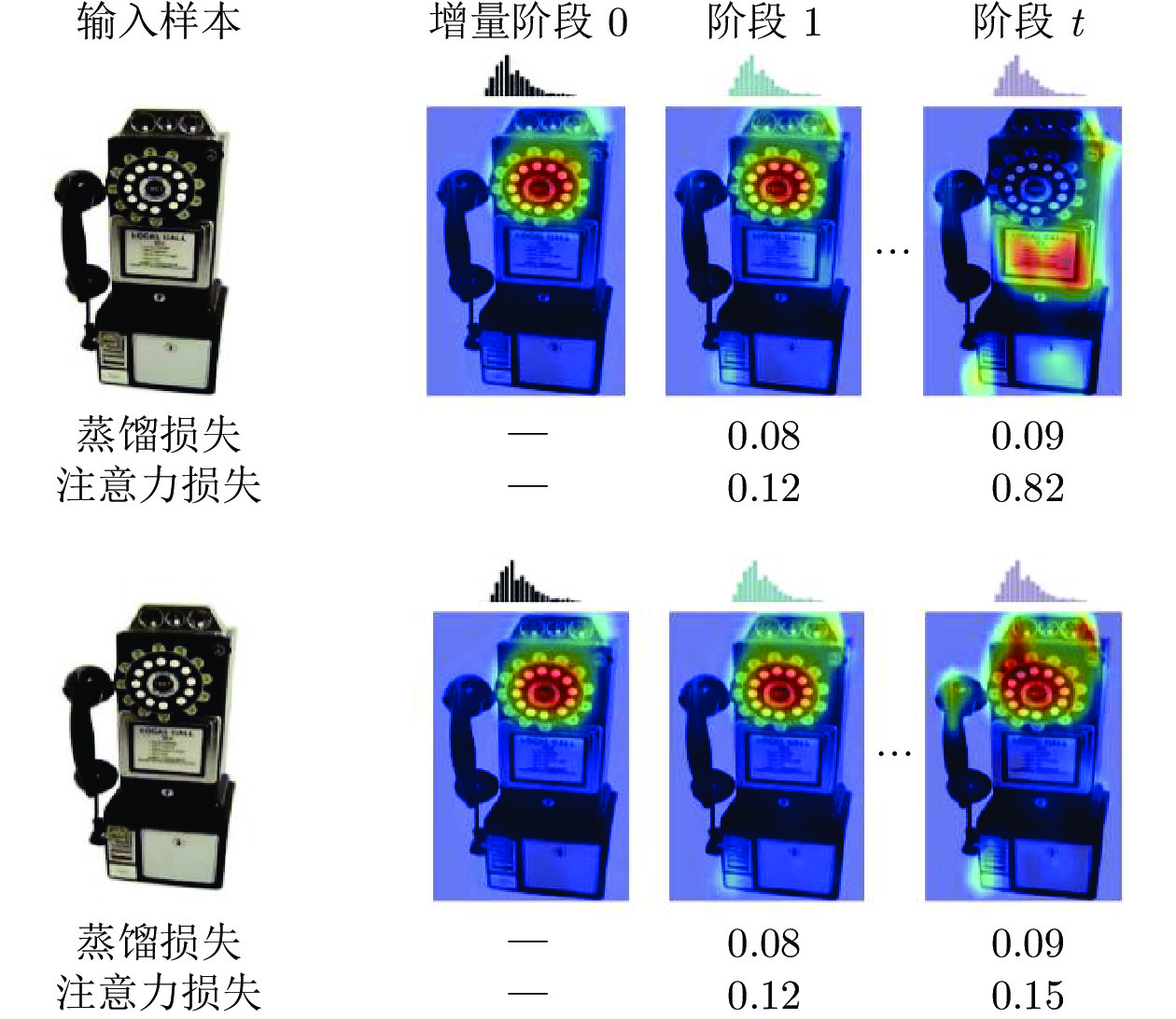
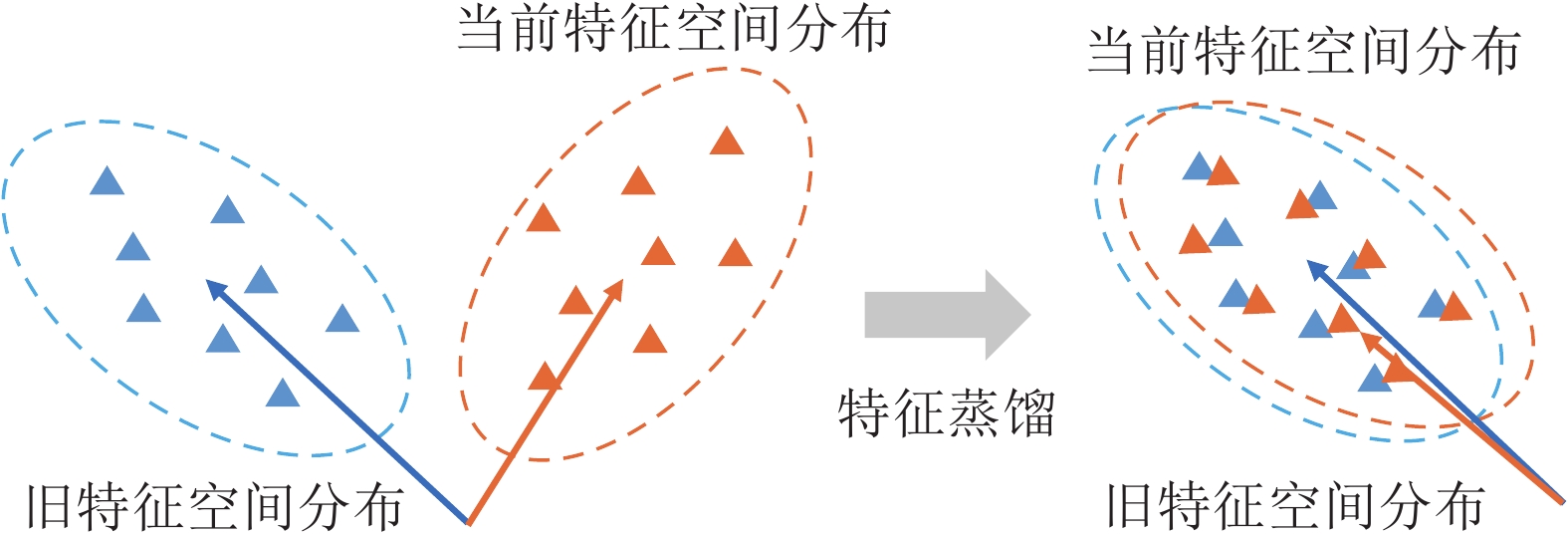
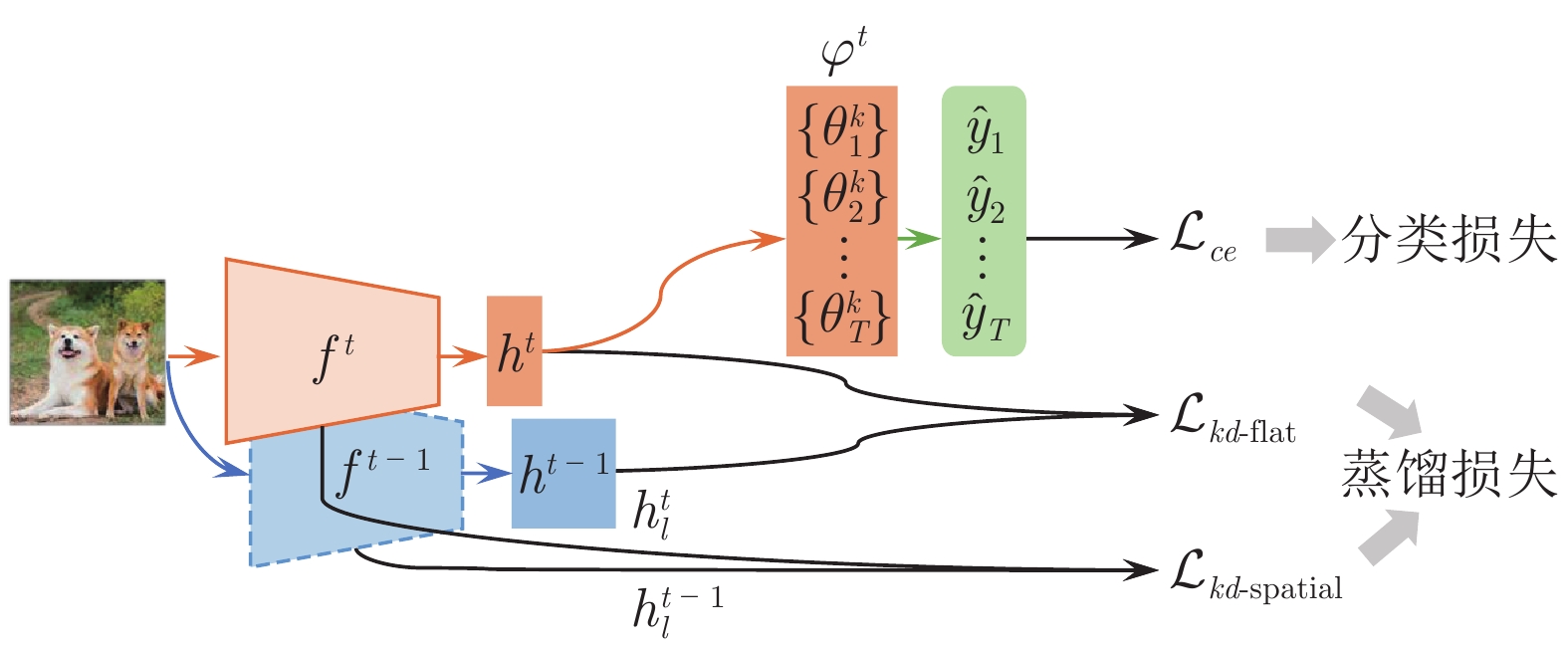
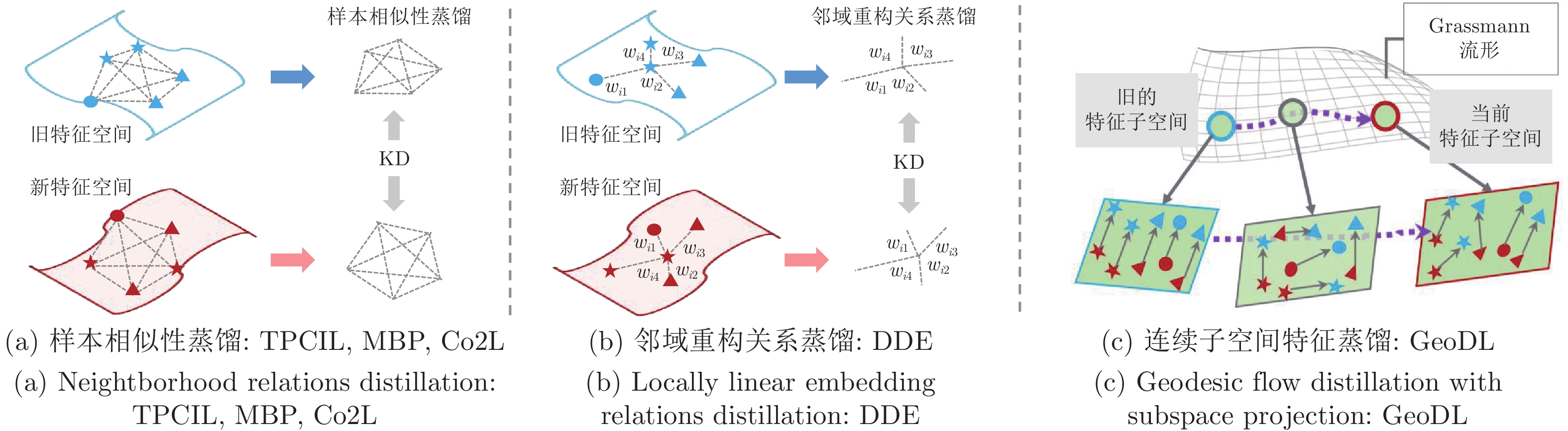
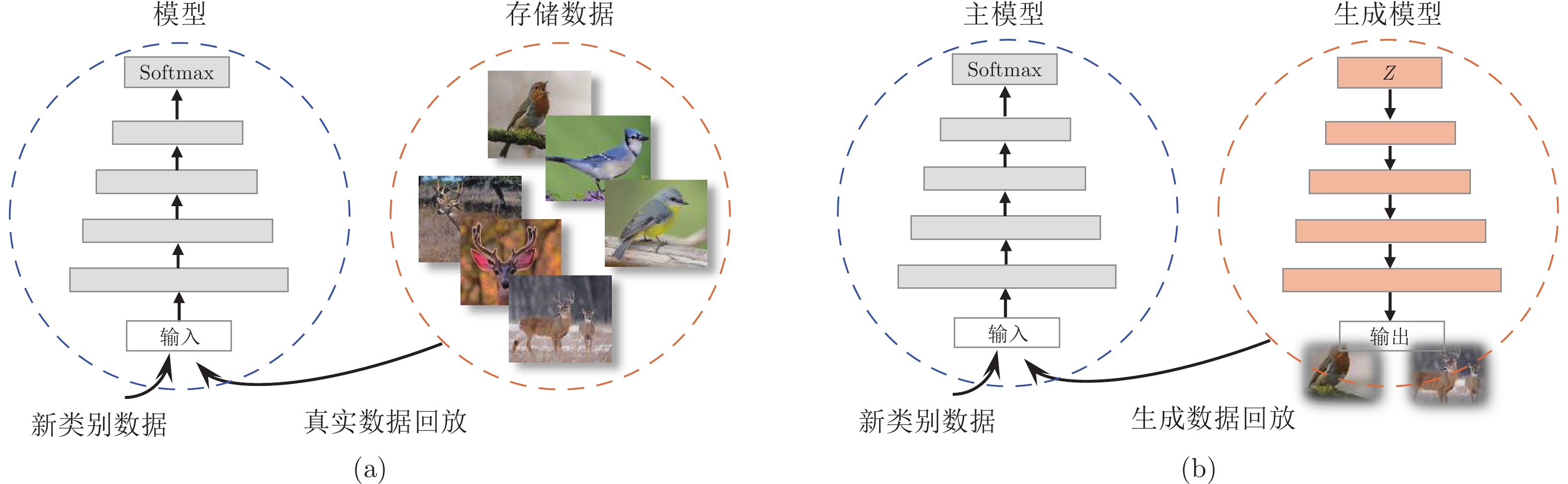
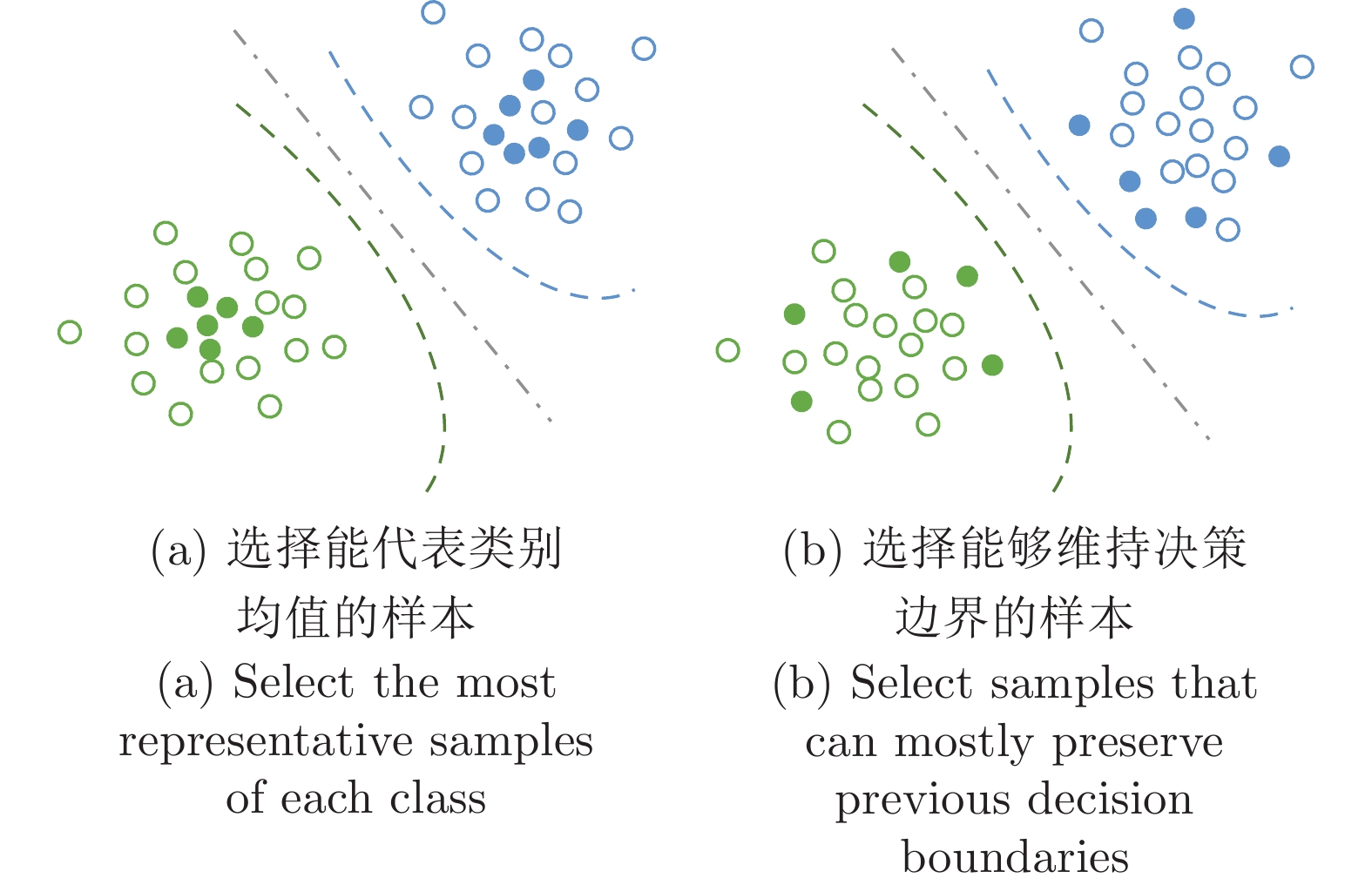
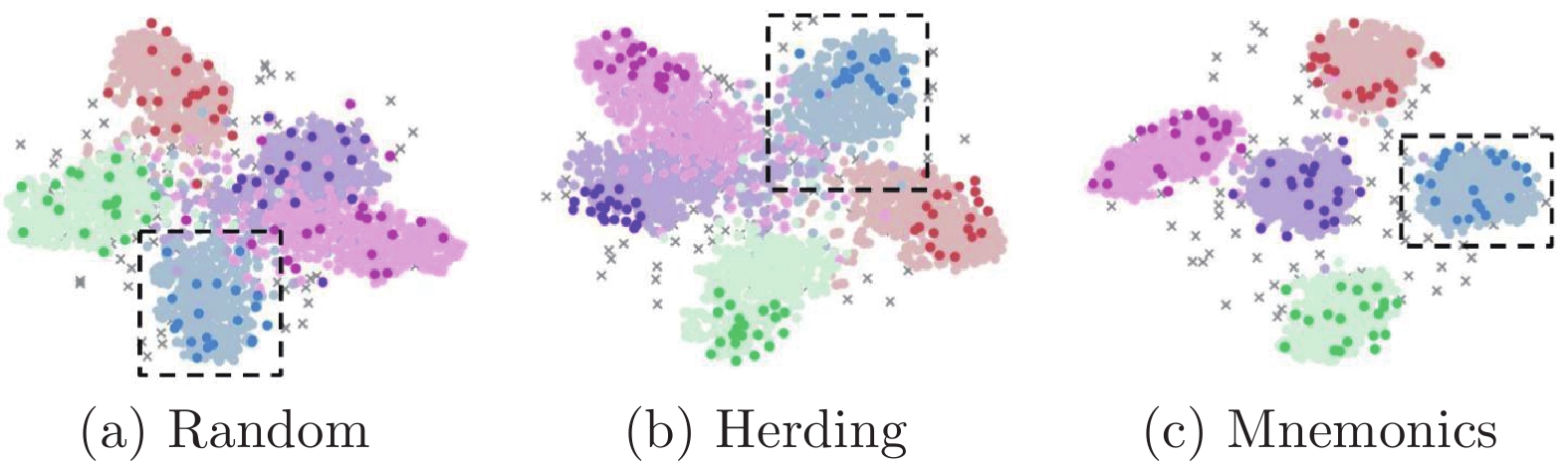
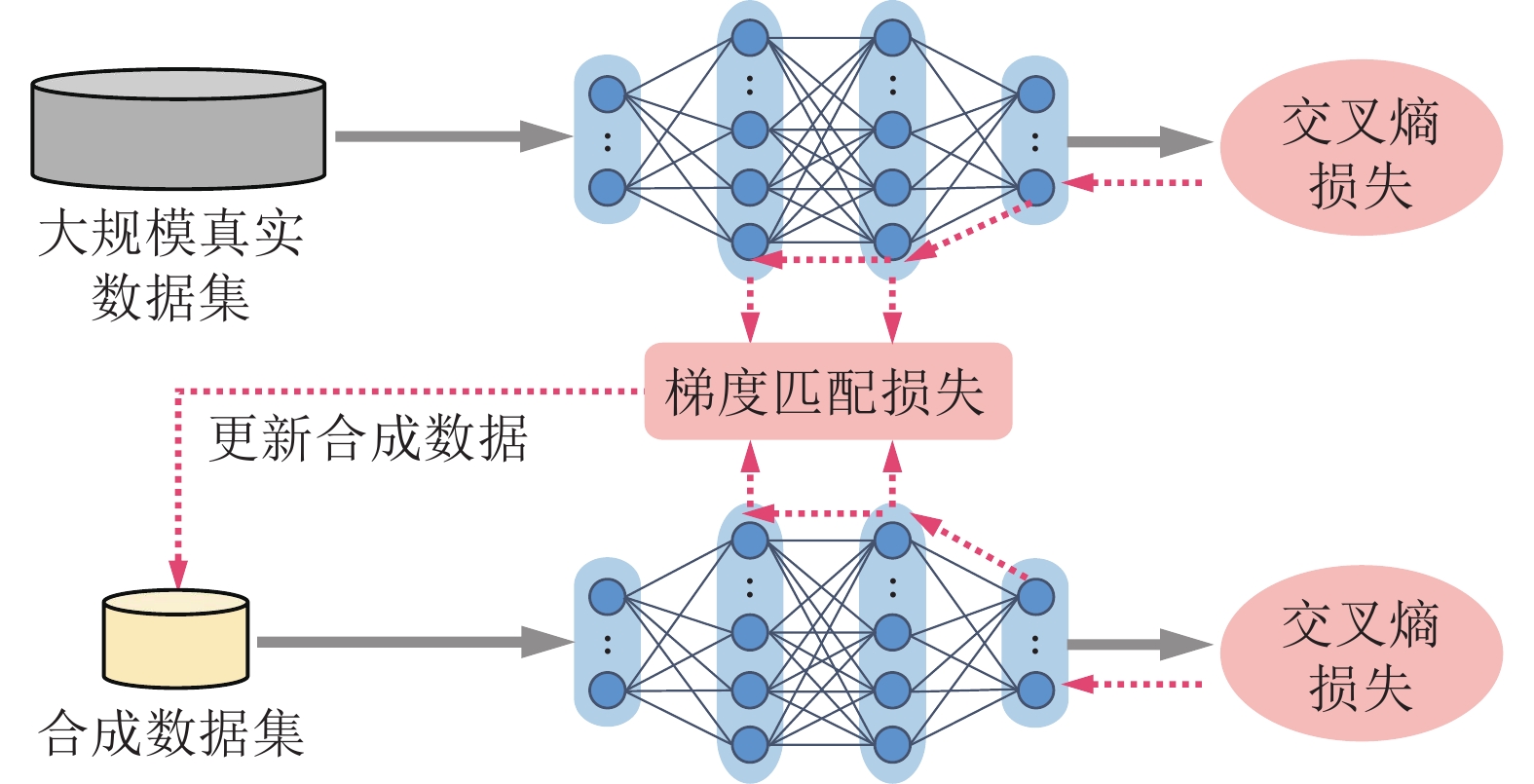
-
摘要: 机器学习技术成功地应用于计算机视觉、自然语言处理和语音识别等众多领域. 然而, 现有的大多数机器学习模型在部署后类别和参数是固定的, 只能泛化到训练集中出现的类别, 无法增量式地学习新类别. 在实际应用中, 新的类别或任务会源源不断地出现, 这要求模型能够像人类一样在较好地保持已有类别知识的基础上持续地学习新类别知识. 近年来新兴的类别增量学习研究方向, 旨在使得模型能够在开放、动态的环境中持续学习新类别的同时保持对旧类别的判别能力(防止“灾难性遗忘”). 本文对类别增量学习(Class-incremental learning, CIL)方法进行了详细综述. 根据克服遗忘的技术思路, 将现有方法分为基于参数正则化、基于知识蒸馏、基于数据回放、基于特征回放和基于网络结构的五类方法, 对每类方法的优缺点进行了总结. 此外, 本文在常用数据集上对代表性方法进行了实验评估, 并通过实验结果对现有算法的性能进行了比较分析. 最后, 对类别增量学习的研究趋势进行展望.Abstract: Machine learning has been successfully applied in many fields such as computer vision, natural language processing, and speech recognition. However, in the current machine learning systems, models are often fixed after training. Consequently, they can only generalize to classes that appear in the training set, and cannot learn newly emerged classes continuously. In real-world applications, new classes or tasks will appear continuously, which requires the model to continuously learn new knowledge without forgetting the knowledge of previous seen classes. The emerging research direction of class incremental learning aims to enable models to continuously learn new classes while preserving the discrimination ability of old classes (defying “catastrophic forgetting”) in the open and dynamic environment. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of class incremental learning (CIL) developed in recent years. Specifically, existing methods are grouped into five categories: parameter regularization based, knowledge distillation based, data replay based, feature replay based and network structure based methods. The advantages and disadvantages of each method are summarized. In addition, extensive experiments are conducted to evaluate and compare those representative methods on benchmark datasets. Finally, this paper prospects the future research directions of class incremental learning.
-
Key words:
- Incremental learning /
- continual learning /
- catastrophic forgetting /
- machine learning /
- deep learning
-
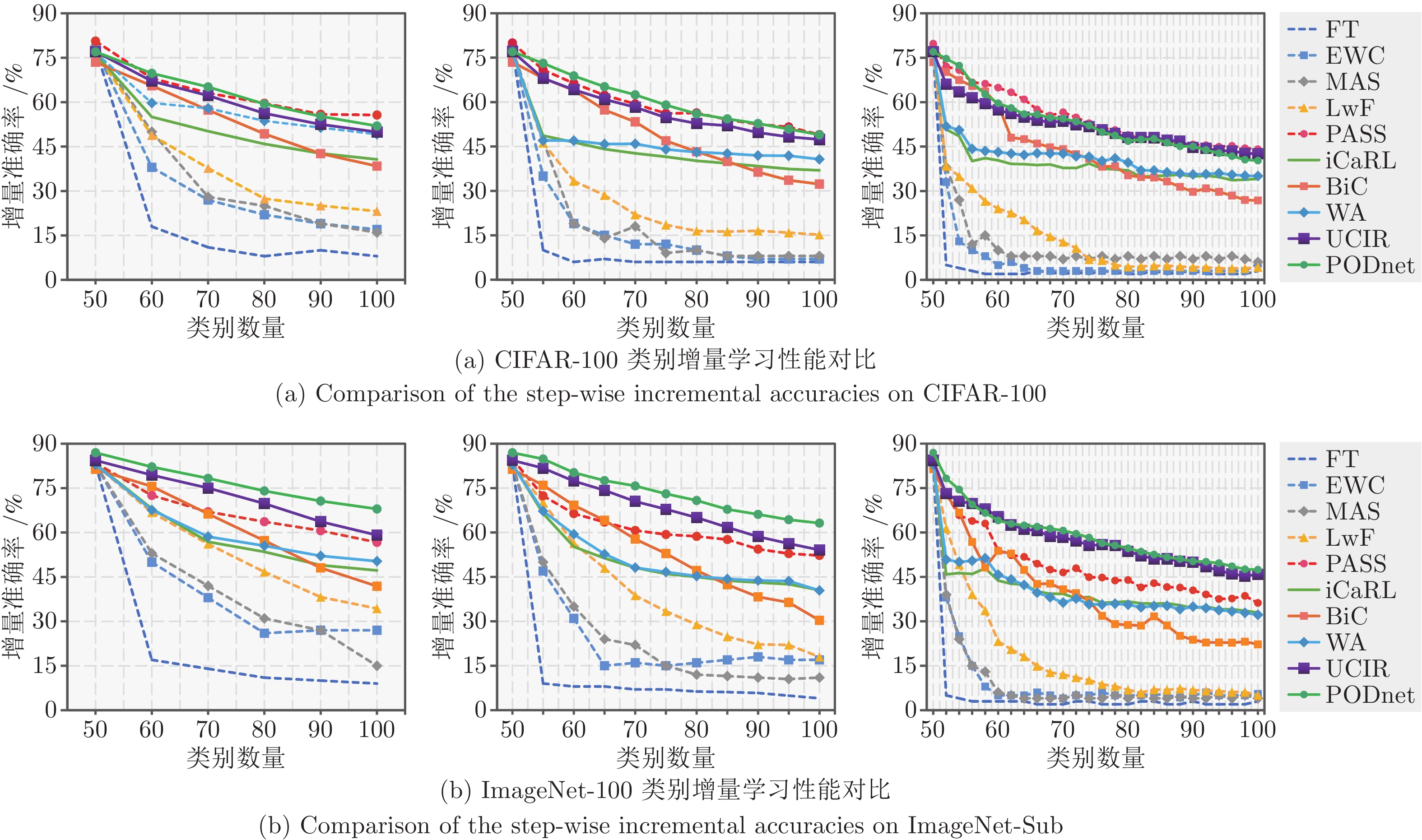
图 24 代表性类别增量学习方法在CIFAR-100和ImageNet-Sub数据集上的性能比较. 数据回放方法为每个旧类别保存10个样本. 从左到右依次为5, 10和25阶段增量学习设定
Fig. 24 Comparisons of the step-wise incremental accuracies on CIFAR-100 and ImageNet-Sub under three different settings: 5, 10, 25 incremental phases. 10 samples are saved for each old class in data replay based methods
表 1 不同增量学习设定对比
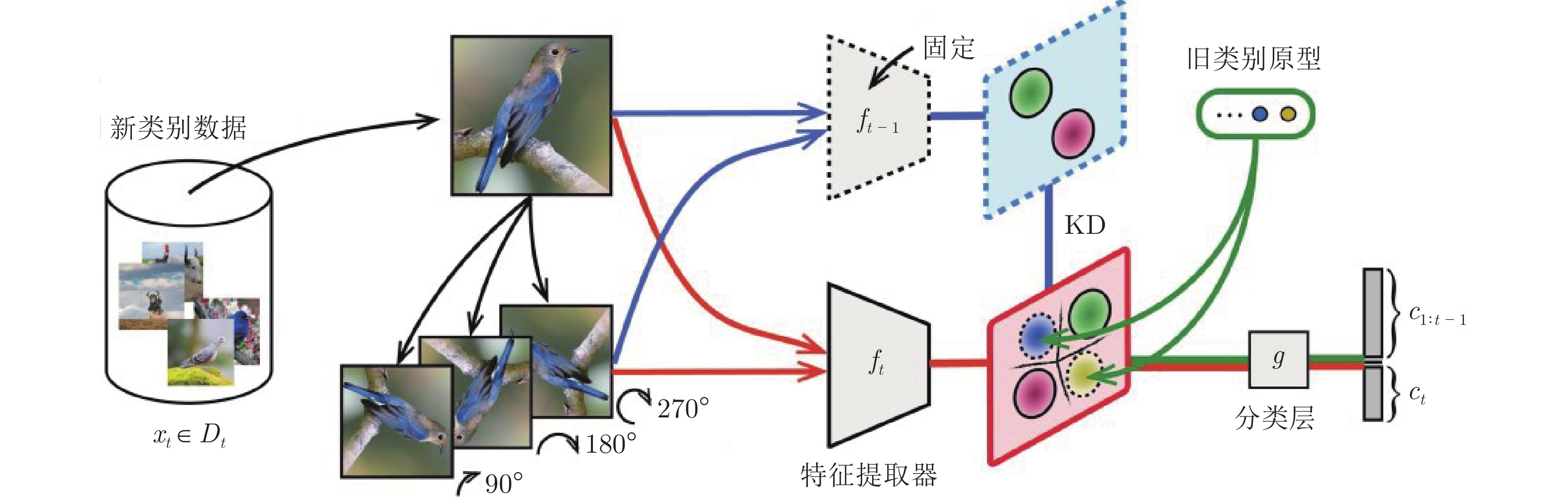
Table 1 Comparison of incremental learning settings
设定 说明 数据增量 类别集不变, 数据以在线的形式到来, 即传统的在线学习 任务增量 类别集变化, 推理阶段在各自任务内部分类 类别增量 类别集变化, 推理阶段在所有已学习类别上分类 表 2 类别增量学习评价指标
Table 2 Evaluation metrics of class incremental learning
增量准确率 在所有已见类别上的分类准确率$A_t$ 增量遗忘率 $F_{t}=\displaystyle\frac{1}{t-1}\sum_{i=1}^{t-1}f_{t}^{i}$ 平均增量准确率 $\bar A = \displaystyle\frac{1}{T}\sum_{i=1}^{T}A_i$ 平均增量遗忘率 $\bar F= \displaystyle\frac{1}{T}\sum_{i=1}^{T}F_i$ 表 3 类别增量学习中的知识蒸馏方法总结
Table 3 Summarization of knowledege distillation strategies in class incremental learning
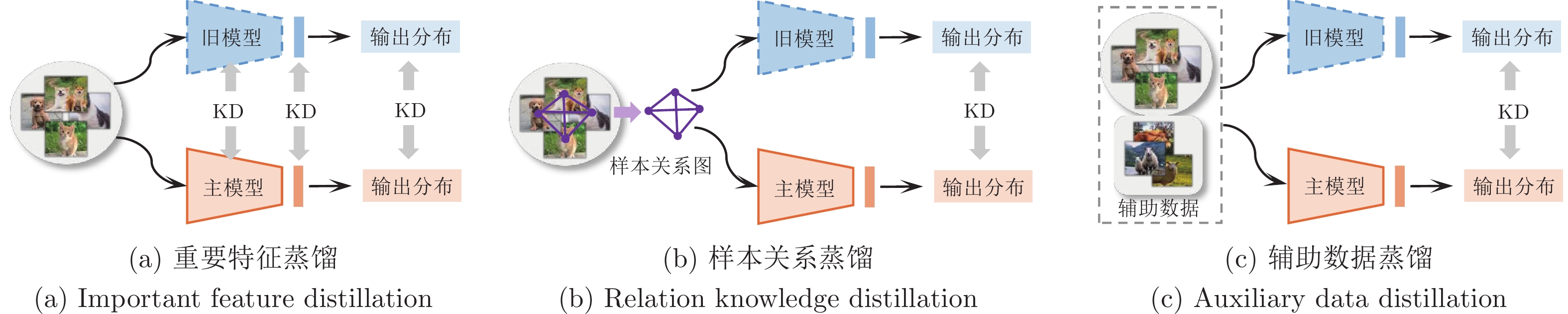
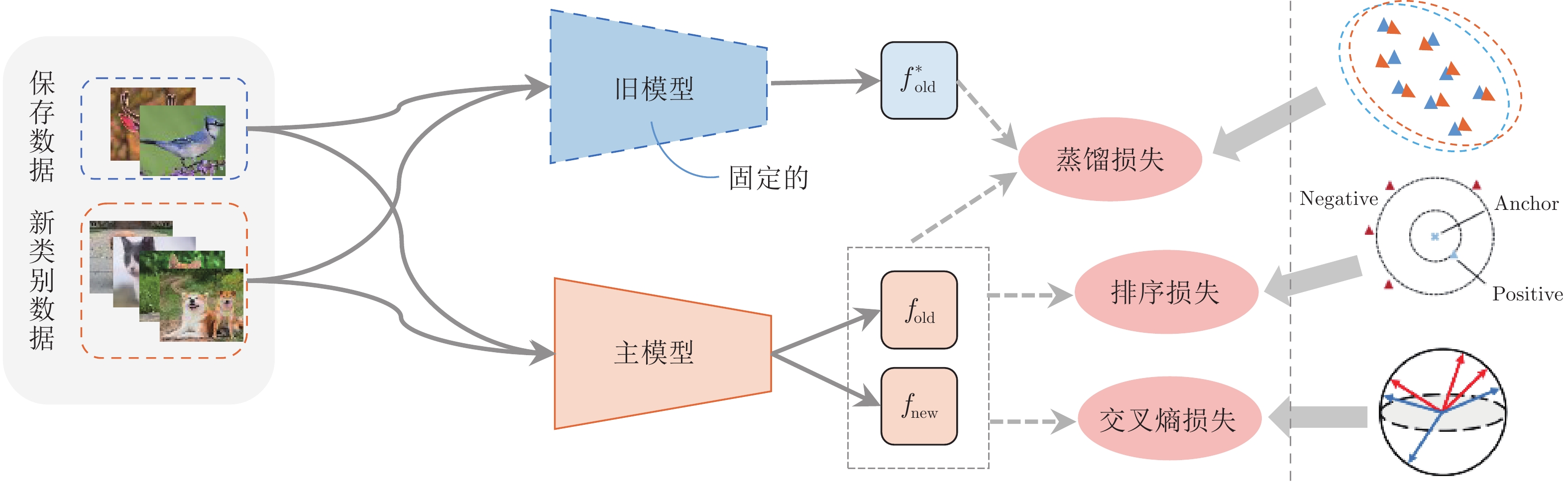
算法 知识蒸馏损失 知识蒸馏策略 LwF, iCaRL, BiC 式(2) 惩罚输出概率分布变化 EBIL, LwM 式(3) 惩罚重要特征变化 UCIR 式(4) 惩罚最终特征变化 PODnet 式(5), 式(6) 惩罚中间和最终特征变化 TPCIL, MBP,
Co2L式(7), 式(8),
式(9)惩罚样本相似性关系变化 DDE 式(10), 式(11) 惩罚邻域重构关系变化 GeoDL 式(12) 惩罚连续子空间中特征变化 DMC, GD 式(2) 无标记数据辅助知识蒸馏 calibrateCIL 式(2) 合成数据辅助知识蒸馏 表 4 基于数据回放的类别增量学习中的新旧类别偏差校准方法总结
Table 4 Summarization of bias calibration strategies in data replay based class incremental learning
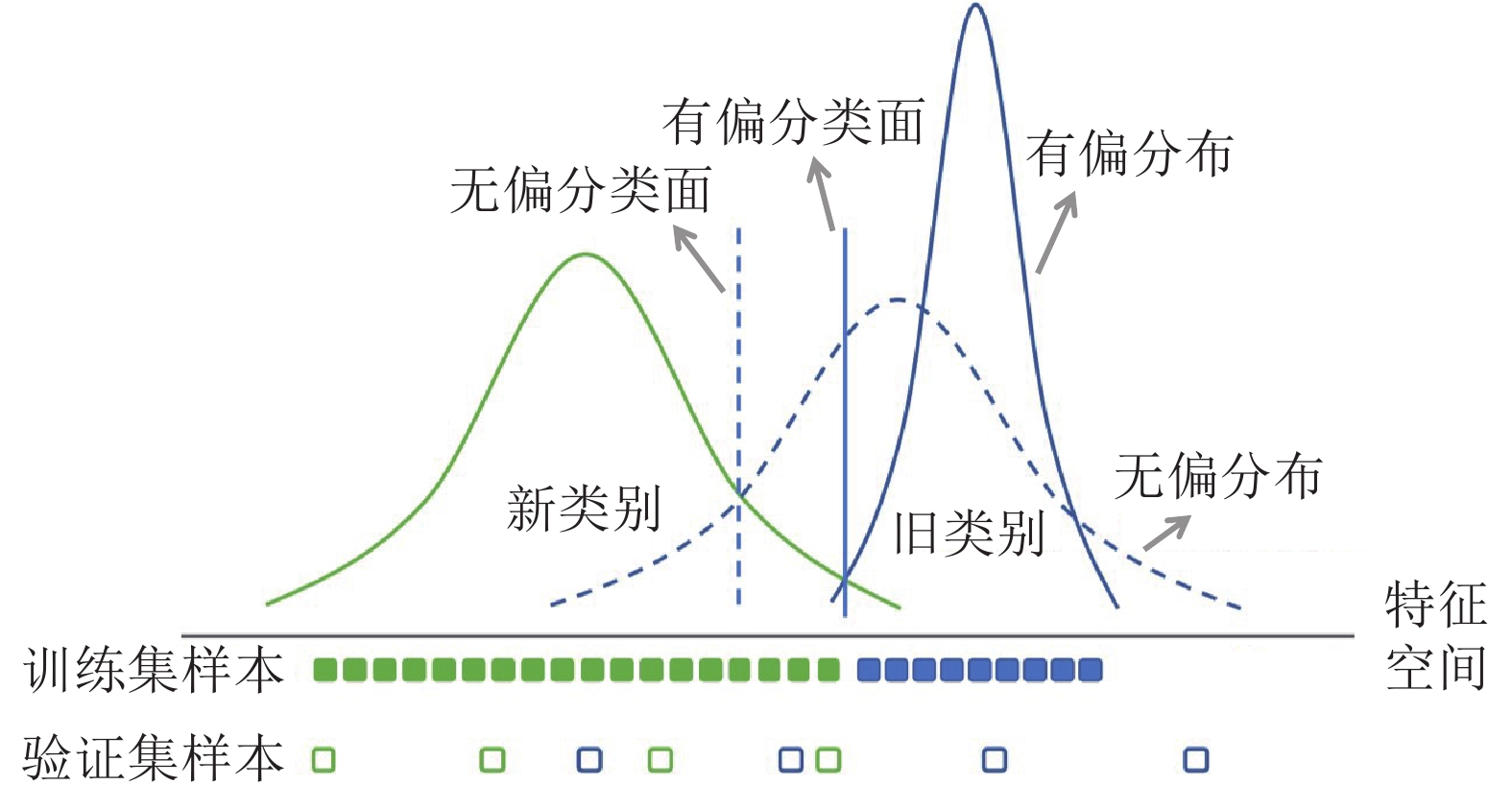
算法 使用阶段 平衡对象 偏差校准策略 E2E 训练阶段 训练数据 两阶段的法, 构建平衡数据集微调模型 GDumb 训练阶段 训练数据 下采样法, 构建平衡数据集直接从头训练模型 SS-IL 训练阶段 分类器 解耦新旧类别的softmax操作和知识蒸馏 RMM 训练阶段 训练数据 平衡训练集, 通过强化学习算法管理新旧类别数据 UCIR 训练阶段 分类器 特征和分类权重模长归一化, 间隔排序损失 iCaRL 测试阶段 分类器 原型生成, 使用最近类别均值分类器 BiC 测试阶段 分类器 概率校准, 使用平衡验证集学习偏差校准变换 WA 测试阶段 分类器 对齐新旧类的权重向量的平均模长 IL2M 测试阶段 分类器 概率校准, 调节模型最终输出的概率分布 表 5 类别增量学习公用数据集的数量信息
Table 5 Quantitative information of class incremental learning public data sets
数据集 数据数量 类别数量 平均类内样本 MNIST 60000 10 6000 CIFAR-10 60000 10 6000 CIFAR-100 60000 100 600 CUB-200 11788 200 58 Tiny-ImageNet 120000 200 600 ImageNet-Sub 60000 100 600 ImageNet-Full 1280000 1000 1280 VGGFace2-Sub 541746 1000 542 GLandmarks-Sub 394367 1000 394 表 6 基于样本回放的方法在CIFAR-100, ImageNet-Sub和ImageNet-Full上的平均增量准确率 (%) 比较
Table 6 Comparisons of average incremental accuracies (%) on CIFAR-100, ImageNet-Sub, and ImageNet-Full
存储个数 算法 发表出处 CIFAR-100 ImageNet-Sub ImageNet-Full $T=5$ $T=10$ $T=25$ $T=5$ $T=10$ $T=25$ $T=5$ $T=10$ $T=25$ $R=10$ iCaRL[29]$^{\dagger}$ CVPR 2017 51.80 44.72 39.49 59.62 51.37 40.38 48.17 42.53 34.83 BiC[79]$^{\dagger}$ ECCV 2018 54.46 49.88 43.53 61.74 54.17 39.37 UCIR[30]$^{\dagger}$ CVPR 2019 60.58 57.59 52.33 71.89 68.35 57.61 65.21 60.43 56.87 UCIR+DDE[58] CVPR 2021 64.41 62.00 — 71.20 69.05 — 67.04 64.98 — WA[31]$^{\dagger}$ CVPR 2020 58.11 46.98 41.78 61.18 52.23 40.52 52.05 47.57 PODnet[53]$^{\dagger}$ ECCV 2020 63.09 60.78 53.23 76.68 73.70 59.09 62.88 63.75 59.19 PODnet+DDE[58] CVPR 2021 63.40 60.52 — 75.76 73.00 — 64.41 62.09 — PASS+exemplar[13]$^{\dagger}$ CVPR 2021 62.54 64.96 — — — — — — — DMIL[134] CVPR 2022 67.08 64.41 — 75.73 74.94 — — — — $R=20$ DMC[62] WACV 2020 38.20 23.80 — 43.07 30.30 — — — — GD[63] ICCV 2019 56.39 51.30 — 58.70 57.70 — — — — iCaRL[29] CVPR 2017 57.12 52.66 48.22 65.44 59.88 52.97 51.50 46.89 43.14 iCaRL+Mnemonics[73] CVPR 2020 60.00 57.37 54.13 72.34 70.50 67.12 60.61 58.62 53.46 iCaRL+AANets[121] CVPR 2021 64.22 60.26 56.43 73.45 71.78 69.22 63.91 61.28 56.97 iCaRL+GeoDL[60] CVPR 2021 62.54 61.40 61.84 70.10 70.86 70.72 60.02 57.98 56.70 BiC[79] CVPR 2019 59.36 54.20 50.00 70.07 64.96 57.73 62.65 58.72 53.47 BiC+Mnemonics[73] CVPR 2020 60.67 58.11 55.51 71.92 70.73 69.22 64.63 62.71 60.20 TPCIL[55] ECCV 2020 65.34 63.58 — 76.27 74.81 — 64.89 62.88 — UCIR[30] CVPR 2019 63.17 60.14 57.54 70.84 68.32 61.44 64.45 61.57 56.56 UCIR+DDE[58] CVPR 2021 65.27 62.36 — 72.34 70.20 — 67.51 65.77 — UCIR+AANets[121] CVPR 2021 66.74 65.29 63.50 72.55 69.22 67.60 64.94 62.39 60.68 UCIR+GeoDL[60] CVPR 2021 65.14 65.03 63.12 73.87 73.55 71.72 65.23 64.46 62.20 UCIR+MRDC[71] ICLR 2022 — — — 73.56 72.70 70.53 67.53 65.29 — UCIR+CwD[142] CVPR 2022 67.26 62.89 56.81 71.94 69.34 65.10 57.42 53.37 — WA[31] CVPR 2020 61.70 56.37 50.78 71.26 64.99 53.61 56.69 52.35 44.58 PODnet[53] ECCV 2020 64.83 63.19 60.72 75.54 74.33 68.31 66.95 64.13 59.17 PODnet+DDE[58] CVPR 2021 65.42 64.12 — 76.71 75.41 — 66.42 64.71 — PODnet+AANets[121] CVPR 2021 66.31 64.31 62.31 76.96 75.58 71.78 67.73 64.85 61.78 PODnet+MRDC[71] ICLR 2022 — — — 78.08 76.02 72.72 68.91 66.31 — PODnet+CwD[142] CVPR 2022 67.44 64.64 62.24 76.91 74.34 67.42 58.18 56.01 — Mnemonics[73] CVPR 2020 63.34 62.28 60.96 72.58 71.37 69.74 64.54 63.01 61.00 Mnemonics+AANets[121] CVPR 2021 67.59 65.66 63.35 72.91 71.93 70.70 65.23 63.60 61.53 RMM[83] NeurIPS 2021 68.42 67.17 64.56 73.58 72.83 72.30 65.81 64.10 62.23 DER[125] CVPR 2021 72.60 72.45 — — 77.73 — — — — SS-IL[78] ICCV 2021 63.02 61.52 58.02 — — — — — — AFC[135] CVPR 2022 66.49 64.98 64.06 76.87 75.75 73.34 68.90 67.02 — DMIL[134] CVPR 2022 68.01 66.47 — 77.20 76.76 — — — — 表 7 基于样本回放的方法在CIFAR-100, ImageNet-Sub和ImageNet-Full上的遗忘率 (%) 比较
Table 7 Comparisons of average forgetting (%) on CIFAR-100, ImageNet-Sub, and ImageNet-Full
存储个数 算法 发表出处 CIFAR-100 ImageNet-Sub ImageNet-Full $T=5$ $T=10$ $T=25$ $T=5$ $T=10$ $T=25$ $T=5$ $T=10$ $T=25$ $R=20$ iCaRL[29] CVPR 2017 31.88 34.10 36.48 43.40 45.84 47.60 26.03 33.76 38.80 iCaRL+Mnemonics[73] CVPR 2020 25.94 26.92 28.92 20.96 24.12 29.32 20.26 24.04 17.49 iCaRL+GeoDL[60] CVPR 2021 12.20 21.10 26.84 26.84 22.44 24.88 21.84 22.87 28.22 BiC[79] CVPR 2019 31.42 32.50 34.60 27.04 31.04 37.88 25.06 28.34 33.17 BiC+Mnemonics[73] CVPR 2020 22.42 24.50 25.52 18.43 19.20 21.43 18.32 19.72 20.50 UCIR[30] CVPR 2019 18.70 21.34 26.46 31.88 33.48 35.40 24.08 27.29 30.30 UCIR+GeoDL[60] CVPR 2021 9.49 9.10 12.01 13.78 12.68 15.21 11.03 12.81 15.11 WA[31] CVPR 2020 13.49 17.07 28.32 24.43 32.72 41.02 22.88 28.11 31.25 Mnemonics[73] CVPR 2021 10.91 13.38 19.80 17.40 17.08 20.83 13.85 15.82 19.17 表 8 非样本回放类别增量学习方法平均增量准确率 (%) 比较
Table 8 Comparisons of average incremental accuracies (%) of non-exemplar based class incremental learning methods
算法 发表出处 CIFAR-100 Tiny-ImageNet ImageNet-Sub $T=5$ $T=10$ $T=20$ $T=5$ $T=10$ $T=20$ $T=10$ LwF-MC[26]$^{\dagger}$ ECCV 2016 33.38 26.01 19.70 34.91 21.38 13.68 35.79 LwM[51]$^{\dagger}$ CVPR 2019 39.60 30.24 20.54 37.32 20.47 12.55 32.57 MUC[161]$^{\dagger}$ ECCV 2020 49.29 35.99 28.97 37.50 26.28 21.60 — calibrateCIL[64]$^{\dagger}$ ICME 2021 60.80 43.58 38.05 36.72 27.64 16.28 41.11 UCIR-DF[30] CVPR 2019 57.82 48.69 — — — — — PODNet-DF[53] ECCV 2020 56.85 52.61 — — — — — ABD[96] ICCV 2021 62.40 58.97 — 44.55 41.64 — — R-DFCIL[97] ECCV 2022 64.78 61.71 — 48.91 47.60 — — IL2A[106]$^{\dagger}$ NeurIPS 2021 66.16 58.20 58.01 47.21 44.69 40.04 57.98 PASS[13]$^{\dagger}$ CVPR 2021 63.84 59.87 58.06 49.53 47.19 41.99 62.09 SSRE[114] CVPR 2022 65.88 65.04 61.70 50.39 48.93 48.17 67.69 SDC-new[107, 115] CVPR 2020 66.20 62.70 59.20 53.29 50.48 48.79 68.60 Fusion[115] CVPR 2022 66.90 64.80 61.50 54.16 52.63 50.24 69.30 表 9 类别增量学习方法对比与总结
Table 9 Comparison and summary of class incremental learning methods
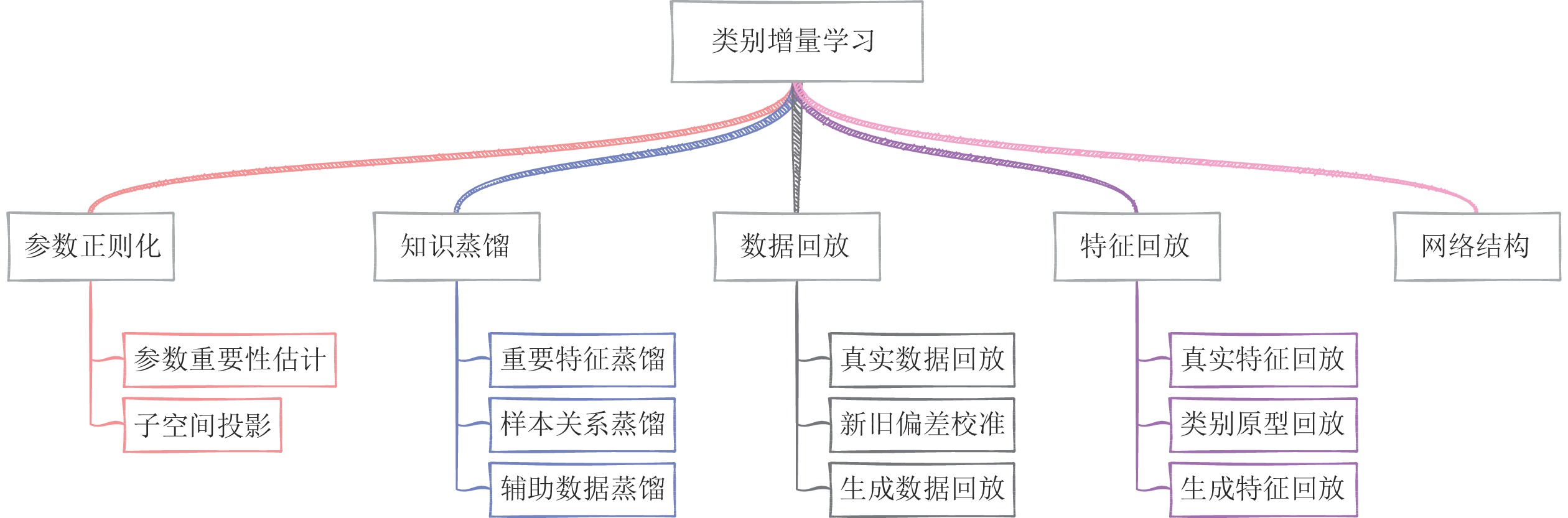
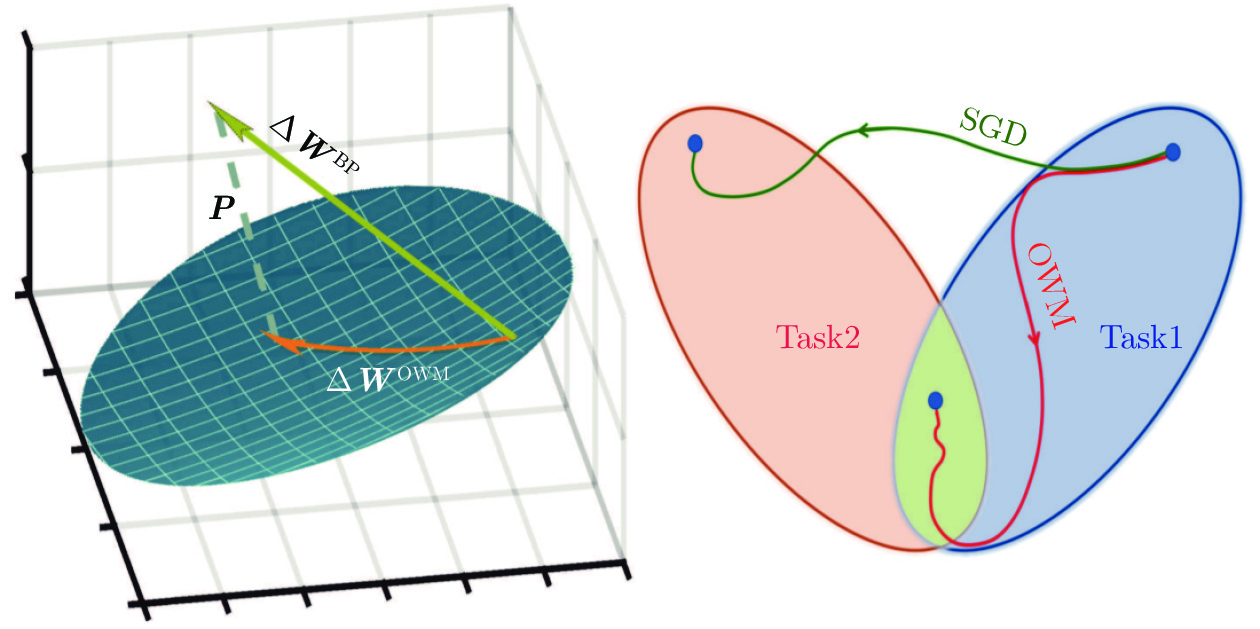
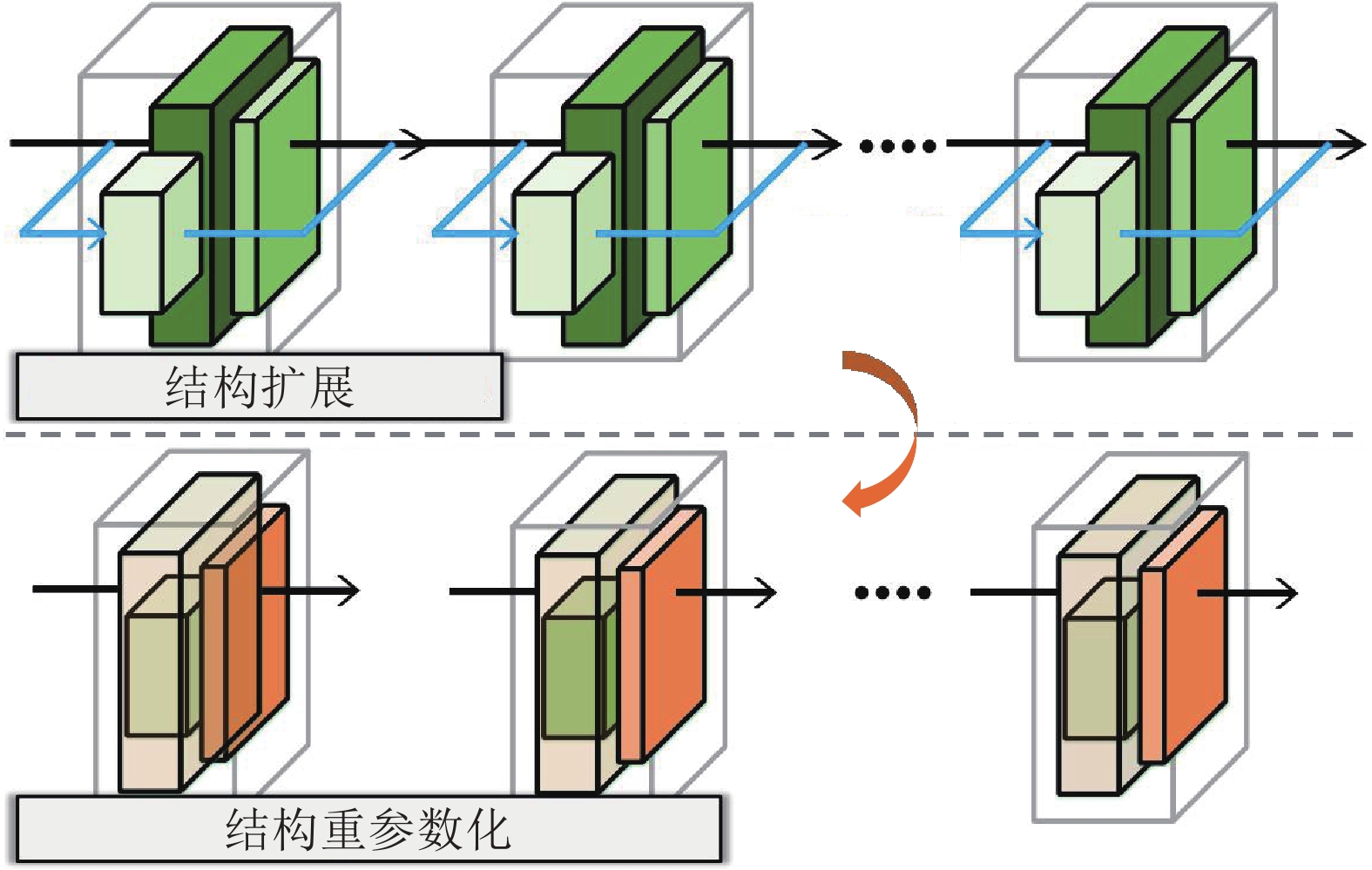
方法分类 包含子类 代表文献 核心思想 优点 缺点 参数正则化 参数重要性估计 [25, 27−28] 显式约束重要参数更新, 或者约束梯度更新方向 不需要保存样本, 模型更新快速, 时间、空间复杂度低 分类器有严重偏差, 类别增量性能差 子空间投影 [46−48] 知识蒸馏 重要特征蒸馏 [26, 30, 50−51, 53] 保持新旧模型对给定数据的输出一致性 能够较好地保持已有知识, 成为很多方法的基础组成部分 需要保存上一增量阶段的模型, 占用存储空间 样本关系蒸馏 [55−60] 辅助数据蒸馏 [62−64, 134] 数据回放 真实数据回放 [29, 66, 73] 保存一小部分旧类别数据用于后续再学习 类别增量学习性能好, 且易于实现 容易过拟合存储的数据, 时间、空间复杂度高, 隐私性不好 新旧偏差校准 [30−31, 77−81] 生成数据回放 [95−100] 特征回放 真实特征回放 [103−105] 保存深度特征空间的旧类别特征来维持决策面 性能较好, 时间、空间复杂度低 随着增量过程中特征提取器的更新, 保存的旧类别特征有效性降低 类别原型回放 [13, 106−107, 114−115] 生成特征回放 [108−109] 网络结构 结构动态扩展 [121, 125] 冻结已有网络参数, 新参数用于学习新类别 较好地保持旧类别知识, 同时能够较充分地学习新类别 网络参数量逐渐增大, 时间、空间复杂度高 -
[1] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [2] Feichtenhofer C, Fan H Q, Malik J, He K M. SlowFast networks for video recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 6201−6210 [3] Qian Y M, Bi M X, Tan T, Yu K. Very deep convolutional neural networks for noise robust speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2016, 24(12): 2263-2276 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2016.2602884 [4] Silver D, Schrittwieser J, Simonyan K, Antonoglou I, Huang A, Guez A, et al. Mastering the game of go without human knowledge. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 354-359 doi: 10.1038/nature24270 [5] Wurman P R, Barrett S, Kawamoto K, MacGlashan J, Subramanian K, Walsh T J, et al. Outracing champion Gran Turismo drivers with deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 2022, 602(7896): 223-228 doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04357-7 [6] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 779−788 [7] Geng C X, Huang S J, Chen S C. Recent advances in open set recognition: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(10): 3614-3631 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2981604 [8] Zhang X Y, Liu C L, Suen C Y. Towards robust pattern recognition: A review. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2020, 108(6): 894-922 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2020.2989782 [9] Hadsell R, Rao D, Rusu A A, Pascanu R. Embracing change: Continual learning in deep neural networks. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2020, 24(12): 1028-1040 doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2020.09.004 [10] Parisi G I, Kemker R, Part J L, Kanan C, Wermter S. Continual lifelong learning with neural networks: A review. Neural Networks, 2019, 113: 54-71 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.01.012 [11] Hendrycks D, Gimpel K. A baseline for detecting misclassified and out-of-distribution examples in neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Toulon, France: OpenReview.net, 2017. [12] Han K, Rebuffi S A, Ehrhardt S, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A. AutoNovel: Automatically discovering and learning novel visual categories. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(10): 6767-6781 [13] Zhu F, Zhang X Y, Wang C, Yin F, Liu C L. Prototype augmentation and self-supervision for incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 5867−5876 [14] Yang J K, Zhou K Y, Li Y X, Liu Z W. Generalized out-of-distribution detection: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2110.11334, 2021. [15] She Q, Feng F, Hao X Y, Yang Q H, Lan C L, Lomonaco V, et al. OpenLORIS-object: A robotic vision dataset and benchmark for lifelong deep learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris, France: IEEE, 2020. 4767−4773 [16] Liu B, Mazumder S. Lifelong and continual learning dialogue systems: Learning during conversation. In: Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI, 2021. 15058−15063 [17] Wang Y Q, Yao Q M, Kwok J T, Ni L M. Generalizing from a few examples: A survey on few-shot learning. ACM Computing Surveys, 2021, 53(3): Article No. 63 [18] Goodfellow I J, Mirza M, Xiao D, Courville A, Bengio Y. An empirical investigation of catastrophic forgetting in gradient-based neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1312.6211, 2013. [19] McCloskey M, Cohen N J. Catastrophic interference in connectionist networks: The sequential learning problem. Psychology of Learning and Motivation, 1989, 24: 109-165 [20] Hoi S C H, Sahoo D, Lu J, Zhao P L. Online learning: A comprehensive survey. Neurocomputing, 2021, 459: 249-289 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.112 [21] Cauwenberghs G, Poggio T. Incremental and decremental support vector machine learning. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Denver, USA: MIT Press, 2000. 388−394 [22] Shrestha P. Incremental learning strategies with random forest classifiers. In: Proceedings of the 32nd WIC Symposium on Information Theory. Brussels, Belgium: WIC, 2011. 1−6 [23] Mensink T, Verbeek J, Perronnin F, Csurka G. Distance-based image classification: Generalizing to new classes at near-zero cost. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(11): 2624-2637 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.83 [24] Ristin M, Guillaumin M, Gall J, Van Gool L. Incremental learning of random forests for large-scale image classification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(3): 490-503 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2459678 [25] Kirkpatrick J, Pascanu R, Rabinowitz N, Veness J, Desjardins G, Rusu A A, et al. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in neural networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(13): 3521-3526 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611835114 [26] Li Z Z, Hoiem D. Learning without forgetting. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(12): 2935-2947 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2773081 [27] Zenke F, Poole B, Ganguli S. Continual learning through synaptic intelligence. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Sydney, Australia: PMLR, 2017. 3987−3995 [28] Aljundi R, Babiloni F, Elhoseiny M, Rohrbach M, Tuytelaars T. Memory aware synapses: Learning what (not) to forget. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 144−161 [29] Rebuffi S A, Kolesnikov A, Sperl G, Lampert C H. iCaRL: Incremental classifier and representation learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 5533−5542 [30] Hou S H, Pan X Y, Loy C C, Wang Z L, Lin D H. Learning a unified classifier incrementally via rebalancing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 831−839 [31] Zhao B W, Xiao X, Gan G J, Zhang B, Xia S T. Maintaining discrimination and fairness in class incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 13205−13214 [32] De Lange M, Aljundi R, Masana M, Parisot S, Jia X, Leonardis A, et al. A continual learning survey: Defying forgetting in classification tasks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(7): 3366-3385 [33] Masana M, Liu X L, Twardowski B, Menta M, Bagdanov A D, van de Weijer J. Class-incremental learning: Survey and performance evaluation on image classification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3213473 [34] Mai Z, Li R W, Jeong J, Quispe D, Kim H, Sanner S. Online continual learning in image classification: An empirical survey. Neurocomputing, 2022, 469: 28-51 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.10.021 [35] 韩亚楠, 刘建伟, 罗雄麟. 连续学习研究进展. 计算机研究与发展, 2022, 59(6): 1213-1239 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.20201058Han Ya-Nan, Liu Jian-Wei, Luo Xiong-Lin. Research progress of continual learning. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2022, 59(6): 1213-1239 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.20201058 [36] 杨静, 李斌, 李少波, 王崎, 于丽娅, 胡建军, 等. 脑启发式持续学习方法: 技术、应用与发展. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(5): 1865-1878 doi: 10.11999/JEIT210932Yang Jing, Li Bin, Li Shao-Bo, Wang Qi, Yu Li-Ya, Hu Jian-Jun, et al. Brain-inspired continuous learning: Technology, application and future. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(5): 1865-1878 doi: 10.11999/JEIT210932 [37] Krizhevsky A, Hinton G. Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. Handbook of Systemic Autoimmune Diseases, 2009, 1(4):1−60 [38] Feng T, Wang M, Yuan H J. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting in incremental object detection via elastic response distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 9417−9426 [39] Joseph K J, Rajasegaran J, Khan S, Khan F S, Balasubramanian V N. Incremental object detection via meta-learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(12): 9209-9216 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3124133 [40] Cermelli F, Fontanel D, Tavera A, Ciccone M, Caputo B. Incremental learning in semantic segmentation from image labels. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 4361−4371 [41] Zhang C B, Xiao J W, Liu X L, Chen Y C, Cheng M M. Representation compensation networks for continual semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 7043-7054 [42] Wang R, Yu T, Zhao H D, Kim S, Mitra S, Zhang R Y, et al. Few-shot class-incremental learning for named entity recognition. In: Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Dublin, Ireland: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2022. 571−582 [43] Yu P F, Ji H, Natarajan P. Lifelong event detection with knowledge transfer. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Punta Cana, Dominican: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021. 5278−5290 [44] Hsu Y C, Liu Y C, Ramasamy A, Kira Z. Re-evaluating continual learning scenarios: A categorization and case for strong baselines. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1810.12488, 2018. [45] van de Ven G M, Tolias A S. Three scenarios for continual learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1904.07734, 2019. [46] Zeng G X, Chen Y, Cui B, Yu S. Continual learning of context-dependent processing in neural networks. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2019, 1(8): 364-372 doi: 10.1038/s42256-019-0080-x [47] Farajtabar M, Azizan N, Mott A, Li A. Orthogonal gradient descent for continual learning. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Palermo, Italy: PMLR, 2020. 3762−3773 [48] Wang S P, Li X R, Sun J, Xu Z B. Training networks in null space of feature covariance for continual learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 184−193 [49] Hinton G, Vinyals O, Dean J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1503.02531, 2015. [50] Rannen A, Aljundi R, Blaschko M B, Tuytelaars T. Encoder based lifelong learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 1329−1337 [51] Dhar P, Singh R V, Peng K C, Wu Z Y, Chellappa R. Learning without memorizing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 5133−5141 [52] Zagoruyko S, Komodakis N. Paying more attention to attention: Improving the performance of convolutional neural networks via attention transfer. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Toulon, France: OpenReview.net, 2017. [53] Douillard A, Cord M, Ollion C, Robert T, Valle E. PODNet: Pooled outputs distillation for small-tasks incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 86−102 [54] Wang L, Yoon K J. Knowledge distillation and student-teacher learning for visual intelligence: A review and new outlooks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(6): 3048-3068 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3055564 [55] Tao X Y, Chang X Y, Hong X P, Wei X, Gong Y H. Topology-preserving class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 254−270 [56] Liu Y, Hong X P, Tao X Y, Dong S L, Shi J G, Gong Y H. Model behavior preserving for class-incremental learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, DOI: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3144183 [57] Cha H, Lee J, Shin J. Co.2L: Contrastive continual learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 9496−9505 [58] Hu X T, Tang K H, Miao C Y, Hua X S, Zhang H W. Distilling causal effect of data in class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 3956−3965 [59] Roweis S T, Saul L K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science, 2000, 290(5500): 2323-2326 doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2323 [60] Simon C, Koniusz P, Harandi M. On learning the geodesic path for incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 1591−1600 [61] Gong B Q, Shi Y, Sha F, Grauman K. Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 2066−2073 [62] Zhang J T, Zhang J, Ghosh S, Li D W, Tasci S, Heck L, et al. Class-incremental learning via deep model consolidation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Snowmass, USA: IEEE, 2020. 1120−1129 [63] Lee K, Lee K, Shin J, Lee H. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting with unlabeled data in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 312−321 [64] Zhu F, Zhang X Y, Liu C L. Calibration for non-exemplar based class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Shenzhen, China: IEEE, 2021. 1−6 [65] DeVries T, Taylor G W. Improved regularization of convolutional neural networks with cutout. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1708.04552, 2017. [66] Javed K, Shafait F. Revisiting distillation and incremental classifier learning. In: Proceedings of the 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV). Perth, Australia: Springer, 2019. 3−17 [67] Welling M. Herding dynamical weights to learn. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning. Montreal, Canada: ACM, 2009. 1121−1128 [68] Chaudhry A, Dokania P K, Ajanthan T, Torr P H S. Riemannian walk for incremental learning: Understanding forgetting and intransigence. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 556−572 [69] Aljundi R, Caccia L, Belilovsky E, Caccia M, Lin M, Charlin L, et al. Online continual learning with maximally interfered retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2019. Article No. 1063 [70] Shim D, Mai Z D, Jeong J, Sanner S, Kim H, Jang J. Online class-incremental continual learning with adversarial Shapley value. In: Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI, 2021. 9630−9638 [71] Wang L Y, Zhang X X, Yang K, Yu L H, Li C X, Hong L Q, et al. Memory replay with data compression for continual learning. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). OpenReview.net, 2022. [72] van der Maaten L, Hinton G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9(86): 2579-2605 [73] Liu Y Y, Su Y T, Liu A A, Schiele B, Sun Q R. Mnemonics training: Multi-class incremental learning without forgetting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 12242−12251 [74] Wang T Z, Zhu J Y, Torralba A, Efros A A. Dataset distillation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1811.10959, 2018. [75] Zhao B, Mopuri K R, Bilen H. Dataset condensation with gradient matching. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Austria: OpenReview.net, 2021. [76] Zhao B, Bilen H. Dataset condensation with differentiable Siamese augmentation. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). PMLR, 2021. [77] Castro F M, Marín-Jiménez M J, Guil N, Schmid C, Alahari K. End-to-end incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 241−257 [78] Ahn H, Kwak J, Lim S, Bang H, Kim H, Moon T. SS-IL: Separated softmax for incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 824−833 [79] Wu Y, Chen Y P, Wang L J, Ye Y C, Liu Z C, Guo Y D, et al. Large scale incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 374−382 [80] Belouadah E, Popescu A. IL2M: Class incremental learning with dual memory. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 583−592 [81] Belouadah E, Popescu A. ScaIL: Classifier weights scaling for class incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Snowmass, USA: IEEE, 2020. 1255−1264 [82] Prabhu A, Torr P H S, Dokania P K. GDumb: A simple approach that questions our progress in continual learning. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 524−540 [83] Liu Y Y, Schiele B, Sun Q R. RMM: Reinforced memory management for class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the 35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. 2021. 3478−3490 [84] Snell J, Swersky K, Zemel R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 4080−4090 [85] Lu Y J, Tian H, Cheng J, Zhu F, Liu B, Wei S S, et al. Decoding lip language using triboelectric sensors with deep learning. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): Article No. 1401 doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29083-0 [86] Yang H M, Zhang X Y, Yin F, Yang Q, Liu C L. Convolutional prototype network for open set recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(5): 2358-2370 [87] Trepte S. The social media privacy model: Privacy and communication in the light of social media affordances. Communication Theory, 2021, 31(4): 549-570 doi: 10.1093/ct/qtz035 [88] Li T, Sahu A K, Talwalkar A, Smith V. Federated learning: Challenges, methods, and future directions. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(3): 50-60 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.2975749 [89] Appari A, Johnson M E. Information security and privacy in healthcare: Current state of research. International Journal of Internet and Enterprise Management, 2010, 6(4): 279-314 doi: 10.1504/IJIEM.2010.035624 [90] Kitamura T, Ogawa S K, Roy D S, Okuyama T, Morrissey M D, Smith L M, et al. Engrams and circuits crucial for systems consolidation of a memory. Science, 2017, 356(6333): 73-78 doi: 10.1126/science.aam6808 [91] Kumaran D, Hassabis D, McClelland J L. What learning systems do intelligent agents need? Complementary learning systems theory updated. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2016, 20(7): 512-534 doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2016.05.004 [92] Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial networks. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139-144 doi: 10.1145/3422622 [93] Odena A, Olah C, Shlens J. Conditional image synthesis with auxiliary classifier GANs. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Sydney, Australia: PMLR, 2017. 2642−2651 [94] Kingma D P, Welling M. An introduction to variational autoencoders. Foundations and Trends\textregistered in Machine Learning, 2019, 12(4): 307-392 doi: 10.1561/2200000056 [95] Yin H X, Molchanov P, Alvarez J M, Li Z Z, Mallya A, Hoiem D, et al. Dreaming to distill: Data-free knowledge transfer via DeepInversion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 8712−8721 [96] Smith J, Hsu Y C, Balloch J, Shen Y L, Jin H X, Kira Z. Always be dreaming: A new approach for data-free class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 9354−9364 [97] Gao Q K, Zhao C, Ghanem B, Zhang J. R-DFCIL: Relat-ion-guided representation learning for data-free class incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 423−439 [98] Shin H, Lee J K, Kim J, Kim J. Continual learning with deep generative replay. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 2994−3003 [99] Wu C S, Herranz L, Liu X L, Wang Y X, van de Weijer J, Raducanu B. Memory replay GANs: Learning to generate images from new categories without forgetting. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2018. 5966−5976 [100] Xiang Y, Fu Y, Ji P, Huang H. Incremental learning using conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 6618−6627 [101] Kemker R, Kanan C. FearNet: Brain-inspired model for incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Vancouver, Canada: OpenReview.net, 2018. [102] Park W, Kim D, Lu Y, Cho M. Relational knowledge distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3962−3971 [103] Iscen A, Zhang J, Lazebnik S, Schmid C. Memory-efficient incremental learning through feature adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 699−715 [104] Pellegrini L, Graffieti G, Lomonaco V, Maltoni D. Latent replay for real-time continual learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2020. 10203−10209 [105] Hayes T L, Kafle K, Shrestha R, Acharya M, Kanan C. REMIND your neural network to prevent catastrophic forgetting. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 466−483 [106] Zhu F, Cheng Z, Zhang X Y, Liu C L. Class-incremental learning via dual augmentation. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. 2021. 14306−14318 [107] Yu L, Twardowski B, Liu X L, Herranz L, Wang K, Cheng Y M, et al. Semantic drift compensation for class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 6980−6989 [108] Liu X L, Wu C S, Menta M, Herranz L, Raducanu B, Bagdanov A D, et al. Generative feature replay for class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 915−924 [109] Shen G H, Zhang S, Chen X, Deng Z H. Generative feature replay with orthogonal weight modification for continual learning. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Shenzhen, China: IEEE, 2021. 1−8 [110] Chopra S, Hadsell R, LeCun Y. Learning a similarity metric discriminatively, with application to face verification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2005. 539−546 [111] Wang J, Song Y, Leung T, Rosenberg C, Wang J B, Philbin J, et al. Learning fine-grained image similarity with deep ranking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 1386−1393 [112] Wang Y L, Huang G, Song S J, Pan X R, Xia Y T, Wu C. Regularizing deep networks with semantic data augmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(7): 3733-3748 [113] van der Maaten L, Chen M M, Tyree S, Weinberger K Q. Learning with marginalized corrupted features. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Atlanta, USA: JMLR.org, 2013. 410−418 [114] Zhu K, Zhai W, Cao Y, Luo J B, Zha Z J. Self-sustaining representation expansion for non-exemplar class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 9286−9295 [115] Toldo M, Ozay M. Bring evanescent representations to life in lifelong class incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 16711−16720 [116] Jazbec M, Ashman M, Fortuin V, Pearce M, Mandt S, Rätsch G. Scalable Gaussian process variational autoencoders. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. PMLR, 2021. 3511−3519 [117] van de Ven G M, Siegelmann H T, Tolias A S. Brain-inspired replay for continual learning with artificial neural networks. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): Article No. 4069 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17866-2 [118] Rusu A A, Rabinowitz N C, Desjardins G, Soyer H, Kirkpatrick J, Kavukcuoglu K, et al. Progressive neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1606.04671, 2016. [119] Mallya A, Lazebnik S. PackNet: Adding multiple tasks to a single network by iterative pruning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 7765−7773 [120] Serrà J, Surís D, Miron M, Karatzoglou A. Overcoming catastrophic forgetting with hard attention to the task. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Stockholmsmässan, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. 4555−4564 [121] Liu Y Y, Schiele B, Sun Q R. Adaptive aggregation networks for class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 2544−2553 [122] McClelland J L, McNaughton B L, O’Reilly R C. Why there are complementary learning systems in the hippocampus and neocortex: Insights from the successes and failures of connectionist models of learning and memory. Psychological Review, 1995, 102(3): 419-457 doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.102.3.419 [123] Pham Q, Liu C H, Hoi S C H. DualNet: Continual learning, fast and slow. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. 2021. 16131−16144 [124] Chen T, Kornblith S, Norouzi M, Hinton G E. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). PMLR, 2020. 1597−1607 [125] Yan S P, Xie J W, He X M. DER: Dynamically expandable representation for class incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 3014−3023 [126] Kang B Y, Xie S N, Rohrbach M, Yan Z C, Gordo A, Feng J S, et al. Decoupling representation and classifier for long-tailed recognition. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: OpenReview.net, 2020. [127] Ding X H, Zhang X Y, Ma N N, Han J G, Ding G G, Sun J. RepVGG: Making VGG-style ConvNets great again. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 13728−13737 [128] Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L J, Li K, Li F F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, USA: IEEE, 2009. 248−255 [129] LeCun Y. The MNIST database of handwritten digits [Online], available: http://yann. lecun. com/exdb/mnist/, March 1, 2023 [130] Welinder P, Branson S, Mita T, Wah C, Schroff F, Belongie S, et al. Caltech-UCSD Birds 200, Technical Report CNS-TR-2010-001, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, USA, 2010 [131] Le Y, Yang X. Tiny imagenet visual recogniti on challenges. CS 231N, 2015 [132] Cao Q, Shen L, Xie W D, Parkhi O M, Zisserman A. VGGFace2: A dataset for recognising faces across pose and age. In: Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition. Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2018. 67−74 [133] Noh H, Araujo A, Sim J, Weyand T, Han B. Large-scale image retrieval with attentive deep local features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 3476−3485 [134] Tang Y M, Peng Y X, Zheng W S. Learning to imagine: Diversify memory for incremental learning using unlabeled data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 9539−9548 [135] Kang M, Park J, Han B. Class-incremental learning by knowledge distillation with adaptive feature consolidation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 16050−16059 [136] Luo M, Chen F, Hu D P, Zhang Y F, Liang J, Feng J S. No fear of heterogeneity: Classifier calibration for federated learning with non-IID data. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. 2021. 5972−5984 [137] Lesort T, Lomonaco V, Stoian A, Maltoni D, Filliat D, Díaz-Rodríguez N. Continual learning for robotics: Definition, framework, learning strategies, opportunities and challenges. Information Fusion, 2020, 58: 52-68 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.12.004 [138] You C S, Huang K B, Chae H, Kim B H. Energy-efficient resource allocation for mobile-edge computation offloading. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(3): 1397-1411 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2633522 [139] Biederman I. Human image understanding: Recent research and a theory. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 1985, 32(1): 29-73 doi: 10.1016/0734-189X(85)90002-7 [140] Hase P, Chen C F, Li O, Rudin C. Interpretable image recognition with hierarchical prototypes. In: Proceedings of the 7th AAAI Conference on Human Computation and Crowdsourcing. Stevenson, USA: AAAI, 2019. 32−40 [141] Gidaris S, Singh P, Komodakis N. Unsupervised representation learning by predicting image rotations. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Vancouver, Canada: OpenReview.net, 2018. [142] Shi Y J, Zhou K Q, Liang J, Jiang Z H, Feng J S, Torr P, et al. Mimicking the oracle: An initial phase decorrelation approach for class incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 16701−16710 [143] Wu Z Y, Baek C, You C, Ma Y. Incremental learning via rate reduction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 1125−1133 [144] Chan K H R, Yu Y D, You C, Qi H Z, Wright J, Ma Y. ReduNet: A white-box deep network from the principle of maximizing rate reduction. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2022, 23(114): 1-103 [145] Wang R Q, Zhang X Y, Liu C L. Meta-prototypical learning for domain-agnostic few-shot recognition. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(11): 6990-6996 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3083650 [146] Wang R Q, Zhu F, Zhang X Y, Liu C L. Training with scaled logits to alleviate class-level over-fitting in few-shot learning. Neurocomputing, 2023, 522: 142-151 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.12.011 [147] Zhang C, Song N, Lin G S, Zheng Y, Pan P, Xu Y H. Few-shot incremental learning with continually evolved classifiers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 12450−12459 [148] Zhu K, Cao Y, Zhai W, Cheng J, Zha Z J. Self-promoted prototype refinement for few-shot class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 6797−6806 [149] Zhou D W, Wang F Y, Ye H J, Ma L, Pu S L, Zhan D C. Forward compatible few-shot class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 9036−9046 [150] Tao X Y, Hong X P, Chang X Y, Dong S L, Wei X, Gong Y H. Few-shot class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 12180−12189 [151] Kalla J, Biswas S. S3C: Self-supervised stochastic classifiers for few-shot class-incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 432−448 [152] Peng C, Zhao K, Wang T R, Li M, Lovell B C. Few-shot class-incremental learning from an open-set perspective. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 382−397 [153] Gidaris S, Komodakis N. Dynamic few-shot visual learning without forgetting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4367−4375 [154] Kukleva A, Kuehne H, Schiele B. Generalized and incremental few-shot learning by explicit learning and calibration without forgetting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 9000−9009 [155] Ye H J, Hu H X, Zhan D C. Learning adaptive classifiers synthesis for generalized few-shot learning. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(6): 1930-1953 doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01381-4 [156] Cheng Z, Zhu F, Zhang X Y, Liu C L. Adversarial training with distribution normalization and margin balance. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 136: Article No. 109182 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109182 [157] Zhu F, Cheng Z, Zhang X Y, Liu C L. Rethinking confidence calibration for failure prediction. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 518−536 [158] Kim G, Liu B, Ke Z X. A multi-head model for continual learning via out-of-distribution replay. In: Proceedings of the 1st Conference on Lifelong Learning Agents. PMLR, 2022. 548−563 [159] Kim G, Xiao C N, Konishi T, Ke Z X, Liu B. A theoretical study on solving continual learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2211.02633, 2022. [160] Villa A, Alhamoud K, Escorcia V, Heilbron F C, Alcázar J L, Ghanem B. vCLIMB: A novel video class incremental learning benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 19013−19022 [161] Liu Y, Parisot S, Slabaugh G, Jia X, Leonardis A, Tuytelaars T. More classifiers, less forgetting: A generic multi-classifier paradigm for incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 699−716 -




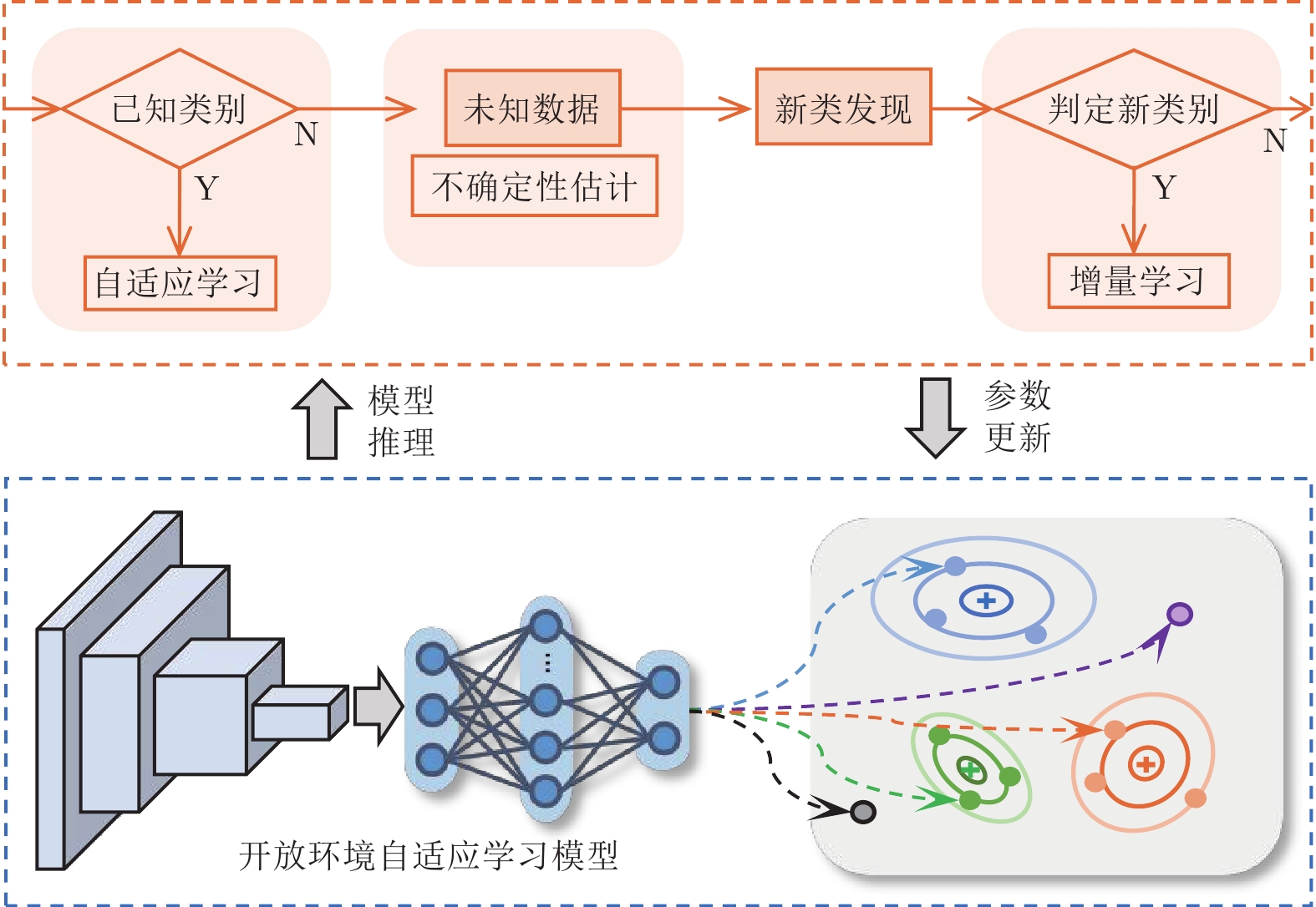
 下载:
下载: