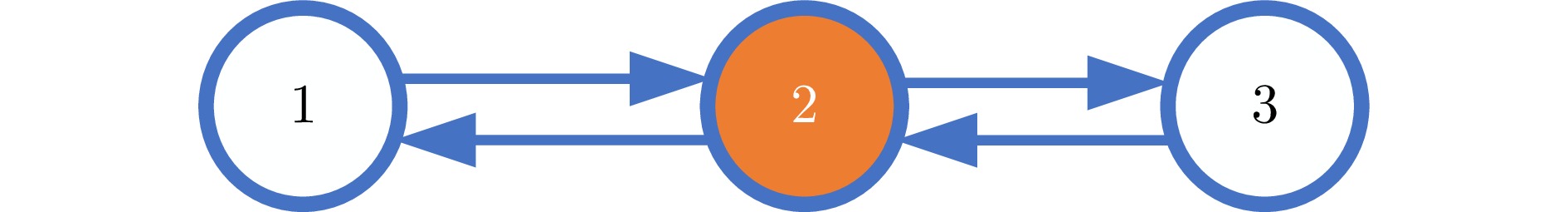
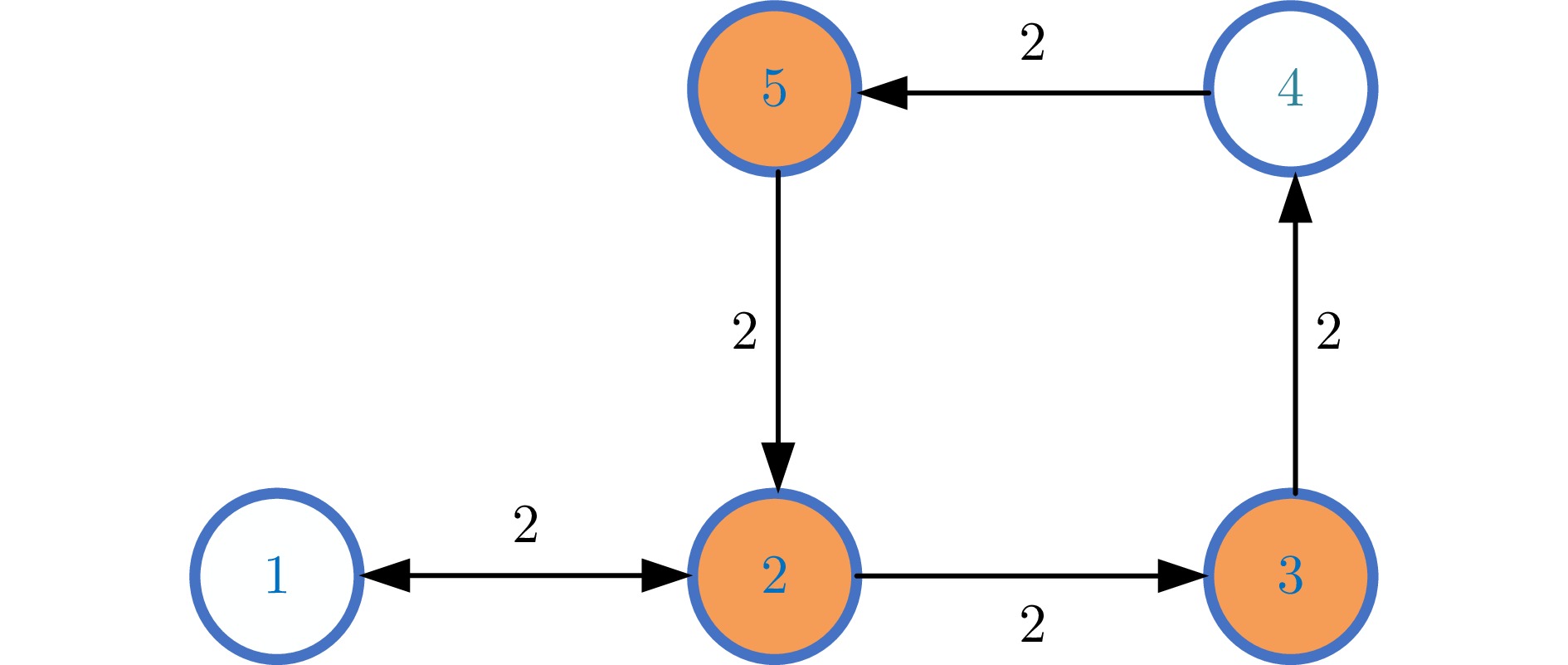
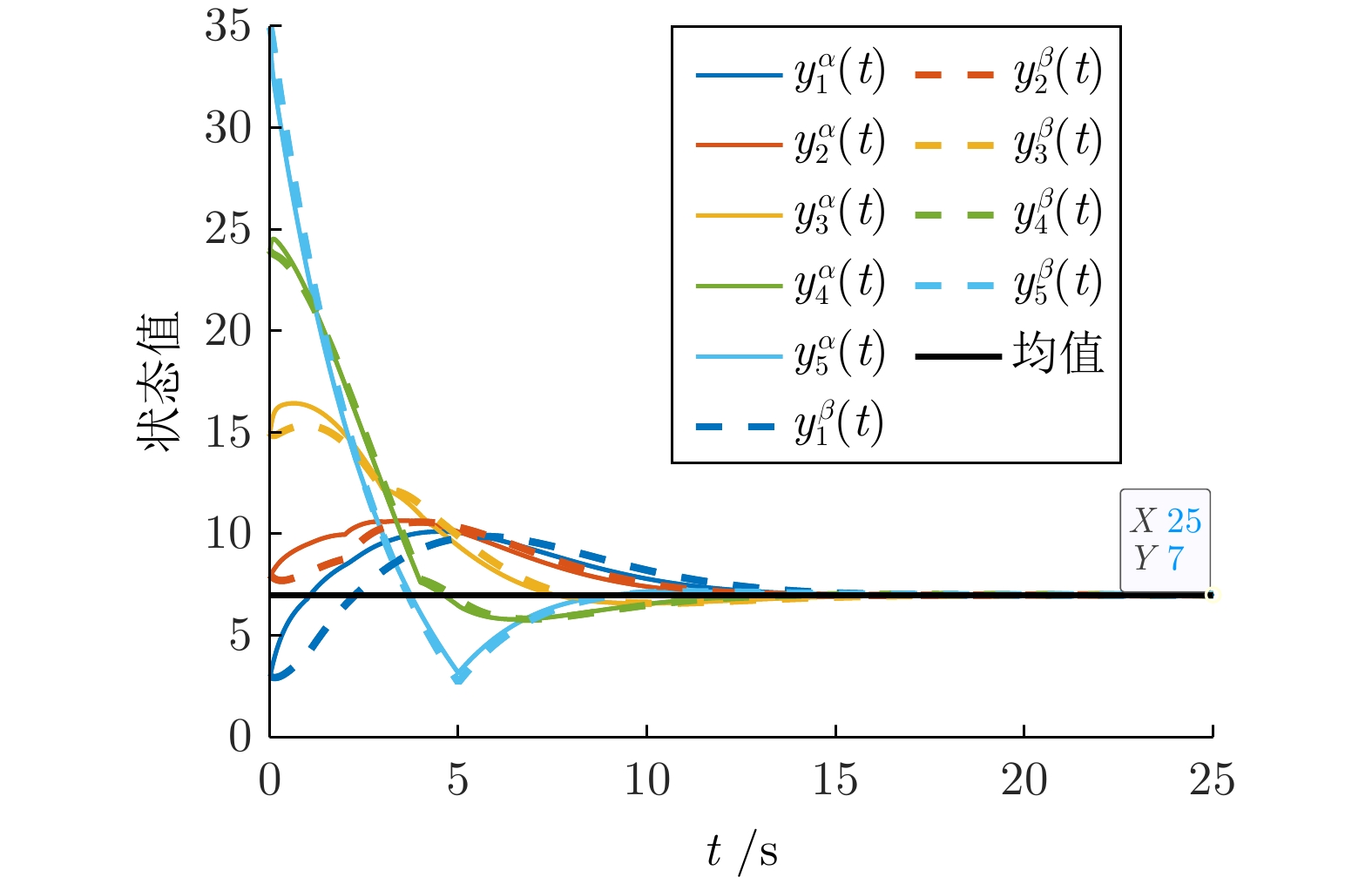
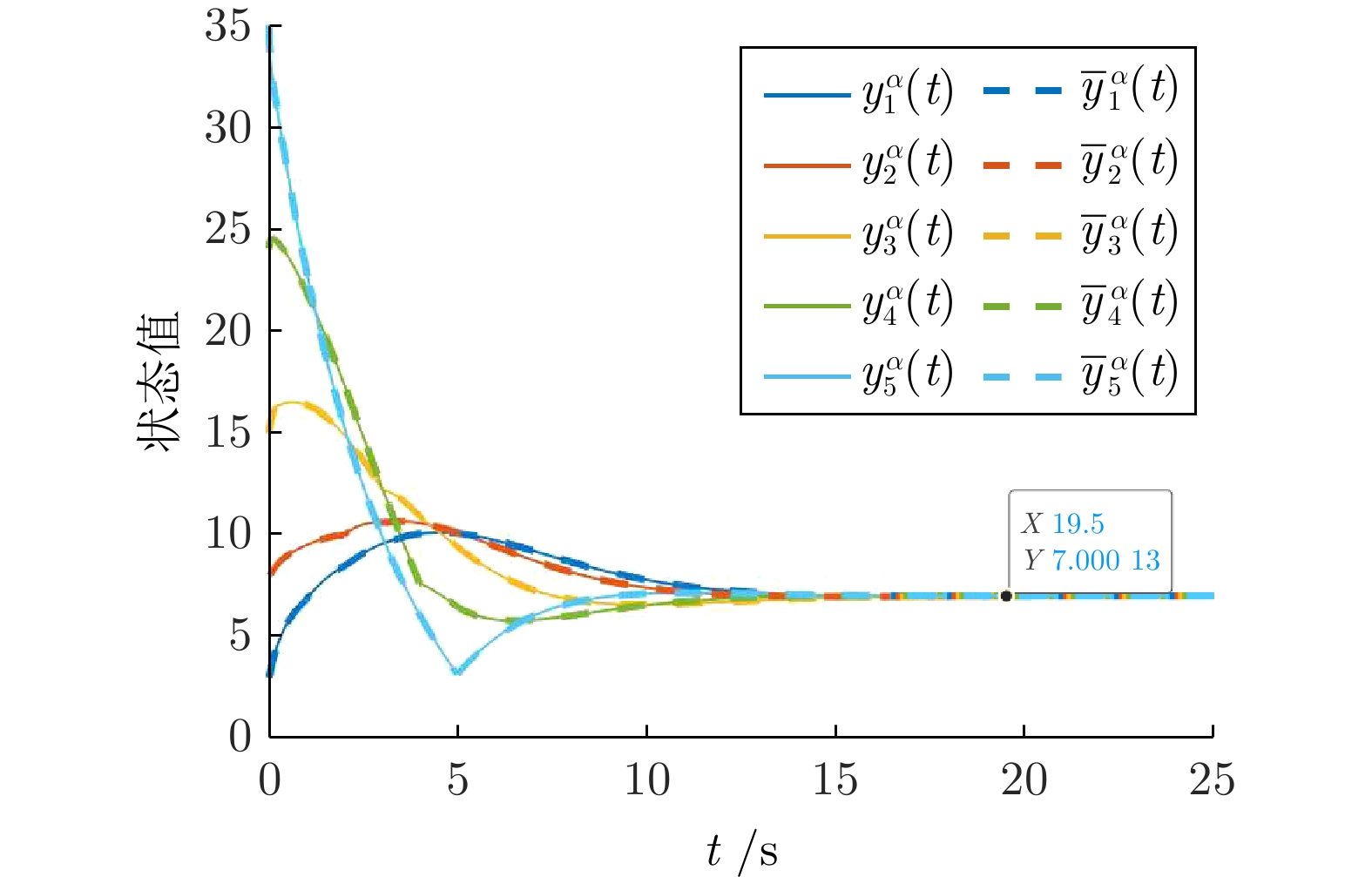
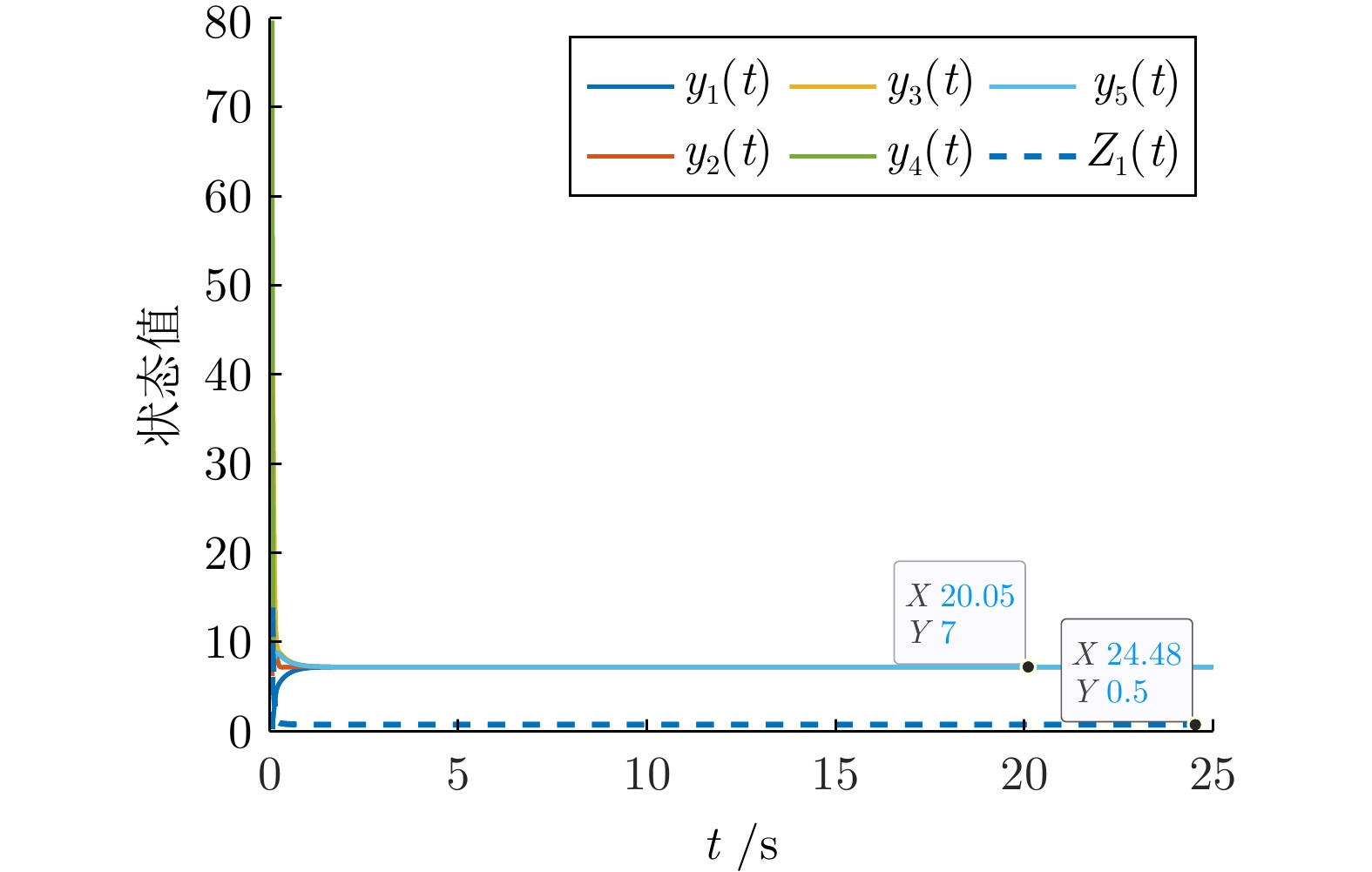
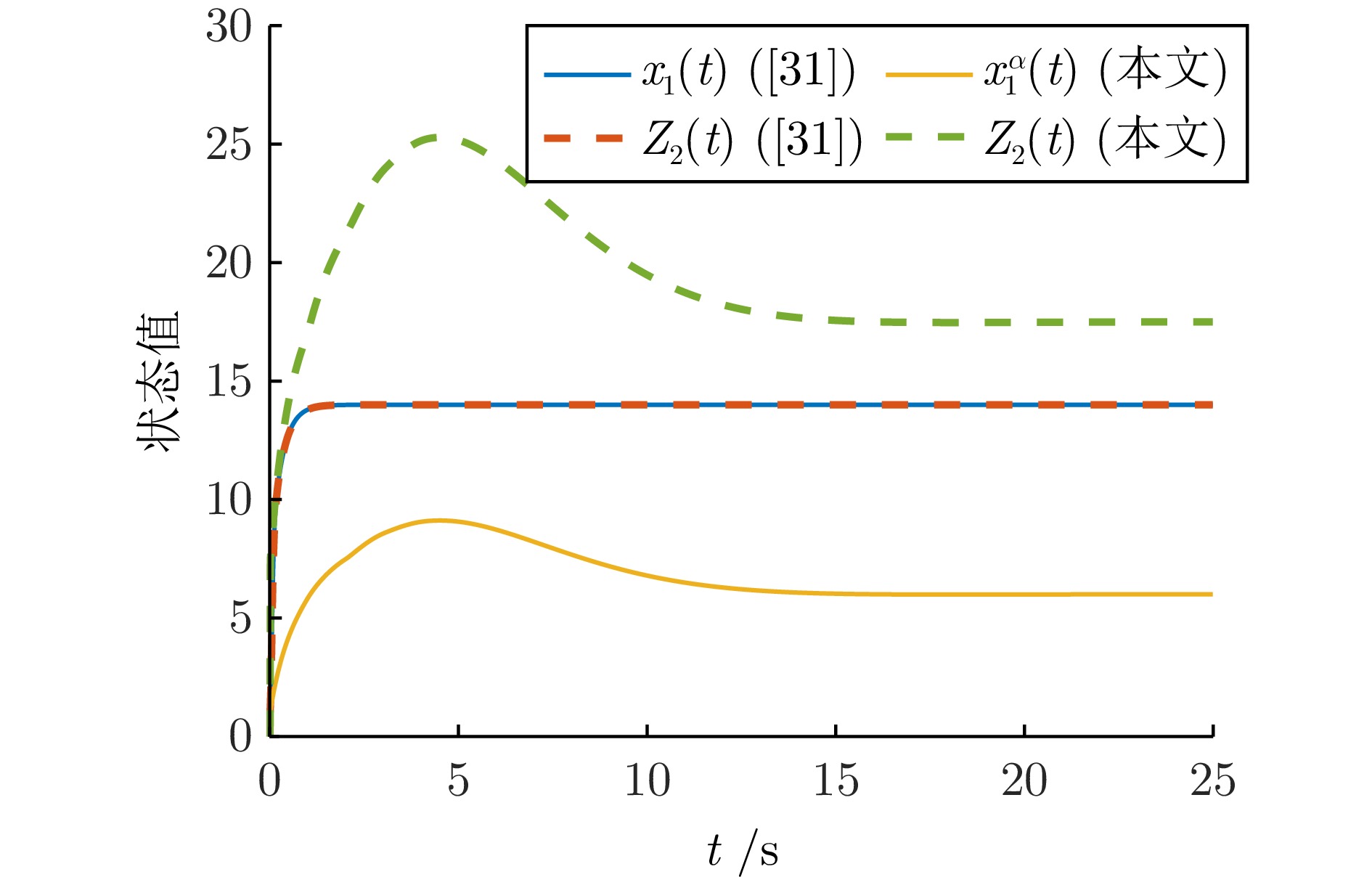
|
[1]
|
Chung Y F, Kia S S. Dynamic active average consensus. IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2020, 5(4): 1177−1182
|
|
[2]
|
Hassani H, Razavi-Far R, Saif M, Herrera-Viedma E. Consensus-based decision support model and fusion architecture for dynamic decision making. Information Sciences, 2022, 597: 86−104 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.03.040
|
|
[3]
|
Du Y H, Hao T, Hui Y, Srdjan L. Accurate consensus-based distributed averaging with variable time delay in support of distributed secondary control algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2020, 11(4): 2918−2928 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2020.2975752
|
|
[4]
|
Alsaadi F E, Wang Z D, Wang D, Alsaadi F E, Alsaade F W. Recursive fusion estimation for stochastic discrete time-varying complex networks under stochastic communication protocol: The state-saturated case. Information Fusion, 2020, 60: 11−19 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2020.01.012
|
|
[5]
|
Zhang K, Li Z J, Wang Y Q, Louati A, Chen J. Privacy-preserving dynamic average consensus via state decomposition: Case study on multi-robot formation control. Automatica, 2022, 139: Article No. 110182
|
|
[6]
|
Dong Y C, Zha Q B, Zhang H J, Kou G, Fujita H, Chiclana F, et al. Consensus reaching in social network group decision making: Research paradigms and challenges. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 162: 3−13 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.06.036
|
|
[7]
|
Yi D, Yu S Y. Rendezvous with connectivity preservation problem of linear multiagent systems via parallel event-triggered control strategies. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 52(5): 2725−2734
|
|
[8]
|
Maity D, Tsiotras P. Multiagent consensus subject to communication and privacy constraints. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2021, 9(2): 943−955
|
|
[9]
|
Wang Z Q, Ma M L, Zhou Q, Xiong L Y, Wang L L, Wang J M, et al. A privacy-preserving distributed control strategy in islanded AC microgrids. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2022, 13(5): 3369−3382 doi: 10.1109/TSG.2022.3171267
|
|
[10]
|
Yao A C. Protocols for secure computations. In: Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. IEEE, 1982. 160−164
|
|
[11]
|
Shamir A. How to share a secret. Communications of the ACM, 1979, 22(11): 612−613 doi: 10.1145/359168.359176
|
|
[12]
|
Chaum D, Crépeau C, Damgard I. Multiparty unconditionally secure protocols. In: Proceedings of the 20th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 1988. 11−19
|
|
[13]
|
Nozari E, Tallapragada P, Cortés J. Differentially private average consensus: Obstructions, trade-offs, and optimal algorithm design. Automatica, 2017, 81: 221−231 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.03.016
|
|
[14]
|
Ruan M H, Gao H, Wang Y Q. Secure and privacy-preserving consensus. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(10): 4035−4049 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2890887
|
|
[15]
|
Mo Y L, Murray R M. Privacy preserving average consensus. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 62(2): 753−765
|
|
[16]
|
Wang Y Q. Privacy-preserving average consensus via state decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(11): 4711−4716 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2902731
|
|
[17]
|
Ramos G, Pequito S. Designing communication networks for discrete-time consensus for performance and privacy guarantees. Systems Control Letters, 2023, 180: Article No. 105608
|
|
[18]
|
Gao L, Deng S J, Ren W. Differentially private consensus with an event-triggered mechanism. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2018, 6(1): 60−71
|
|
[19]
|
Fiore D, Russo G. Resilient consensus for multi-agent systems subject to differential privacy requirements. Automatica, 2019, 106: 18−26 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.04.029
|
|
[20]
|
Hadjicostis C N, Domínguez-García A D. Privacy-preserving distributed averaging via homomorphically encrypted ratio consensus. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 65(9): 3887−3894 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.2968876
|
|
[21]
|
Altafini C. A system-theoretic framework for privacy preservation in continuous-time multiagent dynamics. Automatica, 2020, 122: Article No. 109253
|
|
[22]
|
Xiong Y, Li Z K. Privacy-preserved average consensus algorithms with edge-based additive perturbations. Automatica, 2022, 140: Article No. 110223
|
|
[23]
|
Zhang J, Lu J Q, Lou J G. Privacy-preserving average consensus via finite time-varying transformation. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022, 9(3): 1756−1764 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3151380
|
|
[24]
|
Manitara N E, Hadjicostis C N. Privacy-preserving asymptotic average consensus. In: Proceedings of the European Control Conference. Zurich, Switzerland: IEEE, 2013. 760−765
|
|
[25]
|
Charalambous T, Manitara N E, Hadjicostis C N. Privacy-preserving average consensus over digraphs in the presence of time delays. In: Proceedings of the 57th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing. Monticello, USA: IEEE, 2019. 238−245
|
|
[26]
|
Rezazadeh N, Kia S S. A study of privacy preservation in average consensus algorithm via deterministic obfuscation signals. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2023, 11(1): 534−546
|
|
[27]
|
Ye F, Cao X H, Chow M Y, Cai L. Privacy-preserving average consensus: Fundamental analysis and a generic framework design. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2024, 70(4): 2870−2885 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2024.3370311
|
|
[28]
|
应晨铎, 伍益明, 徐明, 郑宁, 何熊熊. 欺骗攻击下具备隐私保护的多智能体系统均值趋同控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(2): 425−436Ying Chen-Duo, Wu Yi-Ming, Xu Ming, Zheng Ning, He Xiong-Xiong. Privacy-preserving average consensus control for multi-agent systems under deception attacks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(2): 425−436
|
|
[29]
|
Zhang J, Lu J, Liang J, Shi K. Privacy-preserving average consensus in multi-agent systems via partial information transmission. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 53(5): 2781−2791
|
|
[30]
|
Ramos G, Aguiarz A P, Karx S, Pequito S. Privacy preserving average consensus through network augmentation. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(10): 6907−6919 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3383795
|
|
[31]
|
Zhang J, Lu J Q, Liang J L, Zhong J. Average consensus of whole-process privacy protection: A scale parameter method. Information Fusion, 2024, 107: Article No. 102312
|
|
[32]
|
Wang Z Q, Wang J, Scala M L, Xiong L Y. Real-time privacy-preserving average consensus and its application to secondary control for AC microgrid. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(7): 9655−9669 doi: 10.1109/TII.2024.3381645
|
|
[33]
|
Olfati-Saber R, Murray R M. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(9): 1520−1533 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.834113
|




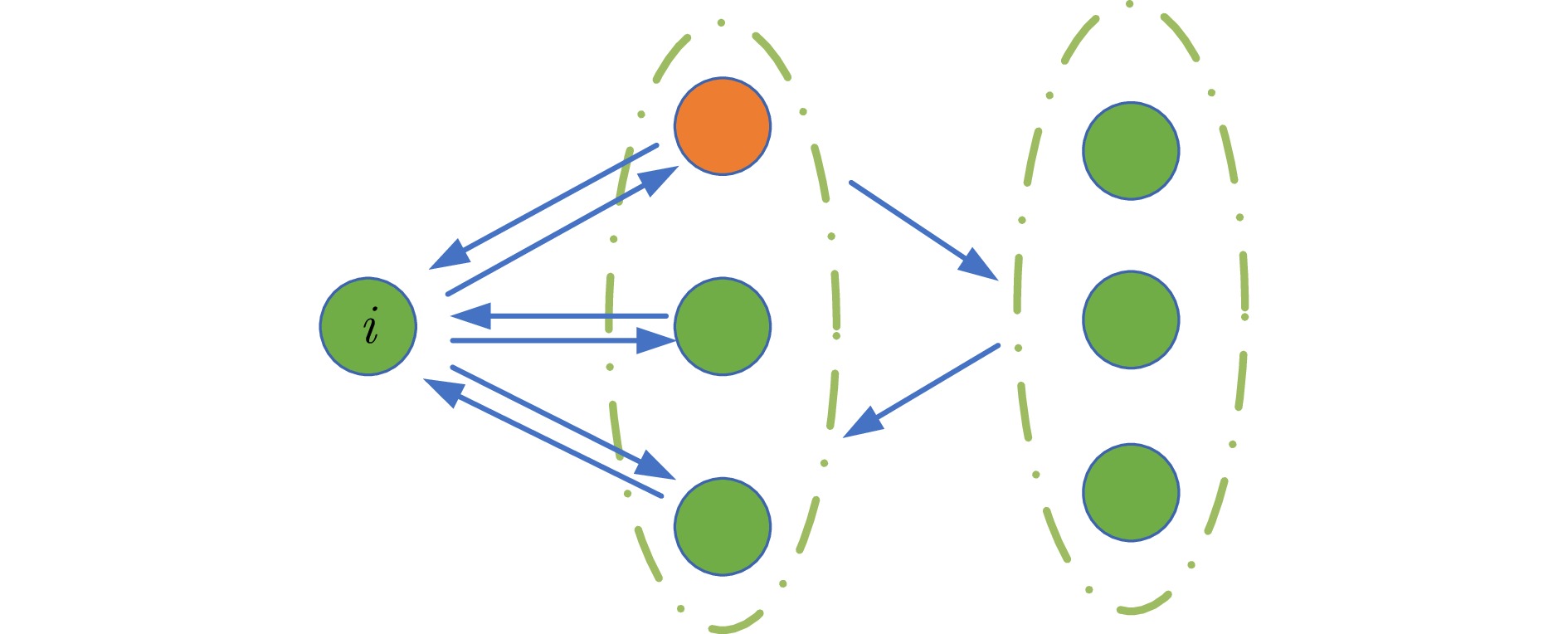
 下载:
下载: