Receding Horizon Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Lateral Control of Intelligent Vehicles
-
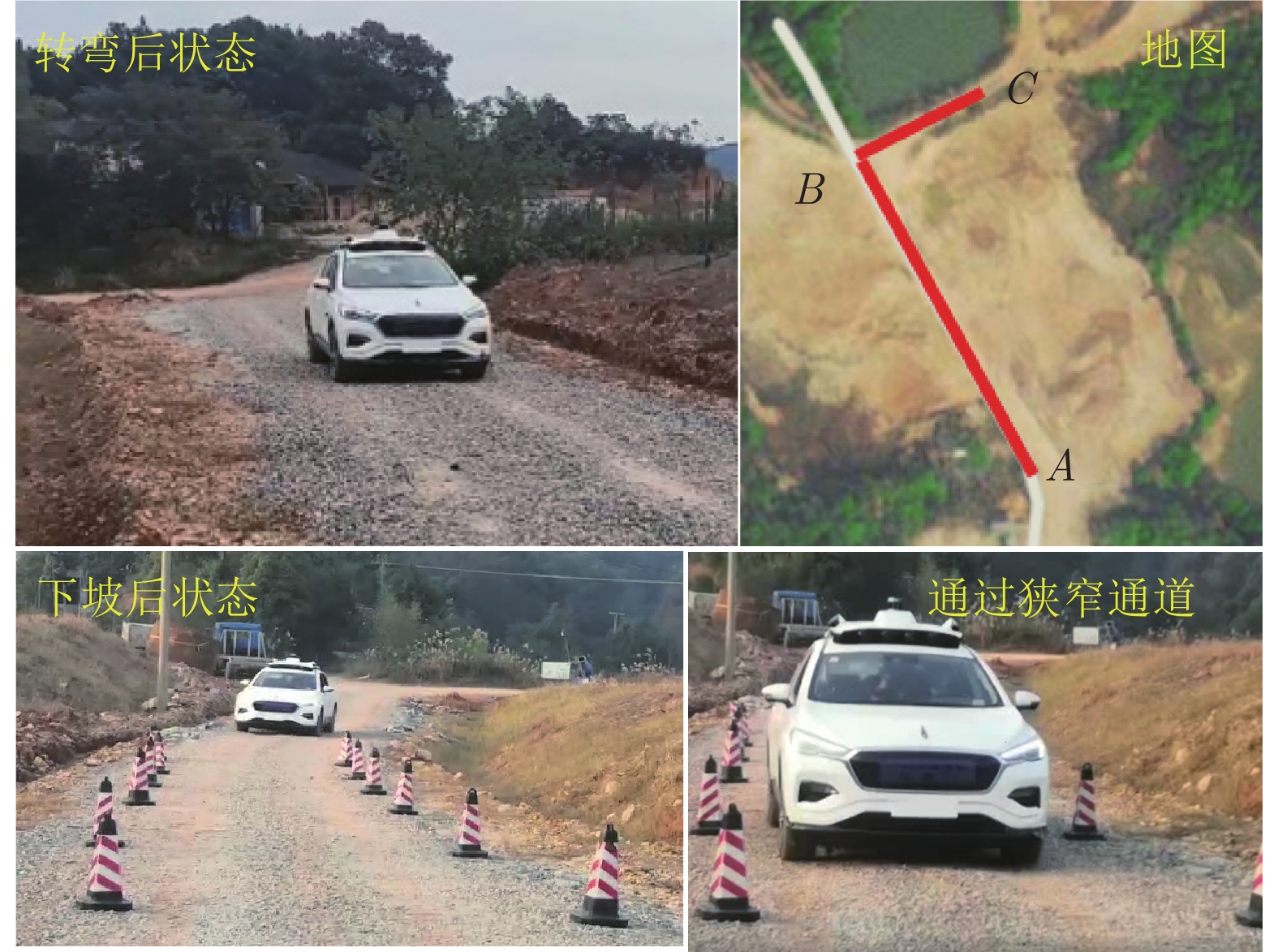
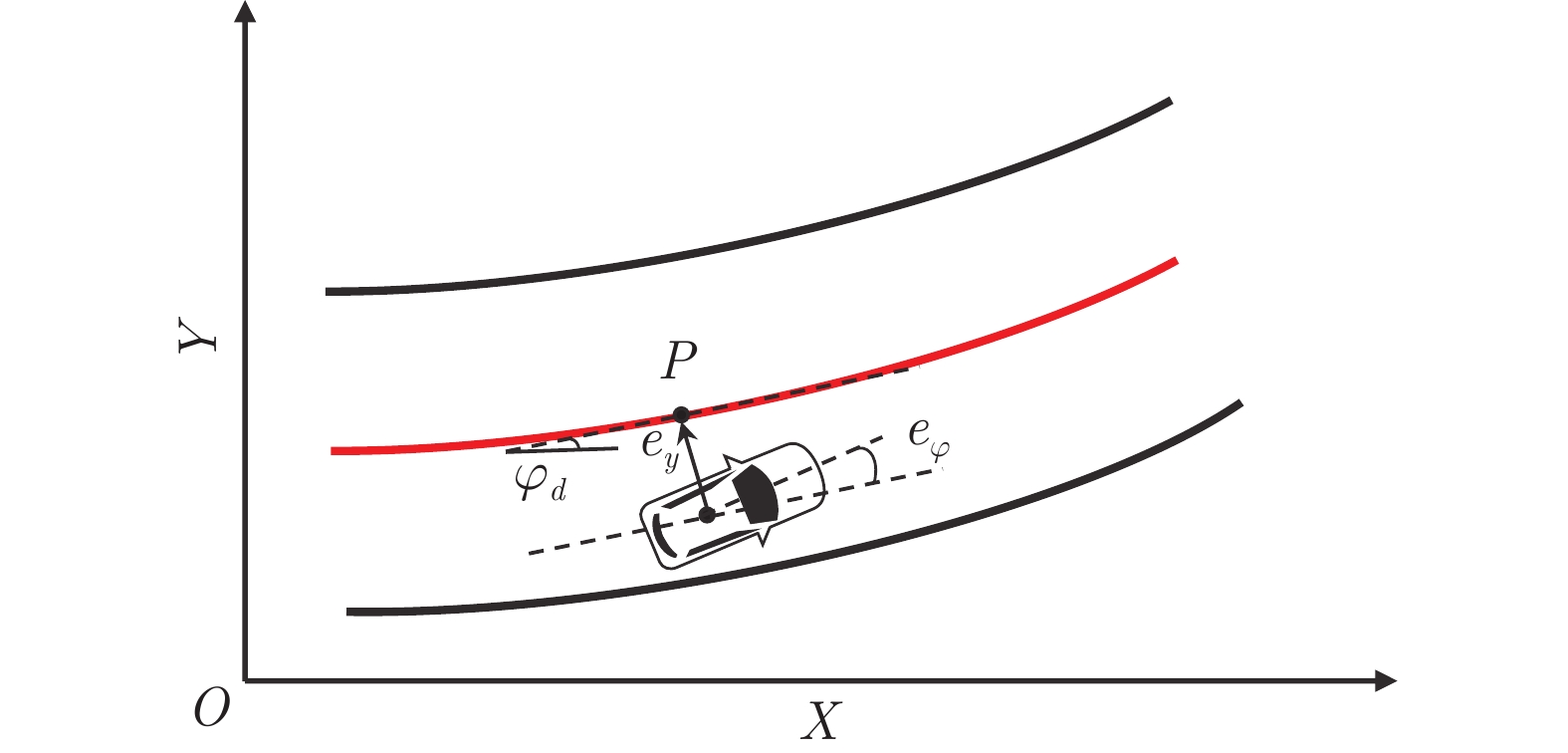
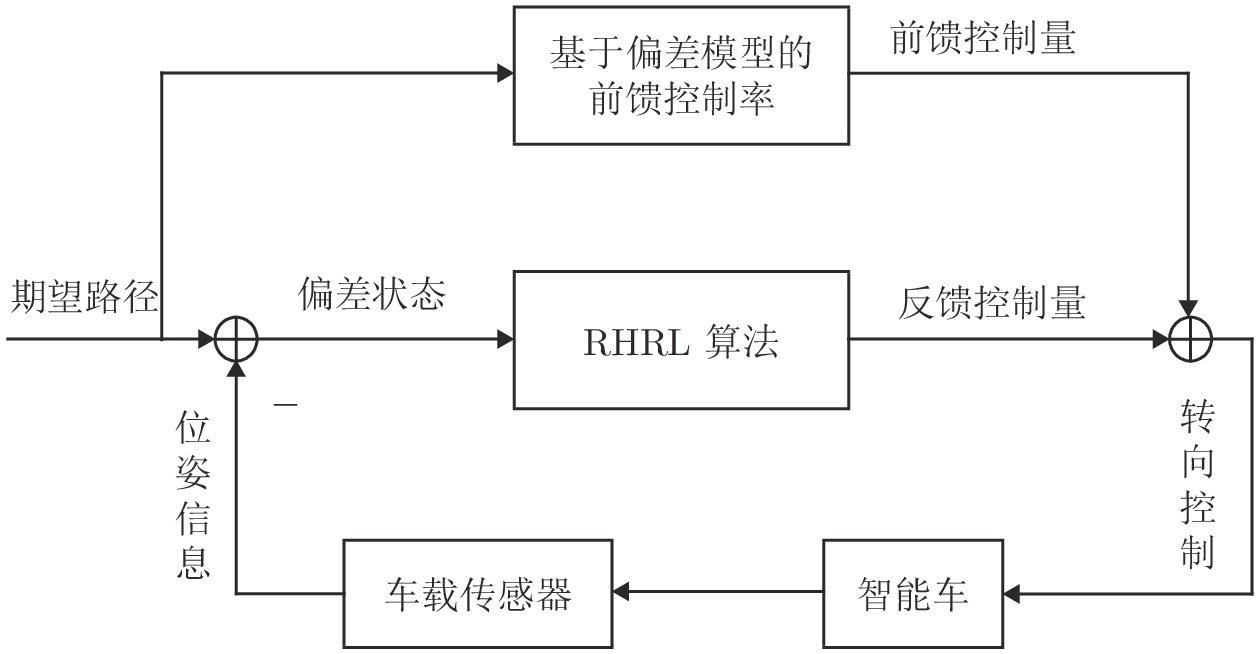
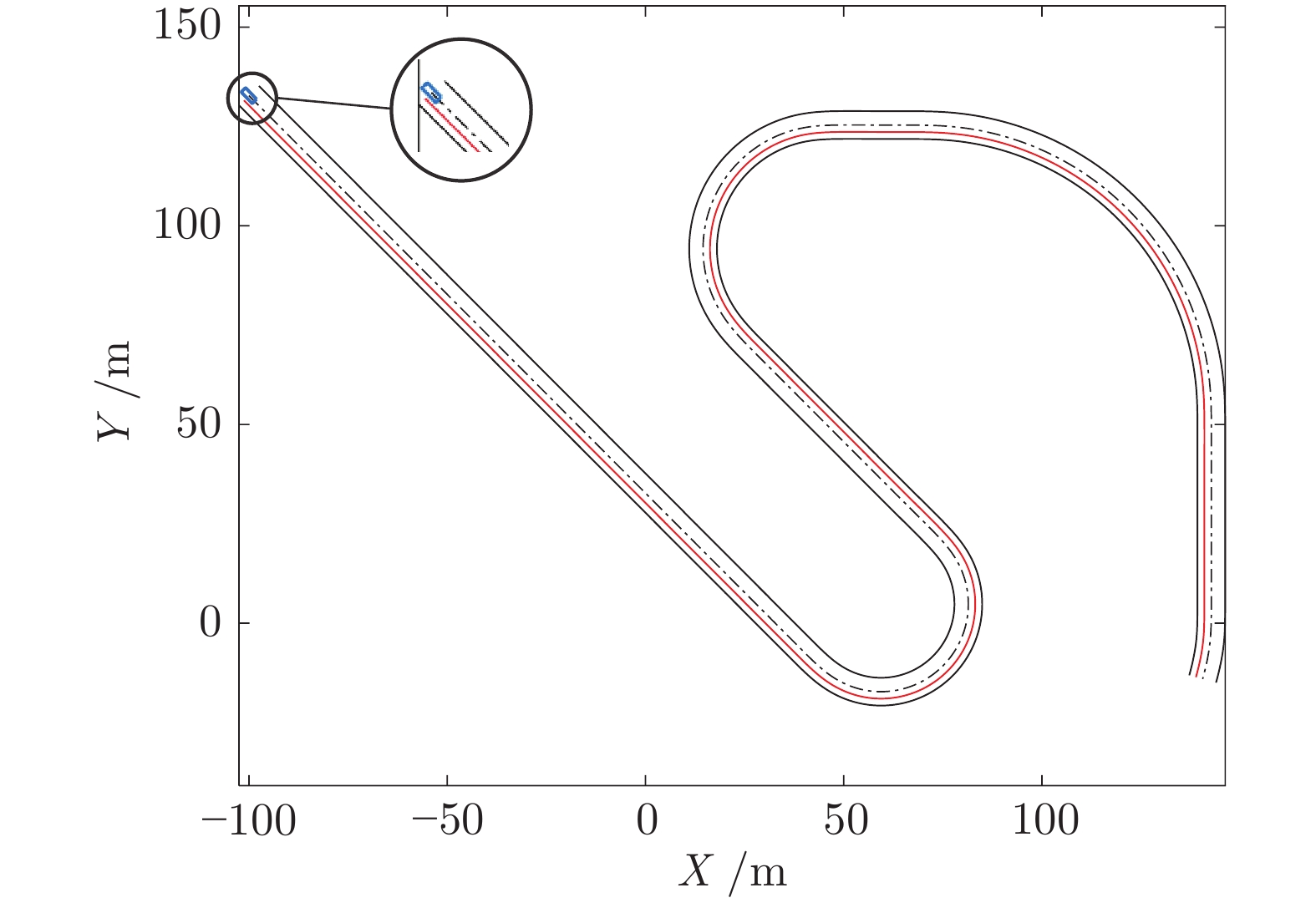
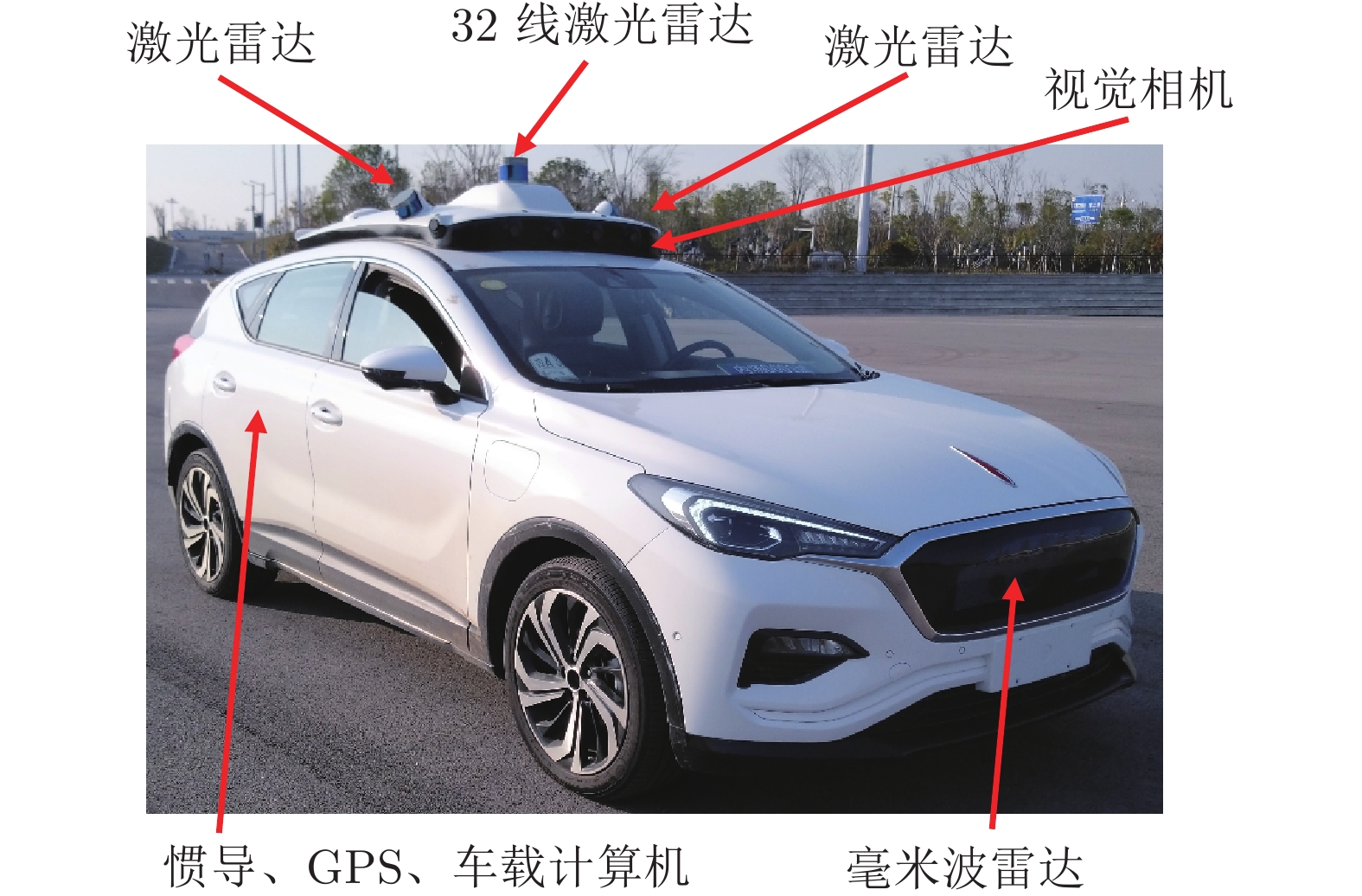
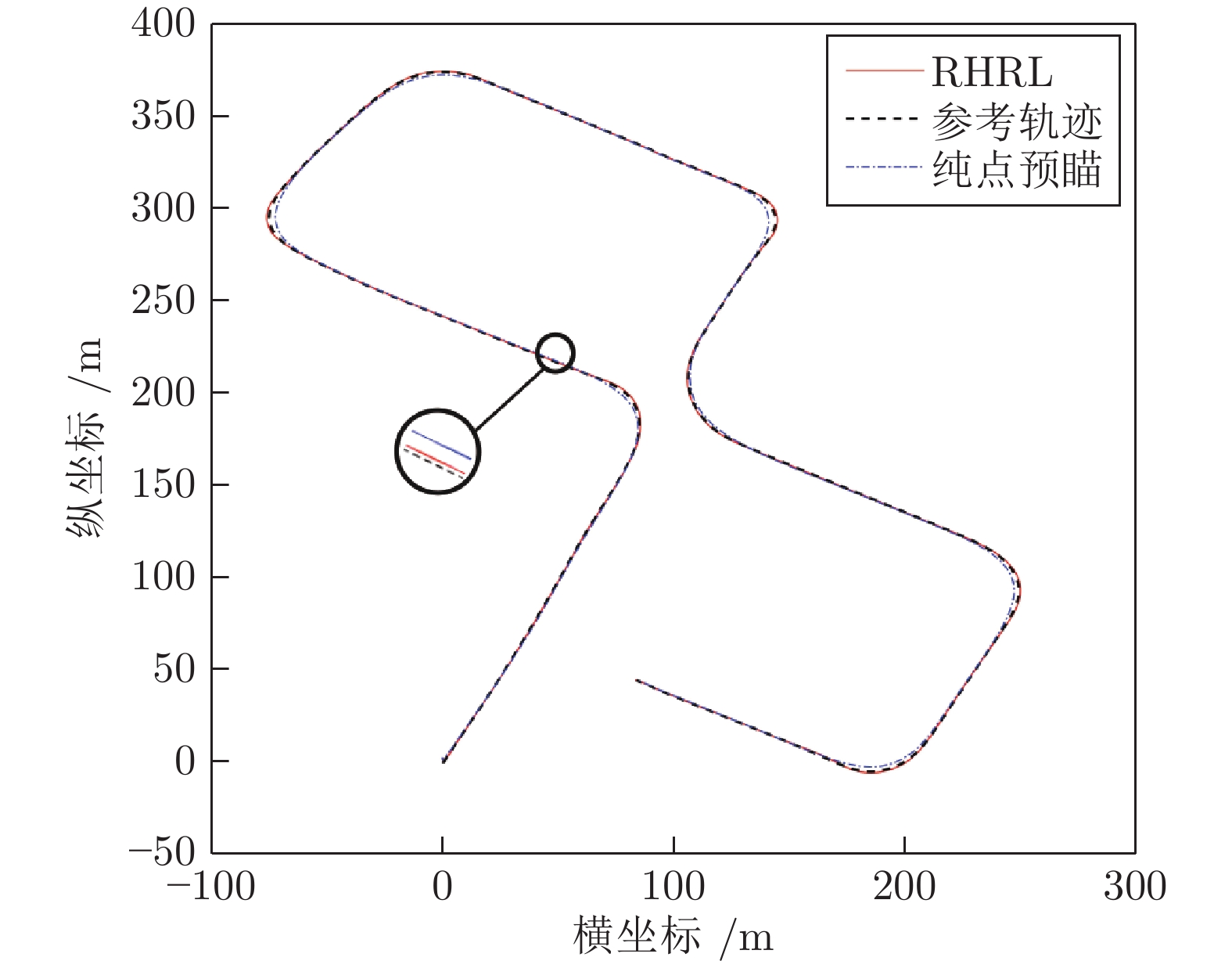
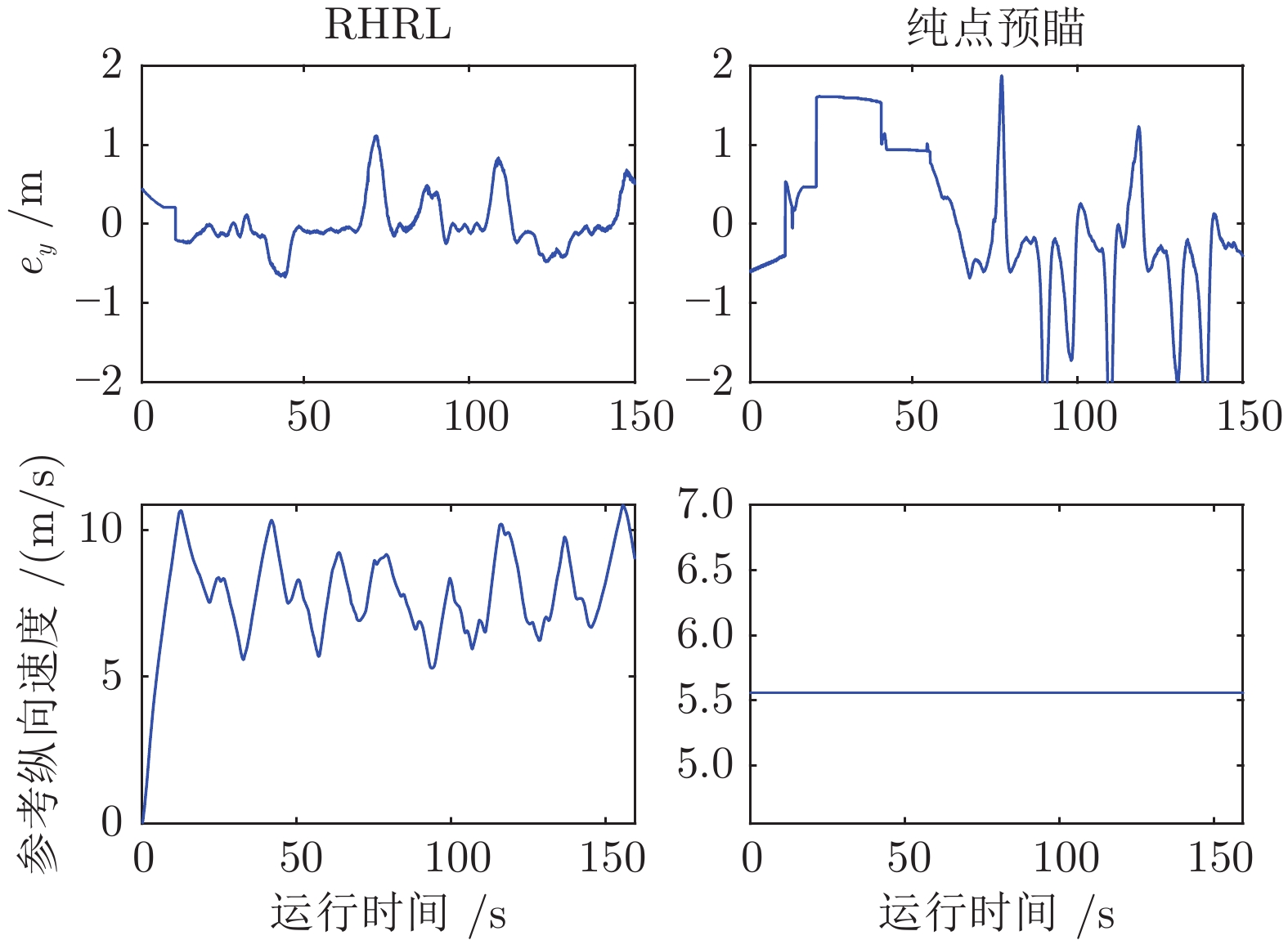
摘要: 针对智能车辆的高精度侧向控制问题, 提出一种基于滚动时域强化学习(Receding horizon reinforcement learning, RHRL)的侧向控制方法. 车辆的侧向控制量由前馈和反馈两部分构成, 前馈控制量由参考路径的曲率以及动力学模型直接计算得出; 而反馈控制量通过采用滚动时域强化学习算法求解最优跟踪控制问题得到. 提出的方法结合滚动时域优化机制, 将无限时域最优控制问题转化为若干有限时域控制问题进行求解. 与已有的有限时域执行器−评价器学习不同, 在每个预测时域采用时间独立型执行器−评价器网络结构学习最优值函数和控制策略. 与模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)方法求解开环控制序列不同, RHRL控制器的输出是一个显式状态反馈控制律, 兼具直接离线部署和在线学习部署的能力. 此外, 从理论上证明了RHRL算法在每个预测时域的收敛性, 并分析了闭环系统的稳定性. 在仿真环境中完成了结构化道路下的车辆侧向控制测试. 仿真结果表明, 提出的RHRL方法在控制性能方面优于现有先进算法, 最后, 以红旗E-HS3电动汽车作为实车平台, 在封闭结构化城市测试道路和乡村起伏砂石道路下进行了侧向控制实验. 实验结果显示, RHRL在结构化城市道路中的侧向控制性能优于预瞄控制, 在乡村道路中具有较强的路面适应能力和较好的控制性能.Abstract: This paper presents a receding horizon reinforcement learning (RHRL) algorithm for realizing high-accuracy lateral control of intelligent vehicles. The overall lateral control is composed of a feedforward control term that is directly computed using the curvature of the reference path and the dynamic model, and a feedback control term that is generated by solving an optimal control problem using the proposed RHRL algorithm. The proposed RHRL adopts a receding horizon optimization mechanism, and decomposes the infinite-horizon optimal control problem into several finite-horizon ones to be solved. Different from existing finite-horizon actor-critic learning algorithms, in each prediction horizon of RHRL, a time-independent actor-critic structure is utilized to learn the optimal value function and control policy. Also, compared with model predictive control (MPC), the control learned by RHRL is an explicit state-feedback control policy, which can be deployed directly offline or learned and deployed synchronously online. Moreover, the convergence of the proposed RHRL algorithm in each prediction horizon is proven and the stability analysis of the closed-loop system is peroformed. Simulation studies on a structural road show that, the proposed RHRL algorithm performs better than current state-of-the-art methods. The experimental studies on an intelligent driving platform built with a Hongqi E-HS3 electric car show that RHRL performs better than the pure pursuit method in the adopted structural city road scenario, and exhibits strong adaptability to road conditions and satisfactory control performance in the country road scenario.
-
Key words:
- Receding horizon /
- reinforcement learning /
- intelligent vehicles /
- lateral control
-
表 1 车辆动力学参数
Table 1 The parameters of the vehicle dynamics
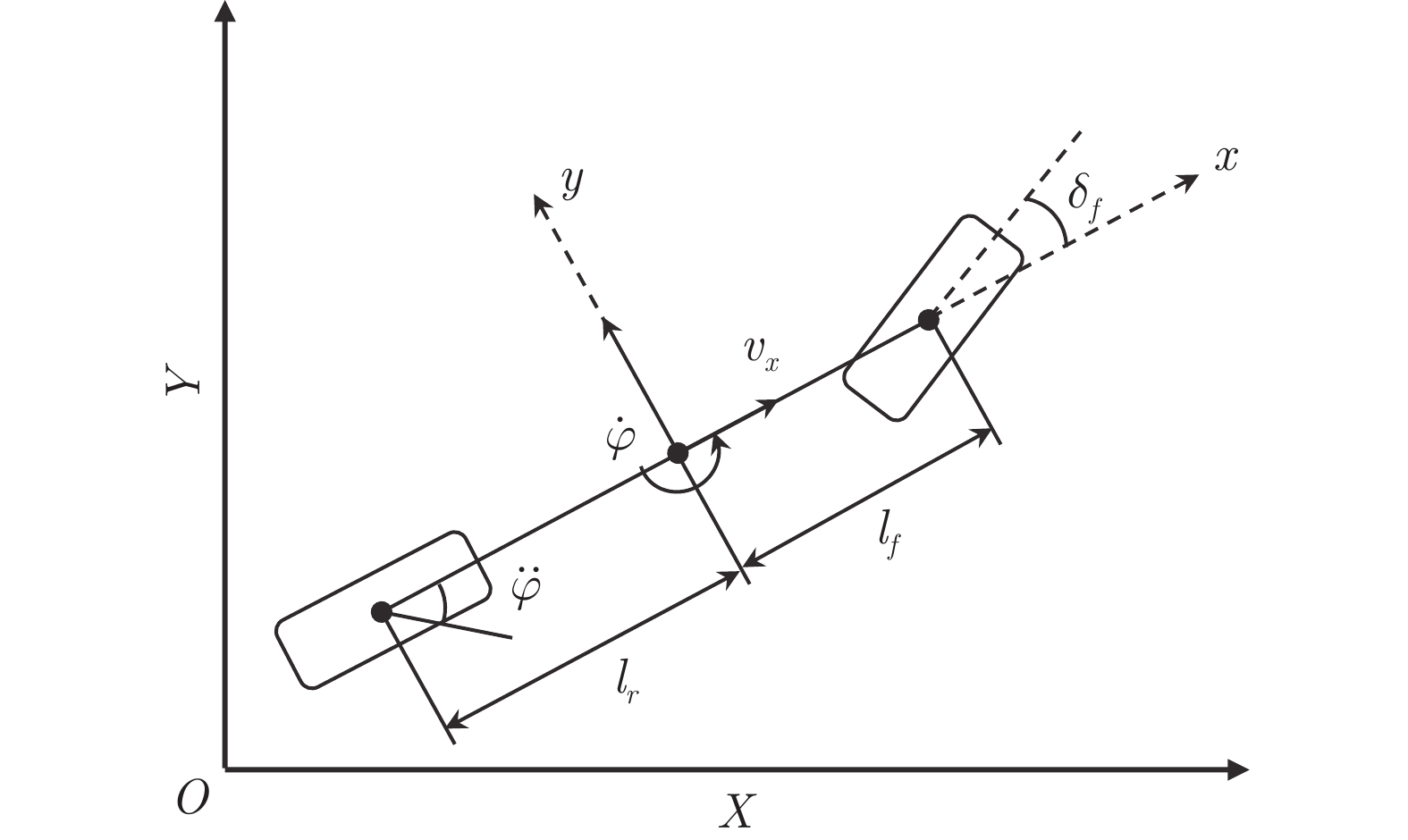
符号 物理意义 数值 单位 $m$ 车身质量 1723 kg $I_z$ 转动惯量 4175 kg·m2 $l_f$ 质心到前轴距离 1.232 m $l_r$ 质心到后轴距离 1.468 m $C_f$ 前轮侧偏刚度 66900 N/rad $C_r$ 后轮侧偏刚度 62700 N/rad 表 2 各控制器的均方根误差对比
Table 2 The RMSE comparison among all the controllers
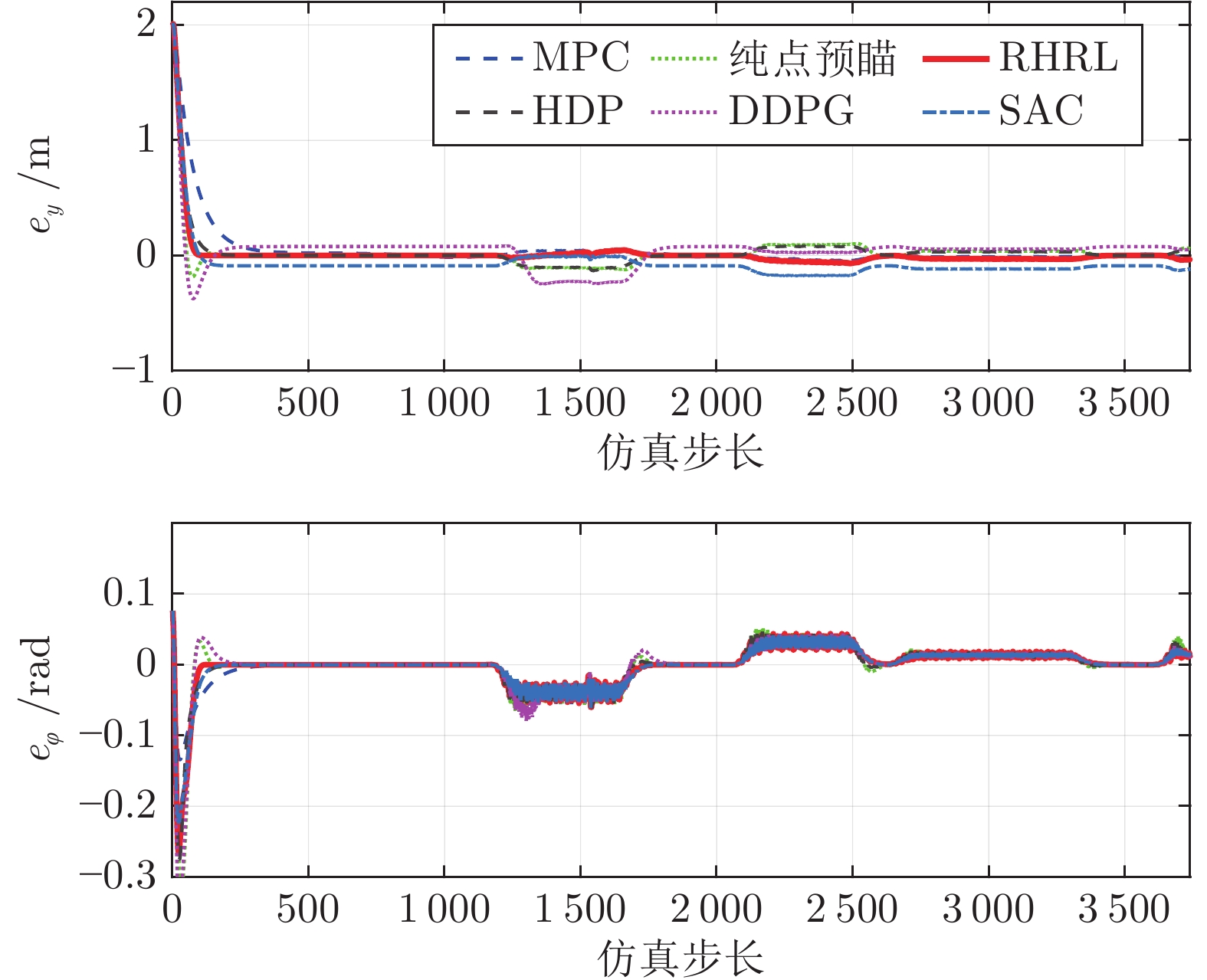
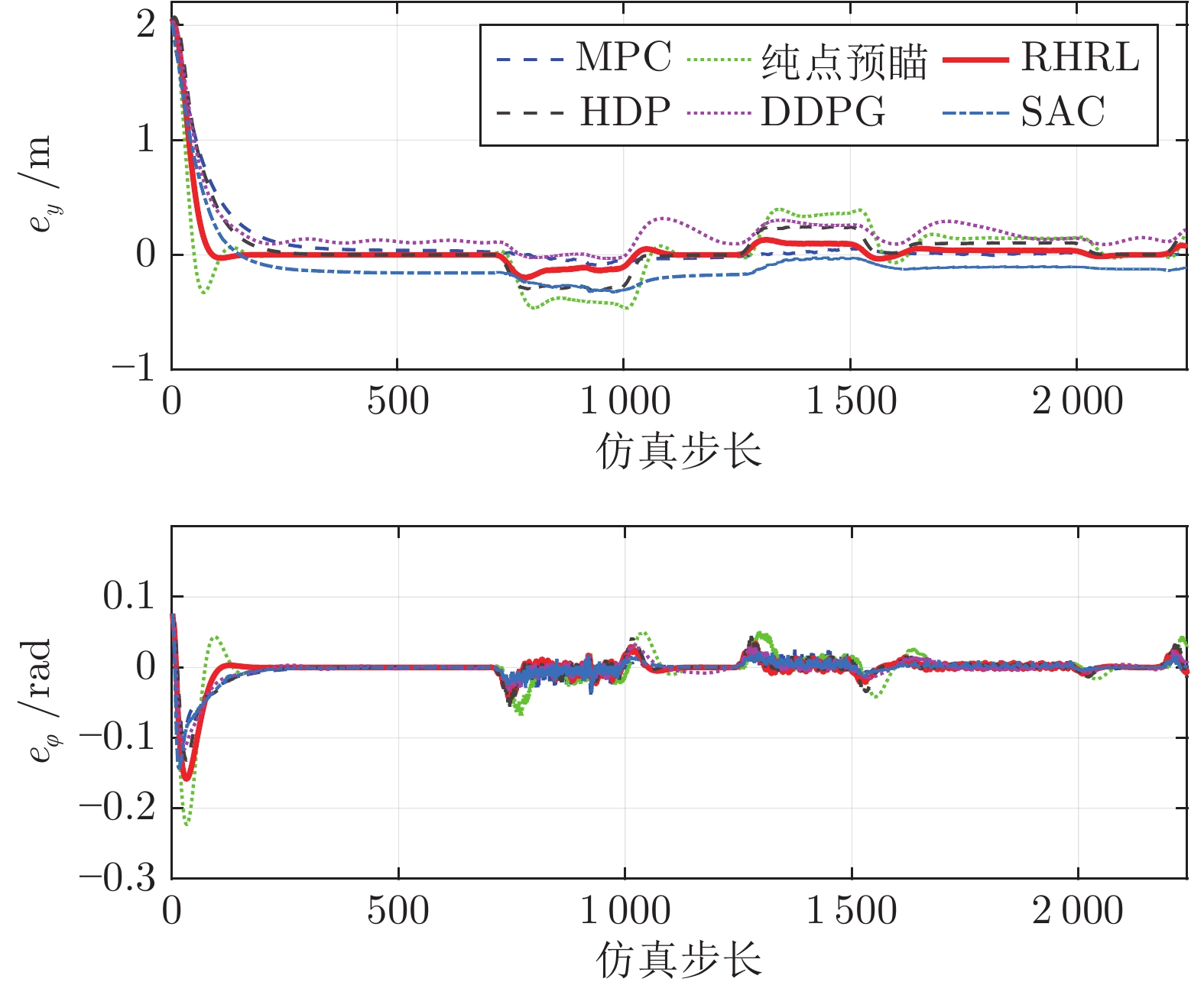
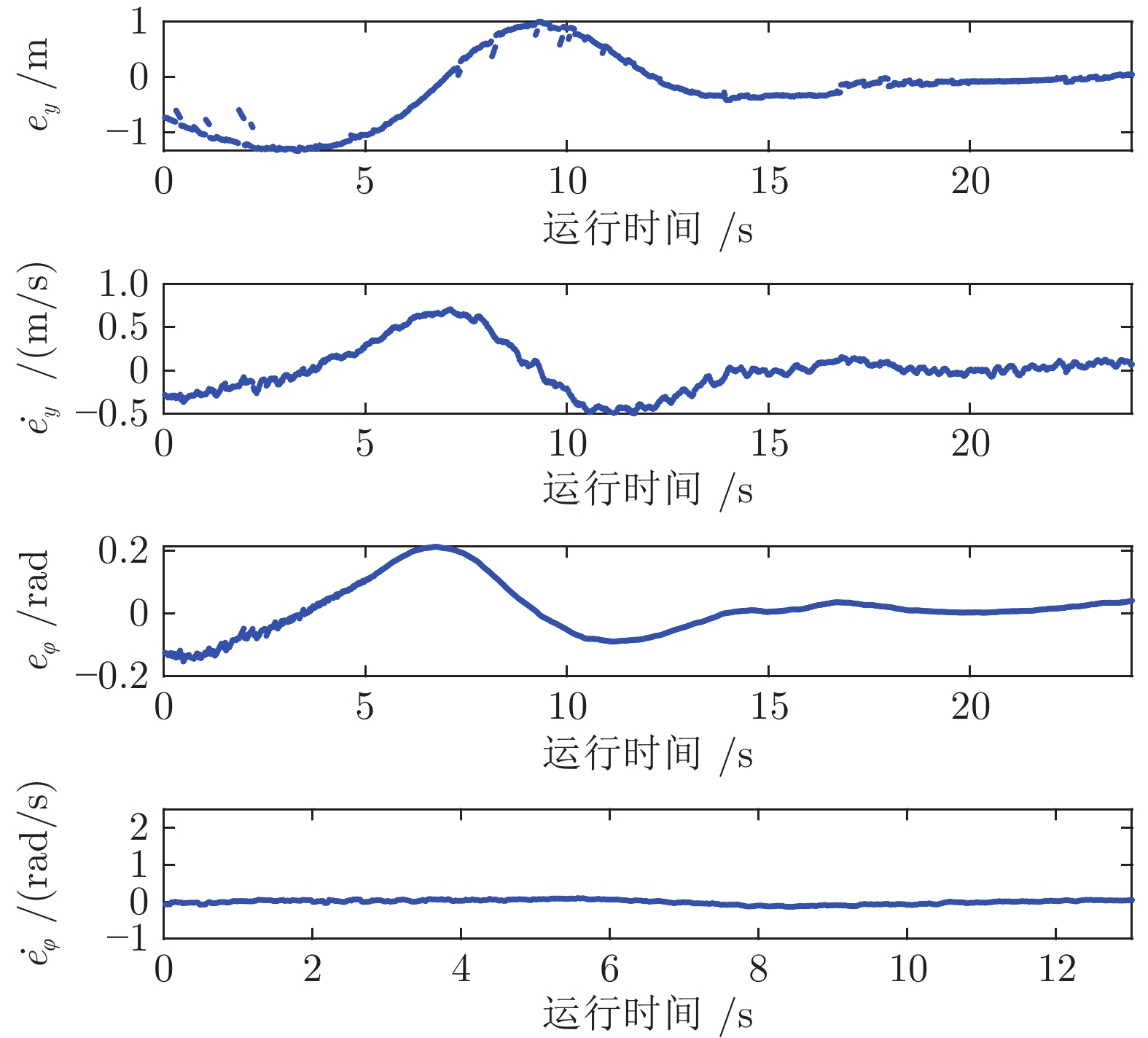
方法 vx = 30 km/h vx = 50 km/h ey (m) $e_\varphi$(rad) ey (m) $e_\varphi $(rad) RHRL 0.156 0.030 0.246 0.020 HDP 0.165 0.030 0.315 0.019 SAC 0.189 0.029 0.283 0.017 DDPG 0.172 0.037 0.319 0.017 MPC 0.212 0.025 0.278 0.015 纯点预瞄 0.159 0.036 0.286 0.030 -
[1] 熊璐, 杨兴, 卓桂荣, 冷搏, 章仁夑. 无人驾驶车辆的运动控制发展现状综述. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(10): 127-143 doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.10.127Xiong Lu, Yang Xing, Zhuo Gui-Rong, Leng Bo, Zhang Ren-Xie. Review on motion control of autonomous vehicles. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(10): 127-143 doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.10.127 [2] 陈虹, 郭露露, 宫洵, 高炳钊, 张琳. 智能时代的汽车控制. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(7): 1313-1332 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190329Chen Hong, Guo Lu-Lu, Gong Xun, Gao Bing-Zhao, Zhang Lin. Automative control in intelligent era. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(7): 1313-1332 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190329 [3] 田涛涛, 侯忠生, 刘世达, 邓志东. 基于无模型自适应控制的无人驾驶汽车横向控制方法. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(11): 1931-1940 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160633Tian Tao-Tao, Hou Zhong-Sheng, Liu Shi-Da, Deng Zhi-Dong. Model-free adaptive control based lateral control of self-driving car. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(11): 1931-1940 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160633 [4] Ahmed A A, Alshandoli A F S. Using of neural network controller and fuzzy PID control to improve electric vehicle stability based on A14-DOF model. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE). Istanbul, Turkey: IEEE, 2020. 1−6 [5] Meng J, Liu A B, Yang Y Q, Wu Z, Xu Q Y. Two-wheeled robot platform based on PID control. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering (ICISCE). Zhengzhou, China: IEEE, 2018. 1011−1014 [6] Farag W. Complex trajectory tracking using PID control for autonomous driving. International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research, 2020, 18(2): 356-366 doi: 10.1007/s13177-019-00204-2 [7] Zhao P, Chen J J, Song Y, Tao X, Xu T J, Mei T. Design of a control system for an autonomous vehicle based on adaptive-PID. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2012, 9(2): Article No. 44 doi: 10.5772/51314 [8] Han G N, Fu W P, Wang W, Wu Z S. The lateral tracking control for the intelligent vehicle based on adaptive PID neural network. Sensors, 2017, 17(6): Article No. 1244 doi: 10.3390/s17061244 [9] Fraichard T, Garnier P. Fuzzy control to drive car-like vehicles. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2001, 34(1): 1-22 doi: 10.1016/S0921-8890(00)00096-8 [10] Pérez J, Milanés V, Onieva E. Cascade architecture for lateral control in autonomous vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2011, 12(1): 73-82 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2010.2060722 [11] Li H M, Wang X B, Song S B, Li H. Vehicle control strategies analysis based on PID and fuzzy logic control. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 137: 234-243 doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.01.255 [12] Park M W, Lee S W, Han W Y. Development of lateral control system for autonomous vehicle based on adaptive pure pursuit algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS). Gyeonggi-do, South Korea: IEEE, 2014. 1443−1447 [13] 郭景华, 胡平, 李琳辉, 王荣本, 张明恒, 郭烈. 基于遗传优化的无人车横向模糊控制. 机械工程学报, 2012, 48(6): 76-82 doi: 10.3901/JME.2012.06.076Guo Jing-Hua, Hu Ping, Li Lin-Hui, Wang Rong-Ben, Zhang Ming-Heng, Guo Lie. Study on lateral fuzzy control of unmanned vehicles via genetic algorithms. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(6): 76-82 doi: 10.3901/JME.2012.06.076 [14] Leonard J, How J, Teller S, Berger M, Campbell S, Fiore G, et al. A perception-driven autonomous urban vehicle. Journal of Field Robotics, 2008, 25(10): 727-774 doi: 10.1002/rob.20262 [15] Rajamani R, Zhu C, Alexander L. Lateral control of a backward driven front-steering vehicle. Control Engineering Practice, 2003, 11(5): 531-540 doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(02)00143-0 [16] Thrun S, Montemerlo M, Dahlkamp H, Stavens D, Aron A, Diebel J, et al. Stanley: The robot that won the DARPA grand challenge. Journal of Field Robotics, 2006, 23(9): 661-692 doi: 10.1002/rob.20147 [17] 龚建伟, 姜岩, 徐威. 无人驾驶车辆模型预测控制. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2014.Gong Jian-Wei, Jiang Yan, Xu Wei. Model Predictive Control for Self-Driving Vehicles. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2014. [18] Falcone P, Borrelli F, Asgari J, Tseng H E, Hrovat D. Predictive active steering control for autonomous vehicle systems. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2007, 15(3): 566-580 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2007.894653 [19] Carvalho A, Gao Y Q, Gray A, Tseng H E, Borrelli F. Predictive control of an autonomous ground vehicle using an iterative linearization approach. In: Proceedings of the 16th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). The Hague, The Netherlands: IEEE, 2013. 2335−2340 [20] Beal C E, Gerdes J C. Model predictive control for vehicle stabilization at the limits of handling. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2013, 21(4): 1258-1269 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2012.2200826 [21] Liniger A, Domahidi A, Morari M. Optimization-based autonomous racing of 1: 43 scale RC cars. Optimal Control Applications and Methods, 2015, 36(5): 628-647 doi: 10.1002/oca.2123 [22] Kabzan J, Hewing L, Liniger A, Zeilinger M N. Learning-based model predictive control for autonomous racing. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, 4(4): 3363-3370 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2019.2926677 [23] Ostafew C J, Schoellig A P, Barfoot T D. Robust constrained learning-based NMPC enabling reliable mobile robot path tracking. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2016, 35(13): 1547-1563 doi: 10.1177/0278364916645661 [24] 由智恒. 基于MPC算法的无人驾驶车辆轨迹跟踪控制研究[硕士学位论文], 吉林大学, 中国, 2018.You Zhi-Heng. Research on Model Predictive Control-based Trajectory Tracking for Unmanned Vehicles [Master thesis], Jilin University, China, 2018. [25] 王鼎. 基于学习的鲁棒自适应评判控制研究进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(6): 1031-1043 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c170701Wang Ding. Research progress on learning-based robust adaptive critic control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(6): 1031-1043 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c170701 [26] Wang D, Ha M M, Qiao J F. Data-driven iterative adaptive critic control toward an urban wastewater treatment plant. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(8): 7362-7369 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3001840 [27] Oh S Y, Lee J H, Choi D H. A new reinforcement learning vehicle control architecture for vision-based road following. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2000, 49(3): 997-1005 doi: 10.1109/25.845116 [28] 杨慧媛. 基于增强学习的优化控制方法及其在移动机器人中的应用[硕士学位论文], 国防科学技术大学, 中国, 2014.Yang Hui-Yuan. Reinforcement Learning-Based Optimal Control Methods with Applications to Mobile Robots [Master thesis], National University of Defense Technology, China, 2014. [29] 连传强. 基于近似动态规划的优化控制方法及在自主驾驶车辆中的应用[博士学位论文], 国防科学技术大学, 中国, 2016.Lian Chuan-Qiang. Optimization Control Methods Based on Approximate Dynamic Programming and Its Applications in Autonomous Land Vehicles [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, China, 2016. [30] 黄振华. 智能驾驶车辆自评价学习控制方法研究[博士学位论文], 国防科学技术大学, 中国, 2017.Huang Zhen-Hua. Researches on Adaptive Critic Learning Control Approaches for Intelligent Driving Vehicles [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, China, 2017. [31] Lian C Q, Xu X, Chen H, He H B. Near-optimal tracking control of mobile robots via receding-horizon dual heuristic programming. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(11): 2484-2496 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2478857 [32] Kuutti S, Bowden R, Jin Y C, Barber P, Fallah S. A survey of deep learning applications to autonomous vehicle control. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(2): 712-733 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2962338 [33] Li D, Zhao D B, Zhang Q C, Chen Y R. Reinforcement learning and deep learning based lateral control for autonomous driving[Application Notes]. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2019, 14(2): 83-98 doi: 10.1109/MCI.2019.2901089 [34] Chen Y X, Hereid A, Peng H E, Grizzle J. Enhancing the performance of a safe controller via supervised learning for truck lateral control. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2019, 141(10): Article No. 101005 doi: 10.1115/1.4043487 [35] Dong L, Yan J, Yuan X, He H B, Sun C Y. Functional nonlinear model predictive control based on adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(12): 4206-4218 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2859801 [36] Rajamani R. Vehicle Dynamics and Control (Second edition). New York: Springer, 2012. [37] Xu X, Chen H, Lian C Q, Li D Z. Learning-based predictive control for discrete-time nonlinear systems with stochastic disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(12): 6202-6213 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2820019 [38] Chmielewski D, Manousiouthakis V. On constrained infinite-time linear quadratic optimal control. Systems & Control Letters, 1996, 29(3): 121-129 [39] Rawlings J B, Mayne D Q, Diehl M M. Model Predictive Control: Theory, Computation, and Design (Second edition). Madison: Nob Hill Publishing, 2017. [40] Mayne D Q, Kerrigan E C, van Wyk E J, Falugi P. Tube-based robust nonlinear model predictive control. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2011, 21(11): 1341-1353 doi: 10.1002/rnc.1758 [41] Zhang X L, Pan W, Scattolini R, Yu S Y, Xu X. Robust tube-based model predictive control with Koopman operators. Automatica, 2022, 137: Article No. 110114 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.110114 [42] Haarnoja T, Zhou A, Abbeel P, Levine S. Soft actor-critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Stockholm, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. 1856−1865 [43] Lillicrap T P, Hunt J J, Pritzel A, Heess N, Erez T, Tassa Y, et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). San Juan, Puerto Rico: 2016. [44] Snider J M. Automatic Steering Methods for Autonomous Automobile Path Tracking, Technical Report CMU-RI-TR-09-08, Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, USA, 2009. -




 下载:
下载: