-
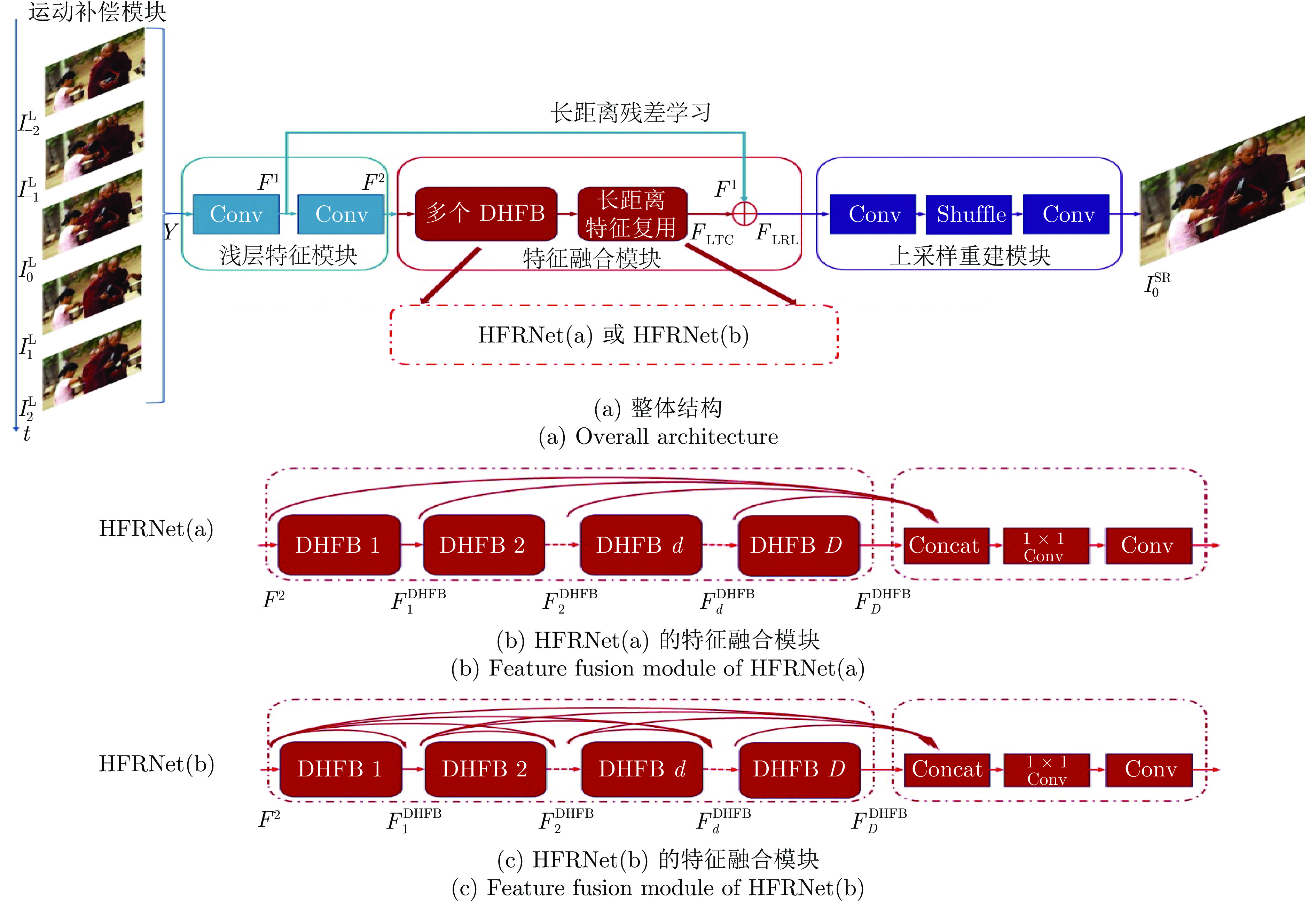
摘要: 当前的深度卷积神经网络方法, 在视频超分辨率任务上实现的性能提升相对于图像超分辨率任务略低, 部分原因是它们对层次结构特征中的某些关键帧间信息的利用不够充分. 为此, 提出一个称作层次特征复用网络(Hierarchical feature reuse network, HFRNet)的结构, 用以解决上述问题. 该网络保留运动补偿帧的低频内容, 并采用密集层次特征块(Dense hierarchical feature block, DHFB)自适应地融合其内部每个残差块的特征, 之后用长距离特征复用融合多个DHFB间的特征, 从而促进高频细节信息的恢复. 实验结果表明, 提出的方法在定量和定性指标上均优于当前的方法.Abstract: The performance improvement of current deep convolution neural network methods in video super-resolution task is slightly lower than that in image super-resolution task, partly because they do not make full use of some key inter-frame information in hierarchical structure features. In this paper, we propose hierarchical feature reuse network (HFRNet) to solve the problem mentioned above. The network retains the low-frequency content of the motion compensation frame, and use dense hierarchical feature block (DHFB) to adaptively fuse the features of each residual block within it, then long-term feature reuse is proposed to fuse the features between multiple dense hierarchical feature block, so as to promote the recovery of high-frequency detail information. Experimental results show that the proposed method is superior to the current method in both quantitative and qualitative metrics.
-
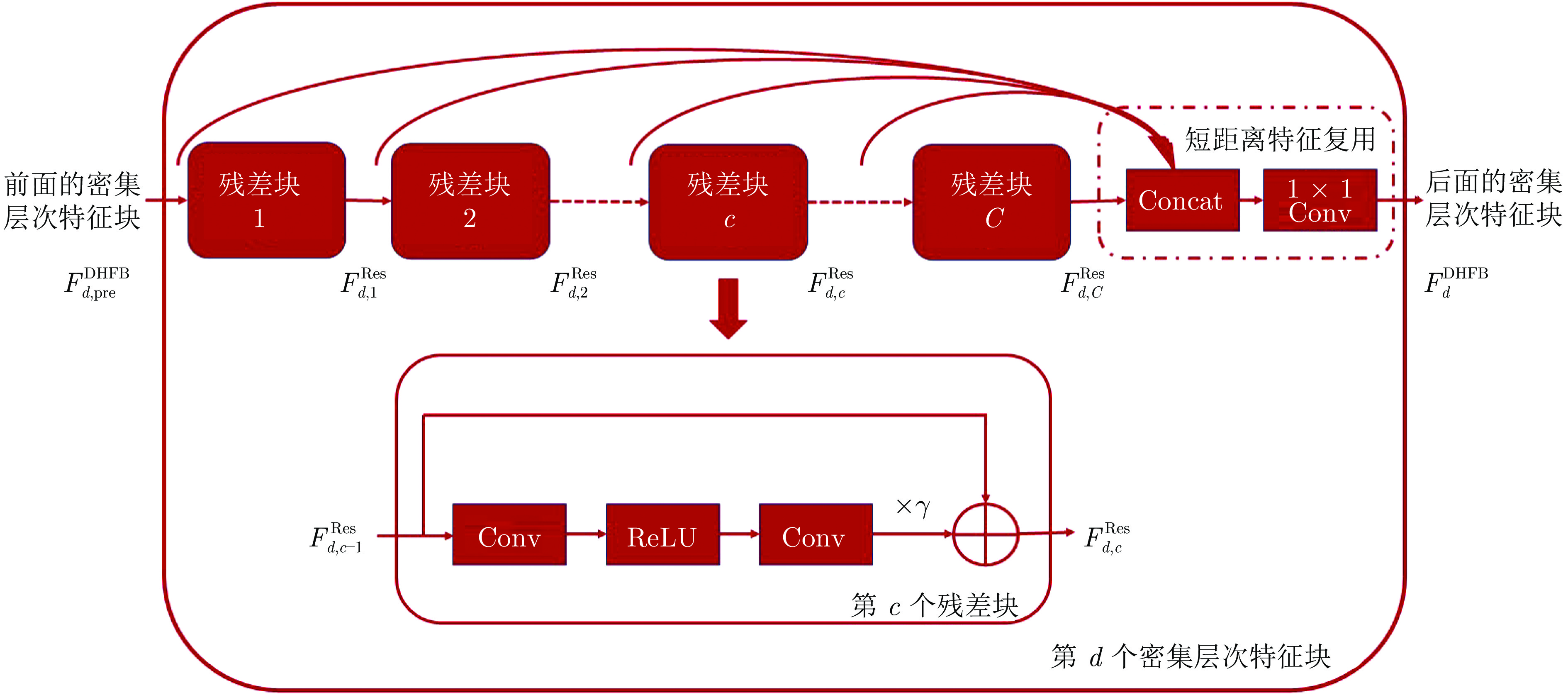
表 1 不同DHFB数目(D)和每个DHFB残差块数目(R)对2倍率超分辨率重建性能的影响(PSNR (dB))
Table 1 The impact (PSNR (dB)) of different numbers of DHFBs (D) and residual blocks (R) on the performance of 2× super-resolution reconstruction task
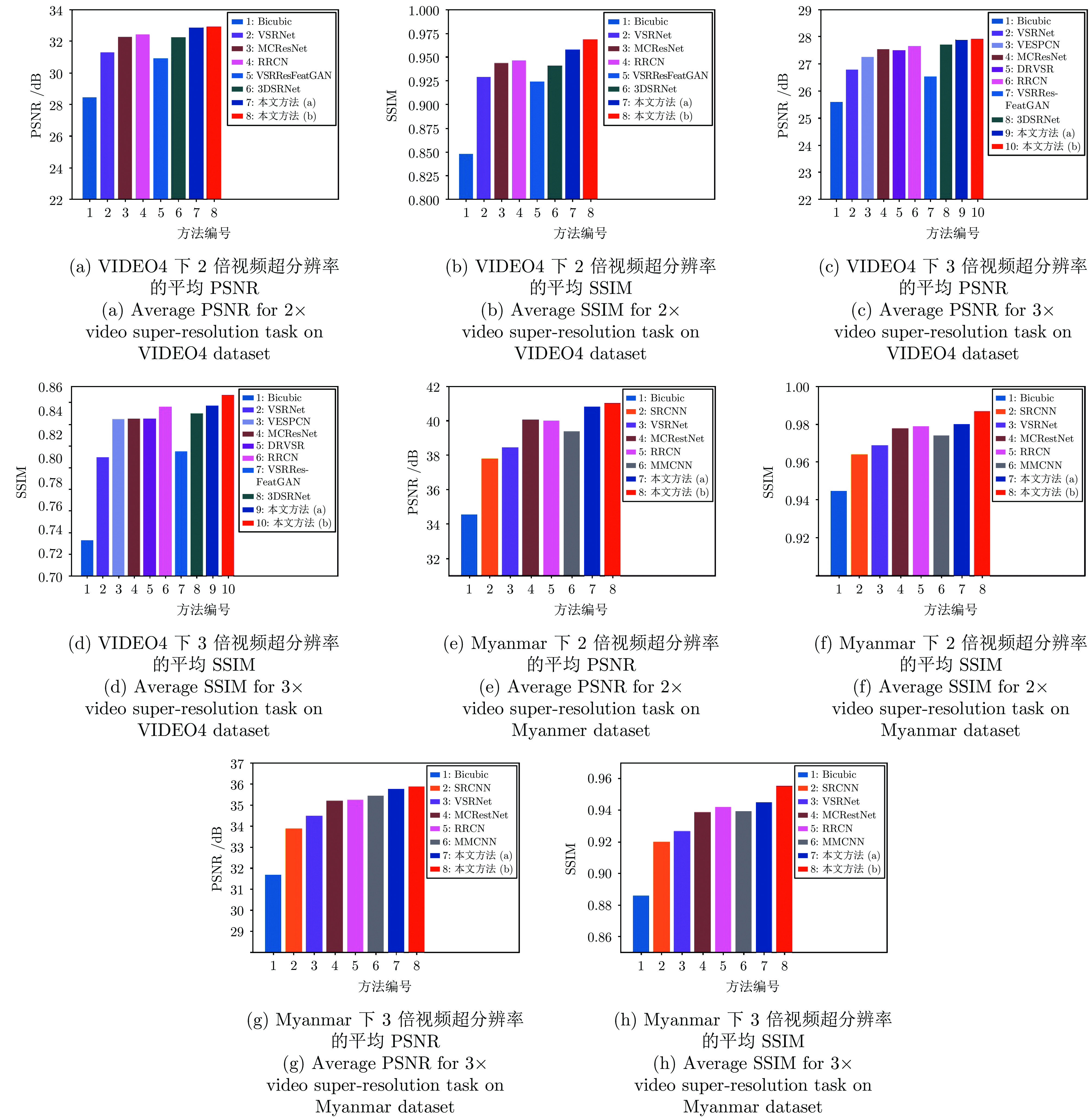
模块组合方式 CITY序列 WALK序列 FOLIAGE序列 CALENDAR序列 平均PSNR R4D6 34.342 36.846 32.045 27.071 32.576 R6D4 34.339 37.101 32.117 27.067 32.656 R6D6 34.896 37.210 32.224 27.137 32.866 R6D8 34.901 (±0.035) 37.102 (±0.054) 32.187 (±0.069) 27.140 (±0.007) 32.833 (±0.041) R8D6 34.633 (±0.039) 36.873 (±0.025) 32.144 (±0.050) 27.109 (±0.019) 32.690 (±0.034) 表 2 不同网络结构实验结果的平均PSNR及所需参数量
Table 2 The average PSNR and number of parameters for different network architectures
尺度 网络结构 参数量 CITY序列 (dB) WALK序列 (dB) FOLIAGE序列 (dB) CALENDAR序列 (dB) 平均PSNR (dB) ×2 无层次特征复用 2.85 M 33.793 35.919 31.884 26.291 31.972 HFRNet(a) 3.01 M 34.896 37.210 32.224 27.137 32.866 HFRNet(b) 3.10 M 35.104 37.218 32.230 27.158 32.927 ×3 无层次特征复用 2.85 M 27.220 30.113 27.019 23.344 26.924 HFRNet(a) 3.01 M 28.235 31.513 27.539 24.190 27.869 HFRNet(b) 3.10 M 28.240 31.613 27.587 24.217 27.914 表 3 不同光流估计方法对超分辨率重建性能的影响(PSNR (dB))
Table 3 The impact (PSNR (dB)) of different optical flow estimation methods on super-resolution reconstruction performance
尺度 光流估计算法 CITY序列 WALK序列 FOLIAGE序列 CALENDAR序列 平均PSNR ×2 CNN-based 35.226 37.106 32.244 27.817 33.098 CLG-TV 35.104 37.218 32.230 27.158 32.927 ×3 CNN-based 28.255 32.103 27.590 24.766 28.179 CLG-TV 28.240 31.613 27.587 24.217 27.914 表 4 不同运动补偿算法对超分辨率重建性能的影响(平均PSNR (dB))
Table 4 Average PSNR (dB) in video super-resolution task, with different motion compensation algorithm
运动补偿算法与参数 尺度 MC (k = 0.050) MC (k = 0.100) MC (k = 0.125) MC (k = 0.175) AMC 平均PSNR (dB) ×2 32.493 32.510 32.714 32.615 32.927 ×3 27.505 27.684 27.822 27.694 27.914 -
[1] Liu C, Sun D. On Bayesian adaptive video super resolution. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(2): 346−360 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.127 [2] Shahar O, Faktor A, Irani M. Space-time super-resolution from a single video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Colorado Springs, USA: IEEE, 2011. 3353−3360 [3] Zhou Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Du X, Liu H, Li C. Manifold learning based super resolution for mixed-resolution multi-view video in visual internet of things. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Communications and Networks. Harbin, China: Springer, 2019. 486−495 [4] Caballero J, Ledig C, Aitken A, Acosta A, Totz J, Wang Z, et al. Real-time video super-resolution with spatio-temporal networks and motion compensation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2848−2857 [5] Tao X, Gao H, Liao R, Wang J, Jia J. Detail-revealing deep video super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4482−4490 [6] Kappeler A, Yoo S, Dai Q, Katsaggelos A K. Video super-resolution with convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2016, 2(2): 109−122 doi: 10.1109/TCI.2016.2532323 [7] Li D, Wang Z. Video super resolution via motion compensation and deep residual learning. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2017, 3(4): 749−762 doi: 10.1109/TCI.2017.2671360 [8] Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Xie X, Kung S-Y. Image super-resolution based on dense convolutional auto-encoder blocks. Neurocomputing, 2021, 423(1): 98−109 [9] 李金新, 黄志勇, 李文斌, 周登文. 基于多层次特征融合的图像超分辨率重建. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(1): 161−171Li Jin-Xin, Huang Zhi-Yong, Li Wen-Bin, Zhou Deng-Wen. Image super-resolution based on multi hierarchical features fusion network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(1): 161−171 [10] 张毅锋, 刘袁, 蒋程, 程旭. 用于超分辨率重建的深度网络递进学习方法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(2): 274−282Zhang Yi-Feng, Liu Yuan, Jiang Cheng, Cheng Xu. A curriculum learning approach for single image super resolution. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(2): 274−282 [11] Zhou Y, Feng L, Hou C, Kung S-Y. Hyperspectral and multispectral image fusion based on local low rank and coupled spectral unmixing. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(10): 5997−6009 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2718728 [12] 周登文, 赵丽娟, 段然, 柴晓亮. 基于递归残差网络的图像超分辨率重建. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(6): 1157−1165Zhou Deng-Wen, Zhao Li-Juan, Duan Ran, Chai Xiao-Liang. Image super-resolution based on recursive residual networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(6): 1157−1165 [13] 孙旭, 李晓光, 李嘉锋, 卓力. 基于深度学习的图像超分辨率复原研究进展. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(5): 697−709Sun Xu, Li Xiao-Guang, Li Jia-Feng, Zhuo Li. Review on deep learning based image super-resolution restoration algorithms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5): 697−709 [14] Xie X K, Zhou Y, Kung S-Y. Exploiting operation importance for differentiable neural architecture earch. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1911.10511, 2019. [15] Huo S, Zhou Y, Xiang W, Kung S-Y. Semi-supervised learning based on a novel iterative optimization model for saliency detection. IEEE Transactions on Neural Network and Learning System, 2019, 30(1): 225−241 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2809702 [16] Zhou Y, Mao A, Huo S, Lei J, Kung S-Y. Salient object detection via fuzzy theory and object-level enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 1(1): 74−85 [17] Jo Y, Oh S W, Kang J, Kim S J. Deep video super-resolution network using dynamic upsampling filters without explicit motion compensation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3224−3232 [18] 潘志勇, 郁梅, 谢登梅, 宋洋, 蒋刚毅. 采用精简卷积神经网络的快速视频超分辨率重建. 光电子 · 激光, 2018, 29(12): 1332−1341Pan Zhi-Yong, Yu Mei, Xie Deng-Mei, Song Yang, Jiang Gang-Yi. Fast video super-resolution reconstruction using a succinct convolutional neural network. Journal of Optoelectronics · Laser, 2018, 29(12): 1332−1341 [19] Drulea M, Nedevschi S. Total variation regularization of local-global optical flow. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems. Washington D C, USA: IEEE, 2011. 318−323 [20] Lucas A, López-Tapia S, Molina R, Katsaggelos A K. Generative adversarial networks and perceptual losses for video super-resolution. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(7): 3312−3327 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2895768 [21] Zhou Y, Yang J X, Li H R, Cao T, Kung S-Y. Adversarial learning for multiscale crowd counting under complex scenes. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(11): 5423−5432 [22] Zhou Y, Huo S, Xiang W, Hou C, Kung S-Y. Semi-supervised salient object detection using a linear feedback control system model. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(4): 1173−1185 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2793278 [23] Huo S, Zhou Y, Lei J, Ling N, Hou C. Iterative feedback control-based salient object segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(6): 1350−1364 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2017.2769801 [24] Zhou Y, Zhang T, Huo S, Hou C, Kung S-Y. Adaptive irregular graph construction based salient object detection. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(6): 1569−1582 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2904463 [25] Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, Sermanet P, Reed S E, Anguelov D, et al. Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1−9 [26] He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [27] Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger K Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2261−2269 [28] Zhang Y, Tian Y, Kong Y, Zhong B, Fu Y. Residual dense network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 2472−2481 [29] Zhou Y, Du X T, Wang M F, Huo S W, Zhang Y D, Kung S-Y. Cross-scale residual network: A general framework for image super-resolution, denoising, and deblocking. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(7): 5855−5867 [30] Yi P, Wang Z, Jiang K, Shao Z, Ma J. Multi-temporal ultra dense memory network for video super-resolution. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(8): 2503−2516 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2925844 [31] Yi P, Wang Z, Jiang K, Jiang J, Ma J. Progressive fusion video super-resolution network via exploiting non-local spatio-temporal correlations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 3106−3115 [32] Yi P, Wang Z Y, Jiang K, Jiang J J, Lu T, Ma J. A progressive fusion generative adversarial network for realistic and consistent video super-resolution. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(5): 2264−2280 [33] H Inc. Myanmar 60p [Online], available: http://www.harmoni-cinc.com/resources/videos/4k-video-clip-center, May 20, 2021 [34] Wang L, Guo Y, Liu L, Lin Z, Deng X, An W. Deep video super-resolution using HR optical flow estimation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29(1): 4323−4336 [35] Dong C, Loy C C, He K, Tang X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295−307 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281 [36] Li D, Liu Y, Wang Z. Video super-resolution using motion compensation and residual bidirectional recurrent convolutional network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2017. 1642−1646 [37] Kim S Y, Lim J, Na T, Kim M. Video super-resolution based on 3D-CNNs with consideration of scene change. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Taipei, China: IEEE, 2019. 2831−2835 [38] Wang Z, Yi P, Jiang K, Jiang J, Han Z, Lu T, et al. Multi-memory convolutional neural network for video super-resolution. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(5): 2530−2544 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2887017 [39] Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1646−1654 [40] Lai W S, Huang J B, Ahuja N, Yang M H. Deep Laplacian pyramid networks for fast and accurate super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 5835−5843 [41] Wang L, Guo Y, Lin Z, Deng X, An W. Learning for video super-resolution through HR optical flow estimation. In: Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Perth, Australia: Springer, 2018. 514−529 -




 下载:
下载: