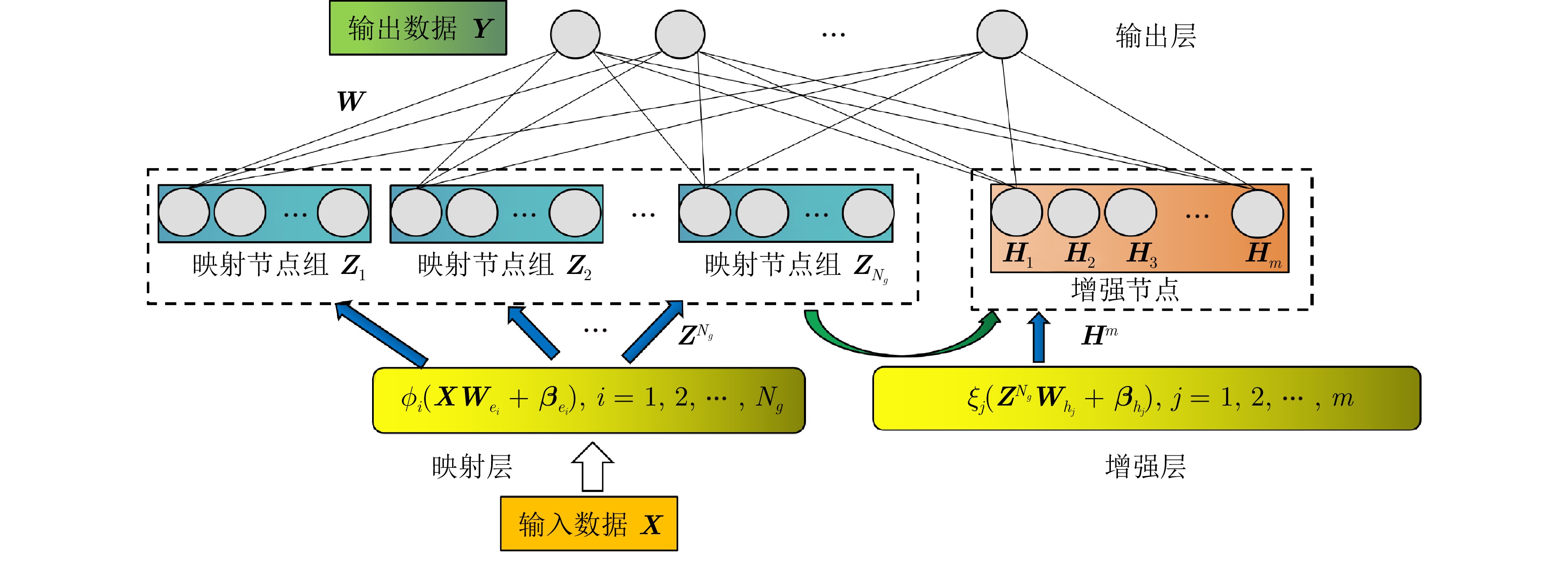
Relaxed-graph Embedding Discriminative Broad Learning System and Its Application in Visual Recognition
-
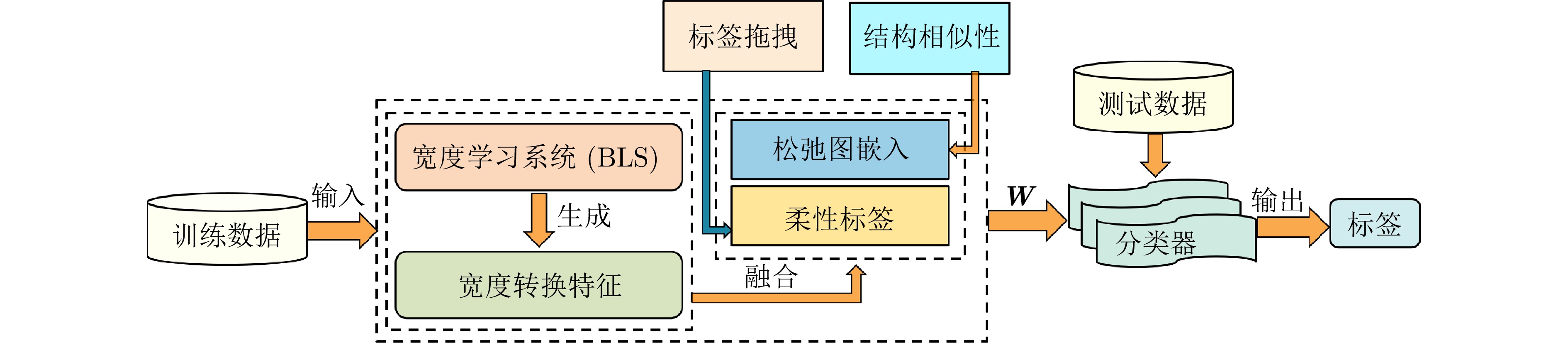
摘要: 宽度学习系统作为一种轻量级网络, 在效率和准确性之间实现了良好的平衡. 然而, 宽度学习系统主要依赖严苛的二元标签进行监督并且在数据变换过程中忽视局部结构信息, 这些问题限制了模型的性能. 为解决此问题, 提出一种松弛图嵌入的判别宽度学习系统模型并将其应用于视觉识别, 旨在通过松弛图结构与柔性标签的引入提升模型性能. 创新性如下: 1)创新地使用双变换矩阵构建松弛图, 将变换矩阵的责任分离, 减少变换矩阵的负担, 从而学习更加灵活的变换矩阵, 解决了模型过拟合问题; 2)引入柔性标签策略, 扩大不同类别标签之间的距离, 解决了严苛二元标签的问题, 提高了模型的判别能力; 3)提出一种基于交替方向乘子法的迭代优化算法, 实现了模型的高效优化. 在人脸图像数据集、物体图像数据集、场景图像数据集以及手写体图像数据集上的大量实验证明提出的模型与其他先进的识别算法相比具有优势.Abstract: The broad learning system, as a lightweight network, achieves a good balance between efficiency and accuracy. However, it primarily relies on strict binary labels for supervision and neglects local structural information during data transformation, limiting the model's performance. To address this issue, this paper proposes a relaxed-graph embedding discriminative broad learning system model and applies it to visual recognition, with the goal of enhancing model performance through the introduction of flexible labels and a relaxed-graph structure. The innovations of this paper are as follows: 1) We innovatively use double transformation matrices to construct the relaxed-graph, separating the responsibilities of the transformation matrix. This reduces the burden on the transformation matrix and allows for the learning of more flexible transformation matrix, thereby mitigating the overfitting problem; 2) We introduce a flexible label strategy that increases the distance between different categories labels, addressing the issue of strict binary labels, and thereby enhancing the model's discriminative ability; 3) An iterative optimization algorithm based on the alternating direction method of multipliers is proposed to achieve efficient model optimization. Extensive experiments on facial image datasets, object image datasets, scene image datasets and handwritten character image datasets demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms other advanced recognition algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Broad learning system /
- relaxed-graph /
- flexible label /
- visual recognition
-
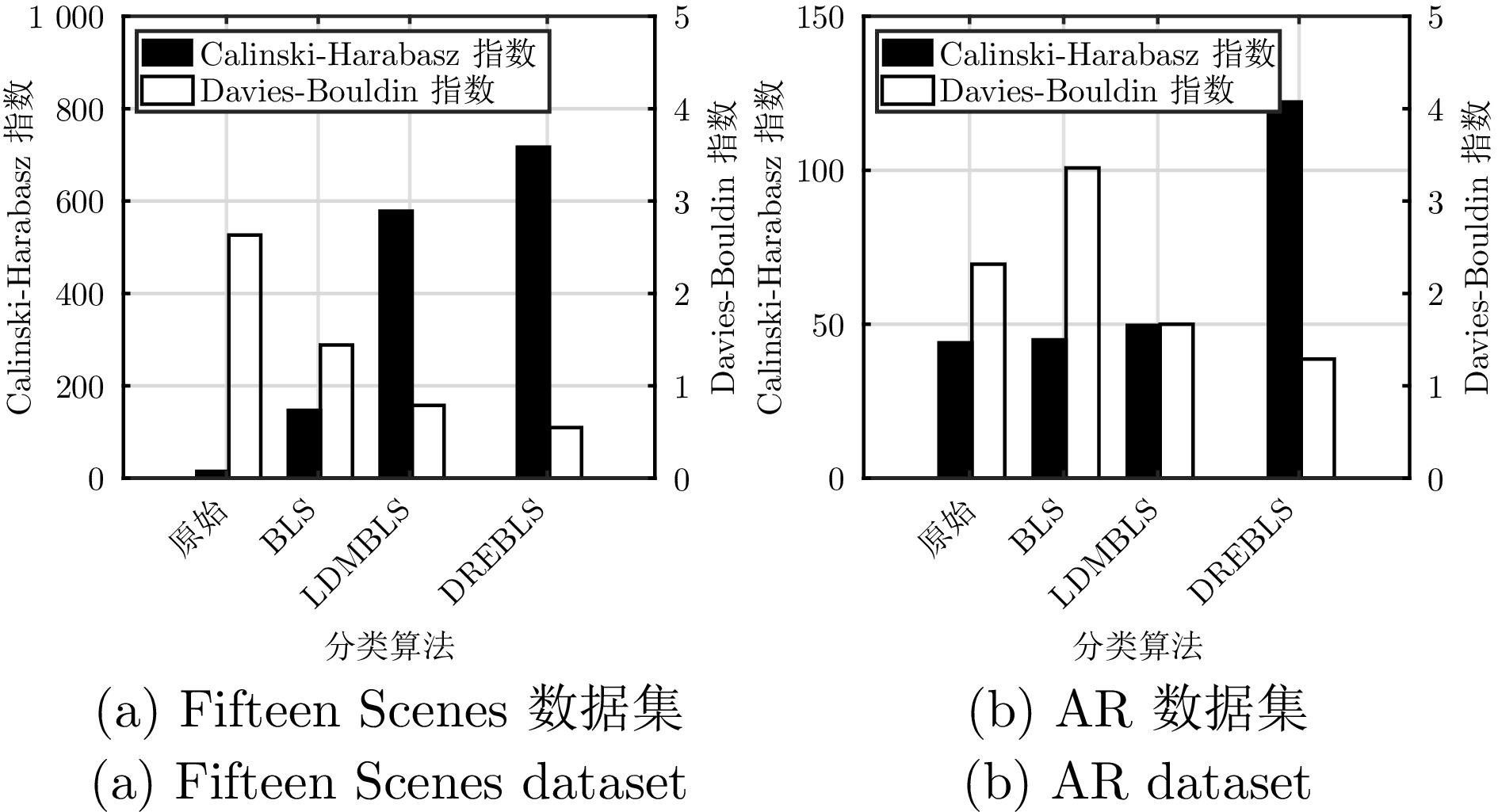
表 1 实验中使用的6个数据集的简要信息
Table 1 The brief information of the 6 datasets used in the experiments
数据集 样本总数量 维度 类别数 Extended YaleB $ 2\ 414 $ $ 1\ 024 $ $ 38 $ AR $ 2\ 600 $ $ 540 $ $ 100 $ Fifteen Scenes $ 4\ 485 $ $ 3\ 000 $ $ 15 $ COIL100 $ 7\ 200 $ $ 1\ 024 $ $ 100 $ MNIST $ 70\ 000 $ $ 784 $ $ 10 $ USPS $ 9\ 298 $ $ 256 $ $ 10 $ 表 2 Extended YaleB数据集不同方法的分类准确率以及标准差(%)
Table 2 Classification accuracy and standard deviation of different methods on the Extended YaleB dataset (%)
算法 10 样本 15 样本 20 样本 25 样本 SRC 87.8 ± 0.3 92.6 ± 0.6 94.4 ± 0.6 96.7 ± 0.5 CRC 86.1 ± 0.5 90.7 ± 0.3 93.0 ± 0.2 94.1 ± 0.3 LRC 83.3 ± 0.4 89.4 ± 0.5 92.4 ± 0.2 93.6 ± 0.3 TDDL 84.3 ± 0.6 88.9 ± 0.3 92.5 ± 0.4 95.0 ± 0.6 Robust PCA 86.1 ± 0.2 90.5 ± 0.4 93.5 ± 0.6 95.4 ± 0.3 LatLRR 84.0 ± 0.5 88.8 ± 0.3 92.1 ± 0.5 93.8 ± 0.6 SVM 81.5 ± 1.4 89.2 ± 0.9 92.6 ± 0.7 94.5 ± 0.6 ELM 85.5 ± 0.2 91.2 ± 0.6 93.7 ± 0.4 95.2 ± 0.5 RF 83.4 ± 0.4 88.5 ± 0.3 91.1 ± 0.5 94.6 ± 0.4 RLR 88.4 ± 0.3 92.8 ± 0.4 96.1 ± 0.3 97.5 ± 0.2 DLSR 86.2 ± 0.9 92.3 ± 0.7 94.7 ± 0.7 95.8 ± 0.4 LRLR 78.2 ± 1.7 82.0 ± 0.9 83.8 ± 1.5 85.0 ± 1.0 SLRR 78.0 ± 1.7 82.3 ± 1.0 84.2 ± 0.7 85.1 ± 1.1 LRSI 87.1 ± 0.6 92.7 ± 0.5 94.2 ± 0.3 96.1 ± 0.5 CBDS 85.8 ± 1.8 93.1 ± 1.3 95.8 ± 1.0 96.3 ± 0.8 DRAGD 88.8 ± 0.7 94.2 ± 0.5 96.7 ± 0.4 97.6 ± 0.4 FRBLS 88.9 ± 1.4 93.0 ± 1.1 95.3 ± 0.6 96.2 ± 0.7 LDMBLS 88.1 ± 1.4 93.3 ± 0.9 96.6 ± 0.8 97.4 ± 1.2 DREBLS 89.0 ± 0.8 94.3 ± 0.6 97.0 ± 0.9 97.9 ± 0.6 表 3 AR数据集不同方法的分类准确率
Table 3 Classification accuracies of different methods on the AR dataset
表 4 Fifteen Scenes数据集不同方法的分类准确率
Table 4 Classification accuracies of different methods on the Fifteen Scenes dataset
算法 准确率(%) 算法 准确率(%) LLC 79.4 Robust PCA 92.1 LLC*[37] 89.2 Lazebnik[37] 81.4 LRC 91.9 SVM 93.6 LRSIC 92.4 RLR 96.8 LRRC 90.1 Yang[37] 80.3 SLRRC 91.3 Lian[37] 86.4 Boureau[37] 84.3 LC-KSVD1[37] 90.4 LC-KSVD2[37] 92.9 DLSR 95.9 ELM 94.5 CBDS 95.7 Gemert[37] 76.7 LRLR 94.5 LRRR 88.1 SLRR 89.6 DRAGD 98.4 FRBLS 98.4 LDMBLS 98.3 DREBLS 98.5 表 5 COIL100数据集不同方法的分类准确率以及标准差(%)
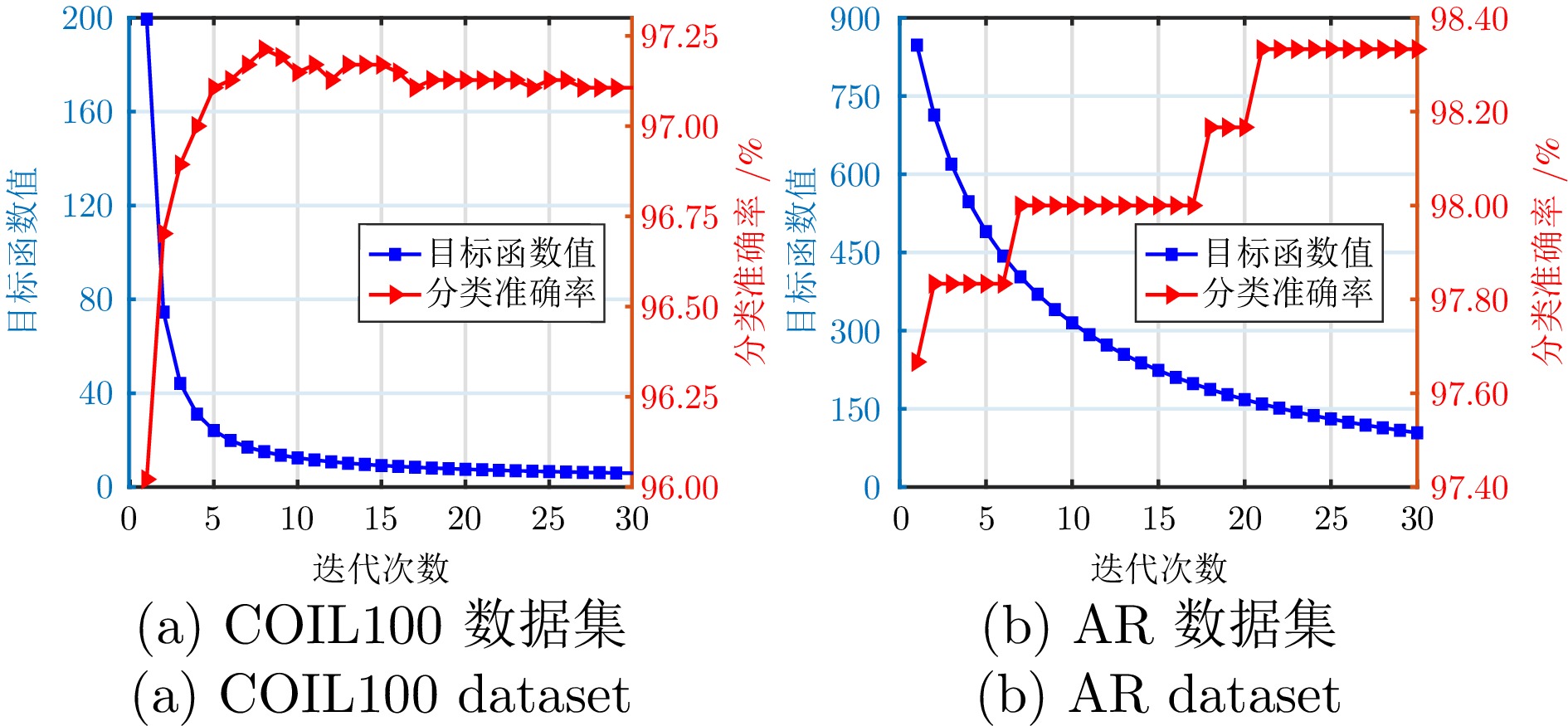
Table 5 Classification accuracy and standard deviation of different methods on the COIL100 dataset (%)
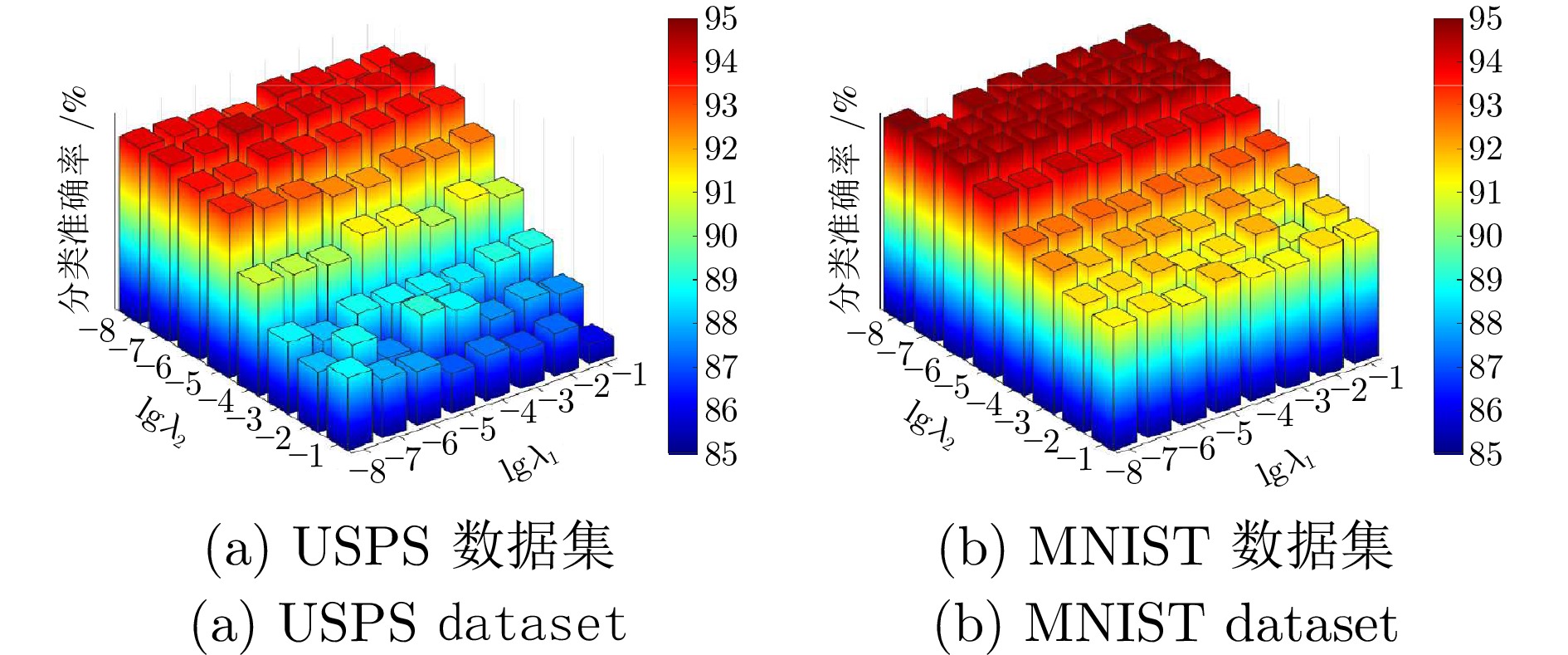
算法 10样本 15样本 20样本 25样本 SRC 80.4 ± 0.6 86.1 ± 0.8 89.4 ± 0.4 91.9 ± 0.4 CRC 76.2 ± 0.6 81.3 ± 0.4 84.2 ± 0.5 86.3 ± 0.5 LRC 79.9 ± 0.7 85.3 ± 0.6 88.7 ± 0.7 91.0 ± 0.5 TDDL 83.3 ± 0.6 87.9 ± 0.3 90.8 ± 0.4 90.0 ± 0.7 Robust PCA 82.5 ± 0.6 88.3 ± 0.8 91.7 ± 0.3 93.5 ± 0.3 LatLRR 79.6 ± 0.5 85.3 ± 0.4 88.4 ± 0.4 90.7 ± 0.4 SVM 79.2 ± 0.5 84.8 ± 0.6 88.1 ± 0.4 90.8 ± 0.6 ELM 81.2 ± 0.4 85.6 ± 0.7 89.7 ± 0.4 92.1 ± 0.6 RF 84.3 ± 0.5 88.3 ± 0.5 91.1 ± 0.5 93.3 ± 0.5 RLR 80.1 ± 0.6 83.4 ± 0.7 85.9 ± 0.8 87.2 ± 0.6 DLSR 84.8 ± 0.5 88.0 ± 0.5 90.1 ± 0.3 92.0 ± 0.4 LRLR 66.2 ± 0.8 71.2 ± 0.6 73.7 ± 0.8 75.7 ± 0.7 SLRR 69.1 ± 0.8 73.0 ± 0.6 74.5 ± 0.6 75.9 ± 0.7 LRSI 79.7 ± 0.5 87.8 ± 0.3 91.4 ± 0.4 93.6 ± 0.6 CBDS 73.7 ± 0.5 78.6 ± 0.8 80.9 ± 0.7 81.3 ± 0.5 DRAGD 83.5 ± 0.5 88.6 ± 0.4 94.8 ± 0.3 96.0 ± 0.3 FRBLS 84.8 ± 0.7 90.2 ± 0.6 94.7 ± 0.7 96.4 ± 0.5 LDMBLS 83.6 ± 1.1 89.3 ± 1.3 94.0 ± 0.9 96.1 ± 1.0 DREBLS 86.0 ± 0.5 91.0 ± 0.6 95.1 ± 0.6 97.2 ± 0.6 表 6 BLS、LDMBLS和DREBLS方法在USPS数据集上的分类准确率及标准差
Table 6 Classification accuracy and standard deviation of BLS, LDMBLS and DREBLS methods on the USPS dataset
样本数量 BLS LDMBLS DREBLS $ N_g $ $ N_f $ $ m $ 准确率(%) $ N_g $ $ N_f $ $ m $ 准确率(%) $ N_g $ $ N_f $ $ m $ 准确率(%) $ 100 $ $ 5 $ $ 15 $ $ 180 $ $ 90.88\pm0.56 $ $ 10 $ $ 10 $ $ 150 $ $ 94.45\pm0.65 $ $ 10 $ $ 15 $ $ 150 $ $ \boldsymbol{94.71\pm0.79} $ $ 150 $ $ 10 $ $ 20 $ $ 300 $ $ 92.62\pm0.87 $ $ 10 $ $ 15 $ $ 200 $ $ 95.38\pm0.37 $ $ 10 $ $ 20 $ $ 200 $ $ \boldsymbol{95.58\pm0.64} $ $ 200 $ $ 20 $ $ 30 $ $ 500 $ $ 93.37\pm0.68 $ $ 15 $ $ 20 $ $ 400 $ $ 96.23\pm0.31 $ $ 18 $ $ 25 $ $ 420 $ $ \boldsymbol{96.70\pm0.52} $ $ 250 $ $ 20 $ $ 40 $ $ 1\ 200 $ $ 94.08\pm0.50 $ $ 20 $ $ 30 $ $ 1\ 000 $ $ 96.99\pm0.59 $ $ 25 $ $ 30 $ $ 1\ 100 $ $ \boldsymbol{97.40\pm0.42} $ 表 7 BLS、LDMBLS和DREBLS方法在MNIST数据集上的分类准确率及标准差
Table 7 Classification accuracy and standard deviation of BLS, LDMBLS and DREBLS methods on the MNIST dataset
样本数量 BLS LDMBLS DREBLS $ N_g $ $ N_f $ $ m $ 准确率(%) $ N_g $ $ N_f $ $ m $ 准确率(%) $ N_g $ $ N_f $ $ m $ 准确率(%) $ 100 $ $ 7 $ $ 15 $ $ 500 $ $ 90.80\pm0.85 $ $ 8 $ $ 10 $ $ 400 $ $ 92.16\pm0.41 $ $ 10 $ $ 10 $ $ 400 $ $ \boldsymbol{92.91\pm0.87} $ $ 300 $ $ 25 $ $ 40 $ $ 1\ 200 $ $ 94.04\pm0.88 $ $ 20 $ $ 35 $ $ 1\ 000 $ $ 94.95\pm0.51 $ $ 30 $ $ 30 $ $ 1\ 000 $ $ \boldsymbol{95.06\pm0.23} $ $ 500 $ $ 30 $ $ 40 $ $ 1\ 500 $ $ 95.94\pm0.52 $ $ 30 $ $ 35 $ $ 1\ 300 $ $ 96.06\pm0.19 $ $ 30 $ $ 38 $ $ 1\ 200 $ $ \boldsymbol{96.16\pm0.15} $ $ 800 $ $ 30 $ $ 50 $ $ 2\ 000 $ $ 96.96\pm0.47 $ $ 30 $ $ 45 $ $ 1\ 500 $ $ 96.67\pm0.11 $ $ 40 $ $ 40 $ $ 1\ 800 $ $ \boldsymbol{96.99\pm0.15} $ 表 8 BLS、LDMBLS、DREBLS* 及DREBLS方法在Fifteen Scenes数据集上的分类多指标评估(%)
Table 8 Classification multi-metric evaluation of BLS, LDMBLS, DREBLS* and DREBLS methods on the Fifteen Scenes dataset (%)
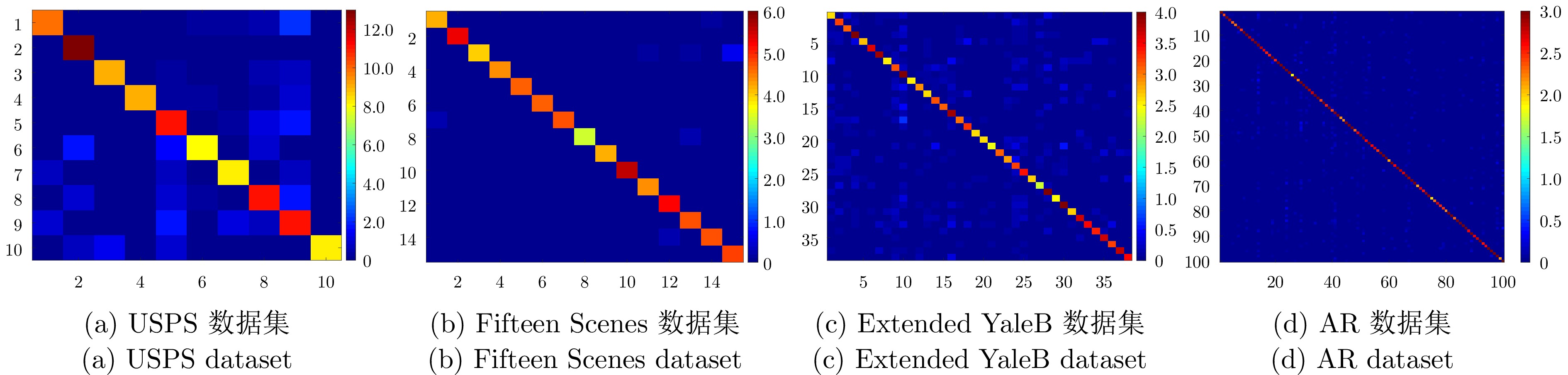
指标 算法 类别1 类别2 类别3 类别4 类别5 类别6 类别7 类别8 类别9 类别10 平均值 准确率 BLS 93.2 94.4 88.3 92.9 86.5 92.4 95.9 96.3 83.6 100.0 92.0 LDMBLS 98.6 95.9 95.8 90.8 100.0 97.5 98.5 99.3 89.3 98.5 95.5 DREBLS* 96.4 92.9 88.3 93.8 99.0 92.1 97.0 97.4 92.2 97.4 94.5 DREBLS 96.8 97.4 98.7 94.6 99.0 97.7 99.5 99.6 95.8 98.5 97.3 召回率 BLS 98.6 98.2 98.6 99.6 94.3 97.9 99.2 100.0 100.0 50.1 94.8 LDMBLS 98.6 98.2 98.6 99.6 94.3 97.9 99.2 100.0 100.0 50.1 94.8 DREBLS* 98.6 99.1 87.5 97.0 82.4 96.5 100.0 100.0 96.0 88.4 94.5 DREBLS 99.1 98.2 95.3 100.0 92.5 97.7 99.2 100.0 98.8 99.0 98.0 F1分数 BLS 95.8 96.3 93.2 96.1 90.2 95.1 97.5 98.1 90.9 66.8 94.0 LDMBLS 98.2 97.5 95.5 94.9 94.0 96.5 99.2 98.7 94.0 93.4 95.2 DREBLS* 97.5 96.0 87.9 95.3 89.9 94.2 98.3 99.0 94.1 92.7 94.0 DREBLS 97.9 97.8 97.0 97.0 95.6 97.7 99.4 100.0 97.3 98.7 98.0 表 9 算法运行的时间效率对比
Table 9 Time efficiency comparison of algorithm execution
数据集 算法 训练时间(s) 测试时间(s) 准确率(%) AR BLS 2.407 0 0.497 8 95.4 LDMBLS 3.973 9 0.628 4 98.3 DREBLS* 3.640 5 0.599 3 98.0 DREBLS 3.847 8 0.598 9 99.2 COIL100 BLS 1.795 7 0.305 4 82.5 LDMBLS 2.796 8 0.476 9 89.3 DREBLS* 2.181 7 0.424 1 86.6 DREBLS 2.872 8 0.432 3 91.0 USPS BLS 1.692 4 0.342 4 92.6 LDMBLS 2.873 9 0.448 8 95.4 DREBLS* 2.556 1 0.401 5 93.7 DREBLS 2.596 8 0.403 5 95.6 -
[1] He M, Zhang J, Shan S, Chen X. Enhancing face recognition with detachable self-supervised bypass networks. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2024, 33: 1588−1599 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2024.3364067 [2] Sun Z, Ke Q, Rahmani H, Bennamoun M, Wang G, Liu J. Human action recognition from various data modalities: A review. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(3): 3200−3225 [3] Huang H, Oh S K, Fu Z, Wu C, Pedrycz W, Kim J Y. FSCNN: Fuzzy channel filter-based separable convolution neural networks for medical imaging recognition. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2024, 32(10): 5449−5461 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2024.3450000 [4] Cheng X, He X, Qiao M, Li P, Chang P, Zhang T, et al. Multi-view graph convolutional network with spectral component decompose for remote sensing images classification. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2025, 35(1): 3−18 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3227172 [5] Li X, Zhao C, Hu Y, Xie H, Wang Y, Zhao J. Precursor of privacy leakage detection for individual user. Computers & Security, 2024, 142: Article No. 103879 [6] Chen C L P, Liu Z. Broad learning system: An effective and efficient incremental learning system without the need for deep architecture. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(1): 10−24 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2716952 [7] Wang Z, Jusup M, Shi L, Lee J H, Iwasa Y, Boccaletti S. Exploiting a cognitive bias promotes cooperation in social dilemma experiments. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): Article No. 2954 doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05259-5 [8] Wu S, Wang J, Sun H, Zhang K, Pal N R. Fractional approximation of broad learning system. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(2): 811−824 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3127152 [9] 赵慧敏, 郑建杰, 郭晨, 邓武. 基于流形正则化框架和MMD的域自适应BLS模型. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(7): 1458−1471Zhao Hui-Min, Zheng Jian-Jie, Guo Chen, Deng Wu. Domain adaptive BLS model based on manifold regularization framework and MMD. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(7): 1458−1471 [10] Duan J, Yao S, Tan J, Liu Y, Chen L, Zhang Z, et al. Extreme fuzzy broad learning system: Algorithm, frequency principle, and applications in classification and regression. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2025, 36(2): 2946−2957 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3347888 [11] Wang Z, Jusup M, Wang R W, Shi L, Iwasa Y, Moreno Y, et al. Onymity promotes cooperation in social dilemma experiments. Science Advances, 2017, 3(3): Article No. e1601444 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1601444 [12] Liu L, Liu T, Chen C L P, Wang Y. Modal-regression-based broad learning system for robust regression and classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(9): 12344−12357 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3256999 [13] Shi M, Ding C, Wang R, Shen C, Huang W, Zhu Z. Semi-supervised class incremental broad network for continuous diagnosis of rotating machinery faults with limited labeled samples. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2024, 286: Article No. 111397 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2024.111397 [14] Wang Z, Jusup M, Guo H, Shi L, Gecek S, Anand M, et al. Communicating sentiment and outlook reverses inaction against collective risks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(30): 17650−17655 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922345117 [15] Jin J, Li Y, Chen C L P. Pattern classification with corrupted labeling via robust broad learning system. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2022, 34(10): 4959−4971 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2021.3049540 [16] Jin J, Chang S, Duan J, Li Y, Ding W, Wang Z, et al. Groupwise label enhancement broad learning system for image classification. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, DOI: 10.1109/TCYB.2025.3550175 [17] Wang Z, Mu C, Hu S, Chu C, Li X. Modelling the dynamics of regret minimization in large agent populations: A master equation approach. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vienna, Austria: Morgan Kaufmann, 2022. 534−540 [18] Xiang S, Nie F, Meng G, Pan C, Zhang C. Discriminative least squares regression for multiclass classification and feature selection. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(11): 1738−1754 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2212721 [19] Jin J, Geng B, Li Y, Liang J, Xiao Y, Chen C L P. Flexible label-induced manifold broad learning system for multiclass recognition. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(11): 16076−16090 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3291793 [20] Rudin W. Principles of Mathematical Analysis. New York: McGraw-hill, 1976. [21] Zhang L, Yang M, Feng X, Ma Y, Zhang D. Collaborative representation based classification for face recognition. arXiv: 1204.2358, 2012. [22] Wang J, Yang J, Yu K, Lv F, Huang T, Gong Y. Locality-constrained linear coding for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 3360−3367 [23] Naseem I, Togneri R, Bennamoun M. Linear regression for face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(11): 2106−2112 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.128 [24] Chen C, Wei C, Wang Y F. Low-rank matrix recovery with structural incoherence for robust face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 2618−2625 [25] Zhang Y, Jiang Z, Davis L S. Learning structured low-rank representations for image classification. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2013. 676−683 [26] Julien M, Francis B, Jean P. Task-driven dictionary learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(4): 791−804 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.156 [27] Fang X, Xu Y, Li X, Lai Z, Wong W K, Fang B. Regularized label relaxation linear regression. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(4): 1006−1018 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2648880 [28] Candès E J, Li X, Ma Y, Wright J. Robust principal component analysis? Journal of the ACM (JACM), 2011, 58(3): 1−37 [29] Liu G, Yan S. Latent low-rank representation for subspace segmentation and feature extraction. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 1615−1622 [30] Cai X, Ding C, Nie F, Huang H. On the equivalent of low-rank linear regressions and linear discriminant analysis based regressions. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Chicago, USA: ACM, 2013. 1124−1132 [31] Wei C, Chen C, Wang Y. Robust face recognition with structurally incoherent low-rank matrix decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(8): 3294−3307 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2329451 [32] Li Y, Liu J, Lu H, Ma S. Learning robust face representation with classwise block-diagonal structure. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2014, 9(12): 2051−2062 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2014.2361936 [33] Fernández-Delgado M, Cernadas E, Barro S, Amorim D. Do we need hundreds of classifiers to solve real world classification problems? The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 3133−3181 [34] Wen J, Deng S, Fei L, Zhang Z, Zhang B, Zhang Z, et al. Discriminative regression with adaptive graph diffusion. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(2): 1797−1809 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3185408 [35] Li X, Wei J, Jin J, Xu T, Yu D. Fisher regularized discriminative broad learning system for visual classification. Applied Soft Computing, 2024, 167: Article No. 112341 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2024.112341 [36] Georghiades A S, Belhumeur P N, Kriegman D J. From few to many: Illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2001, 23(6): 643−660 doi: 10.1109/34.927464 [37] Jiang Z, Lin Z, Davis L S. Label consistent K-SVD: Learning a discriminative dictionary for recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(11): 2651−2664 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.88 [38] Mohan B C, Chaitanya T K, Tirupal T. Fast and accurate content based image classification and retrieval using gaussian hermite moments applied to coil 20 and coil 100. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT). Kanpur, India: IEEE, 2019. 1−5 -




 下载:
下载: