-
摘要:
情感计算是现代人机交互中的一个重要研究方向, 旨在研究与开发能够识别、解释、处理和模拟人类情感的理论、方法与系统. 脑电、心电、皮肤电等生理信号是情感计算中重要的输入信号. 本文总结了近年来基于脑电等生理信号的情感计算研究所取得的进展. 首先介绍情感计算的相关基础理论, 不同生理信号与情感变化之间的联系, 以及基于生理信号的情感计算工作流程和相关公开数据集. 接下来介绍生理信号的特征工程和情感计算中的机器学习算法, 重点介绍适合处理个体差异的迁移学习、降低数据标注量的主动学习和融合特征工程与学习器的深度学习算法. 最后, 指出基于生理信号的情感计算研究中面临的一些挑战.
Abstract:Affective computing is an important research area in modern human-machine interaction. It aims to develop systems that can recognize, interpret, analyze and emulate human emotions. Physiological signals, e.g., electroencephalogram, electrocardiogram, galvanic skin response, etc., are important inputs in affective computing. This paper summarizes recent progresses on physiological signals based affective computing, particularly, electroencephalogram based affective computing. It first introduces the basic theories of affective computing, the relationship between the changes of physiological signals and affects, the flowchart of physiological signals based affective computing, and common public datasets. Next, it introduces typical feature engineering and machine learning algorithms, particularly transfer learning, active learning and deep learning. Finally, it points out some challenges and future research directions in physiological signals based affective computing.
-
表 1 情感计算中常用的生理信号
Table 1 Common physiological signals in affective computing
生理信号类别 英文名称 英文缩写 脑电图 Electroencephalogram EEG 肌电图 Electromyogram EMG 心电图 Electrocardiogram ECG 眼电图 Electrooculogram EOG 心率变异性 Heart rate variability HRV 皮肤电反应 Galvanic skin response GSR 皮肤电应答 Electrodermal response EDR 皮肤电活动 Electrodermal activity EDA 血压信号 Blood pressure BP 皮肤温度 Skin temperature ST 呼吸模式 Respiration pattern RSP 光电容积脉搏波 Photoplethysmogram PPG 眼动信号 Eye movement EM 脉搏信号 Pulse rate PR 血氧饱和度 Oxygen saturation SpO2 表 2 脑电频率划分
Table 2 Frequency bands of EEG
脑波 频率 人体状态 $ \delta $ 0.1 ~ 3 Hz 深度睡眠且没有做梦时 $ \theta $ 4 ~ 7 Hz 成人情绪受到压力、失望或挫折时 $ \alpha $ 8 ~ 12 Hz 放松、平静、闭眼但清醒时 $ \beta $ 12.5 ~ 28 Hz 放松但精神集中、激动或焦虑 $ \gamma $ 29 ~ 50 Hz 提高意识、幸福感、放松、冥想 表 3 谷歌学术中2010年以来基于生理信号的情感计算工作统计
Table 3 Statistics of physiological signal based affective computing Google Scholar publications since 2010
生理信号类型 对应检索关键词 文献数量 脑电图 EEG OR Electroencephalogram 913 心电图 ECG OR Electrocardiogram 70 心率变异性 HRV OR (Heart rate variability) 38 皮肤电 GSR OR EDA OR EDR OR Electrodermal 27 肌电图 EMG OR Electromyogram 25 光电容积脉搏波 PPG OR Photoplethysmogram 13 血压 Blood pressure 7 脉搏 Pulse rate 4 皮肤温度 Skin temperature 3 眼电图 EOG OR Electrooculogram 2 血氧 SpO2 OR (Oxygen saturation) OR (Blood oxygen) 2 总计 1104 注: “情感计算” 对应的检索关键词为: (emotion OR emotional OR affect OR affective) + (recognize OR recognition OR classify OR classification OR detect OR detection OR predict OR prediction OR estimate OR estimation OR model OR state OR computing). 表 4 部分最近的基于生理信号的情感计算工作
Table 4 Some recent studies on physiological signals based affective computing
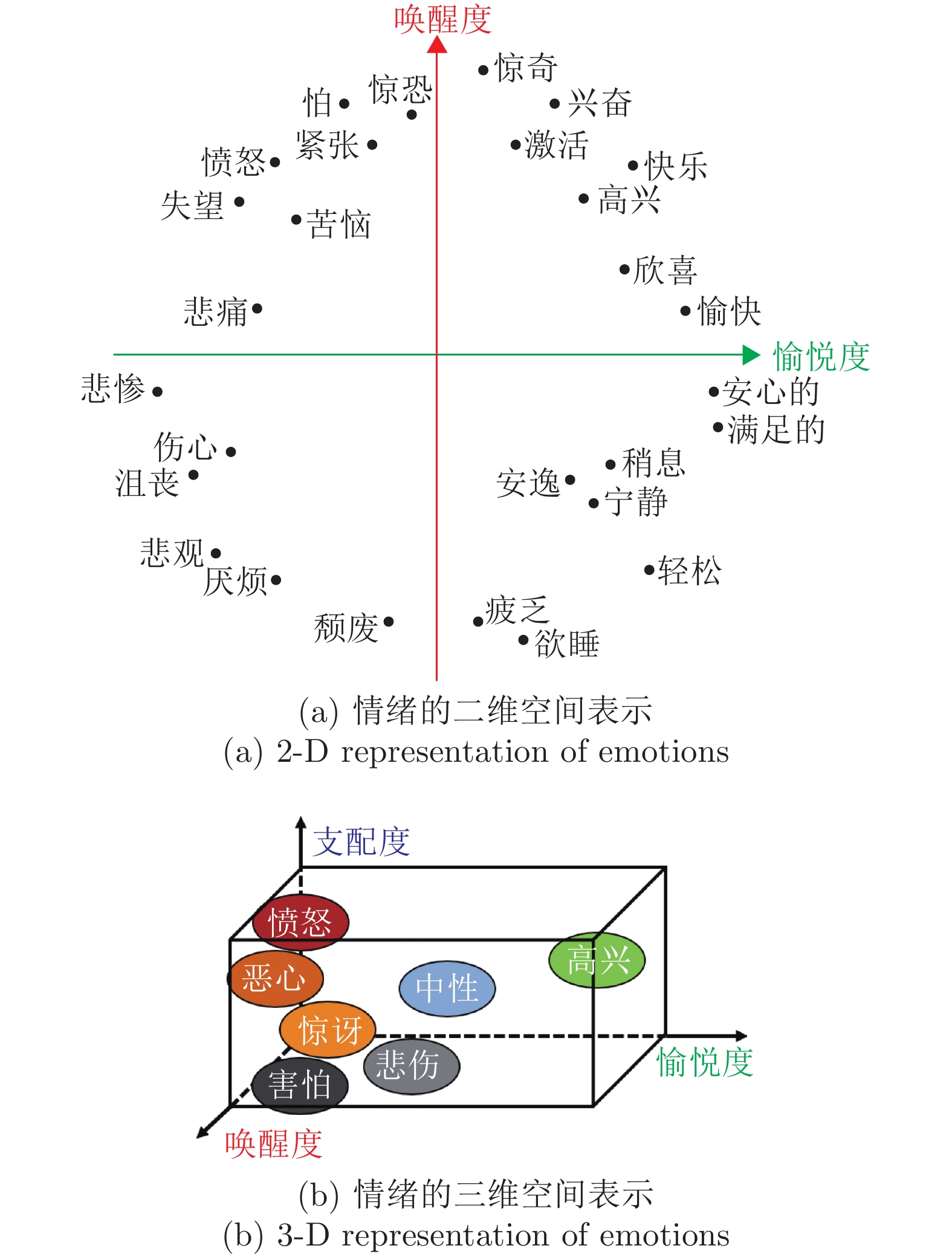
表 5 情感计算常用公开数据集
Table 5 Popular public affective computing datasets
数据集 内容说明 任务模型 MAHNOB-HCI[34] 27 名被试的 EEG 及多种生理信号和图片、视频信息 VAD 模型 RECOLA[35] 46 名被试的 ECG、EOG 及音频、视频信息 VA 模型 DECAF[36] 30 名被试的 EOG、ECG、EMG 和视频信息 VA 模型 ASCERTAIN[37] 58 名被试的 EEG、ECG、GSR 和图片信息 5 种情绪类别, VA 模型 AMIGOS[38] 40 名被试的 EEG、ECG、GSR 及图片、视频信息 5 种情绪类别, VA 模型 DREAMER[39] 23 名被试的 EEG、ECG VAD 模型 RCLS[40] 14 名被试的 EEG 3 种情绪类别 MPED[41] 23 名被试的 EEG、ECG、RSP、GSR 7 种情绪类别 HR-EEG4EMO[42] 27 名被试的 EEG 高兴、悲伤两种情绪类别 SEED[21, 33] 15 名被试, 每名被试 3 次实验的 EEG 3 种情绪类别 SEED-IV[33] 15 名被试, 每名被试 3 次实验的 EEG、EM 4 种情绪类别 DEAP[43] 32 名被试的 EEG、EOG、EMG、GSR、RSP、BP、ST VAD 模型 表 6 不同深度特征提取方式及效果
Table 6 Different deep learning methods of feature extract and their effects
作者及参考文献 神经网络模型 数据集 准确率 Yin等[109] 堆叠式自编码器 DEAP 83.0 % (Valence/2)、84.1 % (Arousal/2) Fourati等[110] 回声状态网络 DEAP 71.0 % (Valence/2)、68.3 % (Arousal/2) Ren等[111] 融合大脑不对称特性的回声状态网络 DEAP 78.2 % (Average/4) Liu等[112] 多层次特征引导胶囊网络 DEAP 98.0 % (Valence/2)、98.3 % (Arousal/2)、98.3 % (Dominance/2) Wu等[113] 关键子网络选择 SEED 81.5 % (Average/3) Yang等[114] 具有子网节点的分层网络模型 SEED 85.7 % (Average/3) Wang等[115] 双向长短期记忆网络 SEED 95.0 % (Average/3) Zhang等[116] 变分路径推理 SEED 94.3 % (Average/3) Cimtay等[117] 卷积神经网络 SEED 73.7 % (Average/3)、82.9 % (Average/2) 注: (Valence/2)表示Valence维度2分类准确率, (Average/4)表示情绪4分类准确率. -
[1] 林崇德, 杨治良, 黄希庭. 心理学大辞典. 上海: 上海教育出版社, 2003.Lin Chong-De, Yang Zhi-Liang, Huang Xi-Ting. The Comprehensive Dictionary of Psychology. Shanghai: Shanghai Educational Publishing House, 2003. [2] 陶建华, 李雅. 情感计算研究进展. 中国计算机学会通讯, 2016, 12(10): 62−70Tao Jian-Hua, Li Ya. Advances in affective computing. Communications of China Computer Federation, 2016, 12(10): 62−70 (查阅所有网上资料, 未找到对应的英文翻译, 请联系作者确认) [3] Affective computing [Online], available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Affective_computing, January 12, 2021 [4] Minsky M. The Society of Mind. New York: Simon and Schuster, 1986. [5] Picard R W. Affective Computing. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1997. [6] Liu Y S, Sourina O, Nguyen M K. Real-time EEG-based emotion recognition and its applications. Transactions on Computational Science XII. Berlin: Springer, 2011. 256−277 [7] 林文倩. 生理信号驱动的情绪识别及交互应用研究 [博士学位论文], 浙江大学, 中国, 2019Lin Wen-Qian. Emotion Recognition and Application Based on Physiological Signals [Ph. D. dissertation], Zhejiang University, China, 2019 [8] Ortony A, Clore G L, Collins A. The Cognitive Structure of Emotions. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1990. [9] 林传鼎. 心理学词典. 南昌: 江西科学技术出版社, 1986.Lin Chuan-Ding. Dictionary of Psychology. Nanchang: Jiangxi Science and Technology Press, 1986. [10] Ekman P, Friesen W V. Constants across cultures in the face and emotion. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 1971, 17(2): 124−129 doi: 10.1037/h0030377 [11] Lazarus R S. From psychological stress to the emotions: A history of changing outlooks. Annual Review of Psychology, 1993, 44: 1−22 doi: 10.1146/annurev.ps.44.020193.000245 [12] Plutchik R. Emotions and Life: Perspectives from Psychology, Biology, and Evolution. Washington: American Psychological Association, 2003. [13] Russell J A. A circumplex model of affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 1980, 39(6): 1161−1178 doi: 10.1037/h0077714 [14] Mehrabian A. Pleasure-arousal-dominance: A general framework for describing and measuring individual differences in temperament. Current Psychology, 1996, 14(4): 261−292 doi: 10.1007/BF02686918 [15] Electroencephalography [Online], available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electroencephalography, January 12, 2021 [16] Zheng W L, Zhu J Y, Lu B L. Identifying stable patterns over time for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2019, 10(3): 417−429 doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2017.2712143 [17] 张冠华, 余旻婧, 陈果, 韩义恒, 张丹, 赵国朕, 等. 面向情绪识别的脑电特征研究综述. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2019, 49(9): 1097−1118Zhang Guan-Hua, Yu Min-Jing, Chen Guo, Han Yi-Heng, Zhang Dan, Zhao Guo-Zhen, et al. A review of EEG features for emotion recognition. Science in China (Information Sciences), 2019, 49(9): 1097−1118 [18] Mehdizadehfar V, Ghassemi F, Fallah A, Pouretemad H. EEG study of facial emotion recognition in the fathers of autistic children. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2020, 56: 101721 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101721 [19] Cacioppo J T, Tassinary L G. Principles of Psychophysiology: Physical, Social and Inferential Elements. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1990. [20] Heart rate variability [Online], available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart_rate_variability, January 12, 2021 [21] Zheng W L, Lu B L. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Autonomous Mental Development, 2015, 7(3): 162−175 doi: 10.1109/TAMD.2015.2431497 [22] Sohaib A T, Qureshi S, Hagelbäck J, Hilborn O, Jerčić P. Evaluating classifiers for emotion recognition using EEG. In: Proceedings of the 7th International. Las Vegas, USA: Springer, 2013. 492−501 [23] Nie D, Wang X W, Shi L C, Lv B L. EEG-based emotion recognition during watching movies. In: Proceedings of the 5th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering. Cancun, Mexico: IEEE, 2011. 667−670 [24] Lin Y P, Wang C H, Jung T P, Wu T L, Jeng S K, Duann J R. EEG-based emotion recognition in music listening. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2010, 57(7): 1798−1806 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2048568 [25] Alarcão S M, Fonseca M J. Emotions recognition using EEG signals: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2019, 10(3): 374−393 doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2017.2714671 [26] Domínguez-Jiménez A, Campo-Landines C, Martínez-Santos J C, Delahoz E J, Contreras-Ortiz S H. A machine learning model for emotion recognition from physiological signals. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2020, 55: 101646 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101646 [27] Joesph C, Rajeswari A, Premalatha B, Balapriya C. Implementation of physiological signal based emotion recognition algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE). Dallas, USA: IEEE, 2020. 2075−2079 [28] Zhu Q Y, Lu G M, Yan J J. Valence-arousal model based emotion recognition using EEG, peripheral physiological signals and facial expression. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Machine Learning and Soft Computing. Haiphong City, Viet Nam: ACM, 2020. 81−85 [29] Fabiano D, Canavan S. Emotion recognition using fused physiological signals. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII). Cambridge, UK: IEEE, 2019. 42−48 [30] Chang E J, Rahimi A, Benini L, Wu A Y A. Hyperdimensional computing-based multimodality emotion recognition with physiological signals. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Circuits and Systems (AICAS). Hsinchu, China: IEEE, 2019. 137−141 [31] Zhu J J, Zhao X B, Hu H, Gao Y. Emotion recognition from physiological signals using multi-hypergraph neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2019. 610−615 [32] Ali M, Machot F A, Mosa A H, Jdeed M, Machot E A, Kyamakya K. A globally generalized emotion recognition system involving different physiological signals. Sensors, 2018, 18(6): Article No. 1905 doi: 10.3390/s18061905 [33] Zheng W L, Liu W, Lu Y F, Lu B L, Cichocki A. EmotionMeter: A multimodal framework for recognizing human emotions. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(3): 1110−1122 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2797176 [34] Soleymani M, Lichtenauer J, Pun T, Pantic M. A multimodal database for affect recognition and implicit tagging. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2012, 3(1): 42−55 doi: 10.1109/T-AFFC.2011.25 [35] Ringeval F, Sonderegger A, Sauer J, Lalanne D. Introducing the RECOLA multimodal corpus of remote collaborative and affective interactions. In: Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG). Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2013. 1−8 [36] Abadi M K, Subramanian R, Kia S M, Avesani P, Patras I, Sebe N. DECAF: MEG-based multimodal database for decoding affective physiological responses. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2015, 6(3): 209−222 doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2015.2392932 [37] Subramanian R, Wache J, Abadi M K, Vieriu R L, Winkler S, Sebe N. ASCERTAIN: Emotion and personality recognition using commercial sensors. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2018, 9(2): 147−160 doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2016.2625250 [38] Miranda-Correa J A, Abadi M K, Sebe N, Patras I. AMIGOS: A dataset for affect, personality and mood research on individuals and groups. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2021, 12(2): 479−493 doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2018.2884461 [39] Katsigiannis S, Ramzan N. DREAMER: A database for emotion recognition through EEG and ECG signals from wireless low-cost off-the-shelf devices. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2018, 22(1): 98−107 doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2017.2688239 [40] Li Y, Zheng W M, Cui Z, Zong Y, Ge S. EEG emotion recognition based on graph regularized sparse linear regression. Neural Processing Letters, 2019, 49(2): 555−571 doi: 10.1007/s11063-018-9829-1 [41] Song T F, Zheng W M, Lu C, Zong Y, Zhang X L, Cui Z. MPED: A multi-modal physiological emotion database for discrete emotion recognition. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 12177−12191 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2891579 [42] Becker H, Fleureau J, Guillotel P, Wendling F, Merlet I, Albera L. Emotion recognition based on high-resolution EEG recordings and reconstructed brain sources. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2020, 11(2): 244−257 doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2017.2768030 [43] Koelstra S, Muhl C, Soleymani M, Lee J S, Yazdani A, Ebrahimi T, et al. DEAP: A database for emotion analysis; using physiological signals. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2012, 3(1): 18−31 doi: 10.1109/T-AFFC.2011.15 [44] Jenke R, Peer A, Buss M. Feature extraction and selection for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2014, 5(3): 327−339 doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2014.2339834 [45] Wang X W, Nie D, Lv B L. EEG-based emotion recognition using frequency domain features and support vector machines. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Shanghai, China: Springer, 2011. 734−743 [46] Mohammadi Z, Frounchi J, Amiri M. Wavelet-based emotion recognition system using EEG signal. Neural Computing and Applications, 2017, 28(8): 1985−1990 doi: 10.1007/s00521-015-2149-8 [47] Duan R N, Zhu J Y, Lv B L. Differential entropy feature for EEG-based emotion classification. In: Proceedings of the 6th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER). San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2013. 81−84 [48] Moon S E, Jang S, Lee J S. Convolutional neural network approach for EEG-based emotion recognition using brain connectivity and its spatial information. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Calgary, Canada, 2018. 2556−2560 [49] Yan X, Zheng W L, Liu W, Lv B L. Identifying gender differences in multimodal emotion recognition using bimodal deep autoencoder. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Guangzhou, China: Springer, 2017. 533−542 [50] Yan X, Zheng W L, Liu W, Lv B L. Investigating gender differences of brain areas in emotion recognition using LSTM neural network. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Guangzhou, China: Springer, 2017. 820−829 [51] Soroush M Z, Maghooli K, Setarehdan S K, Nasrabadi A M. Emotion recognition using EEG phase space dynamics and poincare intersections. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2020, 59: 101918 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101918 [52] Shi L C, Lu B L. Off-line and on-line vigilance estimation based on linear dynamical system and manifold learning. In: Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology. Buenos Aires, Argentina: IEEE, 2010. 6587−6590 [53] Pham T D, Tran D, Ma W, Tran N T. Enhancing performance of EEG-based emotion recognition systems using feature smoothing. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Istanbul, Turkey: Springer, 2015. 95−102 [54] Hu B, Li X W, Sun S T, Ratcliffe M. Attention recognition in EEG-based affective learning research using CFS+KNN algorithm. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2018, 15(1): 38−45 doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2016.2616395 [55] Zheng W M. Multichannel EEG-based emotion recognition via group sparse canonical correlation analysis. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2017, 9(3): 281−290 doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2016.2587290 [56] Özerdem M S, Polat H. Emotion recognition based on EEG features in movie clips with channel selection. Brain Informatics, 2017, 4(4): 241−252 doi: 10.1007/s40708-017-0069-3 [57] Picard R W, Vyzas E, Healey J. Toward machine emotional intelligence: Analysis of affective physiological state. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2001, 23(10): 1175−1191 doi: 10.1109/34.954607 [58] Agrafioti F, Hatzinakos D, Anderson A K. ECG pattern analysis for emotion detection. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2012, 3(1): 102−115 doi: 10.1109/T-AFFC.2011.28 [59] Goshvarpour A, Abbasi A, Goshvarpour A. An accurate emotion recognition system using ECG and GSR signals and matching pursuit method. Biomedical Journal, 2017, 40(6): 355−368 doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2017.11.001 [60] Wu G H, Liu G Y, Hao M. The analysis of emotion recognition from GSR based on PSO. In: Proceedings of the 2010 International Symposium on Intelligence Information Processing and Trusted Computing. Huanggang, China: IEEE, 2010. 360−363 [61] Udovičić G, Derek J, Russo M, Sikora M. Wearable emotion recognition system based on GSR and PPG signals. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Multimedia for Personal Health and Health Care. Mountain View, USA: ACM, 2017. 53−59 [62] Lanatà A, Valenza G, Scilingo E P. A novel EDA glove based on textile-integrated electrodes for affective computing. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2012, 50(11): 1163−1172 [63] Jerritta S, Murugappan M, Wan K, Yaacob S. Emotion recognition from facial EMG signals using higher order statistics and principal component analysis. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2014, 37(3): 385−394 doi: 10.1080/02533839.2013.799946 [64] Yang S X, Yang G Y. Emotion recognition of EMG based on improved L-M BP neural network and SVM. Journal of Software, 2011, 6(8): 1529−1536 [65] Murugappan M. Electromyogram signal based human emotion classification using KNN and LDA. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on System Engineering and Technology. Shah Alam, Malaysia: IEEE, 2011. 106−110 [66] Goshvarpour A, Goshvarpour A. Poincaré' s section analysis for PPG-based automatic emotion recognition. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2018, 114: 400−407 [67] Lee Y K, Kwon O W, Shin H S, Jo J, Lee Y. Noise reduction of PPG signals using a particle filter for robust emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Berlin (ICCE-Berlin). Berlin, Germany: IEEE, 2011. 202−205 [68] Künecke J, Hildebrandt A, Recio G, Sommer W, Wilhelm O. Facial EMG responses to emotional expressions are related to emotion perception ability. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): Article No. 84053 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084053 [69] McCubbin J A, Merritt M M, Sollers III J J, Evans M K, Zonderman A B, Lane R D, et al. Cardiovascular-emotional dampening: The relationship between blood pressure and recognition of emotion. Psychosomatic Medicine, 2011, 73(9): 743−750 doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e318235ed55 [70] Quintana D S, Guastella A J, Outhred T, Hickie I B, Kemp A H. Heart rate variability is associated with emotion recognition: Direct evidence for a relationship between the autonomic nervous system and social cognition. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 2012, 86(2): 168−172 doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2012.08.012 [71] Williams D P, Cash C, Rankin C, Bernardi A, Koenig J, Thayer J F. Resting heart rate variability predicts self-reported difficulties in emotion regulation: A focus on different facets of emotion regulation. Frontiers in Psychology, 2015, 6: Article No. 261 [72] Geisler F C M, Vennewald N, Kubiak T, Weber H. The impact of heart rate variability on subjective well-being is mediated by emotion regulation. Personality and Individual Differences, 2010, 49(7): 723−728 doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2010.06.015 [73] Guo H W, Huang Y S, Lin C H, Chien J C, Haraikawa K, Shieh J S. Heart rate variability signal features for emotion recognition by using principal component analysis and support vectors machine. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE). Taichung, China: IEEE, 2016. 274−277 [74] Goshvarpour A, Abbasi A, Goshvarpour A. Fusion of heart rate variability and pulse rate variability for emotion recognition using lagged poincare plots. Australasian Physical & Engineering Sciences in Medicine, 2017, 40(3): 617−629 [75] Zheng W L, Dong B N, Lu B L. Multimodal emotion recognition using EEG and eye tracking data. In: Proceedings of the 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Chicago, USA: IEEE, 2014 [76] Guo J J, Zhou R, Zhao L M, Lv B L. Multimodal emotion recognition from eye image, eye movement and EEG using deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). Berlin, Germany: IEEE, 2019. 3071−3074 [77] Lu Y F, Zheng W L, Li B B, Lv B L. Combining eye movements and EEG to enhance emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Buenos Aires, Argentina: AAAI, 2015 [78] Wu D P, Han X J, Wang H G, Wang R Y. Robust EEG-based emotion recognition using multi-feature joint sparse representation. In: Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC). Big Island, USA: IEEE, 2020. 802−807 [79] Thammasan N, Fukui K I, Numao M. Multimodal fusion of EEG and musical features in music-emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, USA: AAAI, 2017. 4991−4992 [80] Doma V, Pirouz M. A comparative analysis of machine learning methods for emotion recognition using EEG and peripheral physiological signals. Journal of Big Data, 2020, 7(1): Article No. 18 doi: 10.1186/s40537-020-00289-7 [81] Pan S J, Yang Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2010, 22(10): 1345−1359 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191 [82] Wu D R, Xu Y F, Lv B L. Transfer learning for EEG-based brain-computer interfaces: A review of progress made since 2016. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, to be published [83] Pan S J, Tsang I W, Kwok J T, Yang Q. Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(2): 199−210 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2091281 [84] Sangineto E, Zen G, Ricci E, Sebe N. We are not all equal: Personalizing models for facial expression analysis with transductive parameter transfer. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Orlando, USA: ACM, 2014. 357−366 [85] Zhang X W, Liang W B, Ding T Z, Pan J, Shen J, Huang X, et al. Individual similarity guided transfer modeling for EEG-based emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1156−1161 [86] Zhang X Y, Liu C L. Style transfer matrix learning for writer adaptation. In: Proceedings of the CVPR 2011. Colorado Springs, USA: IEEE, 2011. 393−400 [87] Zhang X Y, Liu C L. Writer adaptation with style transfer mapping. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(7): 1773−1787 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.239 [88] Zheng W L, Lv B L. Personalizing EEG-based affective models with transfer learning. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: IJCAI, 2016. 2732−2739 [89] Scholköpf B, Smola A, Muller K R. Nonlinear component analysis as a kernel eigenvalue problem. Neural Computation, 1998, 10(5): 1299−1319 doi: 10.1162/089976698300017467 [90] Borgwardt K M, Gretton A, Rasch M J, Kriegel H, Schölkopf B, Smola A J. Integrating structured biological data by kernel maximum mean discrepancy. Bioinformatics, 2006, 22(14): e49−e57 doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl242 [91] Li J P, Qiu S, Shen Y Y, Liu C L, He H G. Multisource transfer learning for cross-subject EEG emotion recognition. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(7): 3281−3293 [92] Lan Z R, Sourina O, Wang L P, Scherer R, Müller-Putz G R. Domain adaptation techniques for EEG-based emotion recognition: A comparative study on two public datasets. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2019, 11(1): 85−94 doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2018.2826840 [93] 郑伟龙, 石振锋, 吕宝粮. 用异质迁移学习构建跨被试脑电情感模型. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(2): 177−189 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.00177Zheng Wei-Long, Shi Zhen-Feng, Lü Bao-Liang. Building cross-subject EEG-based affective models using heterogeneous transfer learning. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(2): 177−189 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.00177 [94] Mehrabian A. Basic Dimensions for a General Psychological Theory: Implications for Personality, Social, Environmental, and Developmental Studies. Cambridge, MA: Oelgeschlager, Gunn & Hain, 1980. [95] Grimm M, Kroschel K, Narayanan S. The Vera Am Mittag German audio-visual emotional speech database. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. Hannover, Germany: IEEE, 2008. 865−868 [96] Bradley M M, Lang P J. The International Affective Digitized Sounds (Second edition). Florida: University of Florida, 2007. [97] Settles B. Active Learning Literature Survey, Computer Sciences Technical Report 1648, University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA, 2009 [98] Wu D R, Parsons T D. Active class selection for arousal classification. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction. Memphis, USA: Springer, 2011. 132−141 [99] Wu D R, Lance B J, Parsons T D. Collaborative filtering for brain-computer interaction using transfer learning and active class selection. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): Article No. e56624 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056624 [100] Wu D R, Lawhern V J, Gordon S, Lance B J, Lin C T. Offline EEG-based driver drowsiness estimation using enhanced batch-mode active learning (EBMAL) for regression. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC). Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2016. 730−736 [101] Liu Z, Wu D R. Unsupervised pool-based active learning for linear regression. arXiv: 2001.05028, 2020 [102] Wu D R. Pool-based sequential active learning for regression. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(5): 1348−1359 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2868649 [103] Wu D R, Lin C T, Huang J. Active learning for regression using greedy sampling. Information Sciences, 2019, 474: 90−105 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.09.060 [104] Wu D R, Huang J. Affect estimation in 3D space using multi-task active learning for regression. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, DOI: 10.1109/TAFFC.2019.2916040 [105] Zheng W L, Zhu J Y, Peng Y, Lu B L. EEG-based emotion classification using deep belief networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Chengdu, China: IEEE, 2014. 1−6 [106] Thammasan N, Fukui K I, Numao M. Application of deep belief networks in EEG-based dynamic music-emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2016. 881−888 [107] Li J P, Zhang Z X, He H G. Hierarchical convolutional neural networks for EEG-based emotion recognition. Cognitive Computation, 2018, 10(2): 368−380 doi: 10.1007/s12559-017-9533-x [108] Wei C, Chen L L, Song Z Z, Lou X G, Li D D. EEG-based emotion recognition using simple recurrent units network and ensemble learning. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2020, 58: Article No. 101756 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101756 [109] Yin Z, Zhao M Y, Wang Y X, Yang J D, Zhang J. H. Recognition of emotions using multimodal physiological signals and an ensemble deep learning model. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2017, 140: 93−110 doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.12.005 [110] Fourati R, Ammar B, Aouiti C, Sanchez-Medina J, Alimi A M. Optimized echo state network with intrinsic plasticity for EEG-based emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Guangzhou, China: Springer, 2017. 718−727 [111] Ren F J, Dong Y D, Wang W. Emotion recognition based on physiological signals using brain asymmetry index and echo state network. Neural Computing and Applications, 2019, 31(9): 4491−4501 doi: 10.1007/s00521-018-3664-1 [112] Liu Y, Ding Y F, Li C, Cheng J, Song R C, Wan F, et al. Multi-channel EEG-based emotion recognition via a multi-level features guided capsule network. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2020, 123: Article No. 103927 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103927 [113] Wu X, Zheng W L, Lv B L. Identifying functional brain connectivity patterns for EEG-based emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 9th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER). San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2019. 235−238 [114] Yang Y M, Wu Q M J, Zheng W L, Lu B L. EEG-based emotion recognition using hierarchical network with subnetwork nodes. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2018, 10(2): 408−419 doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2017.2685338 [115] Wang Y X, Qiu S, Li J P, Ma X L, Liang Z Y, Li H, et al. EEG-based emotion recognition with similarity learning network. In: Proceedings of the 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). Berlin, Germany: IEEE, 2019. 1209−1212 [116] Zhang T, Cui Z, Xu C Y, Zheng W M, Yang J. Variational pathway reasoning for EEG emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 2709−2716 [117] Cimtay Y, Ekmekcioglu E. Investigating the use of pretrained convolutional neural network on cross-subject and cross-dataset EEG emotion recognition. Sensors, 2020, 20(7): Article No. 2034 doi: 10.3390/s20072034 [118] Ma J X, Tang H, Zheng W L, Lv B L. Emotion recognition using multimodal residual LSTM network. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Nice, France: ACM, 2019. 176−183 [119] Liu W, Qiu J L, Zheng W L, Lv B L. Multimodal emotion recognition using deep canonical correlation analysis. arXiv: 1908.05349, 2019 [120] Rayatdoost S, Rudrauf D, Soleymani M. Expression-guided EEG representation learning for emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2020. 3222−3226 [121] Du C D, Du C Y, Wang H, Li J P, Zheng W L, Lv B L, et al. Semi-supervised deep generative modelling of incomplete multi-modality emotional data. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Seoul, Republic of Korea: ACM, 2018. 108−116 [122] Long M S, Cao Y, Wang J M, Jordan M. Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille, France: JMLR.org, 2015. 97−105 [123] Gretton A, Sriperumbudur B K, Sejdinovic D, Strathmann H, Balakrishnan S, Pontil M, et al. Optimal kernel choice for large-scale two-sample tests. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, SUA: NIPS, 2012. 1025−1213 [124] Li H, Jin Y M, Zheng W L, Lv B L. Cross-subject emotion recognition using deep adaptation networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Siem Reap, Cambodia: Springer, 2018. 403−413 [125] Long M S, Wang J M, Ding G G, Sun J G, Yu P S. Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 2200−2207 [126] Li J P, Qiu S, Du C D, Wang Y X, He H G. Domain adaptation for EEG emotion recognition based on latent representation similarity. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2020, 12(2): 344−353 doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2019.2949306 [127] Tzeng E, Hoffman J, Saenko K, Darrell T. Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2962−2971 [128] Luo Y, Zhang S Y, Zheng W L, Lv B L. WGAN domain adaptation for EEG-based emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Siem Reap, Cambodia: Springer, 2018. 275−286 [129] Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein GAN. arXiv: 1701.07875, 2017 [130] Ma B Q, Li H, Zheng W L, Lv B L. Reducing the subject variability of EEG signals with adversarial domain generalization. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Sydney, Australia: Springer, 2019. 30−42 [131] Ganin Y, Ustinova E, Ajakan H, Germain P, Larochelle H, Laviolette F, et al. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2016, 17(1): 2096−2030 [132] Li Y, Zheng W M, Cui Z, Zhang T, Zong Y. A novel neural network model based on cerebral hemispheric asymmetry for EEG emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Stockholm, Sweden: IJCAI, 2018. 1561−1567 [133] Soleymani M, Asghari-Esfeden S, Fu Y, Pantic M. Analysis of EEG signals and facial expressions for continuous emotion detection. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2016, 7(1): 17−28 doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2015.2436926 [134] Nath D, Anubhav, Singh M, Sethia D, Kalra D, Indu S. A comparative study of subject-dependent and subject-independent strategies for EEG-based emotion recognition using LSTM network. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Compute and Data Analysis. Silicon Valley, USA: ACM, 2020. 142−147 [135] Zhao S C, Ding G G, Han J G, Gao Y. Personality-aware personalized emotion recognition from physiological signals. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Stockholm, Sweden: IJCAI, 2018. 1660−1667 [136] Zhao S C, Gholaminejad A, Ding G G, Gao Y, Han J G, Keutzer K. Personalized emotion recognition by personality-aware high-order learning of physiological signals. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications. 2019, 15(1S): Article No. 14 [137] Song T F, Liu S Y, Zheng W M, Zong Y, Cui Z. Instance-adaptive graph for EEG emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York, USA: AAAI, 2020. 2701−2708 [138] Song T F, Zheng W M, Song P, Cui Z. EEG emotion recognition using dynamical graph convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2020, 11(3): 532−541 doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2018.2817622 [139] Agarwal A, Dowsley R, McKinney N D, Wu D R, Lin C T, de Cock M, et al. Protecting privacy of users in brain-computer interface applications. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2019, 27(8): 1546−1555 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2926965 [140] de Cock M, Dowsley R, McKinney N, Nascimento A C A, Wu D R. Privacy preserving machine learning with EEG data. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: 2017 -




 下载:
下载: