G-IDRN: A Group-information Distillation Residual Network for Lightweight Image Super-resolution
-
摘要: 目前, 基于深度学习的超分辨算法已经取得了很好性能, 但这些方法通常具有较大内存消耗和较高计算复杂度, 很难应用到低算力或便携式设备上. 为了解决这个问题, 设计一种轻量级的组−信息蒸馏残差网络(Group-information distillation residual network, G-IDRN)用于快速且精确的单图像超分辨率任务. 具体地, 提出一个更加有效的组−信息蒸馏模块(Group-information distillation block, G-IDB)作为网络特征提取基本块. 同时, 引入密集快捷连接, 对多个基本块进行组合, 构建组−信息蒸馏残差组(Group-information distillation residual group, G-IDRG), 捕获多层级信息和有效重利用特征. 另外, 还提出一个轻量的非对称残差Non-local模块, 对长距离依赖关系进行建模, 进一步提升超分性能. 最后, 设计一个高频损失函数, 去解决像素损失带来图像细节平滑的问题. 大量实验结果表明, 该算法相较于其他先进方法, 可以在图像超分辨率性能和模型复杂度之间取得更好平衡, 其在公开测试数据集B100上, 4倍超分速率达到56 FPS, 比残差注意力网络快15倍.Abstract: Recently, most super-resolution algorithms based on deep learning have achieved satisfactory results. However, these methods generally consume large memory and have high computational complexity, and are difficult to apply to low computing power or portable devices. To address this problem, this paper introduces a lightweight group-information distillation residual network (G-IDRN) for fast and accurate single image super-resolution. Specially, we propose a more effective group-information distillation block (G-IDB) as the basic block for feature extraction. Simultaneously, we introduce dense shortcut to combine them to construct a group-information distillation residual group (G-IDRG), which is used to capture multi-level information and effectively reuse the learned features. Moreover, a lightweight asymmetric residual Non-local block is proposed to model the long-range dependencies and further improve the performance of super-resolution. Finally, a high-frequency loss function is designed to alleviate the problem of smoothing image details caused by pixel-wise loss. Extensive experiments show the proposed algorithm achieves a better trade-off between image super-resolution performance and model complexity against other state-of-the-art super-resolution methods and gets 56 FPS on the public test dataset B100 with a scale factor of 4 times, which is 15 times faster than the residual channel attention network.
-
Key words:
- Residual network /
- super-resolution /
- feature distillation /
- high-frequency loss
-
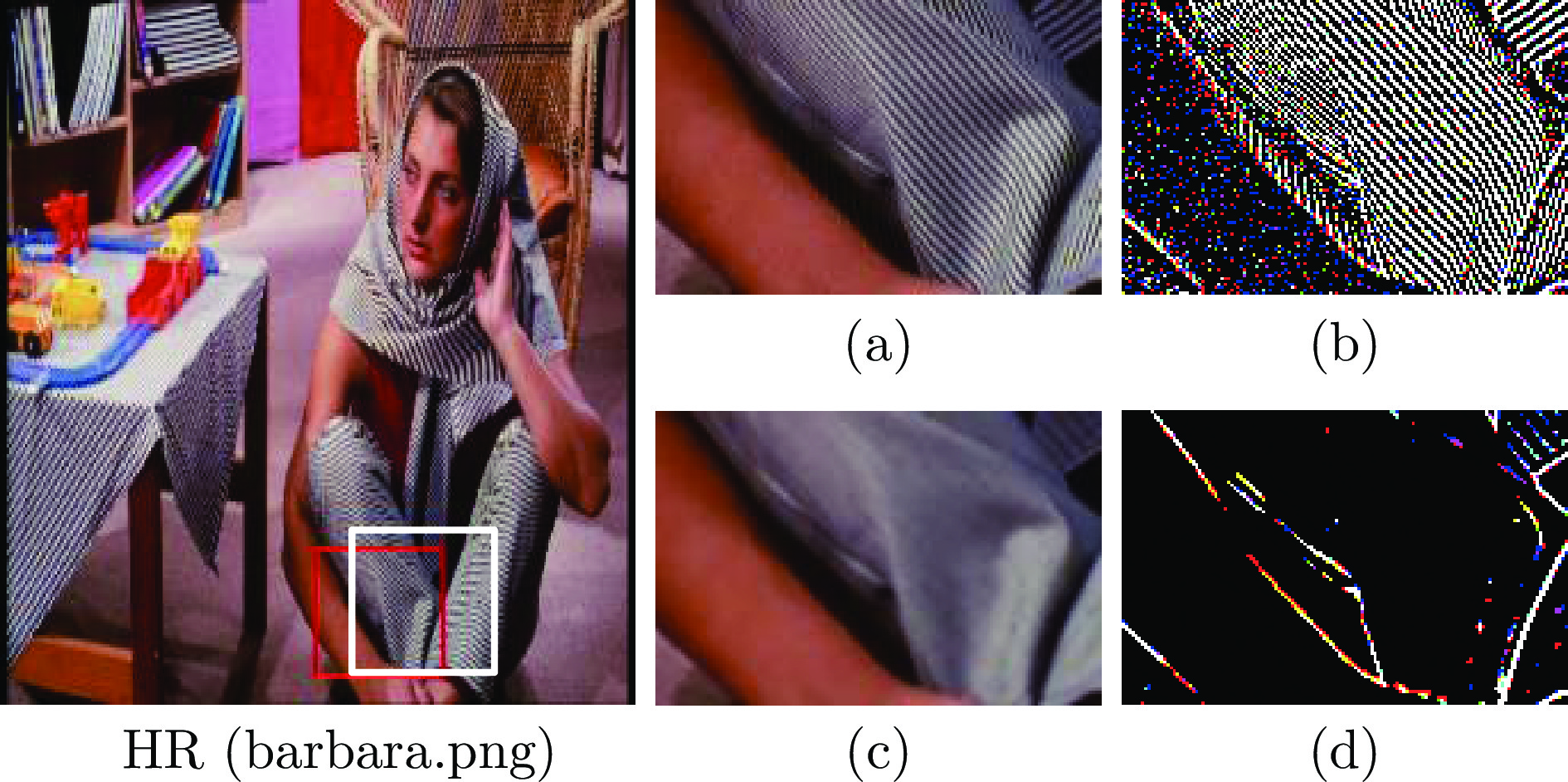
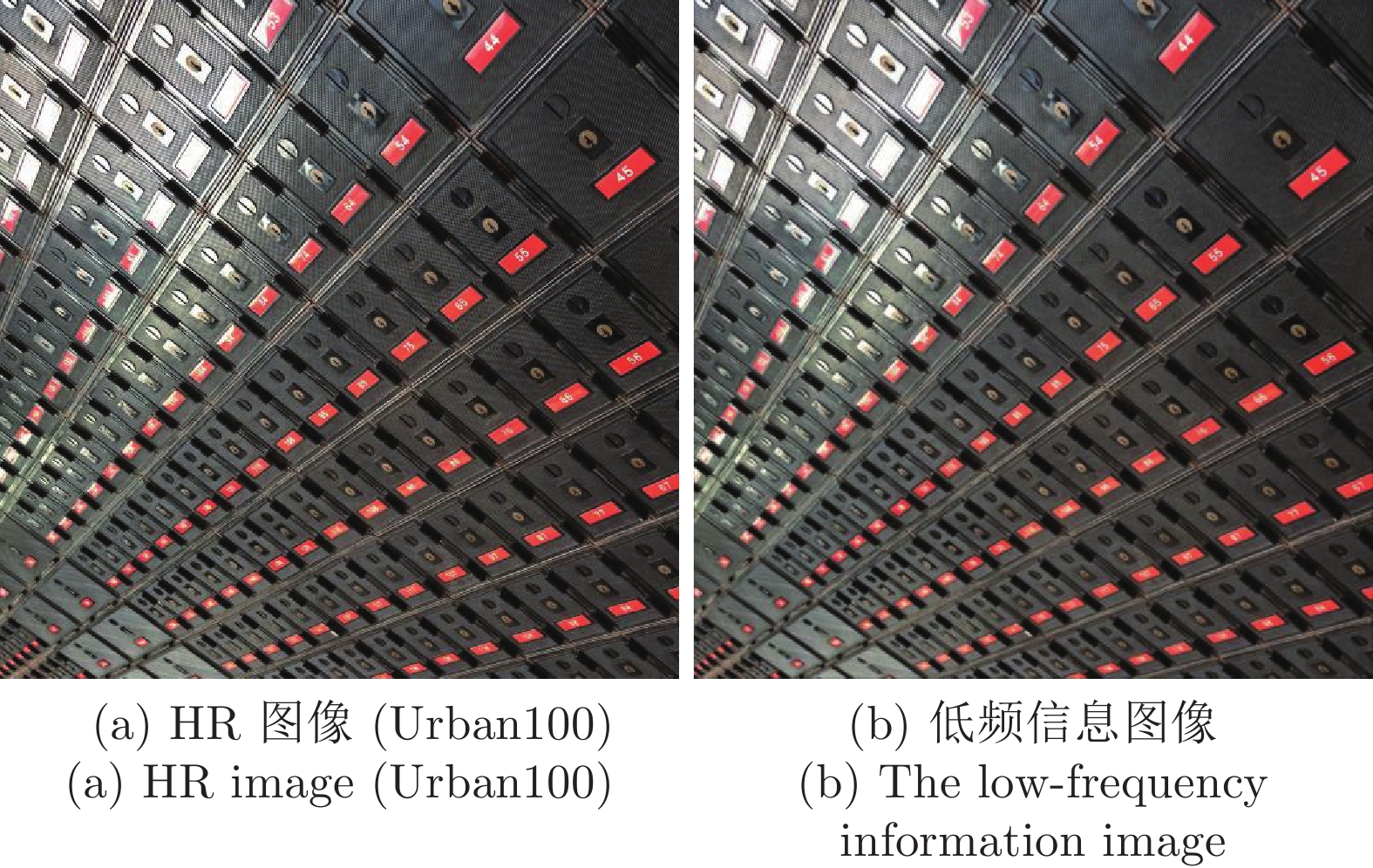
图 6 Set14中barbara.png放大3倍的高频提取图像((a)裁剪的 HR 图像; (b) HR 图像的高频提取图; (c)裁剪的SR图像; (d) SR图像的高频提取图)
Fig. 6 High-frequency extraction images for 3 times barbara.png on Set14 ((a) Cropped HR image; (b) High-frequency extractionimage of HR image; (c) Cropped SR imag; (d) High-frequency extraction image of SR image)
表 1 消融实验结果
Table 1 Ablation experiment results
基本块 双路重建策略 DS连接 ANRB PSNR (dB) 参数量 (K) 增幅PSNR (dB) | 参数量 (K) RFDB ✘ ✘ ✘ 37.893 534.0 0 | 0 $ \checkmark$ ✘ ✘ 37.931 514.2 $\uparrow$ 0.038 | $\downarrow$ 19.8 ✘ $ \checkmark$ ✘ 37.891 520.2 $ \downarrow$ 0.002 | $ \downarrow$ 13.8 ✘ ✘ $ \checkmark$ 37.916 534.3 $ \uparrow$ 0.023 | $ \uparrow$ 0.3 $ \checkmark$ ✘ $ \checkmark$ 37.934 514.4 $ \uparrow$ 0.041 | $ \downarrow$ 19.6 $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ 37.940 500.5 $ \uparrow$ 0.047 | $ \downarrow$ 33.5 G-IDB ✘ ✘ ✘ 37.955 449.4 $ \uparrow$ 0.062 | $ \downarrow$ 84.6 $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ $ \checkmark$ 37.965 383.2 $ \uparrow$ 0.072 | $ \downarrow$ 150.8 表 2 ANRB中, 不同采样特征点数的实验结果
Table 2 The experimental results for different sampled feature points in ANRB
特征点数 Set5
PSNR (dB)Manga109
PSNR (dB)$128\times 128$像素
内存消耗 (MB)$180\times 180$像素
内存消耗 (MB)无ANRB 37.888 38.396 216 419 $S=50$ 37.893 38.439 224 436 $S=110$ 37.895 38.443 232 452 $S=222$ 37.861 38.325 246 480 $S=\infty$ 37.883 内存溢出 2266 8431 表 3 使用不同损失权重系数的PSNR对比结果 (dB)
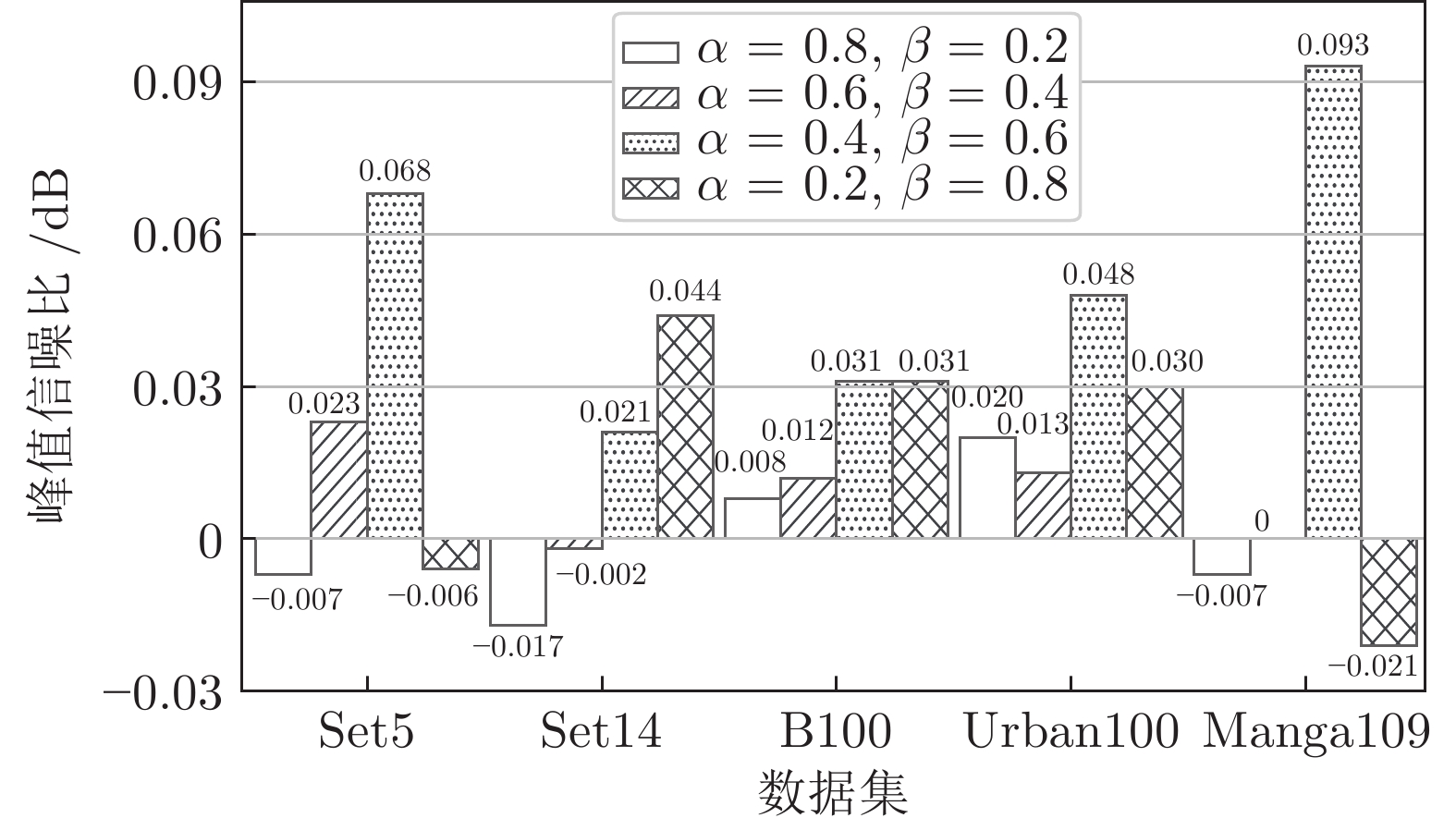
Table 3 Comparison results of PSNR with different loss weights (dB)
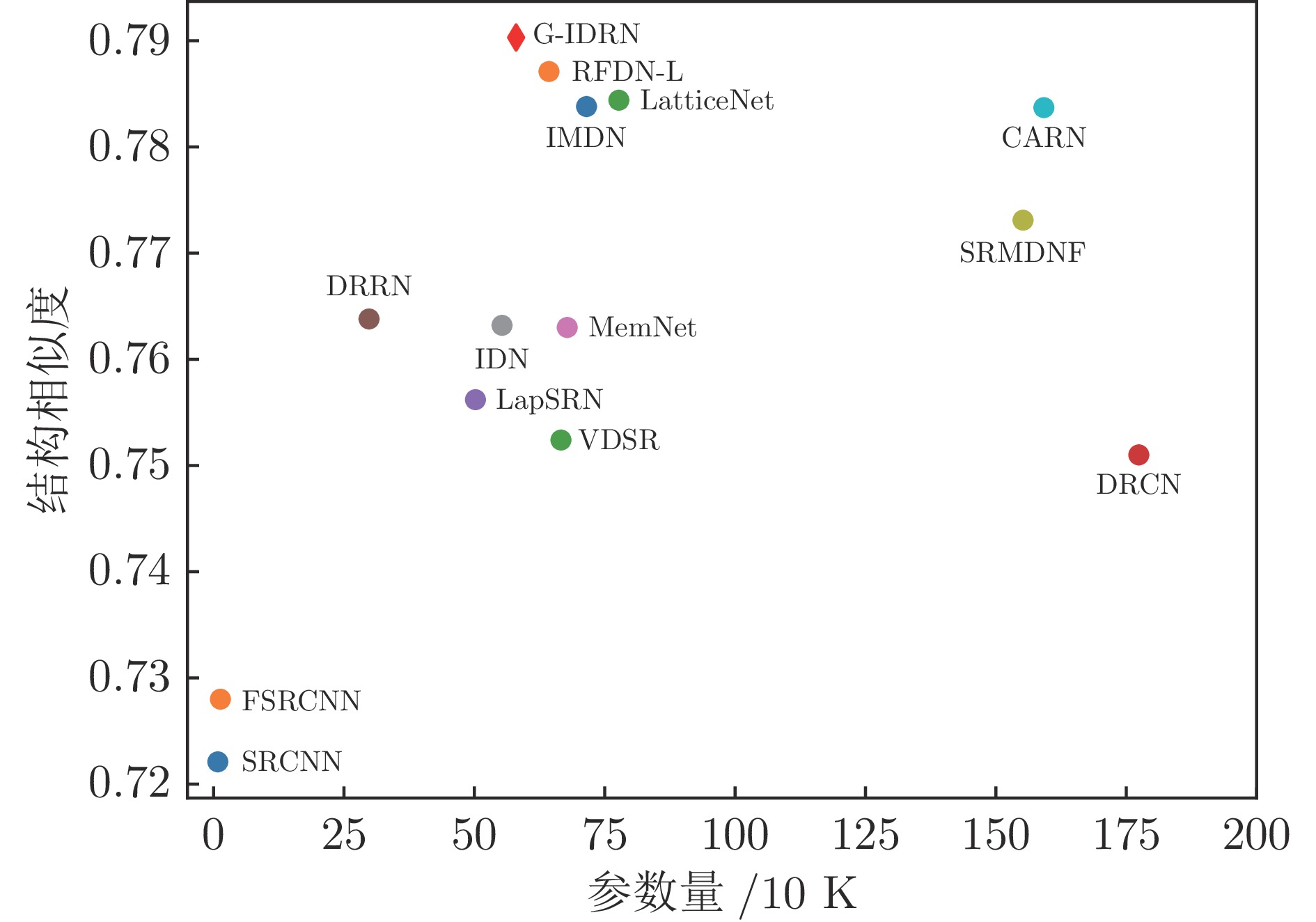
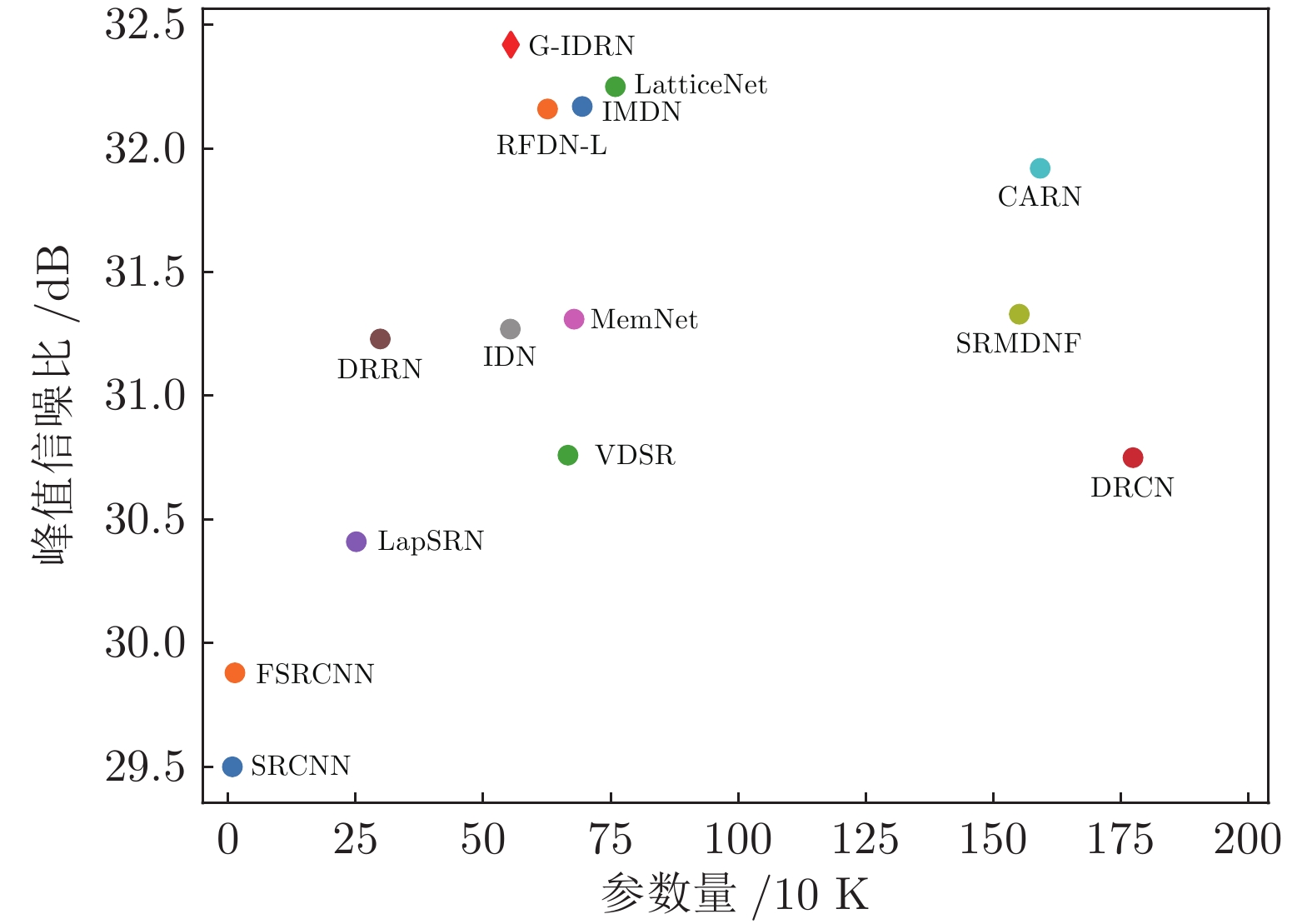
权重系数 Set5 Set14 B100 Urban100 Manga109 $\alpha =1.0$, $\beta =0$ 37.907 33.423 32.063 31.830 38.483 $\alpha =0.8$, $\beta =0.2$ 37.900 33.406 32.071 31.850 38.476 $\alpha =0.6$, $\beta =0.4$ 37.930 33.421 32.075 31.843 38.483 $\alpha =0.4$, $\beta =0.6$ 37.975 33.444 32.084 31.878 38.576 $\alpha =0.2$, $\beta =0.8$ 37.901 33.467 32.084 31.860 38.462 表 4 在5个基准数据集上, 图像放大2倍、3倍和4倍时, 各算法的参数量、PSNR和SSIM定量分析结果
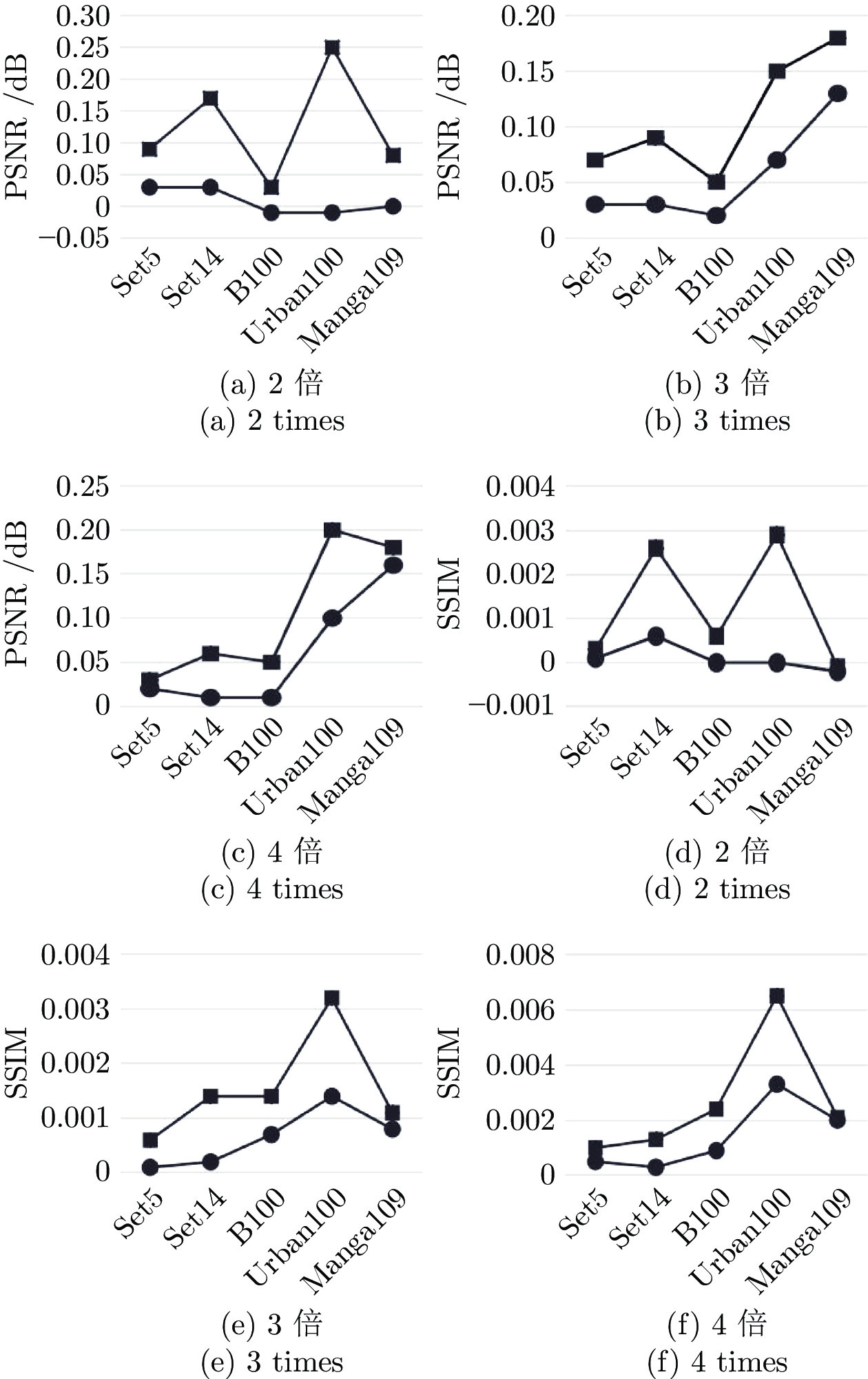
Table 4 Parameters, PSNR and SSIM quantitative comparisons of various algorithms for 2, 3, and 4 times images on the five benchmark datasets
方法 放大
倍数参数量
(K)Set5
PSNR (dB) / SSIMSet14
PSNR (dB) / SSIMB100
PSNR (dB) / SSIMUrban100
PSNR (dB) / SSIMManga109
PSNR (dB) / SSIMBicubic 2倍 − 33.66 / 0.9299 30.24 / 0.8688 29.56 / 0.8431 26.88 / 0.8403 30.80 / 0.9339 SRCNN 8 36.66 / 0.9542 32.45 / 0.9067 31.36 / 0.8879 29.50 / 0.8946 35.60 / 0.9663 DRCN 1774 37.63 / 0.9588 33.04 / 0.9118 31.85 / 0.8942 30.75 / 0.9133 37.55 / 0.9732 LapSRN 251 37.52 / 0.9591 32.99 / 0.9124 31.80 / 0.8952 30.41 / 0.9103 37.27 / 0.9740 DRRN 298 37.74 / 0.9591 33.23 / 0.9136 32.05 / 0.8973 31.23 / 0.9188 37.88 / 0.9749 MemNet 678 37.78 / 0.9597 33.28 / 0.9142 32.08 / 0.8978 31.31 / 0.9195 37.72 / 0.9740 IDN 553 37.83 / 0.9600 33.30 / 0.9148 32.08 / 0.8985 31.27 / 0.9196 38.01 / 0.9749 SRMDNF 1511 37.79 / 0.9601 33.32 / 0.9159 32.05 / 0.8985 31.33 / 0.9204 38.07 / 0.9761 CARN 1592 37.76 / 0.9590 33.52 / 0.9166 32.09 / 0.8978 31.92 / 0.9256 38.36 / 0.9765 SMSR 985 38.00 / 0.9601 33.64 / 0.9179 32.17 / 0.8993 32.19 / 0.9284 38.76 / 0.9771 IMDN 694 38.00 / 0.9605 33.63 / 0.9177 32.19 / 0.8997 32.17 / 0.9282 38.88 / 0.9774 IMDN-JDSR 694 38.00 / 0.9605 33.57 / 0.9176 32.16 / 0.8995 32.09 / 0.9271 − / − PAN 261 38.00 / 0.9605 33.59 / 0.9181 32.18 / 0.8997 32.01 / 0.9273 38.70 / 0.9773 RFDN-L 626 38.03 / 0.9606 33.65 / 0.9183 32.18 / 0.8997 32.16 / 0.9282 38.88 / 0.9772 LatticeNet 759 38.03 / 0.9607 33.70 / 0.9187 32.20 / 0.8999 32.25 / 0.9288 − / − G-IDRN 554 38.09 / 0.9608 33.80 / 0.9203 32.42 / 0.9003 32.42 / 0.9311 38.96 / 0.9773 Bicubic 3倍 − 30.39 / 0.8682 27.55 / 0.7742 27.21 / 0.7385 24.46 / 0.7349 26.95 / 0.8556 SRCNN 8 32.75 / 0.9090 29.30 / 0.8215 28.41 / 0.7863 26.24 / 0.7989 30.48 / 0.9117 DRCN 1774 33.82 / 0.9226 29.76 / 0.8311 28.80 / 0.7963 27.15 / 0.8276 32.24 / 0.9343 LapSRN 502 33.81 / 0.9220 29.79 / 0.8325 28.82 / 0.7980 27.07 / 0.8275 32.21 / 0.9350 DRRN 298 34.03 / 0.9244 29.96 / 0.8349 28.95 / 0.8004 27.53 / 0.8378 32.71 / 0.9379 MemNet 678 34.09 / 0.9248 30.00 / 0.8350 28.96 / 0.8001 27.56 / 0.8376 32.51 / 0.9369 IDN 553 34.11 / 0.9253 29.99 / 0.8354 28.95 / 0.8013 27.42 / 0.8359 32.71 / 0.9381 SRMDNF 1528 34.12 / 0.9254 30.04 / 0.8382 28.97 / 0.8025 27.57 / 0.8398 33.00 / 0.9403 CARN 1592 34.29 / 0.9255 30.29 / 0.8407 29.06 / 0.8034 28.06 / 0.8493 33.50 / 0.9440 SMSR 993 34.40 / 0.9270 30.33 / 0.8412 29.10 / 0.8050 28.25 / 0.8536 33.68 / 0.9445 IMDN 703 34.36 / 0.9270 30.32 / 0.8417 29.09 / 0.8047 28.16 / 0.8519 33.61 / 0.9445 IMDN-JDSR 703 34.36 / 0.9269 30.32 / 0.8413 29.08 / 0.8045 28.12 / 0.8498 − / − PAN 261 34.40 / 0.9271 30.36 / 0.8423 29.11 / 0.8050 28.11 / 0.8511 33.61 / 0.9448 RFDN-L 633 34.39 / 0.9271 30.35 / 0.8419 29.11 / 0.8054 28.24 / 0.8534 33.74 / 0.9453 LatticeNet 765 34.40 / 0.9272 30.32 / 0.8416 29.10 / 0.8049 28.19 / 0.8513 − / − G-IDRN 565 34.43 / 0.9277 30.41 / 0.8431 29.14 / 0.8061 28.32 / 0.8552 33.79 / 0.9456 Bicubic 4倍 − 28.42 / 0.8104 26.00 / 0.7027 25.96 / 0.6675 23.14 / 0.6577 24.89 / 0.7866 SRCNN 8 30.48 / 0.8626 27.50 / 0.7513 26.90 / 0.7101 24.52 / 0.7221 27.58 / 0.8555 DRCN 1774 31.53 / 0.8854 28.02 / 0.7670 27.23 / 0.7233 25.14 / 0.7510 28.93 / 0.8854 LapSRN 502 31.54 / 0.8852 28.09 / 0.7700 27.32 / 0.7275 25.21 / 0.7562 29.09 / 0.8900 DRRN 298 31.68 / 0.8888 28.21 / 0.7720 27.38 / 0.7284 25.44 / 0.7638 29.45 / 0.8946 MemNet 678 31.74 / 0.8893 28.26 / 0.7723 27.40 / 0.7281 25.50 / 0.7630 29.42 / 0.8942 IDN 553 31.82 / 0.8903 28.25 / 0.7730 27.41 / 0.7297 25.41 / 0.7632 29.41 / 0.8942 SRMDNF 1552 31.96 / 0.8925 28.35 / 0.7787 27.49 / 0.7337 25.68 / 0.7731 30.09 / 0.9024 CARN 1592 32.13 / 0.8937 28.60 / 0.7806 27.58 / 0.7349 26.07 / 0.7837 30.47 / 0.9084 SMSR 1006 32.13 / 0.8937 28.60 / 0.7806 27.58 / 0.7349 26.11 / 0.7868 30.54 / 0.9084 IMDN 715 32.21 / 0.8948 28.58 / 0.7811 27.56 / 0.7354 26.04 / 0.7838 30.45 / 0.9075 IMDN-JDSR 715 32.17 / 0.8942 28.62 / 0.7814 27.55 / 0.7350 26.06 / 0.7820 − / − PAN 272 32.13 / 0.8948 28.61 / 0.7822 27.59 / 0.7363 26.11 / 0.7854 30.51 / 0.9095 RFDN-L 643 32.23 / 0.8953 28.59 / 0.7814 27.57 / 0.7363 26.14 / 0.7871 30.61 / 0.9095 LatticeNet 777 32.18 / 0.8943 28.61 / 0.7812 27.57 / 0.7355 26.14 / 0.7844 − / − G-IDRN 580 32.24 / 0.8958 28.64 / 0.7824 27.61 / 0.7378 26.24 / 0.7903 30.63 / 0.9096 表 5 Set14中图像放大4倍时, SSIM、PSNR和FLOPs的比较结果
Table 5 Comparison results of SSIM、PSNR andFLOPs for 4 times images on Set14
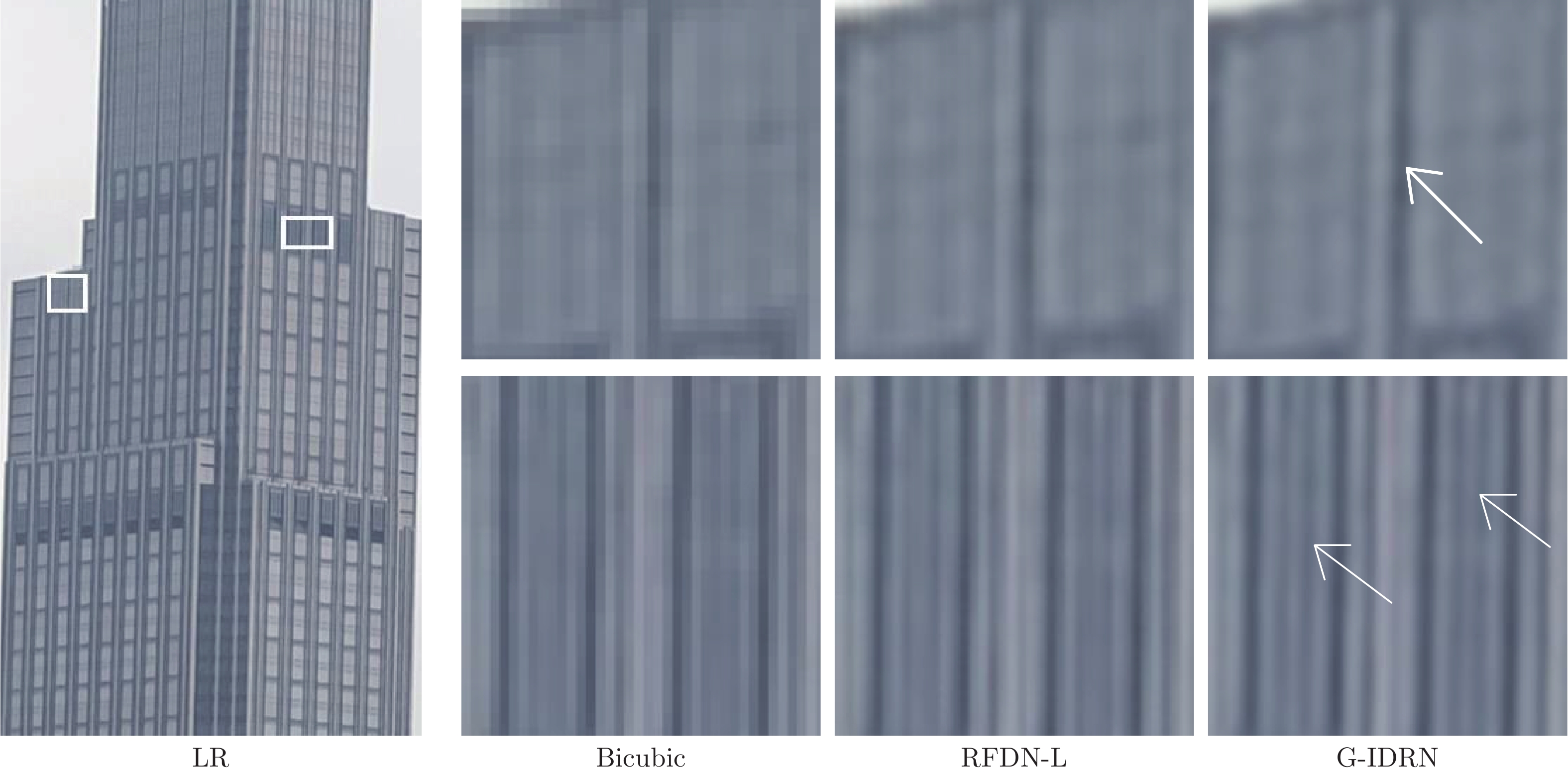
评价指标 CARN IMDN RFDN-L G-IDRN SSIM 0.7806 0.7810 0.7814 0.7826 PSNR (dB) 28.60 28.58 28.59 28.64 FLOPs (GB) 103.58 46.60 41.54 36.19 表 6 B100中图像放大4倍时, 平均运行时间的比较结果
Table 6 Comparison results of average running time for4 times images on B100
方法 PSNR (dB) / SSIM 参数量 (K) 训练时间 (s) 推理时间 (s) EDSR 27.71 / 0.7420 43090 — 0.2178 RCAN 27.77 / 0.7436 15592 — 0.2596 IMDN 27.56 / 0.7354 715 5.4 0.0217 RFDN-L 27.57 / 0.7363 633 6.1 0.0250 G-IDRN 27.61 / 0.7378 580 12.7 0.0177 IDRN 27.64 / 0.7389 2047 8.5 0.0692 -
[1] Isaac J S, Kulkarni R. Super resolution techniques for medical image processing. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Technologies for Sustainable Development. Mumbai, India: IEEE, 2015. 1−6 [2] Rasti P, Uiboupin T, Escalera S, Anbarjafari G. Convolutional neural network super resolution for face recognition in surveillance monitoring. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Articulated Motion and Deformable Objects. Cham, Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 175−184 [3] Sajjadi M S M, Scholkopf B, Hirsch M. Enhancenet: Single image super-resolution through automated texture synthesis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4491−4500 [4] Tan Y, Cai J, Zhang S, Zhong W, Ye L. Image compression algorithms based on super-resolution reconstruction technology. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 4th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing. Xiamen, China: IEEE, 2019. 162− 166 [5] Luo Y, Zhou L, Wang S, Wang Z. Video satellite imagery super resolution via convolutional neural networks. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(12): 2398−2402 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2766204 [6] 杨欣, 周大可, 费树岷. 基于自适应双边全变差的图像超分辨率重建. 计算机研究与发展, 2012, 49(12): Article No. 2696Yang Xin, Zhou Da-Ke, Fei Shu-Min. A self-adapting bilateral total aariation technology for image super-resolution reconstruction. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2012, 49(12): Article No. 2696 [7] Zhang L, Wu X. An edge-guided image interpolation algorithm via directional filtering and data fusion. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(8): 2226−2238 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.877407 [8] 潘宗序, 禹晶, 胡少兴, 孙卫东. 基于多尺度结构自相似性的单幅图像超分辨率算法. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(4): 594−603Pan Zong-Xu, Yu Jing, Hu Shao-Xing, Sun Wei-Dong. Single image super resolution based on multi-scale structural self-similarity. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(4): 594−603 [9] 张毅锋, 刘袁, 蒋程, 程旭. 用于超分辨率重建的深度网络递进学习方法. 自动化学报, 2020, 40(2): 274−282Zhang Yi-Feng, Liu Yuan, Jiang Cheng, Cheng Xu. A curriculum learning approach for single image super-resolution. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 40(2): 274−282 [10] Dai T, Cai J, Zhang Y, Xia S T, Zhang L. Second-order attention network for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 11065−11074 [11] Hui Z, Gao X, Yang Y, Wang X. Lightweight image super-resolution with information multi-distillation network. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2019. 2024−2032 [12] Liu J, Tang J, Wu G. Residual feature distillation network for lightweight image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 20th European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham, Netherlands: Springer, 2020. 41−55 [13] 孙超文, 陈晓. 基于多尺度特征融合反投影网络的图像超分辨率重建. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(7): 1689−1700Sun Chao-Wen, Chen Xiao. Multi-scale feature fusion back-projection network for image super-resolution. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(7): 1689−1700 [14] 孙玉宝, 费选, 韦志辉, 肖亮. 基于前向后向算子分裂的稀疏性正则化图像超分辨率算法. 自动化学报, 2010, 36(9): 1232−1238 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.01232Sun Yu-Bao, Fei Xuan, Wei Zhi-Hui, Xiao Liang. Sparsity regularized image super-resolution model via forward-backward operator splitting method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(9): 1232−1238 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.01232 [15] Dong C, Loy C C, He K, Tang X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern An-alysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 38(2): 295−307 [16] Dong C, Loy C C, Tang X. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Veg-as, USA: IEEE, 2016. 391−407 [17] Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1646−1654 [18] Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1637−1645 [19] Lim B, Son S, Kim H, Nah S, Mu Lee K. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 136−144 [20] Zhang Y, Li K, Li K, Wang L, Zhong B, Fu Y. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. In: Proceedings of the 18th European Conference on Computer Vision. Mohini, Germany: Springer, 2018. 286−301 [21] Ahn N, Kang B, Sohn K A. Fast, accurate, and lightweight super-resolution with cascading residual network. In: Proceedings of the 18th European Conference on Computer Vision. Mohini, Germany: Springer, 2018. 252−268 [22] Hui Z, Wang X, Gao X. Fast and accurate single image super-resolution via information distillation network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 723−731 [23] Zhang C, Benz P, Argaw D M, Lee S, Kim J, Rameau F, et al. Resnet or densenet? Introducing dense shortcuts to resnet. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applicati-ons of Computer Vision. Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2021. 3550−3559 [24] Zhu Z, Xu M, Bai S, Huang T, Bai X. Asymmetric non-local neural networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 593−602 [25] Huang J B, Singh A, Ahuja N. Single image super-resolution from transformed self-exemplars. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Bos-ton, USA: IEEE, 2015. 5197−5206 [26] 安耀祖, 陆耀, 赵红. 一种自适应正则化的图像超分辨率算法. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(4): 601−608 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.00601An Yao-Zu, Lu Yao, Zhao Hong. An adaptive-regularized image super-resolution. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(4): 601−608 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.00601 [27] Tai Y, Yang J, Liu X, Xu C. MemNet: A persistent memory network for image restoration. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4539−4547 [28] Li Z, Yang J, Liu Z, Jeon G, Wu W. Feedback network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3867−3876 [29] Qiu Y, Wang R, Tao D, Cheng J. Embedded block residual network: A recursive restoration model for single-image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 4180−4189 [30] Chu X, Zhang B, Ma H, Xu R, Li Q. Fast, accurate and lightweight super-resolution with neural architecture search. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Milan, Italy: IEEE, 2021. 59−64 [31] Chu X, Zhang B, Xu R. Multi-objective reinforced evolution in mobile neural architecture search. In: Proceedings of the 20th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Sprin-ger, 2020. 99−113 [32] Luo X, Xie Y, Zhang Y, Qu Y, Li C, Fu Y. LatticeNet: Towards lightweight image super-resolution with lattice block. In: Proceedings of the 20th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 23−28 [33] Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 7132−7141 [34] Wang X, Girshick R, Gupta A, He K. Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 7794−7803 [35] Liu D, Wen B, Fan Y, Loy C C, Huang T S. Non-local recurrent network for image restoration. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal, Canada: MIT Press, 2018. 1680–1689 [36] Mei Y, Fan Y, Zhou Y, Huang L, Huang T S, Shi H. Image super-resolution with cross-scale non-local attention and exhaustive self-exemplars mining. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Sea-ttle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 5690−5699 [37] Niu B, Wen W, Ren W, Zhang X, Yang L, Wang S, et al. Single image super-resolution via a holistic attention network. In: Proceedings of the 20th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 191−207 [38] Johnson J, Alahi A, Li F F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 14th Eur-opean Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 694−711 [39] Ledig C, Theis L, Huszár F, Caballero J, Cunningham A, Acosta A, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4681−4690 [40] Yuan Y, Liu S, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Dong C, Lin L. Unsupervised image super-resolution using cycle-in-cycle generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 701−710 [41] Yu J, Fan Y, Huang T. Wide activation for efficient image and video super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 30th British Machine Vision Conference. Cardiff, UK: BMVA Press, 2020. 1−13 [42] Shi W, Caballero J, Huszár F, Totz J, Aitken A P, Bishop R, et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1874−1883 [43] Howard A G, Zhu M, Chen B, Kalenichenko D, Wang W, Weyand T, et al. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications [Online], available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861, April 17, 2017 [44] Xie S, Girshick R, Dollár P, Tu Z, He K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1492−1500 [45] Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, Alemi A A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: Proceedings of the 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, USA: AAAI Press, 2017. 4278–4284 [46] Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger K Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4700−4708 [47] Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, Wang X, Jia J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2881− 2890 [48] Timofte R, Agustsson E, Van Gool L, Yang M H, Zhang L. Ntire 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Methods and results. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 114−125 [49] Bevilacqua M, Roumy A, Guillemot C, Morel M L A. Lowcomplexity single-image super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbor embedding. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. Surrey, UK: BMVA Press, 2012. 1−10 [50] Zeyde R, Elad M, Protter M. On single image scale-up using sparse-representations. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Curves and Surfaces. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2010. 711−730 [51] Arbelaez P, Maire M, Fowlkes C, Malik J. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 33(5): 898−916 [52] Matsui Y, Ito K, Aramaki Y, Fujimoto A, Ogawa T, Yamasaki T, et al. Sketch-based manga retrieval using Manga109 dataset. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 76(20): 21811−21838 doi: 10.1007/s11042-016-4020-z [53] Gao X, Lu W, Tao D, Li X. Image quality assessment based on multi-scale geometric analysis. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(7): 1409−1423 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2018014 [54] Wang Z, Bovik A C, Sheikh H R, Simoncelli E P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600−612 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [55] Chollet F. Xception: Deep learning with depth-wise separable convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 1251−1258 [56] Lai W S, Huang J B, Ahuja N, Yang M H. Deep Laplacian pyramid networks for fast and accurate super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 624−632 [57] Tai Y, Yang J, Liu X. Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3147−3155 [58] Zhang K, Zuo W, Zhang L. Learning a single convolutional super-resolution network for multiple degradations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3262−3271 [59] Wang L, Dong X, Wang Y, Ying X, Lin Z, An W, et al. Exploring sparsity in image super-resolution for efficient inference. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 4917−4926 [60] Luo X, Liang Q, Liu D, Qu Y. Boosting lightweight single image super-resolution via joint-distillation. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Virtual Event: Association for Computing Machinery, 2021. 1535−1543 [61] Zhao H, Kong X, He J, Qiao Y, Dong C. Efficient image super-resolution using pixel attention. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham, Netherlands: Springer, 2020. 56−72 [62] Cai J, Zeng H, Yong H, Cao Z, Zhang L. Toward real-world single image super-resolution: A new benchmark and a new model. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 3086−3095 -




 下载:
下载: