2): 7392−7399 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.1268 [6] Xu J J, Zhang H S. Open-loop decentralized LQ control problem with multiplicative noise. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2022, 9(4): 1887−1898 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2022.3181552 [7] Wang G C, Zhang H. Value iteration algorithm for continuous-time linear quadratic stochastic optimal control problems. Science China Information Sciences, 2024, 67(2): 122204 doi: 10.1007/s11432-023-3820-3 [8] Gravell B J, Esfahani P M, Summers T H. Learning optimal controllers for linear systems with multiplicative noise via policy gradient. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(11): 5283−5298 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3037046 [9] Wang H X, Liu Y H, Liu X Q. A Value Iteration Algorithm for Stochastic Linear Quadratic Regulator. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2025, 207(20): 1−14 [10] Yin Y B, Luo S X, Deng F Q. Stochastic ${H_2}$/ ${H_\infty}$ off-policy reinforcement learning tracking control for linear discrete-time systems with multiplicative noises. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2024107349 [11] Li H D, Li L Q, Li X, Zhang Z R. Reinforcement Learning for Stochastic LQ Control of Discrete-Time Systems with Multiplicative Noises. arxiv preprint, arxiv: 2311.12322, 2023 [12] Ye L W, Zhao Z G, Liu F. Stochastic LQ optimal control for Markov jumping systems with multiplicative noise using reinforcement learning. Systems & Control Letters, 2024, 186: 105765 [13] Pang B, Jiang Z P. Robust reinforcement learning for stochastic linear quadratic control with multiplicative noise. Trends in Nonlinear and Adaptive Control: a Tribute to Laurent Praly for his 65th Birthday. Berlin: Springer, 2022. 249-277 [14] 魏庆来, 张化光, 刘德荣, 赵琰. 基于自适应动态规划的一类带有时滞的离散时间非线性系统的最优控制策略. 自动化学报, 2010, 36(1): 121−129Wei Qing-Lai, Zhang Hua-Guang, Liu De-Rong, Zhao Yan. An optimal control scheme for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems with time delays using adaptive dynamic programming. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(1): 121−129 [15] Chen X Y, Sun W W, Gao X C, Liu Y S. Reinforcement learning-based event-triggered optimal control for unknown nonlinear systems with input delay. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2024, 34(7): 4844−4863 doi: 10.1002/rnc.7236 [16] Xu H, Jagannathan S, Lewis F L. Stochastic optimal control of unknown linear networked control system in the presence of random delays and packet losses. Automatica, 2012, 48(6): 1017−1030 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.03.007 [17] Wang H X, Zhao F Y, Zhang Z R, Xu J J, Li X. Solving optimal predictor-feedback control using approximate dynamic programming. Automatica, 2024, 170: 111848 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2024.111848 [18] Zhang H S, Li L, Xu J J, Fu M Y. Linear quadratic regulation and stabilization of discrete-time systems with delay and multiplicative noise. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(10): 2599−2613 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2411911 [19] Hewer G. An iterative technique for the computation of the steady state gains for the discrete optimal regulator. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1971, 16(4): 382−384 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1971.1099755 [20] Kleinman D. On an iterative technique for Riccati equation computations. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1968, 13(1): 114−115 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1968.1098829 [21] Zhang M, Gan M G, Chen J. Data-driven adaptive optimal control for stochastic systems with unmeasurable state. Neurocomputing, 2020, 397: 1−10 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.12.001 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 16
- HTML全文浏览量: 6
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: