Fast Enhancement Method for Underwater Images Based on Relative Total Variation Statistical Line
-
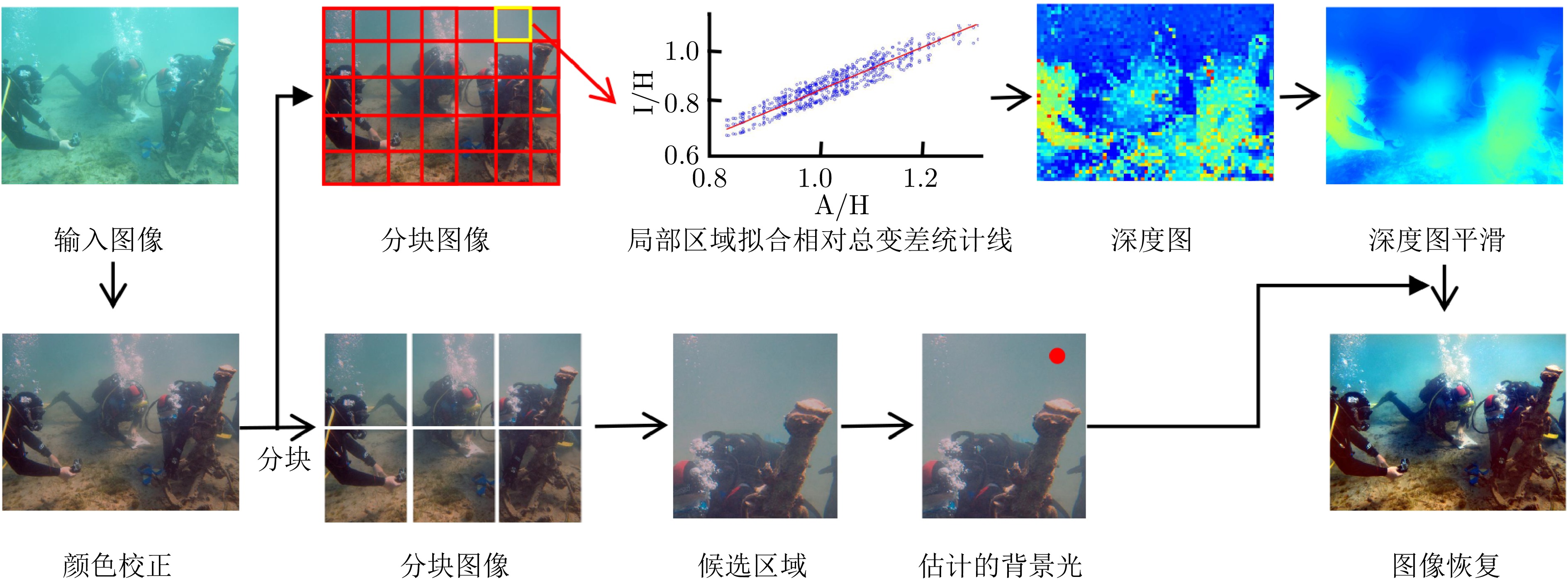
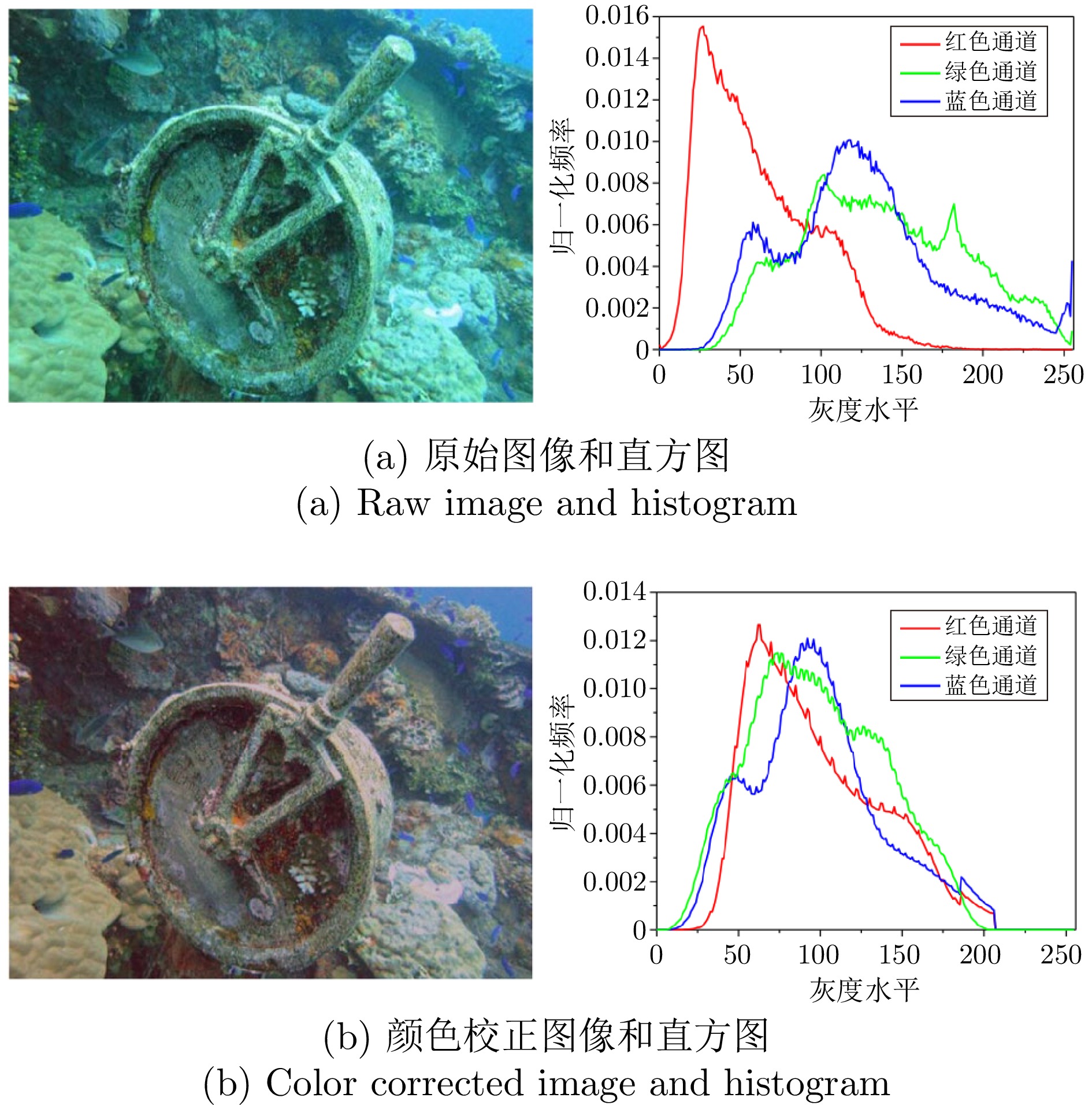
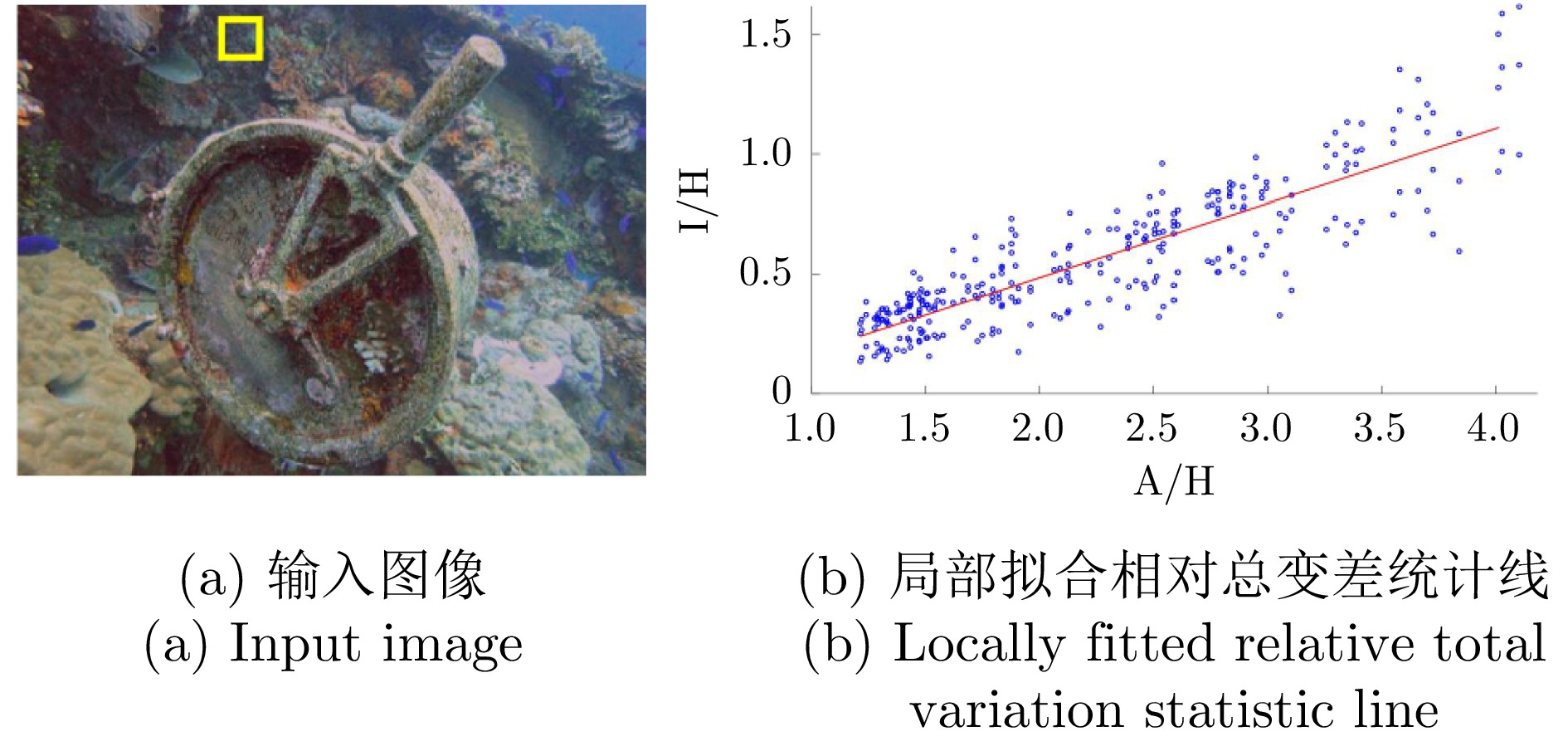
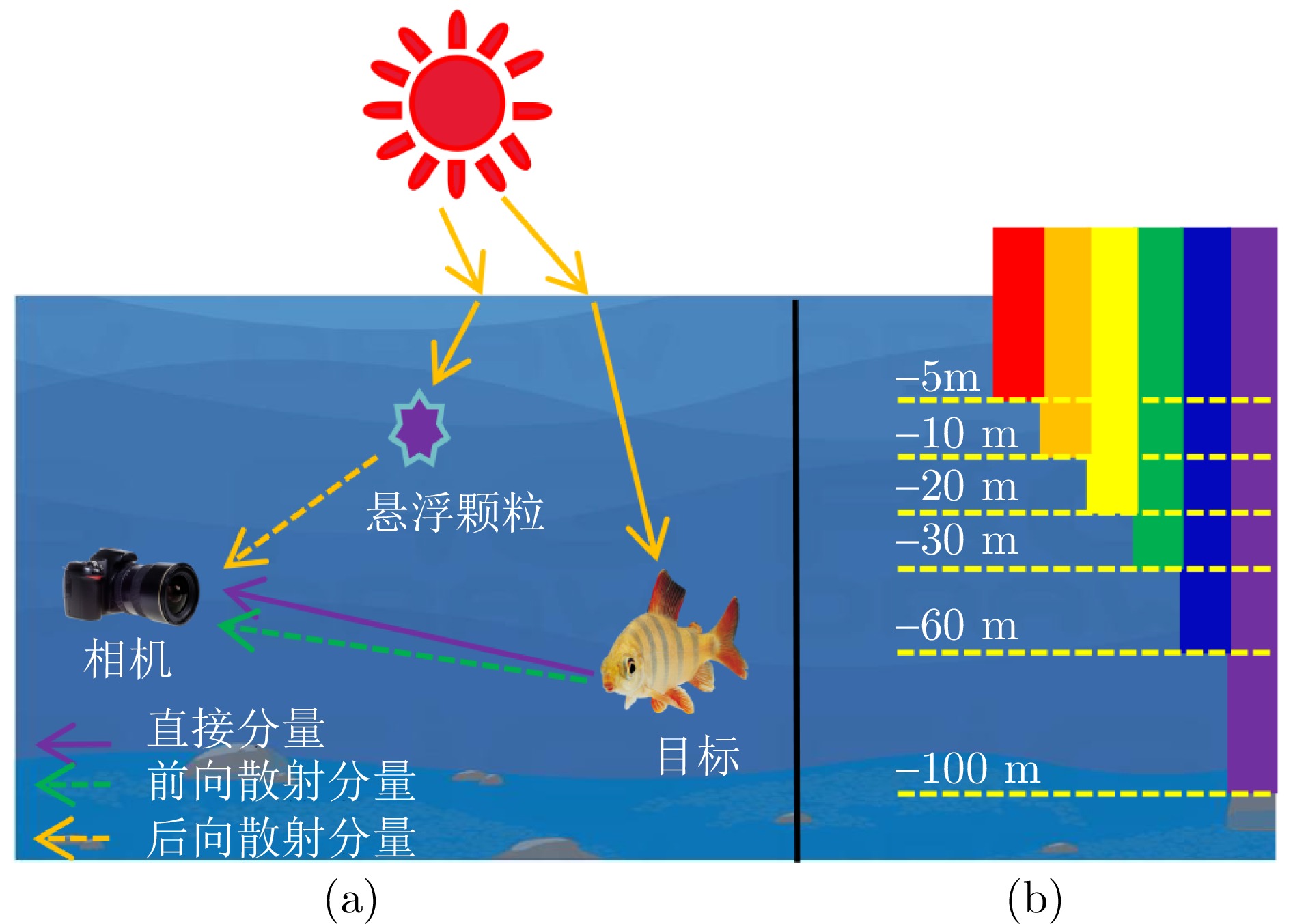
摘要: 针对水下采集的图像存在模糊、低对比度和颜色失真等低质量问题, 提出一种基于相对总变差统计线的水下图像快速增强方法. 首先, 采用线性拉伸的方法来校正图像的颜色信息, 消除颜色偏差并恢复图像的自然度. 其次, 基于大气散射模型, 结合图像的纹理信息构建水下图像的相对总变差统计线模型, 利用该模型准确估计图像深度图. 此外, 提出一种基于图像分块细分的水下背景光估计方法, 得到鲁棒的全局背景光估计值. 最后, 在估计的背景光和深度图基础上得到符合人眼感官视觉的水下增强图像. 实验结果表明, 所提方法不仅在主客观图像质量评价上具有明显优势, 而且在计算效率上优于现有的先进方法.Abstract: To address the low-quality issues such as blurring, low contrast and color distortion in underwater images, a fast enhancement method for underwater images based on relative total variation statistical line is proposed. First, linear stretching method is used to correct the color information in the image, eliminate color deviations and restore the image's natural appearance. Second, the relative total variation statistical line model of underwater images is constructed based on the atmospheric scattering model, combined with the texture information of the images, and the model is utilized to accurately estimate the image depth map. In addition, an underwater background light estimation method based on image chunk segmentation is proposed to obtain robust global background light estimation value. Finally, an enhanced underwater image conforming to the sensory vision of the human eye is obtained on the basis of the estimated background light and the estimated depth map. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method not only exhibits significant advantages in both subjective and objective image quality evaluation but also outperforms existing advanced methods in computational efficiency.
-
Key words:
- Underwater images /
- relative total variation /
- color correction /
- image enhancement /
- statistical line
-
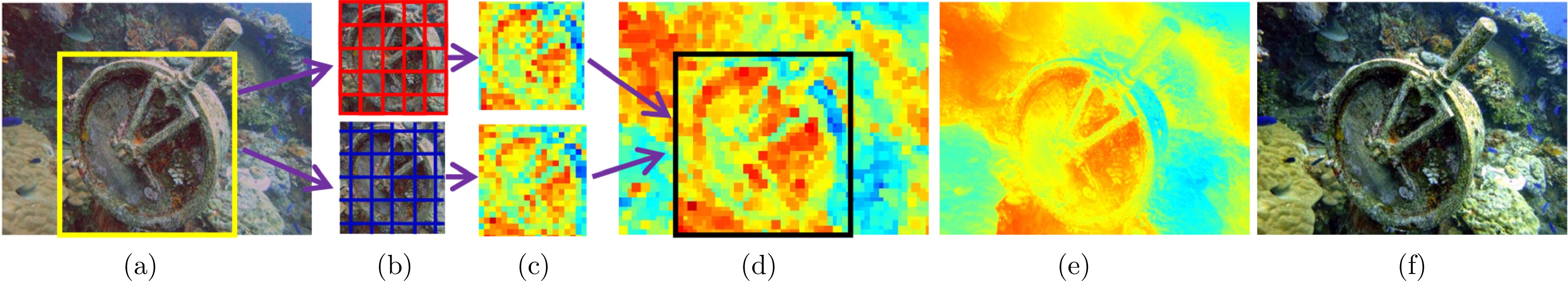
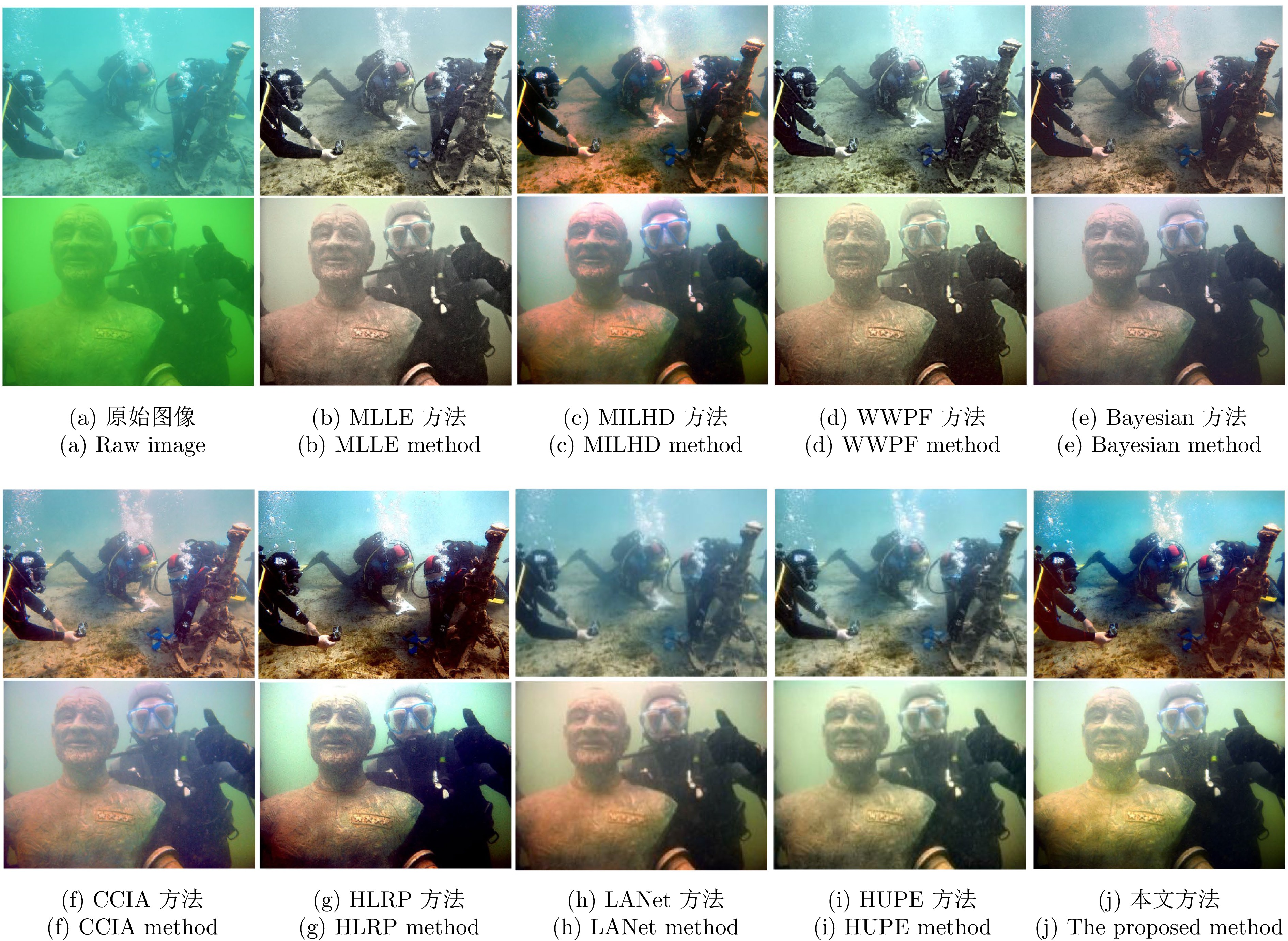
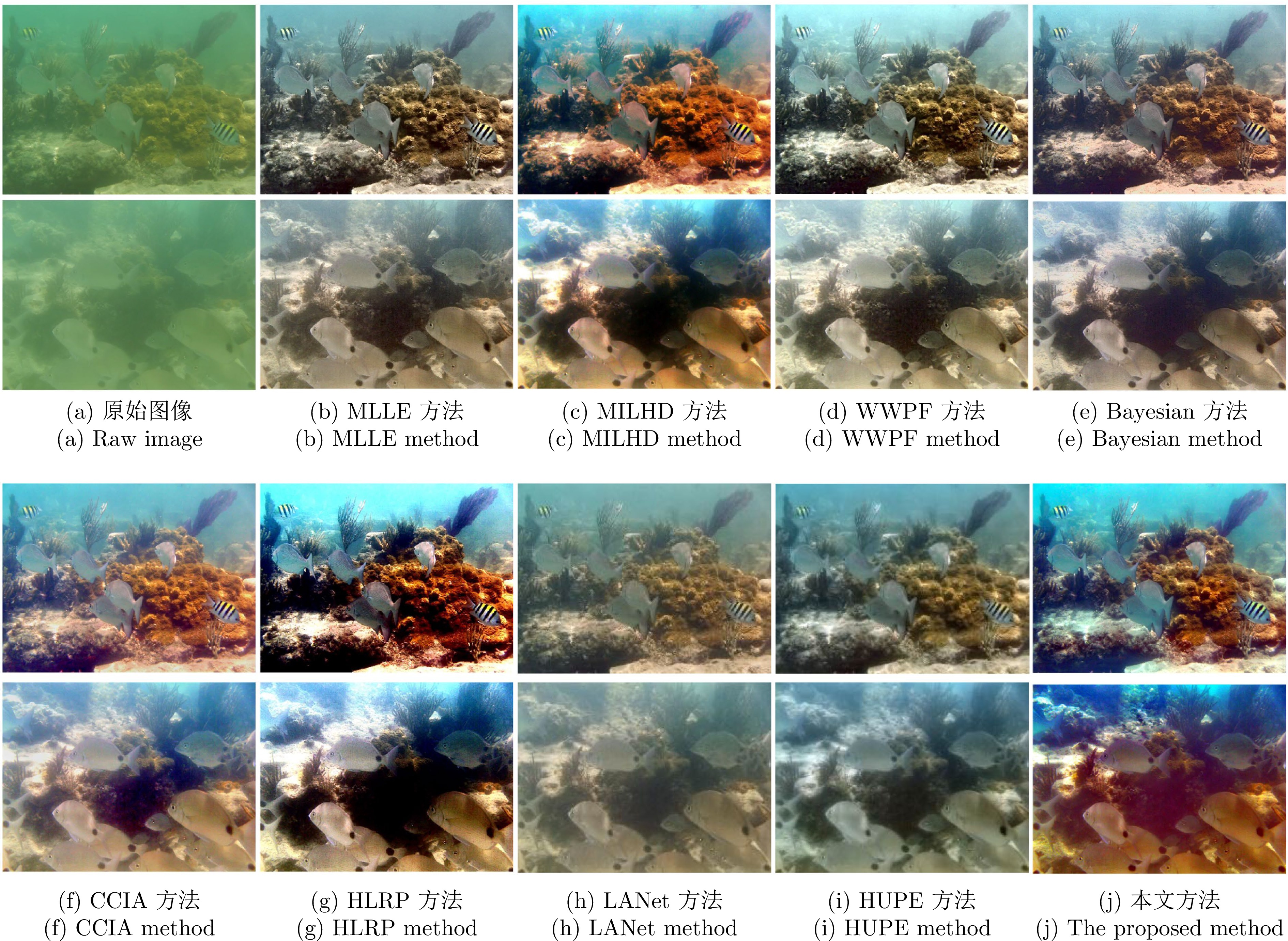
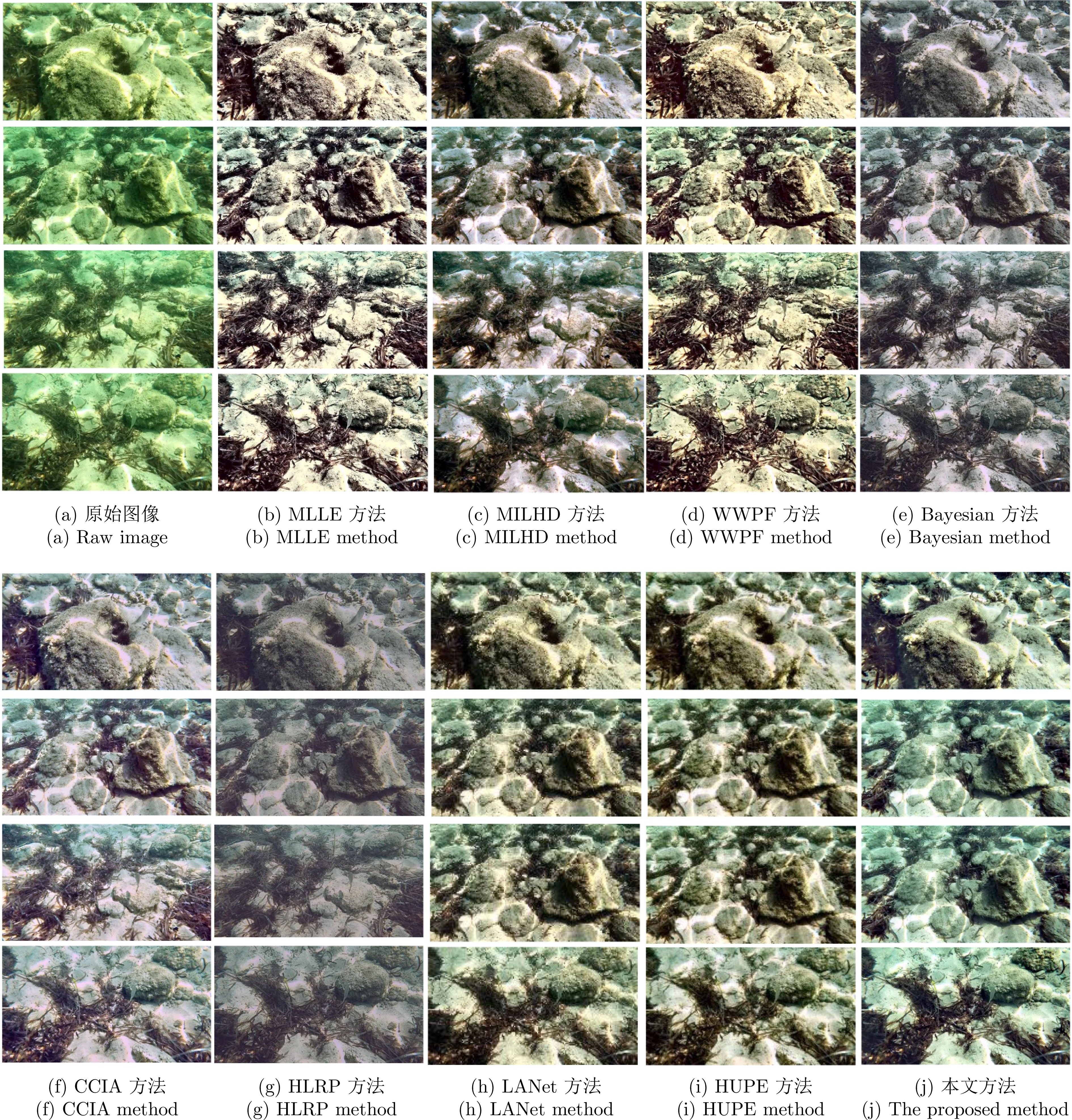
图 5 图像块的不同分割方法((a)输入图像; (b)不同图像分割方法; (c)不同图像分割方法下的深度图; (d)比较生成的深度图; (e)平滑的深度图; (f)增强图像)
Fig. 5 Different segmentation methods of image patches ((a) Input image; (b) Different image segmentation methods; (c) Depth maps for the different image segmentation methods; (d) Comparison of generated depth maps; (e) Smoothed depth maps; (f) Enhanced image)
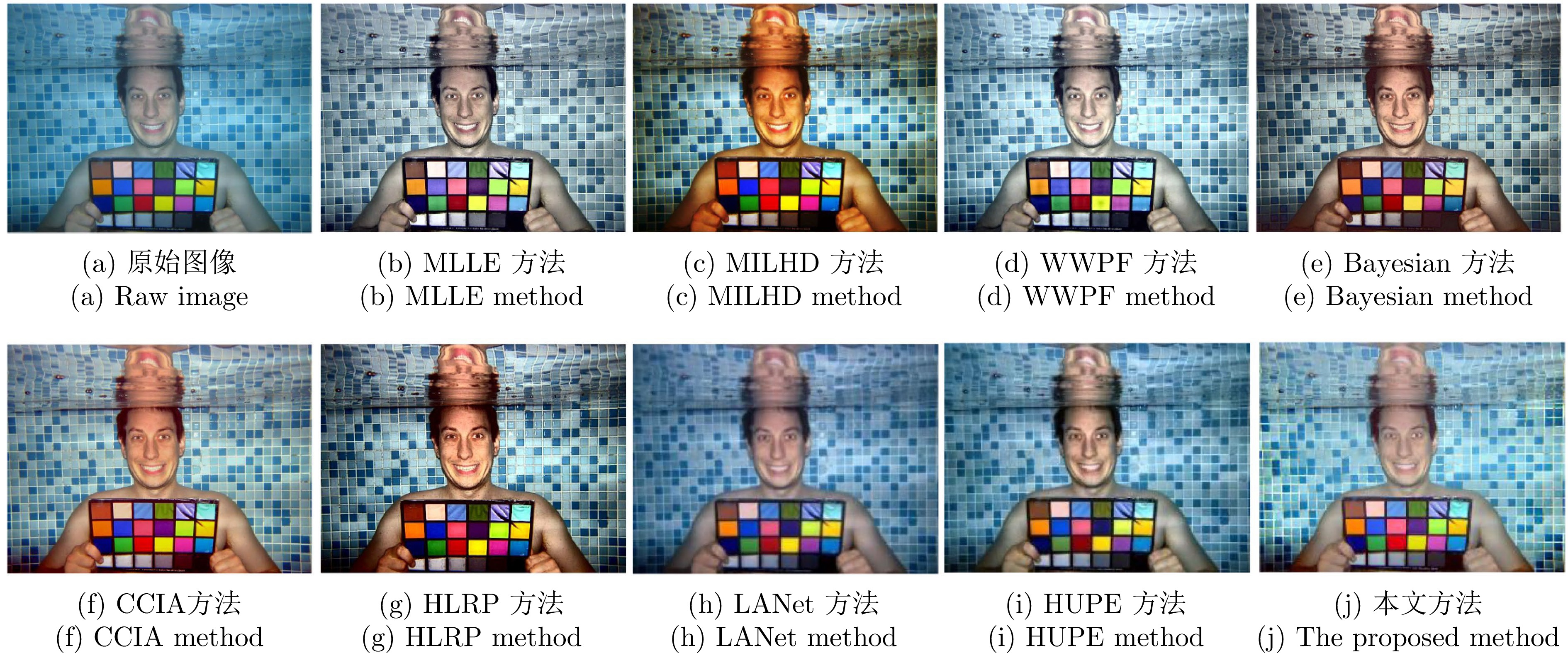
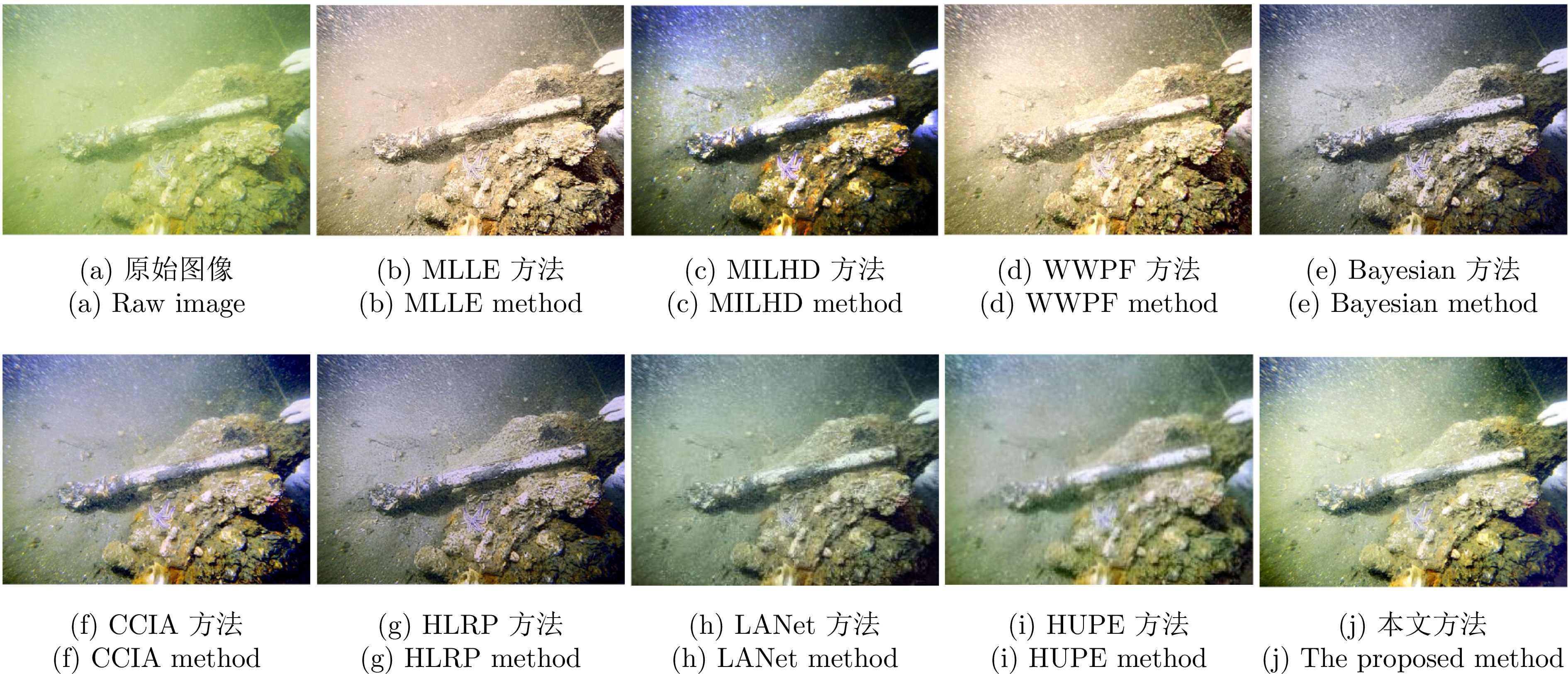
表 1 不同方法的UCIQE值
Table 1 UCIQE values for different methods
序号 原图 MLLE MILHD WWPF Bayesian CCIA HLRP LANet HUPE 本文方法 1 0.4306 0.6074 0.6569 0.6091 0.5773 0.6203 0.6613 0.5426 0.6007 0.6671 2 0.4230 0.5790 0.6505 0.5882 0.5527 0.5681 0.6419 0.6092 0.5893 0.6518 3 0.4136 0.6063 0.6736 0.6126 0.5962 0.6268 0.6630 0.5528 0.5849 0.6663 4 0.2889 0.6334 0.6528 0.6102 0.6286 0.6394 0.6531 0.3468 0.3266 0.6723 5 0.4258 0.6369 0.7027 0.6414 0.6116 0.6529 0.7037 0.5569 0.5983 0.6835 6 0.3683 0.5707 0.6918 0.5948 0.5873 0.6428 0.6849 0.5113 0.5597 0.6919 平均值 0.3917 0.6056 0.6714 0.6094 0.5923 0.6250 0.6680 0.5199 0.6301 0.6721 表 2 不同方法的UIQM值
Table 2 UIQM values for different methods
序号 原图 MLLE MILHD WWPF Bayesian CCIA HLRP LANet HUPE 本文方法 1 0.9615 4.8606 4.6098 3.9214 4.8805 4.4507 3.0289 3.1515 2.9627 4.9770 2 0.7860 4.4556 4.2190 4.5444 4.5228 4.1937 3.1469 4.7041 3.4857 4.7357 3 1.0822 3.7046 4.3577 3.3216 4.0716 4.0807 3.0612 2.9985 3.0857 4.3004 4 1.0064 4.4531 4.6104 3.8922 5.1354 4.4802 3.8992 1.8163 1.3638 4.5014 5 2.3545 4.9188 4.7103 4.0713 4.8579 4.4756 2.5404 4.0396 3.6857 4.6359 6 2.0476 4.9280 4.6299 4.4408 4.9191 4.5424 3.5872 3.8476 3.2337 5.4272 平均值 1.3730 4.5535 4.5228 4.0320 4.7312 4.3706 3.2106 3.4263 2.7806 4.7629 表 3 算法的运行时间比较(s)
Table 3 Comparison of algorithm runtime (s)
算法 运行时间 MLLE 1.85 MILHD 1.74 WWPF 1.61 Bayesian 1.28 CCIA 0.80 HLRP 1.35 本文方法 0.65 -
[1] Fu C P, Liu R S, Fan X, Chen P Y, Fu H, Yuan W Q, et al. Rethinking general underwater object detection: Datasets, challenges and solutions. Neurocomputing, 2023, 517(2023): 243−256 [2] Zhang W D, Zhou L, Zhuang P X, Li G H, Pan X P, Zhao W Y, et al. Underwater image enhancement via weighted wavelet visual perception fusion. IEEE Transactions on Circuits Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 34(4): 2469−2483 [3] 李庆忠, 白文秀, 牛炯. 基于改进CycleGAN的水下图像颜色校正与增强. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(4): 820−829Li Qing-Zhong, Bai Wen-Xiu, Niu Jiong. Underwater image color correction and enhancement based on improved cycle-consistent generative adversarial networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(4): 820−829 [4] Zhang W D, Dong L L, Zhang T, Xu W H. Enhancing underwater image via color correction and bi-interval contrast enhancement. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2021, 90(2021): 116030−116042 [5] Liu H M, Jin F, Zeng H, Pu H Y, Fan B. Image enhancement guided object detection in visually degraded scenes. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks Learning Systems, 2023, 35(10): 14164−14177 [6] Zhang W D, Wang Y D, Li C Y. Underwater image enhancement by attenuated color channel correction and detail preserved contrast enhancement. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2022, 47(3): 718−735 doi: 10.1109/JOE.2022.3140563 [7] Ulutas G, Ustubioglu B. Underwater image enhancement using contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization and layered difference representation. Multimedia Tools Applications, 2021, 80(2021): 15067−15091 [8] Hu Q, Zhong Y Z, Zhu Y Q, Zhong X K, Xiao Q, Dian S Y. Underwater image enhancement based on multichannel adaptive compensation. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation Measurement, 2024, 73(2024): 1−10 [9] Zhuang P X, Li C Y, Wu J M. Bayesian retinex underwater image enhancement. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 101(2021): 104171−104195 [10] Zhuang P X, Wu J M, Porikli F, Li C Y. Underwater image enhancement with hyper-laplacian reflectance priors. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31(2022): 5442−5455 [11] Zhou J C, Wang S Y, Lin Z F, Jiang Q P, Sohel F. A pixel distribution remapping and multi-prior retinex variational model for underwater image enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26(2024): 7838−7849 [12] Wang Y D, Guo J C, Gao H, Yue H H. UIEC2-Net: CNN-based underwater image enhancement using two color space. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2021, 96(2021): 116250−116261 [13] Huang Y F, Liu M Y, Yuan F. Color correction and restoration based on multi-scale recursive network for underwater optical image. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2021, 93(2021): 116174−116184 [14] Shen Z, Xu H Y, Luo T, Song Y, He Z Y. UDAformer: Underwater image enhancement based on dual attention transformer. Computers & Graphics, 2023, 111(2023): 77−88 [15] Zhang H Q, Sun L Y, Wu L F, Gu K. DuGAN: An effective framework for underwater image enhancement. IET Image Processing, 2021, 15(9): 2010−2019 doi: 10.1049/ipr2.12172 [16] Huang Z X, Li J J, Hua Z, Fan L W. Underwater image enhancement via adaptive group attention-based multiscale cascade transformer. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation Measurement, 2022, 71(2022): 1−18 [17] Bakht A B, Jia Z K, Din M U, Akram W, Saoud L S, Seneviratne L, et al. Mula-GAN: Multi-level attention GAN for enhanced underwater visibility. Ecological Informatics, 2024, 81(2024): 102631−102645 [18] Wang Z, Cun X, Bao J, Zhou W, Liu J, Li H. Uformer: A general U-shaped transformer for image restoration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2022. 17662−17672 [19] Wang B, Xu H Y, Jiang G Y, Yu M, Ren T D, Luo T, et al. UIE-Convformer: Underwater image enhancement based on convolution and feature fusion transformer. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2024, 8(2): 1952−1968 doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2024.3359061 [20] Qing Y H, Wang Y Y, Yan H C, Xie X P, Wu Z G. Unformer: A transformer-based approach for adaptive multi-scale feature aggregation in underwater image enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 6(4): 1024−1037 [21] He K M, Sun J, Tang X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis Machine Intelligence, 2010, 33(12): 2341−2353 [22] Zhang W B, Liu W D, Li L, Li J Y, Zhang M J, Li Y L. An adaptive color correction method for underwater single image haze removal. Signal Image Video Processing, 2022, 16(2022): 1003−1010 [23] Wu Q, Guo Y J, Hou J C, Yuan J J, Kong F, Lyu W H, et al. Underwater optical image processing based on double threshold judgements and optimized red dark channel prior method. Multimedia Tools Applications, 2021, 80(2021): 29985−30002 [24] Ding X Y, Liang Z, Wang Y F, Fu X P. Depth-aware total variation regularization for underwater image dehazing. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2021, 98(2021): 116408−116418 [25] Zhang T, Su H B, Fan B, Yang N, Zhong S, Yin J J. Underwater image enhancement based on red channel correction and improved multiscale fusion. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience Remote Sensing, 2024, 62(2024): 1−20 [26] Zhou Y, Wu Q, Yan K M, Feng L Y, Xiang W. Underwater image restoration using color-line model. IEEE Transactions on Circuits Systems for Video Technology, 2018, 29(3): 907−911 [27] Xu L, Yan Q, Xia Y, Jia J Y. Structure extraction from texture via relative total variation. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(6): 1−10 [28] Zhang W D, Zhuang P X, Sun H H, Li G H, Kwong S, Li C Y. Underwater image enhancement via minimal color loss and locally adaptive contrast enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31(2022): 3997−4010 [29] Li C Y, Guo J C, Cong R M, Pang Y W, Wang B. Underwater image enhancement by dehazing with minimum information loss and histogram distribution prior. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(12): 5664−5677 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2612882 [30] Zhang W H, Li G, Ying Z Q. A new underwater image enhancing method via color correction and illumination adjustment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing. St. Petersburg, FL, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1−4 [31] Liu S B, Fan H J, Lin S, Wang Q, Ding N D, Tang Y D. Adaptive learning attention network for underwater image enhancement. IEEE Robotics Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 5326−5333 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3156176 [32] Zhang Z X, Jiang Z Y, Ma L, Liu J Y, Fan X, Liu R S. HUPE: Heuristic underwater perceptual enhancement with semantic collaborative learning. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2025, 133(2025): 1−19 [33] Li C Y, Guo C L, Ren W Q, Cong R M, Hou J H, Kwong S, et al. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29(2019): 4376−4389 [34] Panetta K, Gao C, Agaian S. Human-visual-system-inspired underwater image quality measures. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2015, 41(3): 541−551 [35] Imamoglu N, Lin W S, Fang Y M. A saliency detection model using low-level features based on wavelet transform. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2012, 15(1): 96−105 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 117
- HTML全文浏览量: 92
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: