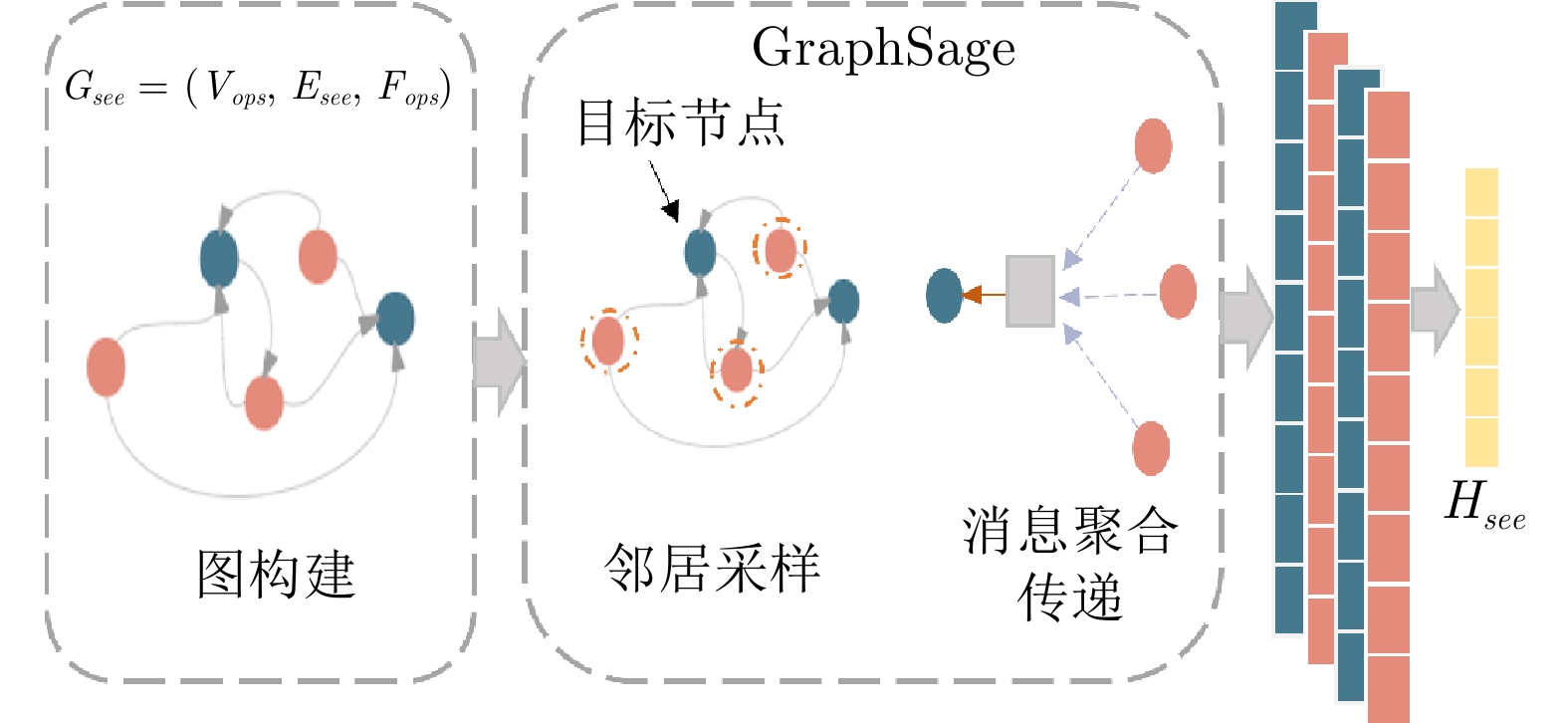
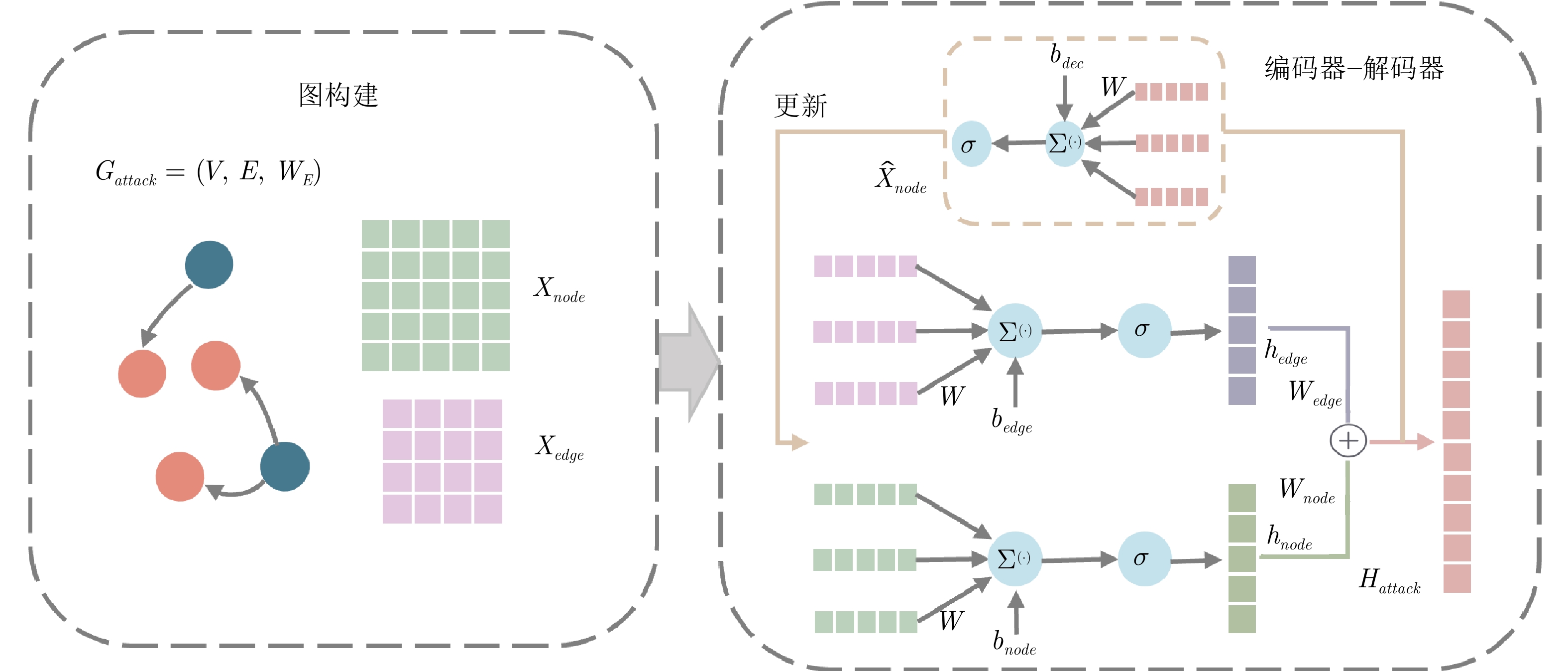
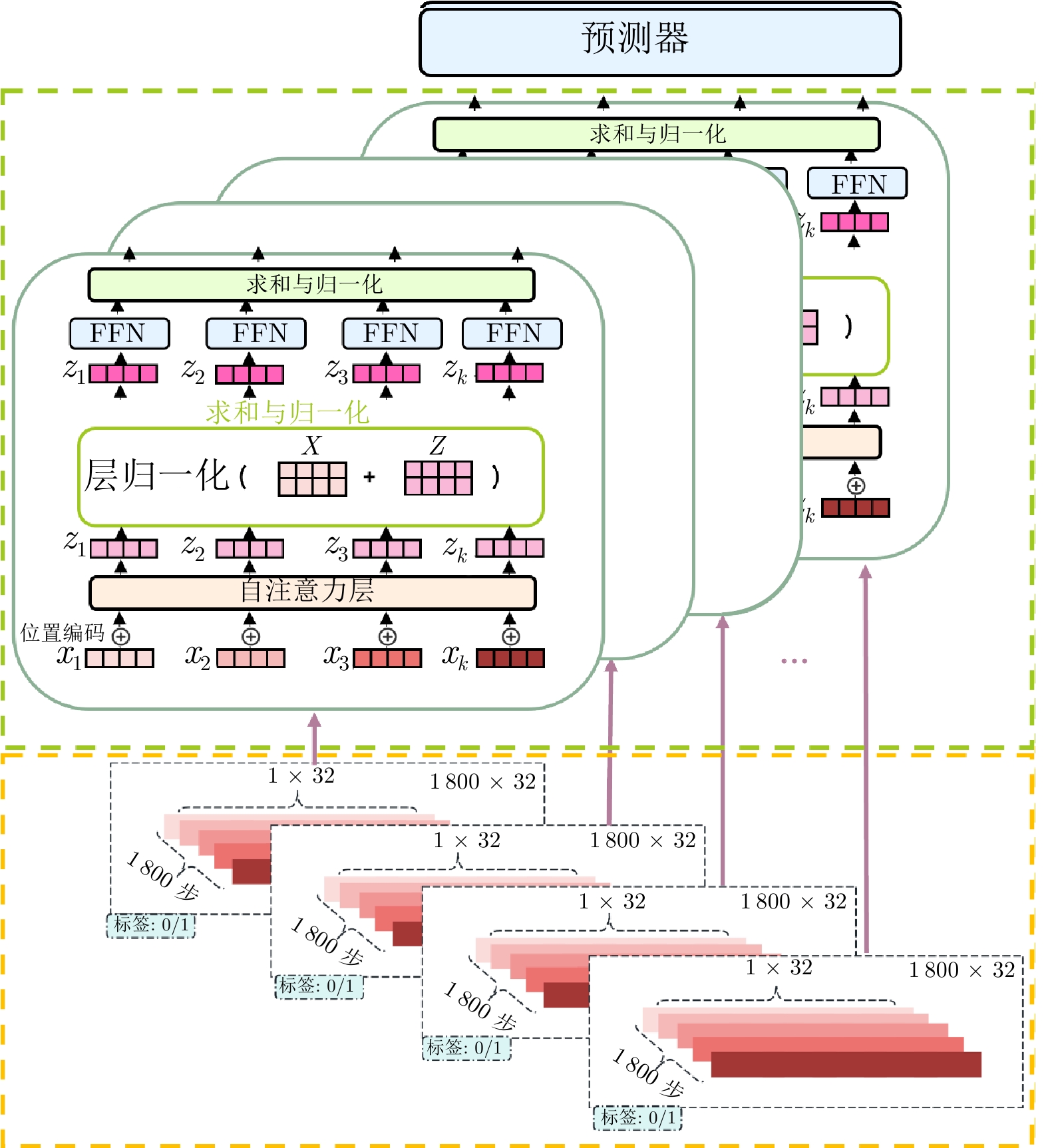
An Interpretable Wargame Situation Prediction Method Based on Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks
-
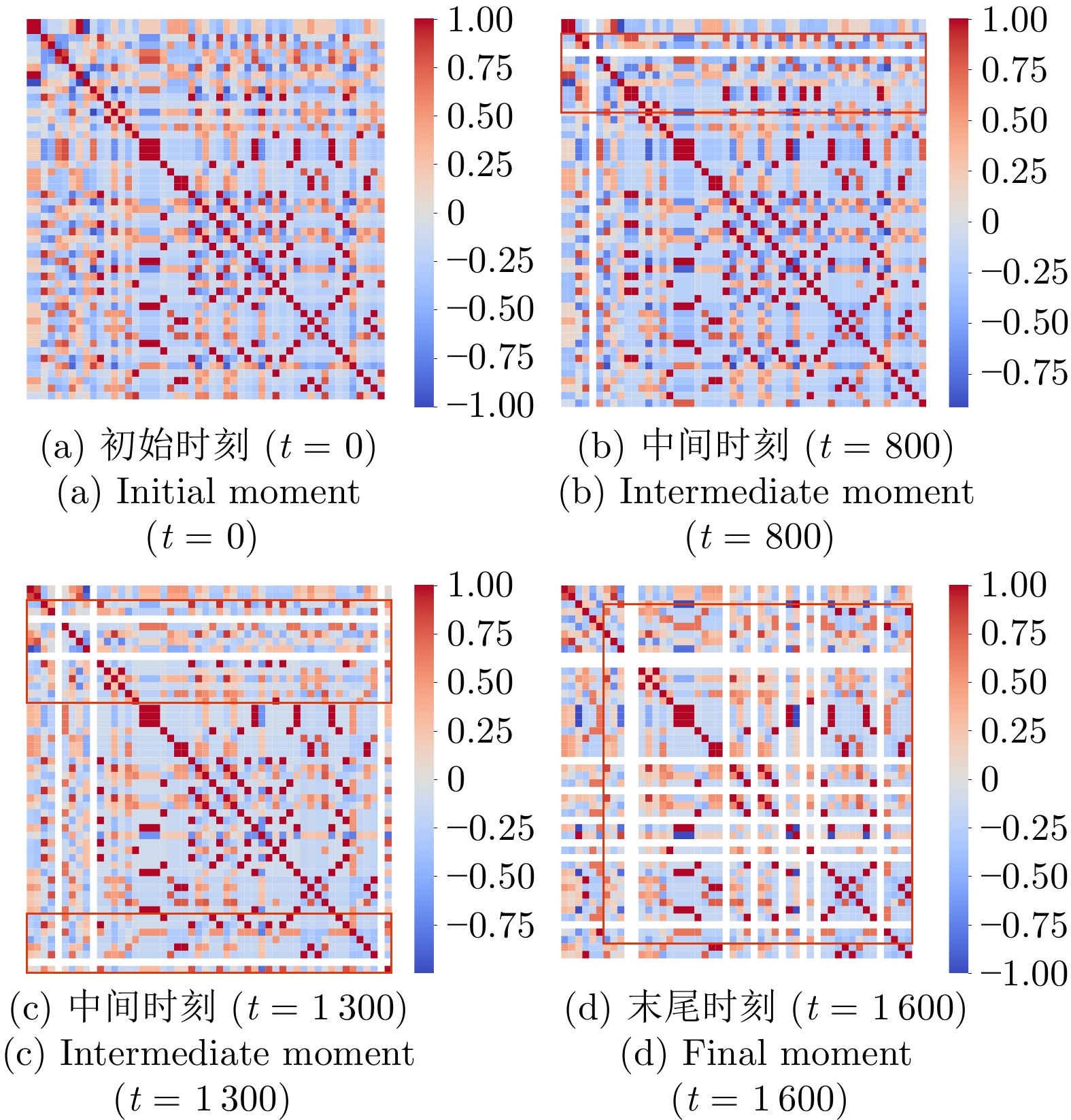
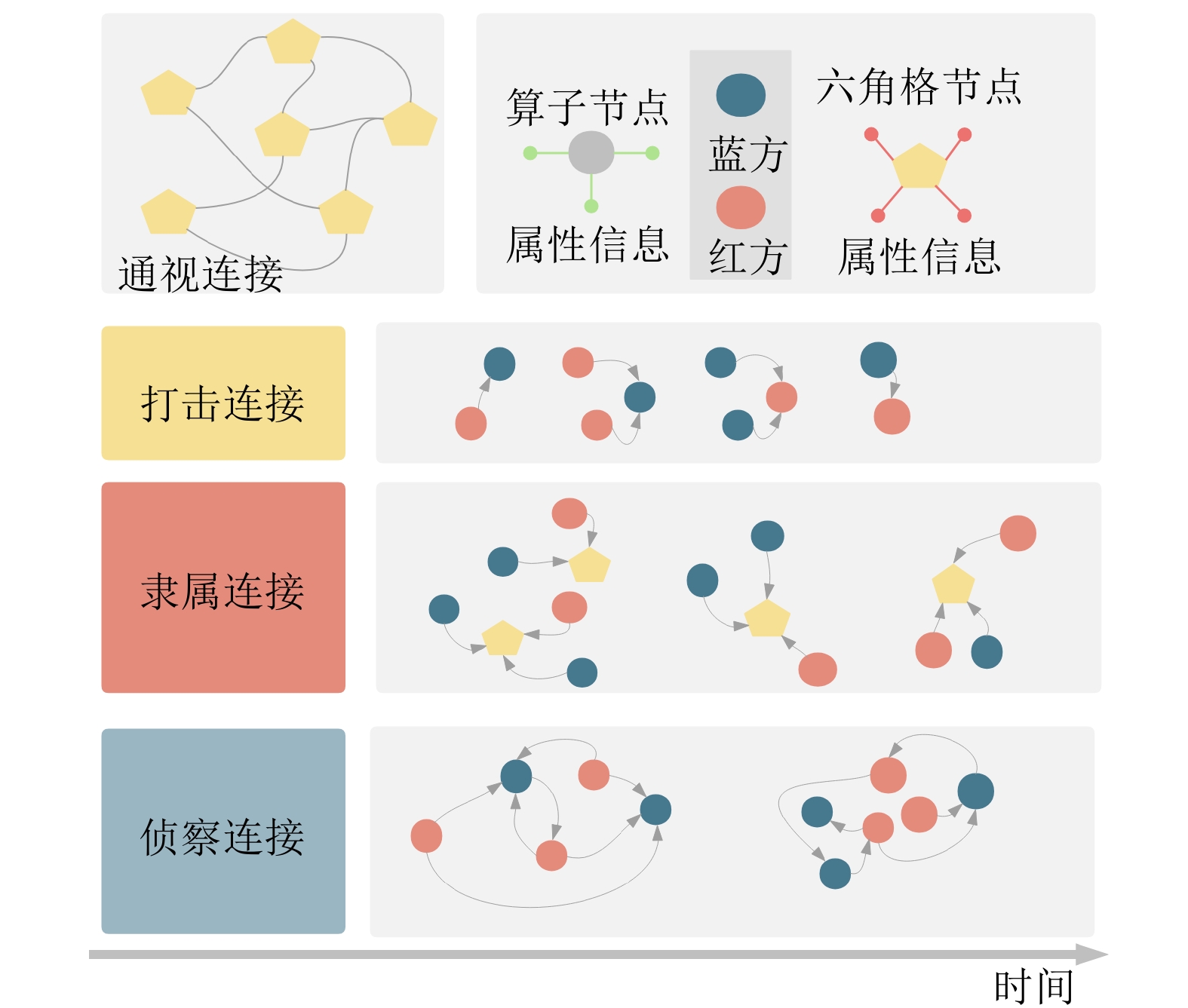
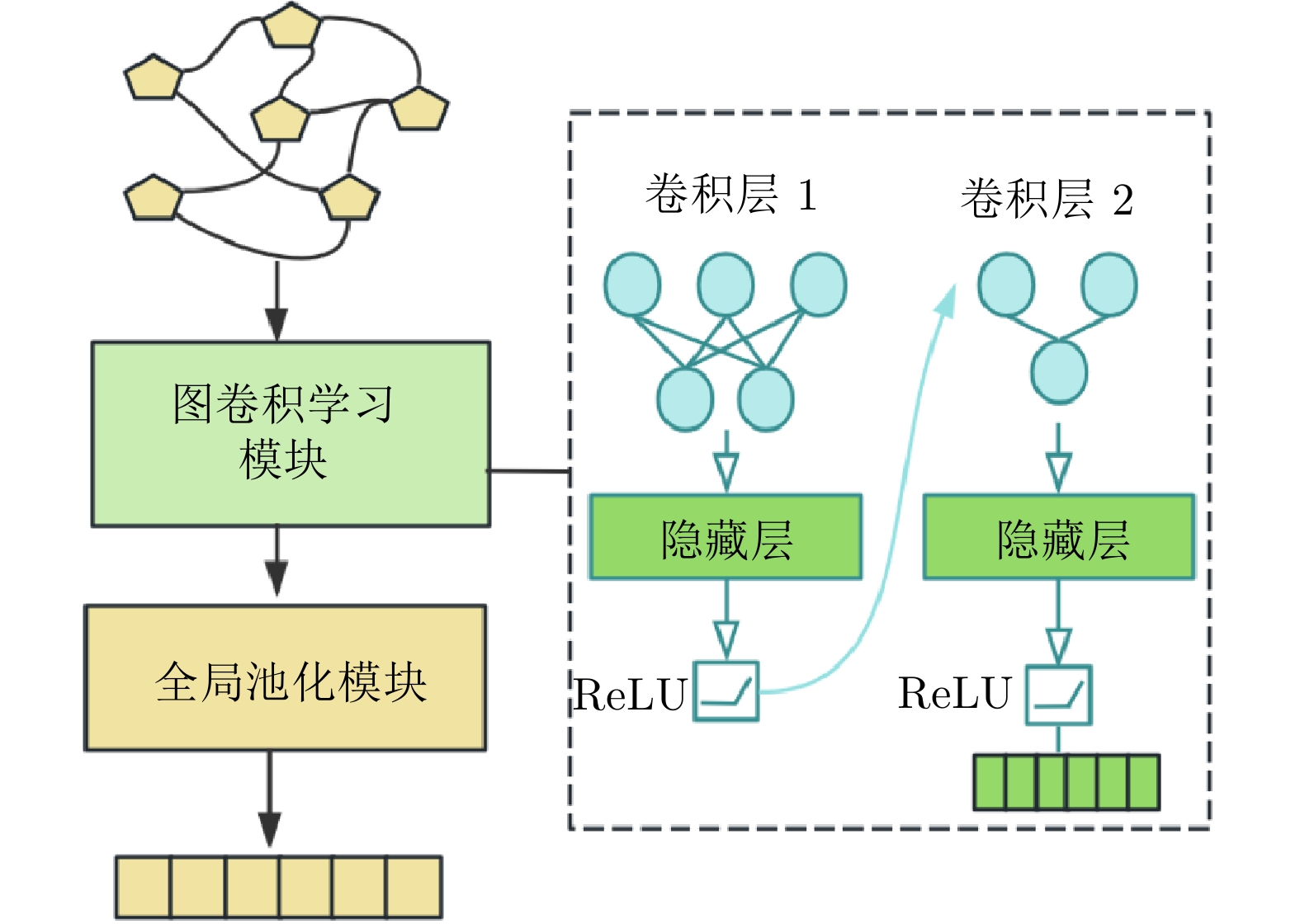
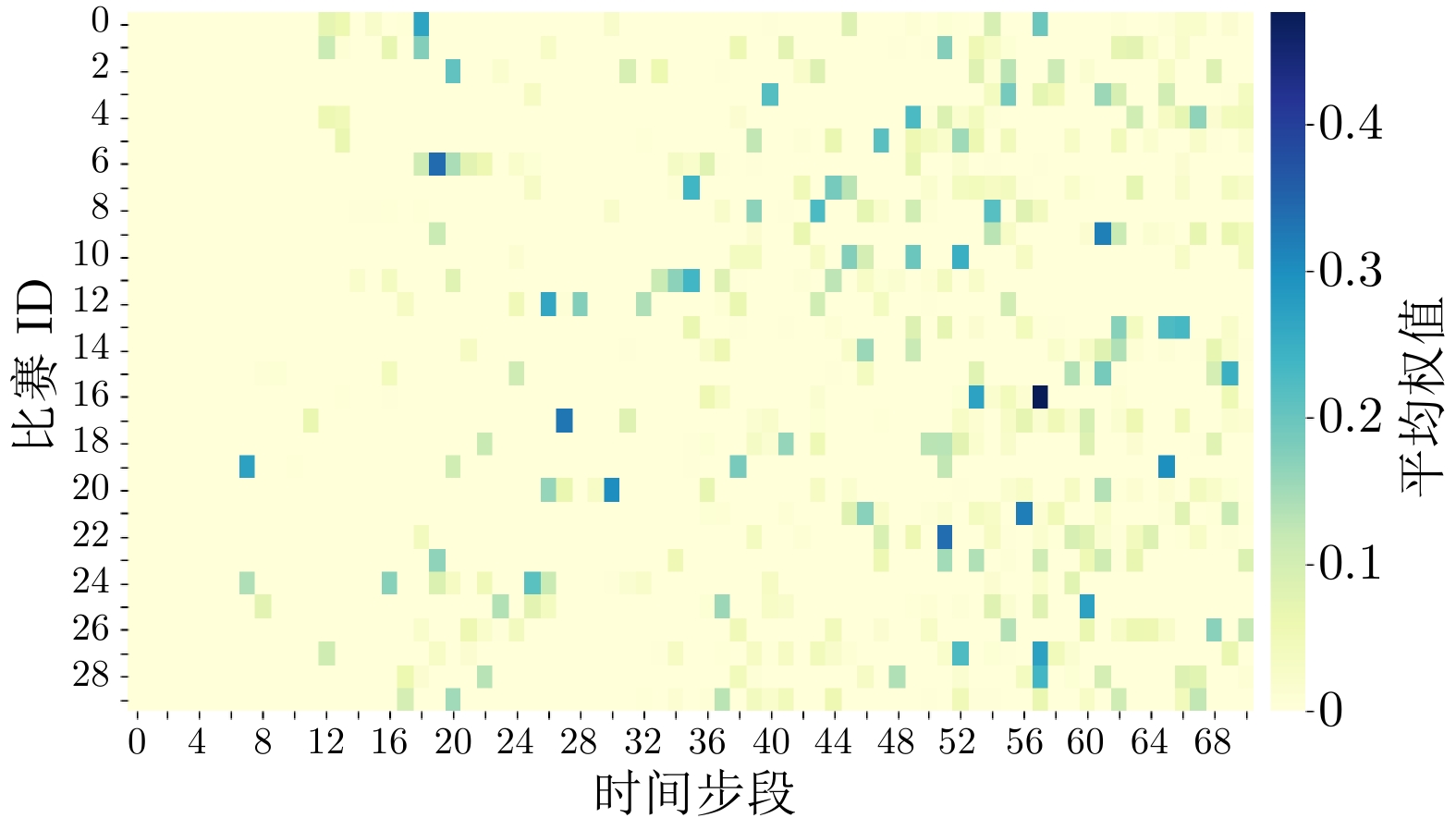
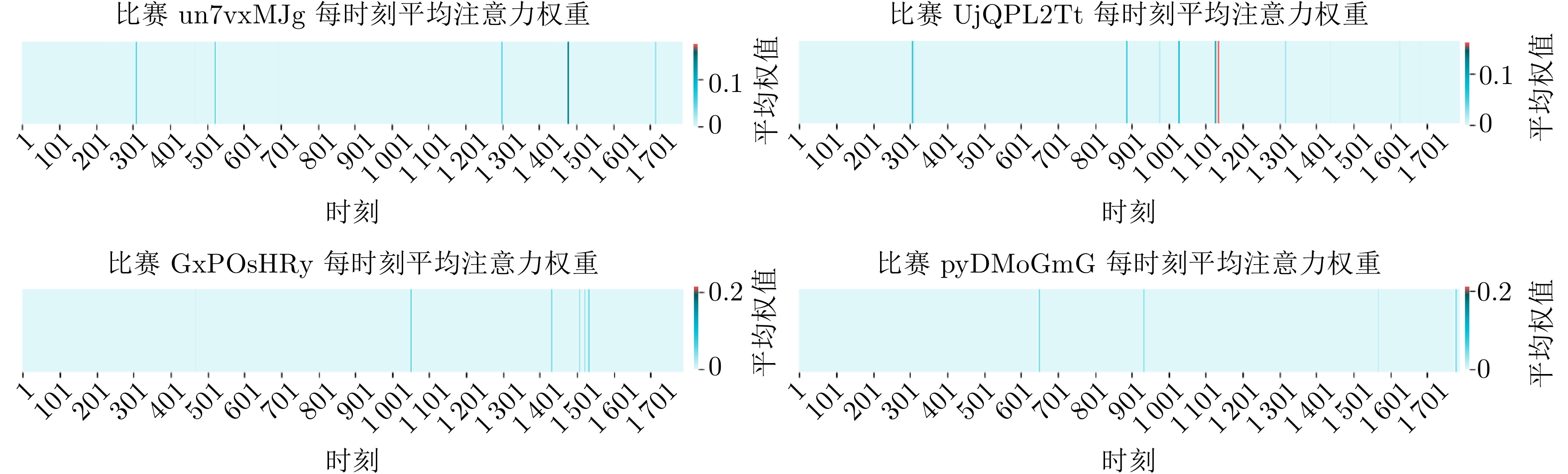
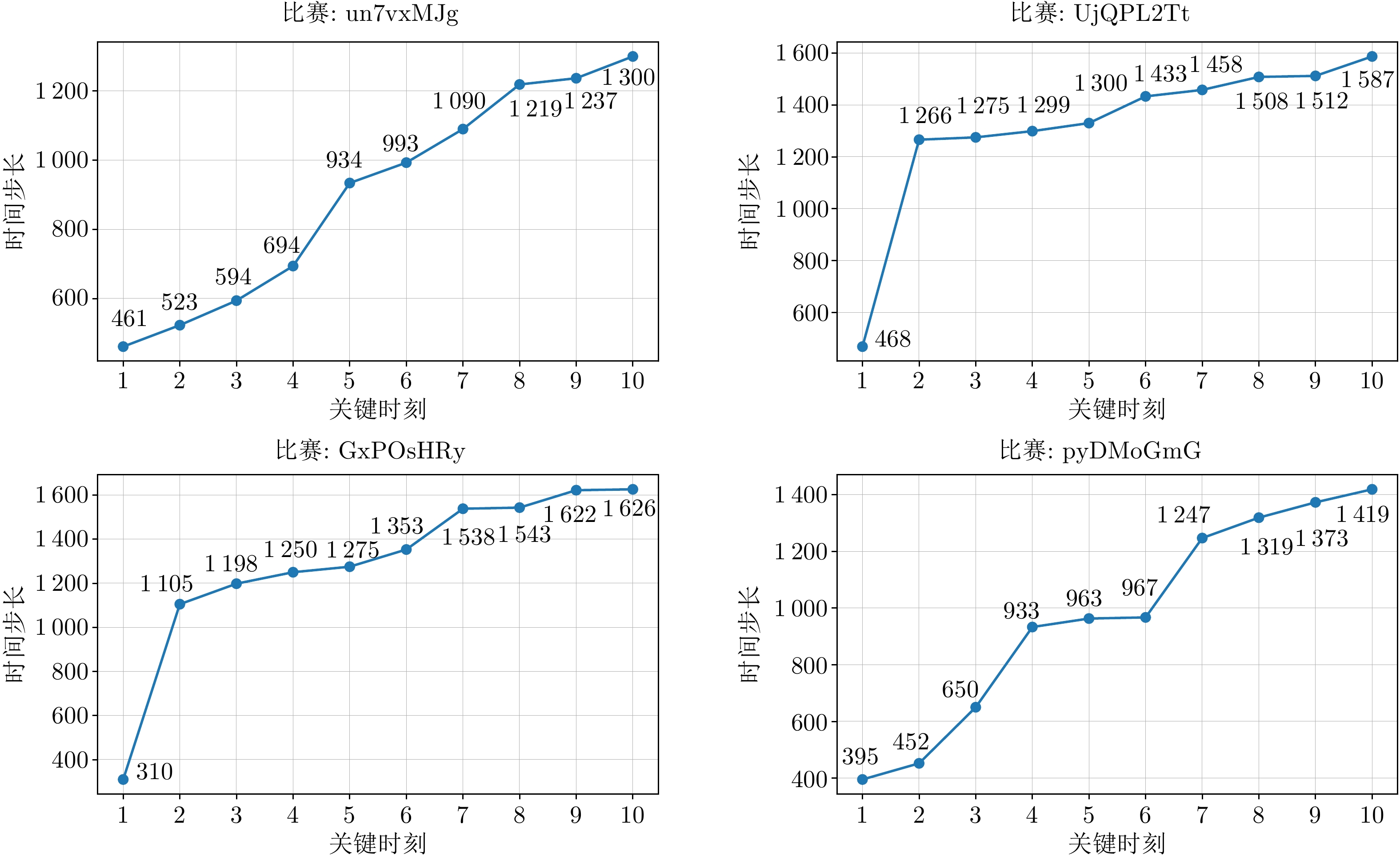
摘要: 复杂多变的现代兵棋模拟中, 精准的战局预测与战场态势解读是提高决策质量的关键. 针对兵棋推演中复杂态势表达困难和模型可解释性不足的挑战, 提出基于异构图神经网络的可解释兵棋预测模型WarGraph, 模型由多关系图建模、时序分析、预测解释三个模块构成. 首先综合复盘数据与先验知识, 将环境与算子之间的多元复杂关系建模为多关系异构图, 从而捕捉作战单元之间以及与环境的复杂交互关系, 实现复杂推演态势的表征; 然后利用Transformer时序分析方法, 动态捕捉整体态势演变, 并通过注意力机制抽取关键决策时刻. 该模型不仅能在复盘推演中精准预测战局胜负, 而且注意力机制的引入能更好地解释决策中的关键因素. 以“庙算·智胜”实时兵棋对抗平台2021年的108场陆战对局复盘数据作为实验数据集, 结果显示本文提出的模型预测准确率可达90.91%, 相比其他模型提高大约9.09%. 通过对注意力系数的可视化分析, 模型在决策过程中捕捉到关键时刻, 进一步验证了模型的可解释性.Abstract: In complex and changeable modern wargame simulations, accurate battlefield situation prediction and interpretation are crucial for high-quality decision-making. To address the challenges of difficult expression of complex situations and insufficient model interpretability in wargame deduction, this paper proposes an interpretable wargame prediction model WarGraph based on heterogeneous graph neural networks. The model consists of three modules: Multi-relational graph modeling, temporal analysis, and interpretable prediction. We first combine replay data with prior knowledge to construct a multi-relational heterogeneous graph, effectively modeling the intricate relationships between the environment and the operators. This enables capturing the complex interactions between combat units and the environment, realizing the representation of complex deduction situations. Then by leveraging Transformer-based temporal analysis, we dynamically track the overall situation evolution and use attention mechanisms to identify key decision-making moments. This model can not only accurately predict the outcome of battles in wargame replays, but also the introduction of the attention mechanism enables a better explanation of the key factors in decision-making. Using replay data of 108 matches from the “MiaoSuan·ZhiSheng” wargame platform in 2021, the results show that the proposed model achieves a prediction accuracy of up to 90.91%, about 9.09% higher than the baseline models. Visualization of the attention coefficients demonstrates that the model captures critical moments in the decision-making process, which further validates its interpretability.
-
Key words:
- Wargame deduction /
- situation prediction /
- graph neural network /
- interpretable analysis /
- deep learning
-
表 1 六角格节点属性
Table 1 Features of hexagonal lattice node
参数名 数据类型 说明 pos 整型 4位整数坐标 elev 整型 高程 node_id 整型 ID cond 整型 地形 can_hide 整型 是否可掩蔽 has_road 整型 有无道路 has_river 整型 有无河流 表 2 算子节点属性
Table 2 Features of operator node
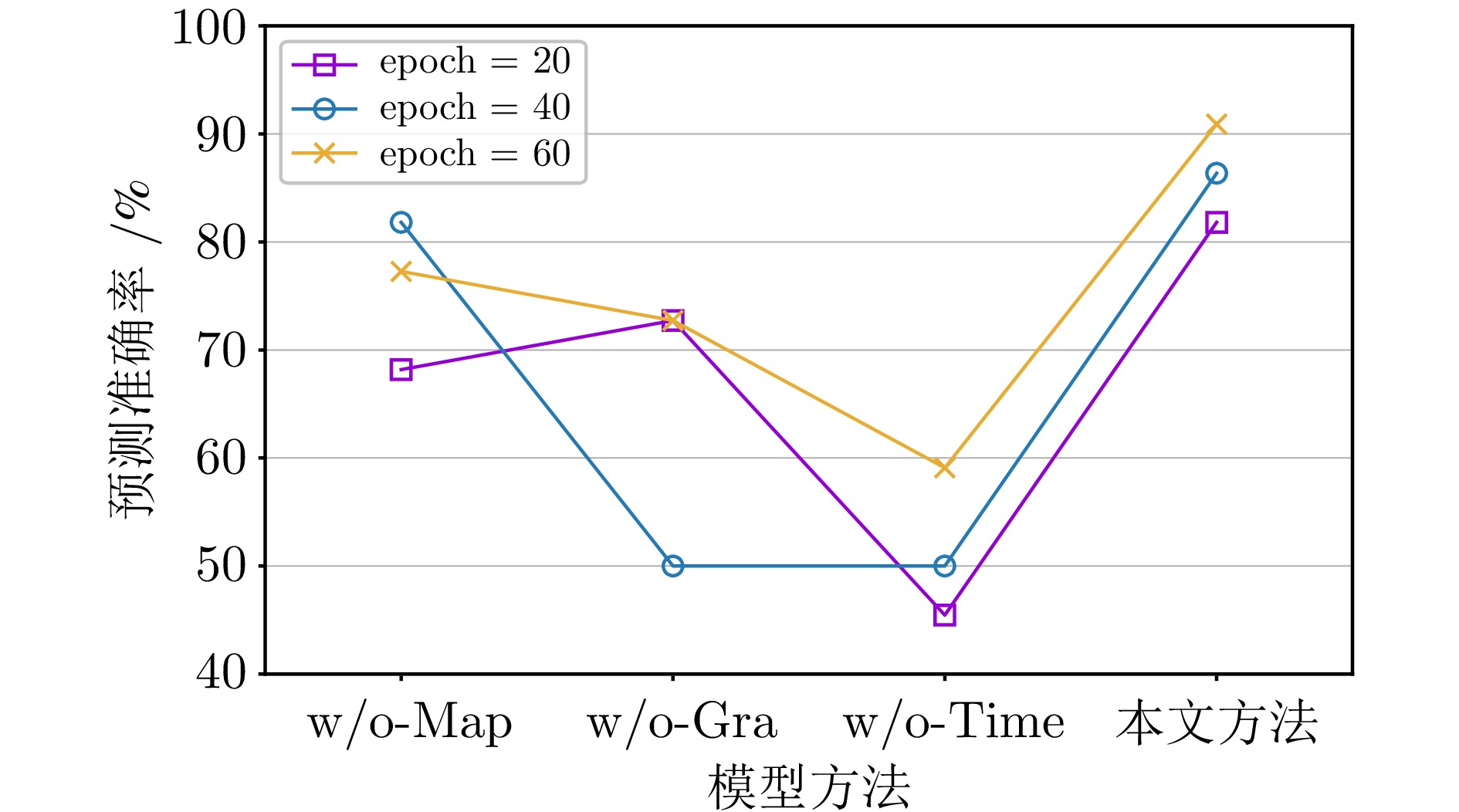
参数名 数据类型 说明 op_id 整型 算子ID color 整型 算子阵营 type 整型 算子类型 sub_type 整型 算子细分类型 basic_speed 整型 基础速度 armor 整型 装甲类型 speed 整型 当前机动速度 表 3 不同LR和epoch下的对比实验结果 (%)
Table 3 Comparative experimental results under different LR and epoch settings (%)
LR 模型 Accuracy
(epoch = 20)Accuracy
(epoch = 40)Accuracy
(epoch = 60)0.01 WarGraph 81.82 86.36 90.91 Trans-CNN 54.55 77.27 72.73 Trans-MLP 45.45 81.82 81.82 LSA-Trans 72.73 68.18 77.27 LSA-CNN 81.82 77.27 63.64 LSA-MLP 36.36 81.82 81.82 ESA-Trans 68.18 54.55 50.00 ESA-CNN 50.00 63.64 63.64 ESA-MLP 50.00 50.50 55.00 0.005 WarGraph 81.82 90.91 86.36 Trans-CNN 77.28 81.82 72.73 Trans-MLP 68.18 81.82 81.82 LSA-Trans 68.18 77.27 81.82 LSA-CNN 63.64 81.82 77.27 LSA-MLP 54.54 81.82 81.82 ESA-Trans 54.54 40.90 45.45 ESA-CNN 63.64 54.55 63.64 ESA-MLP 36.36 50.00 54.55 表 4 超参数选择
Table 4 Selection of hyperparameters
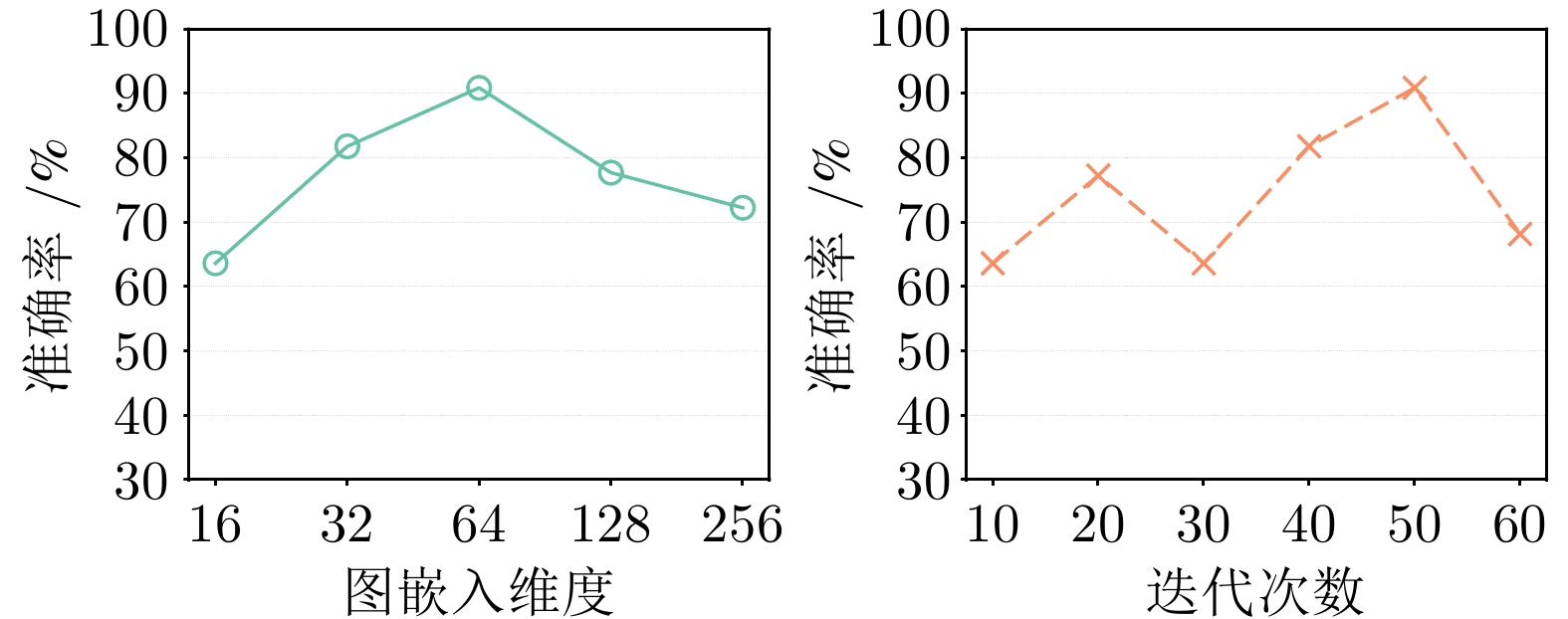
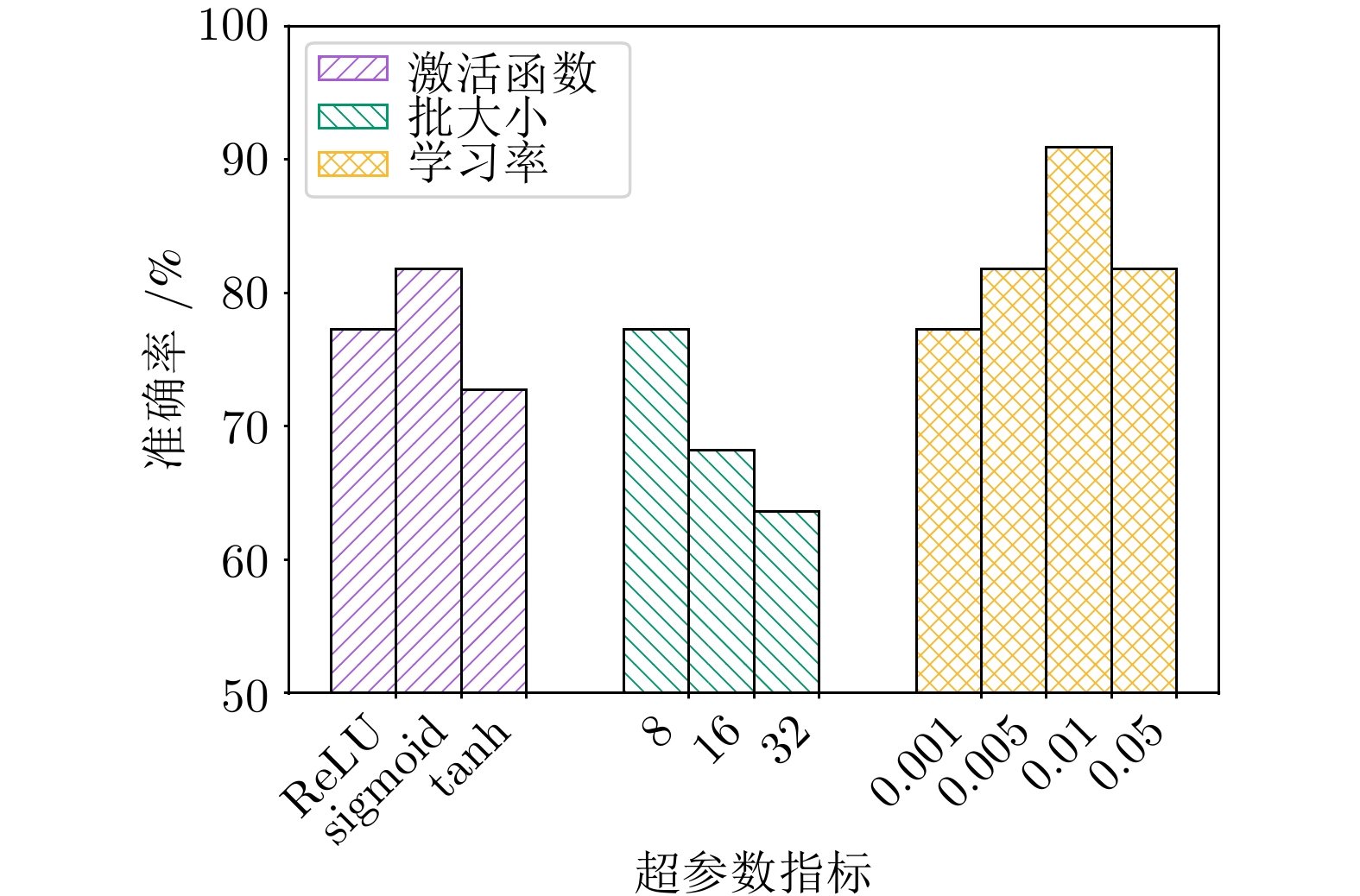
超参数 选取范围 图融合表征维度 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 激活函数 ReLU, sigmoid, tanh 批大小 8, 16, 32 学习率 0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.05 迭代次数 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 -
[1] Mittalf V, Davidson A. Combining wargaming with modeling and simulation to project future military technology requirements. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 2020, 68(4): 1195−1207 [2] Ouriques L, Barbosa C E, Xexéo G. Understanding military collaboration in wargames. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD). Piscataway, USA: IEEE, 2023. 1920−1925 [3] Li L, Yang R, Li H, Lv M, Yue L, Wu A. Unsupervised contrastive learning for automatic grouping of aerial swarms. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(5): 6249−6258 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3342186 [4] Rosen A M, Kerr L. Wargaming for learning: How educational gaming supports student learning and perspectives. Journal of Political Science Education, 2024, 20(2): 318−335 doi: 10.1080/15512169.2024.2304769 [5] 姚昌华, 毕珊宁, 马茹飞, 余晓晗, 李家强, 陈金立. 兵棋智能体兵力协同动态联盟形成方法. 系统仿真学报, DOI: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.24-0058Yao Chang-Hua, Bi Shan-Ning, Ma Ru-Fei, Yu Xiao-Han, Li Jia-Qiang, Chen Jin-Li. Method for dynamic coalition formation of wargame agent for force cooperation. Journal of System Simulation, DOI: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.24-0058 [6] 胡晓峰, 齐大伟. 智能化兵棋系统: 下一代需要改变的是什么. 系统仿真学报, 2021, 33(9): 1997−2009Hu Xiao-Feng, Qi Da-Wei. Intelligent wargaming system: Change needed by next generation need to be changed. Journal of System Simulation, 2021, 33(9): 1997−2009 [7] 胡晓峰, 贺筱媛, 陶九阳. AlphaGo的突破与兵棋推演的挑战. 科技导报, 2017, 35(21): 49−60Hu Xiao-Feng, He Xiao-Yuan, Tao Jiu-Yang. AlphaGo's breakthrough and challenges of wargaming. Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(21): 49−60 [8] 曹占广, 陶帅, 胡晓峰, 何吕龙. 国外兵棋推演及系统研究进展. 系统仿真学报, 2021, 33(9): 2059−2065Cao Zhan-Guang, Tao Shuai, Hu Xiao-Feng, He Lv-Long. Research progress of wargaming simulation methods and system abroad. Journal of System Simulation, 2021, 33(9): 2059−2065 [9] 吴琳, 胡晓峰, 陶九阳, 贺筱媛. 面向智能成长的兵棋推演生态系统. 系统仿真学报, 2021, 33(9): 2048−2058Wu Lin, Hu Xiao-Feng, Tao Jiu-Yang, He Xiao-Yuan. Wargaming eco-system for intelligence growing. Journal of System Simulation, 2021, 33(9): 2048−2058 [10] 刘海洋, 唐宇波, 胡晓峰, 乔广鹏. 基于兵棋推演的联合作战方案评估框架研究. 系统仿真学报, 2018, 30(11): 4115−4123Liu Hai-Yang, Tang Yu-Bo, Hu Xiao-Feng, Qiao Guang-Peng. Research on evaluation framework of COA based on wargaming. Journal of System Simulation, 2018, 30(11): 4115−4123 [11] 刘海洋, 唐宇波, 胡晓峰, 刘戎翔, 崔文华. 面向联合作战评估的兵棋推演实验研究. 指挥与控制学报, 2018, 4(4): 272−280 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2018.04.0272Liu Hai-Yang, Tang Yu-Bo, Hu Xiao-Feng, Liu Rong-Xiang, Cui Wen-Hua. Wargaming experiment oriented evaluation of joint operations. Journal of Command and Control, 2018, 4(4): 272−280 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2018.04.0272 [12] 邢思远, 倪晚成, 张海东, 闫科. 基于兵棋复盘数据的武器效用挖掘. 指挥与控制学报, 2020, 6(2): 132−140 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2020.02.0132Xing Si-Yuan, Ni Wan-Cheng, Zhang Hai-Dong, Yan Ke. Mining of weapon utility based on the replay data of war-game. Journal of Command and Control, 2020, 6(2): 132−140 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2020.02.0132 [13] 尹奇跃, 赵美静, 倪晚成, 张俊格, 黄凯奇. 兵棋推演的智能决策技术与挑战. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(5): 913−928Yin Qi-Yue, Zhao Mei-Jing, Ni Wan-Cheng, Zhang Jun-Ge, Huang Kai-Qi. Intelligent decision making technology and challenge of wargame. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(5): 913−928 [14] Chen L, Zhang Y, Feng Y, Zhang L, Liu Z. A human-machine agent based on active reinforcement learning for target classification in wargame. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(7): 9858−9870 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3236944 [15] 周雷, 尹奇跃, 黄凯奇. 人机对抗中的博弈学习方法. 计算机学报, 2022, 45(9): 1859−1876 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.01859Zhou Lei, Yin Qi-Yue, Huang Kai-Qi. Game-theoretic learning in human-computer gaming. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2022, 45(9): 1859−1876 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.01859 [16] Sun Y, Yuan B, Xiang Q, Zhou J, Yu J, Dai D, et al. Intelligent decision-making and human language communication based on deep reinforcement learning in a wargame environment. IEEE Transactions on Human-machine Systems, 2022, 53(1): 201−214 [17] 刘满, 张宏军, 程恺, 郝文宁, 王之腾. 知识与数据互补的战术级兵棋行为决策框架设计与实现. 指挥与控制学报, 2023, 9(2): 182−191 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2023.02.0182Liu Man, Zhang Hong-Jun, Cheng Kai, Hao Wen-Ning, Wang Zhi-Teng. Framework design and application for tactical-level wargame behavior decision-making based on complementary knowledge and data. Journal of Command and Control, 2023, 9(2): 182−191 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2023.02.0182 [18] Xue Y, Sun Y, Zhou J, Peng L, Zhou X. Multiattribute decision-making in wargames leveraging the entropy-weight method in conjunction with deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Games, 2024, 16(1): 151−161 doi: 10.1109/tg.2023.3236065 [19] 许霄, 李东, 郭圣明, 吴琳, 胡晓峰. 面向联合作战兵棋推演的智能决策建模框架. 指挥与控制学报, 2023, 9(4): 449−456 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2023.04.0449Xu Xiao, Li Dong, Guo Sheng-Ming, Wu Lin, Hu Xiao-Feng. An intelligent decision-making modeling architecture for joint operation-oriented wargaming. Journal of Command and Control, 2023, 9(4): 449−456 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2023.04.0449 [20] Chen L, Liang X, Feng Y, Zhang L, Yang J, Liu Z. Online intention recognition with incomplete information based on a weighted contrastive predictive coding model in wargame. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(10): 7515−7528 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3144171 [21] Sun D, Qi S. Relation extraction on the wargame based on pre-trained models. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Dependable Systems and Their Applications (DSA). Urumchi, China: IEEE, 2022. 941−944 [22] Liu X, Zhao M, Dai S, Yin Q, Ni W. Tactical intention recognition in wargame. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS). Chengdu, China: IEEE, 2021. 429−434 [23] 孙宇祥, 赵俊杰, 解宇轩, 喻车澄, 周献中. 自生成兵棋AI: 基于大语言模型的双层Agent任务规划. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(12): 3927−3936Sun Yu-Xiang, Zhao Jun-Jie, Xie Yu-Xuan, Yu Che-Cheng, Zhou Xian-Zhong. Self generated wargame AI: Double layer agent task planning based on large language mode. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(12): 3927−3936 [24] Dong L, Li N, Yuan H, Gong G. Accelerating wargaming reinforcement learning by dynamic multi-demonstrator ensemble. Information Sciences, 2023, 648: Article No. 119534 [25] Sun Y, Sun Y, Yu J, Li Y, Zhou X. Predicting wargame outcomes and evaluating player performance from an integrated strategic and operational perspective. IEEE Transactions on Games, 2024, 16(4): 770−782 [26] Ma R, Liu S, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Ni Y. Research on fuzzy dynamic route choice model and algorithm of wargame. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2024, 15: 2863−2880 [27] Wang T, Dai S, Liu X, Zhao M, Zhang H, Yin Q. MFSCD* lite: A situation-based path planning algorithm for agent in wargame. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Computer Science and Intelligent Control (ISCSIC). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2022. 244−249 [28] Jensen B, Valeriano B, Whitt S. How cyber operations can reduce escalation pressures: Evidence from an experimental wargame study. Journal of Peace Research, 2024, 61(1): 119−133 [29] 黄洪原. 浅议兵棋系统的发展及军事运用. 中国军转民, 2022(16): 53−55 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5874.2022.04.026Huang Hong-Yuan. A brief discussion on the development and military applications of wargaming systems. Defence Industry Conversion in China, 2022(16): 53−55 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5874.2022.04.026 [30] 张大永, 杨镜宇, 马骏, 宋晨烨. 面向兵棋推演复盘分析的机器学习数据集构建. 系统仿真学报, 2024, 36(3): 608−624Zhang Da-Yong, Yang Jing-Yu, Ma Jun, Song Chen-Ye. Construction of machine learning data set for the analysis of the replay of the wargaming. Journal of System Simulation, 2024, 36(3): 608−624 [31] 余晓晗, 王启迪, 于坤. 基于图神经网络GraphVAE的兵棋态势预测方法. 指挥控制与仿真, 2023, 45(5): 129−136 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2023.05.018Yu Xiao-Han, Wang Qi-Di, Yu Kun. A wargame situation prediction method based on a graph neural network GraphVAE. Command Control & Simulation, 2023, 45(5): 129−136 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3819.2023.05.018 [32] 陈锦阳, 郝文宁, 靳大尉, 陈刚, 余晓晗. 基于注意力机制的兵棋对抗态势预测方法. 火力与指挥控制, 2023, 48(3): 18−24 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2023.03.003Chen Jin-Yang, Hao Wen-Ning, Jin Da-Wei, Chen Gang, Yu Xiao-Han. Research on the prediction method of wargame confrontation situation based on attention mechanism. Fire Control & Command Control, 2023, 48(3): 18−24 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2023.03.003 [33] Kipf T, Welling M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1609.02907, 2016. [34] Hamilton W L, Ying R, Leskovec J. Inductive representation learning on large graphs. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 1025−1035 [35] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez A N, et al. Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 6000−6010 -




 下载:
下载: