-
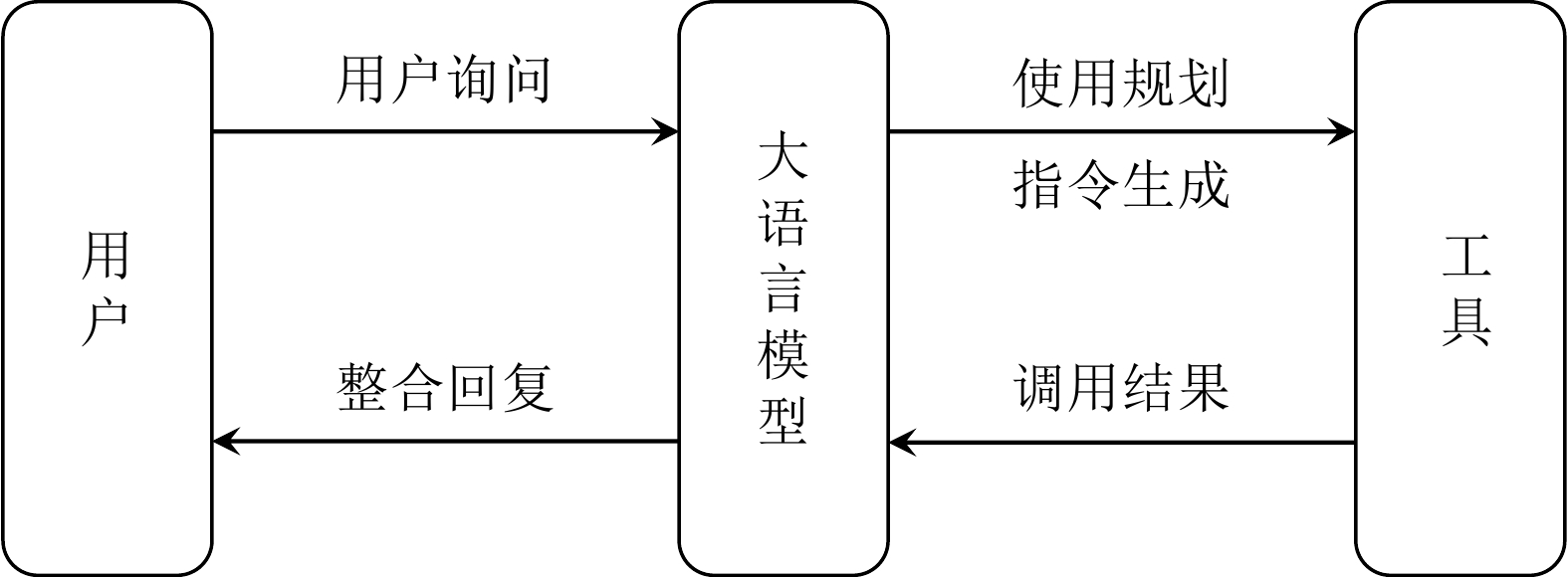
摘要: 大语言模型因其强大的生成和理解能力受到广泛关注, 但在获取实时信息和执行复杂计算上仍存在局限性. 为使其更好地响应用户需求, 赋予大语言模型工具使用能力成为当下的研究热点. 首先, 明确大语言模型工具使用的基本概念, 并按照时间顺序梳理工具使用的发展脉络. 随后, 总结与工具使用相关的数据集和技术方法, 并分析其在智能体和具身智能等领域的应用. 最后, 梳理大语言模型工具使用领域未来的研究重点与发展方向.Abstract: Large language models have garnered significant attention due to their strong generative and comprehension capabilities. However, they still face limitations in accessing real-time information and performing complex calculations. To better address user needs, empowering large language models with tool use capabilities has become a major topic of current research. Firstly, we clarify the fundamental concepts of tool use in large language models and then trace its developmental trajectory in chronological order. Subsequently, we summarize the datasets and technical approaches related to tool use, and analyze their applications in fields such as agent and embodied intelligence. Finally, we present an outlook on future research priorities and development directions in the field of tool use in large language models.
-
Key words:
- Large language models /
- tool use /
- tool-augmented generation /
- agent /
- embodied intelligence
-
表 1 大语言模型工具使用的发展
Table 1 The development of tool use in large language models
发布年份 名称 工具的类型 对话轮次 工具数量及关系 工具使用能力的获取方法 2022年 TALM[5] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 有监督微调 2022年 PAL[4] Python解释器 单次询问 多工具 情境学习 2023年 Toolformer[6] 接口式工具 单次询问 单工具 有监督微调 2023年 GPT4-Plugin[1] 接口式工具 多轮对话 多工具 有监督微调 + 强化学习 2023年 HuggingGPT[11] 神经网络模块 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 情境学习 2023年 ViperGPT[23] Python函数 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 情境学习 2023年 MOSS[7] 接口式工具 多轮对话 多工具 有监督微调 2023年 API-Bank[19] 接口式工具 多轮对话 多工具 有监督微调 2023年 APIBench[31] Python函数 单次询问 单工具 有监督微调 2023年 GPT4Tools[15] 神经网络模块 多轮对话 多工具 情境学习 2023年 ToolkenGPT[32] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 有监督微调 2023年 TRICE[18] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 有监督微调 + 强化学习 2023年 CRITIC[12] Python函数 单次询问 多工具 情境学习 2023年 LATM[24] Python函数 单次询问 单工具 情境学习 + 创建工具 2023年 CREATOR[25] Python函数 单次询问 多工具 情境学习 + 创建工具 2023年 ToolBench[17] 接口式工具 单次询问 单工具 情境学习 2023年 ToolAlpaca[20] 接口式工具 多轮对话 多工具 有监督微调 2023年 ToolLLM[14] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具 有监督微调 2023年 Confucius[33] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具 多阶段的有监督微调 2023年 ToRA[26] Python解释器 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 有监督微调 2023年 CRAFT[34] Python函数 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 情境学习 2023年 MetaTool[10] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具 情境学习 2023年 ToolChain[35] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具 情境学习 + 决策过程优化 2023年 ToolTalk[36] Python函数 多轮对话 多工具(含复杂关系) 情景学习 2023年 CLOVA[37] Python函数 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 情境学习 2023年 T-Eval[13] 接口式工具 多轮对话 多工具(含复杂关系) 情境学习 2024年 ToolEyes[38] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具 有监督微调 2024年 MLLM-Tool[39] 神经网络模块 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 有监督微调 2024年 TroVE[40] Python函数 单次询问 多工具 情境学习 + 创建工具 2024年 EasyTools[41] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具 情境学习 + 工具文档压缩 2024年 AnyTool[42] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具 情境学习 + 检索过程优化 2024年 SciToolBench[43] Python函数 单次询问 多工具 有监督微调 2024年 ToolRerank[44] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具 情境学习 + 检索过程优化 2024年 STE[16] 接口式工具 单次询问 单工具 有监督微调 + 对错误反馈处理 2024年 Seal-Tools[45] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 有监督微调 2024年 ToolPreference[46] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具 有监督微调 + 偏好优化 2024年 UltraTool[47] 接口式工具 多轮对话 多工具(含复杂关系) 情境学习 2024年 GTA[48] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 情境学习 2024年 Llama-3.1[8] 接口式工具 多轮对话 多工具 有监督微调 + 强化学习 2024年 AppWorld[27] 手机应用 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 情境学习 2024年 ShortcutsBench[28] 手机应用 单次询问 多工具 情境学习 2024年 ToolSandbox[29] 手机应用 多轮对话 多工具(含复杂关系) 有监督微调 2024年 ToolACE[2] 接口式工具 多轮对话 多工具(含复杂关系) 有监督微调 2024年 StepTool[49] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具 强化学习 2024年 MTU-Bench[50] 接口式工具 多轮对话 多工具(含复杂关系) 有监督微调 2024年 ToolGen[51] 接口式工具 单次询问 多工具 有监督微调 + 工具文档压缩 2024年 AndroidWorld[30] 手机应用 单次询问 多工具(含复杂关系) 情境学习 表 2 工具使用数据集概览
Table 2 The overview of tool use datasets
数据集 工具数量 数据数量 单轮 多轮 单工具 多工具 独立关系 依赖关系 嵌套关系 Toolformer[6] 5 12 500 √ × √ × × × × API-Bank[19] 2 211 2 202 √ √ √ √ √ × × APIBench[31] 11 645 16 450 √ × √ × × × × ToolBench[17] 232 2 764 √ × √ × × × × ToolAlpaca[20] 426 3 938 √ √ √ √ √ × × RestBench[56] 94 157 √ × √ × × × × ToolQA[57] 13 530 √ × √ √ √ × × ToolLLM[14] 16 464 126 486 √ × √ √ √ × × MetaTool[10] 199 21 127 √ × √ √ √ √ × TaskBench[58] 103 28 127 √ × √ √ √ √ × ToolTalk[36] 28 78 √ √ √ √ √ √ × T-Eval[13] 15 533 × √ × √ √ √ × ToolEyes[38] 568 382 √ × √ √ √ × × UltraTool[47] 2 032 5 824 √ × √ √ √ √ √ MLLM-Tool[39] 932 11 642 √ × √ √ √ × × SciToolBench[43] 2 446 856 √ × √ √ × √ × Seal-Tools[45] 4 076 14 076 √ × √ √ √ √ √ ShortcutsBench[28] 1 414 7 627 √ × √ √ √ × × GTA[48] 14 229 √ × √ √ √ √ × AppWorld[27] 457 750 √ × √ √ √ √ √ ToolSandbox[29] 34 1 032 √ √ √ √ √ √ × CToolEval[59] 398 6 816 √ × √ √ √ √ × ToolACE[2] 26 507 11 300 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ MTU-Bench[50] 136 159 061 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ -
[1] Achiam J, Adler S, Agarwal S, Ahmad L, Akkaya I, Aleman F L, et al. GPT-4 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2303.08774, 2024. [2] Liu W W, Huang X, Zeng X S, Hao X L, Yu S, Li D X, et al. ToolACE: Winning the points of LLM function calling. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2409.00920, 2024. [3] Abdelaziz I, Basu K, Agarwal M, Kumaravel S, Stallone M, Panda R, et al. Granite-function calling model: Introducing function calling abilities via multi-task learning of granular tasks. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Industry Track. Miami, USA: ACL, 2024. 1131−1139 [4] Gao L Y, Madaan A, Zhou S Y, Alon U, Liu P F, Yang Y M, et al. PAL: Program-aided language models. In: Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning. Honolulu, USA: PMLR, 2023. 10764−10799 [5] Parisi A, Zhao Y, Fiedel N. TALM: Tool augmented language models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2205.12255, 2022. [6] Schick T, Dwivedi-Yu J, Dessi R, Raileanu R, Lomeli M, Hambro E, et al. Toolformer: Language models can teach themselves to use tools. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. 68539−68551 [7] Sun T X, Zhang X T, He Z F, Li P, Cheng Q Y, Liu X Y, et al. MOSS: An open conversational large language model. Machine Intelligence Research, 2024, 21(5): 888−905 doi: 10.1007/s11633-024-1502-8 [8] Grattafiori A, Dubey A, Jauhri A, Pandey A, Kadian A, Al-Dahle A, et al. The llama 3 herd of models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2407.21783, 2024. [9] Qwen Team. QwQ-32B: Embracing the power of reinforcement learning [Online], available: https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwq-32b/, May 14, 2025 [10] Huang Y, Shi J W, Li Y, Fan C R, Wu S Y, Zhang Q H, et al. MetaTool benchmark for large language models: Deciding whether to use tools and which to use. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. [11] Shen Y L, Song K T, Tan X, Li D S, Lu W M, Zhuang Y T. HuggingGPT: Solving AI tasks with ChatGPT and its friends in hugging face. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 1657 [12] Gou Z B, Shao Z H, Gong Y Y, Shen Y L, Yang Y J, Duan N, et al. CRITIC: Large language models can self-correct with tool-interactive critiquing. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. [13] Chen Z H, Du W H, Zhang W W, Liu K K, Liu J N, Zheng M, et al. T-eval: Evaluating the tool utilization capability of large language models step by step. In: Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Bangkok, Thailand: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2024. 9510−9529 [14] Qin Y J, Liang S H, Ye Y N, Zhu K L, Yan L, Lu Y X, et al. ToolLLM: Facilitating large language models to master 16000+ real-world APIs. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. [15] Yang R, Song L, Li Y W, Zhao S J, Ge Y X, Li X, et al. GPT4Tools: Teaching large language model to use tools via self-instruction. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 3149 [16] Wang B S, Fang H, Eisner J, van Durme B, Su Y. LLMs in the imaginarium: Tool learning through simulated trial and error. In: Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Bangkok, Thailand: ACL, 2024. 10583−10604 [17] Xu Q T, Hong F L, Li B, Hu C R, Chen Z Y, Zhang J. On the tool manipulation capability of open-source large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2305.16504, 2023. [18] Qiao S F, Gui H H, Lv C F, Jia Q H, Chen H J, Zhang N Y. Making language models better tool learners with execution feedback. In: Proceedings of the Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Volume 1: Long Papers). Mexico City, Mexico: ACL, 2024. 3550−3568 [19] Li M H, Zhao Y X, Yu B W, Song F F, Li H Y, Yu H Y, et al. API-bank: A comprehensive benchmark for tool-augmented LLMs. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Singapore, Singapore: ACL, 2023. 3102−3116 [20] Tang Q Y, Deng Z L, Lin H Y, Han X P, Liang Q, Cao B X, et al. ToolAlpaca: Generalized tool learning for language models with 3000 simulated cases. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2306.05301, 2023. [21] Raffel C, Shazeer N, Roberts A, Lee K, Narang S, Matena M, et al. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2020, 21(1): Article No. 140 [22] Chen M, Tworek J, Jun H W, Yuan Q M, de Oliveira Pinto H P, Kaplan J, et al. Evaluating large language models trained on code. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2107.03374, 2021. [23] Surís D, Menon S, Vondrick C. ViperGPT: Visual inference via python execution for reasoning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Paris, France: IEEE, 2023. 11854−11864 [24] Cai T L, Wang X Z, Ma T Y, Chen X Y, Zhou D. Large language models as tool makers. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. [25] Qian C, Han C, Fung Y, Qin Y J, Liu Z Y, Ji H. CREATOR: Tool creation for disentangling abstract and concrete reasoning of large language models. In: Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023. Singapore, Singapore: ACL, 2023. 6922−6939 [26] Gou Z B, Shao Z H, Gong Y Y, Shen Y L, Yang Y J, Huang M L, et al. ToRA: A tool-integrated reasoning agent for mathematical problem solving. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. [27] Trivedi H, Khot T, Hartmann M, Manku R, Dong V, Li E, et al. AppWorld: A controllable world of apps and people for benchmarking interactive coding agents. In: Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). Bangkok, Thailand: ACL, 2024. 16022−16076 [28] Shen H Y, Li Y, Meng D S, Cai D Q, Qi S, Zhang L, et al. ShortcutsBench: A large-scale real-world benchmark for API-based agents. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations. Singapore, Singapore: OpenReview.net, 2025. [29] Lu J R, Holleis T, Zhang Y Z, Aumayer B, Nan F, Bai H P, et al. ToolSandbox: A stateful, conversational, interactive evaluation benchmark for LLM tool use capabilities. In: Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: NAACL 2025. Albuquerque, USA: ACL, 2025. 1160−1183 [30] Rawles C, Clinckemaillie S, Chang Y F, Waltz J, Lau G, Fair M, et al. AndroidWorld: A dynamic benchmarking environment for autonomous agents. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations. Singapore, Singapore: OpenReview.net, 2025. [31] Patil S G, Zhang T J, Wang X, Gonzalez J E. Gorilla: Large language model connected with massive APIs. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: NeurIPS, 2024. [32] Hao S B, Liu T Y, Wang Z, Hu Z T. ToolkenGPT: Augmenting frozen language models with massive tools via tool embeddings. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 1988 [33] Gao S, Shi Z L, Zhu M H, Fang B W, Xin X, Ren P J, et al. Confucius: Iterative tool learning from introspection feedback by easy-to-difficult curriculum. In: Proceedings of the 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI Press, 2024. 18030−18038 [34] Yuan L F, Chen Y Y, Wang X Y, Fung Y, Peng H, Ji H. CRAFT: Customizing LLMs by creating and retrieving from specialized toolsets. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. [35] Zhuang Y C, Chen X, Yu T, Mitra S, Bursztyn V, Rossi R A, et al. ToolChain*: Efficient action space navigation in large language models with A* search. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. [36] Farn N, Shin R. ToolTalk: Evaluating tool-usage in a conversational setting. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2311.10775, 2023. [37] Gao Z, Du Y T, Zhang X T, Ma X J, Han W, Zhu S C, et al. CLOVA: A closed-loop visual assistant with tool usage and update. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 13258−13268 [38] Ye J J, Li G Y, Gao S Y, Huang C S, Wu Y L, Li S X, et al. ToolEyes: Fine-grained evaluation for tool learning capabilities of large language models in real-world scenarios. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Computational Linguistics. Abu Dhabi, UAE: ACL, 2025. 156−187 [39] Wang C Y, Luo W X, Dong S X, Xuan X H, Li Z X, Ma L, et al. MLLM-Tool: A multimodal large language model for tool agent learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Tucson, USA: IEEE, 2025. 6678−6687 [40] Wang Z R, Neubig G, Fried D. TroVE: Inducing verifiable and efficient toolboxes for solving programmatic tasks. In: Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. [41] Yuan S Y, Song K T, Chen J J, Tan X, Shen Y L, Ren K, et al. EASYTOOL: Enhancing LLM-based agents with concise tool instruction. In: Proceedings of the ICLR Workshop on Large Language Model (LLM) Agents. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. [42] Du Y, Wei F Y, Zhang H Y. AnyTool: Self-reflective, hierarchical agents for large-scale API calls. In: Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. [43] Ma Y B, Gou Z B, Hao J H, Xu R C, Wang S H, Pan L M, et al. SciAgent: Tool-augmented language models for scientific reasoning. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Miami, USA: ACL, 2024. 15701−15736 [44] Zheng Y H, Li P, Liu W, Liu Y, Luan J, Wang B. ToolRerank: Adaptive and hierarchy-aware reranking for tool retrieval. In: Proceedings of the Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024). Torino, Italia: ACL, 2024. 16263−16273 [45] Wu M S, Zhu T, Han H, Tan C Y, Zhang X, Chen W L. Seal-tools: Self-instruct tool learning dataset for agent tuning and detailed benchmark. In: Proceedings of the 13th National CCF Conference on Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing. Hangzhou, China: Springer, 2024. 372−384 [46] Chen S J, Wang Y B, Wu Y F, Chen Q G, Xu Z, Luo W H, et al. Advancing tool-augmented large language models: Integrating insights from errors in inference trees. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: NeurIPS, 2024. [47] Huang S J, Zhong W J, Lu J Q, Zhu Q, Gao J H, Liu W W, et al. Planning, creation, usage: Benchmarking LLMs for comprehensive tool utilization in real-world complex scenarios. In: Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2024. Bangkok, Thailand: ACL, 2024. 4363−4400 [48] Wang J Z, Ma Z R, Li Y N, Zhang S Y, Chen C L, Chen K, et al. GTA: A benchmark for general tool agents. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: NeurIPS, 2024. [49] Yu Y Q, Wang Z F, Ma W Z, Guo Z C, Zhan J T, Wang S, et al. StepTool: A step-grained reinforcement learning framework for tool learning in LLMs. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2410.07745, 2024. [50] Wang P, Wu Y N, Wang N, Liu J H, Song X S, Peng Z Y, et al. MTU-Bench: A multi-granularity tool-use benchmark for large language models. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations. Singapore, Singapore: OpenReview.net, 2025. [51] Wang R X, Han X D, Ji L, Wang S, Baldwin T, Li H N. ToolGen: Unified tool retrieval and calling via generation. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations. Singapore, Singapore: OpenReview.net, 2025. [52] RapidAPI. RapidAPI: A platform for discovering and connecting to APIs [Online], available: https://rapidapi.com/, May 15, 2024 [53] Georgiev P, Lei V I, Burnell R, Bai L B, Gulati A, Tanzer G, et al. Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2403.05530, 2024. [54] Yang A, Yang B S, Hui B Y, Zheng B, Yu B W, Zhou C, et al. Qwen2 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2407.10671, 2024. [55] Zhu Q H, Guo D Y, Shao Z H, Yang D J, Wang P Y, Xu R X, et al. DeepSeek-coder-V2: Breaking the barrier of closed-source models in code intelligence. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2406.11931, 2024. [56] Song Y F, Xiong W M, Zhu D W, Wu W H, Qian H, Song M B, et al. RestGPT: Connecting large language models with real-world RESTful APIs. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2306.06624, 2023. [57] Zhuang Y C, Yu Y, Wang K, Sun H T, Zhang C. ToolQA: A dataset for LLM question answering with external tools. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 2180 [58] Shen Y L, Song K T, Tan X, Zhang W Q, Ren K, Yuan S Y, et al. TaskBench: Benchmarking large language models for task automation. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: NeurIPS, 2024. [59] Guo Z S, Huang Y F, Xiong D Y. CToolEval: A Chinese benchmark for LLM-powered agent evaluation in real-world API interactions. In: Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2024. Bangkok, Thailand: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2024. 15711−15724 [60] Basu K, Abdelaziz I, Chaudhury S, Dan S, Crouse M, Munawar A, et al. API-BLEND: A comprehensive corpora for training and benchmarking API LLMs. In: Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). Bangkok, Thailand: ACL, 2024. 12859−12870 [61] Wang H R, Wang R, Xue B Y, Xia H M, Cao J T, Liu Z M, et al. AppBench: Planning of multiple APIs from various APPs for complex user instruction. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Miami, USA: ACL, 2024. 15322−15336 [62] Wang W X, Shi J L, Wang C Z, Lee C, Yuan Y L, Huang J T, et al. Learning to ask: When LLMs meet unclear instruction. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2409.00557, 2024. [63] Ye J J, Li S X, Li G Y, Huang C S, Gao S Y, Wu Y L, et al. ToolSword: Unveiling safety issues of large language models in tool learning across three stages. In: Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). Bangkok, Thailand: ACL, 2024. 2181−2211 [64] Ye J J, Wu Y L, Gao S Y, Huang C S, Li S X, Li G Y, et al. RoTBench: A multi-level benchmark for evaluating the robustness of large language models in tool learning. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Miami, USA: ACL, 2024. 313−333 [65] Guo Z C, Cheng S J, Wang H, Liang S H, Qin Y J, Li P, et al. StableToolBench: Towards stable large-scale benchmarking on tool learning of large language models. In: Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2024. Bangkok, Thailand: ACL, 2024. 11143−11156 [66] Papineni K, Roukos S, Ward T, Zhu W J. BLEU: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Philadelphia, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2002. 311−318 [67] Lin C Y. ROUGE: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: Proceedings of the Text Summarization Branches Out. Barcelona, Spain: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2004. 74−81 [68] Bergroth L, Hakonen H, Raita T. A survey of longest common subsequence algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on String Processing and Information Retrieval. SPIRE 2000. A Curuna, Spain: IEEE, 2000. 39−48 [69] Liu Y M, Peng X Y, Zhang Y W, Cao J N, Zhang X H, Cheng S, et al. Tool-planner: Dynamic solution tree planning for large language model with tool clustering. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2406.03807, 2024. [70] Qiao S F, Fang R N, Qiu Z S, Wang X B, Zhang N Y, Jiang Y, et al. Benchmarking agentic workflow generation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2410.07869, 2024. [71] OpenMOSS. UnifiedToolHub [Online], available: https://github.com/OpenMOSS/UnifiedToolHub, May 14, 2025 [72] Zhou S Y, Xu F F, Zhu H, Zhou X H, Lo R, Sridhar A, et al. WebArena: A realistic web environment for building autonomous agents. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. [73] Kim G, Baldi P, McAleer S. Language models can solve computer tasks. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 1723 [74] Liu Y L, Yuan Y L, Wang C W, Han J H, Ma Y Q, Zhang L, et al. From summary to action: Enhancing large language models for complex tasks with open world APIs. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2402.18157, 2024. [75] Liu X, Qin B, Liang D Z, Dong G, Lai H Y, Zhang H C, et al. AutoGLM: Autonomous foundation agents for GUIs. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2411.00820, 2024. [76] Qi Z H, Liu X, Iong I L, Lai H Y, Sun X Q, Sun J D, et al. WebRL: Training LLM web agents via self-evolving online curriculum reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations. Singapore, Singapore: OpenReview.net, 2025. [77] Wu Q Z, Liu W, Luan J, Wang B. ToolPlanner: A tool augmented LLM for multi granularity instructions with path planning and feedback. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Miami, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2024. 18315−18339 [78] Chen K, Cusumano-Towner M, Huval B, Petrenko A, Hamburger J, Koltun V, et al. Reinforcement learning for long-horizon interactive LLM agents. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2502.01600, 2025. [79] Kong Y L, Ruan J Q, Chen Y H, Zhang B, Bao T P, Shiwei S, et al. TPTU-v2: Boosting task planning and tool usage of large language model-based agents in real-world industry systems. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Industry Track. Miami, US: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2024. 371−385 [80] Liu X K, Peng Z Y, Yi X Y, Xie X, Xiang L R, Liu Y C, et al. ToolNet: Connecting large language models with massive tools via tool graph. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2403.00839, 2024. [81] Huang W L, Abbeel P, Pathak D, Mordatch I. Language models as zero-shot planners: Extracting actionable knowledge for embodied agents. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore, USA: PMLR, 2022. 9118−9147 [82] Xu H S, Zhu S, Wang Z H, Zheng H, Ma D, Cao R S, et al. Reducing tool hallucination via reliability alignment. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2412.04141, 2024. [83] Xu G W, Jin P, Li H, Song Y B, Sun L C, Yuan L. LLaVA-CoT: Let vision language models reason step-by-step. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2411.10440, 2024. [84] Koh J Y, McAleer S, Fried D, Salakhutdinov R. Tree search for language model agents. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2407.01476, 2024. [85] Chen P, Bu P, Song J, Gao Y, Zheng B. Can VLMs play action role-playing games? Take black myth Wukong as a study case. In: Proceedings of the NeurIPS Workshop on Open-World Agents. Vancouver, Canada: NeurIPS, 2024. [86] Nakano R, Hilton J, Balaji S, Wu J, Ouyang L, Kim C, et al. WebGPT: Browser-assisted question-answering with human feedback. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2112.09332, 2022. [87] Yao S Y, Chen H, Yang J, Narasimhan K. WebShop: Towards scalable real-world web interaction with grounded language agents. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 1508 [88] Qiao S F, Fang R N, Zhang N Y, Zhu Y Q, Chen X, Deng S M, et al. Agent planning with world knowledge model. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: NeurIPS, 2024. [89] Cao H Y, Zhang Y Q, Feng S, Yang X C, Wang D L, Zhang Y F. TOOL-ED: Enhancing empathetic response generation with the tool calling capability of LLM. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Computational Linguistics. Abu Dhabi, UAE: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2025. 5305−5320 [90] Liao Z Y, Mo L B, Xu C J, Kang M T, Zhang J W, Xiao C W, et al. EIA: Environmental injection attack on generalist web agents for privacy leakage. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2409.11295, 2025. [91] Chen Z R, Xiang Z, Xiao C W, Song D, Li B. AgentPoison: Red-teaming LLM agents via poisoning memory or knowledge bases. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: NeurIPS, 2024. [92] Xiang Z, Zheng L Z, Li Y J, Hong J Y, Li Q B, Xie H, et al. GuardAgent: Safeguard LLM agents by a guard agent via knowledge-enabled reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2406.09187, 2024. [93] Andrychowicz M, Baker B, Chociej M, Józefowicz R, McGrew B, Pachocki J, et al. Learning dexterous in-hand manipulation. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2020, 39(1): 3−20 doi: 10.1177/0278364919887447 [94] Kavraki L E, Svestka P, Latombe J C, Overmars M H. Probabilistic roadmaps for path planning in high-dimensional configuration spaces. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1996, 12(4): 566−580 doi: 10.1109/70.508439 [95] Shen Z Y, Wilson J P, Harvey R, Gupta S. MRRT: Multiple rapidly-exploring random trees for fast online replanning in dynamic environments. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2104.11059, 2021. [96] Liang J, Huang W L, Xia F, Xu P, Hausman K, Ichter B, et al. Code as policies: Language model programs for embodied control. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). London, UK: IEEE, 2023. 9493−9500 [97] Ichter B, Brohan A, Chebotar Y, Finn C, Hausman K, Herzog A, et al. Do as I can, not as I say: Grounding language in robotic affordances. In: Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Robot Learning. Auckland, New Zealand: PMLR, 2022. 287−318 [98] Yu Q J, Huang S Y, Yuan X B, Jiang Z K, Hao C, Li X, et al. UniAff: A unified representation of affordances for tool usage and articulation with vision-language models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2409.20551, 2024. [99] Huang W L, Wang C, Zhang R H, Li Y Z, Wu J J, Fei-Fei L. VoxPoser: Composable 3D value maps for robotic manipulation with language models. In: Proceedings of the 7th Conference on Robot Learning. Atlanta, USA: PMLR, 2023. 540−562 [100] Huang W L, Wang C, Li Y Z, Zhang R H, Fei-Fei L. Rekep: Spatio-temporal reasoning of relational keypoint constraints for robotic manipulation. In: Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Robot Learning. Munich, Germany: PMLR, 2025. 4573−4602 [101] Cai M X, Wang D L, Feng S, Zhang Y F. PECER: Empathetic response generation via dynamic personality extraction and contextual emotional reasoning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2024. 10631−10635 [102] Jin Q, Yang Y F, Chen Q Y, Lu Z Y. GeneGPT: Augmenting large language models with domain tools for improved access to biomedical information. Bioinformatics, 2024, 40(2): btae075 doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae075 [103] Xiao S T, Liu Z, Zhang P T, Muennighoff N, Lian D, Nie J Y. C-pack: Packed resources for general Chinese embeddings. In: Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. Washington, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2024. 641−649 [104] Li Z C, Wang J H, Jiang Z S, Mao H Y, Chen Z X, Du J Z, et al. DMQR-RAG: Diverse multi-query rewriting for RAG. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2411.13154, 2024. [105] Guo D Y, Yang D J, Zhang H W, Song J X, Zhang R Y, Xu R X, et al. DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing reasoning capability in LLMs via reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2501.12948, 2025. [106] Zeng Z Y, Cheng Q Y, Yin Z Y, Wang B, Li S M, Zhou Y H, et al. Scaling of search and learning: A roadmap to reproduce o1 from reinforcement learning perspective. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2412.14135, 2024. -




 下载:
下载:

