-
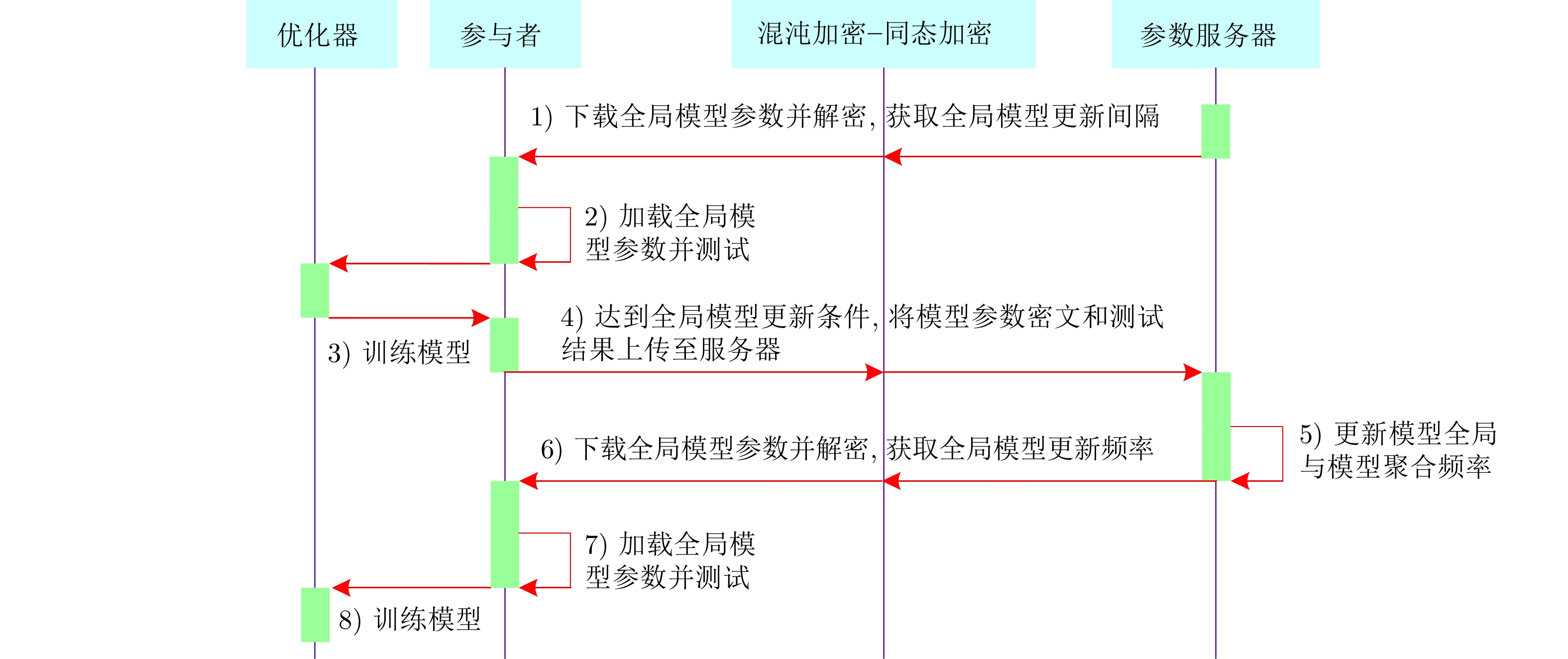
摘要: 近些年, 联邦学习(Federated learning, FL)由于能够打破数据壁垒, 实现孤岛数据价值变现, 受到了工业界和学术界的广泛关注. 然而, 在实际工程应用中, 联邦学习存在着数据隐私泄露和模型性能损失的问题. 为此, 首先对这两个问题进行数学描述与分析. 然后, 提出一种自适应模型聚合方案, 该方案能够设定各参与者的Mini-batch值和自适应调整全局模型聚合间隔, 旨在保证模型精度的同时, 提高联邦学习训练效率. 并且, 混沌系统被首次引入联邦学习领域中, 用于构建一种基于混沌系统和同态加密的混合隐私保护方案, 从而进一步提升系统的隐私保护水平. 理论分析与实验结果表明, 提出的联邦学习算法能够保证参与者的数据隐私安全. 并且, 在非独立同分布数据的场景下, 该算法能够在保证模型精度的前提下提高训练效率, 降低系统通信成本, 具备实际工业场景应用的可行性.Abstract: In recent years, federated learning (FL) that can break data barriers and realize the value of isolated data, has been received wide-spread attention from industry and academia. However, in real industry applications, federated learning has problems with privacy leakage and model accuracy loss, which is analyzed through mathematical demonstration in this study. To solve the issues, this paper proposes an adaptive global model aggregation scheme that can adaptively set the Mini-batch value of each participant and the global model aggregation interval for the parameter server, which aims to improve the training efficiency while ensuring the accuracy of the model. Moreover, this paper introduces the chaos system into the federated learning field, which is used to construct a hybrid privacy-preserving scheme based on chaos system and homomorphic encryption, thereby further improving the privacy protection level. Theoretical analysis and experimental results show that the proposed approach can guarantee the data privacy security of participants. Moreover, in the non-independent and identically distributed (Non-IID) data scenario, the proposed method can improve the training efficiency and reduce communication cost while ensuring the model accuracy, which is feasible for real industrial applications.
-
Key words:
- Federated learning (FL) /
- deep learning /
- privacy-preserving /
- homomorphic encryption /
- chaos system
-
表 1 加密/解密算法的执行时间
Table 1 Execution time of the encryption/ decryption operations
操作类型 500个参数 2000个参数 54000个参数 随机数生成 12.05 ms 25.50 ms 0.40 s CKKS 加密 9.37 ms 9.68 ms 0.54 s CKKS 解密 1.56 ms 17.18 ms 0.03 s CKKS 密文加法 0.15 ms 0.15 ms 0.02 s Paillier 加密 3.82 s 14.61 s 410.32 s Paillier 解密 1.06 s 4.22 s 115.92 s Paillier 密文加法 7.87 ms 30.03 ms 0.87 s 表 2 加密/解密算法的执行次数
Table 2 Execution numbers of the encryption/ decryption operations
表 3 不同联邦学习方案的功能分析
Table 3 The functionality analysis of the different FLs
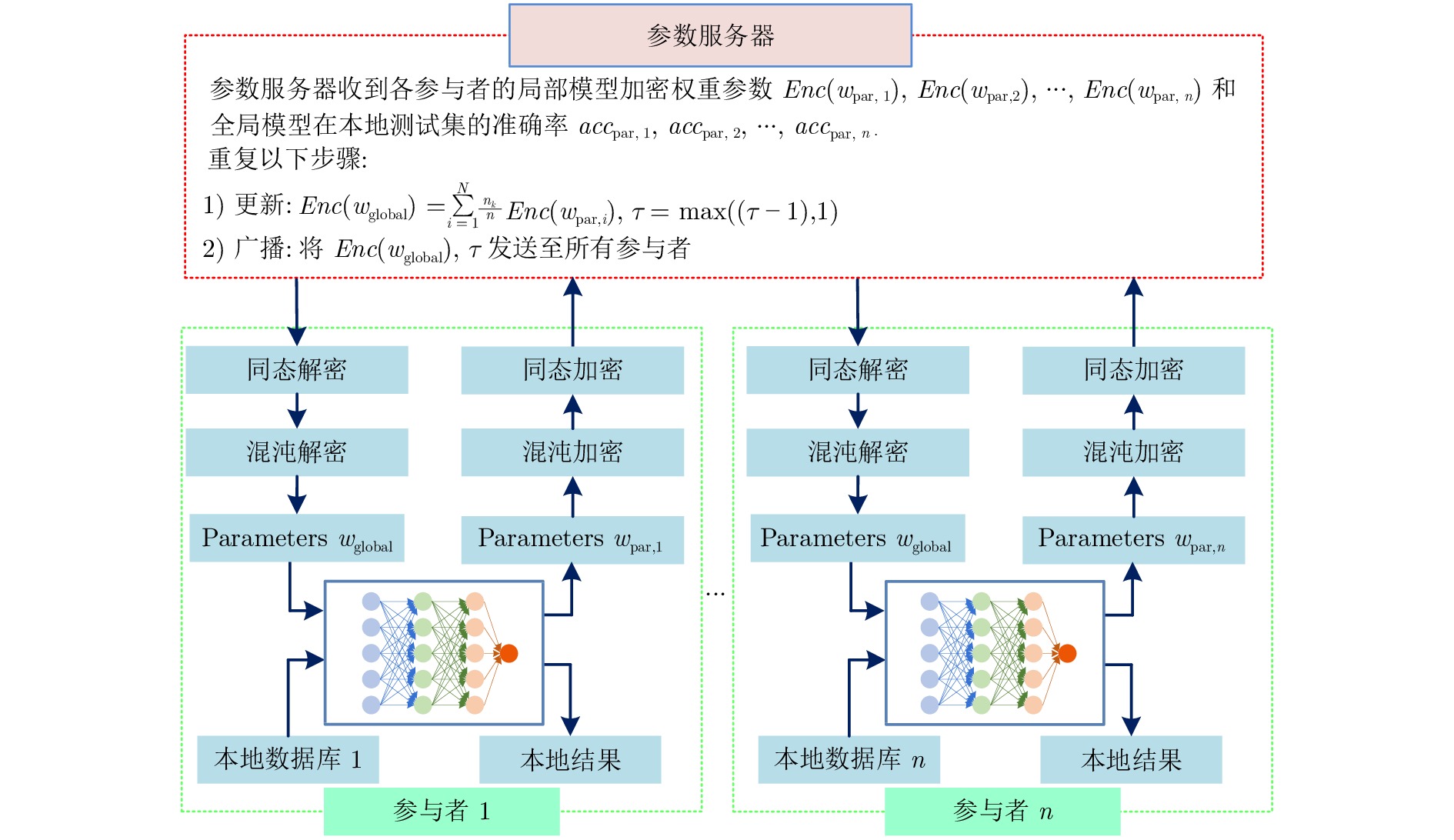
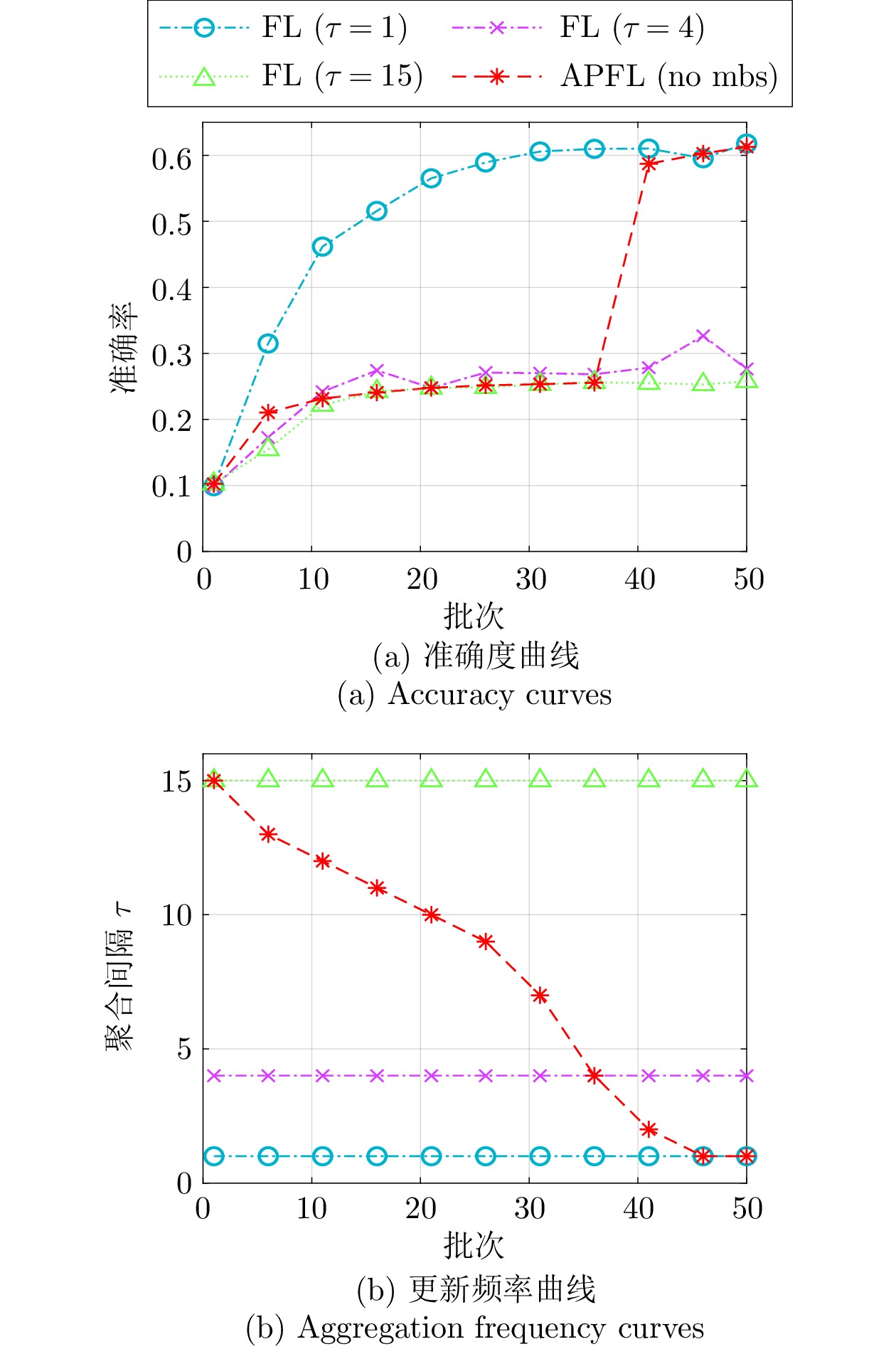
功能 PFL AFL MFL APFL 隐私保护 √ × × √ 自适应调整$\tau $ × √ × √ Mini-batch 设定 × × × √ 动量项加速 × × √ √ 表 4 CIFAR10上不同联邦学习模型的分类结果(%)
Table 4 Classification results of the different federated learning models on CIFAR10 (%)
表 5 F-MNIST上不同联邦学习模型的分类结果(%)
Table 5 Classification results of the different federated learning models on F-MNIST (%)
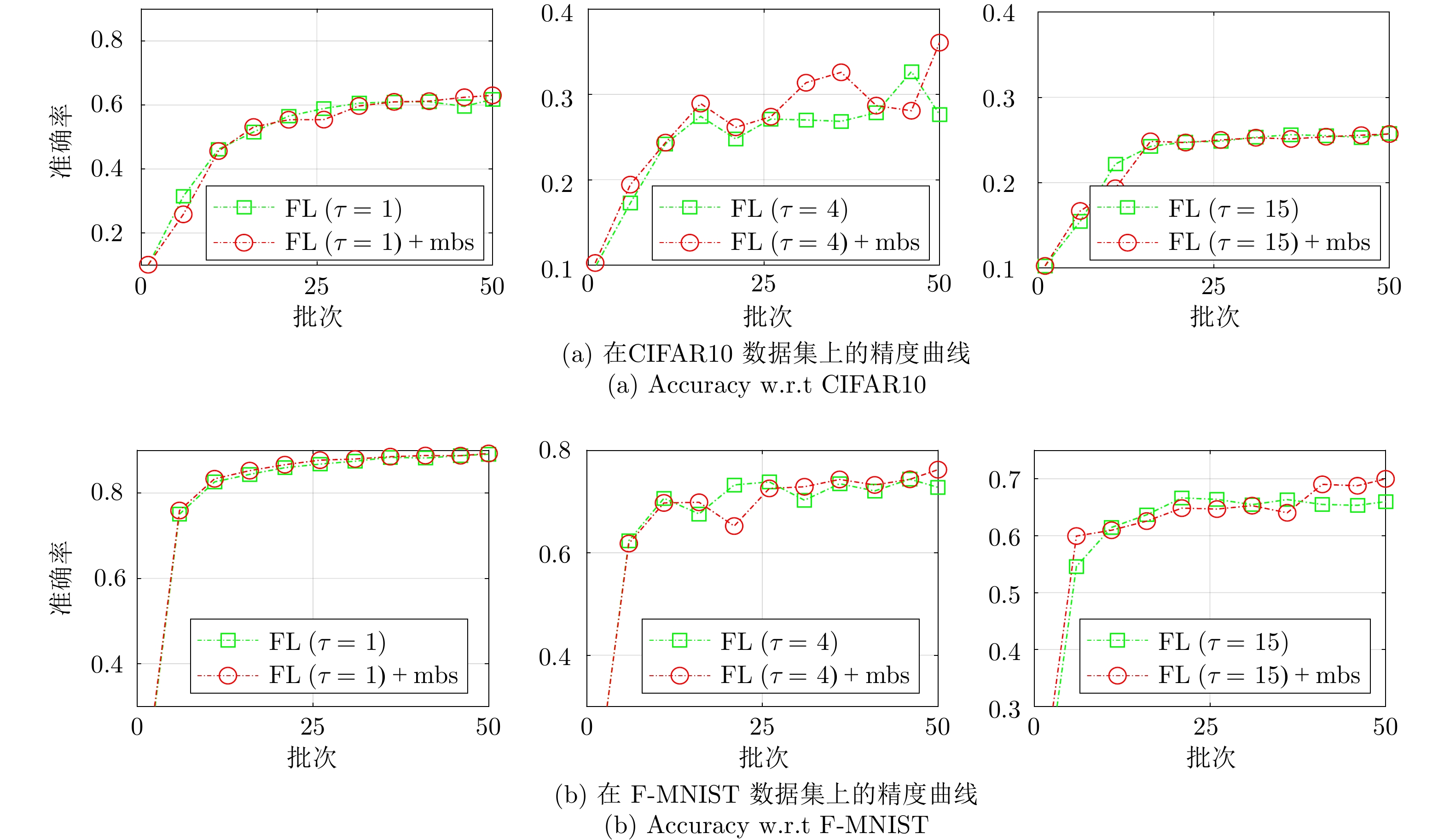
表 6 CIFAR10下的Mini-batch设定消融实验结果(%)
Table 6 Ablation experiment results of the Mini-batch size setting on CIFAR10 (%)
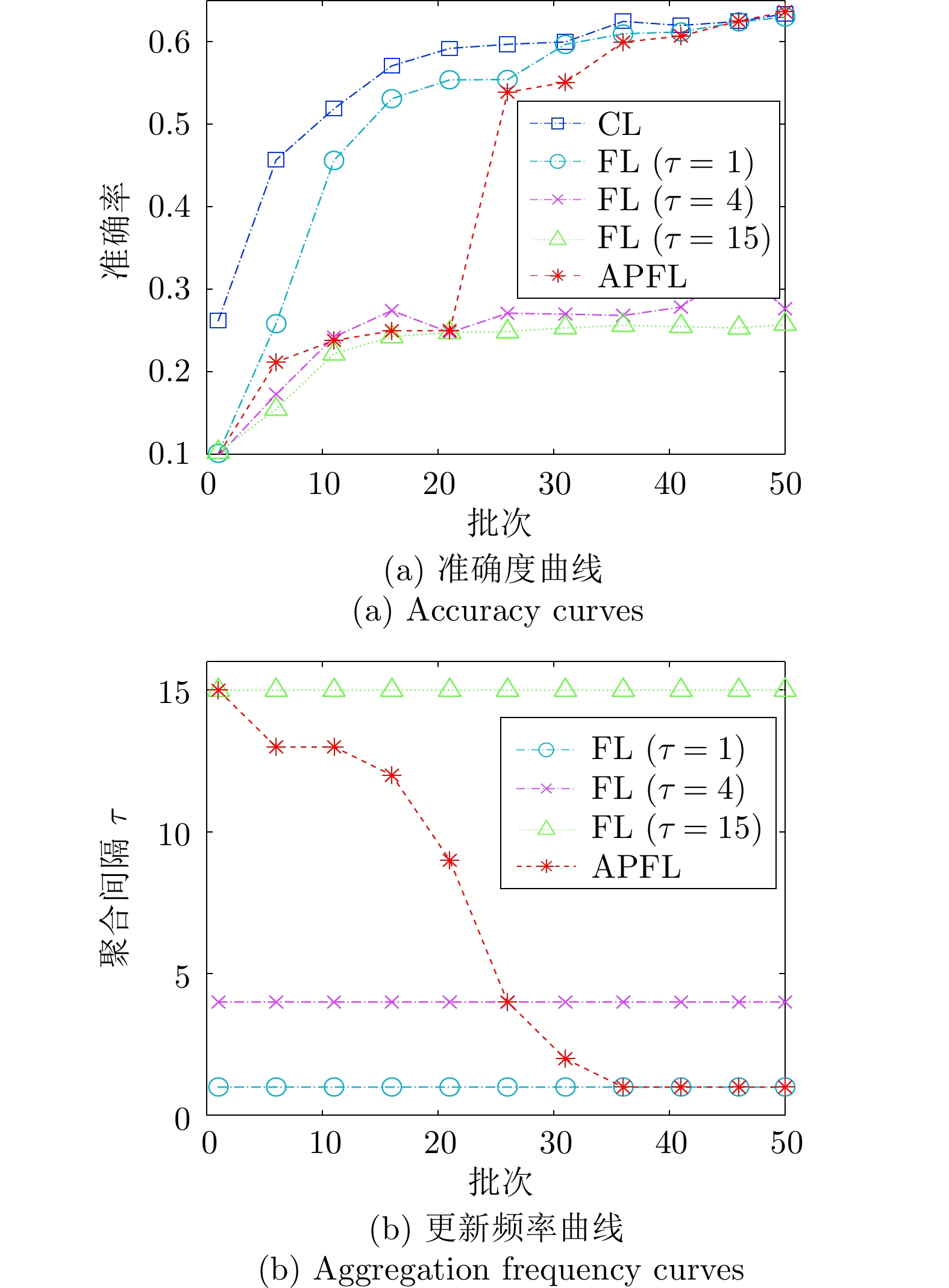
方法 Accuracy Precision Recall Devavg CL 63.36 63.92 63.29 — ${\rm{FL} }\; (\tau= 15)$[33] 25.76 9.34 25.87 49.91 ${\rm{FL} }\; (\tau= 15)+{\rm{mbs} }$ 25.70 9.14 25.78 50.07 ${\rm{FL} }\;(\tau= 4)$ 27.64 50.14 27.76 45.04 ${\rm{FL} }\;(\tau= 4)+{\rm{mbs} }$ 63.66 60.93 36.06 32.90 ${\rm{FL} }\;(\tau= 1)$[18] 61.78 62.76 61.77 1.91 ${\rm{FL} }\;(\tau= 1)+{\rm{mbs} }$ 63.02 64.08 62.27 1.53 表 7 F-MNIST下的Mini-batch设定消融实验结果(%)
Table 7 Ablation experiment results of the Mini-batch size setting on F-MNIST (%)
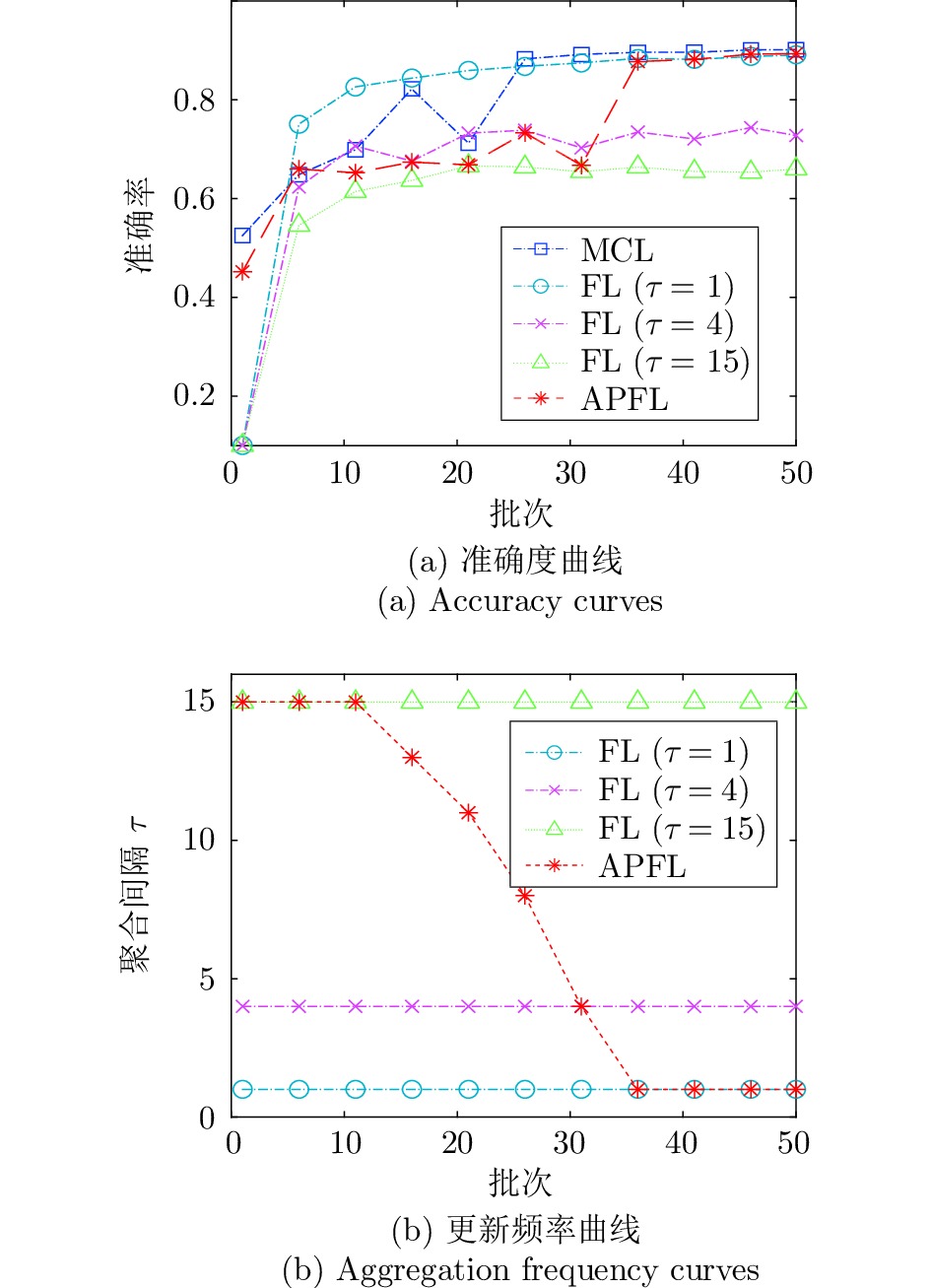
方法 Accuracy Precision Recall Devavg CL 90.15 90.07 90.15 — ${\rm{FL} }\; (\tau= 15)$[33] 65.99 62.18 65.99 31.43 ${\rm{FL} }\; (\tau= 15)+{\rm{mbs} }$ 69.99 64.29 69.99 26.05 ${\rm{FL} }\;(\tau= 4)$ 27.76 50.14 27.76 45.04 ${\rm{FL} }\;(\tau= 4)+{\rm{mbs} }$ 76.23 84.84 76.23 14.85 ${\rm{FL} }\;(\tau= 1)$[18] 89.10 89.25 89.10 0.88 ${\rm{FL} }\;(\tau= 1)+{\rm{mbs} }$ 89.27 89.25 89.27 0.99 表 8 CIFAR10下的自适应更新间隔消融实验结果(%)
Table 8 Ablation experiment results of the adaptive model aggregation interval on CIFAR10 (%)
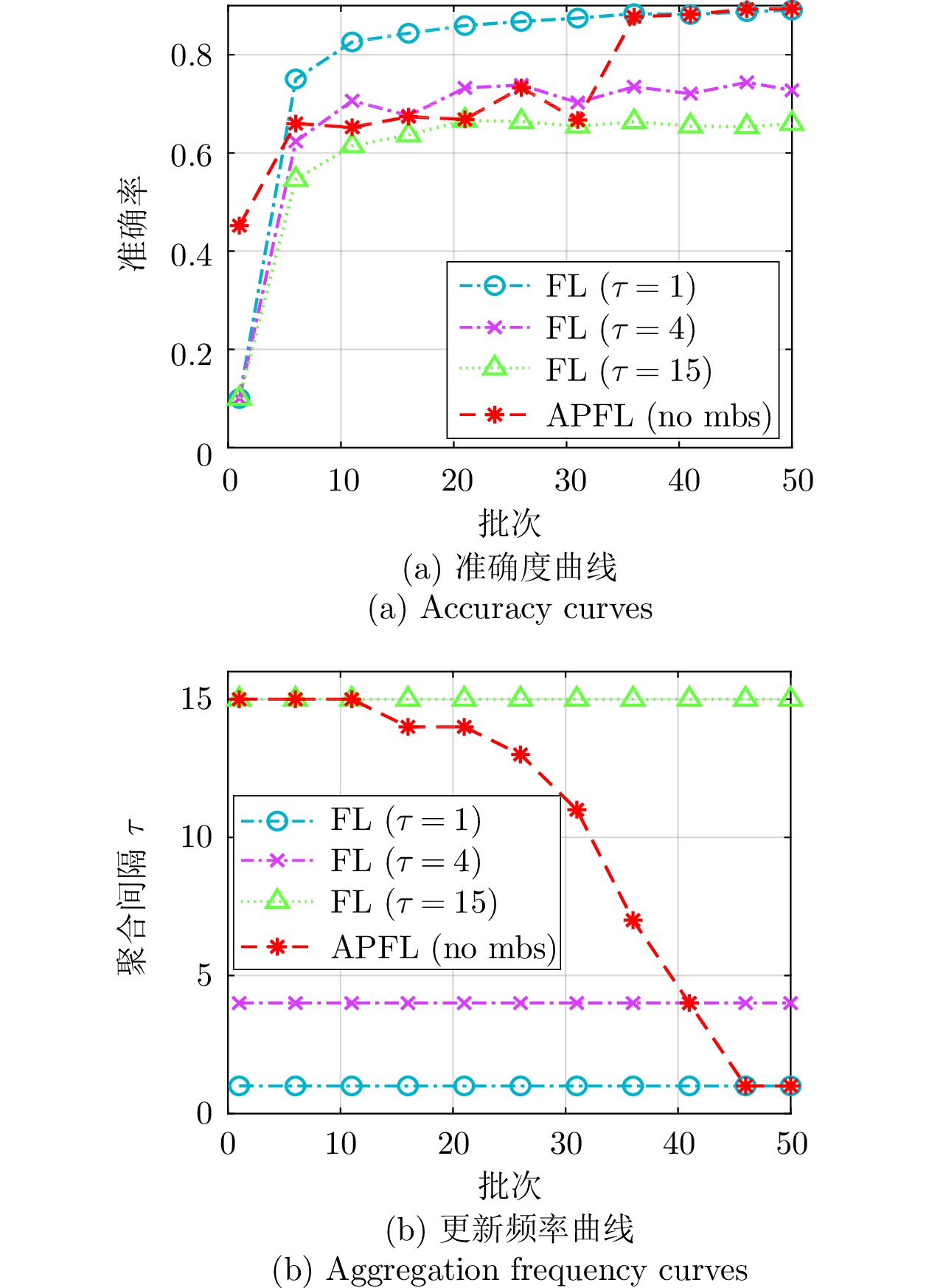
表 9 F-MNIST下的自适应更新间隔消融实验结果(%)
Table 9 Ablation experiment results of the adaptive model aggregation interval on F-MNIST (%)
-
[1] 孙长银, 穆朝絮. 多智能体深度强化学习的若干关键科学问题. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(7): 1301−1312Sun Chang-Yin, Mu Chao-Xu. Important scientific problems of multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(7): 1301−1312 [2] 金侠挺, 王耀南, 张辉, 刘理, 钟杭, 贺振东. 基于贝叶斯CNN和注意力网络的钢轨表面缺陷检测系统. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(12): 2312−2327Jin Xia-Ting, Wang Yao-Nan, Zhang Hui, Liu Li, Zhong Hang, He Zhen-Dong. DeepRail: Automatic visual detection system for railway surface defect using Bayesian CNN and attention Network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(12): 2312−2327 [3] Zhang Z H, Guan C, Liu Z Y. Real-time optimization energy management strategy for fuel cell hybrid ships considering power sources degradation. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 87046−87059 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2991519 [4] Chen H, Zhang Z H, Guan C, Gao H B. Optimization of sizing and frequency control in battery/supercapacitor hybrid energy storage system for fuel cell ship. Energy, 2020, 197: 117285 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.117285 [5] 鲜征征, 李启良, 黄晓宇, 吕威, 陆寄远. 基于差分隐私和SVD++的协同过滤算法. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(1): 43−54Xian Zheng-Zheng, Li Qi-Liang, Huang Xiao-Yu, Lv Wei, Lu Ji-Yuan. Collaborative filtering via SVD++ with differential privacy. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(1): 43−54 [6] Li J, Kuang X H, Lin S J, Ma X, Tang Y. Privacy preservation for machine learning training and classification based on homomorphic encryption schemes. Information Sciences, 2020, 526: 166−179 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.03.041 [7] Gong M G, Pan K, Xie Y, Qin A K, Tang Z D. Preserving differential privacy in deep neural networks with relevance-based adaptive noise imposition. Neural Networks, 2020, 125: 131−141 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2020.02.001 [8] 张超, 李强, 陈子豪, 黎祖睿, 张震. Medical Chain: 联盟式医疗区块链系统. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1495−1510Zhang Chao, Li Qiang, Chen Zi-Hao, Li Zu-Rui, Zhang Zhen. Medical Chain: Alliance medical blockchain system. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1495−1510 [9] Yang Q, Liu Y, Chen T J, Tong Y X. Federated machine learning: Concept and applications. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2019, 10(2): Article No. 12 [10] Li T, Sahu A K, Talwalkar A, Smith V. Federated learning: Challenges, methods, and future directions. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(3): 50−60 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.2975749 [11] Zhang W, Li X, Ma H, Luo Z, Li X. Federated learning for machinery fault diagnosis with dynamic validation and self-supervision. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 213: Article No. 106679 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106679 [12] Sheller M J, Edwards B, Reina G A, Martin J, Pati S, Kotrotsou A, et al. Federated learning in medicine: Facilitating multi-institutional collaborations without sharing patient data. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): Article No. 12598 doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69250-1 [13] Kwon D, Jeon J, Park S, Kim J, Cho S. Multiagent DDPG-based deep learning for Smart Ocean federated learning IoT networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(10): 9895−9903 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2988033 [14] Rothchild D, Panda A, Ullah E, Ivkin N, Stoica I, Braverman V, et al. FetchSGD: Communication-efficient federated learning with sketching. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. Vienna, Austria: JMLR.org, 2020. Article No. 764 [15] Duan M M, Liu D, Chen X Z, Liu R P, Tan Y J, Liang L. Self-balancing federated learning with global imbalanced data in mobile systems. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2021, 32(1): 59−71 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2020.3009406 [16] Liu W, Chen L, Chen Y F, Zhang W Y. Accelerating federated learning via momentum gradient descent. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2020, 31(8): 1754−1766 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2020.2975189 [17] Wang S Q, Tuor T, Salonidis T, Leung K K, Makaya C, He T, et al. Adaptive federated learning in resource constrained edge computing systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(6): 1205−1221 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2904348 [18] Li Q B, Wen Z Y, Wu Z M, Hu S X, Wang N B, Li Y, et al. A survey on federated learning systems: Vision, hype and reality for data privacy and protection. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2023, 35(4): 3347−3366 [19] 张泽辉, 富瑶, 高铁杠. 支持数据隐私保护的联邦深度神经网络模型研究. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(5): 1273−1284Zhang Ze-Hui, Fu Yao, Gao Tie-Gang. Research on federated deep neural network model for data privacy preserving. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(5): 1273−1284 [20] Lyu L J, Li Y T, Nandakumar K, Yu J S, Ma X J. How to democratise and protect AI: Fair and differentially private decentralised deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 19(2): 1003−1017 [21] Wang Y F, Gu M, Ma J H, Jin Q. DNN-DP: Differential privacy enabled deep neural network learning framework for sensitive crowdsourcing data. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2020, 7(1): 215−224 doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2019.2950017 [22] Carpov S, Gama N, Georgieva M, Troncoso-Pastoriza J R. Privacy-preserving semi-parallel logistic regression training with fully homomorphic encryption. BMC Medical Genomics, 2019, 13(7): Article No. 88 [23] 宋蕾, 马春光, 段广晗, 袁琪. 基于数据纵向分布的隐私保护逻辑回归. 计算机研究与发展, 2019, 56(10): 2243−2249 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190414Song Lei, Ma Chun-Guang, Duan Guang-Han, Yuan Qi. Privacy-preserving logistic regression on vertically partitioned data. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(10): 2243−2249 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190414 [24] Phong L T, Aono Y, Hayashi T, Wang L H, Moriai S. Privacy-preserving deep learning via additively homomorphic encryption. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(5): 1333−1345 (本条文献与第18条文献重复, 请联系作者确认) doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2017.2787987 [25] Ou W, Zeng J H, Guo Z J, Yan W Q, Liu D W, Fuentes S. A homomorphic-encryption-based vertical federated learning scheme for rick management. Computer Science and Information Systems, 2020, 17(3): 819−834 doi: 10.2298/CSIS190923022O [26] Chen H, Chillotti I, Song Y. Improved bootstrapping for approximate homomorphic encryption. In: Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Darmstadt, Germany: Springer, 2019. 34−54 [27] Xiao X D, Wu T, Chen Y F, Fan X Y. Privacy-preserved approximate classification based on homomorphic encryption. Mathematical and Computational Applications, 2019, 24(4): Article No. 92 doi: 10.3390/mca24040092 [28] Zhang Z H, Yao F, Gao T G. A hybrid image encryption algorithm based on chaos system and simplified advanced encryption system. International Journal of Multimedia Data Engineering and Management (IJMDEM), 2020, 11(4): Article No. 1 doi: 10.4018/IJMDEM.2020100101 [29] Luo Y Q, Yu J, Lai W R, Liu L F. A novel chaotic image encryption algorithm based on improved baker map and logistic map. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78(15): 22023−22043 doi: 10.1007/s11042-019-7453-3 [30] Sathiyamurthi P, Ramakrishnan S. Speech encryption algorithm using FFT and 3D-Lorenz–logistic chaotic map. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79(25): 17817−17835 [31] Sattler F, Müller K, Samek W. Clustered federated learning: Model-agnostic distributed multitask optimization under privacy constraints. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 32(8): 3710−3722 [32] Al-Sharman M, Murdoch D, Cao D P, Lv C, Zweiri Y, Rayside D, et al. A sensorless state estimation for a safety-oriented cyber-physical system in urban driving: Deep learning approach. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2021, 8(1): 169−178 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2020.1003474 [33] Weng J S, Weng J, Zhang J L, Li M, Zhang Y, Luo W Q, et al. DeepChain: Auditable and privacy-preserving deep learning with blockchain-based incentive. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2021, 18(5): 2438−2455 [34] Sattler F, Wiedemann S, Müller K R, Samek W. Robust and communication-efficient federated learning from non-i.i.d. data. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(9): 3400−3413 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2944481 [35] Xu G W, Li H W, Zhang Y, Xu S M, Ning J T, Deng R H. Privacy-preserving federated deep learning with irregular users. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 19(2): 1364−1381 [36] Teng S H, Wu N Q, Zhu H B, Zhang W. SVM-DT-based adaptive and collaborative intrusion detection. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2018, 5(1): 108−118 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510730 -




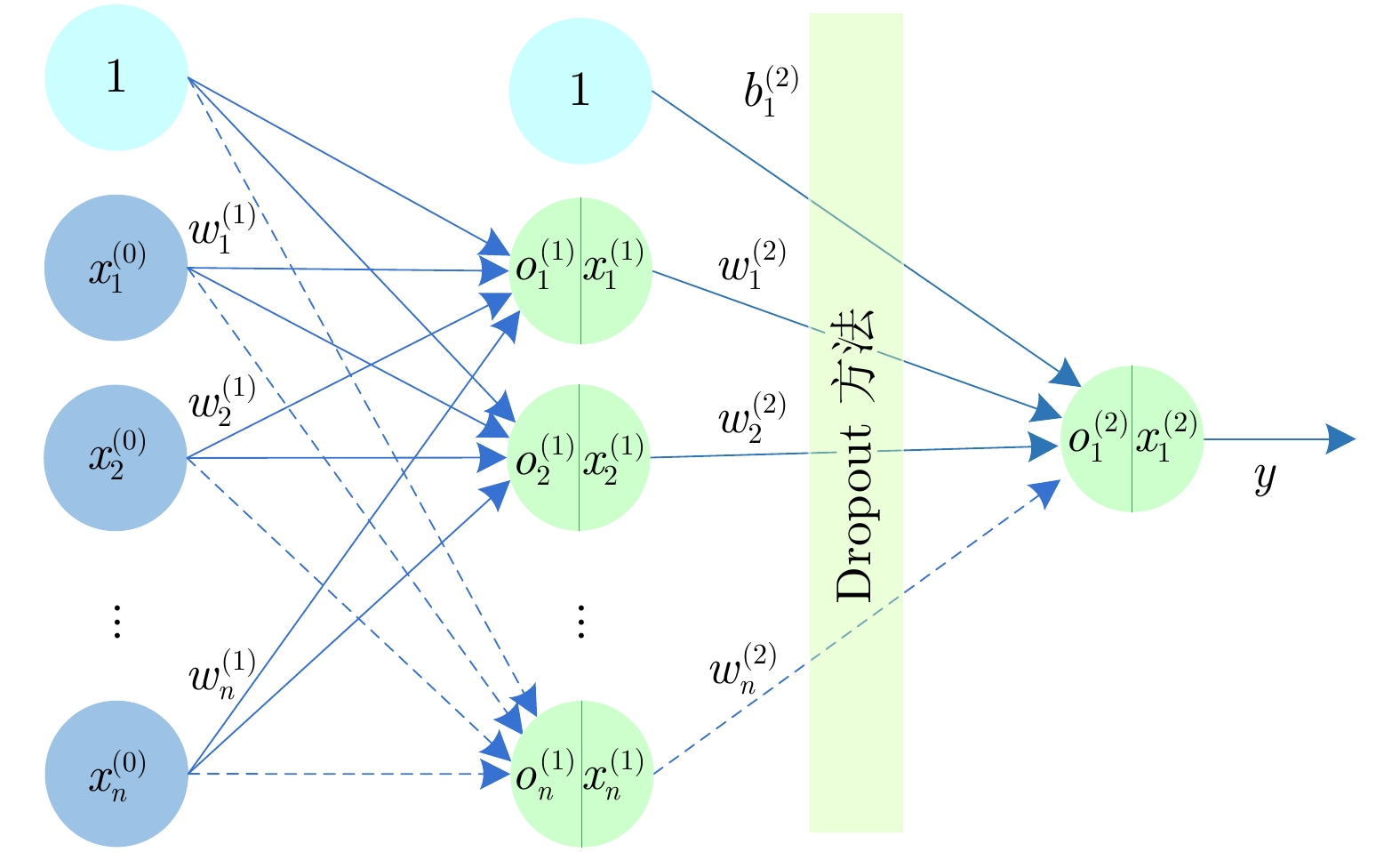
 下载:
下载: