Artifact-prompt Based Method for Simultaneous Sparse-view and Metal Artifact Reduction in CT Images
-
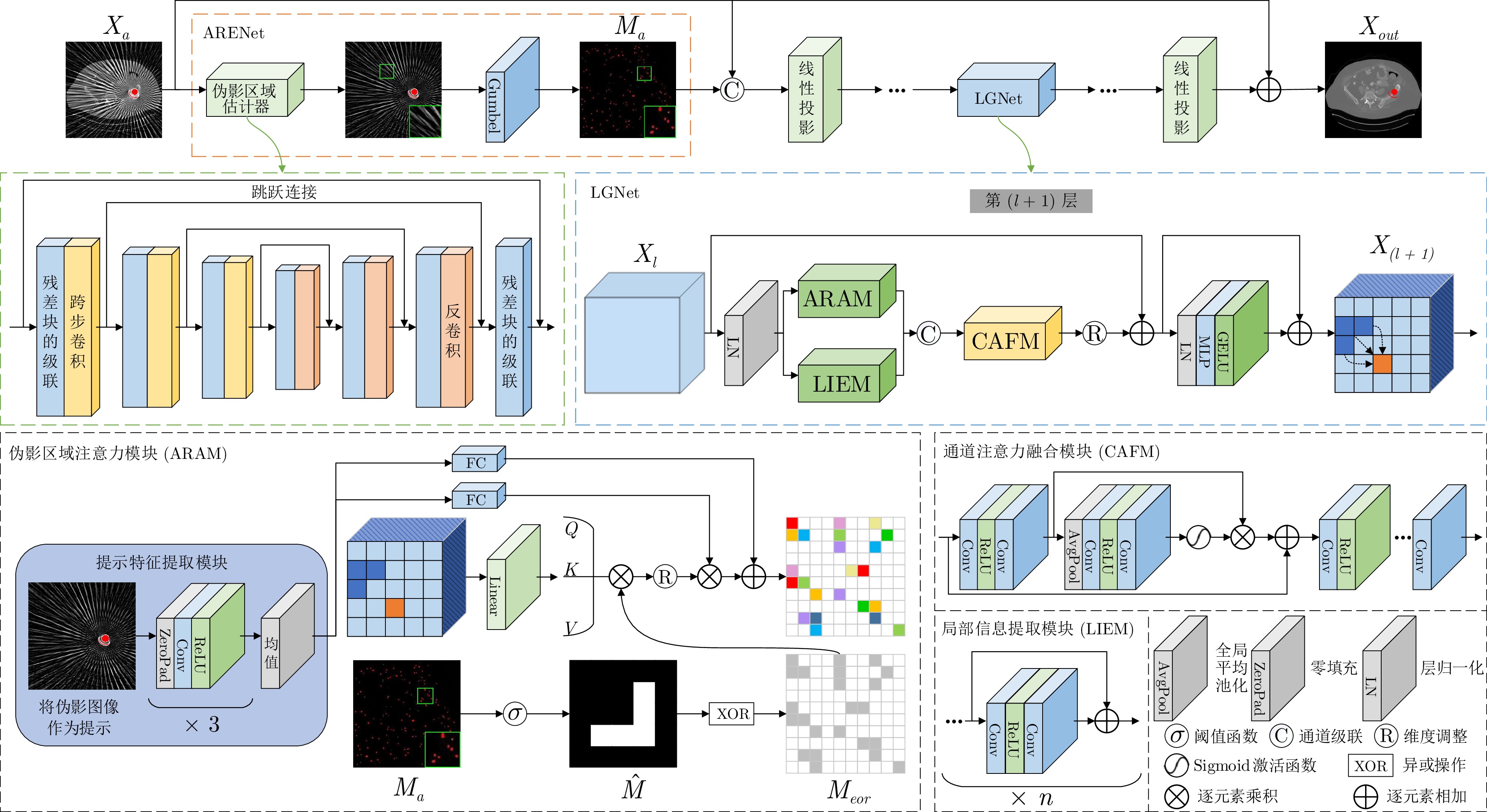
摘要: 联合稀疏角度CT重建和金属伪影校正任务旨在通过受金属迹污染的少视角投影数据重建高质量的CT图像. 现有稀疏角度CT重建方法和金属伪影校正方法通常依赖于CT图像或投影数据, 但其存在临床投影数据难以获取和校正精度差的问题. 为解决这些问题, 提出一种基于伪影提示Transformer的图像域方法, 仅利用受伪影影响的CT图像即可同时实现稀疏角度CT重建和金属伪影校正. 该方法将伪影区域作为提示, 并将提示特征融入Transformer提取的特征中, 提出伪影提示Transformer架构. 该架构能够通过伪影区域特征提示, 利用伪影区域和非伪影区域之间的全局上下文相关性提升伪影校正精度. 针对多种伪影校正问题, 在包含伪影的CT图像上构建伪影区域估计网络来估计伪影区域, 并设计由局部信息提取模块、伪影区域注意力模块和通道注意力融合模块构成的局部−全局信息交互网络来融合局部与全局信息. 实验结果表明, 该方法能够同时进行高精度CT重建并有效去除金属伪影.
-
关键词:
- 稀疏角度CT重建 /
- 金属伪影校正 /
- 提示学习 /
- Transformer
Abstract: The task of joint sparse-view CT reconstruction and metal artifact reduction (SVMAR) aims to reconstruct high-quality CT images from few-view projection data contaminated by metal traces. Existing sparse-view CT reconstruction methods and metal artifact reduction methods typically depend on CT images or projection data, but they are plagued by the difficulty in acquiring clinical projection data and insufficient correction accuracy. To address these problems, a novel artifact-prompt Transformer-based image domain method is proposed, which accomplishes SVMAR using only artifact-affected CT images. This method utilizes the artifact regions as prompt and incorporates the prompt features into the features extracted by Transformer to propose the artifact-prompt Transformer architecture. By leveraging features of the artifact regions as prompt, this architecture can improve the accuracy of artifact reduction by capturing the global contextual correlation between artifact and the non-artifact regions. Regarding multiple artifact reduction problems, we construct an artifact region estimation network to estimate the artifact regions in CT images containing artifacts, and design a local-global information interaction network composed of a local information extraction module, an artifact region attention module and a channel attention fusion module to integrate local and global information. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve high-accuracy CT reconstruction and reduce metal artifacts effectively.-
Key words:
- Sparse-view CT reconstruction /
- metal artifact reduction /
- prompt learning /
- Transformer
-
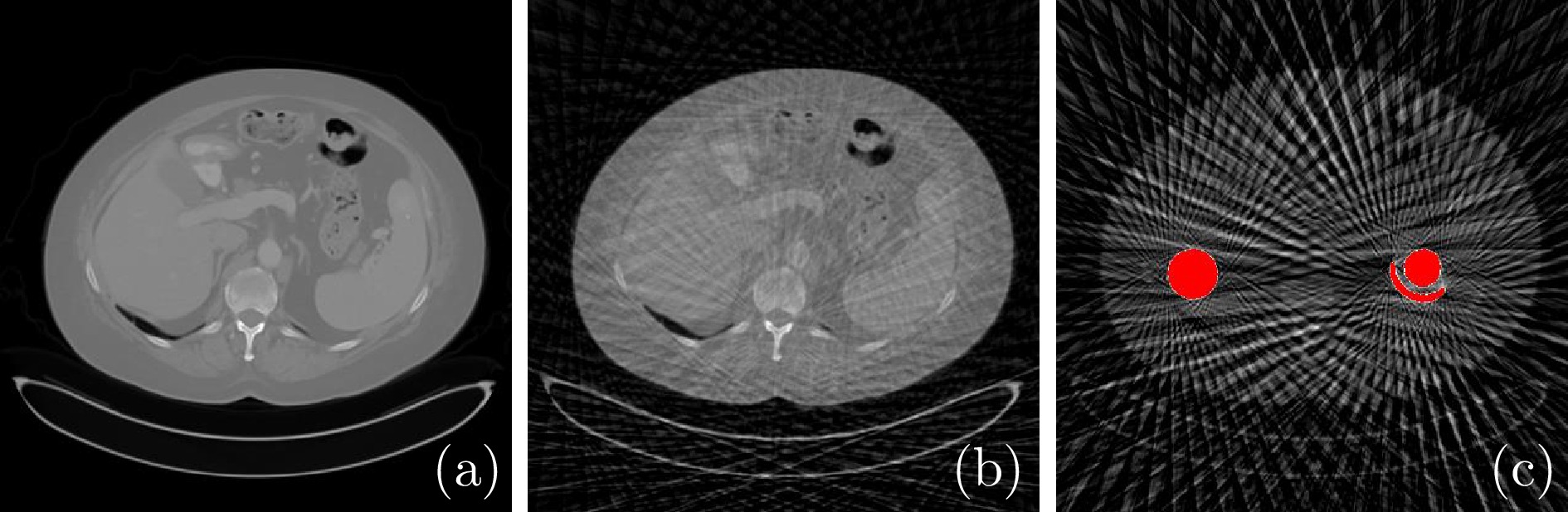
图 1 不同情况下重建图像的对比 ((a) 原始CT图像; (b) 稀疏角度采样下重建的CT图像; (c) 稀疏角度采样下重建的含金属植入物的CT图像)
Fig. 1 Comparison of the reconstructed images in different situations ((a) The original CT image; (b) The reconstructed CT image under the sparse-view sampling condition; (c) The reconstructed CT image with metallic implants under the sparse-view sampling condition)
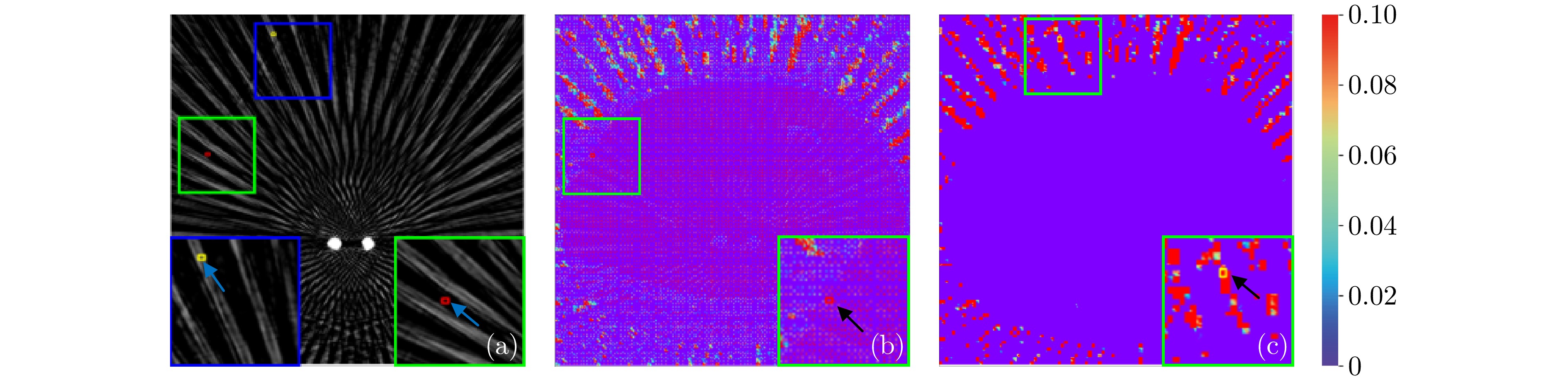
图 3 在ARAM模块中对两个关键点(红、黄)在伪影与非伪影区域之间的相关映射进行可视化 ((a) 伪影图像; (b) 红色点对应的注意力映射; (c) 黄色点对应的注意力映射)
Fig. 3 Visualization of correlation maps in ARAM for two key points (red and yellow) between artifact and non-artifact regions ((a) Artifact image; (b) Attention map for the red point; (c) Attention map for the yellow point)
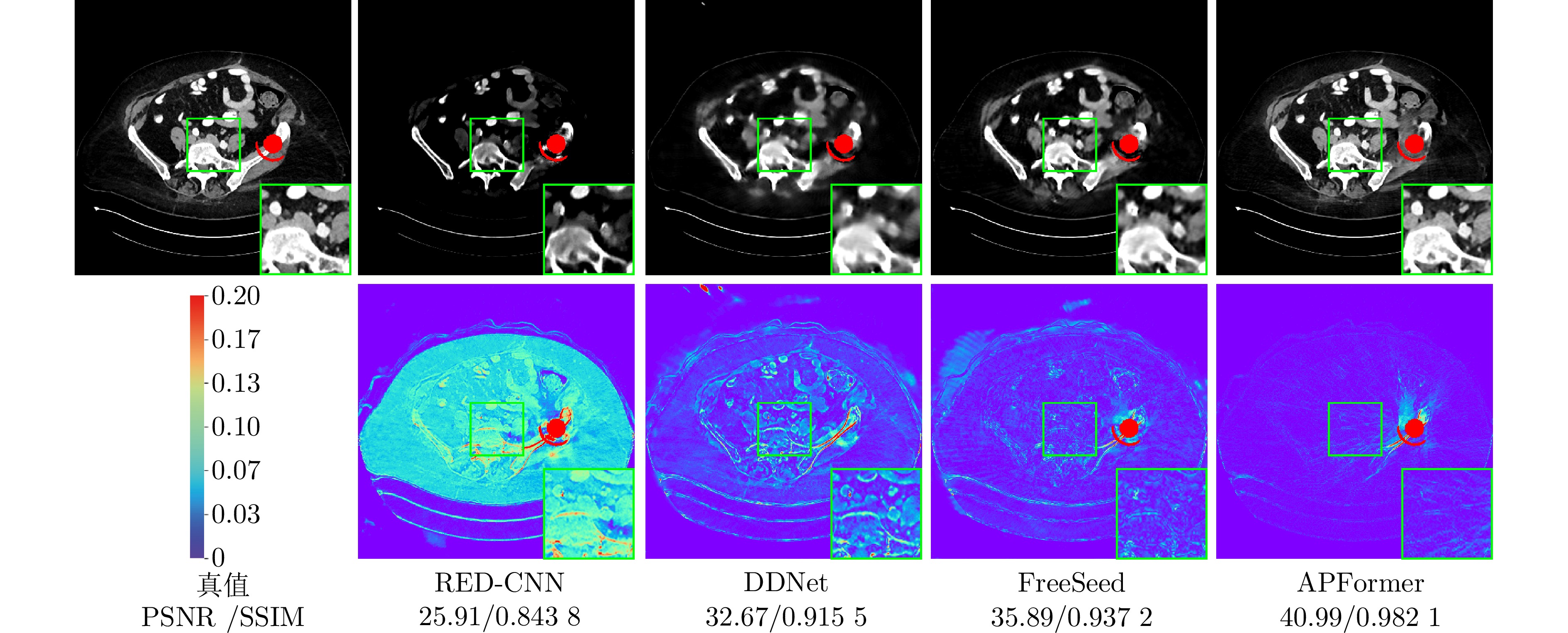
表 1 各模块消融实验的PSNR (dB)和SSIM值对比
Table 1 Comparison of PSNR (dB) and SSIM values in each module ablation experiments
网络 大尺寸金属 小尺寸金属 平均值 PSNR SSIM PSNR SSIM PSNR SSIM 网络1 35.78 0.963 6 40.81 0.976 5 38.23 0.968 9 网络2 38.07 0.974 5 42.92 0.983 4 40.30 0.977 8 网络3 38.82 0.976 9 43.65 0.985 0 41.08 0.980 0 网络4 39.06 0.977 6 43.60 0.985 2 41.08 0.980 3 网络5 39.30 0.978 6 43.84 0.985 6 41.41 0.981 2 网络6 38.99 0.974 1 43.27 0.982 8 41.09 0.977 5 网络7 39.35 0.979 1 44.07 0.986 3 41.50 0.981 8 表 2 使用PSNR (dB)、SSIM和RMSE值比较三种不同的稀疏角度设置下的金属伪影校正效果
Table 2 Comparison of metal artifact reduction effects under three different sparse-view settings using PSNR (dB), SSIM and RMSE values
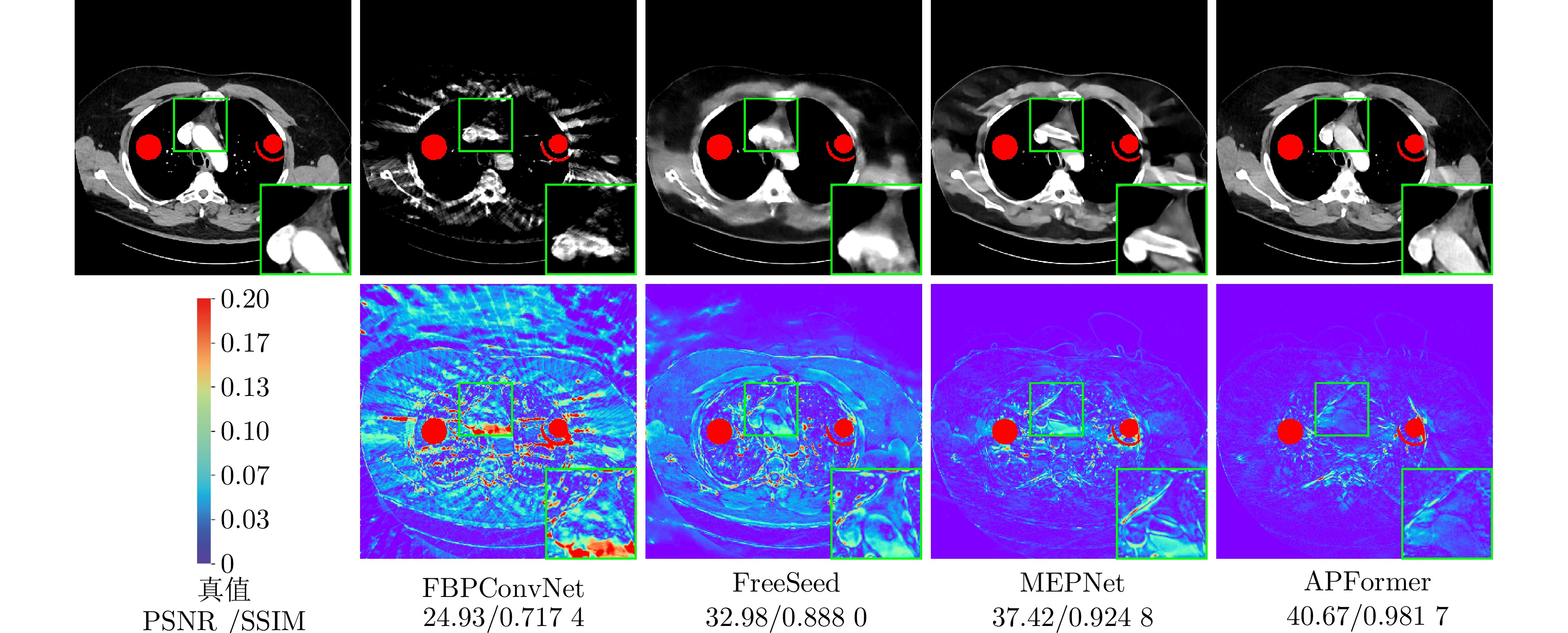
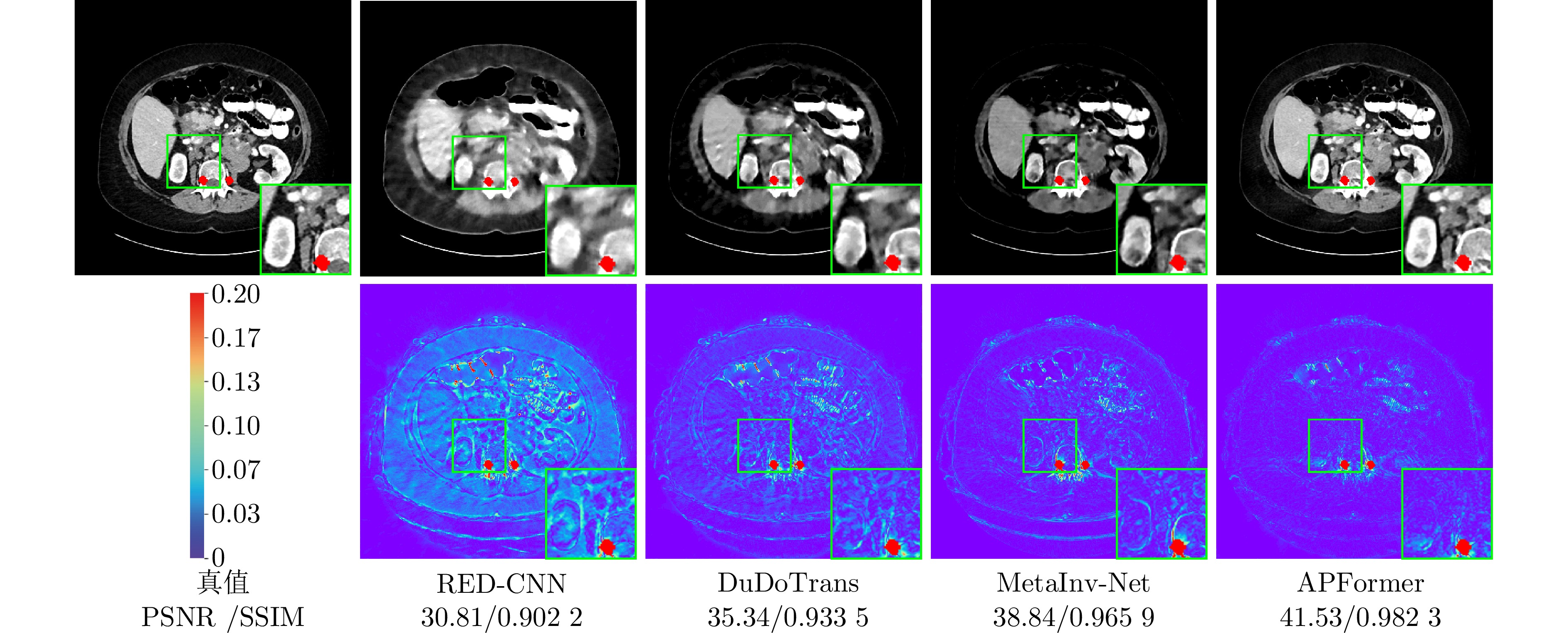
方法 PSNR SSIM RMSE × 6 × 4 × 2 × 6 × 4 × 2 × 6 × 4 × 2 FBP[4] 14.24 15.10 22.34 0.120 2 0.118 0 0.231 2 517.92 468.80 205.85 RED-CNN[45] 33.75 35.55 39.10 0.903 6 0.924 4 0.959 1 54.86 44.78 30.03 FBPConvNet[46] 33.99 36.14 38.87 0.855 3 0.899 1 0.943 9 55.67 43.98 32.93 DDNet[5] 34.17 36.14 39.54 0.907 9 0.923 7 0.957 4 51.88 41.38 28.11 CNNMAR[36] 36.01 37.56 40.03 0.939 1 0.952 1 0.970 8 42.38 35.49 27.15 DuDoTrans[11] 35.05 37.04 40.29 0.908 7 0.935 7 0.964 2 46.89 37.51 26.05 MetaInv-Net[9] 37.38 37.64 40.05 0.960 6 0.961 3 0.977 6 36.02 35.24 27.65 FreeSeed[27] 34.45 35.34 37.27 0.872 7 0.880 1 0.911 3 49.73 44.83 35.84 MEPNet[39] 38.93 39.43 41.04 0.961 1 0.963 9 0.960 8 30.31 30.28 24.95 APFormer 41.50 41.91 42.80 0.981 8 0.982 0 0.985 1 23.43 22.11 19.86 表 3 不同方法的模型参数量与计算效率比较
Table 3 Comparison of the model parameters and computational efficiency of different methods
-
[1] de Basea M B, Thierry-Chef I, Harbron R, Hauptmann M, Byrnes G, Bernier M O, et al. Risk of hematological malignancies from CT radiation exposure in children, adolescents and young adults. Nature Medicine, 2023, 29(12): 3111−3119 [2] Lee H, Lee J, Kim H, Cho B, Cho S. Deep-neural-network-based sinogram synthesis for sparse-view CT image reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2019, 3(2): 109−119 [3] Zhou B, Zhou S K, Duncan J S, Liu C. Limited view tomographic reconstruction using a cascaded residual dense spatial-channel attention network with projection data fidelity layer. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2021, 40(7): 1792−1804 [4] Pan X C, Sidky E Y, Vannier M. Why do commercial CT scanners still employ traditional, filtered back-projection for image reconstruction? Inverse Problems, 2009, 25(12): Article No. 1230009 [5] Zhang Z C, Liang X K, Dong X, Xie Y Q, Cao G H. A sparse-view CT reconstruction method based on combination of DenseNet and deconvolution. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1407−1417 [6] Sun C, Liu Y T, Yang H W. Degradation-aware deep learning framework for sparse-view CT reconstruction. Tomography, 2021, 7(4): 932−949 [7] Xia W J, Yang Z Y, Zhou Q Z, Lu Z X, Wang Z X, Zhang Y. A transformer-based iterative reconstruction model for sparse-view CT reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2022). Singapore, Singapore: Springer, 2022. 790−800 [8] Cheng W L, Wang Y, Li H W, Duan Y P. Learned full-sampling reconstruction from incomplete data. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020, 6: 945−957 [9] Zhang H M, Liu B D, Yu H Y, Dong B. MetaInv-Net: Meta inversion network for sparse view CT image reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2021, 40(2): 621−634 [10] Pan J Y, Zhang H Y, Wu W F, Gao Z F, Wu W W. Multi-domain integrative Swin transformer network for sparse-view tomographic reconstruction. Patterns, 2022, 3(6): Article No. 100498 [11] Wang C, Shang K, Zhang H M, Li Q, Zhou S K. DuDoTrans: Dual-domain transformer for sparse-view CT reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Machine Learning for Medical Image Reconstruction. Singapore, Singapore: Springer, 2022. 84−94 [12] Ghani M U, Karl W C. Fast enhanced CT metal artifact reduction using data domain deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020, 6: 181−193 [13] Zhang Y B, Yu H Y. Convolutional neural network based metal artifact reduction in X-ray computed tomography. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1370−1381 [14] Wang H, Li Y X, He N J, Ma K, Meng D Y, Zheng Y F. DICDNet: Deep interpretable convolutional dictionary network for metal artifact reduction in CT images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2022, 41(4): 869−880 [15] Wang H, Li Y X, Meng D Y, Zheng Y F. Adaptive convolutional dictionary network for CT metal artifact reduction. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vienna, Austria: IJCAI, 2022. 1401−1407 [16] Wang H, Xie Q, Li Y X, Huang Y W, Meng D Y, Zheng Y F. Orientation-shared convolution representation for CT metal artifact learning. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2022). Singapore, Singapore: Springer, 2022. 665−675 [17] Lyu Y Y, Lin W A, Liao H F, Lu J J, Zhou S K. Encoding metal mask projection for metal artifact reduction in computed tomography. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2020). Lima, Peru: Springer, 2020. 147−157 [18] Wang T, Lu Z X, Yang Z Y, Xia W J, Hou M Z, Sun H Q, et al. IDOL-Net: An interactive dual-domain parallel network for CT metal artifact reduction. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2022, 6(8): 874−885 [19] Li B Y, Liu X, Hu P, Wu Z Q, Lv J C, Peng X. All-in-one image restoration for unknown corruption. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 17431−17441 [20] Potlapalli V, Zamir S W, Khan S, Khan F S. PromptIR: Prompting for all-in-one blind image restoration. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 3121 [21] Yazdanpanah A P, Regentova E E. Sparse-view CT reconstruction using curvelet and TV-based regularization. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Image Analysis and Recognition. Póvoa de Varzim, Portugal: Springer, 2016. 672−677 [22] Okamoto T, Ohnishi T, Haneishi H. Artifact reduction for sparse-view CT using deep learning with band patch. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2022, 6(8): 859−873 [23] Sun X Q, Li X R, Chen P. An ultra-sparse view CT imaging method based on X-ray2CTNet. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2022, 8: 733−742 [24] Guan B, Yang C L, Zhang L, Niu S Z, Zhang M H, Wang Y H, et al. Generative modeling in sinogram domain for sparse-view CT reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2024, 8(2): 195−207 [25] Song Y, Shen L Y, Xing L, Ermon S. Solving inverse problems in medical imaging with score-based generative models. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations. Virtual Event: ICLR, 2022. 1−18 [26] Ding C, Zhang Q C, Wang G, Ye X J, Chen Y M. Learned alternating minimization algorithm for dual-domain sparse-view CT reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2023). Vancouver, Canada: Springer, 2023. 173−183 [27] Ma C L, Li Z L, Zhang J P, Zhang Y, Shan H M. FreeSeed: Frequency-band-aware and self-guided network for sparse-view CT reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2023). Vancouver, Canada: Springer, 2023. 250−259 [28] Verburg J M, Seco J. CT metal artifact reduction method correcting for beam hardening and missing projections. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2012, 57(9): 2803−2818 [29] Liao H F, Lin W A, Huo Z M, Vogelsang L, Sehnert W J, Zhou S K, et al. Generative mask pyramid network for CT/CBCT metal artifact reduction with joint projection-sinogram correction. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2019). Shenzhen, China: Springer, 2019. 77−85 [30] Shi B S, Zhang S L, Fu Z R. Artifact region-aware transformer: Global context helps CT metal artifact reduction. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2024, 31: 1249−1253 [31] Lin W A, Liao H F, Peng C, Sun X H, Zhang J D, Luo J B, et al. DuDoNet: Dual domain network for CT metal artifact reduction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 10504−10513 [32] Wang T, Xia W J, Huang Y Q, Sun H, Liu Y, Chen H, et al. DAN-net: Dual-domain adaptive-scaling non-local network for CT metal artifact reduction. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2021, 66(15): Article No. 155009 [33] Wang H, Li Y X, Zhang H M, Chen J W, Ma K, Meng D Y, et al. InDuDoNet: An interpretable dual domain network for CT metal artifact reduction. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2021). Strasbourg, France: Springer, 2021. 107−118 [34] Wang H, Li Y X, Zhang H M, Meng D Y, Zheng Y F. InDuDoNet+: A deep unfolding dual domain network for metal artifact reduction in CT images. Medical Image Analysis, 2023, 85: Article No. 102729 [35] Shi B S, Zhang S L, Jiang K, Lian Q S. Coupling model- and data-driven networks for CT metal artifact reduction. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2024, 10: 415−428 [36] Ketcha M D, Marrama M, Souza A, Uneri A, Wu P W, Zhang X X, et al. Sinogram + image domain neural network approach for metal artifact reduction in low-dose cone-beam computed tomography. Journal of Medical Imaging, 2021, 8(5): Article No. 052103 [37] Zhou B, Chen X C, Zhou S K, Duncan J S, Liu C. DuDoDR-Net: Dual-domain data consistent recurrent network for simultaneous sparse view and metal artifact reduction in computed tomography. Medical Image Analysis, 2022, 75: Article No. 102289 [38] Zhou B, Chen X C, Xie H D, Zhou S K, Duncan J S, Liu C. DuDoUFNet: Dual-domain under-to-fully-complete progressive restoration network for simultaneous metal artifact reduction and low-dose CT reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2022, 41(12): 3587−3599 [39] Wang H, Zhou M H, Wei D, Li Y X, Zheng Y F. MEPNet: A model-driven equivariant proximal network for joint sparse-view reconstruction and metal artifact reduction in CT images. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2023). Vancouver, Canada: Springer, 2023. 109−120 [40] Shi B S, Jiang K, Zhang S L, Lian Q S, Qin Y W, Zhao Y S. Mud-Net: Multi-domain deep unrolling network for simultaneous sparse-view and metal artifact reduction in computed tomography. Machine Learning: Science and Technology, 2024, 5(1): Article No. 015010 [41] Bahnemiri S G, Ponomarenko M, Egiazarian K. Learning-based noise component map estimation for image denoising. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022, 29: 1407−1411 [42] Wang L G, Dong X Y, Wang Y Q, Ying X Y, Lin Z P, An W, et al. Exploring sparsity in image super-resolution for efficient inference. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 4915−4924 [43] Guo L Q, Huang S Y, Liu D, Cheng H, Wen B H. ShadowFormer: Global context helps shadow removal. In: Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Washington, USA: AAAI Press, 2023. 710−718 [44] Yan K, Wang X S, Lu L, Zhang L, Harrison A P, Bagheri M, et al. Deep lesion graphs in the wild: Relationship learning and organization of significant radiology image findings in a diverse large-scale lesion database. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 9261−9270 [45] Chen H, Zhang Y, Kalra M K, Lin F, Chen Y, Liao P X, et al. Low-dose CT with a residual encoder-decoder convolutional neural network. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36(12): 2524−2535 [46] Jin K H, McCann M T, Froustey E, Unser M. Deep convolutional neural network for inverse problems in imaging. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(9): 4509−4522 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 8
- HTML全文浏览量: 3
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: