Design and Digital Implementation of Spatial Repetitive Control for Fast Tool Servo System
-
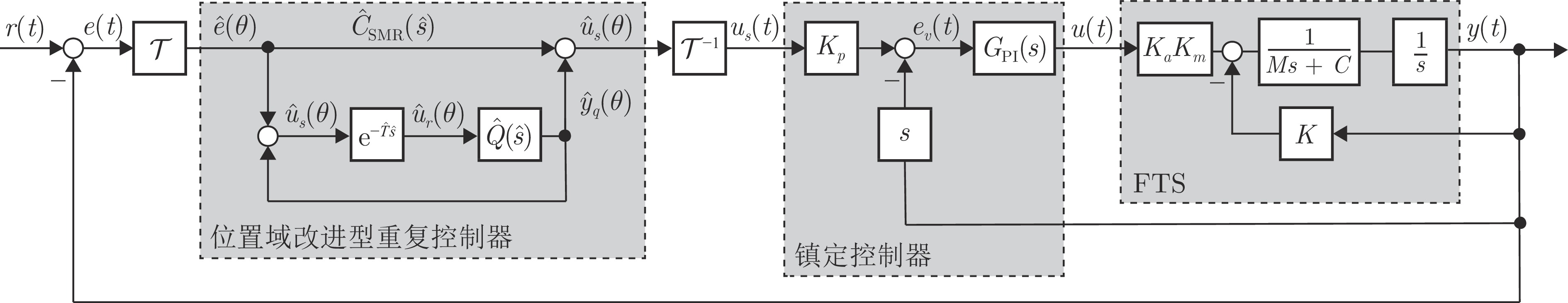
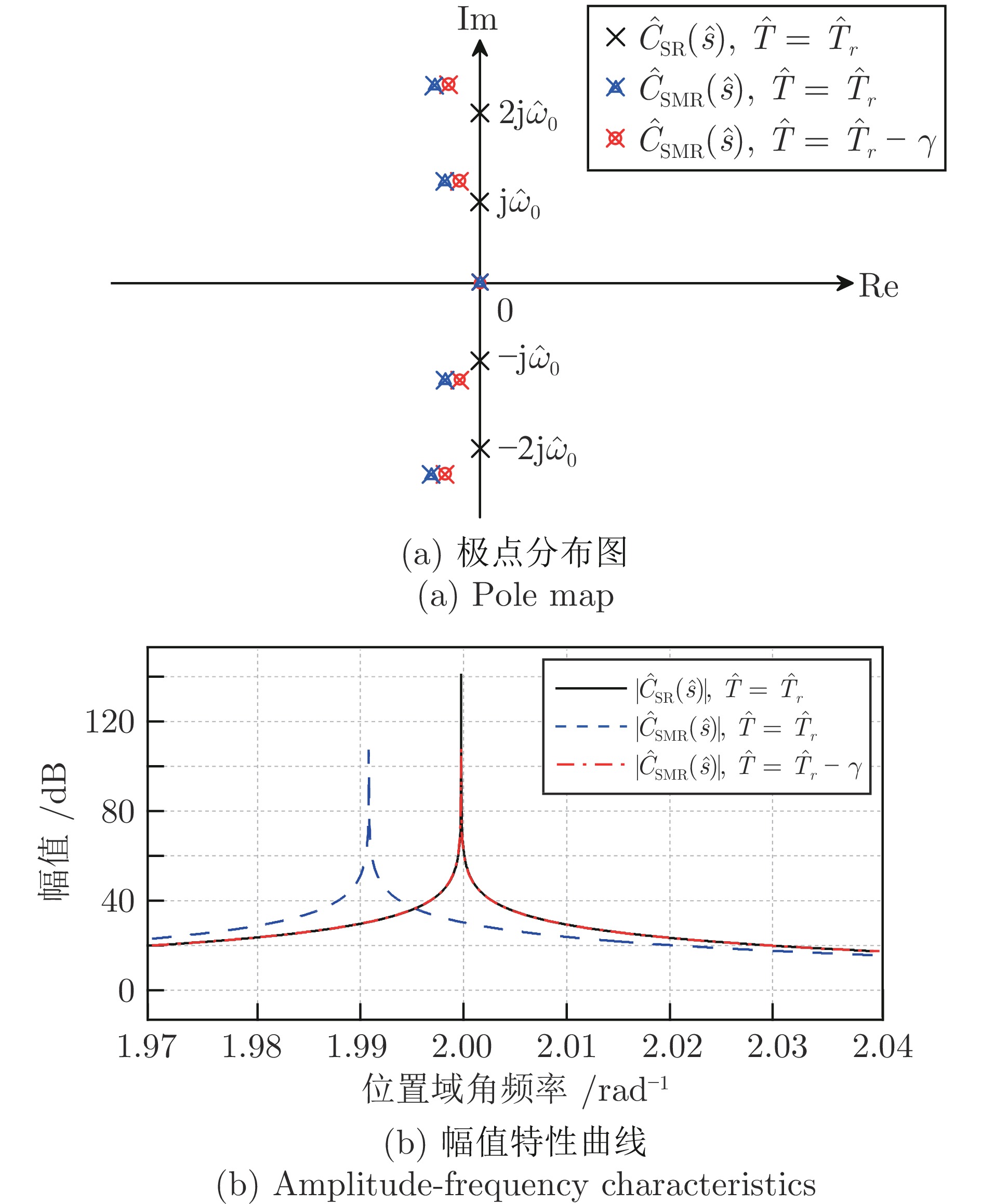
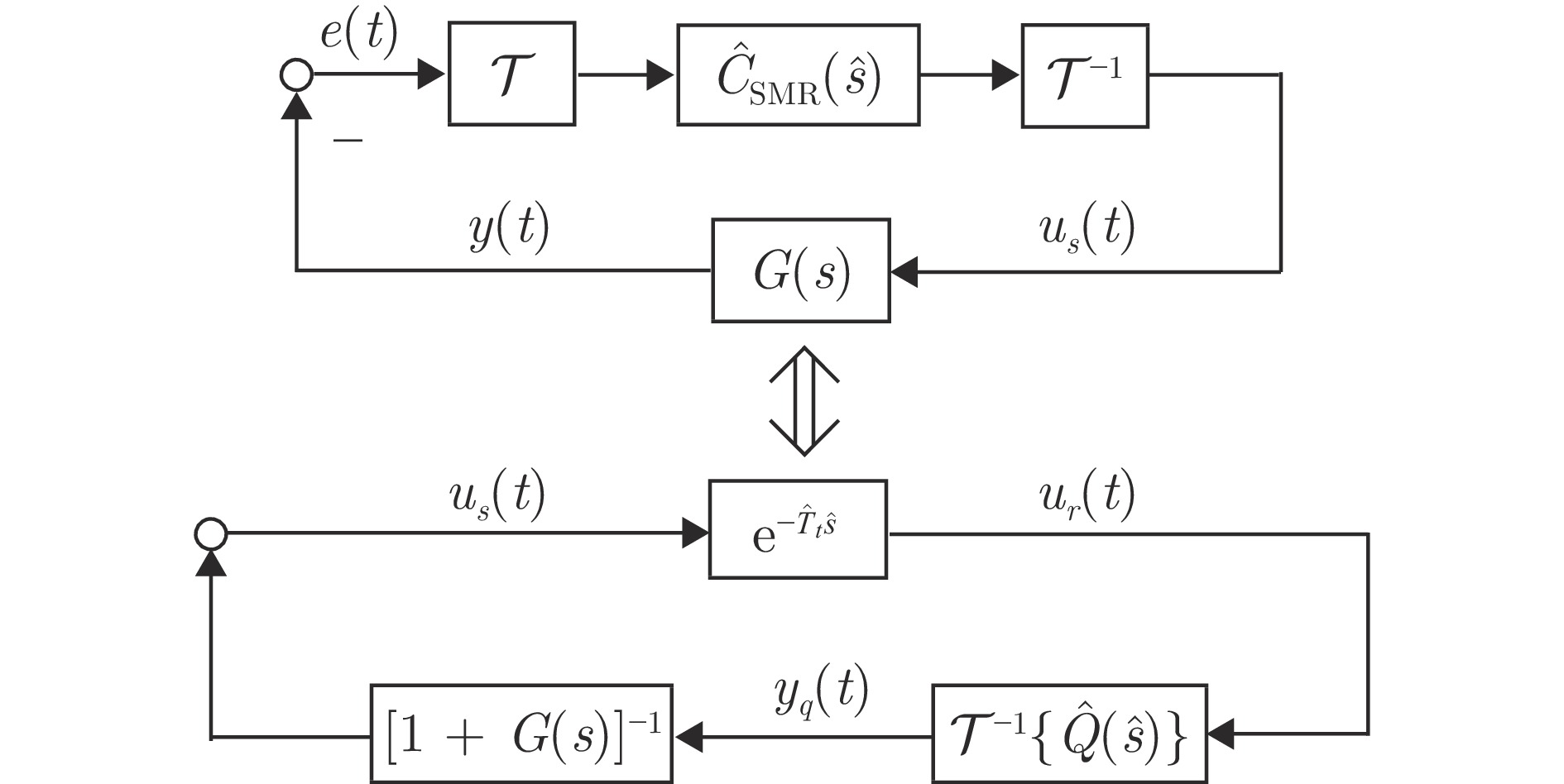
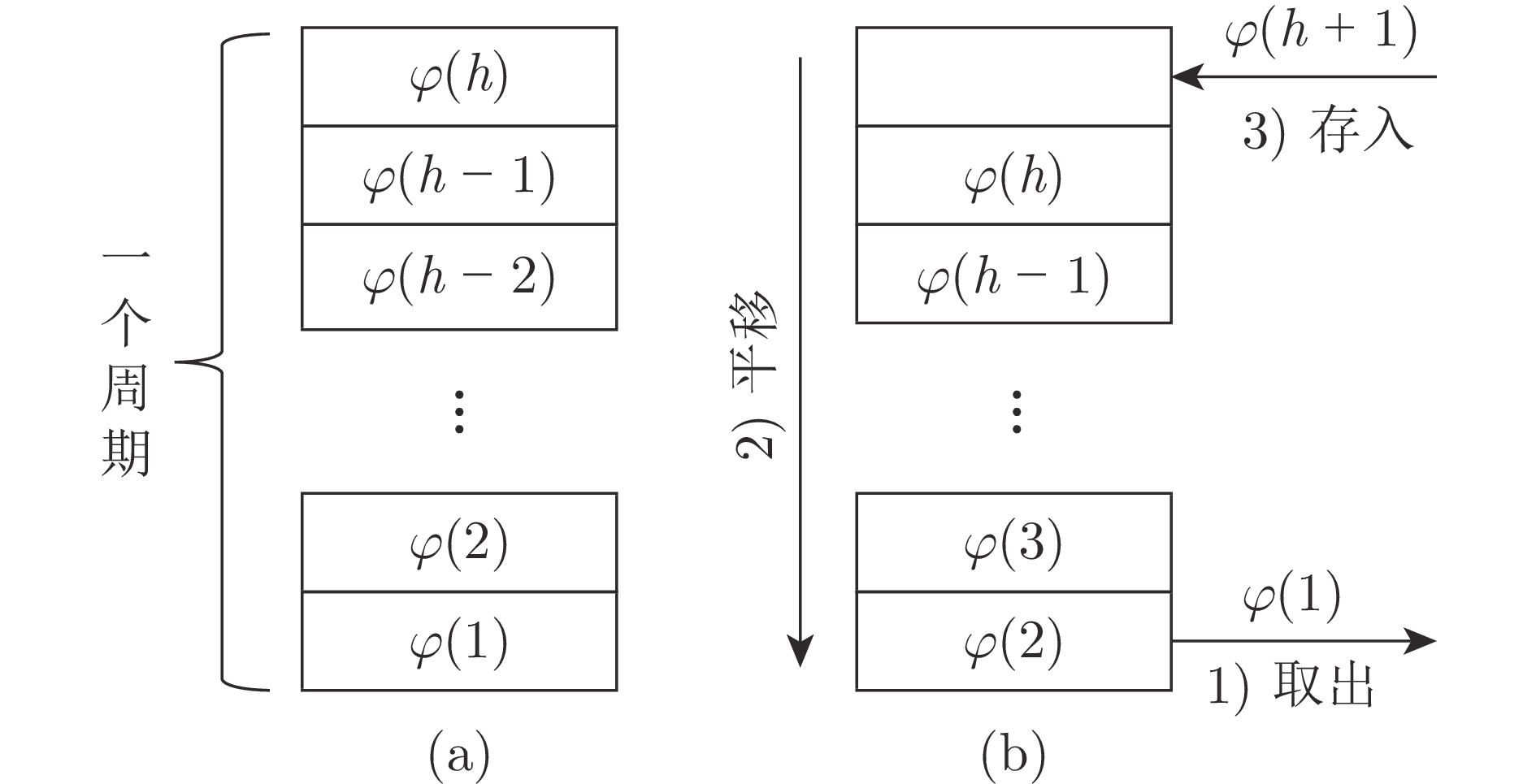
摘要: 在非圆零件车削过程中, 快速刀具伺服(Fast tool servo, FTS)的运动精度直接影响零件的加工质量. 主轴变速加工使得FTS的参考目标信号周期时变而不确定, 这对实现其渐近跟踪提出了极大的挑战. 本文利用FTS的位置域周期特性, 提出一种基于位置域重复控制和时域速度反馈镇定的FTS系统复合控制设计方法, 并给出位置域改进型重复控制器(Spatial modified repetitive controller, SMRC)的数字实现算法, 实现对时变周期参考目标信号的高精度跟踪. 首先, 建立包含位置相关时变周期参考目标信号内模的SMRC, 并引入位置域相位超前装置对镇定补偿器引起的相位滞后进行补偿, 在此基础上构建复合控制律. 然后应用小增益定理和算子理论, 推导出控制系统的稳定性条件, 在保持系统采样频率不变的条件下, 应用插值法建立SMRC的数字实现算法, 确保位置域重复控制和时域镇定控制器的同步执行. 最后, 通过仿真验证所设计的FTS控制系统具有满意的时变周期跟踪性能和鲁棒性, 并通过与其他位置域重复控制方法的比较, 说明所提方法同时具有更好的暂态和稳态性能.Abstract: The motion accuracy of the fast tool servo (FTS) directly affects the machining quality of the non-circular parts. In variable spindle speed machining, the period of the reference signal of the FTS is time-varying and uncertain, which poses a great challenge to achieve its asymptotic tracking. In this paper, we propose a composite control design method based on spatial repetitive control and temporal velocity feedback stabilization for an FTS system, and present a digital implementation algorithm of the spatial modified-repetitive-controller (SMRC) to achieve high-precision tracking of time-varying periodic reference signals. First, an SMRC with the internal mode of the position-dependent time-varying periodic reference input signal is constructed, in which a phase-lead alignment segment is used to compensate for the phase lag caused by the temporal stabilization controller. And based on this, a composite control law is established. Then, the stability criteria of the control system are derived using the small gain theorem and operator theory. A digital implementation algorithm of the SMRC is developed to ensure the synchronous execution of the SMRC and the temporal stabilization controller through a regular fixed time sampling. Finally, simulation results show that the designed FTS control system has satisfactory time-varying-period tracking performance and robustness. A comparison with other spatial repetitive control methods verifies that the proposed method achieves better performance in both transient and steady state aspects.
-
表 1 音圈式直线电机相关参数
Table 1 Parameters of the voice coil type linear motor
参数 符号 单位 数值 弹簧刚度系数 $ K $ ${\rm{N/m }} $ 4 980 阻尼系数 $ C $ ${\rm{N\cdot s\cdot m^{-1}}}$ 14.51 动子质量 $ M $ ${\rm{kg } }$ 0.32 电机力常数 $ K_{m} $ ${\rm{N/A }} $ 12.325 放大器增益 $ K_a $ ${\rm{A/v}} $ 1.6 表 2 性能指标对比
Table 2 Comparison of performance indices
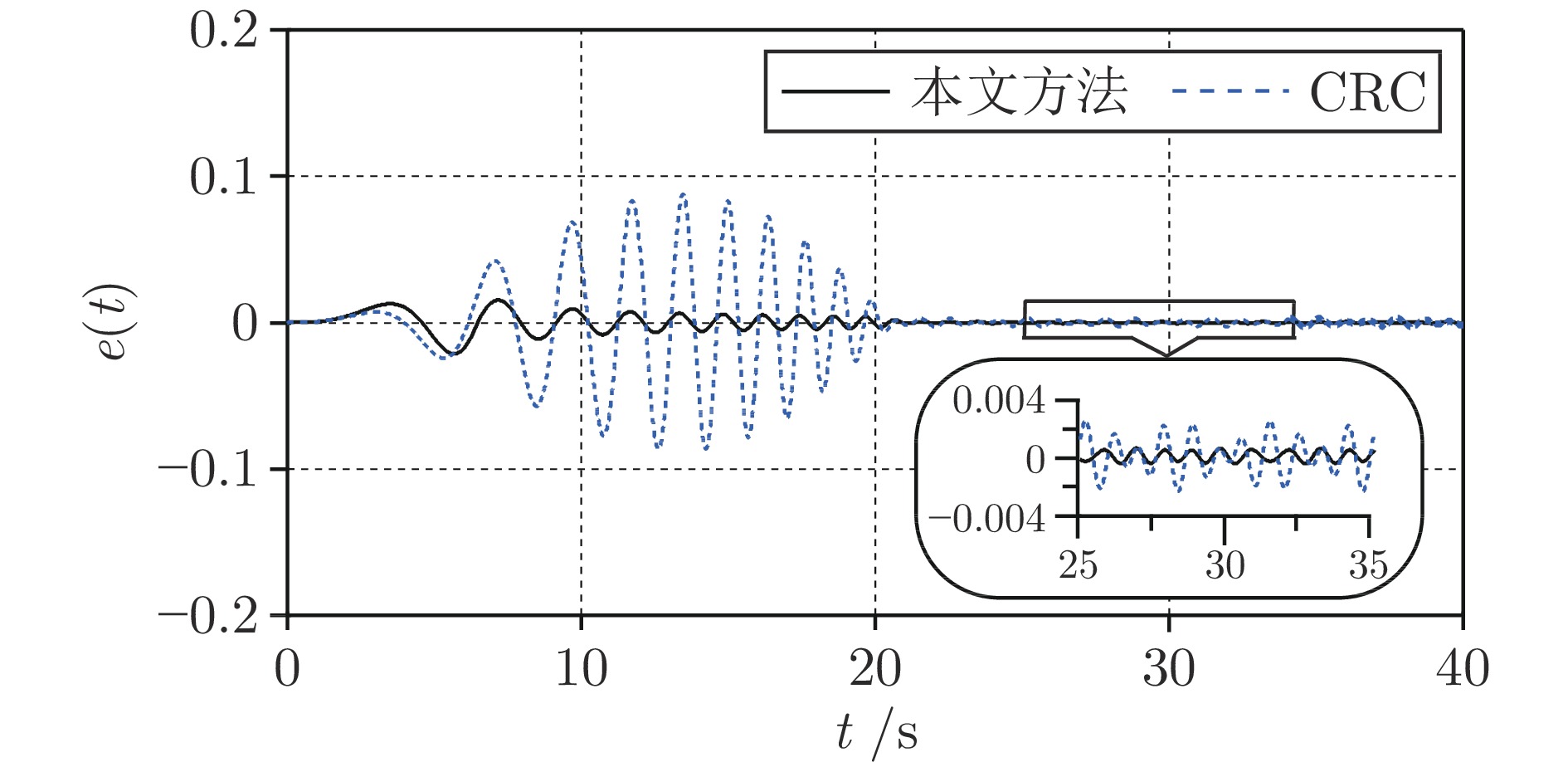
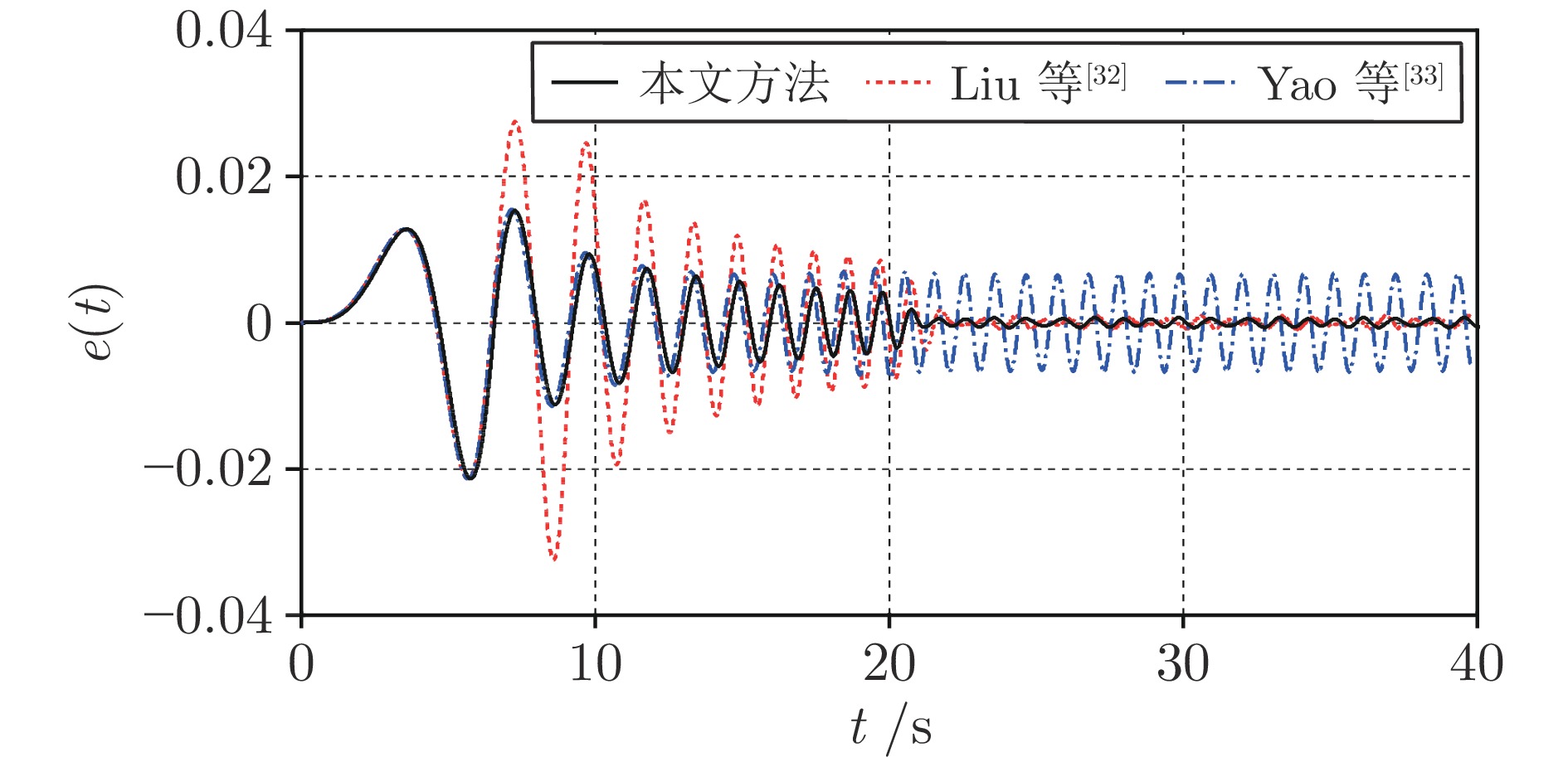
控制方法 $\max|e(t)|_{0<t\leq 20}$ $e_{pp}\;(0 < t\leq 20)$ $\max|e(t)|_{t>20} $ $e_{pp}\;(t > 20)$ CRC $8.744\times10^{-2} $ $17.393\times10^{-2} $ $9.707\times10^{-3} $ $1.580\times10^{-2} $ Liu等[32] $3.246\times10^{-2} $ $5.993\times10^{-2} $ $1.006\times10^{-3} $ $1.992\times10^{-3} $ Yao等[33] $2.315\times10^{-2} $ $3.684\times10^{-2} $ $6.737\times10^{-3} $ $1.347\times10^{-2} $ 本文方法 2.315 × 10−2 3.665 × 10−2 6.759 × 10−4 1.334 × 10−3 -
[1] Zhu Z H, Huang P, To S, Zhu L M, Zhu Z W. Fast-tool-servo-controlled shear-thickening micropolishing. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2023, (184): Article No. 103968 [2] Zhao D P, Zhu Z H, Huang P, Guo P, Zhu L M, Zhu Z W. Development of a piezoelectrically actuated dual-stage fast tool servo. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 144: Article No. 106873 [3] Ding F, Luo X C, Zhong W B, Chang W L. Design of a new fast tool positioning system and systematic study on its positioning stability. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2019, 142: 54−65 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2019.04.008 [4] 吴丹, 赵彤, 陈恳. 快速刀具伺服系统自抗扰控制的研究与实践. 控制理论与应用, 2013, 30(12): 1534−1542Wu Dan, Zhao Tong, Chen Ken. Research and industrial applications of active disturbance rejection control to fast tool servos. Control Theory & Applications, 2013, 30(12): 1534−1542 [5] 吴丹, 王先逵, 易旺民, 高杨. 重复控制及其在变速非圆车削中的应用. 中国机械工程, 2004, 15(5): 446−449Wu Dan, Wang Xian-Kui, Yi Wang-Min, Gao Yang. Repetitive control and its applications to variable spindle speed noncircular turning. China Mechanical Engineering, 2004, 15(5): 446−449 [6] Qin X B, Wan M, Zhang W H, Yang Y. Chatter suppression with productivity improvement by scheduling a C3 continuous feedrate to match spindle speed variation. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2023, 118: Article No. 110021 [7] Dong X F, Shen X H, Fu Z F. Stability analysis in turning with variable spindle speed based on the reconstructed semi-discretization method. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 117(11): 3393−3403 [8] Zhu W L, Yang X, Duan F, Zhu Z W, Ju B F. Design and adaptive terminal sliding mode control of a fast tool servo system for diamond machining of freeform surfaces. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(6): 4912−4922 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2786281 [9] Huang W W, Guo P, Hu C X, Zhu L M. High-performance control of fast tool servos with robust disturbance observer and modified H∞ control. Mechatronics, 2022, 84: Article No. 102781 [10] Zhou L, Liao C C, She J H, He Y, Li H Y. Command-filtered backstepping repetitive control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems based on additive state decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(5): 5150−5160 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3186332 [11] 吴敏, 周兰, 佘锦华, 何勇. 一类不确定线性系统的输出反馈鲁棒重复控制设计. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2010, 40(1): 54−62Wu Min, Zhou Lan, She Jin-Hua, He Yong. Design of robust output-feedback repetitive controller for class of linear systems with uncertainties. Science China Information Sciences, 2010, 40(1): 54−62 [12] Ye J, Liu L G, Xu J B, Shen A W. Frequency adaptive proportional-repetitive control for grid-connected inverters. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(9): 7965−7974 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3016247 [13] Lu C J, Zhou B, Meng F S, Chang Q Y. Control scheme based on improved odd-harmonic repetitive control for third-harmonic injection two-stage matrix converter. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2023, 11(4): 3839−3852 doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2023.3279414 [14] Tian M H, Wang B, Yu Y, Dong Q H, Xu D G. Discrete-time repetitive control-based ADRC for current loop disturbances suppression of PMSM drives. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(5): 3138−3149 doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3107635 [15] Kurniawan E, Harno H G, Wang H, Prakosa J A, Sirenden B H, Septanto H, et al. Robust adaptive repetitive control for unknown linear systems with odd-harmonic periodic disturbances. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(12): Article No. 222202 [16] Huang W W, Zhang X Q, Zhu L M. Band-stop-filter-based repetitive control of fast tool servos for diamond turning of micro-structured functional surfaces. Precision Engineering, 2023, 83: 124−133 doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2023.05.008 [17] Zhou L, Gao D X, She J H. Tracking control for a position-dependent periodic signal in a variable-speed rotational system. Automatica, 2023, 158: Article No. 111282 [18] Steinbuch M, Weiland S, Singh T. Design of noise and period-time robust high-order repetitive control, with application to optical storage. Automatica, 2007, 43(12): 2086−2095 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2007.04.011 [19] Zhou K L, Tang C, Chen Y X, Zhang B, Lu W Z. A generic multi-frequency repetitive control scheme for power converters. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(12): 12680−12688 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3239855 [20] Wu Y L, Song X D, Li H, Chen B D. Suppression of harmonic current in permanent magnet synchronous motors using improved repetitive controller. Electronics Letters, 2019, 55(1): 47−49 doi: 10.1049/el.2018.7035 [21] Liu Z C, Zhou K L, Yang Y H, Wang J C, Zhang B. Frequency-adaptive virtual variable sampling-based selective harmonic repetitive control of power inverters. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(11): 11339−11347 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3031452 [22] Kurniawan E, Cao Z W, Man Z H. Digital design of adaptive repetitive control of linear systems with time-varying periodic disturbances. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2014, 8(17): 1995−2003 [23] Wu C, Nian H, Pang B, Cheng P. Adaptive repetitive control of DFIG-DC system considering stator frequency variation. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2019, 34(4): 3302−3312 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2018.2854261 [24] Olm J M, Ramos G A, Costa-Castelló R. Stability analysis of digital repetitive control systems under time-varying sampling period. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2011, 5(1): 29−37 [25] 陈强, 胡如海, 胡轶. 一类非参数不确定运动系统的自适应空间重复学习控制. 高技术通讯, 2022, 32(6): 565−575Chen Qiang, Hu Ru-Hai, Hu Yi. Adaptive spatial repetitive learning control for a class of nonparametric uncertain motion systems. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2022, 32(6): 565−575 [26] Nakano M, She J H, Mastuo Y, Hino T. Elimination of position-dependent disturbances in constant-speed-rotation control systems. Control Engineering Practice, 1996, 4(9): 1241−1248 doi: 10.1016/0967-0661(96)00130-X [27] Huo X, Wang M Y, Liu K Z, Tong X G. Attenuation of position-dependent periodic disturbance for rotary machines by improved spatial repetitive control with frequency alignment. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2020, 25(1): 339−348 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2019.2946675 [28] Chen C L, Chiu G T C. Spatially periodic disturbance rejection with spatially sampled robust repetitive control. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2008, 130(2): Article No. 021002 [29] Castro R S, Flores J V, Salton A T. Robust discrete-time spatial repetitive controller. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2019, 27(6): 2696−2702 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2018.2866978 [30] Kolluri S, Gorla N B Y, Sapkota R, Panda S K. A new control architecture with spatial comb filter and spatial repetitive controller for circulating current harmonics elimination in a droop-regulated modular multilevel converter for wind farm application. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2019, 34(11): 10509−10523 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2019.2897150 [31] Chen C L, Yang Y H. Position-dependent disturbance rejection using spatial-based adaptive feedback linearization repetitive control. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2009, 19(12): 1337−1363 doi: 10.1002/rnc.1382 [32] Liu Q Q, Huo X, Liu K Z, Zhao H. Accurate cycle aligned repetitive control for the rejection of spatially cyclic disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(6): 6173−6181 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3086705 [33] Yao W S, Tsai M C, Yamamoto Y. Implementation of repetitive controller for rejection of position-based periodic disturbances. Control Engineering Practice, 2013, 21(9): 1226−1237 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2013.04.010 [34] Tang M, Gaeta A, Formentini A, Zanchetta P. A fractional delay variable frequency repetitive control for torque ripple reduction in PMSMs. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2017, 53(6): 5553−5562 doi: 10.1109/TIA.2017.2725824 [35] Mahawan B, Luo Z H. Repetitive control of tracking systems with time-varying periodic references. International Journal of Control, 2000, 73(1): 1−10 doi: 10.1080/002071700219885 [36] 邓中亮, 王先逵. 基于傅里叶级数的非圆截面车削进给运动特征分析. 机械工程学报, 1999, 35(2): 10−14Deng Zhong-Liang, Wang Xian-Kui. Analyses on feed kinematic behaviors in turning of noncircular sectional element based on Fourier series. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 1999, 35(2): 10−14 [37] Hara S, Yamamoto Y, Omata T, Nakano M. Repetitive control system: A new type servo system for periodic exogenous signals. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1988, 33(7): 659−668 doi: 10.1109/9.1274 [38] 黄科元, 周滔滔, 黄守道, 黄庆. 含前馈补偿和微分反馈的数控位置伺服系统. 中国机械工程, 2014, 25(15): 2017−2023Huang Ke-Yuan, Zhou Tao-Tao, Huang Shou-Dao, Huang Qing. CNC position servo system with feedforward compensation and differential feedback. China Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 25(15): 2017−2023 [39] Khalil H K. Nonlinear Systems (Third edition). Upper Saddle River: Patience Hall, 2002. [40] Du Z Q, Zhou Z D, Ai W, Chen Y P. A linear drive system for the dynamic focus module of SLS machines. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2007, 32(11): 1211−1217 -




 下载:
下载: